生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (10): 2002-2009.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.10.008
李梦丽1( ), 徐墨馨1, 陈永山2, 叶丽丽1, 蒋金平1,3,*(
), 徐墨馨1, 陈永山2, 叶丽丽1, 蒋金平1,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-06-14
出版日期:2022-10-18
发布日期:2022-12-09
通讯作者:
*蒋金平(1972年生),男,研究员,博士,主要从事土壤环境与污染修复研究工作。E-mail: jiangjinping74@163.com作者简介:李梦丽(1996年生),女,硕士研究生,主要从事土壤环境与污染修复研究工作。E-mail: LiMengli1218@163.com
基金资助:
LI Mengli1( ), XU Moxin1, CHEN Yongshan2, YE Lili1, JIANG Jinping1,3,*(
), XU Moxin1, CHEN Yongshan2, YE Lili1, JIANG Jinping1,3,*( )
)
Received:2022-06-14
Online:2022-10-18
Published:2022-12-09
摘要:
广西石灰性土壤面积较广,其较高碳酸盐含量能够影响土壤中物质循环。为了明确石灰性土壤中碳酸盐含量对土壤秸秆有机碳矿化过程的影响,加深对石灰性土壤有机碳的周转与固存机制的认识,开展了土壤外源秸秆添加培养试验,分别设置无添加对照(CK)、添加5%秸秆(C0)、5%秸秆+5%碳酸钙(C1)、5%秸秆+15%碳酸钙(C2)和5%秸秆+25%碳酸钙(C3)处理,以研究石灰性土壤中外源秸秆有机碳的转化与土壤碳酸钙含量的关系。结果表明,与对照相比,添加秸秆后土壤CO2释放速率、累积释放量、活性有机碳含量均得到大幅提升。培养期间,各处理土壤CO2释放速率均表现为前期(第2—5天)快速下降、中期(第5—39天)缓慢下降、后期(第39—60天)趋于稳定。不同碳酸钙处理使土壤CO2累积释放量提升了5.10%—15.69%,但C3处理的土壤CO2释放速率、累积释放量均低于C1和C2处理,并对土壤有机碳矿化表现出强烈负激发效应,最高为183.33%。随着土壤碳酸钙含量的增加,土壤微生物生物量碳(MBC)含量逐渐降低。土壤碳酸钙能够促进土壤溶解性有机碳(DOC)含量增加,与C0相比,C1处理DOC含量提高了106.35%。相关分析表明,土壤CO2累积释放量和土壤MBC、DOC含量均呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),土壤MBC含量和DOC含量呈显著正相关关系(P<0.05)。
中图分类号:
李梦丽, 徐墨馨, 陈永山, 叶丽丽, 蒋金平. 石灰性土壤添加不同量碳酸钙对秸秆有机碳矿化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 2002-2009.
LI Mengli, XU Moxin, CHEN Yongshan, YE Lili, JIANG Jinping. Effects of Different Amounts of Calcium Carbonate on the Mineralization of Straw Organic Carbon in Calcareous Soil[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(10): 2002-2009.
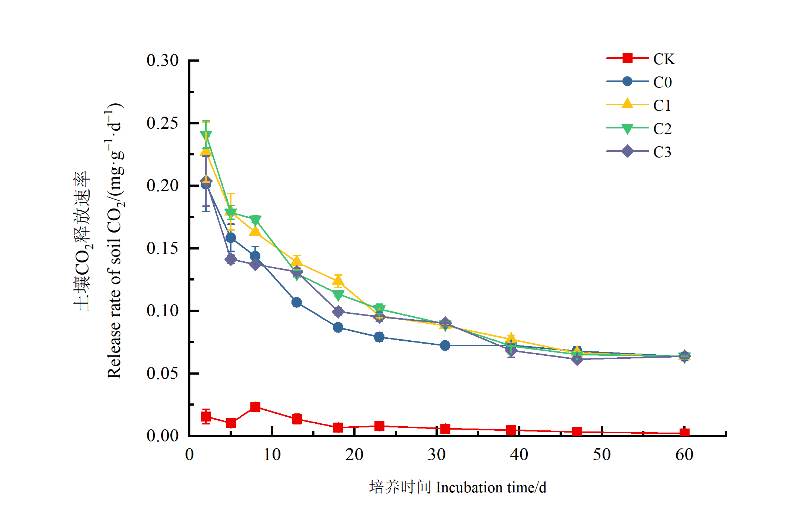
图1 不同含量碳酸钙土壤的CO2释放速率 CK:不添加任何外源物质处理;C0:5%秸秆处理;C1:5%秸秆+5%碳酸钙处理;C2:5%秸秆+15%碳酸钙处理;C3:5%秸秆+25%碳酸钙处理,下同
Figure 1 Release rate of soil CO2 with different content of calcium carbonate CK: without adding any exogenous substances; C0: 5% straw treatment; C1: 5% straw+5% calcium carbonate treatment; C2: 5% straw+15% calcium carbonate treatment; C3: 5% straw+25% calcium carbonate treatment, The same below
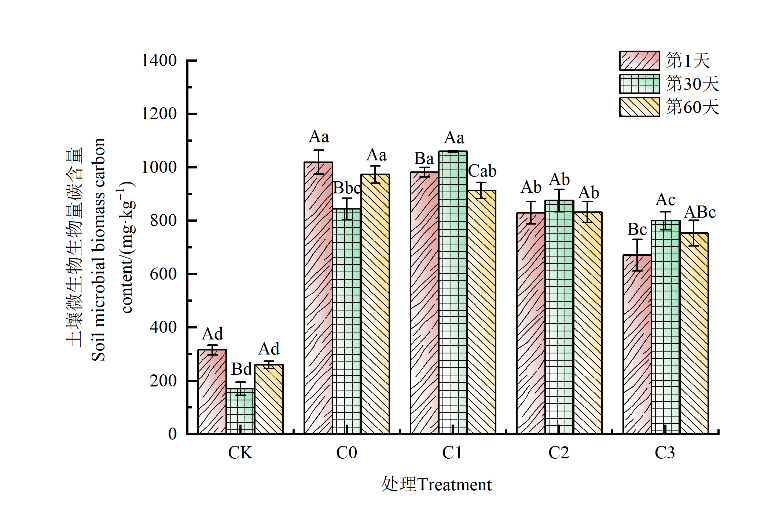
图4 不同含量碳酸钙对土壤微生物生物量碳的影响 不同大写字母表示相同处理不同培养天数间差异显著,不同小写字母表示相同培养天数不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。下同
Figure 4 Effects of different contents of calcium carbonate on soil microbial biomass carbon Different capital letters indicate that there is significant difference between different culture days of the same treatment, and different small letters indicate that there is significant difference between different treatments of the same culture days (P<0.05). The same below
| 因子 factor | CO2累积释放量 Cumulative release of soil CO2 | 微生物生物量碳 Microbial biomass carbon (MBC) | 溶解性有机碳 Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO2累积释放量 Cumulative release of soil CO2 | 1 | 0.931** | 0.841** |
| 微生物生物量碳 Microbial biomass carbon (MBC) | 1 | 0.633* | |
| 溶解性有机碳 Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) | 1 |
表1 土壤CO2累积释放量和活性有机碳含量的相关性分析
Table 1 Correlation analysis between cumulative release of soil CO2 and active organic carbon content
| 因子 factor | CO2累积释放量 Cumulative release of soil CO2 | 微生物生物量碳 Microbial biomass carbon (MBC) | 溶解性有机碳 Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO2累积释放量 Cumulative release of soil CO2 | 1 | 0.931** | 0.841** |
| 微生物生物量碳 Microbial biomass carbon (MBC) | 1 | 0.633* | |
| 溶解性有机碳 Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) | 1 |
| [1] |
BINGEMAN C W, VARNER J E, MARTIN W P, 1953. The effect of the addition of organic materials on the decomposition of an organic soil[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 17(1): 34-38.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BERTRAND I, DELFOSSE O, MARY B, 2007. Carbon and nitrogen mineralization in acidic, limed and calcareous agricultural soils: Apparent and actual effects[J]. Soil biology & biochemistry, 39(1): 276-288.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
CHEN S, XU C M, YAN J X, et al., 2016. The influence of the type of crop residue on soil organic carbon fractions: An 11-year field study of rice-based cropping systems in southeast china[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 223(1): 261-269.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
DAI W, GAO H, SHA Z M, et al., 2020. Changes in soil organic carbon fractions in response to wheat straw incorporation in a subtropical paddy field in china[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 184(2): 198-207.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
EI-NAGGAR A H, USMAN A R A, AL-OMRAN A, et al., 2015. Carbon mineralization and nutrient availability in calcareous sandy soils amended with woody waste biochar[J]. Chemosphere, 138: 67-73.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
FATIMA S, RIAZ M, AL-WABEL M I, et al., 2021. Higher biochar rate strongly reduced decomposition of soil organic matter to enhance c and n sequestration in nutrient-poor alkaline calcareous soil[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 21(1): 148-162.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
FENG S Z, HUANG Y, GE Y H, et al., 2016. Variations in the patterns of soil organic carbon mineralization and microbial communities in response to exogenous application of rice straw and calcium carbonate[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 571: 615-623.
DOI URL |
| [8] | GOCKE M, PUSTOVOYTOV K, KUZYAKOV Y, 2012. Pedogenic carbonate formation: Recrystallization versus migration—process rates and periods assessed by 14C labeling[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 26(1): 1-12. |
| [9] |
GUO L Y, WU G L, LI Y, et al., 2016. Effects of cattle manure compost combined with chemical fertilizer on topsoil organic matter, bulk density and earthworm activity in a wheat-maize rotation system in eastern china[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 156: 140-147.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
HAMER U, MARSCHNER B, 2005. Priming effects in different soil types induced by fructose, alanine, oxalic acid and catechol additions[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 37(3): 445-454.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
KALBITZ K, SOLINGER S, PARK J H, et al., 2000. Controls on the dynamics of dissolved organic matter in soils: A review[J]. Soil Science, 165(4): 277-304.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
KUZYAKOV Y, BOL R, 2006. Sources and mechanisms of priming effect induced in two grassland soils amended with slurry and sugar[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 38(4): 747-758.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
LI Y S, YU Z H, YANG S C, et al., 2019. Impact of elevated CO2on C꞉N꞉P ratio among soybean cultivars[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 694(1): 133784.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
LI Z P, LIU M, WU X C, et al., 2010. Effects of long-term chemical fertilization and organic amendments on dynamics of soil organic C and total N in paddy soil derived from barren land in subtropical china[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 106(2): 268-274.
DOI URL |
| [15] | SETIA R, MARSCHNER P, BALDOCK J, et al., 2010. Is CO2 evolution in saline soils affected by an osmotic effect and calcium carbonate?[J]. Biology & Fertility of Soils, 46(8): 781-792. |
| [16] |
SHEN L D, WU H S, GAO Z Q, et al., 2016. Comparison of community structures of Candidatus Methylomirabilis oxyfera-like bacteria of NC10 phylum in different freshwater habitats[J]. Scientific Reports, 6(1): 25647.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
SONG X, HUANG L P, LU H, et al., 2020. An external magnetic field for efficient acetate production from inorganic carbon in Serratia marcescens catalyzed cathode of microbial electrosynthesis system[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 155: 107467.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
WU J, BROOKES P C, JENKINSON D S, 1993. Formation and destruction of microbial biomass during the decomposition of glucose and ryegrass in soil[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 25(10): 1435-1441.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
XU M G, LOU Y L, SUN X L, et al., 2011. Soil organic carbon active fractions as early indicators for total carbon change under straw incorporation[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 47(7): 745.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
YAGI K, MINAMI K, 1990. Effect of organic matter application on methane emission from some japanese paddy fields[J]. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 36(4): 599-610.
DOI URL |
| [21] | 陈春梅, 谢祖彬, 朱建国, 2006. 土壤有机碳激发效应研究进展[J]. 土壤, 38(4): 359-365. |
| CHEN C M, XIE Z B, ZHU J G, 2006. Advances in research on priming effect of soil organic carbon[J]. Soils, 38(4): 359-365. | |
| [22] | 陈磊, 熊康宁, 杭红涛, 2019. 贵州喀斯特地区野生饲用牧草资源的开发与保护[J]. 中国饲料, 21(1): 4-8. |
| CHEN L, XIONG K N, HANG H T, 2019. Development and protection of wild forage resources in karst region of Guizhou Province[J]. China Food, 21(1): 4-8. | |
| [23] | 陈晓芬, 刘明, 江春玉, 等, 2018. 不同施肥处理红壤性水稻土团聚体有机碳矿化特征[J]. 中国农业科学, 51(17): 3325-3334. |
| CHEN X F, LIU M, JIANG C Y, et al., 2018. Organic carbon mineralization in aggregate fractions of red paddy soil under different fertilization treatments[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 51(17): 3325-3334. | |
| [24] | 陈佑启, VERBUGR P H, 2000. 中国土地利用/土地覆盖的多尺度空间分布特征分析[J]. 地理科学, 20(3): 197-202. |
| CHEN Y Q, VERBUGR P H, 2000. Multi-scale spatial distribution of land use/land cover in China[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 20(3): 197-202. | |
| [25] | 杜雪, 王海燕, 2022. 中国森林土壤有机碳活性组分及其影响因素[J]. 世界林业研究, 35(1): 76-81. |
| DU X, WANG H Y, 2022. Active components of forest soil organic carbon and its influencing factors in china[J]. World Forestry Research, 35(1): 76-81. | |
| [26] | 段文军, 王金叶, 2013. 广西喀斯特和红壤地区桉树人工林土壤理化性质对比研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 22(4): 595-597. |
| DUAN W J, WANG J Y, 2013. Comparative study on the physical and chemical properties of eucalyptus plantation soil in Guangxi Karst and red soil area[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 22(4): 595-597. | |
| [27] | 葛云辉, 苏以荣, 邹冬生, 等, 2012. 桂西北石灰土土壤有机碳矿化对外源有机物质和碳酸钙的响应[J]. 生态学杂志, 31(11): 2748-2754. |
| GE Y H, SU Y R, ZOU D S, et al., 2012. Organic carbon mineralization in lime soils in Karst region of Guangxi, South China in response to exogenous organic substrate and calcium carbonate[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 31(11): 2748-2754. | |
| [28] | 黄媛, 苏以荣, 梁士楚, 等, 2013. 桂西北典型土壤有机碳矿化对碳酸钙与水分含量的响应[J]. 生态学杂志, 32(10): 2695-2702. |
| HUANG Y, SU Y R, LIANG S C, et al., 2013. Responses of organic carbon mineralization in typical soils in northwest Guangxi of China to calcium carbonate and soil moisture[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 32(10): 2695-2702. | |
| [29] |
贾生强, 范惠珊, 陈喜靖, 等, 2021. 长期秸秆还田下土壤反硝化细菌群落的有机碳驱动机制[J]. 浙江农业学报, 33(9): 1686-1699.
DOI |
| JIA S Q, FAN H S, CHEN X J, et al., 2021. Driving mechanism of soil denitrifying bacterial community by soil organic carbon after long term of straw return[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 33(9): 1686-1699. | |
| [30] | 冷雪梅, 钱九盛, 张旭辉, 等, 2022. 添加外源有机物对长期不同施肥处理水稻土有机碳矿化的影响[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 45(1): 103-112. |
| LENG X M, QIAN J S, ZHANG X H, et al., 2022. Effects of maize straw addition on the mineralization of organic carbon in paddy soils with long-term fertilizations[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 45(1): 103-112. | |
| [31] | 李艾蒙, 李慧, 裴久渤, 等, 2019. 玉米秸秆施用对棕壤有机碳激发效应及温度敏感性的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 38(12): 2788-2796. |
| LI A M, LI H, PEI J B, et al., 2019. Effects of maize straw application on organic carbon' s priming effect and temperature sensitivity in brown earth[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 38(12): 2788-2796. | |
| [32] | 李顺姬, 邱莉萍, 张兴昌, 2010. 黄土高原土壤有机碳矿化及其与土壤理化性质的关系[J]. 生态学报, 30(5): 1217-1226. |
| LI S J, QIU L P, ZHANG X C, 2010. Mineralization of soil organic carbon and its relations with soil physical and chemical properties on the Loess Plateau[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30(5): 1217-1226. | |
| [33] | 李杨, 苏以荣, 何寻阳, 等, 2012. 桂西北棕色石灰土和红壤有机碳矿化特征和差异[J]. 农业现代化研究, 33(5): 632-635. |
| LI Y, SU Y R, HE X Y, et al., 2012. Characteristics and discrepancies of soil organic carbon mineralization for brown limestone soil and red soil in northwest Guangxi[J]. Research of Agricultural Modernization, 33(5): 632-635. | |
| [34] | 李忠佩, 张桃林, 陈碧云, 2004. 可溶性有机碳的含量动态及其与土壤有机碳矿化的关系[J]. 土壤学报, 41(4): 544-552. |
| LI Z P, ZHANG T L, CHEN B Y, 2004. Dynamics of soluble organic carbon and its relation to mineralization of soil organic carbon[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 41(4): 544-552. | |
| [35] | 林仕芳, 王小利, 段建军, 等, 2022. 有机肥替代化肥对旱地黄壤有机碳矿化及活性有机碳的影响[J]. 环境科学, 43(4): 2219-2225. |
| LIN S F, WANG X L, DUAN J J, et al., 2022. Effects of organic fertilizer replacing chemical fertilizer on organic carbon mineralization and active organic carbon in dryland yellow soil[J]. Environmental Science, 43(4): 2219-2225. | |
| [36] | 刘赛男, 高尚, 程效义, 等, 2019. 玉米秸秆生物炭对秸秆腐熟进程、养分含量和CO2排放量的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 30(4): 1312-1318. |
| LIU S N, GAO S, CHENG X Y, et al., 2019. Effects of corn straw biochar on process, nutrient content, and CO2emissions of corn straw decomposition[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 30(4): 1312-1318. | |
| [37] | 罗梅, 田冬, 高明, 等, 2018. 紫色土壤有机碳活性组分对生物炭施用量的响应[J]. 环境科学, 39(9): 4327-4337. |
| LUO M, TIAN D, GAO M, et al., 2018. Soil organic carbon of purple soil as affected by different application of biochar[J]. Environmental Science, 39(9): 4327-4337. | |
| [38] | 马欣, 魏亮, 唐美玲, 等, 2018. 长期不同施肥对稻田土壤有机碳矿化及激发效应的影响[J]. 环境科学, 39(12): 5680-5686. |
| MA X, WEI L, TANG M L, et al., 2018. Effects of varying long-term fertilization on organic carbon mineralization and priming effect of paddy soil[J]. Environmental Science, 39(12): 5680-5686. | |
| [39] |
史登林, 王小利, 段建军, 等, 2020. 氮肥减量配施生物炭对黄壤稻田土壤有机碳活性组分和矿化的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 31(12): 4117-4124.
DOI |
| SHI D L, WANG X L, DUAN J J, et al., 2020. Effects of chemical N fertilizer reduction combined with biochar application on soil organic carbon active components and mineralization in paddy fields of yellow soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 31(12): 4117-4124. | |
| [40] | 苏有健, 廖万有, 王烨军, 等, 2014. 茶园土壤中钙迁移行为的土柱模拟研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 28(1): 26-30. |
| SU Y J, LIAO W Y, WANG Y J, et al., 2014. Modeling vertical migration behavior of calcium in tea garden by soil columns leaching[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 28(1): 26-30. | |
| [41] | 魏圆云, 崔丽娟, 张曼胤, 等, 2019. 土壤有机碳矿化激发效应的微生物机制研究进展[J]. 生态学杂志, 38(4): 1202-1211. |
| WEI Y Y, CUI L J, ZHANG M Y, et al., 2019. Research advances in microbial mechanisms underlying priming effect of soil organic carbon mineralization[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 38(4): 1202-1211. | |
| [42] | 吴静, 陈书涛, 胡正华, 等, 2015. 不同温度下的土壤微生物呼吸及其与水溶性有机碳和转化酶的关系[J]. 环境科学, 36(4): 1497-1506. |
|
WU J, CHEN S T, HU Z H, et al., 2015. Soil microbial respiration under different soil temperature conditions and its relationship to soil dissolved organic carbon and invertase[J]. Environmental Science, 36(4): 1497-1506.
DOI URL |
|
| [43] | 肖谋良, 陈香碧, 李杨, 等, 2014. 棕色石灰土和红壤碳释放对添加矿物质(Fe(OH)3和CaCO3)的响应[J]. 生态学杂志, 33(11): 2936-2942. |
| XIAO M L, CHEN X B, LI Y, et al., 2014. Carbon release from brown limestone and red soils in response to addition of Fe(OH)3and CaCO3[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 33(11): 2936-2942. | |
| [44] | 肖烨, 黄志刚, 2019. 湿地土壤有机碳稳定性的微生物学影响机制[J]. 安徽农业科学, 47(20): 15-17. |
| XIAO Y, HUANG Z G, 2019. Mechanism of microbiological influence on soil organic carbon stability in wetland[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 47(20): 15-17. | |
| [45] | 闫雷, 周丽婷, 孟庆峰, 等, 2020. 有机物料还田对黑土有机碳及其组分的影响[J]. 东北农业大学学报, 51(5): 40-46. |
| YAN L, ZHOU L T, MENG Q F, et al., 2020. Effect of organic materials returning on soil organic carbon concentration and soil organic fractions in the black soil area[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 51(5): 40-46. | |
| [46] | 杨开军, 杨万勤, 贺若阳, 等, 2017. 川西亚高山3种典型森林土壤碳矿化特征[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 23(5): 851-856. |
| YANG K J, YANG W Q, HE R Y, et al., 2017. Soil organic carbon mineralization characteristics of three dominant subalpine forests in western Sichuan, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 23(5): 851-856. | |
| [47] | 郑斯尹, 陈莉莎, 谢德晋, 2019. 不同氮肥用量对玉米田土壤酶活性及微生物量碳、氮的影响[J]. 中国水土保持, 448(7): 58-60, 73. |
| ZHENG S Y, CHEN L S, XIE D J, 2019. Effects of different nitrogen application rates on soil enzyme activity and microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen in maize farmland[J]. Soil and Water Conservation in China, 448(7): 58-60, 73. | |
| [48] | 周萍, 潘根兴, 李恋卿, 等, 2009. 南方典型水稻土长期试验下有机碳积累机制v.碳输入与土壤碳固定[J]. 中国农业科学, 42(12): 4260-4268. |
| ZHOU P, PAN G X, LI L Q, et al., 2009. SOC enhancement in major types of paddy soils in a long-term agro-ecosystem experiment in south China. v. relationship between carbon input and soil carbon sequestration[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 42(12): 4260-4268. |
| [1] | 徐敏, 许超, 余光辉, 尹力初, 张泉, 朱捍华, 朱奇宏, 张杨珠, 黄道友. 地下水位和长期秸秆还田对土壤镉有效性及稻米镉含量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 150-157. |
| [2] | 王洁, 单燕, 马兰, 宋延静, 王向誉. 秸秆/生物质炭协同还田措施对黄河三角洲盐碱土壤的改良效果研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 90-98. |
| [3] | 龚玲玄, 王丽丽, 赵建宁, 刘红梅, 杨殿林, 张贵龙. 不同覆盖作物模式对茶园土壤理化性质及有机碳矿化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1141-1150. |
| [4] | 贺晓佳, 冯书华, 蒋明, 李明锐, 湛方栋, 李元, 何永美. UV-B辐射对水稻根际土壤活性有机碳转化和产甲烷潜力的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 556-564. |
| [5] | 黄巧义, 于俊红, 黄建凤, 黄旭, 李苹, 付弘婷, 唐拴虎, 刘一锋, 徐培智. 广东省主要农作物秸秆养分资源量及替代化肥潜力[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 297-306. |
| [6] | 郝小雨, 王晓军, 高洪生, 毛明艳, 孙磊, 马星竹, 周宝库, 迟凤琴, 李伟群. 松嫩平原不同秸秆还田方式下农田温室气体排放及碳足迹估算[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 318-325. |
| [7] | 宋瑞朋, 杨起帆, 郑智恒, 习丹. 3种林下植被类型对杉木人工林土壤有机碳及其组分特征的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2283-2291. |
| [8] | 石含之, 刘帆, 黄永东, 吴志超, 李富荣, 徐守俊, 邓腾灏博, 文典, 王旭, 王富华, 江棋, 杜瑞英. 土壤溶解性有机物的动态变化对水溶态铜的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(9): 1896-1902. |
| [9] | 邹晨怡, 丁洪, 王亚萨, 张玉树, 余居华, 郑祥洲. 秸秆对尿素氮在土壤中转化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1213-1219. |
| [10] | 陈思, 王灿, 李想, 李明锐, 湛方栋, 李元, 祖艳群, 何永美. 不同UV-B辐射增幅对稻田土壤酶活性、活性有机碳含量及温室气体排放的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1260-1268. |
| [11] | 徐志宇, 薛颖昊, 张军, 孙仁华, 石祖梁, 赫天一, 王久臣. 基于文献计量的秸秆综合利用研究热点与前沿分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1310-1320. |
| [12] | 张兵兵, 杨照, 薛斌, 丁小艳, 娄金分, 王盛, 陈蔚洁, 徐国敏. 薏仁米秸秆生物炭对水中Hg2+的吸附特性及机制[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(5): 1051-1059. |
| [13] | 丛鑫, 李瑶, 王宇, 郑力. 生物炭基针铁矿复合材料对水中莠去津吸附特性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(10): 2067-2075. |
| [14] | 张子璇, 牛蓓蓓, 李新举. 不同改良模式对滨海盐渍土土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2020, 29(2): 275-284. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
