生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (9): 1855-1864.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.09.010
许冬雪1( ), 李兴1,2,3,*(
), 李兴1,2,3,*( ), 王勇2,4,*(
), 王勇2,4,*( ), 勾芒芒5
), 勾芒芒5
收稿日期:2021-01-03
出版日期:2021-09-18
发布日期:2021-12-08
通讯作者:
王勇,(1970年生)男,研究员,研究方向为节水灌溉和污水资源化利用方面的研究。E-mail: wangyonglsx@163.com作者简介:许冬雪,(1996年生),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为水污染控制与水环境保护方面的研究。E-mail: 2582334187@qq.com
基金资助:
XU Dongxue1( ), LI Xing1,2,3,*(
), LI Xing1,2,3,*( ), WANG Yong2,4,*(
), WANG Yong2,4,*( ), GOU Mangmang5
), GOU Mangmang5
Received:2021-01-03
Online:2021-09-18
Published:2021-12-08
摘要:
湖泊水体中氮、磷和叶绿素a空间分布特征及其响应关系对辨识水环境质量具有重要意义。尤其对于冰封期典型的水文气候条件,将表现出特殊的环境地球化学行为,冰封期结冰过程使水体不同形态的氮、磷由冰层向水体迁移,导致冰下水体中营养盐浓度、叶绿素a浓度大于冰层,冰下水体污染物浓度增加。为量化不同污染物质在冰-水介质中迁移规律,于2020年1月14日采集乌梁素海12个样点的冰样和冰体,检测了各采样点不同形态氮磷和叶绿素a浓度。结果表明:冰样中高值ρ(TN) 0.838 mg∙L-1、ρ(NH4+-N) 0.109 mg∙L-1、ρ(NO3--N) 0.347 mg∙L-1分别位于湖心区的Q8采样点和北湖区的J11采样点。TN、NH4+-N、NO3--N集中分布在中层冰、下层冰和上层冰,冰下水体中北湖区的ρ(TN)、ρ(NH4+-N)、ρ(NO3--N)、ρ(NO2--N)出现高值。在冰样和冰下水体中总磷(TP)和溶解性总磷(DTP)的分布规律均为北湖区最高,南湖区最低。并且TP和DTP集中分布在下冰层。冰样中Chl-a在北湖区、湖心区和南湖区的平均质量浓度分别为2.455、1.407和1.210 mg∙L-1,41.6%采样点的中层冰和下层冰中含有高浓度的Chl-a。冰下水体中Chl-a的质量浓度范围是1.530—12.280 mg∙L-1,均值为7.874 mg∙L-1。冰封期乌梁素海的氮、磷和叶绿素a集中分布在冰下水体中。线性回归分析表明冰层和冰下水体中不同形态的氮、磷对叶绿素a的响应存在不同程度的差异。研究结果可为乌梁素海进一步的污染治理提供参考和借鉴。
中图分类号:
许冬雪, 李兴, 王勇, 勾芒芒. 冰封期乌梁素海不同形态氮、磷和叶绿素a的空间分布特征及其响应关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(9): 1855-1864.
XU Dongxue, LI Xing, WANG Yong, GOU Mangmang. Spatial Distribution Characteristics and the Response of Different Forms of Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Chlorophyll-a in Lake Ulansuhai during the Frozen Period[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(9): 1855-1864.
| 项目 Items | 分析方法 Analysis method | 检出限 Detection limit |
|---|---|---|
| 总氮 Total nitrogen | 碱性过硫酸钾消解紫外分光光度法HJ 636—2012 Alkaline potassium persulfate digestion UV spectrophotometric method HJ 636—2012 | 0.05 mg∙L-1 |
| 氨态氮Ammonia nitrogen | 纳氏试剂分光光度法HJ 535—2009 Nessler's reagent spectrophotometry HJ 535—2009 | 0.025 mg∙L-1 |
| 硝态氮 Nitrate | 离子色谱法HJ 84—2016 Ion Chromatography HJ 84—2016 | 0.016 mg∙L-1 |
| 亚硝态氮 Nitrate nitrogen | 分光光度法GB 7493-87 Spectrophotometric method GB 7493-87 | 0.003 mg∙L-1 |
| 总磷 Total phosphorus | 钼酸铵分光光度法GB 11893-89 Ammonium molybdate spectrophotometry GB 11893-89 | 0.01 mg∙L-1 |
| 溶解性总磷 Dissolved total phosphorus | 钼酸铵分光光度法GB 11893-89 Ammonium molybdate spectrophotometry GB 11893-89 | 0.01 mg∙L-1 |
| 叶绿素a Chlorophyll a | 分光光度法HJ 897—2017 Spectrophotometric method HJ 897—2017 | 2 μg∙L-1 |
表1 水质检测方法
Table 1 Methods of water quality test
| 项目 Items | 分析方法 Analysis method | 检出限 Detection limit |
|---|---|---|
| 总氮 Total nitrogen | 碱性过硫酸钾消解紫外分光光度法HJ 636—2012 Alkaline potassium persulfate digestion UV spectrophotometric method HJ 636—2012 | 0.05 mg∙L-1 |
| 氨态氮Ammonia nitrogen | 纳氏试剂分光光度法HJ 535—2009 Nessler's reagent spectrophotometry HJ 535—2009 | 0.025 mg∙L-1 |
| 硝态氮 Nitrate | 离子色谱法HJ 84—2016 Ion Chromatography HJ 84—2016 | 0.016 mg∙L-1 |
| 亚硝态氮 Nitrate nitrogen | 分光光度法GB 7493-87 Spectrophotometric method GB 7493-87 | 0.003 mg∙L-1 |
| 总磷 Total phosphorus | 钼酸铵分光光度法GB 11893-89 Ammonium molybdate spectrophotometry GB 11893-89 | 0.01 mg∙L-1 |
| 溶解性总磷 Dissolved total phosphorus | 钼酸铵分光光度法GB 11893-89 Ammonium molybdate spectrophotometry GB 11893-89 | 0.01 mg∙L-1 |
| 叶绿素a Chlorophyll a | 分光光度法HJ 897—2017 Spectrophotometric method HJ 897—2017 | 2 μg∙L-1 |
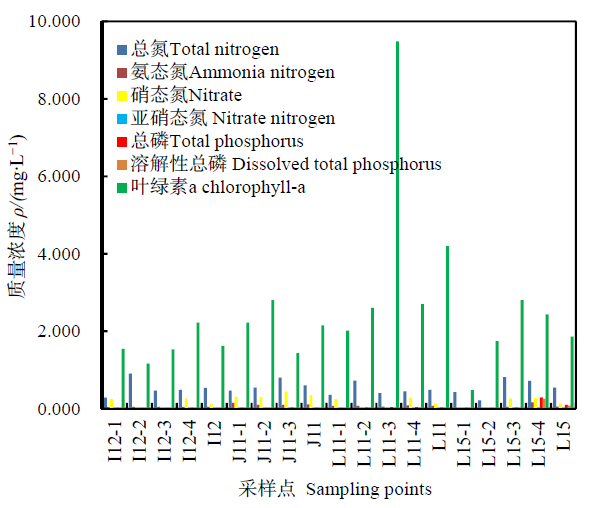
图2 北湖区不同冰层中不同形态氮磷和叶绿素分布 -1表示采样点冰下10 cm,-2表示采样点冰下20 cm,-3表示采样点冰下30 cm,-4表示采样点冰下40 cm。下同
Fig. 2 Distribution of different forms of nitrogen, phosphorus andchlorophyll-ain different ice layers in the North Lake area -1 means 10 cm under the ice of the sampling point, -2 means 20 cm under the ice of the sampling point, -3 means 30 cm under the ice of the sampling point, -4 means 40 cm under the ice of the sampling point. The same below
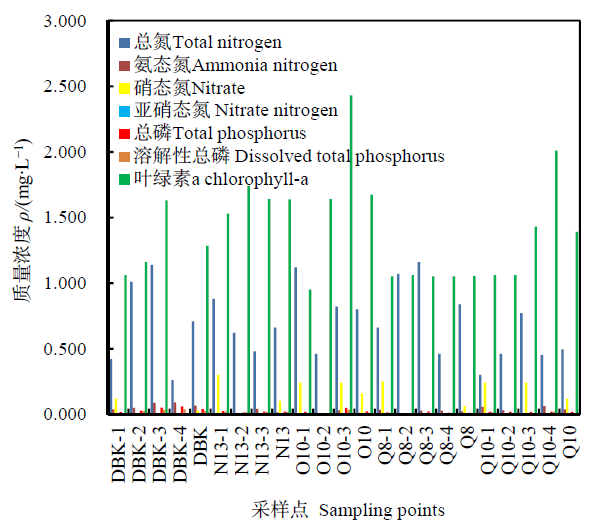
图3 湖心区不同冰层中不同形态氮磷和叶绿素分布
Fig. 3 Distribution of different forms of nitrogen, phosphorus and chlorophyll-a in different ice layers in the central of lake area
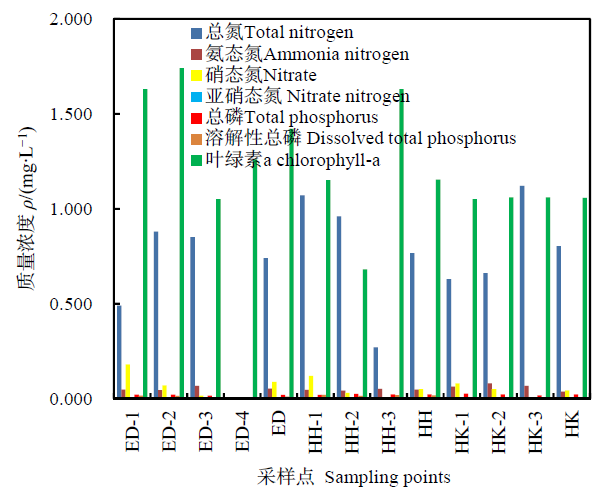
图4 南湖区不同冰层中不同形态氮磷和叶绿素分布
Fig. 4 Distribution of different forms of nitrogen, phosphorus and chlorophyll-a in different ice layers in the South Lake area
| 项目 Items | 线性回归方程 Linear regression equation | 相关系数r Correlation coefficient r | F | 显著性P Significant P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总氮 Total nitrogen | ρ(Chl-a)= -4.004 ρ(TN)+4.362 | 0.615 | 6.070 | 0.033 |
| 氨态氮 Ammonia nitrogen | ρ(Chl-a)= 12.338 ρ(NH4+-N)+1.143 | 0.391 | 1.803 | 0.209 |
| 硝态氮 Nitrate | ρ(Chl-a)= 4.004 ρ(NO3--N)+1.242 | 0.393 | 1.831 | 0.206 |
| 总磷 Total phosphorus | ρ(Chl-a)= 7.014 ρ(TP)+1.511 | 0.168 | 0.290 | 0.602 |
| 溶解性总磷 Dissolved total phosphorus | ρ(Chl-a)= 10.597 ρ(DTP)+1.518 | 0.243 | 0.627 | 0.447 |
表2 冰体中叶绿素a与不同形态氮磷的线性回归方程
Table 2 Linear regression equation of chlorophyll a and different forms of nitrogen and phosphorus in ice sample
| 项目 Items | 线性回归方程 Linear regression equation | 相关系数r Correlation coefficient r | F | 显著性P Significant P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总氮 Total nitrogen | ρ(Chl-a)= -4.004 ρ(TN)+4.362 | 0.615 | 6.070 | 0.033 |
| 氨态氮 Ammonia nitrogen | ρ(Chl-a)= 12.338 ρ(NH4+-N)+1.143 | 0.391 | 1.803 | 0.209 |
| 硝态氮 Nitrate | ρ(Chl-a)= 4.004 ρ(NO3--N)+1.242 | 0.393 | 1.831 | 0.206 |
| 总磷 Total phosphorus | ρ(Chl-a)= 7.014 ρ(TP)+1.511 | 0.168 | 0.290 | 0.602 |
| 溶解性总磷 Dissolved total phosphorus | ρ(Chl-a)= 10.597 ρ(DTP)+1.518 | 0.243 | 0.627 | 0.447 |
| 项目 Items | 线性回归方程 Linear regression equation | 相关系数r Correlation coefficient r | F | 显著性P Significant P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总氮 Total nitrogen | ρ(Chl-a)= -1.851 ρ(TN)+11.731 | 0.758 | 13.506 | 0.004 |
| 氨态氮 Ammonia nitrogen | ρ(Chl-a)= -4.725 ρ(NH4+-N)+11.174 | 0.553 | 4.405 | 0.062 |
| 硝态氮 Nitrate | ρ(Chl-a)= -2.027 ρ(NO3--N)+9.878 | 0.658 | 7.630 | 0.020 |
| 亚硝态氮 Nitrate nitrogen | ρ(Chl-a)= -128.019 ρ(NO2--N)+9.836 | 0.647 | 7.219 | 0.023 |
| 总磷 Total phosphorus | ρ(Chl-a)= 113.371 ρ(TP)+3.471 | 0.178 | 0.327 | 0.580 |
| 溶解性总磷Dissolved total phosphorus | ρ(Chl-a)= -99.425 ρ(DTP)+10.541 | 0.184 | 0.350 | 0.567 |
表3 冰下水体中叶绿素a与不同形态氮磷的线性回归方程
Table 3 Linear regression equation of chlorophyll a and different forms of nitrogen and phosphorus in subglacial water
| 项目 Items | 线性回归方程 Linear regression equation | 相关系数r Correlation coefficient r | F | 显著性P Significant P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总氮 Total nitrogen | ρ(Chl-a)= -1.851 ρ(TN)+11.731 | 0.758 | 13.506 | 0.004 |
| 氨态氮 Ammonia nitrogen | ρ(Chl-a)= -4.725 ρ(NH4+-N)+11.174 | 0.553 | 4.405 | 0.062 |
| 硝态氮 Nitrate | ρ(Chl-a)= -2.027 ρ(NO3--N)+9.878 | 0.658 | 7.630 | 0.020 |
| 亚硝态氮 Nitrate nitrogen | ρ(Chl-a)= -128.019 ρ(NO2--N)+9.836 | 0.647 | 7.219 | 0.023 |
| 总磷 Total phosphorus | ρ(Chl-a)= 113.371 ρ(TP)+3.471 | 0.178 | 0.327 | 0.580 |
| 溶解性总磷Dissolved total phosphorus | ρ(Chl-a)= -99.425 ρ(DTP)+10.541 | 0.184 | 0.350 | 0.567 |
| [1] | CAVALIERE E, BAULCH H M, 2019. Winter nitrification in ice-covered lakes[J]. PLoS ONE, 14(11): 1-20. |
| [2] |
DOMINGUES R B, BARBOSA A B, SOMMER U, et al., 2011. Ammonium, nitrate and phytoplankton interactions in a freshwater tidal estuarine zone: Potential effects of cultural eutrophication[J]. Aquatic Sciences, 73(3): 331-343.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
HAMPTON S E, MOORE M V, OZERSKY T, et al., 2015. Heating up a cold subject: prospects for under-ice plankton research in lakes[J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 37(2): 277-284.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
HUANG J G, LL S, WANG Y, et al., 2012. Distribution characteristics of nutrients and chlorophyll-a in a lake during the icebound season: A case study of a landscape lake in Changchun, China[J]. APCBEE Procedia, 1: 8-15.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
MAMUN M, KWON S, KIM J, et al., 2020. Evaluation of algal chlorophyll and nutrient relations and the N꞉P ratios along with trophic status and light regime in 60 Korea reservoirs[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 741: 140451-140464.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
MENG P J, TEW K S, HSIEH H Y, et al., 2017. Relationship between magnitude of phytoplankton blooms and rainfall in a hyper-eutrophic lagoon: A continuous monitoring approach[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 124(2): 897-902.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
NOMURA D, MINN M A, HATTORI H, et al., 2011. Incorporation of nitrogen compounds into sea ice from atmospheric deposition[J]. Marine Chemistry, 127(1-4): 90-99.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
ÖZKUNDAKCI D, GSELL A S, HINTZE T, et al., 2016. Winter severity determines functional trait composition of phytoplankton in seasonally ice-covered lakes[J]. Global Change Biology, 22(1): 284-298.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
PHILLIPS G, PIETILӒINEN O P, CARVALHO L, et al., 2008. Chlorophyll-nutrient relationships of different lake types using a large European dataset[J]. Aquatic Ecology, 42(2): 213-226.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
POWERS S M, LABOU S G, BAULCH H M, et al., 2017. Ice duration drives winter nitrate accumulation in north temperate lakes[J]. Limnology and Oceanography Letters, 2(5): 177-186.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
SOUED C, GIORGIO P A, MARANGER R, 2015. Nitrous oxide sinks and emissions in boreal aquatic networks in Québec[J]. Nature Geoscience, 9(2): 116-120.
DOI URL |
| [12] | WANG W D, LIU W Y, WU D, et al., 2019. Differentiation of nitrogen and microbial community in the littoral and limnetic sediments of a large shallow eutrophic lake (Chaohu Lake, China)[J]. Journal of Soils & Sediments: Protection, Risk Assessment, & Remediation, 19(2): 1005-1016. |
| [13] | YANG T T, HEI P F, SONG J D, et al., 2019. Nitrogen variations during the ice-on season in the eutrophic lakes[J]. Environmental Pollution (Baking, Essex:1987), 247: 1089-1099. |
| [14] | 杜丹丹, 李畅游, 史小红, 等, 2019. 乌梁素海水体营养状态季节性变化特征研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 33(12): 186-192. |
| DU D, LI C Y, SHI X H, et al., 2019. Seasonal changes of nutritional status of lake Wuliangsuhai[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 33(12): 186-192. | |
| [15] | 高宁, 2018. 水体结冰和融冰过程中典型污染物的迁移规律研究[D]. 烟台: 烟台大学: 47-51. |
| GAO N, 2018. Study on the migration of typical pollutants during freezing and melting[D]. Yantai: Yantai University: 47-51. | |
| [16] | 郭劲松, 陈园, 李哲, 等, 2011. 三峡小江回水区叶绿素 a 季节变化及其同主要藻类的相互关系[J]. 环境科学, 32(4): 976-981. |
| GUO J S, CHEN Y, LI Z, et al., 2011. Seasonal Variation of Chlorophyll A and Its Potential Relationship with Various Algal Species in Xiaojiang River Backwater Area, Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Environmental Science, 32(4): 976-981. | |
| [17] | 郭子扬, 李畅游, 史小红, 等, 2019. 寒旱区呼伦湖水体叶绿素a含量的时空分布特征及其影响因子分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(7): 1434-1442. |
| GUO Z Y, LI C Y, SHI X H, et al., 2019. Spatial and Temporal Distribution Characteristics of Chlorophyll A Content and Its Influencing Factor Analysis in Hulun Lake of Cold and Dry Areas[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28(7): 1434-1442. | |
| [18] | 蒋鑫艳, 李畅游, 史小红, 等, 2019. 乌梁素海叶绿素a的时空分布及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(5): 964-973. |
| JIANG X Y, LI C Y, SHI X H, et al., 2019. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Chlorophyll-a Concentration and its Relationships with Environmental Factors in Lake Ulansuhai[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28(5): 964-973. | |
| [19] | 李卫平, 徐静, 于玲红, 等, 2014. 乌梁素海冰封期营养盐及浮游植物的分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 23(6): 1007-1013. |
| LI W P, XU J, YU L H, et al., 2014. Distribution characteristics of nutrients and phytoplankton in Wuliangsuhai Lake during the icebound season[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 23(6): 1007-1013. | |
| [20] | 李兴, 何婷婷, 勾芒芒, 2018. 乌梁素海冰封期浮游植物群落特征与环境因子CCA分析[J]. 东北农业大学学报, 49(4): 67-78. |
| LI X, HE T T, GOU M M, 2018. CCA analysis of phytoplankton community characteristics and environmental factors in Wuliangsuhai Lake during ice-season[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 49(4): 67-78. | |
| [21] | 吕超, 2013. 乌梁素海冰封期富营养化特征研究[D]. 包头: 内蒙古科技大学. |
| LV C, 2013. Research on icebound eutrophication's feature of Wuliangsuhai Lake[D]. Baotou: Lnner Mongolia University of Science and Technolog. | |
| [22] | 孙鑫, 李兴, 勾芒芒, 2019. 乌梁素海冻融前后浮游植物群落结构特征及其影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(4): 812-821. |
| SUN X, LI X, GOU M M, 2019. Phytoplankton Community Structure Characteristics and Its Influencing Factors before and after Freezing and Thawing in Wuliangsuhai Lake[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28(4): 812-821. | |
| [23] | 王晓云, 于玲红, 王非, 等, 2017. 包头南海子湿地冰封期污染物迁移特征分析[J]. 环境化学, 36(4): 867-874. |
| WANG X Y, YU L H, WANG F, et al., 2017. Analysis on the characterristics of contaminant migration in period of ice sealed in Baotou Nanhaizi[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 36(4): 867-874. | |
| [24] | 王鑫磊, 2012. 基于遥感信息提取的乌梁素海水生植被演化及驱动机制研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学: 1. |
| WANG X L, 2012. Study on the evolution of aquatic vegetations and its driving mechanism of Wuliangsuhai Lake based on extracting remote sensing information[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University: 1. | |
| [25] | 吴怡, 郭亚飞, 曹旭, 等, 2013. 成都府南河叶绿素a和氮、磷的分布特征与富营养化研究[J]. 中国环境监测, 29(4): 43-49. |
| WU Y, GUO Y F, CAO X, et al., 2013. Eutrophication and Spatial Distribution of Chlorophyll-a, Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Fu-Nan River, Chengdu City[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 29(4): 43-49. | |
| [26] | 杨芳, 李畅游, 史小红, 等, 2016. 乌梁素海冰封期湖泊冰盖组构特征对污染物分布的影响[J]. 湖泊科学, 28(2): 455-462. |
|
YANG F, LI C Y, SHI X H, et al., 2016. Impact of seasonal ice structure characteristics on ice cover impurity distributions in Lake Ulansuhai[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 28(2): 455-462.
DOI URL |
|
| [27] | 杨文焕, 崔亚楠, 李卫平, 等, 2018. 包头市南海湖冰封期营养盐和叶绿素a时空分布特征研究[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 37(3): 72-77. |
| YANG W H, CUI Y N, LI W P, et al., 2018. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of nutrient and chlorophyll a in the ice-capped period of Lake Nanhai in Baotou City[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 37(3): 72-77. | |
| [28] | 于爱鑫, 2020. 模拟结冰和融冰过程中阿特拉津的迁移规律[D]. 烟台: 烟台大学: 3. |
| YU A X, 2020. Migration law of atrazine during simulated freezing and melting processes[D]. Yantai: Yantai University: 3. | |
| [29] | 于爱鑫, 张岩, 高宁, 等, 2020. 水体结冰过程中物质的迁移规律[J]. 烟台大学学报(自然科学与工程版), 33(3): 365-372. |
| YU A X, ZHANG Y, GAO N, et al., 2020. Migration law of substance in water lcing process[J]. Journal of Yantai University (Natural Science and Engineering Edition), 33(3): 365-372. | |
| [30] | 于玲红, 吕超, 李卫平, 2013. 冰封期乌梁素海冰层中营养盐垂直分布特征分析[J]. 环境工程, 31(S1): 170-174. |
| YU L H, LV C, LI W P, 2013. Analysis of vertical distribution of nutrientsalts in ice of Wuliangsuhai ice closed period[J]. Environmental Engineering, 31(S1): 170-174. | |
| [31] | 袁轶君, 何鹏程, 刘娜娜, 等, 2020. 温度与扰动对鄱阳湖沉积物氮释放的影响[J]. 东华理工大学学报(自然科学版), 43(5): 495-500. |
| YUAN Y J, HE P C, LIU N N, et al., 2020. Effects of Temperature and Disturbance on Nitrogen Release from Sediment of Poyang Lake[J]. Journal of East China University of Technology (Natural Science), 43(5): 495-500. | |
| [32] | 张岩, 2012. 乌梁素海结冰过程中污染物迁移机理及其应用研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学:64. |
| ZHANG Y, 2012. Migration mechanism of pollutants and its application in Ulansuhai Lake in freezing process[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University:64. | |
| [33] | 张岩, 李畅游, 高宁, 等, 2017. 结冰对乌梁素海水体富营养化的影响[J]. 湖泊科学, 29(4): 811-818. |
|
ZHANG Y, LI C Y, GAO N, et al., 2017. Effect of freezing on eutrophication in Lake Ulansuhai[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 29(4): 811-818.
DOI URL |
|
| [34] | 赵旭德, 许大毛, 刘婷, 等, 2018. 青山湖叶绿素a分布及其与水质因子的关联特征[J]. 环境化学, 37(7): 1482-1490. |
| ZHAO X D, XU D M, LIU T, et al., 2018. Spatial distribution of chlorophyll-a and its correlation with and water quality indicators in Qingshan Lake[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 37(7): 1482-1490. | |
| [35] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部, 2020. 2019中国生态环境状况公报[R]. 北京: 中华人民共和国生态环境部:28. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Republic of China, 2020. Communique on China's ecological environment in 2019[R]. Beijing: Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Republic of China: 28. | |
| [36] | 朱广伟, 秦伯强, 张运林, 等, 2018. 2005-2017年北部太湖水体叶绿素a和营养盐变化及影响因素[J]. 湖泊科学, 30(2): 279-295. |
|
ZHU G W, QIN B Q, ZHANG Y L, et al., 2018. Variation and driving factors of nutrients and chlorophyll-a concentrations in northern region of Lake Taihu, China, 2005-2017 [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 30(2): 279-295.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 王家一, 孙亭亭, 沙润钰, 谌婷红, 邢冉, 秦伯强, 施文卿. 富营养化湖泊蓝藻打捞减污降碳效果模拟研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1108-1114. |
| [2] | 董智今, 张呈春, 展秀丽, 张维福. 宁夏河东沙地生物土壤结皮及其下伏土壤养分的空间分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 910-919. |
| [3] | 黄伟佳, 刘春, 刘岳, 黄斌, 李定强, 袁再健. 南岭山地不同海拔土壤生态化学计量特征及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 80-89. |
| [4] | 魏岚, 黄连喜, 李翔, 王泽煌, 陈伟盛, 黄庆, 黄玉芬, 刘忠珍. 生物炭基质可显著地促进香蕉幼苗生长[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 732-739. |
| [5] | 贺斌, 胡茂川. 广东省各区县农业面源污染负荷估算及特征分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 771-776. |
| [6] | 盛基峰, 李垚, 于美佳, 韩艳英, 叶彦辉. 氮磷添加对高寒草地土壤养分和相关酶活性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2302-2309. |
| [7] | 袁伟皓, 王华, 夏玉宝, 曾一川, 邓燕青, 李媛媛, 张心悦. 基于GAM模型的鄱阳湖叶绿素a与水质因子相关性分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1716-1723. |
| [8] | 李海萍, 李光一, 万华伟, 李利平. 基于矩阵分析法的鸟类与哺乳动物物种丰富度空间差异研究——以新疆为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(7): 1333-1341. |
| [9] | 郝丽虹, 刘桂青, 张世晨, 苗宇萍. 城市加油站场地典型有机污染物空间分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(11): 2175-2184. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
