生态环境学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (10): 1732-1740.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.10.002
收稿日期:2022-12-05
出版日期:2023-10-18
发布日期:2024-01-16
通讯作者:
*张晓曼。E-mail: zhangxiaoman1977@163.com作者简介:赵蔓(1995年生),女,博士研究生,主要从事园林植物培育与环境生态学方面的研究工作。E-mail: sxyqpdzm@163.com
基金资助:
ZHAO Man1,2( ), ZHANG Xiaoman1,*(
), ZHANG Xiaoman1,*( ), YANG Mingjie1
), YANG Mingjie1
Received:2022-12-05
Online:2023-10-18
Published:2024-01-16
摘要:
以山西省药林寺森林公园受到中度、重度以及周边未受到林火干扰的栓皮栎 (Quercus variabilis)-辽东栎(Quercus wutaishansea)混交林为研究对象,采用典型样地法对栓皮栎-辽东栎混交林植物多样性特征、土壤理化性质等进行分析,采用冗余分析的方法,探讨林火干扰后土壤理化性质对植被物种多样性的影响机制,以期为林火干扰迹地植物多样性恢复和森林的可持续经营提供理论基础。结果表明,1)研究区维管植物38种,各林火干扰程度下科属种数目均表现为草本层>灌木层>乔木层。2)在不同程度林火干扰下,乔木层的Simpson指数、Margalef指数表现为重度>中度>对照(CK),Shannon-wiener指数、Pielou指数表现为中度>重度>CK;灌木层的α多样性指数均表现为在重度林火干扰下最高,在中度林火干扰下最低;草本层的Simpson指数、Shannon-wiener指数、Margalef指数表现为CK>中度>重度,Pielou指数的变化规律为重度>CK>中度。3)重度林火干扰后,在0-10 cm土层土壤中,林下土壤含水率、pH值、全磷、全钾、速效磷、速效钾含量与CK相比显著降低3.2%、20.36%、14.03%、7.8%、5.9%;在10-20 cm土层土壤中,林下土壤全氮、全磷、速效钾含量在林火干扰后与CK相比显著降低36%、24.07%、2.06%。4)冗余分析结果表明:0-10 cm土层中的有机质、速效钾与10-20 cm土层中的碱解氮、全钾是显著影响乔、灌、草物种多样性的环境因子。综上所述,林火干扰后栓皮栎-辽东栎混交林植被物种多样性与土壤理化性质具有相关性,在火烧迹地生态恢复中适量补充土壤有机质、氮与钾,可为更多物种的生存和发育提供良好的土壤条件。
中图分类号:
赵蔓, 张晓曼, 杨明洁. 林火干扰对栓皮栎-辽东栎混交林植物多样性与土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(10): 1732-1740.
ZHAO Man, ZHANG Xiaoman, YANG Mingjie. Effects of Forest Fire Disturbance on Species Diversity and Soil Physicochemical Properties of Quercus variabilis and Quercus wutaishansea Mixed Forests[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(10): 1732-1740.
| 林火程度 | 对照 (CK) | 中度 | 重度 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 火烧特征 | 树木完好, 地表无火烧痕迹 | 30%<乔木死亡率≤70% | 乔木死亡率>70%, 树皮烧焦, 树根被烧 | ||||||
| 样本量 | 3 | 3 | 3 | ||||||
| 平均海拔/m | 1025.86 | 1074.79 | 1075.11 | ||||||
| 乔木平均胸径/cm | 14.6±0.94a 1) | 13.57±1.41a | 14.32±1.55a | ||||||
| 乔木平均高度/m | 11.28±0.59b | 9.28±0.61a | 12.48±0.33c | ||||||
| 郁闭度 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| 坡度/(°) | 34 | 20 | 25 | 38 | 45 | 30 | 35 | 32 | 27 |
| 坡向 | 西 | 西南 | 西南 | 南 | 东 | 东北 | 东南 | 东南 | 东南 |
表1 研究样地基本概况
Table 1 Basic characteristics of the sampling plots
| 林火程度 | 对照 (CK) | 中度 | 重度 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 火烧特征 | 树木完好, 地表无火烧痕迹 | 30%<乔木死亡率≤70% | 乔木死亡率>70%, 树皮烧焦, 树根被烧 | ||||||
| 样本量 | 3 | 3 | 3 | ||||||
| 平均海拔/m | 1025.86 | 1074.79 | 1075.11 | ||||||
| 乔木平均胸径/cm | 14.6±0.94a 1) | 13.57±1.41a | 14.32±1.55a | ||||||
| 乔木平均高度/m | 11.28±0.59b | 9.28±0.61a | 12.48±0.33c | ||||||
| 郁闭度 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| 坡度/(°) | 34 | 20 | 25 | 38 | 45 | 30 | 35 | 32 | 27 |
| 坡向 | 西 | 西南 | 西南 | 南 | 东 | 东北 | 东南 | 东南 | 东南 |
| 层次 | 物种 | 科 | 属 | 重要值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照 (CK) | 中度 | 重度 | ||||
| 乔木层 | 辽东栎 Quercus wutaishansea Mary | 壳斗科 | 栎属 | 0.53 | 0.44 | 0.38 |
| 栓皮栎 Quercus variabilis Bl. | 壳斗科 | 栎属 | 0.39 | 0.40 | 0.49 | |
| 垂枝榆 Ulmus pumila L. cv. Tenue | 榆科 | 榆属 | 0.08 | - | 0.13 | |
| 油松 Pinus tabuliformis Carrière | 松科 | 松属 | - | 0.16 | - | |
| 灌木层 | 紫穗槐 Amorpha L. | 豆科 | 紫穗槐属 | 0.11 | - | - |
| 垂枝榆 Ulmus pumila L. cv. Tenue | 榆科 | 榆属 | - | 0.08 | 0.12 | |
| 田菁 Sesbania cannabina (Retz.) Poir. | 豆科 | 田菁属 | 0.08 | - | - | |
| 蛇葡萄 Ampelopsis sinica (Mig.) W. T. Wang. | 蛇葡萄科 | 蛇葡萄属 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.10 | |
| 桑 Morus alba L. | 桑科 | 桑属 | 0.07 | - | - | |
| 牛至 Origanum vulgare L. | 唇形科 | 牛至属 | 0.05 | - | 0.12 | |
| 曼陀罗 Datura stramonium L. | 茄科 | 曼陀罗属 | - | - | 0.07 | |
| 马兜铃 Aristolochia debilis Sieb. et Zucc | 马兜铃科 | 马兜铃属 | 0.07 | - | - | |
| 栓皮栎 Quercus variabilis Bl. | 壳斗科 | 栎属 | 0.30 | 0.42 | 0.25 | |
| 荆条 Vitex negundo.var. Heterophylla (Franch.) Rehd. | 马鞭草科 | 牡荆属 | - | 0.05 | 0.13 | |
| 锦鸡儿 Caragana sinica (Buc'hoz) Rehd. | 豆科 | 锦鸡儿属 | 0.08 | - | - | |
| 黄栌 Cotinus coggygria Scop. | 漆树科 | 黄栌属 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.11 | |
| 槲树 Quercus dentata Thunb. | 壳斗科 | 栎属 | - | 0.07 | - | |
| 白首乌 Cynanchum bungei Decne. | 萝藦科 | 鹅绒藤属 | - | 0.06 | - | |
| 艾草 Artemisia argyi Lévl. et Van. | 菊科 | 蒿属 | 0.05 | - | - | |
| 沿阶草 Ophiopogon bodinieri Levl. | 百合科 | 沿阶草属 | - | 0.06 | - | |
| 小红菊 Chrysanthemum chanetii H. Léveillé | 菊科 | 菊属 | - | 0.04 | 0.14 | |
| 委陵菜 Potentilla chinensis Ser. | 蔷薇科 | 委陵菜属 | 0.05 | - | - | |
| 天门冬 Asparagus cochinchinensis (Lour.) Merr. | 百合科 | 天门冬属 | 0.10 | 0.03 | - | |
| 牛筋草 Eleusine indica (L.) Gaertn. | 禾本科 | 穇属 | - | - | 0.14 | |
| 草本层 | 茅梅 Rubus parvifolius Linn. | 蔷薇科 | 悬钩子属 | - | 0.08 | - |
| 葎草 Humulus scandens (Lour.) Merr. | 桑科 | 葎草属 | 0.09 | - | - | |
| 藜 Chenopodium album L. | 藜科 | 藜属 | 0.07 | - | - | |
| 堇菜 Viola verecumda A.Gray | 堇菜科 | 堇菜属 | - | 0.15 | 0.09 | |
| 鸡眼草 Kummerowia striata (Thunb.) Schindl. | 豆科 | 鸡眼草属 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.16 | |
| 黄栌 Cotinus coggygria Scop. | 漆树科 | 黄栌属 | - | 0.07 | - | |
| 黄刺玫 Rosa xanthina Lindl. | 蔷薇科 | 蔷薇属 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.02 | |
| 胡枝子 Lespedeza bicolor Turcz. | 豆科 | 胡枝子属 | - | 0.10 | - | |
| 厚皮菜 Beta vulgaris var. Cicla L. | 藜科 | 甜菜属 | - | 0.04 | 0.26 | |
| 枸杞 Lycium chinense Miller | 茄科 | 枸杞属 | - | - | 0.08 | |
| 狗尾草 Setaria viridis (L.) Beauv. | 禾本科 | 狗尾草属 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.07 | |
| 狭叶柴胡 Bupleurum scorzonerifolium Willd. | 伞形科 | 柴胡属 | 0.05 | - | - | |
| 草木犀 Melilotus officinalis (L.) Pall. | 豆科 | 草木犀属 | 0.08 | - | 0.03 | |
| 艾草 Artemisia argyi Lévl. et Van. | 菊科 | 蒿属 | 0.09 | - | - | |
表2 林地不同程度火烧迹地植被群落物种组成及其重要值
Table 2 Species composition and importance values of vegetation communities in different degree of burning in woodland
| 层次 | 物种 | 科 | 属 | 重要值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照 (CK) | 中度 | 重度 | ||||
| 乔木层 | 辽东栎 Quercus wutaishansea Mary | 壳斗科 | 栎属 | 0.53 | 0.44 | 0.38 |
| 栓皮栎 Quercus variabilis Bl. | 壳斗科 | 栎属 | 0.39 | 0.40 | 0.49 | |
| 垂枝榆 Ulmus pumila L. cv. Tenue | 榆科 | 榆属 | 0.08 | - | 0.13 | |
| 油松 Pinus tabuliformis Carrière | 松科 | 松属 | - | 0.16 | - | |
| 灌木层 | 紫穗槐 Amorpha L. | 豆科 | 紫穗槐属 | 0.11 | - | - |
| 垂枝榆 Ulmus pumila L. cv. Tenue | 榆科 | 榆属 | - | 0.08 | 0.12 | |
| 田菁 Sesbania cannabina (Retz.) Poir. | 豆科 | 田菁属 | 0.08 | - | - | |
| 蛇葡萄 Ampelopsis sinica (Mig.) W. T. Wang. | 蛇葡萄科 | 蛇葡萄属 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.10 | |
| 桑 Morus alba L. | 桑科 | 桑属 | 0.07 | - | - | |
| 牛至 Origanum vulgare L. | 唇形科 | 牛至属 | 0.05 | - | 0.12 | |
| 曼陀罗 Datura stramonium L. | 茄科 | 曼陀罗属 | - | - | 0.07 | |
| 马兜铃 Aristolochia debilis Sieb. et Zucc | 马兜铃科 | 马兜铃属 | 0.07 | - | - | |
| 栓皮栎 Quercus variabilis Bl. | 壳斗科 | 栎属 | 0.30 | 0.42 | 0.25 | |
| 荆条 Vitex negundo.var. Heterophylla (Franch.) Rehd. | 马鞭草科 | 牡荆属 | - | 0.05 | 0.13 | |
| 锦鸡儿 Caragana sinica (Buc'hoz) Rehd. | 豆科 | 锦鸡儿属 | 0.08 | - | - | |
| 黄栌 Cotinus coggygria Scop. | 漆树科 | 黄栌属 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.11 | |
| 槲树 Quercus dentata Thunb. | 壳斗科 | 栎属 | - | 0.07 | - | |
| 白首乌 Cynanchum bungei Decne. | 萝藦科 | 鹅绒藤属 | - | 0.06 | - | |
| 艾草 Artemisia argyi Lévl. et Van. | 菊科 | 蒿属 | 0.05 | - | - | |
| 沿阶草 Ophiopogon bodinieri Levl. | 百合科 | 沿阶草属 | - | 0.06 | - | |
| 小红菊 Chrysanthemum chanetii H. Léveillé | 菊科 | 菊属 | - | 0.04 | 0.14 | |
| 委陵菜 Potentilla chinensis Ser. | 蔷薇科 | 委陵菜属 | 0.05 | - | - | |
| 天门冬 Asparagus cochinchinensis (Lour.) Merr. | 百合科 | 天门冬属 | 0.10 | 0.03 | - | |
| 牛筋草 Eleusine indica (L.) Gaertn. | 禾本科 | 穇属 | - | - | 0.14 | |
| 草本层 | 茅梅 Rubus parvifolius Linn. | 蔷薇科 | 悬钩子属 | - | 0.08 | - |
| 葎草 Humulus scandens (Lour.) Merr. | 桑科 | 葎草属 | 0.09 | - | - | |
| 藜 Chenopodium album L. | 藜科 | 藜属 | 0.07 | - | - | |
| 堇菜 Viola verecumda A.Gray | 堇菜科 | 堇菜属 | - | 0.15 | 0.09 | |
| 鸡眼草 Kummerowia striata (Thunb.) Schindl. | 豆科 | 鸡眼草属 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.16 | |
| 黄栌 Cotinus coggygria Scop. | 漆树科 | 黄栌属 | - | 0.07 | - | |
| 黄刺玫 Rosa xanthina Lindl. | 蔷薇科 | 蔷薇属 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.02 | |
| 胡枝子 Lespedeza bicolor Turcz. | 豆科 | 胡枝子属 | - | 0.10 | - | |
| 厚皮菜 Beta vulgaris var. Cicla L. | 藜科 | 甜菜属 | - | 0.04 | 0.26 | |
| 枸杞 Lycium chinense Miller | 茄科 | 枸杞属 | - | - | 0.08 | |
| 狗尾草 Setaria viridis (L.) Beauv. | 禾本科 | 狗尾草属 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.07 | |
| 狭叶柴胡 Bupleurum scorzonerifolium Willd. | 伞形科 | 柴胡属 | 0.05 | - | - | |
| 草木犀 Melilotus officinalis (L.) Pall. | 豆科 | 草木犀属 | 0.08 | - | 0.03 | |
| 艾草 Artemisia argyi Lévl. et Van. | 菊科 | 蒿属 | 0.09 | - | - | |
| 土壤因子 | 土层深度/cm | 林火程度 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照 (CK) | 中度 | 重度 | ||
| w(SWC)/ % | 0-10 | 19.57±3.38Aa | 19.77±0.97Aa | 18.95±3.78Aa |
| 10-20 | 12.87±2.49Ab | 16.76±0.62Aab | 20.30±2.72Aa | |
| pH | 0-10 | 6.58±0.09Aa | 6.33±0.33Aa | 5.24±0.32Ab |
| 10-20 | 6.62±0.12Aa | 6.60±0.71Aa | 6.93±0.05Aa | |
| w(OM)/ (g∙kg−1) | 0-10 | 42.58±8.77Ac | 76.93±8.20Ab | 118.80±3.30Aa |
| 10-20 | 17.60±1.91Ac | 45.10±8.30Ab | 64.90±6.87Aa | |
| w(TN)/ (g∙kg−1) | 0-10 | 0.14±0.00Ab | 0.16±0.02Aab | 0.18±0.02Aa |
| 10-20 | 0.25±0.01Bb | 0.37±0.06Aa | 0.16±0.02Ac | |
| w(TP)/ (g∙kg−1) | 0-10 | 0.57±0.08Aa | 0.44±0.09Aa | 0.49±0.06Aa |
| 10-20 | 0.54±0.05Aa | 0.37±0.08Ab | 0.41±0.02Ab | |
| w(TK)/ (g∙kg−1) | 0-10 | 532.08±17.09Aa | 507.72±19.74Aab | 490.46±20.99Ac |
| 10-20 | 482.91±23.62Ab | 555.55±8.33Aa | 482.63±12.57Ab | |
| w(AN)/ (g∙kg−1) | 0-10 | 23.92±8.81Ab | 56.42±7.49Aa | 50.25±6.54Aa |
| 10-20 | 8.92±0.29Ac | 23.75±2.18Ab | 40.25±3.50Aa | |
| w(AP)/ (g∙kg−1) | 0-10 | 26.19±7.22Aa | 11.83±3.27Ab | 21.8±1.82Aa |
| 10-20 | 6.68±1.30Bab | 5.02±0.53Bb | 8.48±1.50Aa | |
| w(AK)/ (g∙kg−1) | 0-10 | 230.91±6.10Aa | 193.44±5.94Ab | 217.31±18.26Aa |
| 10-20 | 197.83±7.79Aa | 178.51±5.86Ab | 193.75±3.06Aa | |
表3 林火干扰对林下土壤理化性质的影响
Table 3 Effects of forest fire disturbance on physical and chemical properties of soil under forest
| 土壤因子 | 土层深度/cm | 林火程度 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照 (CK) | 中度 | 重度 | ||
| w(SWC)/ % | 0-10 | 19.57±3.38Aa | 19.77±0.97Aa | 18.95±3.78Aa |
| 10-20 | 12.87±2.49Ab | 16.76±0.62Aab | 20.30±2.72Aa | |
| pH | 0-10 | 6.58±0.09Aa | 6.33±0.33Aa | 5.24±0.32Ab |
| 10-20 | 6.62±0.12Aa | 6.60±0.71Aa | 6.93±0.05Aa | |
| w(OM)/ (g∙kg−1) | 0-10 | 42.58±8.77Ac | 76.93±8.20Ab | 118.80±3.30Aa |
| 10-20 | 17.60±1.91Ac | 45.10±8.30Ab | 64.90±6.87Aa | |
| w(TN)/ (g∙kg−1) | 0-10 | 0.14±0.00Ab | 0.16±0.02Aab | 0.18±0.02Aa |
| 10-20 | 0.25±0.01Bb | 0.37±0.06Aa | 0.16±0.02Ac | |
| w(TP)/ (g∙kg−1) | 0-10 | 0.57±0.08Aa | 0.44±0.09Aa | 0.49±0.06Aa |
| 10-20 | 0.54±0.05Aa | 0.37±0.08Ab | 0.41±0.02Ab | |
| w(TK)/ (g∙kg−1) | 0-10 | 532.08±17.09Aa | 507.72±19.74Aab | 490.46±20.99Ac |
| 10-20 | 482.91±23.62Ab | 555.55±8.33Aa | 482.63±12.57Ab | |
| w(AN)/ (g∙kg−1) | 0-10 | 23.92±8.81Ab | 56.42±7.49Aa | 50.25±6.54Aa |
| 10-20 | 8.92±0.29Ac | 23.75±2.18Ab | 40.25±3.50Aa | |
| w(AP)/ (g∙kg−1) | 0-10 | 26.19±7.22Aa | 11.83±3.27Ab | 21.8±1.82Aa |
| 10-20 | 6.68±1.30Bab | 5.02±0.53Bb | 8.48±1.50Aa | |
| w(AK)/ (g∙kg−1) | 0-10 | 230.91±6.10Aa | 193.44±5.94Ab | 217.31±18.26Aa |
| 10-20 | 197.83±7.79Aa | 178.51±5.86Ab | 193.75±3.06Aa | |
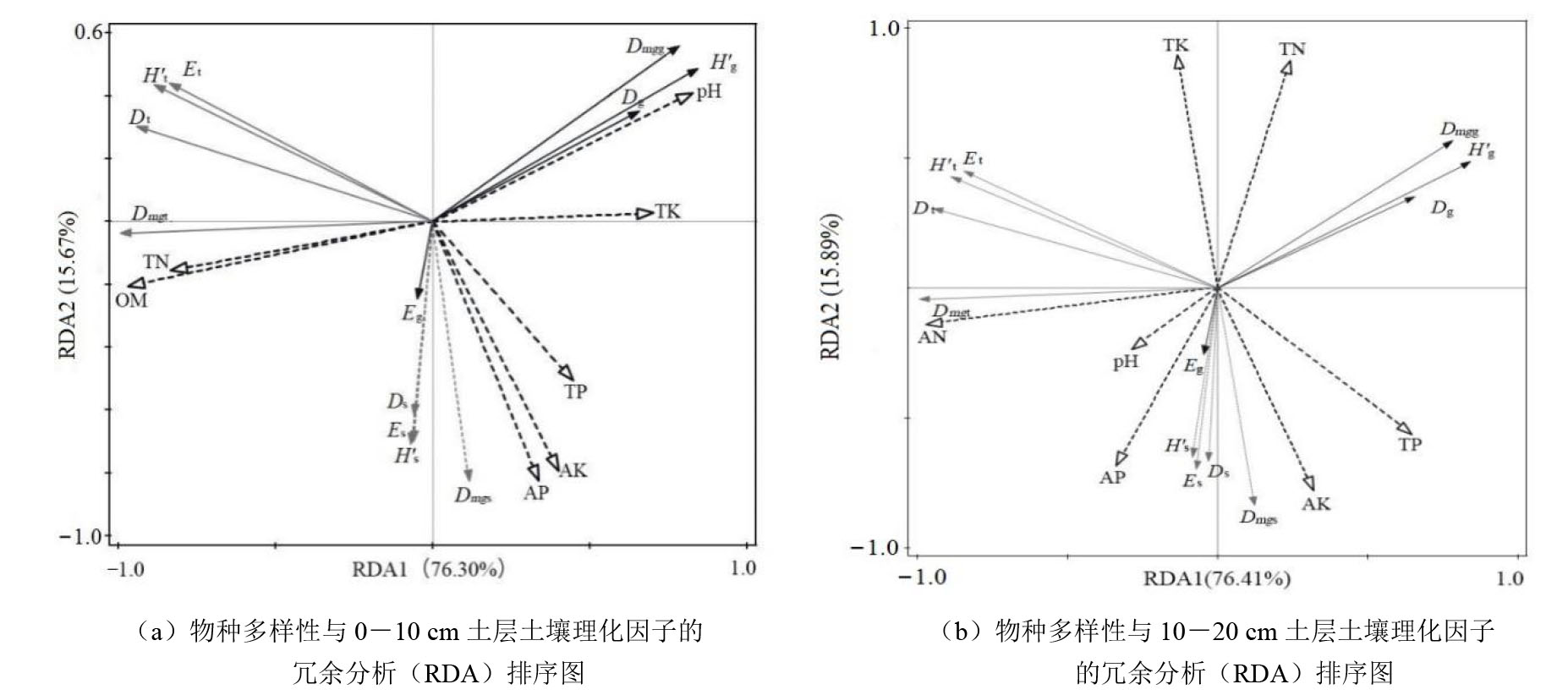
图2 物种多样性与土壤理化因子的冗余分析(RDA)排序图 Dt:乔木层Simpson指数;Ds:灌木层Simpson指数;Dg:草本层Simpson指数;H′t:乔木层Shannon-Wiener指数;H′s:灌木层Shannon-Wiener指数;H′g:草本层Shannon-Wiener指数;Et:乔木层Pielou指数;Es:灌木层Pielou指数;Eg:草本层Pielou指数;Dmgt:乔木层Margalef指数;Dmgs:灌木层Margalef指数;Dmgg:草本层Margalef指数;SWC:含水率;pH:pH值;OM:有机质;TN:全氮;TP:全磷;TK:全钾;AN:碱解氮;AP:速效磷;AK:速效钾
Figure 2 Redundancy analysis (RDA) ordination map of species diversity and soil physicochemical factors
| [1] |
BARBIER S, GOSSELIN F, BALANDIER P, 2008. Influence of tree species on understory vegetation diversity and mecha-nisms involved- A critical review for temperate and bo-real forests[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 254(1): 1-15.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
CERTINI G, 2005. Effects of fire on properties of forest soils: A review[J]. Oecologia, 143(1): 1-10.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
COVINGTON W W, SACKETT S S, 1992. Soil mineral nitrogen changes following prescribed burning in Ponderosa pine [J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 54(1-4): 175-191.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
GAYLOR M O, MEARS G L, HARVEY E, et al., 2014. Polybrominated diphenyl ether accumulation in an agricultural soil ecosystem receiving wastewater sludge amendments[J]. Environmental science & technology, 48(12): 7034-7043.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
GHALEY B B, PORTER J R, 2014. Ecosystem function and service quantification and valuation in a conventional winter wheat production system with DAISY model in Denmark[J]. Ecosystem Services, 10: 79-83.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
KUTIEL P, NAVEH Z, 1987. The effect of fire on nutrients in a pine forest soil[J]. Plant and Soil, 104(2): 269-274.
DOI URL |
| [7] | MIESEL J R, HOCKADAY W C, KOLKA R K, et al., 2015. Soil organic matter composition and quality across fire severity gradients in coniferous and deciduous forests of the southern boreal region[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research-Biogeosciences, 120(6): 1424-1141. |
| [8] |
VINÍCIUS D L D, MARINA H, RAFAEL S O, et al., 2016. Disturbance maintains alternative biome states[J]. Ecology Letters, 19(1): 12-9.
DOI PMID |
| [9] | 戴伟, 1994. 人工油松林火烧前后土壤化学性质变化的研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 16(1): 102-105. |
| DAI W, 1994. Study on the changes in some chemical soil properties after burning[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 16(1): 102-105. | |
| [10] | 董灵波, 刘兆刚, 2020. 不同强度的林火干扰对天然落叶松林分物种多样性及碳储量的影响[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 48(9): 45-50. |
| DONG L B, LIU Z G, 2020. Effects of different fire intensities on biodiversity and carbon stocks of Natural Larix gmelinii forest in Daxing’an Mountains[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 48(9): 45-50. | |
| [11] |
杜京旗, 张巧仙, 田晓东, 等, 2016. 云顶山亚高山草甸植被分布、物种多样性与土壤化学因子的相关性[J]. 植物研究, 36(3): 444-451.
DOI |
| DU J Q, ZHANG Q X, TIAN X D, et al., 2016. Relationships between vegetation distribution, species diversity of subalpine meadow and soil chemical factors in the Yundingshan, China[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 36(3): 444-451. | |
| [12] | 冯健, 高慧淋, 王骞春, 等, 2021. 辽东山区落叶松-水曲柳混交林及其纯林生长与生物量分配特征[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 49(7): 22-27. |
| FENG J, GAO H L, WANG Q C, et al., 2021. Growth and biomass allocation of mixed larch-ash forest and its pure stand in the eastern mountainous area of Liaoning province[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 49(7): 22-27. | |
| [13] | 谷会岩, 金靖博, 陈祥伟, 等, 2010. 不同火烧强度林火对大兴安岭北坡兴安落叶松林土壤化学性质的长期影响[J]. 自然资源学报, 25(7): 1114-1121. |
| GU H Y, JIN J B, CHEN X W, et al., 2010. The long-term impacts on chemical properties of Larix gmelini forest on the northern slope of Greater Hinggan Mountains from a forest fire of varing fite intensity[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 25(7): 1114-1121. | |
| [14] | 贺婷, 2015. 火烧对大兴安岭地区森林土壤理化性状的影响[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学. |
| HE T, 2015. The impact of forest soil physical and chemical properties on fire in Daxing’an Mourtains Region[D]. Inner Mongolia: Agricultural University. | |
| [15] | 胡海清, 魏书精, 孙龙, 2012. 大兴安岭呼中区2010年森林火灾碳排放的计量估算[J]. 林业科学, 48(10): 109-119. |
| HU H Q, WEI S J, SONG L, 2012. Estimation of carbon emissions from forest fires in 2010 in Huzhong of Daxing’anling Mountain[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 48(10): 109-119. | |
| [16] | 黄泽东, 2014. 能源植物栓皮栎与辽东栎果实的发育和成分分析[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学. |
| HUANG Z D, 2014. Development and component analysis on fruits of energy plants Quercus variabilis and Quercus wutaishanica[D]. Beijing: Forestry University. | |
| [17] | 李威, 周梅, 赵鹏武, 等, 2020. 大兴安岭东麓火烧迹地恢复初期植被特征[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 48(1): 51-55. |
| LI W, ZHOU M, ZHAO P W, et al., 2020. Vegetation characteristics in the early stage of restoration of burned area in eastern Daxing’an Mountains[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 48(1): 51-55. | |
| [18] | 刘发林, 张思玉, 2009. 火干扰下马尾松林物种多样性和土壤养分特征[J]. 西北林学院学报, 24(5): 36-40. |
| LIU F L, ZHANG S Y, 2009. Characters of species diversity and soil nutrition of pinus massoniana forest under fire desturbance[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 24(5): 36-40. | |
| [19] |
刘瑞斌, 李莉, 陈鹏东, 等, 2016. 森林火灾对烟台蓁山次生林土壤性质的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 25(8): 1300-1305.
DOI |
| LIU R B, LI L, CHEN P D, et al., 2016. Effects of forest fire on soil properties of secondary forests on Zhenshan mountain in Yantai, Shandong province[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 25(8): 1300-1305. | |
| [20] | 吕倩, 康文斯, 郭茂金, 等, 2019. 柏木人工林目标树经营初期对林下植物多样性及土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 25(5): 1036-1043. |
| LÜ Q, KANG W S, GUO M J, et al., 2019. Early effects of target tree management on undergrowth plant diversity and soil physicochemical properties in Cupressus funebris plantations[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied & Environmental Biology, 25(5): 1036-1043. | |
| [21] | 马克平, 刘玉明, 1994. 生物群落多样性的测度方法Ⅰα多样性的测度方法(下)[J]. 生物多样性, 2(4): 231-239. |
|
MA K P, LIU Y M, 1994. Measurement method of biological community diversity Ⅰα measurement method of diversity (Part2)[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2(4): 231-239.
DOI URL |
|
| [22] | 孟莹莹, 周莉, 周旺明, 等, 2015. 长白山风倒区植被恢复26年后物种多样性变化特征[J]. 生态学报, 35(1): 142-149. |
|
MENG Y Y, ZHOU L, ZHOU W M, et al., 2015. Characteristics of plant species diversity in a windthrow area on Changbai Mountain after 26 years of natural recovery[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35(1): 142-149.
DOI URL |
|
| [23] | 牛学银, 2011. 对黑龙江省栎林种类和生态习性的探讨[J]. 林业勘查设计 (3): 71-72. |
| NIU X Y, 2011. Discussion on the species and ecological habits of Oak forestsin Heilongjiang province[J]. Forest Investigation Design (3): 71-72. | |
| [24] | 彭剑华, 肖泽鑫, 詹潮安, 等, 2010. 广东南澳岛中华楠群落结构及种间相关性分析[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 31(4): 90-94. |
| PENG J H, XIAO Z X, ZHAN C A, et al., 2010. The structure and interspecific correlation of Machilus chinensis community in Nan’ao Island Guangdong[J]. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 31(4): 90-94. | |
| [25] | 覃炳醒, 2012. 林火干扰对大兴安岭典型林型植被特征的影响[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学. |
| QIN B X, 2012. The Effects of forest fire on vegetation characteristics in Great Xing’an Mountain[D]. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University. | |
| [26] | 石亮, 周梅, 王鼎, 等, 2016. 林火干扰对兴安落叶松林下植被多样性和生物量的影响[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 44(1): 44-47. |
| SHI L, ZHOU M, WANG D, et al., 2016. Effects of forest fire on understory vegetation diversity and biomass of Larix Gmelini forest[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 44(1): 44-47. | |
| [27] | 孙家宝, 张海林, 胡海清, 2009. 火干扰强度对兴安落叶松林物种组成及多样性的影响[J]. 森林工程, 25(6): 1-5. |
| SUN J B, ZHANG H L, HU H Q, 2009. Effect of fire disturbance intensity on species composition and species diversity of Larix gmelinii forestin Daxing’anling Mountain[J]. Forest Engineering, 25(6): 1-5. | |
| [28] | 田昆, 1997. 火烧迹地土壤磷含量变化的研究[J]. 西南林业大学学报, 17(1): 22-26. |
| TIAN K, 1997. A study on the variations of phosphorus content in fire slash[J]. Journal of Southwest Forestry University, 17(1): 22-26. | |
| [29] | 王鼎, 周梅, 赵鹏武, 等, 2016. 森林火灾后兴安落叶松林植被群落乔木更新状况研究[J]. 林业资源管理 (6): 64-70. |
| WANG D, ZHOU M, ZHAO P W, et al., 2016. Study on characteristics of plant regeneration at burned area of Daxing’an Mountains[J]. Forest Resources Management (6): 64-70. | |
| [30] | 魏云敏, 袁强, 蔡恒明, 2016. 火干扰对土壤含水率的影响[J]. 林业科技, 41(6): 24-26. |
| WEI Y M, YUAN Q, CAI H M, 2016. Effect of fire disturbance on soil moisture content[J]. Forestry Science & Technology, 41(6): 24-26. | |
| [31] | 辛颖, 赵雨森, 陈强, 2013. 大兴安岭火烧迹地植被恢复后土壤理化性质[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 41(8): 65-68. |
| XIN Y, ZHAO Y S, CHEN Q, 2013. Soil physical and chemical properties of different forests in burned area of Daxing’an Mountains after vegetation restoration[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 41(8): 65-68. | |
| [32] | 许鹏波, 屈明, 薛立, 2013. 火对森林土壤的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 32(6): 1596-1606. |
| XU P B, QU M, XUE L, 2013. Effects of forest fire on forest soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 32(6): 1596-1606. | |
| [33] | 杨寅, 邱钰明, 王中斌, 等, 2020. 不同主伐方式对兴安落叶松 (Larix gmelinii) 根际土壤理化性质及微生物群落的影响[J]. 生态学报, 40(21): 7621-7629. |
| YANG Y, QIU Y M, WANG Z B, et al., 2020. Effects of different harvest methods on physicochemical proerties and micobial community of Larix gmelinii rhizosphere soil[J]. Acta Ecologica Siniea, 40(21): 7621-7629. | |
| [34] | 曾素平, 刘发林, 赵梅芳, 等, 2020. 火干扰强度对亚热带四种森林类型土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 生态学报, 40(1): 233-246. |
| ZENG S P, LIU F L, ZHAO M F, et al., 2020. Effects of fire disturbance intensities on soil physiochemical properties of pour subtropical forest types[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(1): 233-246. | |
| [35] | 张喜, 朱军, 崔迎春, 等, 2011. 火烧对黔中喀斯特山地马尾松林土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 生态学报, 31(19): 5809-5817. |
| ZHANG X, ZHU J, CUI Y C, et al., 2011. Influence of fire on a Pinus massoniana soil in a karst mountain area at the center of Guizhou province, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31(19): 5809-5817. | |
| [36] | 张玉红, 覃炳醒, 孙铭隆, 等, 2012. 林火对大兴安岭典型林型林下植被与土壤的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 34(2): 7-13. |
| ZHANG Y H, QIN B X, SUN M L, et al., 2012. Impact of forest fire onunderstory vegetation and soil in typical forest types of Daxing’an Mountains, northeastern China[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 34(2): 7-13. | |
| [37] | 赵彬, 孙龙, 胡海清, 等, 2011. 兴安落叶松林火后对土壤养分和土壤微生物生物量的影响[J]. 自然资源学报, 26(3): 450-459. |
| ZHAO B, SUN L, HU H Q, et al., 2011. Post-fire soil microbial biomass and nutrient content of Larix gmelinii forest in autumn[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 26(3): 450-459. | |
| [38] | 中国林业科学研究院, 1999. 森林土壤分析方法: LY/T 1213-1239—1999 [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| Chinese Academy of Forestry, 1999. Methods of forest soil analysis: LY/T 1213-1239—1999 [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China. | |
| [39] | 周瑞莲, 张普金, 徐长林, 1997. 高寒山区火烧土壤对其养分含量和酶活性的影响及灰色关联分析[J]. 土壤学报, 34(1): 89-96. |
| ZHOU R L, ZHANG P J, XU C L, 1997. Effect of burning turf on nutrient contents and enzymatic activities of alpine meadow soil and its grey relationship analysis[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 34(1): 89-96. | |
| [40] | 朱学灵, 崔向慧, 刘晓静, 2011. 宝天曼自然保护区林火干扰下不同恢复阶段栎林群落幼苗库动态特征[J]. 林业科学研究, 24(5): 572-578. |
| ZHU X L, CUI X H, LIU X J, 2011. The dynamic characteristics of the seedling bank of Quercus community at different restoration stages under the disturbance offorest fire in Baotianman Nature Reserve[J]. Forest Research, 24(5): 572-578. |
| [1] | 宋思梦, 林冬梅, 周恒宇, 罗宗志, 张丽丽, 易超, 林辉, 林兴生, 刘斌, 苏德伟, 郑丹, 余世葵, 林占熺. 种植巨菌草对乌兰布和沙漠植物物种多样性与土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(9): 1595-1605. |
| [2] | 王玉琴, 宋梅玲, 周睿, 王宏生. 黄帚橐吾扩散对高寒草甸土壤理化特性及酶活性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(8): 1384-1391. |
| [3] | 杜丹丹, 高瑞忠, 房丽晶, 谢龙梅. 旱区盐湖盆地土壤重金属空间变异及对土壤理化因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1123-1132. |
| [4] | 张立进, 杜虎, 曾馥平, 黄国勤, 宋敏, 宋同清. 喀斯特峰丛洼地植被恢复过程中生产力与多样性关系探讨[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 26-35. |
| [5] | 王礼霄, 刘晋仙, 柴宝峰. 华北亚高山土壤细菌群落及氮循环对退耕还草的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1537-1546. |
| [6] | 王磊, 温远光, 周晓果, 朱宏光, 孙冬婧. 尾巨桉与红锥混交对林下植被和土壤性质的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1340-1349. |
| [7] | 舒洋, 陈魁, 李航, 魏江生, 赵鹏武, 周梅. 高纬度冻土区林火干扰对土壤碳释放影响研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1278-1284. |
| [8] | 杨冲, 王春燕, 王文颖, 毛旭峰, 周华坤, 陈哲, 索南吉, 靳磊, 马华清. 青藏高原黄河源区高寒草地土壤营养特征变化及质量评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 896-908. |
| [9] | 冯凌, 喻理飞, 王阳, 张丽敏, 赵庆, 李方兵. 喀斯特地区植被不同恢复阶段功能冗余和功能多样性对群落稳定性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 670-678. |
| [10] | 陈瑶, 李云红, 邵英男, 刘玉龙, 刘延坤. 阔叶红松林物种多样性与土壤理化特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 679-687. |
| [11] | 夏开, 邓鹏飞, 马锐豪, 王斐, 温正宇, 徐小牛. 马尾松次生林转换为湿地松和杉木林对土壤细菌群落结构和多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 460-469. |
| [12] | 刘佩伶, 刘效东, 冯英杰, 苏宇乔, 甘先华, 张卫强. 新丰江水库库区水源涵养林土壤饱和导水率特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 1993-2001. |
| [13] | 王瑞, 宋祥云, 柳新伟. 黄河三角洲不同植被类型土壤酶活性的季节变化[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 62-69. |
| [14] | 洪文君, 莫罗坚, 张浩. 华南地区马占相思人工林不同改造模式对林分结构的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(7): 1360-1367. |
| [15] | 何斌, 李青, 陈群利, 李望军, 游萍. 黔西北黄杉群落物种多样性的海拔梯度格局[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1111-1120. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
