生态环境学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (8): 1419-1432.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.08.007
刘晨1,2( ), 白雪冬1,2, 赵海超1,2,*(
), 白雪冬1,2, 赵海超1,2,*( ), 黄智鸿1,2, 刘松涛1,2, 卢海博1,2, 刘子刚1,2, 刘雪玲1,2
), 黄智鸿1,2, 刘松涛1,2, 卢海博1,2, 刘子刚1,2, 刘雪玲1,2
收稿日期:2023-05-11
出版日期:2023-08-18
发布日期:2023-11-08
通讯作者:
*赵海超。E-mail: haichaozhao19@163.com作者简介:刘晨(1999年生),女,硕士研究生,主要研究方向作物学。E-mail: 463923989@qq.com
基金资助:
LIU Chen1,2( ), BAI Xuedong1,2, ZHAO Haichao1,2,*(
), BAI Xuedong1,2, ZHAO Haichao1,2,*( ), HUANG Zhihong1,2, LIU Songtao1,2, LU Haibo1,2, LIU Zigang1,2, LIU Xueling1,2
), HUANG Zhihong1,2, LIU Songtao1,2, LU Haibo1,2, LIU Zigang1,2, LIU Xueling1,2
Received:2023-05-11
Online:2023-08-18
Published:2023-11-08
摘要:
通过连续4年定点秸秆还田试验,设置大垄轮播、翻耕、旋耕3种还田方式,以秸秆不还田为对照,利用三维荧光光谱和紫外光谱测定不同土层(0-20、20-40、40-60、60-80、80-100 cm)及玉米各生育时期(播种前期、苗期、拔节期、灌浆期、收获期)0-20 cm土层DOM组分特征,以期优化寒旱区春玉米秸秆还田方式。结果表明,土壤DOC质量分数在202-364 mg?kg-1之间,DOM类胡敏酸组分(23.6%-54.3%)占比最高,类富里酸组分(23.6%-31.6%)占比次之,秸秆还田降低土壤(0-20 cm)DOM类胡敏酸组分占比,增加土壤DOM类蛋白组分占比、陆源特征及芳香性。随着土壤深度的增加DOM质量分数增加,类胡敏酸组分占比、腐殖化程度和生物源特征降低,疏水性分子增加。大垄轮播提高0-40 cm土层DOM类胡敏酸组分占比、腐殖化程度及芳香性,翻耕提高20-40 cm土层DOM类蛋白组分、疏水性组分占比,旋耕提高0-20 cm土层DOM类富里酸组分占比、腐殖化程度及芳香性。随着玉米的生长土壤DOM质量分数降低,类胡敏酸组分呈先降后升趋势,DOM小分子组分占比增加,生物源增强,腐殖化程度减弱。大垄轮播增加灌浆期土壤DOM类富里酸、类蛋白组分占比,翻耕降低拔节期DOM类胡敏酸组分占比,旋耕增加苗期DOM类蛋白组分占比。秸秆还田通过提高微生物及酶活性和作物产量影响DOM组分,大垄轮播通过延长根际秸秆腐解时间影响土壤DOM组分,提高DOM供肥能力及春玉米产量;翻耕和旋耕通过机械作用影响DOM含量和组分,增强DOM腐解。因此,寒旱区春玉米秸秆还田适宜采用大垄轮播秸秆还田方式。
中图分类号:
刘晨, 白雪冬, 赵海超, 黄智鸿, 刘松涛, 卢海博, 刘子刚, 刘雪玲. 寒旱区春玉米秸秆还田方式对土壤DOM光谱特征的影响机制[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(8): 1419-1432.
LIU Chen, BAI Xuedong, ZHAO Haichao, HUANG Zhihong, LIU Songtao, LU Haibo, LIU Zigang, LIU Xueling. The Effect Mechanism of Spring Maize Straw Returning Method on Soil DOM Spectral Characteristics in Cold and Arid Regions of China[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(8): 1419-1432.
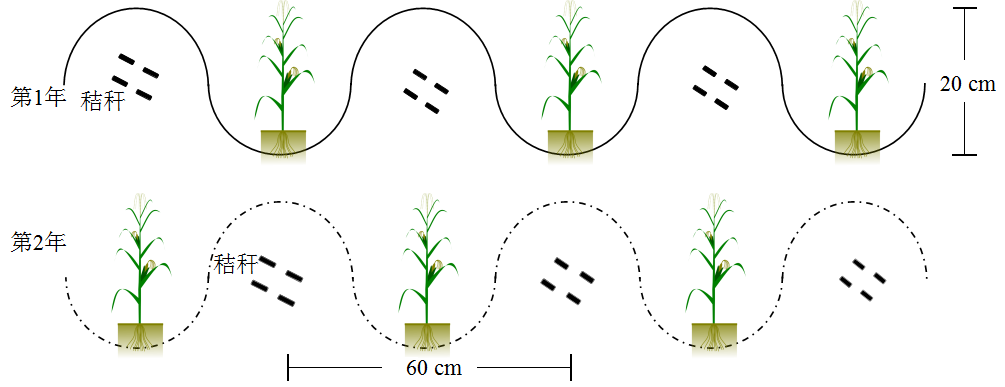
图1 春玉米大垄轮播示意图 大垄轮播秸秆还田处理,春玉米采用高起垄种植,垄高20 cm,垄距60 cm,秋季采用机械收获秸秆粉碎还田,秸秆还田后在冬季风力作用下聚集在垄沟中,第2年在上一年的垄背开沟种植,开沟后的土壤向两侧翻压
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of large ridge rotation of spring corn
| 荧光光谱参数 | 意义 | 定义 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 荧光指数 (FI) | 表征DOM中腐殖质来源 | 激发波长为370 nm时, 发射波长在450 nm和500 nm处荧光强度比值 | McKnight et al., |
| 腐殖化指数 (HIX) | 表征DOM的腐殖化程度 | 激发波长为254 nm时, 发射波长在435-480 nm间与300-345 nm间荧光强度积分值比值 | 肖隆庚等, |
| 自生源指数 (BIX) | 表征DOM自生源特征强弱 | 激发波长为310 nm时, 发射波长在380 nm和430 nm处荧光强度比值 | 李帅东等, |
表1 可溶性有机物(DOM)的三维荧光光谱特征参数描述及表征意义
Table 1 Description and characterization significance of three-dimensional fluorescence spectral characteristic parameters of soluble organic matter
| 荧光光谱参数 | 意义 | 定义 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 荧光指数 (FI) | 表征DOM中腐殖质来源 | 激发波长为370 nm时, 发射波长在450 nm和500 nm处荧光强度比值 | McKnight et al., |
| 腐殖化指数 (HIX) | 表征DOM的腐殖化程度 | 激发波长为254 nm时, 发射波长在435-480 nm间与300-345 nm间荧光强度积分值比值 | 肖隆庚等, |
| 自生源指数 (BIX) | 表征DOM自生源特征强弱 | 激发波长为310 nm时, 发射波长在380 nm和430 nm处荧光强度比值 | 李帅东等, |
| 吸光度 | 意义 | 定义 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| SUVA254 nm | 表征DOM腐殖化程度 | 单位DOC浓度在波长在254 nm处的吸收系数 | 李帅东等, |
| SUVA260 nm | 表征DOM疏水性组分含量 | 单位DOC浓度在波长在260 nm处的吸收系数 | 龚香宜等, |
| A253 nm/A203 nm | 反映分子结构和取代基情况, 与取代基的复杂程度呈正相关 | 紫外-可见光谱在253 nm和203 nm处吸光度的比值 | 周萌等, |
| A250 nm/A365 nm | 表征DOM的芳香性和分子量大小 | 紫外-可见光谱在250 nm和365 nm处吸光度的比值 | 石含之等, |
| SR | 表征DOM的来源组成和结构变化 | 紫外-可见光谱在275-295 nm和350-400 nm处吸光度的斜率比值 | 赵雄威等, |
表2 可溶性有机物(DOM)的紫外-可见光谱特征参数描述及表征意义
Table 2 Description and significance of characteristic parameters of ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy of dissolved organic matter
| 吸光度 | 意义 | 定义 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| SUVA254 nm | 表征DOM腐殖化程度 | 单位DOC浓度在波长在254 nm处的吸收系数 | 李帅东等, |
| SUVA260 nm | 表征DOM疏水性组分含量 | 单位DOC浓度在波长在260 nm处的吸收系数 | 龚香宜等, |
| A253 nm/A203 nm | 反映分子结构和取代基情况, 与取代基的复杂程度呈正相关 | 紫外-可见光谱在253 nm和203 nm处吸光度的比值 | 周萌等, |
| A250 nm/A365 nm | 表征DOM的芳香性和分子量大小 | 紫外-可见光谱在250 nm和365 nm处吸光度的比值 | 石含之等, |
| SR | 表征DOM的来源组成和结构变化 | 紫外-可见光谱在275-295 nm和350-400 nm处吸光度的斜率比值 | 赵雄威等, |
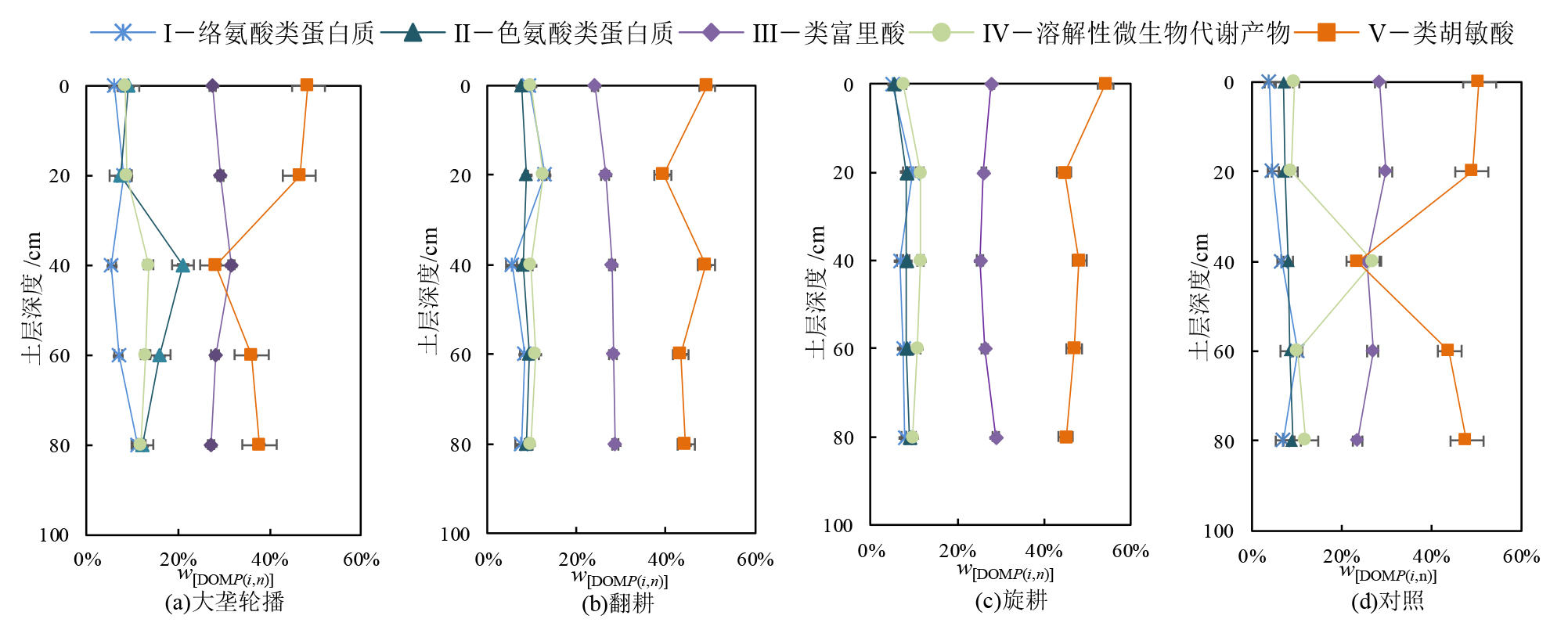
图5 不同秸秆还田方式下土壤DOM三维荧光Pi,n百分比垂向分布特征
Figure 5 Vertical distribution characteristics of soil DOM three-dimensional fluorescence Pi, n percentage under different straw returning methods

图6 不同秸秆还田方式下土壤DOM三维荧光Pi, n百分比生育时期动态变化特征
Figure 6 Dynamic changes of soil DOM three-dimensional fluorescence Pi, n percentage during growth period under different straw returning methods
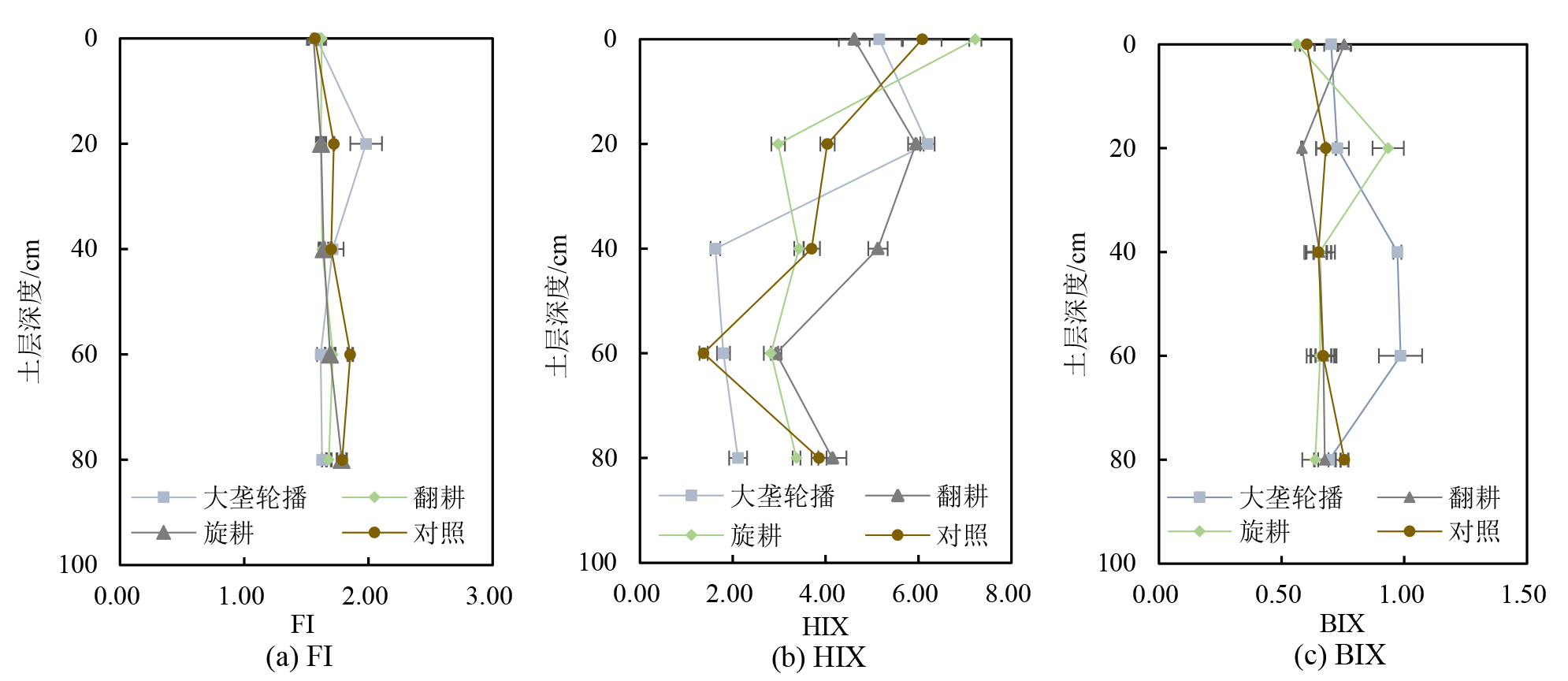
图7 不同秸秆还田方式下土壤DOM荧光指数FI、腐殖化指数HIX、自生源指数BIX垂向变化特征
Figure 7 Vertical variation characteristics of soil DOM fluorescence index, humification index and autochthonous index under different straw returning methods
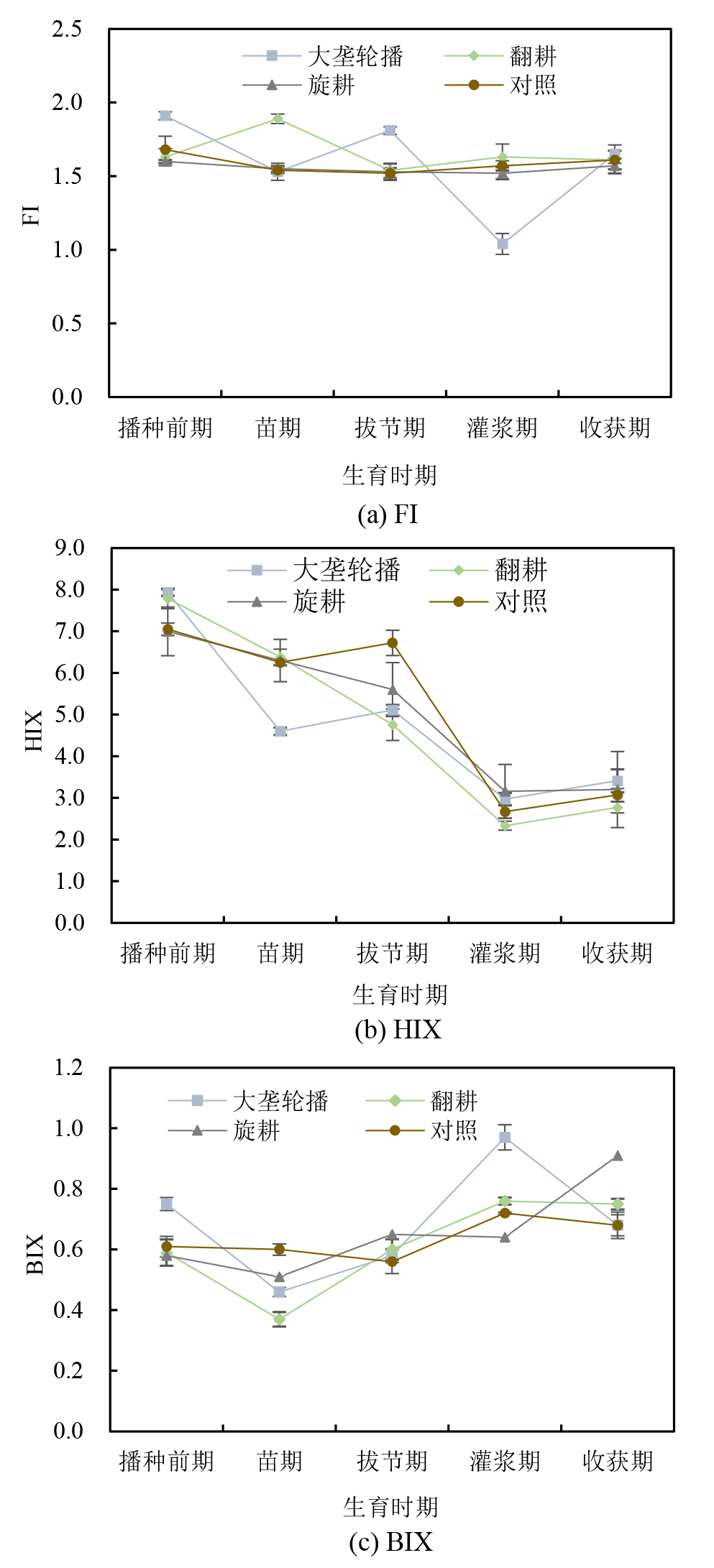
图8 不同秸秆还田方式下土壤DOM荧光指数FI、腐殖化指数HIX、自生源指数BIX生育时期动态变化特征
Figure 8 Dynamic changes in soil DOM fluorescence index, humification index, and autochthonous index during growth period under different straw returning methods
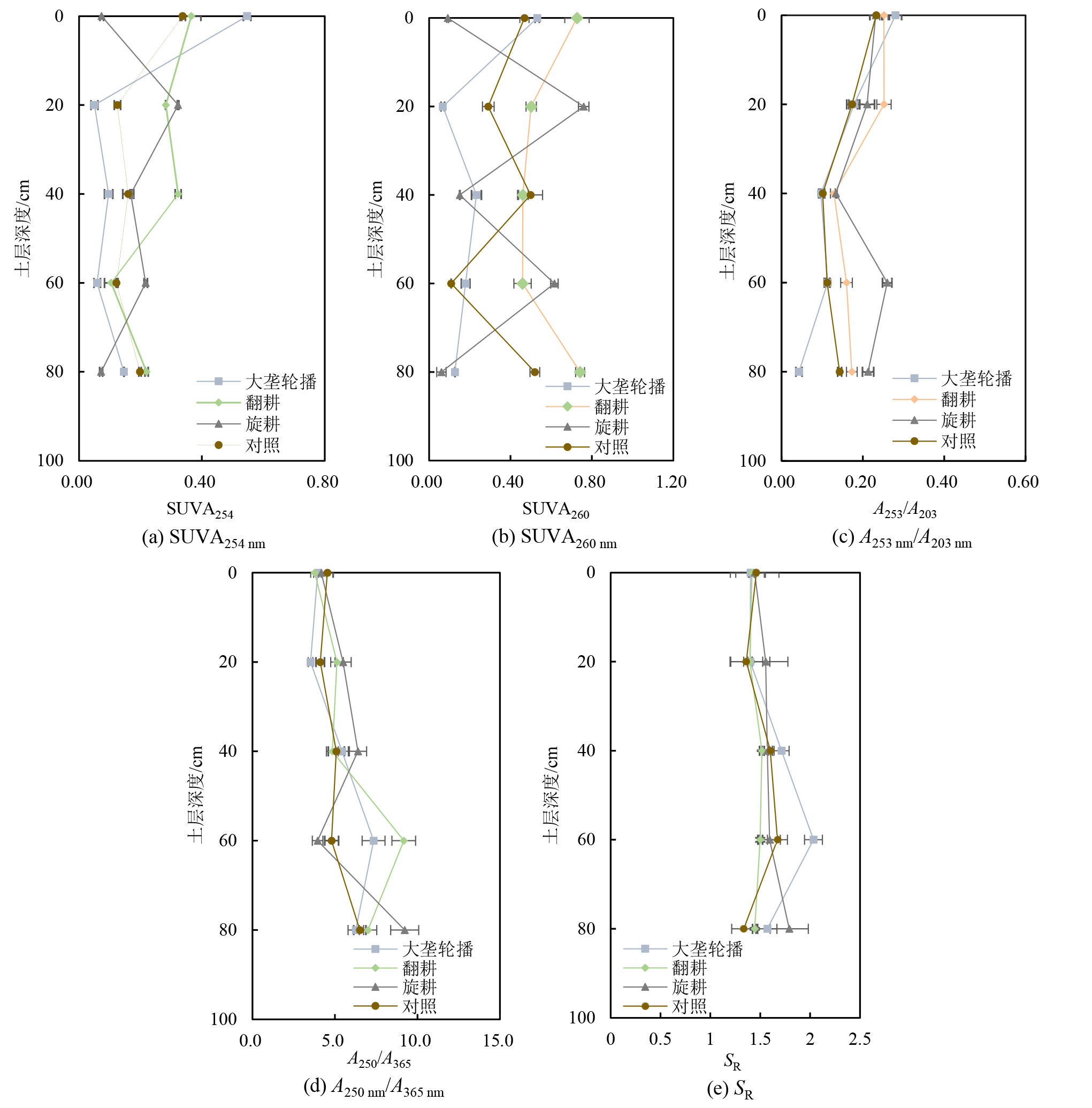
图9 不同秸秆还田方式下土壤DOM紫外光谱参数SUVA254 nm、SUVA260 nm、A253 nm/A203 nm、A250 nm/A365 nm 及光谱斜率SR垂向变化特征
Figure 9 Vertical variation characteristics of soil DOM UV spectral parameters SUVA254 nm, SUVA260 nm, A253 nm/A203 nm, A250 nm/A365 nm and spectral slope SR under different straw returning methods

图10 不同秸秆还田方式下土壤DOM紫外光谱参数SUVA254 nm、SUVA260 nm、A253 nm/A203 nm、A250 nm/A365 nm 及光谱斜率SR生育时期动态变化特征
Figure 10 Dynamic changes of soil DOM UV spectral parameters SUVA 254 nm, SUVA 260 nm, A253 nm/A203 nm, A250 nm/A365 nm and spectral slope SR during the growth period of different straw returning methods
| 指标 | 区域 I | 区域 II | 区域 III | 区域 IV | 区域 V | FI | HIX | BIX | A253 nm/ A203 nm | A250 nm/ A365 nm | SUVA254 nm | SUVA260 nm | SR | w(DOC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| w(MBC) | -0.134 | 0.166 | 0.283 | -0.274 | -0.069 | -0.423 | 0.098 | -0.077 | -0.324 | -0.682** 1) | 0.233 | -0.066 | -0.132 | 0.197 |
| w(MBN) | -0.157 | -0.305 | 0.040 | -0.590** | 0.382 | -0.376 | 0.240 | -0.485 | -0.091 | -0.488* 2) | 0.487* | 0.049 | -0.195 | 0.429* |
| w(MBP) | -0.296 | -0.103 | - 0.116 | -0.305 | 0.291 | -0.305 | 0.470* | -0.212 | -0.461* | -0.264 | 0.366 | 0.001 | -0.311 | 0.160 |
| w(SUC) | -0.279 | -0.109 | 0.042 | -0.400 | 0.261 | -0.336 | 0.120 | -0.160 | -0.371 | -0.484* | 0.600** | 0.111 | -0.327 | 0.272 |
| w(URE) | -0.334 | -0.259 | - 0.034 | -0.563* | 0.437* | -0.297 | 0.083 | -0.286 | -0.245 | -0.467* | 0.568** | 0.942** | -0.385 | 0.461* |
表3 土壤DOM荧光组分、荧光光谱参数和紫外光谱参数垂向变化特征与微生物量和酶活性相关分析
Table 3 Correlation analysis of vertical variation characteristics of soil DOM fluorescence components, fluorescence spectral parameters and ultraviolet spectral parameters with microbial biomass and enzyme activity
| 指标 | 区域 I | 区域 II | 区域 III | 区域 IV | 区域 V | FI | HIX | BIX | A253 nm/ A203 nm | A250 nm/ A365 nm | SUVA254 nm | SUVA260 nm | SR | w(DOC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| w(MBC) | -0.134 | 0.166 | 0.283 | -0.274 | -0.069 | -0.423 | 0.098 | -0.077 | -0.324 | -0.682** 1) | 0.233 | -0.066 | -0.132 | 0.197 |
| w(MBN) | -0.157 | -0.305 | 0.040 | -0.590** | 0.382 | -0.376 | 0.240 | -0.485 | -0.091 | -0.488* 2) | 0.487* | 0.049 | -0.195 | 0.429* |
| w(MBP) | -0.296 | -0.103 | - 0.116 | -0.305 | 0.291 | -0.305 | 0.470* | -0.212 | -0.461* | -0.264 | 0.366 | 0.001 | -0.311 | 0.160 |
| w(SUC) | -0.279 | -0.109 | 0.042 | -0.400 | 0.261 | -0.336 | 0.120 | -0.160 | -0.371 | -0.484* | 0.600** | 0.111 | -0.327 | 0.272 |
| w(URE) | -0.334 | -0.259 | - 0.034 | -0.563* | 0.437* | -0.297 | 0.083 | -0.286 | -0.245 | -0.467* | 0.568** | 0.942** | -0.385 | 0.461* |
| 指标 | 区域 I | 区域 II | 区域 III | 区域 IV | 区域 V | FI | HIX | BIX | A253 nm/ A203 nm | A250 nm/ A365 nm | SUVA254 nm | SUVA260 nm | SR | w(DOC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| w(MBC) | -0.127 | 0.635** | 0.384 | 0.510* | -0.481* | -0.198 | -0.530* | 0.611** | 0.511* | -0.135 | 0.541* | -0.021 | 0.582** | -0.269 |
| w(MBN) | -0.398 | 0.359 | 0.478* | 0.313 | -0.351 | -0.240 | -0.356 | 0.359 | 0.298 | 0.384 | 0.223 | -0.250 | 0.369 | -0.499* |
| w(MBP) | 0.103 | 0.008 | -0.223 | 0.019 | 0.005 | 0.128 | -0.065 | 0.155 | -0.351 | 0.218 | -0.231 | -0.175 | -0.019 | 0.027 |
| w(SUC) | 0.194 | -0.070 | -0.137 | -0.152 | 0.243 | -0.010 | 0.381 | 0.092 | -0.384 | -0.514* | -0.356 | -0.234 | 0.144 | 0.295 |
| w(URE) | 0.070 | -0.250 | 0.002 | -0.488* | 0.123 | -0.061 | -0.032 | -0.235 | -0.158 | -0.189 | 0.020 | 0.188 | 0.002 | 0.559** |
| w(SOM) | 0.394 | -0.430 | -0.288 | -0.492* | 0.441* | -0.008 | 0.452* | -0.452* | -0.214 | -0.131 | -0.103 | 0.322 | -0.228 | 0.926** |
| w(TP) | -0.176 | 0.455* | 0.361 | 0.489* | -0.253 | -0.168 | -0.388 | 0.456 | 0.472* | -0.269 | 0.245 | -0.385 | -0.076 | -0.295 |
| w(TN) | -0.020 | -0.084 | 0.280 | -0.346 | -0.262 | -0.168 | -0.332 | -0.250 | 0.304 | -0.058 | 0.469* | 0.604** | -0.343 | 0.343 |
表4 土壤DOM荧光组分、荧光光谱参数和紫外光谱参数生育时期动态变化特征与微生物量和酶活性相关分析
Table 4 Correlation analysis of dynamic changes in soil DOM fluorescence components, fluorescence spectral parameters, and ultraviolet spectral parameters during growth period with microbial biomass and enzyme activity
| 指标 | 区域 I | 区域 II | 区域 III | 区域 IV | 区域 V | FI | HIX | BIX | A253 nm/ A203 nm | A250 nm/ A365 nm | SUVA254 nm | SUVA260 nm | SR | w(DOC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| w(MBC) | -0.127 | 0.635** | 0.384 | 0.510* | -0.481* | -0.198 | -0.530* | 0.611** | 0.511* | -0.135 | 0.541* | -0.021 | 0.582** | -0.269 |
| w(MBN) | -0.398 | 0.359 | 0.478* | 0.313 | -0.351 | -0.240 | -0.356 | 0.359 | 0.298 | 0.384 | 0.223 | -0.250 | 0.369 | -0.499* |
| w(MBP) | 0.103 | 0.008 | -0.223 | 0.019 | 0.005 | 0.128 | -0.065 | 0.155 | -0.351 | 0.218 | -0.231 | -0.175 | -0.019 | 0.027 |
| w(SUC) | 0.194 | -0.070 | -0.137 | -0.152 | 0.243 | -0.010 | 0.381 | 0.092 | -0.384 | -0.514* | -0.356 | -0.234 | 0.144 | 0.295 |
| w(URE) | 0.070 | -0.250 | 0.002 | -0.488* | 0.123 | -0.061 | -0.032 | -0.235 | -0.158 | -0.189 | 0.020 | 0.188 | 0.002 | 0.559** |
| w(SOM) | 0.394 | -0.430 | -0.288 | -0.492* | 0.441* | -0.008 | 0.452* | -0.452* | -0.214 | -0.131 | -0.103 | 0.322 | -0.228 | 0.926** |
| w(TP) | -0.176 | 0.455* | 0.361 | 0.489* | -0.253 | -0.168 | -0.388 | 0.456 | 0.472* | -0.269 | 0.245 | -0.385 | -0.076 | -0.295 |
| w(TN) | -0.020 | -0.084 | 0.280 | -0.346 | -0.262 | -0.168 | -0.332 | -0.250 | 0.304 | -0.058 | 0.469* | 0.604** | -0.343 | 0.343 |
| 处理 | 大垄轮播 | 翻耕 | 旋耕 | 对照 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 百粒质量/ g | 37.91± 4.21a | 35.66± 2.87b | 34.96± 4.85b | 34.44± 1.29c |
| 产量/ (kg∙hm-2) | 11682.63± 884.25a | 10720.05± 612.93b | 10751.55± 901.28b | 9063.75± 856.82c |
表5 不同秸秆还田方式对玉米产量的影响
Table 5 Effect of different straw return methods on maize yield
| 处理 | 大垄轮播 | 翻耕 | 旋耕 | 对照 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 百粒质量/ g | 37.91± 4.21a | 35.66± 2.87b | 34.96± 4.85b | 34.44± 1.29c |
| 产量/ (kg∙hm-2) | 11682.63± 884.25a | 10720.05± 612.93b | 10751.55± 901.28b | 9063.75± 856.82c |
| [1] | BU R Y, REN T, LEI M J, et al., 2020. Tillage and straw-returning practices effect on soil dissolved organic matter, aggregate fraction and bacteria community under rice-rice-rapeseed rotation system[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 287: 106-119. |
| [2] |
BERND M, KARSTEN K, 2003. Controls of bioavailability and biodegradability of dissolved organic matter in soils[J]. Geoderma, 113(3): 211-235.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
CHAUDHARI D D, PATELV J, PATEL B D, et al., 2019. Integrated weed management in garlic with and without rice straw mulch[J]. Indian Journal of Weed Science, 51(3): 270-274.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
CHEN H L, ZHOU J M, XIAO B H, 2010. Characterization of dissolved organic matter derived from rice straw at different stages of decay[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 10(5): 915-922.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
CHEN W, WESTERHOFF P, LEENHEER J A, et al., 2003. Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 37(24): 5701-5710.
PMID |
| [6] |
FUENTES M, GONZÁLEZ-GAITANO G, GARCÍA-MINA J M, 2006. The usefulness of UV-visible and fluorescence spectroscopies to study the chemical nature of humic substances from soils and composts[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 37(12): 1949-1959.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
GE G F, LI Z J, FAN F L, et al., 2010. Soil biological activity and their seasonal variations in response to long-term application of organic and inorganic fertilizers[J]. Plant Soil, 326: 31-44.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
GU N T, SONG Q B, YANG X L, et al., 2020. Fluorescence characteristics and biodegradability of dissolved organic matter (DOM) leached from non-point sources in southeastern China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 258: 113807.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
LIU J H, GENG Y H, LI J, et al., 2021. Effect of straw substituting partial mineral N fertilizer on N distribution of maize plants and soil in northeast China[J]. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research, 19(1): 625-639.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
MAESTRE F T, DELGADO-BAQUERIZO M, JEFFRIES T C, et al., 2015. Increasing aridity reduces soil microbial diversity and abundance in global drylands[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 112(51): 15684-15689.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
MCKNIGHT D M, BOYER E W, WESTERHOFF P K, et al., 2001. Spectrofluorometric characterization of dissolved organic matter for indication of precursor organic material and aromaticity[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 46(1): 38-48.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
WELIKALA D, ROBINSON B H, MOLTCHANOVA E, et al., 2021. Soil cadmium mobilisation by dissolved organic matter from soil amendments[J]. Chemosphere, 271: 129536.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
ZHAO H L, ABDUL G S, LI S, et al., 2018. Effect of straw return mode on soil aggregation and aggregate carbon content in an annual maize-wheat double cropping system[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 175: 178-186.
DOI URL |
| [14] | 白伟, 逄焕成, 牛世伟, 等, 2015. 秸秆还田与施氮量对春玉米产量及土壤理化性状的影响[J]. 玉米科学, 23(3): 99-106. |
| BAI W, FENG H C, NIU S W, et al., 2015. Effects of straw incorporation and nitrogen rate on spring maize yield and soil physicochemical property[J]. Corn Science, 23(3): 99-106. | |
| [15] | 蔡丽君, 张敬涛, 盖志佳, 等, 2015. 免耕条件下秸秆还田量对土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 46(5): 1127-1132. |
| CAI L J, ZHANG J T, GAI Z J, et al., 2015. Effect of the amount of stalk return to field on soil enzyme activities under no-tillage[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 46(5): 1127-1132. | |
| [16] | 蔡影, 付思伟, 张博睿, 等, 2022. 秸秆连续还田配施化肥对稻-油轮作土壤碳库及作物产量的影响[J]. 环境科学, 43(10): 4716-4724. |
| CAI Y, FU S W, ZHANG B R, et al., 2022. Effects of continuous straw returning with chemical fertilizer on the carbon pool and crop yield of rice-rape rotation soils[J]. Environmental Science, 43(10): 4716-4724. | |
| [17] | 丛聪, 2019. 耕作方式及有机物还田对黑土坡耕地土壤物理性质和玉米生长的影响[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院:44. |
| CONG C, 2019. Effect of tillage practices and organic material application on soil physical properties and maize growth in sloping farmland of mollisol[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences:44. | |
| [18] | 邓汝乐, 高鹏, 贾松, 等, 2022. 燃烧生成棕色碳的三维荧光光谱分析[J]. 中国环境科学, 42(9): 3983-3990. |
| DENG R L, GAO P, JIA S, et al., 2022. Comparisons of three-dimensional fluorescence spectra of brown carbon from combustion[J]. Chinese Environmental Science, 42(9): 3983-3990. | |
| [19] | 范春辉, 张颖超, 王家宏, 2015. pH值对秸秆腐殖化溶解性有机质紫外光谱和荧光光谱的影响[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 35(7): 1933-1937. |
| FAN C H, ZHANG Y C, WANG J H, 2015. Effect of pH on the ultraviolet spectra and fluorescence characteristics of dissolved organic matter in the process of straw humification[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 35(7): 1933-1937. | |
| [20] | 范之馨, 张焕朝, 陈捷, 等, 2021. 有机物料添加后滨海盐渍土壤溶解性有机碳变化及其紫外-可见光谱特征[J]. 安徽农业大学学报, 48(3): 444-451. |
| FAN Z X, ZHANG H C, CHEN J, et al., 2021. Ultraviolet-visible spectral characteristics of soil dissolved organic carbon (DOC) in coastal saline soil after adding organic materials[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University, 48(3): 444-451. | |
| [21] | 高盼, 刘玉涛, 徐莹莹, 等, 2021. 秸秆覆盖与翻埋两种还田模式对农田土壤物理性质及玉米产量的影响[J]. 黑龙江农业科学 (11): 13-17. |
| GAO P, LIU Y T, XU Y Y, et al., 2021. Effects of maize straw mulching and burying returning to the field on soil physical properties and maize yield[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Science (11): 13-17. | |
| [22] | 高日平, 赵思华, 刁生鹏, 等, 2019. 秸秆还田对黄土风沙区土壤微生物、酶活性及作物产量的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 50(6): 1370-1377. |
| GAO R P, ZHAO S H, DIAO S P, et al., 2019. Effects of straw mulching on soil microorganism, enzyme activity and crop yield in loess desert[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 50(6): 1370-1377. | |
| [23] | 龚香宜, 徐威, 何炎志, 2017. 溶解性有机质的光谱特征及其对土壤吸附β-HCH的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 37(1): 318-325. |
| GONG X Y, XU W, HE Y Z, 2017. Spectral characteristics of dissolved organic matter and its effects on the adsorption of β-HCH in the soil[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 37(1): 318-325. | |
| [24] | 和江鹏, 王雨晴, 赵海超, 等, 2021. 春玉米秸秆还田对土壤碳组分及碳库管理指数的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 49(21): 224-230. |
| HE J P, WANG Y Q, ZHAO H C, et al., 2021. Effects of spring maize stover return on soil carbon fractions and carbon pool management indices[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 49(21): 224-230. | |
| [25] | 李帅东, 张明礼, 杨浩, 等, 2017. 昆明松华坝库区表层土壤溶解性有机质 (DOM) 的光谱特性[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 37(4): 1183-1188. |
| LI S D, ZHANG M L, YANG H, et al., 2017. Spectroscopic characteristics of dissolved organic matter from top soils on Songhuaba reservoir in Kunmimg[J]. Spectroscopy and Light Analysis, 37(4): 1183-1188. | |
| [26] | 李帅东, 姜泉良, 黎烨, 等, 2017. 环滇池土壤溶解性有机质 (DOM )的光谱特征及来源分析[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 37(5): 1448-1454. |
| LI S D, JIANG Q L, LI Y, et al., 2017. Spectroscopic characteristics and sources of dissolved organic matter from soils around Dianchi Lake, Kunming[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 37(5): 1448-1454. | |
| [27] | 李晓童, 杨仁杰, 雷涛, 等, 2020. 土壤有机质对多环芳烃荧光影响校正方法研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 40(10): 215-216. |
| LI X T, YANG R J, LEI T, et al., 2020. Study on the correction method for the effect of organic matter on the fluorescence of PAHs in soil[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 40(10): 215-216. | |
| [28] | 梁俭, 2016. 三峡库区消落带土壤溶解性有机质淹水释放行为与结构表征[D]. 重庆: 西南大学:3-8. |
| LIANG J, 2016. The flooding behavior and structure characteristics of soil dissolved organic matter in water-level-fluctuating zone of three gorges reservoir areas[D]. Chongqing: Dissertation of Southwest University: 3-8. | |
| [29] | 缪闯和, 吕贻忠, 于越, 等, 2020. 基于光谱学方法研究土壤对堆肥中可溶性有机物的吸附行为[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 40(12): 3832-3838. |
| MIAO C H, LÜ Y Z, YU Y, et al., 2020. Study on adsorption behavior of dissolved organic matter onto soil with spectroscopic method[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 40(12): 3832-3838. | |
| [30] | 刘子刚, 卢海博, 赵海超, 等, 2022. 旱作区春玉米秸秆还田方式对土壤微生物量碳氮磷及酶活性的影响[J]. 西北农业学报, 31(2): 183-192. |
| LIU Z G, LU H B, ZHAO H C, et al., 2022. Effects of methods for spring maize straw-returning to field on soil microbial biomass C, N, P and enzyme activities in dry farming area[J]. Northwest Journal of Agriculture, 31(2): 183-192. | |
| [31] | 罗德芳, 彭杰, 冯春晖, 等, 2021. 可见光-近红外、中红外光谱的土壤有机质组分反演[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 41(10): 3069-3076. |
| LUO D F, PENG J, FENG C H, et al., 2021. Inversion of soil organic matter fraction in southern Xinjiang by visible-near-infrared and mid-infrared spectra[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 41(10): 3069-3076. | |
| [32] | 马俊永, 李科江, 曹彩云, 等, 2007. 有机-无机肥长期配施对潮土土壤肥力和作物产量的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 13(2): 236-241. |
| MA J Y, LI K J, CAO C Y, et al., 2007. Effect of long-term located organic-inorganic fertilizer application on fluvo-aquic soil fertility and crop yield[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 13(2): 236-241. | |
| [33] |
牛丽, 白文波, 李霞, 等, 2021. 地膜覆盖对黄土高原地区两种种植密度下玉米叶片代谢组的影响[J]. 作物学报, 47(8): 1551-1562.
DOI |
| NIU L, BAI W B, LI X, et al., 2021. Effects of plastic film mulching on leaf metabolic profiles of maize in the loess plateau with two planting densities[J]. Journal of Crop Science, 47(8): 1551-1562. | |
| [34] |
石含之, 刘帆, 黄永东, 等, 2021. 土壤溶解性有机物的动态变化对水溶态铜的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(9): 1896-1902.
DOI |
| SHI H Z, LIU F, HUANG Y D, et al., 2021. Effects of dynamic change of dissolved organic matter in soil on water-soluble copper[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(9): 1896-1902. | |
| [35] | 王鹏, 商帅帅, 郭璠, 等, 2021. 基于EEM-PARAFAC分析冻融作用对高寒泥炭湿地土壤溶解性有机质的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 43(11): 99-108. |
| WANG P, SHANG S S, GUO F, et al., 2021. Analyzing the effects of freeze-thaw on dissolved organic matter in alpine peat wetland soil based on EEM-PARAFAC[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 43(11): 99-108. | |
| [36] | 王圣瑞, 2014. 湖泊沉积物-水界面过程基本理论与常用测定方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社:108-111. |
| WANG S R, 2014. Basic Theory and Common Measurement Methods for Lake Sediment-Water Interface Processes[M]. Beijing: Science Press:108-111. | |
| [37] | 王学敏, 刘兴, 郝丽英, 等, 2020. 秸秆还田结合氮肥减施对玉米产量和土壤性质的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 39(2): 507-516. |
| WANG X M, LIU X, HAO L Y, et al., 2020. Effects of straw returning in conjunction with different nitrogen fertilizer dosages on corn yield and soil properties[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 39(2): 507-516. | |
| [38] | 伍玉鹏, 刘田, 彭其安, 等, 2014. 氮肥配施下不同C/N作物残渣还田对红壤温室气体排放的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 33(10): 2053-2062. |
| WU Y P, LIU T, PENG Q A, et al., 2014. Greenhouse gas emissions in red soil as influenced by different C/N residues under nitrogen applications[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 33(10): 2053-2062. | |
| [39] | 肖隆庚, 陈文松, 陈国丰, 等, 2014. 中国南海CDOM三维荧光光谱特征研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 34(1): 160-167. |
| XIAO L G, CHEN W S, CHEN G F, et al., 2014. Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix spectroscopy of chromophoric dissolved organic matter in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Environmental Science, 34(1): 160-167. | |
| [40] |
徐敏, 许超, 余光辉, 等, 2023. 地下水位和长期秸秆还田对土壤镉有效性及稻米镉含量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 32(1): 150-157.
DOI |
| XU M, XU C, YU G H, et al., 2023. Effects of groundwater level and long-term straw return on soil cadmium availability and cadmium concentration in rice[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 32(1): 150-157. | |
| [41] | 尤锦伟, 王俊, 胡红青, 等, 2020. 秸秆还田对再生稻田土壤有机碳组分的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 26(8): 1451-1458. |
| YOU J W, WANG J, HU H Q, et al., 2020. Effects of straw returning on soil organic carbon components in ratoon rice field[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 26(8): 1451-1458. | |
| [42] | 战秀梅, 宋涛, 冯小杰, 等, 2017. 耕作及秸秆还田对辽南地区土壤水分及春玉米水分利用效率的影响[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 48(6): 666-672. |
| ZHAN X M, SONG T, FENG X J, et al., 2017. Effect of tillage and straw application on soil water and water use efficiency of spring maize in southern area of Liaoning province[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 48(6): 666-672. | |
| [43] | 张海洋, 杨清贤, 杨倩, 等, 2020. 水环境中秸秆源溶解有机质的组成及光化学活性特征[J]. 中国环境科学, 40(6): 2521-2528. |
| ZHANG H Y, YANG Q X, YANG Q, et al., 2020. Compositional characteristics and photochemical activity of dissolved organic matter derived from straw in aquatic environment[J]. China Environmental Science, 40(6): 2521-2528. | |
| [44] | 张雅洁, 陈晨, 陈曦, 等, 2015. 小麦-水稻秸秆还田对土壤有机质组成及不同形态氮含量的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 34(11): 2155-2161. |
| ZHANG Y J, CHEN C, CHEN X, et al., 2015. Effects of wheat and rice straw returning on soil organic matter composition and content of different nitrogen forms in soil[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 34(11): 2155-2161. | |
| [45] | 赵雄威, 吴东明, 李勤奋, 等, 2022. 基于紫外-可见光光谱法研究长期不同施肥对砖红壤溶解性有机质化学性质的影响[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 42(10): 3210-3216. |
| ZHAO X W, WU D M, LI Q F, et al., 2022. Response of dissolved organic matter chemical properties to long-term different fertilization in latosol: Insight from ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 42(10): 3210-3216. | |
| [46] | 周萌, 肖扬, 刘晓冰, 2020. 土壤活性有机质组分的光谱分析方法及应用[J]. 土壤, 52(6): 1093-1104. |
| ZHOU M, XIAO Y, LIU X B, 2020. Methods and applications of spectral analysis for soil labile organic matter components[J]. Soils, 52(6): 1093-1104. | |
| [47] | 周向军, 2020. 秸秆溶解性有机质的光谱解析及其对环境污染物的影响[J]. 天水师范学院学报, 40(5): 57-60. |
| ZHOU X J, 2020. Spectrum analysis of dissolved organic matter from straw and its effects on environmental pollution[J]. Journal of Tianshui Normal University, 40(5): 57-60. |
| [1] | 王超, 杨倩楠, 张池, 刘同旭, 张晓龙, 陈静, 刘科学. 丹霞山不同土地利用方式土壤磷组分特征及其有效性[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 889-897. |
| [2] | 李传福, 朱桃川, 明玉飞, 杨宇轩, 高舒, 董智, 李永强, 焦树英. 有机肥与脱硫石膏对黄河三角洲盐碱地土壤团聚体及其有机碳组分的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 878-888. |
| [3] | 潘昱伶, 璩向宁, 李琴, 王磊, 王筱平, 谭鹏, 崔庚, 安雨, 佟守正. 黄河宁夏段典型滩涂湿地土壤理化因子空间分布特征及其对微地形的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 668-677. |
| [4] | 唐海明, 石丽红, 文丽, 程凯凯, 李超, 龙泽东, 肖志武, 李微艳, 郭勇. 长期施肥对双季稻田根际土壤氮素的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 492-499. |
| [5] | 郎漫, 许力文, 朱恺文, 吴泓瑾, 张佳音, 李平. 碳氮施加对农田黑土氮素转化和温室气体排放的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 235-244. |
| [6] | 宋孝帅, 丁武泉, 刘新敏, 李廷真. 离子特异性效应对紫色土孔隙状况的影响机制研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 292-298. |
| [7] | 朱生堡, 唐光木, 张云舒, 徐万里, 葛春辉, 马海刚. 水旱长期耕作下土壤团聚体及有机碳动态变化[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2152-2160. |
| [8] | 李梦丽, 徐墨馨, 陈永山, 叶丽丽, 蒋金平. 石灰性土壤添加不同量碳酸钙对秸秆有机碳矿化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 2002-2009. |
| [9] | 张晓丽, 王国丽, 常芳弟, 张宏媛, 逄焕成, 张建丽, 王婧, 冀宏杰, 李玉义. 生物菌剂对根际盐碱土壤理化性质和微生物区系的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 1984-1992. |
| [10] | 崔乔, 李宗省, 张百娟, 赵越, 南富森. 冻融作用对土壤可溶性碳氮和微生物量碳氮含量影响的荟萃分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1700-1712. |
| [11] | 龚玲玄, 王丽丽, 赵建宁, 刘红梅, 杨殿林, 张贵龙. 不同覆盖作物模式对茶园土壤理化性质及有机碳矿化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1141-1150. |
| [12] | 颜明娟, 陈贤玉, 曹榕彬, 林诚, 吴一群, 黄丁一, 吴海玲, 陈子聪. 福建典型白茶产区茶园土壤锰锌形态特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 885-895. |
| [13] | 杨冲, 王春燕, 王文颖, 毛旭峰, 周华坤, 陈哲, 索南吉, 靳磊, 马华清. 青藏高原黄河源区高寒草地土壤营养特征变化及质量评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 896-908. |
| [14] | 王玉洁, 雷琴凯, 卜红玲, 童辉, 董乐恒, 陈曼佳, 刘承帅. Fe(Ⅱ)aq与纤铁矿-胡敏酸复合物交互反应及其结构转化过程研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 777-784. |
| [15] | 郝小雨, 王晓军, 高洪生, 毛明艳, 孙磊, 马星竹, 周宝库, 迟凤琴, 李伟群. 松嫩平原不同秸秆还田方式下农田温室气体排放及碳足迹估算[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 318-325. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
