生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (12): 2292-2301.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.12.003
高歌1,2,3( ), 葛晓改1,3, 周君刚4, 周本智1,3, 李正才1,3,*(
), 葛晓改1,3, 周君刚4, 周本智1,3, 李正才1,3,*( ), 杨南5
), 杨南5
收稿日期:2022-08-19
出版日期:2022-12-18
发布日期:2023-02-15
通讯作者:
*李正才,E-mail: lizccaf@126.com作者简介:高歌(1999年生),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为森林生态系统结构与功能。E-mail: Gaogewy@163.com
基金资助:
GAO Ge1,2,3( ), GE Xiaogai1,3, ZHOU Jungang4, ZHOU Benzhi1,3, LI Zhengcai1,3,*(
), GE Xiaogai1,3, ZHOU Jungang4, ZHOU Benzhi1,3, LI Zhengcai1,3,*( ), YANG Nan5
), YANG Nan5
Received:2022-08-19
Online:2022-12-18
Published:2023-02-15
摘要:
探究氮素添加后不同亚热带树种生物量和根系形态对干旱的响应特征,为干旱下植物幼苗的水肥管理和抗旱能力的提升提供理论依据。试验选取杉木(Cunninghamia lanceolata)和青冈(Cyclobalanopsis glauca)为研究对象,设置未施氮(N0,0 mg?kg?1,以N计,下同)和施氮(N1,100 mg?kg?1)2个氮处理及正常水分(CK,80%—85% FC)、中度干旱(MD,50%—55% FC)和重度干旱(SD,30%—35% FC)3个土壤水分梯度,氮处理结束后于8月中旬展开水分控制试验,干旱60 d后进行破坏性采样,测定和分析两树种生物量及根系形态特征。结果显示,施氮促进了相同干旱水平下杉木和青冈地上部生物量的积累,并促使重度干旱下(N1SD)青冈的根干质量(31.7%)和总生物量(17.5%)显著增加(P<0.05),但对干旱下(N1MD和N1SD)杉木根干质量和总生物量表现为抑制作用;施氮改变了干旱下青冈和杉木的生物量分配格局,不同水分条件下青冈生物量分配对氮素的响应有所不同,且中度干旱下氮肥作用效果更强,氮添加促使相同干旱组杉木的茎生物量比、叶生物量比及茎叶比增加,而根生物量比(19.4%和30.0%)、比根长(39.8%和28.5%)和根冠比(28.3%和38.1%)均显著降低(P<0.05);施氮显著抑制了干旱组(N1MD和N1SD)杉木各径级根长、根表面积和根体积(P<0.05),这种抑制作用在中度干旱时更为强烈,而氮素对重度干旱下青冈根系生长及形态的影响较大且表现为正效应。研究表明,干旱下杉木和青冈在生物量积累与分配和根系形态方面对氮素添加表现出不同的利用策略,适量的氮素在一定程度上能够促使青冈幼苗抵御重度干旱的威胁,尽管施氮对干旱胁迫下杉木幼苗的生长无促进效果,但幼苗期的杉木亦能通过权衡地上及地下的生物量分配以缓解干旱胁迫对自身的伤害。
中图分类号:
高歌, 葛晓改, 周君刚, 周本智, 李正才, 杨南. 施氮和干旱对杉木和青冈幼苗生物量及根系形态的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2292-2301.
GAO Ge, GE Xiaogai, ZHOU Jungang, ZHOU Benzhi, LI Zhengcai, YANG Nan. Effect of Drought Stress and Nitrogen Addition on the Biomass and Root Morphology of Cunninghamia lanceolata and Cyclobalanopsis glauca Seedlings[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(12): 2292-2301.
| 因素 Factors | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 59.13** | 10.54** | 140.17** | 36.02** | 2.72NS | 170.55** | 49.88** | 20.79** | 3.35NS | 159.93** | 165.61** |
| W | 88.32** | 23.47** | 105.96** | 64.86** | 111.79** | 8.59** | 2.15NS | 4.52* | 2.59NS | 7.28** | 18.19** |
| N×W | 7.83** | 2.88NS | 0.36NS | 6.81** | 6.51** | 1.05NS | 0.27NS | 0.16NS | 0.02NS | 0.66NS | 1.02NS |
表1 不同水氮条件下杉木幼苗生物量累积及其分配的双因素方差分析(F值)
Table 1 Two-way ANOVA results of effects of water, N and their interaction on the biomass accumulation and distribution of C. lanceolata seedlings (F)
| 因素 Factors | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 59.13** | 10.54** | 140.17** | 36.02** | 2.72NS | 170.55** | 49.88** | 20.79** | 3.35NS | 159.93** | 165.61** |
| W | 88.32** | 23.47** | 105.96** | 64.86** | 111.79** | 8.59** | 2.15NS | 4.52* | 2.59NS | 7.28** | 18.19** |
| N×W | 7.83** | 2.88NS | 0.36NS | 6.81** | 6.51** | 1.05NS | 0.27NS | 0.16NS | 0.02NS | 0.66NS | 1.02NS |
| 因素 Factors | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 134.60** | 31.30** | 3.10NS | 122.49** | 72.98** | 112.80** | 74.13** | 0.05NS | 28.96** | 107.31** | 32.89** |
| W | 68.78** | 65.21** | 2.82NS | 113.43** | 88.84** | 52.53** | 14.00** | 5.80** | 3.59* | 49.40** | 39.58** |
| N×W | 8.66** | 19.24** | 45.64** | 13.92** | 5.73** | 72.59** | 15.89** | 21.76** | 9.37** | 74.01** | 10.45** |
表2 不同水氮条件下青冈幼苗生物量累积及其分配的双因素方差分析(F值)
Table 2 Two-way ANOVA results of effects of water, N and their interaction on the biomass accumulation and distribution of C. glauca seedlings (F)
| 因素 Factors | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 134.60** | 31.30** | 3.10NS | 122.49** | 72.98** | 112.80** | 74.13** | 0.05NS | 28.96** | 107.31** | 32.89** |
| W | 68.78** | 65.21** | 2.82NS | 113.43** | 88.84** | 52.53** | 14.00** | 5.80** | 3.59* | 49.40** | 39.58** |
| N×W | 8.66** | 19.24** | 45.64** | 13.92** | 5.73** | 72.59** | 15.89** | 21.76** | 9.37** | 74.01** | 10.45** |
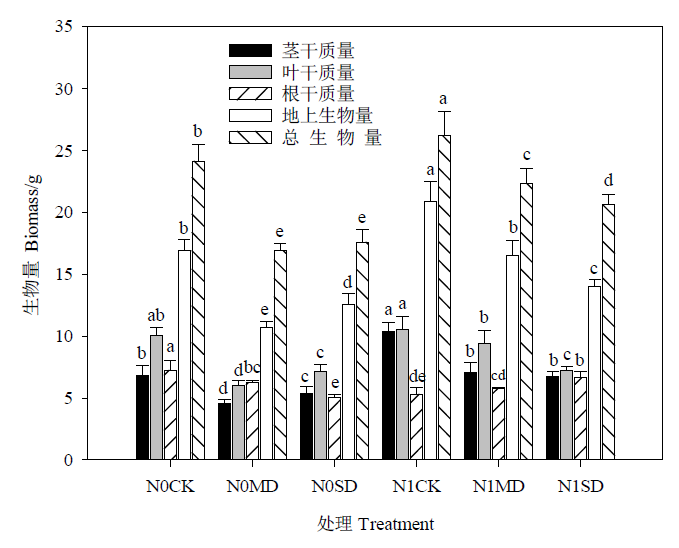
图1 施氮对不同水分条件下杉木幼苗生物量的影响 N0:未施氮;N1:施氮;CK:正常水分;MD:中度干旱;SD:重度干旱。不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。下同
Figure 1 Effects of nitrogen on biomass of C. lanceolata seedlings under different water treatments N0: No nitrogen addition; N1: Nitrogen addition; CK: Normal water; MD: Moderate drought; SD: Severe drought. Different letters meant significant difference at 0.05 level between all combinations. The same as below
| 处理 Treatment | 根生物量比 Leaf biomass ratio/% | 茎生物量比 Stem biomass ratio/% | 叶生物量比 Root biomass ratio/% | 茎叶比 Stem leaf ratio/% | 根冠比 Root top ratio/% | 比根长 Specific root length/(cm∙g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N0CK | 0.32±0.02a | 0.3±0.02b | 0.38±0.04c | 0.81±0.11ab | 0.46±0.05a | 394.89±27.81b |
| N0MD | 0.31±0.01a | 0.29±0.01b | 0.39±0.01bc | 0.74±0.04b | 0.46±0.02a | 438.53±28.13a |
| N0SD | 0.3±0.03a | 0.3±0.02b | 0.41±0.02bc | 0.74±0.06b | 0.42±0.05a | 475.73±59.91a |
| N1CK | 0.23±0.01b | 0.35±0.02a | 0.42±0.03ab | 0.85±0.11a | 0.3±0.02bc | 250.39±14.1d |
| N1MD | 0.25±0.01b | 0.33±0.02a | 0.42±0.01ab | 0.79±0.07ab | 0.33±0.02b | 263.92±36.78d |
| N1SD | 0.21±0.02c | 0.35±0.03a | 0.44±0.01a | 0.79±0.08ab | 0.26±0.03c | 340.38±27.87c |
表3 施氮对不同水分处理下杉木幼苗生物量分配的影响
Table 3 Effects of nitrogen on biomass distribution of C. lanceolata seedlings under different water treatments
| 处理 Treatment | 根生物量比 Leaf biomass ratio/% | 茎生物量比 Stem biomass ratio/% | 叶生物量比 Root biomass ratio/% | 茎叶比 Stem leaf ratio/% | 根冠比 Root top ratio/% | 比根长 Specific root length/(cm∙g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N0CK | 0.32±0.02a | 0.3±0.02b | 0.38±0.04c | 0.81±0.11ab | 0.46±0.05a | 394.89±27.81b |
| N0MD | 0.31±0.01a | 0.29±0.01b | 0.39±0.01bc | 0.74±0.04b | 0.46±0.02a | 438.53±28.13a |
| N0SD | 0.3±0.03a | 0.3±0.02b | 0.41±0.02bc | 0.74±0.06b | 0.42±0.05a | 475.73±59.91a |
| N1CK | 0.23±0.01b | 0.35±0.02a | 0.42±0.03ab | 0.85±0.11a | 0.3±0.02bc | 250.39±14.1d |
| N1MD | 0.25±0.01b | 0.33±0.02a | 0.42±0.01ab | 0.79±0.07ab | 0.33±0.02b | 263.92±36.78d |
| N1SD | 0.21±0.02c | 0.35±0.03a | 0.44±0.01a | 0.79±0.08ab | 0.26±0.03c | 340.38±27.87c |
| 处理 Treatment | 根生物量比 Leaf biomass ratio/% | 茎生物量比 Stem biomass ratio/% | 叶生物量比 Root biomass ratio/% | 茎叶比 Stem leaf ratio/% | 根冠比 Root top ratio/% | 比根长 Specific root length/(cm∙g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N0CK | 0.3±0.02c | 0.28±0.03c | 0.42±0.02a | 0.68±0.09b | 0.43±0.04c | 149.05±20.85bc |
| N0MD | 0.37±0.01a | 0.27±0.02c | 0.36±0.02b | 0.76±0.07b | 0.59±0.03a | 127.82±21.13c |
| N0SD | 0.29±0.02c | 0.31±0.02b | 0.41±0.02a | 0.76±0.09b | 0.4±0.03c | 205.28±15.33a |
| N1CK | 0.2±0.01e | 0.4±0.01a | 0.4±0.02a | 0.99±0.08a | 0.25±0.02e | 84.87±6.23d |
| N1MD | 0.26±0.01d | 0.32±0.03b | 0.42±0.03a | 0.76±0.12b | 0.35±0.03d | 131.24±18.63c |
| N1SD | 0.32±0.02b | 0.33±0.01b | 0.35±0.01b | 0.94±0.06a | 0.47±0.04b | 157.86±25.15b |
表4 施氮对不同水分处理下青冈幼苗生物量分配的影响
Table 4 Effects of nitrogen on biomass distribution of C. glauca seedlings under different water treatments
| 处理 Treatment | 根生物量比 Leaf biomass ratio/% | 茎生物量比 Stem biomass ratio/% | 叶生物量比 Root biomass ratio/% | 茎叶比 Stem leaf ratio/% | 根冠比 Root top ratio/% | 比根长 Specific root length/(cm∙g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N0CK | 0.3±0.02c | 0.28±0.03c | 0.42±0.02a | 0.68±0.09b | 0.43±0.04c | 149.05±20.85bc |
| N0MD | 0.37±0.01a | 0.27±0.02c | 0.36±0.02b | 0.76±0.07b | 0.59±0.03a | 127.82±21.13c |
| N0SD | 0.29±0.02c | 0.31±0.02b | 0.41±0.02a | 0.76±0.09b | 0.4±0.03c | 205.28±15.33a |
| N1CK | 0.2±0.01e | 0.4±0.01a | 0.4±0.02a | 0.99±0.08a | 0.25±0.02e | 84.87±6.23d |
| N1MD | 0.26±0.01d | 0.32±0.03b | 0.42±0.03a | 0.76±0.12b | 0.35±0.03d | 131.24±18.63c |
| N1SD | 0.32±0.02b | 0.33±0.01b | 0.35±0.01b | 0.94±0.06a | 0.47±0.04b | 157.86±25.15b |
| [1] |
AUJLA M S, THIND H S, BUTTAR G S, 2007. Fruit yield and water use efficiency of eggplant (Solanum melongema L.) as influenced by different quantities of nitrogen and water applied through drip and furrow irrigation[J]. Scientia Horticulturae, 112(2): 142-148.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BAUHUS J, KHANNA P K, MENDEN N, 2000. Aboveground and belowground interactions in mixed plantations of Eucalyptus globulus and Acacia mearnsii[J]. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 30(12): 1886-1894.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
CHEN G S, YANG Z J, GAO R, et al., 2013. Carbon storage in a chronosequence of Chinese fir plantations in southern China[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 300: 68-76.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
DICHIO B, XILOYANNIS C, SOFO A, et al., 2007. Effects of post-harvest regulated deficit irrigation on carbohydrate and nitrogen partitioning, yield quality and vegetative growth of peach trees[J]. Plant and Soil, 290: 127-137.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
DREWNIAK B, GONZALEZ M A, 2017. Earth system model needs for including the interactive representation of nitrogen deposition and drought effects on forested ecosystems[J]. Forests, 8: 267.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
EGBERT, BORKEN W M, 2009. Reappraisal of drying and wetting effects on C and N mineralization and fluxes in soils[J]. Global Change Biology, 15(4): 808-824.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
HUANG Y X, ZHAO X Y, ZHANG H X, et al., 2009. Allometric effects of Agriophyllum squarrosum in response to soil nutrients, water, and population density in the Horqin Sandy Land of China[J]. Journal of Plant Biology, 52: 210-219.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
JOHANSSON M, 2000. The influence of ammonium nitrate on the root growth and ericoid mycorrhizal colonization of Calluna vulgaris (L.) Hull from a Danish heathland[J]. Oecologia, 123: 418-424.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
JOHANSSON O, PALMQVIST K, OLOFSSON J, 2012. Nitrogen deposition drives lichen community changes through differential species responses[J]. Global Change Biology, 18(8): 2626-2635.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
KNAPP A K, BEIER C, BRISKE D D, et al., 2008. Consequences of more extreme precipitation regimes for terrestrial ecosystems[J]. BioScience, 58(9): 811-821.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
KNUTE J N, 2000. Research review: The potential effects of nitrogen deposition on fine-root production in forest ecosystems[J]. New Phytologist, 147: 131-139.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
KUDOYAROVA G R, DODD I C, VESELOV D S, et al., 2015. Common and specific responses to availability of mineral nutrients and water[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 66(8): 2133-2144.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | MAO W, ALLINGTON G, LI Y L, et al., 2012. Life history strategy influences biomass allocation in response to limiting nutrients and water in an Arid system[J]. Polish Journal of Ecology, 60(3): 545-557. |
| [14] |
MUHAMMAD R, SALAHUDDIN, SHEN H L, et al., 2017. Influence of biochar and nitrogen on fine root morphology, physiology, and chemistry of Acer mono[J]. Scientific reports, 7(1): 5367.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
POORTER H, RYSER P, 2015. The limits to leaf and root plasticity: What is so special about specific root length?[J]. New Phytologist, 206: 1188-1190.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
SCHUSTER M J, SMITH N G, DUKES J S, 2016. Responses of aboveground C and N pools to rainfall variability and nitrogen deposition are mediated by seasonal precipitation and plant community dynamics[J]. Biogeochemistry, 129(3): 389-400.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
SPARRIUS L B, SEVINK J, KOOIJMAN A M, 2012. Effects of nitrogen deposition on soil and vegetation in primary succession stages in inland drift sands[J]. Plant Soil, 353(1-2): 261-272.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
WANG C H, WAN S Q, XING X R, et al., 2005. Temperature and soil moisture interactively affected soil net N mineralization in temperate grassland in Northern China[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 38(5): 1101-1110.
DOI URL |
| [19] | WU G L, DU G Z, 2008. Relationships between seed size and seedling growth strategy of herbaceous plant: a review[J]. The Journal of Applied Ecology, 19(1): 191-197. |
| [20] |
YANG H J, YANG L, WU M Y, et al., 2011. Plant community responses to nitrogen addition and increased precipitation: the importance of water availability and species traits[J]. Global Change Biology, 17(9): 2936-2944.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
YIN C Y, PANG X Y, CHEN K, et al., 2012. The water adaptability of Jatropha curcas is modulated by soil nitrogen availability[J]. Biomass and Bioenergy, 47(12): 71-81.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
YU Z P, HUANG Z Q, WANG M H, et al., 2015. Nitrogen addition enhances home-field advantage during litter decomposition in subtropical forest plantations[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 90: 188-196.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
ZHOU X B, ZHANG Y M, NIKLAS K J, 2014. Sensitivity of growth and biomass allocation patterns to increasing nitrogen: a comparison between ephemerals and annuals in the Gurbantunggut Desert, north-western China[J]. Annals of Botany, 113: 501-511.
DOI PMID |
| [24] | 白亚梅, 李毅, 单立山, 等, 2020. 降水变化和氮添加对红砂幼苗根系形态特征的影响[J]. 干旱区研究, 37(5): 1284-1292. |
| BAI Y M, LI Y, SHAN L S, et al., 2020. Effects of precipitation change and nitrogen addition on root morphological characteristics of Reaumuria soongorica [J]. Arid Zone Research, 37(5): 1284-1292. | |
| [25] | 常宏, 杨洪国, 赵广东, 等, 2019. 施氮和减水对中亚热带壳斗科三种幼树生物量及其分配的影响[J]. 生态学报, 39(18): 6753-6761. |
| CHANG H, YANG H G, ZHAO G D, et al., 2019. Effects of nitrogen application and rainfall exclusion on biomass and biomass allocation in saplings from three species of the Fagaceae family in the mid-subtropical region of China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(18): 6753-6761. | |
| [26] | 常杰, 葛滢, 陈增鸿, 等, 1999. 青冈常绿阔叶林主要植物种叶片的光合特性及其群落学意义[J]. 植物生态学报, 23(5): 393-400. |
| CHANG J, GE Y, CHEN Z H, et al., 1999. Characteristics of the leaf net photosynthesis of the evergreen broad-leaved forest dominated by Quercus glauca and their significance in coenology[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 23(5): 393-400. | |
| [27] | 陈云玉, 熊德成, 邓飞, 等, 2016. 土壤增温与氮添加对杉木幼苗细根径级根长分布的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 27(4): 1009-1014. |
| CHEN Y Y, XIONG D C, DENG F, et al., 2016. Effects of soil warming and nitrogen addition on the length distributions of different diameter class fine roots of Chinese fir seedlings[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 27(4): 1009-1014. | |
| [28] | 崔婉莹, 刘思佳, 魏亚伟, 等, 2019. 氮添加和水分胁迫对红松、水曲柳幼苗生物量分配的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 30(5): 1454-1462. |
| CUI W Y, LIU S J, WEI Y W, et al. 2019. Effects of nitrogen addition on biomass allocation of Pinus koraiensis and Fraxinus mandshurica seedlings under water stress. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 30(5): 1454-1462. | |
| [29] | 丁红, 张智猛, 戴良香, 等, 2015. 水分胁迫和氮肥对花生根系形态发育及叶片生理活性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 26(2): 450-456. |
| DING H, ZHANG M Z, DAI L X, et al., 2013. Effects of drought stress on the root growth and development and physiological characteristics of Peanut[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 24(6): 1586-1592. | |
| [30] | 董雯怡, 赵燕, 张志毅, 等, 2010. 水肥耦合效应对毛白杨苗木生物量的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 21(9): 2194-2200. |
| DONG W Y, ZHAO Y, ZHANG Z Y, et al., 2010. Coupling effects of water and fertilizeron the biomass of Populus tomentosa seedlings[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 21(9): 2194-2200. | |
| [31] | 高小敏, 刘世荣, 王一, 等, 2021. 穿透雨减少和氮添加对毛竹叶片和细根化学计量学的影响[J]. 生态学报, 41(4): 1440-1450. |
| GAO X M, LIU S R, WANG Y, et al., 2021. Effects of throughfall reduction and nitrogen addition on stoichiometry of leaf and fine root in Phyllostachys edulis forests[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(4): 1440-1450. | |
| [32] |
郭京衡, 曾凡江, 李尝君, 等, 2014. 塔克拉玛干沙漠南缘三种防护林植物根系构型及其生态适应策略[J]. 植物生态学报, 38(1): 36-44.
DOI |
|
GUO J H, ZENG F J, LI C J, et al., 2014. Root architecture and ecological adaptation strategies in three shelterbelt plant species in the southern Taklimakan Desert[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 38(1): 36-44.
DOI URL |
|
| [33] | 何佩云, 张余, 周良, 等, 2022. 干旱胁迫及氮肥调控对苦荞植株形态、生理特性及产量的影响[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 28(1): 128-134. |
| HE P Y, ZHANG Y, ZHOU L, et al., 2022. Effects of drought stress and nitrogen fertilizer regulation on morphology, physiological characteristics and yield of Fagopyrum tataricum[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 28(1): 128-134. | |
| [34] | 黄彩变, 曾凡江, 张波, 2021. 不同水氮条件下骆驼刺幼苗生长及氮效率变化特征[J]. 生态学报, 41(9): 3612-3624. |
| HUANG C B, ZENG F J, ZHANG B, 2021. Responses of plant growth and nitrogen efficiency of Alhagi sparsifolia seedlings to different water and nitrogen levels[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(9): 3612-3624. | |
| [35] | 李茂, 洪凯, 许珊珊, 等, 2020. 指数施肥对杉木优良无性系幼苗生长和养分含量的影响[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 26(6): 1490-1497. |
| LI M, HONG K, XU S S, et al., 2020. Effects of exponential fertilization on Cunninghamia lanceolata superior clone seedling growth and nutrient content[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 26(6): 1490-1497. | |
| [36] | 吕豪豪, 马晓东, 张瑞群, 等, 2016. 水分胁迫下不同氮素对多枝柽柳幼苗生长及生理的影响[J]. 草业学报, 25(9): 54-63. |
| LÜ H H, MA X D, ZHANG R Q, et al., 2016. Effects of different forms nitrogen on the growth and physiology of Tamarix ramosissima seedlings under water stress[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 25(9): 54-63. | |
| [37] | 祁瑜, 黄永梅, 王艳, 等, 2011. 施氮对几种草地植物生物量及其分配的影响[J]. 生态学报, 31(18): 5121-5129. |
| QI Y, HUANG Y M, WANG Y, et al., 2011. Biomass and its allocation of four grassland species under different nitrogen levels[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31(18): 5121-5129. | |
| [38] | 全文选, 丁贵杰, 2017. 干旱胁迫下马尾松幼苗针叶挥发性物质与内源激素的变化[J]. 林业科学, 53(4): 49-55. |
| QUAN W X, DING G J, 2017. Dynamic of volatiles and endogenous hormones in Pinus massoniana needles under drought stress[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinica, 53(4): 49-55. | |
| [39] | 孙百生, 钱金平, 赵欢蕊, 2018. 西北典型荒漠植物红砂生物量及根系形态特征对降水格局的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 27(11): 1993-1999. |
| SUN B S, QIAN J P, ZHAO H R, 2018. Response of biomass and root morphology of desert plants Corispermum candelabrum to precipitation change in northwest China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 27(11): 1993-1999. | |
| [40] | 孙誉育, 唐波, 尹春英, 等, 2015. 水氮耦合效应对红桦幼苗生长的影响及其生理机制[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 21(4): 710-716. |
| SUN Y Y, TANG B, YIN C Y, et al., 2015. Effects of water and nitrogen coupling on growth of Betual albo-sinensis seedlings and its physiological mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 21(4): 710-716. | |
| [41] | 王海艺, 韩烈保, 杨永利, 等, 2006. 水肥对洋白蜡生物量的耦合效应研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 28(S1): 64-68. |
| WANG H Y, HAN L B, YANG Y L, et al., 2006. Coupling effects of water and fertilizer on the biomass of Fraxinus pennsylvanica [J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 28(S1): 64-68. | |
| [42] |
王清奎, 李艳鹏, 张方月, 等, 2015. 短期施氮肥降低杉木幼林土壤的根系和微生物呼吸[J]. 植物生态学报, 39(12): 1166-1175.
DOI |
|
WANG Q K, LI Y P, ZHANG F Y, et al., 2015. Short-term nitrogen fertilization decreased root and microbial respiration in a young Cunninghamia lanceolata plantation[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 39(12): 1166-1175.
DOI URL |
|
| [43] | 吴丽君, 李志辉, 2014. 不同种源赤皮青冈幼苗生长和生理特性对干旱胁迫的响应[J]. 生态学杂志, 33(4): 996-1003. |
| WU L J, LI Z H, 2014. Response of growth and physiological characteristics of Cyclobalanopsis gilva seedlings from different provenances to drought stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 33(4): 996-1003. | |
| [44] | 吴茜, 丁佳, 闫慧, 等, 2011. 模拟降水变化和土壤施氮对浙江古田山5个树种幼苗生长和生物量的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 35(3): 256-267. |
|
WU Q, DING J, YAN H, et al., 2011. Effects of simulated precipitation and nitrogen addition on seedling growth and biomass in five tree species in Gutian Mountain, Zhejiang Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 35(3): 256-267.
DOI URL |
|
| [45] | 肖冬梅, 王淼, 姬兰柱, 2004. 水分胁迫对长白山阔叶红松林主要树种生长及生物量分配的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 23(5): 93-97. |
| XIAO D M, WANG M, JI L Z, 2004. Influence of water stress on growth and biomass allocation of dominant tree species in mixed forest of broad-leaved and Korean pine at Changbai Mountain[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 23(5): 93-97. | |
| [46] |
徐炳成, 山仑, 2003. 苜蓿和沙打旺苗期需水及其根冠比[J]. 草地学报, 11(1): 78-82.
DOI |
| XU B C, SHAN L, 2003. A study comparing water use efficiency and root /shoot ratio of Alfalfa and Astragalus adsurgens at seedling stage[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 11(1): 78-82. | |
| [47] | 许文斌, 余坦蔚, 洪小敏, 等, 2021. 亚热带4种典型人工林幼树光合特征和生物量对土壤水肥因子的响应[J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 50(1): 61-68. |
| XU W B, YU T W, HONG X M, et al., 2021. Effects of soil water and nutrient on photosynthetic characteristics and biomass of young trees under four typical plantations in subtropical region[J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 50(1): 61-68. | |
| [48] | 闫小莉, 林智熠, 胡文佳, 等, 2020. 林木氮素吸收偏好性及其形成机制研究进展[J]. 世界林业研究, 33(5): 25-30. |
| YAN X L, LIN Z Y, HU W J, et al., 2020. A review of nitrogen uptake preference of trees and its formation mechanism[J]. World Forestry Research, 33(5): 25-30. | |
| [49] | 杨腾, 马履一, 段劼, 等, 2014. 氮处理对文冠果幼苗光合、干物质积累和根系生长的影响[J]. 林业科学, 50(6): 82-89. |
| YANG T, MA L Y, DUAN J, et al., 2014. Effect of N application on photosynthesis, dry matter accumulation and root growth of Xanthoceras sorbifolia seedlings[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 50(6): 82-89. | |
| [50] | 杨振亚, 周本智, 陈庆标, 等, 2018. 干旱对杉木幼苗根系构型及非结构性碳水化合物的影响[J]. 生态学报, 38(18): 6729-6740. |
| YANG Z Y, ZHOU B Z, CHEN Q B, et al., 2018. Effects of drought on root architecture and non-structural carbohydrate of Cunninghamia lanceolata[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(18): 6729-6740. | |
| [51] | 尹丽, 胡庭兴, 刘永安, 等, 2011. 施氮量对麻疯树幼苗生长及叶片光合特性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 31(17): 4977-4984. |
| YIN L, HU T X, LIU Y A, et al., 2011. Effect of nitrogen application rate on growth and leaf photosynthetic characteristics of Jatropha curcas L. seedlings[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31(17): 4977-4984. | |
| [52] | 尹丽, 刘永安, 谢财永, 等, 2012. 干旱胁迫与施氮对麻疯树幼苗渗透调节物质积累的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 23(3): 632-638. |
| YIN L, LIU Y A, XIE C Y, et al., 2012. Effects of drought stress and nitrogen fertilization rate on the accumulation of osmolytes in Jatropha curcas seedlings[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 23(3): 632-638. | |
| [53] |
赵松实, 林茂森, 王安志, 等, 2021. 水氮胁迫对长白山阔叶红松林优势树种水分利用的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 32(1): 39-45.
DOI |
| ZHAO S S, LIN M S, WANG A Z, et al., 2021. Effects of water and nitrogen stress on water utilization of dominant species in broadleaved Korean pine forest in Changbai Mountain, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 32(1): 39-45. | |
| [54] | 周国逸, 闫俊华, 2001. 鼎湖山区域大气降水特征和物质元素输入对森林生态系统存在和发育的影响[J]. 生态学报, 21(12): 2002-2012. |
| ZHOU G Y, YAN J H, 2001. The influences of regional atmospheric precipitation characteristics and its element inputs on the existence and development of Dinghushan forest ecosystems[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 21(12): 2002-2012. |
| [1] | 王雪梅, 杨雪峰, 赵枫, 安柏耸, 黄晓宇. 基于机器学习算法的干旱区绿洲地上生物量估算[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1007-1015. |
| [2] | 陈科屹, 林田苗, 王建军, 何友均, 张立文. 天保工程20年对黑龙江大兴安岭国有林区森林碳库的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1016-1025. |
| [3] | 胡启瑞, 吉春容, 李迎春, 王雪姣, 杨明凤, 郭燕云. 膜下滴灌棉花蕾期干旱胁迫对光合特性及产量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1045-1052. |
| [4] | 葛元凯, 赵龙龙, 陈劲松, 任彦霓, 李洪忠. 1983-2020年西南地区气象干旱时空演变趋势及干旱事件识别[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 920-932. |
| [5] | 杨耀东, 陈玉梅, 涂鹏飞, 曾清如. 经济作物轮作模式下镉污染农田修复潜力[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 627-634. |
| [6] | 宋志斌, 周佳诚, 谭路, 唐涛. 高原河流着生藻类群落沿海拔梯度的变化特征--以西藏黑曲、雪曲为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 274-282. |
| [7] | 崔远远, 张征云, 刘鹏, 张运春, 张桥英. 镉与聚乙烯微塑料胁迫对小白菜根系的形态特征和分形维数的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 158-165. |
| [8] | 李威闻, 黄金权, 齐瑜洁, 刘小岚, 刘纪根, 毛治超, 高绣纺. 土壤侵蚀条件下土壤微生物生物量碳含量变化及其影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 47-55. |
| [9] | 黄伟佳, 刘春, 刘岳, 黄斌, 李定强, 袁再健. 南岭山地不同海拔土壤生态化学计量特征及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 80-89. |
| [10] | 陈科屹, 王建军, 何友均, 张立文. 黑龙江大兴安岭重点国有林区森林碳储量及固碳潜力评估[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1725-1734. |
| [11] | 刘桢迪, 宋艳宇, 王宪伟, 谭稳稳, 张豪, 高晋丽, 高思齐, 杜宇. 冻土区泥炭地植物生长及碳氮特征对模拟增温的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1765-1772. |
| [12] | 韩翠, 康扬眉, 余海龙, 李冰, 黄菊莹. 荒漠草原凋落物分解过程中降水量对土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1802-1812. |
| [13] | 陈乐, 卫伟. 西北旱区典型流域土地利用与生境质量的时空演变特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1909-1918. |
| [14] | 崔乔, 李宗省, 张百娟, 赵越, 南富森. 冻融作用对土壤可溶性碳氮和微生物量碳氮含量影响的荟萃分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1700-1712. |
| [15] | 王磊, 温远光, 周晓果, 朱宏光, 孙冬婧. 尾巨桉与红锥混交对林下植被和土壤性质的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1340-1349. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
