生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (5): 929-937.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.05.005
张静1,2( ), 杜加强1,*(
), 杜加强1,*( ), 盛芝露1, 张杨成思1, 吴金华1, 刘博1
), 盛芝露1, 张杨成思1, 吴金华1, 刘博1
收稿日期:2020-11-20
出版日期:2021-05-18
发布日期:2021-08-06
通讯作者:
* 杜加强,男,研究员,研究方向为生态遥感、生态模拟、生态规划、生态恢复等。E-mail:dujq@craes.org.cn作者简介:张静(1997年生),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为生态遥感。E-mail:zhj19@lzu.eud.cn
基金资助:
ZHANG Jing1,2( ), DU Jiaqiang1,*(
), DU Jiaqiang1,*( ), SHENG Zhilu1, ZHANG Yangchengsi1, WU Jinhua1, LIU Bo1
), SHENG Zhilu1, ZHANG Yangchengsi1, WU Jinhua1, LIU Bo1
Received:2020-11-20
Online:2021-05-18
Published:2021-08-06
摘要:
在全球变化的背景下,刻画植被动态、定量分析气候和人类活动对植被变化的影响对于改善生态系统结构和功能具有重要意义。基于GIMMS-NDVI3g数据、结合土地利用数据和气象数据,采用趋势分析、残差趋势等方法,多尺度、多时段、多类型研究1982—2015年黄河流域植被动态变化,并定量分析气候变化和人类活动对NDVI变化的贡献。结果表明,(1)1982—2015年间,生长季、春季、夏季和秋季NDVI均显著增加;植被明显改善地区主要分布在黄河中下游,而明显退化区域则主要分布在西南部。基于嵌套数据分析发现,随时间序列长度的增加,NDVI增加区域显著扩大。不同土地覆盖类型NDVI的增长速度不同,耕地和林地的增长速度大于其他土地覆盖类型。(2)黄河流域NDVI与气温的相关性更强,植被与温度/降水量相关性随着时段延长而增强。(3)残差趋势法表明,1982—2015年生长季人类活动对黄河流域植被变化的平均贡献率为69%,空间分布上呈现西北部、东部高而西南部、中部低的特征;人类活动贡献率在不同季节存在差异,但均大于气候变化;人类活动对不同季节NDVI变化的贡献率空间分布存在区域差异。黄河流域植被覆盖改善与人类活动息息相关,建议应进一步发挥其在黄河流域西南部地区植被恢复中的作用。
中图分类号:
张静, 杜加强, 盛芝露, 张杨成思, 吴金华, 刘博. 1982—2015年黄河流域植被NDVI时空变化及影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(5): 929-937.
ZHANG Jing, DU Jiaqiang, SHENG Zhilu, ZHANG Yangchengsi, WU Jinhua, LIU Bo. Spatio-temporal Changes of Vegetation Cover and Their Influencing Factors in the Yellow River Basin from 1982 to 2015[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(5): 929-937.
| 指标 Index | 时段 Period | P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | P5 | P6 | P7 | P8 | P9 | P10 | P11 | P12 | P13 | P14 | P15 | P16 | P17 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NDVI & Temperature(气温) | 生长季 Growing | 0.43 | 0.38 | 0.36 | 0.38 | 0.38 | 0.38 | 0.41 | 0.40 | 0.42 | 0.43 | 0.50 | 0.51 | 0.51 | 0.50 | 0.55 | 0.56 | 0.56 |
| 春季 Spring | 0.48 | 0.43 | 0.42 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.47 | 0.48 | 0.49 | 0.52 | 0.55 | 0.59 | 0.53 | 0.54 | 0.58 | 0.58 | 0.60 | 0.59 | |
| 夏季 Summer | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.19 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.14 | 0.20 | 0.22 | |
| 秋季 Autumn | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.17 | 0.12 | 0.16 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.21 | 0.26 | 0.30 | 0.29 | 0.22 | 0.25 | 0.28 | 0.29 | |
| NDVI & Precipitation(降水) | 生长季 Growing | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.11 | 0.18 | 0.22 | 0.16 |
| 春季 Spring | 0.30 | 0.31 | 0.32 | 0.36 | 0.37 | 0.33 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.27 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.25 | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.26 | 0.29 | |
| 夏季 Summer | 0.23 | 0.24 | 0.28 | 0.22 | 0.20 | 0.19 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.15 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.17 | 0.27 | 0.23 | 0.09 | |
| 秋季 Autumn | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.14 | 0.09 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.17 | 0.21 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.20 | 0.20 |
表1 17个时段各季节NDVI与气候要素的相关系数(R 2)
Table 1 Correlations between seasonal NDVI and climate factors during seventeen periods
| 指标 Index | 时段 Period | P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | P5 | P6 | P7 | P8 | P9 | P10 | P11 | P12 | P13 | P14 | P15 | P16 | P17 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NDVI & Temperature(气温) | 生长季 Growing | 0.43 | 0.38 | 0.36 | 0.38 | 0.38 | 0.38 | 0.41 | 0.40 | 0.42 | 0.43 | 0.50 | 0.51 | 0.51 | 0.50 | 0.55 | 0.56 | 0.56 |
| 春季 Spring | 0.48 | 0.43 | 0.42 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.47 | 0.48 | 0.49 | 0.52 | 0.55 | 0.59 | 0.53 | 0.54 | 0.58 | 0.58 | 0.60 | 0.59 | |
| 夏季 Summer | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.19 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.14 | 0.20 | 0.22 | |
| 秋季 Autumn | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.17 | 0.12 | 0.16 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.21 | 0.26 | 0.30 | 0.29 | 0.22 | 0.25 | 0.28 | 0.29 | |
| NDVI & Precipitation(降水) | 生长季 Growing | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.11 | 0.18 | 0.22 | 0.16 |
| 春季 Spring | 0.30 | 0.31 | 0.32 | 0.36 | 0.37 | 0.33 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.27 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.25 | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.26 | 0.29 | |
| 夏季 Summer | 0.23 | 0.24 | 0.28 | 0.22 | 0.20 | 0.19 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.15 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.17 | 0.27 | 0.23 | 0.09 | |
| 秋季 Autumn | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.14 | 0.09 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.17 | 0.21 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.20 | 0.20 |
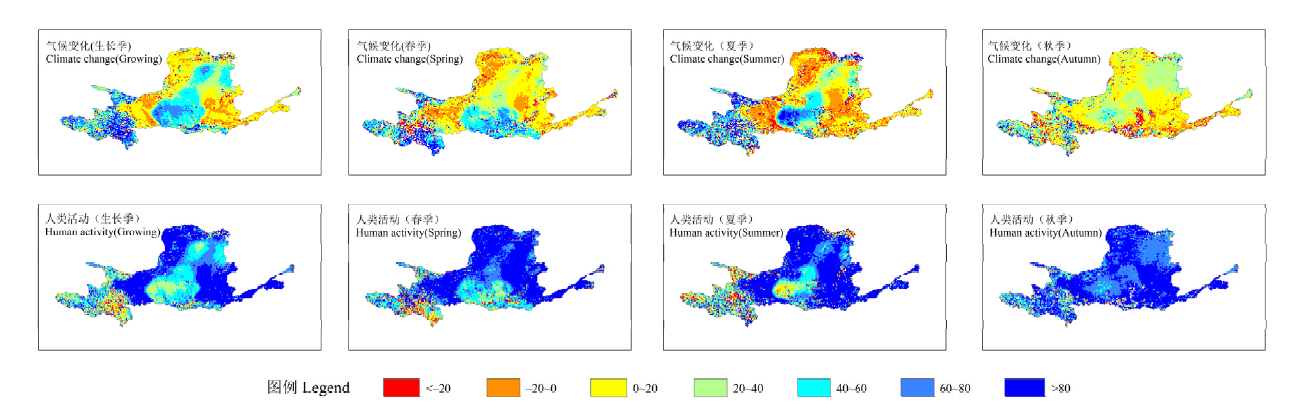
图7 各季节1982—2015年气候变化和人类活动对植被变化的影响空间分布
Fig. 7 Spatial distribution of impacts of climate change and human activities on vegetation change in each season from 1982 to 2015
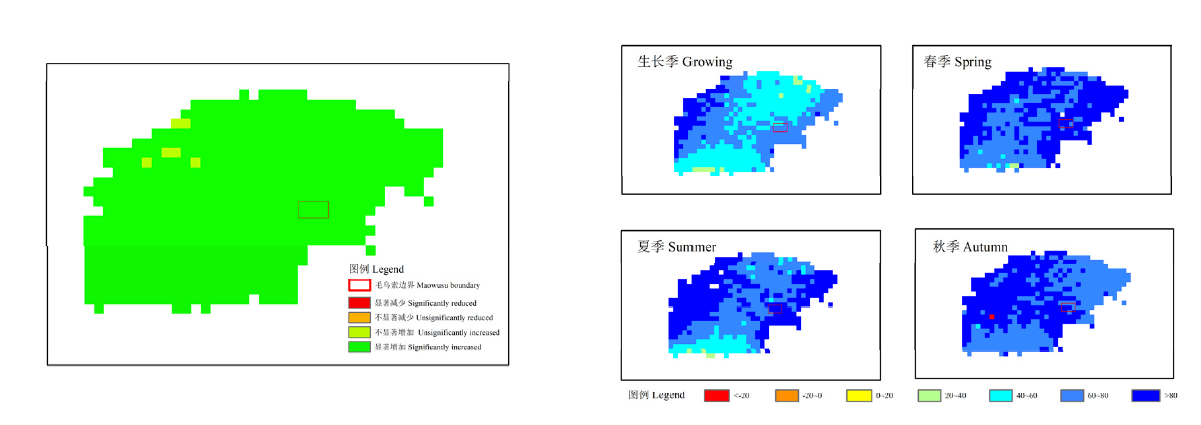
图8 1982—2015年毛乌素生长季NDVI变化趋势和人类活动对其影响分布
Fig. 8 NDVI trends during the growth season and the impact of human activities on vegetation changes in Maowusu from 1982 to 2015
| [1] |
DU J Q, SHU J M, YIN J Q, et al., 2015. Analysis on spatio-temporal trends and drivers in vegetation growth during recent decades in Xinjiang, China[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 38: 216-228.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
DU J Q, FU Q, FANG S F, et al., 2019. Effects of rapid urbanization on vegetation cover in the metropolises of China over the last four decades[J]. Ecological Indicators, 107: 105458.
DOI URL |
| [3] | DU J Q, QUAN Z J, FANG S F, et al., 2019. Spatiotemporal changes in vegetation coverage and its causes in China since the Chinese economic reform[J]. Enviromental Science and Pollution Research, 27(1): 1144-1159. |
| [4] |
EVANS J, GEERKEN R, 2004. Discrimination between climate and human-induced dryland degration[J]. Journal of Arid Environments, 57(4): 535-554.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
HU Y F, DAO R N, HU Y, 2019. Vegetation Change and Driving Factors: Contribution Analysis in the Loess Plateau of China during 2000-2015 [J]. Sustainability, DOI:10.3390/su11051320.
DOI |
| [6] |
JIANG H L, XU X, GUAN M X, et al., 2020. Determining the contributions of climate change and human activities to vegetation dynamics in agro-pastural transitional zone of northern China from 2000 to 2015 [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 718: 134871.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
LI Y, XIE Z X, QIN Y C, et al., 2019. Responses of the Yellow River basin vegetation: climate change[J]. International Journal of Climate Change Strategies and Management, 11(4): 483-498.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
NIE Q, XU J H, LI Z, et al., 2012. Spatial-temporal variations of vegetation cover in Yellow River Basin of China during 1998-2008 [J]. Sciences in Cold and Arid Regions, 4(3): 211-221.
DOI URL |
| [9] | PENG S S, CHEN A P, XU L, et al., 2011. Recent change of vegetation growth trend in China[J]. Enviromental Research Letters, 6(7): 044027. |
| [10] |
PIAO S L, WANG X H, CIAIS P, et al., 2011. Changes in satellite‐derived vegetation growth trend in temperate and boreal Eurasia from 1982 to 2006 [J]. Global Change Biology, 17(10): 3228-3239.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
PAN T, WU S H, LIU Y J, 2015. Relative Contributions of Land Use and Climate Change to Water Supply Variations over Yellow River Source Area in Tibetan Plateau during the Past Three Decades[J]. Plos One, 10(4): e0123793.
DOI URL |
| [12] | SUN Y L, YANG Y L, ZHANG L, et al., 2015. The relative roles of climate variations and human activities in vegetation change in North China[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 87-88: 67-78. |
| [13] |
XIU L N, YAN C Z, LI X S, et al., 2018. Monitoring the response of vegetation dynamics to ecological engineering in the Mu Us Sandy Land of China from 1982 to 2014 [J]. Environmental monitoring and assessmen, 190(9): 543-561.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
ZENG Z Z, CHEN A P, PIAO S L, et al., 2014. Environmental determinants of tropical forest and savanna distribution: A quantitative model evaluation and its implication[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 119(7): 1432-1445.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
ZHANG W, WANG L C, XIANG F F, et al., 2020. Vegetation dynamics and the relations with climate change at multiple time scales in the Yangtze River and Yellow River Basin, China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 110: 105892.
DOI URL |
| [16] | 曹巍, 黄麟, 肖桐, 等, 2019. 人类活动对中国国家级自然保护区生态系统的影响[J]. 生态学报, 39(4): 1338-1350. |
| XAO W, HUANG L, XIAO T, et al., 2019. Effects of human activities on the ecosystems of China’s National Nature Reserves[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(4): 1338-1350. | |
| [17] | 曹艳萍, 庞营军, 贾晓红, 2019. 2001—2016年毛乌素沙地植被的生长状况[J]. 水土保持通报, 39(2): 29-37. |
| CAO Y P, PANG Y J, JIA X H, 2019. Vegetation Growth in Mu Us Sandy Land from 2001 to 2016 [J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 39(2): 29-37. | |
| [18] | 杜加强, 贾尔恒·阿哈提,赵晨曦, 等, 2015. 1982—2012年新疆植被NDVI的动态变化及其对气候变化和人类活动的响应[J]. 应用生态学报, 26(12): 3567-3578. |
| DU J Q, JIAERHENG A, ZHAO C X, et al., 2015. Dynamic changes in vegetation NDVI from 1982 to 2012 and its responses to climate change and human activities in Xinjiang, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 26(12): 3567-3578. | |
| [19] | 贺振, 贺俊平, 2017. 近32年黄河流域植被覆盖时空演化遥感监测[J]. 农业机械学报, 48(2): 179-185. |
| HE Z, HE J P, 2017. Remote Sensing on Spatio-temporal Evolution of Vegetation Cover in the Yellow River Basin during 1982-2013 [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 48(2): 179-185. | |
| [20] | 贺振, 贺俊平, 2012. 基于SPOT-VGT的黄河流域植被覆盖时空演变[J]. 生态环境学报, 21(10): 1655-1659. |
| HE Z, HE J P, 2012. Spatio-temporal variation of vegetation cover based on SPOT-VGT in Yellow River Basin[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 21(10): 1655-1659. | |
| [21] | 马启民, 贾晓鹏, 王海兵, 等, 2019. 气候和人为因素对植被变化影响的评价方法综述[J]. 中国沙漠, 39(6): 48-55. |
| MA Q M, JIA X P, WANG H B, et al., 2019. Recent Advances in Driving Mechanisms of Climate and Anthropogenic Factors on Vegetation Change[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 39(6): 48-55. | |
| [22] | 马丽, 田华征, 康蕾, 2020. 黄河流域矿产资源开发的生态环境影响与空间管控路径[J]. 资源科学, 42(1): 137-149. |
| MA L, TIAN H Z, KANG L, 2020. Eco-environmental impact and spatial control of mineral resources exploitation in the Yellow River Basin[J]. Resources Science, 42(1): 137-149. | |
| [23] | 王伟, 阿里木·赛买提, 吉力力∙阿不都外力,2019. 基于地理探测器模型的中亚NDVI时空变化特征及其驱动因子分析[J]. 国土资源遥感, 31(4): 32-40. |
| WANG W, SAMAT A, ABUDUWAILI J, 2019. Geo-detector based spatio-temporal variation characteristics and driving factors analysis of NDVI in Central Asia[J]. Remote Sensing for Land and Resources, 31(4): 32-40. | |
| [24] | 徐浩杰, 杨太保, 曾彪, 2012. 黄河源区植被生长季NDVI时空特征及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 21(7): 1205-1210. |
| XU H J, YANG T B, ZENG B, 2012. Spatial-temporal variation of growing-season NDVI and its responses to climate change over the source region of the Yellow River[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 21(7): 1205-1210. | |
| [25] | 颜明, 贺莉, 王随继, 等, 2018. 基于NDVI的1982—2012年黄河流域多时间尺度植被覆盖变化[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 16(3): 86-94. |
| YAN M, HE L, WANG S J, et al., 2018. Changing trends of NDVI in the Yellow River basin from1982 to 2012 at different temporal scales[J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 16(3): 86-94. | |
| [26] | 于泉洲, 梁春玲, 刘煜杰, 等, 2015. 基于MODIS的山东省植被覆盖时空变化及其原因分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 24(11): 1799-1807. |
| YU Q Z, LIANG C L, LIU Y J, et al., 2015. Analysis of Vegetation Spatio-temporal Variation and Driving Factors in Shandong Province Based on MODIS[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 24(11): 1799-1807. | |
| [27] | 杨胜天, 刘昌明, 孙睿, 2002. 近20年来黄河流域植被覆盖变化分析[J]. 地理学报, 57(6): 679-684. |
| YANG S T, LIU C M, SUN R, 2002. The Vegetation Cover Last 20 Years in Yellow River Basin[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 57(6): 679-684. | |
| [28] | 袁丽华, 蒋卫国, 申文明, 等, 2013. 2000—2010年黄河流域植被覆盖的时空变化[J]. 生态学报, 33(24): 7798-7806. |
| YUAN L H, JIANG W G, SHEN W M, et al., 2013. The spatio-temporal variations of vegetation cover in the Yellow River Basin from 2000 to 2010 [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33(24): 7798-7806. | |
| [29] | 杨尚武, 2015. 黄河流域不同时间尺度植被覆盖变化及与气候因子的关系[D]. 兰州: 西北师范大学. |
| YANG S W, 2015. The relationship between the different time scales vegetation coverage change and climatic factors in the Yellow River Basin[D]. Lanzhou: Northwest Normal University. | |
| [30] | 于璐, 武志涛, 杜自强, 等, 2020. 气候变化背景下京津风沙源区人类活动对植被影响的量化分析[J]. 应用生态学报, 31(6): 2007-2014. |
| YU L, WU Z T, DU Z Q, et al., 2020. Quantitative analysis of the effects of human activities on vegetation in the Beijing-Tianjin sandstorm source region under the climate change[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 31(6): 2007-2014. | |
| [31] | 易浪, 任志远, 张翀, 等, 2014. 黄土高原植被覆盖变化与气候和人类活动的关系[J]. 资源科学, 36(1): 166-174. |
| YI L, REN Z Y, ZHANG C, et al., 2014. Vegetation Cover, Climate And Human Activities on the Loess Plateau[J]. Resources Science, 36(1): 166-174. | |
| [32] | 张亚玲, 苏惠敏, 张小勇, 2014. 1998—2012年黄河流域植被覆盖变化时空分析[J]. 中国沙漠, 34(2): 597-602. |
| ZHANG Y L, SUN H M, ZHANG X Y, 2014. The Spatial-temporal Changes of Vegetation Restoration in the Yellow River Basin From 1998 to 2012 [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 34(2): 597-602. |
| [1] | 郝蕾, 翟涌光, 戚文超, 兰穹穹. 2001-2020年内蒙古植被碳源/碳汇时空动态及对气候因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 825-834. |
| [2] | 陈俊芳, 吴宪, 刘啸林, 刘娟, 杨佳绒, 刘宇. 不同土壤水分下元素化学计量对微生物多样性的塑造特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 898-909. |
| [3] | 李晖, 李必龙, 葛黎黎, 韩琛惠, 杨倩, 张岳军. 2000-2021年汾河流域植被时空演变特征及地形效应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 439-449. |
| [4] | 张鐥文, 杨冉, 侯文星, 王丽丽, 刘爽, 宋汉扬, 赵文吉, 李令军. 生态补水前后永定河两岸植被覆盖度变化及驱动力分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 264-273. |
| [5] | 贾志峰, 刘鹏程, 刘宇, 吴博博, 陈丹姿, 张向飞. 气候变化和人类活动对松辽流域植被覆盖的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 1-10. |
| [6] | 秦艳培, 徐少君, 田耀武. 黄河流域河南段植被和土壤及其碳密度空间分异研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1745-1753. |
| [7] | 阮惠华, 许剑辉, 张菲菲. 2001—2020年粤港澳大湾区植被和地表温度时空变化研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1510-1520. |
| [8] | 齐月, 张强, 胡淑娟, 蔡迪花, 赵福年, 陈斐, 张凯, 王鹤龄, 王润元. 黄土高原地区气候变化及其对冬小麦生产潜力的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1521-1529. |
| [9] | 邓天乐, 谢立勇, 张凤哲, 赵洪亮, 蒋语童. CO2浓度升高条件下稗草与水稻生长空间竞争关系研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1566-1572. |
| [10] | 苏泳松, 宋松, 陈叶, 叶子强, 钟润菲, 王昭尧. 珠江三角洲人类活动净氮输入时空特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1599-1609. |
| [11] | 卢燕宇, 孙维, 方砚秋, 唐为安, 邓汗青, 何冬燕. 基于种植结构的安徽省气候生产潜力估算及粮食安全气候承载力分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1293-1305. |
| [12] | 李梦华, 韩颖娟, 赵慧, 王云霞. 基于地理探测器的宁夏植被覆盖度时空变化特征及其驱动因子分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1317-1325. |
| [13] | 李登科, 王钊. 气候变化和人类活动对陕西省植被NPP影响的定量分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1071-1079. |
| [14] | 曹晓云, 祝存兄, 陈国茜, 孙树娇, 赵慧芳, 朱文彬, 周秉荣. 2000—2021年柴达木盆地地表绿度变化及地形分异研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1080-1090. |
| [15] | 高思琦, 董国涛, 蒋晓辉, 聂桐, 郭欣伟, 党素珍, 李心宇, 李昊洋. 黄河源植被覆盖度变化及空间分布自然驱动力分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 429-439. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
