生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (2): 380-390.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.02.019
梅闯1( ), 蔡昆争1, 黎紫珊2, 徐美丽2, 黄飞1,2,*(
), 蔡昆争1, 黎紫珊2, 徐美丽2, 黄飞1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-01-10
出版日期:2022-02-18
发布日期:2022-04-14
通讯作者:
*黄飞,E-mail: feihuang2011@163.com作者简介:梅闯(1995年生),男,硕士研究生,主要从事重金属污染土壤修复研究。E-mail: chuangm1230@163.com
基金资助:
MEI Chuang1( ), CAI Kunzheng1, LI Zishan2, XU Meili2, HUANG Fei1,2,*(
), CAI Kunzheng1, LI Zishan2, XU Meili2, HUANG Fei1,2,*( )
)
Received:2022-01-10
Online:2022-02-18
Published:2022-04-14
摘要:
为阐明稻秆生物炭介导土壤Cd形态转化过程中化学性质与微生物群落多样性变化特征,通过室内培养实际污染土壤实验,研究施加稻秆生物炭对土壤Cd形态、pH值、阳离子交换量(CEC)、有机质(SOM)、碱解氮(AN)、有效磷(AP)、速效钾(AK)含量,以及土壤蔗糖酶(CA)、脲酶(UA)、过氧化氢酶(IA)活性等的影响特征,并通过高通量测序手段揭示土壤细菌和真菌群落结构组成与多样性的变化规律。结果表明,稻秆生物炭能够显著降低土壤中酸提取态Cd含量(23.19%),增加残渣态Cd含量(28.42%),促进Cd形态由不稳定态向稳定态转化。生物炭在不同程度上提高土壤pH、CEC、SOM、AN、AP和AK含量,其中SOM和AK含量增幅最显著,分别达到48.42%和81.28%。生物炭的添加显著影响土壤细菌和真菌群落中的优势类群丰度,其中Bacillus、Streptomyces、Aspergillus等与重金属形态有关的功能菌种丰度增加,细菌群落相较于真菌群落可能更容易受到环境因子的影响;影响土壤Cd形态转化的关键因素主要包括土壤pH值、SOM和AK以及细菌群落。稻秆生物炭主要通过影响土壤pH值、有机质、速效钾含量以及土壤中细菌群落多样性与优势类群丰度,进而促进Cd形态由不稳定态向稳定态转化,降低重金属污染程度。该研究结果可为重金属污染土壤修复实践提供理论参考。
中图分类号:
梅闯, 蔡昆争, 黎紫珊, 徐美丽, 黄飞. 稻秆生物炭对稻田土壤Cd形态转化和微生物群落的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 380-390.
MEI Chuang, CAI Kunzheng, LI Zishan, XU Meili, HUANG Fei. Effects of Rice-straw Biochar on the Transformation of Cadmium Fractions and Microbial Community in Paddy Soils[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(2): 380-390.
| 指标 Index | 解释度 Explains/% | F检验 Pseudo-F | P值 P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| SOM | 92.5 | 123 | 0.002 |
| AK | 60.3 | 15.2 | 0.004 |
| pH | 41.2 | 7 | 0.018 |
| CEC | 28.6 | 4 | 0.066 |
| AP | 19.2 | 2.4 | 0.166 |
| AN | 12.4 | 1.4 | 0.228 |
表1 各指标对Cd形态影响的解释度
Table 1 Explanation of the influence of each index on Cd fractions
| 指标 Index | 解释度 Explains/% | F检验 Pseudo-F | P值 P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| SOM | 92.5 | 123 | 0.002 |
| AK | 60.3 | 15.2 | 0.004 |
| pH | 41.2 | 7 | 0.018 |
| CEC | 28.6 | 4 | 0.066 |
| AP | 19.2 | 2.4 | 0.166 |
| AN | 12.4 | 1.4 | 0.228 |
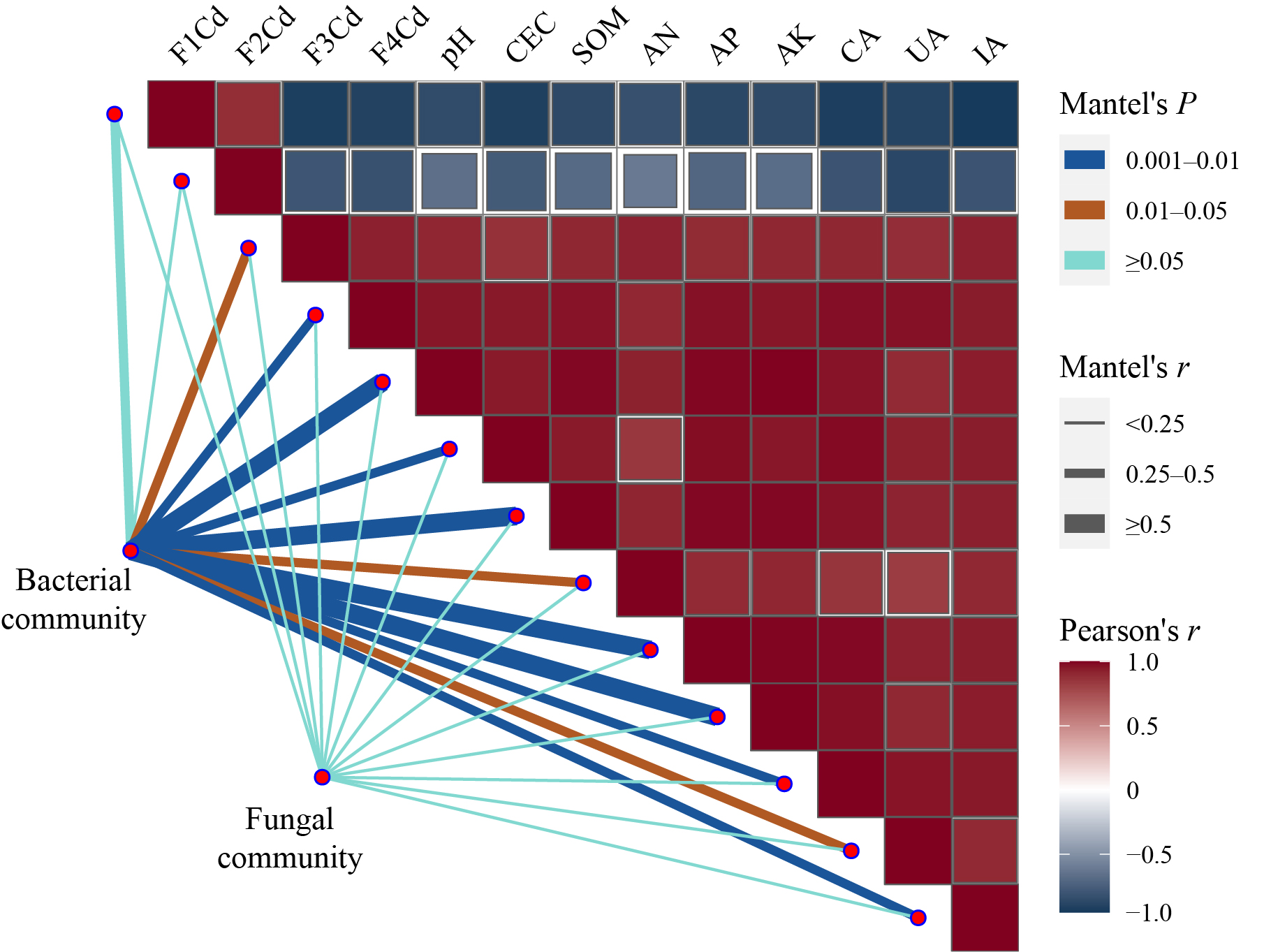
图8 细菌和真菌群落与环境因子的Mantel test分析 酸提取态Cd(F1Cd),可还原态Cd(F2Cd),可氧化态Cd(F3Cd),残渣态Cd(F4Cd),阳离子交换量(CEC),土壤有机质(SOM),碱解氮(AN),有效磷(AP),速效钾(AK),氧化还原酶活性(CA),脲酶活性(UA),蔗糖酶活性(IA)。下同 The same below
Figure 8 Relationships between soil variables and microbial community structures
| [1] |
ALI A, SHAHEEN S, GUO D, et al., 2020. Apricot shell-and apple tree derived biochar affect the fractionation and bioavailability of Zn and Cd as well as the microbial activity in smelter contaminated soil[J]. Environmental Pollution, DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114773.
DOI |
| [2] | BERIHUM T, TADELE M, KEBEDE F, 2017. The application of biochar on soil acidity and other physico-chemical properties of soils in southern Ethiopia[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition & Soil Science, 180(3): 381-388. |
| [3] | BHATTACHARJYA S, CHANDRA R, PAREEK N, et al., 2016. Biochar and crop residue application to soil: Effect on soil biochemical properties, nutrient availability and yield of rice (Oryza sativa L.) and wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)[J]. Archives of Agronomy & Soil Science, 62(8): 1058-1108. |
| [4] |
CUI L Q, PAN G X, LI L Q, et al., 2016. Continuous immobilization of cadmium and lead in biochar amended contaminated paddy soil: A five-year field experiment[J]. Ecological Engineering, 93: 1-8.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
FAZLI M M, SOLEIMANI N, MEHRASBI M, et al., 2015. Highly cadmium tolerant fungi: Their tolerance and removal potential[J]. Journal of Environmental Health Science and Engineering, DOI: 10.1186/s40201-015-0176-0.
DOI |
| [6] |
GAO L Y, DENG J H, HUANG G F, et al., 2019. Relative distribution of Cd2+ adsorption mechanisms on biochars derived from rice straw and sewage sludge[J]. Bioresource Technology, 272: 114-122.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
GRAY C W, DUNHAM S J, DENNIS P G, et al., 2006. Field evaluation of in situ remediation of a heavy metal contaminated soil using lime and re-mud[J]. Environmental Pollution, 142(3): 530-539.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
HUANG F, GAO L Y, WU R R, et al., 2020. Qualitative and quantitative characterization of adsorption mechanisms for Cd2+ by silicon-rich biochar[J]. Science of the Total Environment, DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139163.
DOI |
| [9] |
KANDELER E, LURIENEGGER G, SCHWARZ S, 1997. Influence of heavy metals on the functional diversity of soil microbial community[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soil, 23: 299-306.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
KAVITHA B, REDDY P V L, KIM B, et al., 2018. Benefits and limitations of biochar amendment in agricultural soils: A reviews[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 227: 146-154.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
KHALID S, SHAHID M, NIAZI N, et al., 2017. A comparison of technologies for remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 182: 247-268.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
MA H, WEI M Y, WANG Z R, et al., 2020. Bioremediation of cadmium polluted soil using a novel cadmium immobilizing plant growth promotion strain Bacillus sp. TZ5 loaded on biochar[J]. Journal of Hazardous Material, DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122065.
DOI |
| [13] |
SAHMOUNE M N, 2018. Performance of Streptomyces rimosus biomass in biosorption of heavy metals from aqueous solutions[J]. Microchemical Journal, 141: 87-95.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
SELVIN J, SHANMUGHA PRIYA S, SEGHAL K G, et al., 2009. Bai, sponge-associated marine bacteria as indicators of heavy metal pollution[J]. Microbiological Research, 164: 352-363.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
TANG J Y, ZHANG L H, ZHANG J C, et al., 2020. Physicochemical features, metal availability and enzyme activity in heavy metal-polluted soil remediated by biochar and compost[J]. Science of the Total Environment, DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134751.
DOI |
| [16] |
TU C, WEI J, GUAN F, et al., 2020. Biochar and bacteria inoculated biochar enhanced Cd and Cu immobilization and enzymatic activity in a polluted soil[J]. Environment International, DOI: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.105576.
DOI |
| [17] |
WANG L, CHEN H R, WU J Z, et al., 2021. Effects of magnetic biochar-microbe composite on Cd remediation and microbial responses in paddy soil[J]. Journal of Hazardous Material, DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125494.
DOI |
| [18] |
WANG X, FANG L C, BEIYUAN J Z, et al., 2021. Improvement of alfalfa resistance against Cd stress through rhizobia and arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi co-inoculation in Cd-contaminated soil[J]. Environmental Pollution, 277: 116758.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
WANG Z Y, CHEM L, SUN F L, et al., 2017. Effects of adding biochar on the properties and nitrogen bioavailability of an acidic soil[J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 68(4): 559-572.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
WILLIAMS P N, LEI M, SUN G X, et al., 2009. Occurrence and partitioning of cadmium, arsenic and lead in mine impacted paddy rice: Hunan, China[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 43(3): 637-642.
DOI URL |
| [21] | XIAO R, WANG P, MI S S, et al., 2019. Effects of crop straw and its derived biochar on the mobility and bioavailability in Cd and Zn in two smelter-contaminated alkaline soils[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 181: 151-163. |
| [22] |
XIAO X, CHEN B L, CHEN Z M, et al., 2018. Insight into multiple and multilevel structures of biochars and their potential environmental applications: A critical review[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 52(9): 5027-5047.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
YUAN J H, XU R K, ZHANG H, 2011. The forms of alkalis in the biochar produced from crop residues at different temperatures[J]. Bioresource Technology, 102(3): 3488-3497.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
ZAHEDIFAR M, 2020. Effect of biochar on cadmium fractions in some polluted saline and sodic soils[J]. Environmental Management, 66(6): 1133-1141.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
ZHU X M, CHEN B L, ZHU L H, et al., 2017. Effects and mechanisms of biochar-microbe interactions in soil improvement and pollution remediation: A review[J]. Environmental Pollution, 227: 98-115.
DOI URL |
| [26] | 包建平, 袁根生, 董方圆, 等, 2020. 生物质炭与秸秆施用对红壤有机碳组会和微生物活性的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 57(3): 721-729. |
| BAO J P, YUAN G S, DONG F Y, et al., 2020. Effects of biochar application and straw returning on organic carbon fractionations and microbial activities in a red soil[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 57(3): 721-729. | |
| [27] | 鲍士旦, 2000. 土壤农化分析[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社. |
| BAO S D, 2000. Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Press. | |
| [28] | 陈乐, 詹思维, 刘梦洁, 等, 2020. 生物炭对不同酸化水平稻田土壤性质和重金属Cu、Cd有效性影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 34(1): 358-634. |
| CHEN L, ZHAN S W, LIU M J, et al., 2020. Effects of biochar on the properties and the availability of Cu and Cd in paddy soil with different acidification levels[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 34(1): 358-364. | |
| [29] | 陈志良, 袁志辉, 黄玲, 等, 2016. 生物炭来源、性质及其在重金属污染土壤修复中的研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 25(11): 1879-1884. |
| CHEN Z L, YUAN Z H, HUANG L, et al., 2016. Pyrolysis materials, characteristics of biochar and its application on remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil: A review[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 25(11): 1879-1884. | |
| [30] | 关松荫, 1986. 土壤酶及其研究方法[M]. 北京: 农业出版社. |
| GUAN S Y, 1986. Study on soil enzyme and its methods[M]. Beijing: Agricultural Press. | |
| [31] | 郭碧林, 陈效民, 景锋, 等, 2019. 施用生物炭对红壤性水稻土重金属钝化与土壤肥力的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 33(3): 298-304. |
| GUO B L, CHEN X M, JING F, et al., 2019. Effects of biochar application on heavy mental passivation and soil fertility in the red paddy soil[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 33(3): 298-304. | |
| [32] | 黄家庆, 赖永翔, 翁伯琦, 等, 2020. 花生壳生物炭对镉污染菜园土壤细菌群落结构的影响[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 26(5): 1115-1128. |
| HUANG J Q, LAI Y X, WENG B Q, et al., 2020. Effect of peanut shell biochar on the bacterial community structure in cadmium-containing vegetable soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 26(5): 1115-1128. | |
| [33] | 李光炫, 石岸, 张黎明, 等, 2021. 不同粒径生物质炭对土壤重金属钝化及细菌群落的影响[J/OL]. 生态环境学报, https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/44.1661.X.20211217.2119.004.html . |
| LI G X, SHI A, ZHANG L M, et al., 2021. Effects of biochar with different particle sizes on soil heavy metal immobilization and bacterial community[J/OL]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/44.1661.X.20211217.2119.004.html . | |
| [34] | 李洪达, 李艳, 周薇, 等, 2018. 稻壳生物炭对矿区重金属复合污染土壤中Cd、Zn形态转化的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 37(9): 1856-1865. |
| LI H D, LI Y, ZHOU W, et al., 2018. Effects of rice-husk-derived biochar on the morphological transformation of Cd and Zn in mining area soils polluted by heavy metals[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 37(9): 1856-1865. | |
| [35] | 梁妮, 净婷菲, 李中文, 等, 2021. 不同钝化剂对土壤环境中重金属有效性和微生物群落的影响[J]. 生态毒理学报, 16(1): 177-187. |
| LIANG N, JING T F, LI Z W, et al., 2021. Effects of different amendments on the availability of heavy metals and microbial communities in contaminated soils[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 16(1): 177-187. | |
| [36] | 刘娟, 张乃明, 袁启慧, 等, 2021. 不同钝化剂对铅镉复合污染土壤钝化效果及影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(8): 1732-1741. |
| LIU J, ZHANG N M, YUAN Q H, et al., 2021. Passivation effect and influencing factors of different passivators on lead-cadmium compound contaminated soils[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(8): 1732-1741. | |
| [37] | 梅闯, 王衡, 蔡昆争, 等, 2021. 生物炭对土壤重金属化学形态影响的作用机制研究进展[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 37(4): 421-429. |
| MEI C, WANG H, CAI K Z, et al., 2021. Advances on effects and mechanisms of biochar on chemical forms of heavy metals in contaminated soil[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 37(4): 421-429. | |
| [38] | 孟立君, 吴凤芝, 2004. 土壤酶研究进展[J]. 东北农业大学学报, 35(5): 622-626. |
| MENG L J, WU F Z, 2004. Advances on soil enzymes[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 35(5): 622-626. | |
| [39] | 谭向平, 何金红, 郭志明, 等, 2022. 土壤酶对重金属污染的响应及指示研究进展[J/OL]. 土壤学报, https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/32.1119.P.20211126.1624.010.html . |
| TAN X P, HE J H, GUO Z M, et al., 2022. Research progresses on soil enzymes as indicators of soil health and their responses to heavy metal pollution[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/32.1119.P.20211126.1624.010.html . | |
| [40] | 吴春艳, 陈义, 闵航, 等, 2006. Cd2+和Cu2+对水稻土微生物及酶活性的影响[J]. 浙江农业科学, 47(3): 303-307. |
| WU C Y, CHEN Y, MIN H, et al., 2006. Effects of heavy metals on microorganisms and enzyme activities in paddy soil[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 47(3): 303-307. | |
| [41] | 吴萍萍, 李录久, 王家嘉, 等, 2017. 稻秆生物炭对矿区污染土壤重金属形态转化的影响[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 33(5): 453-459. |
| WU P P, LI L J, WANG J J, et al., 2017. Effects of application of straw-derived biochar on forms of heavy metals in mining contaminated soil[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 33(5): 453-459. | |
| [42] | 吴伟健, 陈艺杰, 李高洋, 等, 2021. 水稻秸秆生物炭对镉污染农田中番茄产量和品质的影响机制[J/OL]. 农业环境科学学报, https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/12.1347.S.20210928.0850.008.html . |
| WU W J, CHEN Y J, LI G Y, et al., 2021. Effects of rice straw biochar on tomato yield and quality in farmland affected by Cd contamination[J/OL]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/12.1347.S.20210928.0850.008.html . | |
| [43] | 于寿娜, 2008. Cd、Hg污染对土壤及青菜-土壤系统土壤酶活性的影响[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学. |
| YU S N, 2008. Effects of cadmium mercury on soil enzyme activities in soil and soil-greengrocery systems[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University. | |
| [44] | 张华纬, 甄华杨, 岳士忠, 等, 2017. 水稻秸秆生物炭对污染土壤中镉生物有效性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 26(6): 1068-1074. |
| ZHANG H W, ZHEN H Y, YUE S Z, et al., 2017. Bioavailability of Cd in contaminated soil after short-term application of rice straw biochar[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 26(6): 1068-1074. | |
| [45] | 中华人民共和国环境保护部, 中华人民共和国国土资源部, 2014. 全国土壤污染状况调查公报[J]. 中国环保产业 (5): 10-11. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Republic of China, Ministry of Natural Resources of the People's Republic of China, 2014. Report on the national general survey of soil contamination[J]. China Environmental Protection Industry (5): 10-11. | |
| [46] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部,国家市场监督管理总局, 2018. 土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准 (试行) 第4部分: GB 15618-2018 [S]. 北京: 中国环境出版集团. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation, 2018. Soil environmental quality-Risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural hand Part 4: GB 15618-2018 [S]. Beijing: China Environment Publishing Group. |
| [1] | 王云, 郑西来, 曹敏, 李磊, 宋晓冉, 林晓宇, 郭凯. 滨海含水层咸-淡水过渡带反硝化性能与控制因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 980-988. |
| [2] | 赵维彬, 唐丽, 王松, 刘玲玲, 王树凤, 肖江, 陈光才. 两种生物炭对滨海盐碱土的改良效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 678-686. |
| [3] | 阳涅, 孙晓旭, 孔天乐, 孙蔚旻, 陈泉源, 高品. 微生物群落对河流底泥中锑含量变化的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 609-618. |
| [4] | 游宏建, 张文文, 兰正芳, 马兰, 张宝娣, 穆晓坤, 李文慧, 曹云娥. 蚯蚓原位堆肥与生物炭对黄瓜根结线虫及根际微生物的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 99-109. |
| [5] | 陈小弯, 田华川, 常军军, 陈礼强, 舒兴权, 冯秀祥. 杞麓湖中河河口表流湿地净化河道污染水的效果及其微生物群落特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1865-1875. |
| [6] | 李晓晖, 艾仙斌, 李亮, 王玺洋, 辛在军, 孙小艳. 新型改性稻壳生物炭材料对镉污染土壤钝化效果的研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1901-1908. |
| [7] | 花莉, 成涛之, 梁智勇. 固定化混合菌对陕北黄土地区石油污染土壤的修复效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1610-1615. |
| [8] | 陶玲, 黄磊, 周怡蕾, 李中兴, 任珺. 污泥-凹凸棒石共热解生物炭对矿区土壤重金属生物有效性和环境风险的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1637-1646. |
| [9] | 房献宝, 张智钧, 赖阳晴, 叶脉, 刁增辉. 新型污泥生物炭对土壤重金属Cr和Cd的修复研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1647-1656. |
| [10] | 钱莲文, 余甜甜, 梁旭军, 王义祥, 陈永山. 茶园土壤酸化改良中生物炭应用5 a后的稳定性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1442-1447. |
| [11] | 高鹏, 高品, 孙蔚旻, 孔天乐, 黄端仪, 刘华清, 孙晓旭. 蜈蚣草根际及内生微生物群落对砷污染胁迫的响应机制研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1225-1234. |
| [12] | 张慧琦, 李子忠, 秦艳. 玉米秸秆生物炭用量对砂土孔隙和持水性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1272-1277. |
| [13] | 朱奕豪, 李青梅, 刘晓丽, 李娜, 宋凤玲, 陈为峰. 不同土地整治类型新增耕地土壤微生物群落特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 909-917. |
| [14] | 邓晓, 武春媛, 杨桂生, 李怡, 李勤奋. 椰壳生物炭对海南滨海土壤的改良效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 723-731. |
| [15] | 魏岚, 黄连喜, 李翔, 王泽煌, 陈伟盛, 黄庆, 黄玉芬, 刘忠珍. 生物炭基质可显著地促进香蕉幼苗生长[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 732-739. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 271
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 288
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
