生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (11): 2189-2197.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.11.010
李亮亮1( ), 代良羽2, 高维常3, 张淑怡1,3, 刘涛泽1,*(
), 代良羽2, 高维常3, 张淑怡1,3, 刘涛泽1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-05-25
出版日期:2022-11-18
发布日期:2022-12-22
通讯作者:
*刘涛泽(1981年生),男,副研究员,博士,研究方向为生物环境地球化学。E-mail: liutaoze@foxmail.com作者简介:李亮亮(1994年生),男,硕士研究生,从事农业生态研究。E-mail: 791904591@qq.com
基金资助:
LI Liangliang1( ), DAI Liangyu2, GAO Weichang3, ZHANG Shuyi1,3, LIU Taoze1,*(
), DAI Liangyu2, GAO Weichang3, ZHANG Shuyi1,3, LIU Taoze1,*( )
)
Received:2022-05-25
Online:2022-11-18
Published:2022-12-22
摘要:
地膜作为重要的农业生产资料被广泛应用于农作物种植,而且覆膜种植面积正迅速增加。地膜是一种人工合成的高分子聚合物,在自然条件下短期内很难降解,不合理的应用和不健全的回收体系导致中国农田生态环境出现严重的白色污染问题。地膜在土壤中的残留不仅改变了农田土壤的理化性状,而且对农作物的生长、农耕操作和生态环境都会产生不利的影响。贵州地处长江和珠江上游,是中国重要的生态屏障之一。当前地膜残留的增加正带来流域内严重的塑料污染,而针对该区域地膜残留现状和赋存特征方面的研究尚且有限。通过问卷调查与取样监测相结合的方法对贵州省主要覆膜作物(烤烟、蔬菜和辣椒)的地膜使用和残留情况等进行调查和采样分析,并探讨区域内土壤残膜赋存特征及影响因素。对不同覆膜年限(1-20 a)的29个农田样地的分析结果表明,土壤中残膜含量分布在8.18-235.39 kg·hm-2,平均值为70.84 kg·hm-2。随着覆膜年限增加,地膜平均残留含量和数量整体表现为先增加后减少的趋势。与覆膜1-5 a相比,6-10 a和11-15 a平均残膜含量增加了87.69%和146.59%,平均残膜数量增加了69.30%和235.10%;而当覆膜16-20 a,平均残膜含量和数量均低于11-15 a。残膜破碎度值也随覆膜年限增加呈现逐年减小趋势,表明覆膜时间越久,残膜破碎程度越大。另外,土壤质地和覆膜作物种类也是影响地膜残留量的重要因素。不同土壤类型平均残膜含量表现为壤土>黏土>砂土;在相同覆膜年限的情况下,蔬菜种植区平均残膜量最大,其次是烤烟,辣椒平均残膜量最小。该研究将为加强地膜残留污染监管和防控提供科学的依据和技术支持。
中图分类号:
李亮亮, 代良羽, 高维常, 张淑怡, 刘涛泽. 贵州省典型覆膜耕地残膜赋存特征及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2189-2197.
LI Liangliang, DAI Liangyu, GAO Weichang, ZHANG Shuyi, LIU Taoze. The Occurrence Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Residual Mulching Film of Typical Farmland with Plastic Film in Guizhou Province[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(11): 2189-2197.
| 地区 Regions | 样地 Sampling sites | 覆膜年限 Years of film mulching/a | 作物种类 Corp type | 地膜厚度 Film thickness/ mm | 地膜宽度 Film width/ mm | 覆膜量 Input of plastic film/ (kg·hm-2) | 土壤类型 Soil texture | 回收方式 Recovery style |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 开阳县 Kaiyang County | S1 | 6-10 | 烤烟 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 |
| S2 | 1-5 | 烤烟 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| S3 | 6-10 | 辣椒 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| 播州区 Bozhou County | S4 | 6-10 | 辣椒 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 |
| S5 | 6-10 | 烤烟 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 粘土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| 盘州市 Panzhou County | S6 | 1-5 | 蔬菜 | 0.01 | 1200 | 76 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 |
| S7 | 16-20 | 蔬菜 | 0.01 | 900 | 73 | 粘土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| S8 | 6-10 | 烤烟 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 粘土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| 平坝县 Pingba County | S9 | 11-15 | 蔬菜 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 粘土 | 人工捡拾 |
| S10 | 11-15 | 蔬菜 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 粘土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| 石阡县 Shiqian County | S11 | 6-10 | 烤烟 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 |
| S12 | 1-5 | 烤烟 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 砂土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| 威宁县 Weining county | S13 | 16-20 | 蔬菜 | 0.01 | 2000 | 78 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 |
| S14 | 6-10 | 蔬菜 | 0.01 | 2000 | 78 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| S15 | 11-15 | 烤烟 | 0.01 | 900 | 73 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| S16 | 11-15 | 烤烟 | 0.01 | 900 | 73 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| 七星关区 Qixing guan County | S17 | 6-10 | 烤烟 | 0.01 | 2000 | 78 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 |
| S18 | 1-5 | 烤烟 | 0.01 | 2000 | 78 | 粘土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| S19 | 1-5 | 蔬菜 | 0.01 | 2000 | 78 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| 黄平县 Huangping County | S20 | 1-5 | 蔬菜 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 |
| S21 | 6-10 | 烤烟 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| S22 | 6-10 | 烤烟 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| 贵定县 Guiding County | S23 | 1-5 | 辣椒 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 |
| S24 | 6-10 | 辣椒 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| S25 | 6-10 | 辣椒 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 砂土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| 兴义市 Xingyi County | S26 | 16-20 | 烤烟 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 |
| S27 | 16-20 | 烤烟 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| S28 | 11-15 | 蔬菜 | 0.01 | 1200 | 76 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| S29 | 11-15 | 蔬菜 | 0.01 | 1200 | 76 | 砂土 | 人工捡拾 |
表1 地膜使用及回收情况(2021年)
Table 1 Input and recovery of plastic film (2021)
| 地区 Regions | 样地 Sampling sites | 覆膜年限 Years of film mulching/a | 作物种类 Corp type | 地膜厚度 Film thickness/ mm | 地膜宽度 Film width/ mm | 覆膜量 Input of plastic film/ (kg·hm-2) | 土壤类型 Soil texture | 回收方式 Recovery style |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 开阳县 Kaiyang County | S1 | 6-10 | 烤烟 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 |
| S2 | 1-5 | 烤烟 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| S3 | 6-10 | 辣椒 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| 播州区 Bozhou County | S4 | 6-10 | 辣椒 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 |
| S5 | 6-10 | 烤烟 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 粘土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| 盘州市 Panzhou County | S6 | 1-5 | 蔬菜 | 0.01 | 1200 | 76 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 |
| S7 | 16-20 | 蔬菜 | 0.01 | 900 | 73 | 粘土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| S8 | 6-10 | 烤烟 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 粘土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| 平坝县 Pingba County | S9 | 11-15 | 蔬菜 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 粘土 | 人工捡拾 |
| S10 | 11-15 | 蔬菜 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 粘土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| 石阡县 Shiqian County | S11 | 6-10 | 烤烟 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 |
| S12 | 1-5 | 烤烟 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 砂土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| 威宁县 Weining county | S13 | 16-20 | 蔬菜 | 0.01 | 2000 | 78 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 |
| S14 | 6-10 | 蔬菜 | 0.01 | 2000 | 78 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| S15 | 11-15 | 烤烟 | 0.01 | 900 | 73 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| S16 | 11-15 | 烤烟 | 0.01 | 900 | 73 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| 七星关区 Qixing guan County | S17 | 6-10 | 烤烟 | 0.01 | 2000 | 78 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 |
| S18 | 1-5 | 烤烟 | 0.01 | 2000 | 78 | 粘土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| S19 | 1-5 | 蔬菜 | 0.01 | 2000 | 78 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| 黄平县 Huangping County | S20 | 1-5 | 蔬菜 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 |
| S21 | 6-10 | 烤烟 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| S22 | 6-10 | 烤烟 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| 贵定县 Guiding County | S23 | 1-5 | 辣椒 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 |
| S24 | 6-10 | 辣椒 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| S25 | 6-10 | 辣椒 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 砂土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| 兴义市 Xingyi County | S26 | 16-20 | 烤烟 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 |
| S27 | 16-20 | 烤烟 | 0.01 | 1000 | 75 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| S28 | 11-15 | 蔬菜 | 0.01 | 1200 | 76 | 壤土 | 人工捡拾 | |
| S29 | 11-15 | 蔬菜 | 0.01 | 1200 | 76 | 砂土 | 人工捡拾 |
| 项目 Items | 地膜残留量 Residue film amount/ (kg·hm-2) | 残膜数量 Quantity of residual film/ (104 piece·hm-2) | 残膜破碎度 Fragmentation index of residual film/(mg·piece-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 最大值 Maximum value | 235.39 | 582.00 | 165.24 |
| 最小值 Minimum value | 8.18 | 10.00 | 16.22 |
| 平均数 Average | 70.84 | 164.52 | 66.84 |
| 变异系数 Coefficient of variation | 84.53% | 101.93% | 59.90% |
表2 土壤中地膜残留分布情况
Table 2 Distribution of plastic film residue in soil
| 项目 Items | 地膜残留量 Residue film amount/ (kg·hm-2) | 残膜数量 Quantity of residual film/ (104 piece·hm-2) | 残膜破碎度 Fragmentation index of residual film/(mg·piece-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 最大值 Maximum value | 235.39 | 582.00 | 165.24 |
| 最小值 Minimum value | 8.18 | 10.00 | 16.22 |
| 平均数 Average | 70.84 | 164.52 | 66.84 |
| 变异系数 Coefficient of variation | 84.53% | 101.93% | 59.90% |
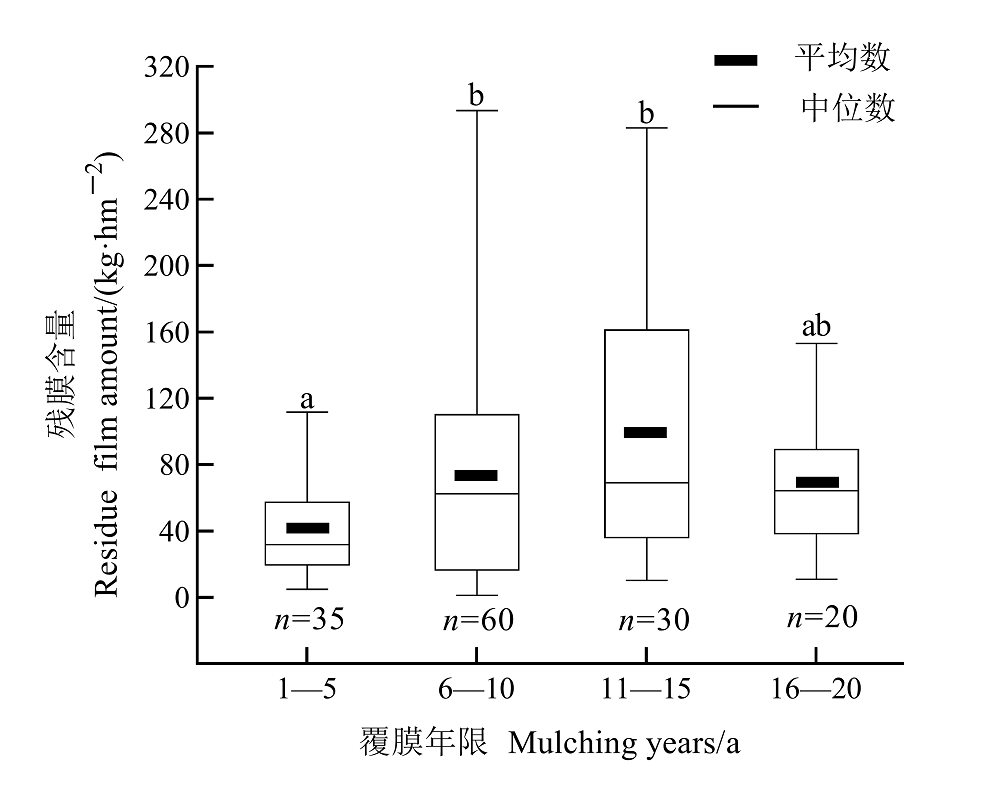
图5 不同覆膜年限地膜残留量 不同小写字母表示不同覆膜年限之间差异显著(P<0.05)。下同
Figure 5 The residual film amount of different mulching years Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different mulching years (P<0.05). The same below
| 残膜 大小 Film length/ cm | 覆膜年限 Years of film mulching/a | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-5 | 6-10 | 11-15 | 16-20 | ||||||||
| 残膜数量 Quantity of residual film/ (104 piece·hm-2) | 比例Percentage/ % | 残膜数量 Quantity of residual film/(104 piece·hm-2) | 比例Percentage/ % | 残膜数量 Quantity of residual film/(104 piece·hm-2) | 比例Percentage/ % | 残膜数量 Quantity of residual film/ (104 piece·hm-2) | 比例Percentage/ % | ||||
| <5 | 27.61±7.39a | 34.99 | 50.87±7.58a | 36.14 | 114.73±19.14a | 43.20 | 115.35±24.01a | 45.12 | |||
| 5-10 | 28.05±6.64a | 35.55 | 50.72±6.03a | 36.03 | 100.13±17.21a | 37.71 | 100.65±21.34a | 39.37 | |||
| 10-15 | 11.85±2.95a | 15.02 | 22.25±3.20b | 14.87 | 33.20±5.16b | 12.50 | 23.25±3.60b | 9.09 | |||
| >15 | 11.40±3.02a | 14.44 | 18.24±2.75b | 12.96 | 17.50±2.32b | 6.59 | 16.41±2.14b | 6.42 | |||
表3 不同覆膜年限残膜大小分布特征
Table 3 The distribution characteristics of residual film size in different mulching years
| 残膜 大小 Film length/ cm | 覆膜年限 Years of film mulching/a | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-5 | 6-10 | 11-15 | 16-20 | ||||||||
| 残膜数量 Quantity of residual film/ (104 piece·hm-2) | 比例Percentage/ % | 残膜数量 Quantity of residual film/(104 piece·hm-2) | 比例Percentage/ % | 残膜数量 Quantity of residual film/(104 piece·hm-2) | 比例Percentage/ % | 残膜数量 Quantity of residual film/ (104 piece·hm-2) | 比例Percentage/ % | ||||
| <5 | 27.61±7.39a | 34.99 | 50.87±7.58a | 36.14 | 114.73±19.14a | 43.20 | 115.35±24.01a | 45.12 | |||
| 5-10 | 28.05±6.64a | 35.55 | 50.72±6.03a | 36.03 | 100.13±17.21a | 37.71 | 100.65±21.34a | 39.37 | |||
| 10-15 | 11.85±2.95a | 15.02 | 22.25±3.20b | 14.87 | 33.20±5.16b | 12.50 | 23.25±3.60b | 9.09 | |||
| >15 | 11.40±3.02a | 14.44 | 18.24±2.75b | 12.96 | 17.50±2.32b | 6.59 | 16.41±2.14b | 6.42 | |||
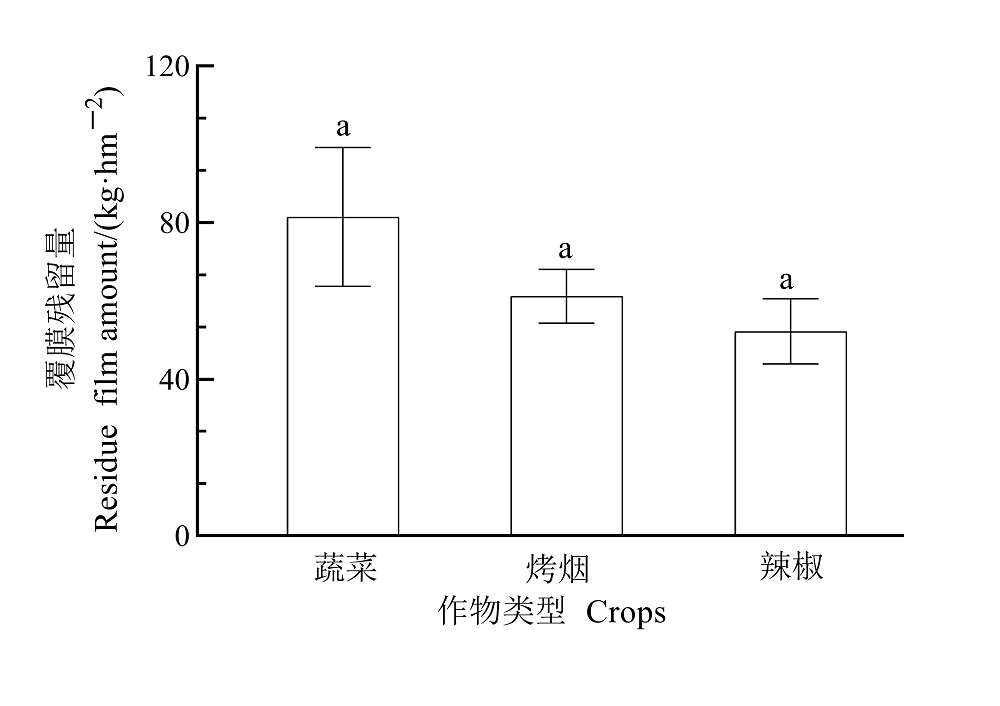
图8 不同作物类型覆膜残留量 小字母相同表示不同作物之间差异不显著(P>0.05)
Figure 8 The residual film amount of different crops The same letter indicates that the difference between different crops is not significant (P>0.05)
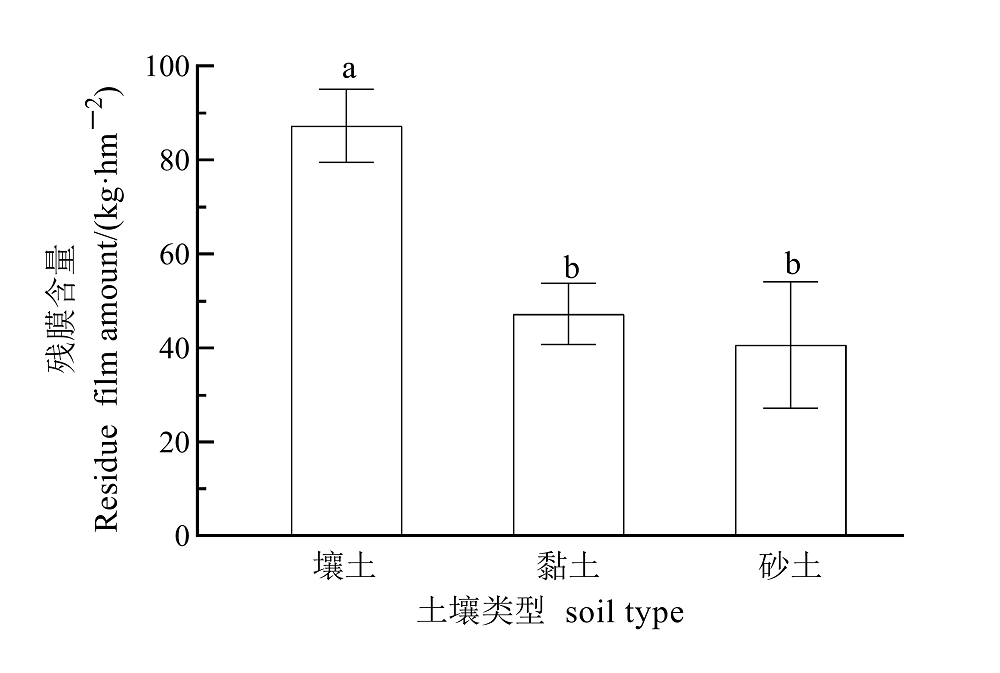
图9 不同土壤类型中残膜的含量 不同小写字母表示不同土壤类型之间差异显著(P<0.05)
Figure 9 The film residual amount of different soil type Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different soil type (P<0.05)
| 样地所在地区 The regions of Sampling sites | 样地个数 Number of plots | 覆膜年限 Years of film mulching/a | 作物种类 Crop species | 地膜残留量分布范围 Distribution range of residual film/(kg·hm-2) | 平均残留量 Average residual film/(kg·hm-2) | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 贵州省 Guizhou Province | 29 | 1-20 | 蔬菜、烤烟、辣椒 | 8.18-235.39 | 70.84 | 本研究 |
| 南方平原 South our country plain area | 67 | 1-35 | 草莓、花生、棉花、蔬菜 | 1.79-72.15 | 14.28 | 2013 |
| 四川攀西 Pan xi Area, Sichuan Province | 12 | 1-15以上 | 烟草、玉米、蔬菜 | 5.61-30.44 | 16.27 | 2012 |
| 河南省 Henan Province | 15 | 1-20以上 | 花生、棉花 | 6.80-37.30 | 20.4 | 2016 |
| 山东省 Shandong Province | 10 | 1-18 | 花生、棉花 | 5.33-46.99 | 23.91 | 2018 |
| 青岛市 Qingdao | 27 | 8-32 | 马铃薯、花生、大蒜、 生姜、西红柿 | 10.7-69.3 | 32.3 | 2017 |
| 内蒙古 Inner Mongolia | 125 | 1-30以上 | 玉米、向日葵 | 18.20-418.60 | 130.42 | 2022 |
| 新疆 Xinjiang | 20 | 15以上 | 棉花 | 116.64-179.88 | 134.09 | 2016 |
表4 不同地区地膜残留量
Table 4 Film residue in different regions
| 样地所在地区 The regions of Sampling sites | 样地个数 Number of plots | 覆膜年限 Years of film mulching/a | 作物种类 Crop species | 地膜残留量分布范围 Distribution range of residual film/(kg·hm-2) | 平均残留量 Average residual film/(kg·hm-2) | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 贵州省 Guizhou Province | 29 | 1-20 | 蔬菜、烤烟、辣椒 | 8.18-235.39 | 70.84 | 本研究 |
| 南方平原 South our country plain area | 67 | 1-35 | 草莓、花生、棉花、蔬菜 | 1.79-72.15 | 14.28 | 2013 |
| 四川攀西 Pan xi Area, Sichuan Province | 12 | 1-15以上 | 烟草、玉米、蔬菜 | 5.61-30.44 | 16.27 | 2012 |
| 河南省 Henan Province | 15 | 1-20以上 | 花生、棉花 | 6.80-37.30 | 20.4 | 2016 |
| 山东省 Shandong Province | 10 | 1-18 | 花生、棉花 | 5.33-46.99 | 23.91 | 2018 |
| 青岛市 Qingdao | 27 | 8-32 | 马铃薯、花生、大蒜、 生姜、西红柿 | 10.7-69.3 | 32.3 | 2017 |
| 内蒙古 Inner Mongolia | 125 | 1-30以上 | 玉米、向日葵 | 18.20-418.60 | 130.42 | 2022 |
| 新疆 Xinjiang | 20 | 15以上 | 棉花 | 116.64-179.88 | 134.09 | 2016 |
| [1] |
HE L Z, GIELEN G, BOLAN N S, et al., 2015. Contamination and remediation of phthalic acid esters in agricultural soils in China: A review[J]. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 35(2): 519-534.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
WANG D, XI Y, SHI X Y, et al., 2021. Effect of plastic film mulching and film residues on phthalate esters concentrations in soil and plants, and its risk assessment[J]. Environmental Pollution, 286: 117546.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
WANG W F, GE J, YU X Y, et al., 2020. Environmental fate and impacts of microplastics in soil ecosystems: Progress and perspective[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 708: 134841.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
包明哲, 红梅, 赵巴音那木拉, 等, 2022. 内蒙古河套灌区农田地膜残留量分布特征及影响因素[J/OL]. 农业资源与环境学报, [2022-10-15]. https://doi.org/10.13254/j.jare.2021.0596.
DOI |
|
BAO M Z, HONG M, ZHAO B, et al., 2022. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors concerning residual quantity of agricultural mulch film in Hetao irrigation area, Inner Mongolia[J/OL]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, [2022-10-15]. https://doi.org/10.13254/j.jare.2021.0596.
DOI |
|
| [5] | 蔡金洲, 张富林, 范先鹏, 等, 2013. 南方平原地区地膜使用与残留现状调查分析[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 30(5): 23-30. |
| CAI J Z, ZHANG F L, FAN X P, et al., 2013. The Status Quo of Film Application and Residue in the Southern Plains of China[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 30(5): 23-30. | |
| [6] | 丁凡, 吕军, 刘勤, 等, 2021. 我国棉花主产区变化与地膜残留污染研究[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 40(6): 60-67. |
| DING F, LÜ J, LIU Q, et al., 2021. Migration of cotton planting regions and residual pollution of mulch film in China[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 40(6): 60-67. | |
| [7] | 董合干, 王栋, 王迎涛, 等, 2013. 新疆石河子地区棉田地膜残留的时空分布特征[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 27(9): 182-186. |
| DONG H G, WANG D, WANG Y T, et al., 2013. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of mulch residues in cotton field in Shihezi, Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 27(9): 182-186. | |
| [8] | 杜利, 李援农, 陈朋朋, 等, 2018. 不同残膜量对土壤环境及玉米生长发育的影响[J]. 节水灌溉, [2022-10-15]. http://www.irrigate.com.cn/jsgg/CN/Y2018/V0/I7/4. |
| DU L, LI Y N, CHEN P P, et al., 2018. Effects of Different Residual Film on the Growth and Soil Environment of Maize[J]. Water Saving Irrigation, [2022-10-15]. http://www.irrigate.com.cn/jsgg/CN/Y2018/V0/I7/4. | |
| [9] | 杜泽玉, 孙多鑫, 杨荣, 等, 2020. 张掖绿洲农田地膜残留量分布特征及影响因素[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 39(12): 2789-2797. |
| DU Z Y, SUN D X, YANG R, et al., 2020. Spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of plastic film residue in Zhangye Oasis[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 39(12): 2789-2797. | |
| [10] | 贵州统计局, 2021. 贵州统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社. |
| Guizhou Bureau of Statistics, 2021. Guizhou statistical yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press. | |
| [11] | 国家统计局, 2021. 中国统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社. |
| National Bureau of Statistics of China, 2021. China statistical yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press. | |
| [12] | 郭战玲, 张薪, 寇长林, 等, 2016. 河南省典型覆膜作物地膜残留状况及其影响因素研究[J]. 河南农业科学, 45(12): 58-61, 71. |
| GUO Z L, ZHANG X, KOU C L, et al., 2016. Status and influencing factors of residual mulching film of typical crops mulched with plastic film in Henan province[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 45(12): 58-61, 71. | |
| [13] | 贺怀杰, 王振华, 郑旭荣, 等, 2019. 典型绿洲区长期膜下滴灌棉田残膜分布现状研究[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 38(2): 63-69. |
| HE H J, WANG Z H, ZHENG X R, et al., 2019. Distribution of size and quantity of film residuals in cotton fields under film-mulched drip irrigation in oasis region[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 38(2): 63-69. | |
| [14] | 黑龙江省质量技术监督局, 2017. 农田地膜残留调查与评价技术规程: DB23/T 2033-2017[S]. |
| Heilongjiang Provincial Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision, 2017. Technical Specification for Investigation and Evaluation of Farmland Film Residue: DB23/T 2033-2017[S]. | |
| [15] | 黄晶晶, 庞良玉, 罗春燕, 等, 2012. 四川攀西地区地膜残留量及影响因素[J]. 西南农业学报, 25(6): 2203-2206. |
| HUANG J J, PANG L Y, LUO C Y, et al., 2012. Amount of plastic film residues and influence factors in Panxi district of Sichuan province[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 25(6): 2203-2206. | |
| [16] | 胡会军, 张秀芝, 李强, 等, 2013. 吉林省主要覆膜作物地膜残留情况调查[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 30(6): 50-52. |
| HU H J, ZHANG X Z, LI Q, et al., 2013. Mulch plastic film residue investigation of the main crops in Jilin province, China[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 30(6): 50-52. | |
| [17] | 刘锐涵, 王艳华, 赵建, 等, 2022. 土壤微塑料污染与生态健康风险[J]. 环境化学, 41(10): 1-17. |
| LIU R H, WANG Y H, ZHAO J, et al., 2022. Microplastics pollution in soil and the potential ecological health risks[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 41(10): 1-17. | |
| [18] | 李妍超, 李海萍, 王永显, 等, 2017. 青岛市农田土壤残膜污染现状及其治理对策[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 34(3): 226-233. |
| LI Y C, LI H P, WANG Y X, et al., 2017. Pollution status and control countermeasures of polyethylene mulch film residue in farmland soils of Qingdao city, China[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 34(3): 226-233. | |
| [19] | 李珍, 孙丽娜, 范琪, 等, 2022. 土壤中聚乙烯和聚苯乙烯微塑料对多环芳烃的吸附行为和机理分析[J/OL]. 环境科学学报, [2022-10-15]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1843.X.20220617.2322.002.html. |
| LI Z, SUN L N, FAN Q, et al., 2022. Adsorption behavior and mechanism analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by polyethylene and polystyrene microplastics in the soil[J/OL]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, [2022-10-15]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1843.X.20220617.2322.002.html. | |
| [20] | 马辉, 梅旭荣, 严昌荣, 等, 2008. 华北典型农区棉田土壤中地膜残留特点研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 27(2): 570-573. |
| MA H, MEI X R, YAN C R, et al., 2008. The residue of mulching plastic film of cotton field in north China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 27(2): 570-573. | |
| [21] | 马彦, 杨虎德, 2015. 甘肃省农田地膜污染及防控措施调查[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 31(4): 478-483. |
| MA Y, YANG H D, 2015. Investigation on pollution caused by mulching plastic film in Gansu province and the countermeasures[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 31(4): 478-483. | |
| [22] | 牛瑞坤, 王旭峰, 胡灿, 等, 2016. 新疆阿克苏地区棉田残膜污染现状分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 53(2): 283-288. |
| NIU R K, WANG X F, HU C, et al., 2016. Analysis of the current situations of plastic films residue pollution of cotton field in Xinjiang Aksu area[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 53(2): 283-288. | |
| [23] | 王学霞, 宋宁宁, 薛颖昊, 等, 2021. 山东省花生种植区耕层土壤残膜赋存特征[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 40(8): 1729-1737. |
| WANG X X, SONG N N, XUE Y H, et al., 2021. Occurrence characteristics of residual film in cultivated soil of peanut planting area in Shandong province, China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 40(8): 1729-1737. | |
| [24] | 王永宁, 张雷, 傅建伟, 等, 2022. 内蒙古农田地膜残留污染成因分析及对策建议[J]. 天津农业科学, 28(3): 79-84. |
| WANG Y N, ZHANG L, FU J W, et al., 2022. Cause analysis and countermeasure suggestion of farmland mulch film residual pollution in Inner Mongolia[J]. Tianjin Agricultural Sciences, 28(3): 79-84. | |
| [25] | 向午燕, 冯晨, 冯良山, 等, 2021. PBAT全生物降解地膜在辽西半干旱区的降解及残留特性[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 26(12): 45-53. |
| XIANG W Y, FENG C, FENG L S, et al., 2021. Degradation and residual characteristics of PBAT biodegradable plastic film in semi-arid area in western Liaoning[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 26(12): 45-53. | |
| [26] | 徐钰, 江丽华, 石璟, 等, 2018. 山东省典型覆膜作物地膜残留情况解析[J]. 山东农业科学, 50(8): 91-95, 99. |
| XU Y, JIANG L H, SHI J, et al., 2018. Analysis on film residual status of typical mulching crops in Shandong province[J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 50(8): 91-95, 99. | |
| [27] | 严昌荣, 刘恩科, 舒帆, 等, 2014. 我国地膜覆盖和残留污染特点与防控技术[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 31(2): 95-102. |
| YAN C R, LIU E K, SHU F, et al., 2014. Review of agricultural plastic mulching and its residual pollution and prevention measures in China[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 31(2): 95-102. | |
| [28] | 严昌荣, 何文清, 刘爽, 等, 2015. 中国地膜覆盖及残留污染防控[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| YAN C R, HE W Q, LIU S, et al., 2015. Application of mulch films and prevention of its residual pollution in China[M]. Beijing: Science Press. | |
| [29] | 尹少媛, 赵宝平, 米俊珍, 等, 2022. 内蒙古农田耕层土壤地膜残留现状及发展趋势[J/OL]. 农业环境科学学报, 41(9):1985-1992. |
| YIN S Y, ZHAO B P, MI J Z, et al., 2022. Current scenario and future trends of plastic film residue in farmland topsoil in Inner Mongolia, China[J/OL]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 41(9): 1985-1992. | |
| [30] | 曾招兵, 姚建武, 李盟军, 等, 2014. 广东省典型地区地膜残留现状分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 30(32): 189-193. |
| ZENG Z B, YAO J W, LI M J, et al., 2014. The status quo of mulching film residues in representative regions of Guangdong province[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 30(32): 189-193. | |
| [31] | 张丹, 胡万里, 刘宏斌, 等, 2016. 华北地区地膜残留及典型覆膜作物残膜系数[J]. 农业工程学报, 32(3): 1-5. |
| ZHANG D, HU W L, LIU H B, et al., 2016. Characteristics of residual mulching film and residual coefficient of typical crops in north China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 32(3): 1-5. | |
| [32] | 中国国家标准化管理委员会, 2011. 农田地膜残留量限值及测定: GB/T 25413-2010[S]. 北京: 中国标准质检出版社. |
| Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China, 2011. Limit and testmethod for residual quantity of agricultural mulch film: GB/T 2541-2010[S]. Beijing: China Standard Quality Inspection Publishing House. | |
| [33] | 张丹, 刘宏斌, 马忠明, 等, 2017. 残膜对农田土壤养分含量及微生物特征的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 50(2): 310-319. |
| ZHANG D, LIU H B, MA Z M, et al., 2017. Effects of residual film on soil nutrient content and microbial characteristics in farmland[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 50(2): 310-319. | |
| [34] | 邹小阳, 牛文全, 刘晶晶, 等, 2017. 残膜对土壤和作物的潜在风险研究进展[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 36(7): 47-54. |
| ZOU X Y, NIU W Q, LIU J J, et al., 2017. Potential risks of plastic film residuals on soils and crops: A review[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 36(7): 47-54. |
| [1] | 杜丹丹, 高瑞忠, 房丽晶, 谢龙梅. 旱区盐湖盆地土壤重金属空间变异及对土壤理化因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1123-1132. |
| [2] | 李传福, 朱桃川, 明玉飞, 杨宇轩, 高舒, 董智, 李永强, 焦树英. 有机肥与脱硫石膏对黄河三角洲盐碱地土壤团聚体及其有机碳组分的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 878-888. |
| [3] | 王超, 杨倩楠, 张池, 刘同旭, 张晓龙, 陈静, 刘科学. 丹霞山不同土地利用方式土壤磷组分特征及其有效性[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 889-897. |
| [4] | 陈俊芳, 吴宪, 刘啸林, 刘娟, 杨佳绒, 刘宇. 不同土壤水分下元素化学计量对微生物多样性的塑造特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 898-909. |
| [5] | 董智今, 张呈春, 展秀丽, 张维福. 宁夏河东沙地生物土壤结皮及其下伏土壤养分的空间分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 910-919. |
| [6] | 周沁苑, 董全民, 王芳草, 刘玉祯, 冯斌, 杨晓霞, 俞旸, 张春平, 曹铨, 刘文亭. 放牧方式对高寒草地瑞香狼毒根际土壤团聚体及有机碳特征的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 660-667. |
| [7] | 潘昱伶, 璩向宁, 李琴, 王磊, 王筱平, 谭鹏, 崔庚, 安雨, 佟守正. 黄河宁夏段典型滩涂湿地土壤理化因子空间分布特征及其对微地形的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 668-677. |
| [8] | 赵维彬, 唐丽, 王松, 刘玲玲, 王树凤, 肖江, 陈光才. 两种生物炭对滨海盐碱土的改良效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 678-686. |
| [9] | 李建辉, 党争, 陈琳. 黄河几字弯都市圈PM2.5时空特征及影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 697-705. |
| [10] | 冯树娜, 吕家珑, 何海龙. KI淋洗对黄绵土汞污染的去除效果及土壤理化性状的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 776-783. |
| [11] | 陈敏毅, 朱航海, 佘伟铎, 尹光彩, 黄祖照, 杨巧玲. 珠三角某遗留造船厂场地土壤重金属人体健康风险评估及源解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 794-804. |
| [12] | 张林, 齐实, 周飘, 伍冰晨, 张岱, 张岩. 北京山区针阔混交林地土壤有机碳含量的影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 450-458. |
| [13] | 秦浩, 李蒙爱, 高劲, 陈凯龙, 张殷波, 张峰. 芦芽山不同海拔灌丛土壤细菌群落组成和多样性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 459-468. |
| [14] | 何艳虎, 龚镇杰, 吴海彬, 蔡宴朋, 杨志峰, 陈晓宏. 粤港澳大湾区城市生态效率时空演变及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 469-480. |
| [15] | 唐海明, 石丽红, 文丽, 程凯凯, 李超, 龙泽东, 肖志武, 李微艳, 郭勇. 长期施肥对双季稻田根际土壤氮素的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 492-499. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
