Ecology and Environmental Sciences ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (7): 1090-1099.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2025.07.009
• Research Article [Ecology] • Previous Articles Next Articles
CAI Min1( ), ZHOU Li1,*(
), ZHOU Li1,*( ), ZHANG Xu1,2, CUI Naxin1, PANG Si1, ZOU Guoyan1, YUAN Quan1, HUANG Weiwei1, ZHAO Zhiyong3
), ZHANG Xu1,2, CUI Naxin1, PANG Si1, ZOU Guoyan1, YUAN Quan1, HUANG Weiwei1, ZHAO Zhiyong3
Received:2024-11-09
Online:2025-07-18
Published:2025-07-11
蔡敏1( ), 周丽1,*(
), 周丽1,*( ), 张旭1,2, 崔娜欣1, 庞思1, 邹国燕1, 袁泉1, 黄伟伟1, 赵志勇3
), 张旭1,2, 崔娜欣1, 庞思1, 邹国燕1, 袁泉1, 黄伟伟1, 赵志勇3
通讯作者:
*E-mail: 作者简介:蔡敏(1991年生),男,助理研究员,硕士,主要从事水环境治理研究。E-mail: caiminjay@foxmail.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
CAI Min, ZHOU Li, ZHANG Xu, CUI Naxin, PANG Si, ZOU Guoyan, YUAN Quan, HUANG Weiwei, ZHAO Zhiyong. Effects of Plant Extracts on Phytoplankton Community Structure and Function in Aquaculture Water[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2025, 34(7): 1090-1099.
蔡敏, 周丽, 张旭, 崔娜欣, 庞思, 邹国燕, 袁泉, 黄伟伟, 赵志勇. 植物提取液对养殖水体浮游植物群落结构和功能的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(7): 1090-1099.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2025.07.009
| 水体基本理化指标 | 处理 | 时间/d | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | ||
| 水温(WT)/℃ | CK | 24.50±0.36 | 26.37±0.15 | 31.37±0.15 | 29.47±0.06 | 26.47±0.12 |
| T | 24.60±0.50 | 26.53±0.12 | 31.50±0.36 | 29.30±0.35 | 26.27±0.15 | |
| pH | CK | 8.42±0.44 | 7.06±0.12 | 7.72±0.12 | 7.44±0.33 | 7.00±0.24 |
| T | 8.25±0.32 | 7.39±0.08 | 7.83±0.10 | 7.87±0.06 | 7.52±0.06 | |
| 溶解氧(DO)质量浓度/ (mg·L−1) | CK | 7.53±0.04 | 8.13±0.06 | 7.52±0.08 | 7.58±0.09 | 7.69±0.02 |
| T | 7.59±0.05 | 7.72±0.04 | 7.56±0.04 | 7.54±0.05 | 7.83±0.03 | |
| 电导率/(µS·cm−1) | CK | 447.00±2.65 | 577.33±0.58 | 559.33±7.09 | 547.00±7.21 | 554.00±6.08 |
| T | 442.00±5.29 | 540.67±0.58 | 535.67±5.03 | 530.00±0.00 | 541.33±0.58 | |
Table 1 Physicochemical parameters in the water bodies of the culture ponds
| 水体基本理化指标 | 处理 | 时间/d | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | ||
| 水温(WT)/℃ | CK | 24.50±0.36 | 26.37±0.15 | 31.37±0.15 | 29.47±0.06 | 26.47±0.12 |
| T | 24.60±0.50 | 26.53±0.12 | 31.50±0.36 | 29.30±0.35 | 26.27±0.15 | |
| pH | CK | 8.42±0.44 | 7.06±0.12 | 7.72±0.12 | 7.44±0.33 | 7.00±0.24 |
| T | 8.25±0.32 | 7.39±0.08 | 7.83±0.10 | 7.87±0.06 | 7.52±0.06 | |
| 溶解氧(DO)质量浓度/ (mg·L−1) | CK | 7.53±0.04 | 8.13±0.06 | 7.52±0.08 | 7.58±0.09 | 7.69±0.02 |
| T | 7.59±0.05 | 7.72±0.04 | 7.56±0.04 | 7.54±0.05 | 7.83±0.03 | |
| 电导率/(µS·cm−1) | CK | 447.00±2.65 | 577.33±0.58 | 559.33±7.09 | 547.00±7.21 | 554.00±6.08 |
| T | 442.00±5.29 | 540.67±0.58 | 535.67±5.03 | 530.00±0.00 | 541.33±0.58 | |
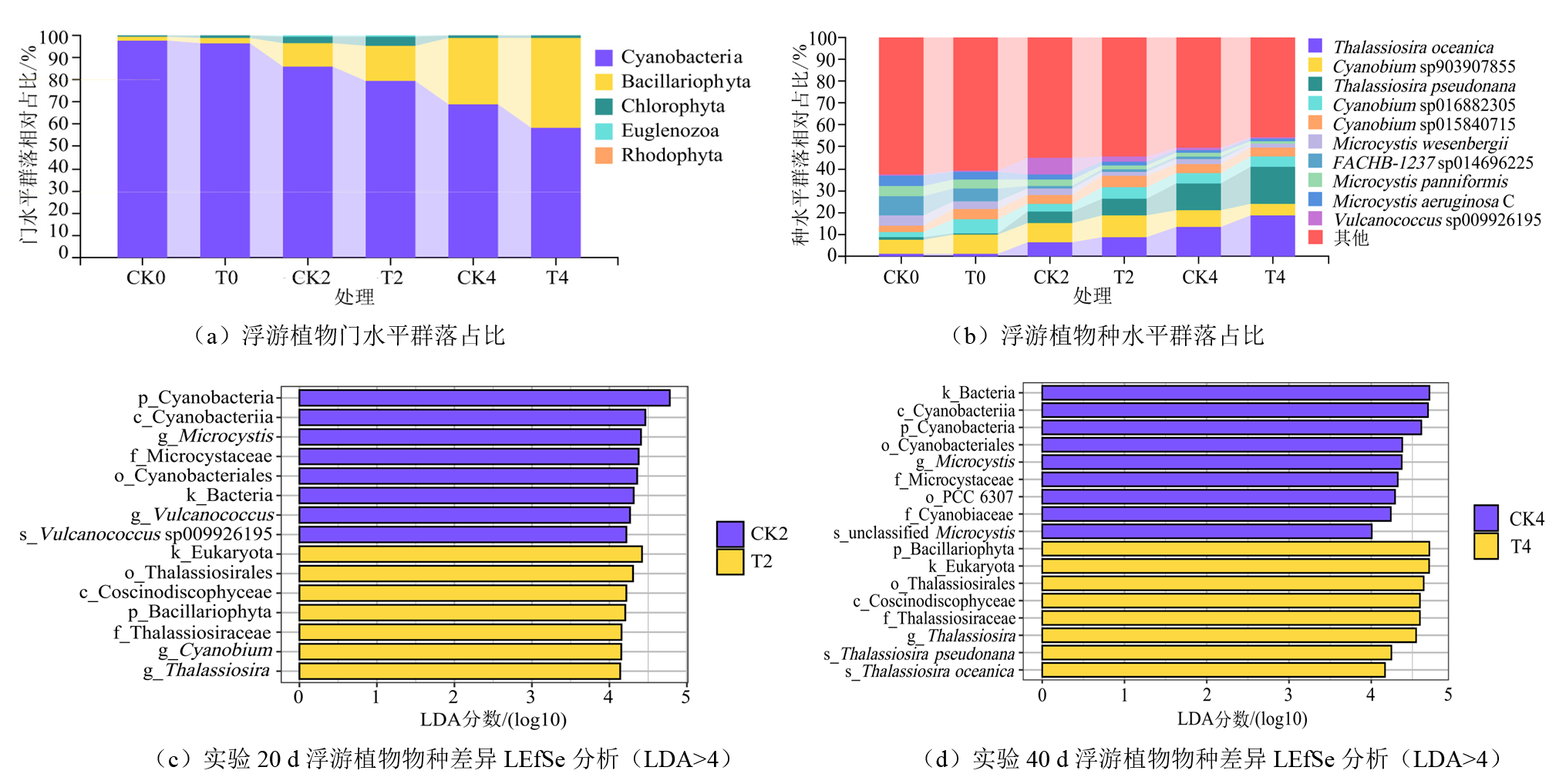
Figure 2 The composition of phytoplankton communities at the phylum and species level and LEfSe analysis of species differences at 20 and 40 days in the aquaculture water
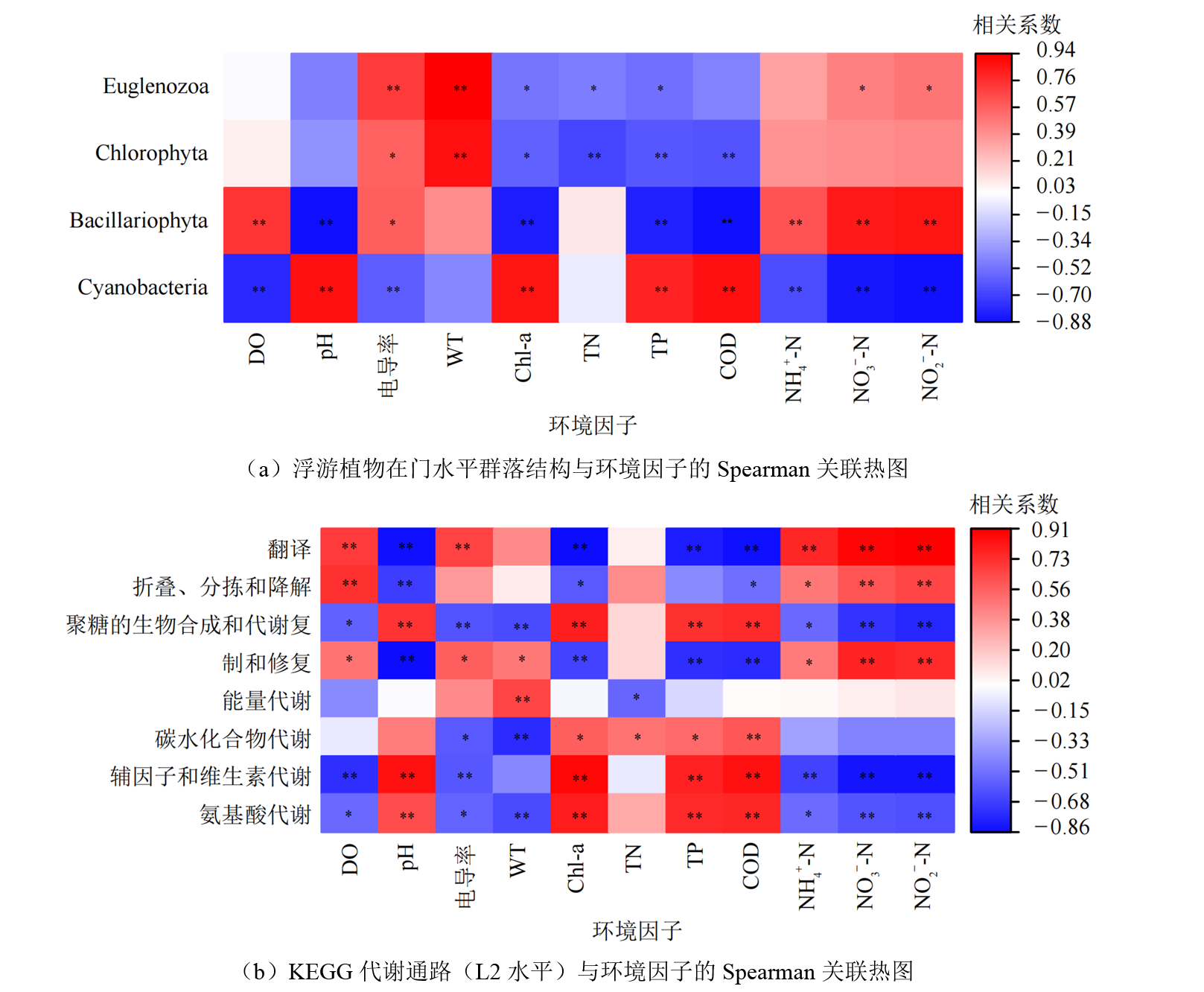
Figure 5 Spearman correlation heatmap analysis of phytoplankton community structure at the phylum level and KEGG metabolic pathways at L2 level with environmental factors
| [1] |
AGRAWAL S, ACHARYA D, ADHOLEYA A, et al., 2017. Nonribosomal peptides from marine microbes and their antimicrobial and anticancer potential[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 8: 828.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
BAEK S H, SON M, KIM Y O, et al., 2019. Can algicide (the thiazolidinedione derivative TD49) truly contribute to the restoration of microbial communities?[J]. Environmental Research, 173: 517-527.
DOI PMID |
| [3] | CHEN L F, WANG Y, SHI L L, et al., 2019. Identification of allelochemicals from pomegranate peel and their effects on Microcystis aeruginosa growth[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(22): 22389-22399. |
| [4] | DE VARGAS C, AUDIC S, HENRY N, et al., 2015. Eukaryotic plankton diversity in the sunlit ocean[J]. Science, 348(6237): 1261605. |
| [5] | DOWNING T G, MEYER C, GEHRINGER M M, et al., 2005. Microcystin content of Microcystis aeruginosa is modulated by nitrogen uptake rate relative to specific growth rate or carbon fixation rate[J]. Environmental Toxicology, 20(3): 257-262. |
| [6] | EL-BILAWY E H, AL-MANSORI A N A, ALOTIBI F O, et al., 2022. Antiviral and antifungal of Ulva fasciata extract: HPLC analysis of polyphenolic compounds[J]. Sustainability, 14(19): 12799. |
| [7] | FAYED W M A, KHALIL R H, SALLAM G R, et al., 2019. Estimating the effective level of Yucca schidigera extract for improvement of the survival, haematological parameters, immunological responses and Water quality of European seabass juveniles (dicentrarchus labrax)[J]. Aquaculture Reports, 15: 100208. |
| [8] |
GUARDIA T, ROTELLI A E, JUAREZ A O, et al., 2001. Anti-inflammatory properties of plant flavonoids. Effects of rutin, quercetin and hesperidin on adjuvant arthritis in rat[J]. Farmaco, 56(9): 683-687.
DOI PMID |
| [9] | HALSEY K H, JONES B M., 2015. Phytoplankton strategies for photosynthetic energy allocation[J]. Annual Review of Marine Science, 7(1): 265-297. |
| [10] | SANTONJA M, LE ROUZIC B, THIÉBAU G, 2018. Seasonal dependence and functional implications of macrophyte-phytoplankton allelopathic interactions[J]. Freshwater Biology, 63(9): 1161-1172. |
| [11] | YI Y L, LEI Y, YIN Y B, et al., 2012. The antialgal activity of 40 medicinal plants against Microcystis aeruginosa[J]. Journal of Applied Physiology, 24(4): 847-856. |
| [12] | ZHAO G P, HONG Y, LI L H, et al., 2022. Selection and characterization of plant-derived alkaloids with strong antialgal inhibition: Growth inhibition selectivity and inhibitory mechanism[J]. Harmful Algae, 117: 102272. |
| [13] | ZHOU L R, BI Y H, JIANG L H, et al., 2012. Effect of black wattle (Acacia mearnsii) Extract on blue‐Green algal bloom control and plankton structure optimization: A Field Mesocosm Experiment[J]. Water Environment Research, 84(12): 2133-2142. |
| [14] |
ZHOU L, HOU L L, HU Y Y, et al., 2010. Effects of wattle extract on Microcystic aeruginosa growth and the simulated mini fresh water ecosystem-Web of Science Core Collection[J]. Journal of Environmental Biology, 31(6): 1023-1030.
PMID |
| [15] | 曹雪, 孙佳, 杨质楠, 等, 2023. 中草药在水产动物养殖中的研究进展[J]. 饲料研究, 46(24): 133-137. |
| CAO X, SUN J, YANG Z N, et al., 2023. Research progress of Chinese herbal medicine in aquaculture[J]. Feed Research, 46(24): 133-137. | |
| [16] | 陈静, 盖建军, 王晶晶, 等, 2023. 青鱼生态养殖池塘浮游生物群落结构初探[J]. 水产养殖, 44(12): 26-30. |
| CHEN J, GAI J J, WANG J J, et al., 2023. Preliminary study on plankton community structure in ecological aquaculture pond of black carp Hypophthalmichthys molitrix[J]. Journal of Aquaculture, 44(12): 26-30. | |
| [17] | 侯德昌, 张莹莹, 魏文志, 2022. 不同中华鳖养殖模式浮游植物功能群特征及水环境评价[J]. 安徽农业科学, 50(9): 96-99. |
| HOU D C, ZHANG Y Y, WEI W Z, 2022. Phytoplankton community structure and water environment evaluation in different culture modes of Pelodiscus sinensis[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 50(9): 96-99. | |
| [18] | 李宗岩, 尹业师, 2023. 植物提取物抗菌剂耐药性研究进展[J]. 湖南科技学院学报, 44(5): 6-9. |
| LI Z Y, YIN Y S, 2023. Research progress on antimicrobial resistance of plant extracts[J]. Journal of Hunan University of Science and Technology, 44(5): 6-9. | |
| [19] | 刘克奉, 2013. 不同中草药对水体主要理化因子的调控作用[J]. 河北渔业 (11): 10-12, 66. |
| LIU K F, 2013. Regulation effect of different Chinese herbs on main physicochemical factors in water body[J]. Hebei Fisheries (11): 10-12, 66. | |
| [20] | 刘荣军, 梁佳, 赵露, 等, 2023. 植物提取物在水产养殖中的应用[J]. 水产养殖, 44(1): 57-58. |
| LIU R J, LIANG J, ZHAO L, et al., 2023. Application of plant extracts in aquaculture[J]. Journal of Aquaculture, 44(1): 57-58. | |
| [21] | 毛梦哲, 2017. 硅藻定向培育对池塘水质和浮游植物的影响[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学: 3-4. |
| MAO M Z, 2017. The effects of the oriented cultivation of Bacillariophyta on the water quality and phytoplankton in culture pond[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University: 3-4. | |
| [22] | 蒲炜佳, 董世鹏, 张东旭, 等, 2022. 三疣梭子蟹池塘综合养殖系统浮游植物群落结构及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 中国水产科学, 29(4): 549-561. |
| PU W J, DONF S P, ZHANG D X, et al., 2022. Community structure of phytoplankton and their relationships with environmental factors within an integrated pond aquaculture system of Portunus trituberculatus[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 29(4): 549-561. | |
| [23] | 钱福根, 闵婕, 钱韧, 2018. 采用植物提取液治理污染河道的试验——以常熟地区水系为例[J]. 净水技术, 37(7): 114-118. |
| QIAN F G, MIN J, QIAN R, 2018. Experiment of applying plant extracts for polluted river remediation: An example of Changshu river system[J]. Water Purification Technology, 37(7): 114-118. | |
| [24] | 钱福根, 闵婕, 钱韧, 等, 2020. 植物提取液治理水产养殖尾水的工程实践[J]. 净水技术, 39(2): 140-145. |
| QIAN F G, MIN J, QIAN R, et al., 2020. Engineering practice of plant extract for aquaculture tail water treatment[J]. Water Purification Technology, 39(2): 140-145. | |
| [25] | 乔玲, 常志强, 李健, 等, 2022. 基于形态学和高通量测序的海水池塘生态养殖系统中浮游植物多样性比较[J]. 渔业科学进展, 43(2): 32-43. |
| QIAO L, CHANG Z Q, LI J, et al., 2022. Comparison of phytoplankton community diversity in the ecological aquaculture system of a marine pond using morphological analysis and high-throughput sequencing[J]. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 43(2): 32-43. | |
| [26] | 魏复盛, 2002. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 第4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社: 180-183. |
| WEI F S, 2002. Methods for monitoring and analysis of water and wastewater[M]. The fourth edition. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press: 180-183. | |
| [27] | 卫鹏, 毕相东, 戴伟, 等, 2022. 淡水养殖池塘微型和超微型浮游植物的群落结构组成[J]. 大连海洋大学学报, 37(1): 113-119. |
| WEI P, BI X D, DAI W, et al., 2022. Community structure composition of nanophytoplankton and picophytoplankton in freshwater culture ponds[J]. Journal of Dalian Fisheries University, 37(1): 113-119. | |
| [28] | 韦毓, 翁旭东, 于瑾, 等, 2024. 不同养殖模式对鲫鱼 (Carassius auratus) 营养品质及特征风味的影响研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 55(1): 243-252. |
| WEI Y, WENG X D, YU J, et al., 2024. Study on the effects of different culture modes on the nutritional quality and characteristic flavor of Carassius auratus[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 55(1): 243-252. | |
| [29] | 吴天浩, 刘劲松, 邓建明, 等, 2019. 大型过水性湖泊——洪泽湖浮游植物群落结构及其水质生物评价[J]. 湖泊科学, 31(2): 440-448. |
| WU T H, LIU J S, LIU J M, et al., 2019. Community structure of phytoplankton and bioassessment of water quality in a large water-carrying lake, Lake Hongze[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 31(2): 440-448. | |
| [30] | 吴振斌, 2016. 大型水生植物对藻类的化感作用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 1-8. |
| WU Z B, 2016. Allelopathic effects of large aquatic plants on algae[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 1-8. | |
| [31] | 徐洪凯, 2018. 东海浮游植物藻华爆发期的动态宏蛋白质组学研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学: 4-5. |
| XU H K, 2018. Dynamic metaproteomic study of phytoplankton blooms in the east China sea[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences: 4-5. | |
| [32] | 徐沙, 2019. 基于宏基因组技术探究甲藻水华生消过程中微生物群落特征及功能代谢变化[D]. 重庆: 西南大学: 49-51. |
| XU S, 2019. Microbial community characteristics and functional metabolic changes during the progress of Dinoflagellates blooming based on Metagenomic technology[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University: 49-51. | |
| [33] | 许歆, 2018. 秦皇岛近海浮游植物群落结构变化及其组学研究[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院海洋研究所): 5-6. |
| XU X, 2018. Study on the changes in community structure of phytoplankton and its omic research in the coastal waters of Qinhuangdao[D]. Qingdao: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Institute of Oceanology): 5-6. | |
| [34] | 杨航, 杨志刚, 周俊宇, 等, 2017. 植物提取物在水产养殖中的应用[J]. 饲料研究 (22): 30-33, 38. |
| YANG H, YANG Z G, ZHOU J Y, et al., 2017. Application of plant extracts in aquaculture[J]. Feed Research (22): 30-33, 38. | |
| [35] | 王储, 2022. Luteovulum azotoformans与Chlorella vulgaris联用对鲫鱼的益生作用及养殖水质净化能力研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学: 2-3. |
| WANG C, 2022. Study on probiotic effect of Luteovulum azotoformans and Chlorella vulgaris on Crucian carp and its water purification ability[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University: 2-3. | |
| [36] | 张瑞芳, 2023. 养殖池塘蓝藻丰度及影响其竞争优势形成的因素研究[D]. 陕西: 西北农林科技大学: 17-19. |
| ZHANG R F, 2023. Abundance of Cyanobacteria in aquaculture ponds and competitive predominance of blue-green algae with different environmental factors[D]. Shaanxi: Northwest Agriculture & Forestry University: 17-19. | |
| [37] | 赵文, 2015. 水生生物学[M]. 第2版. 北京: 中国农业出版社: 1-3. |
| ZHAO W, 2015. Hydrobiology[M]. The second edition. Beijing: China Agriculture Press: 1-3. | |
| [38] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部, 1989. 渔业水质标准: GB 11607—1989[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社: 1-6. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, 1989. Water Quality Standards for Fisheries: GB 11607—1989[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press: 1-6. | |
| [39] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部,国家市场监督管理总局, 2002. 地表水环境质量标准: GB 3838—2002[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社: 1-12. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation, 2002. Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water: GB 3838—2002[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press: 1-12. | |
| [40] | 邹国燕, 蔡敏, 周丽, 等, 2022. 一种用于猪舍除臭的方法: 中国, ZL202110276293.6[P]. 2022-03-08 [2024-11-09]. https://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/patent/ChhQYXRlbnROZXdTMjAyNTAzMTgwODIxNTASE0NOMjAyMTEwMjc2MjkzLjZfc3EaCGdldTdiM2No. |
| ZOU G Y, CAI M, ZHOU L, et al., 2022. A method for pig house deodorization: China, ZL202110276293.6[P]. 2022-03-08 [2024-11-09]. https://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/patent/ChhQYXRlbnROZXdTMjAyNTAzMTgwODIxNTASE0NOMjAyMTEwMjc2MjkzLjZfc3EaCGdldTdiM2No. |
| [1] | LI Yanlin, CHEN Yangyang, YANG Shuangrong, LIU Jumei. Study on the Effects of Organic Acids in Plant Root Exudates on Soil Organic Carbon and Nitrogen Mineralization [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2024, 33(9): 1362-1371. |
| [2] | ZHANG Baodong, WANG Biao, WU Yanlan, MENG Yu, XU Sheng, QIAN Zhenbing, QIN Jun. Analysis and Identification of Characteristics of Rural Black and Odorous Water Bodies in Anhui Province [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2024, 33(8): 1257-1268. |
| [3] | HUANG Qian, ZHU Shiying, LI Tianshun, LI Mingyan, SUO Nancuo, PU Bu. Distribution Pattern of Soil Protozoa Community along Altitude and Its Correlation with Environmental Factors in Rating National Forest Park in Tibet, China [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2024, 33(4): 499-508. |
| [4] | MA Yuan, TIAN Lulu, LÜ Jie, LIU Pei, ZHANG Xu, LI Eryang, ZHANG Qinghang. Soil Microbial Communities and Influencing Factors of Picea schrenkiana Forest on the Northern Slope of Tianshan Mountains [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2024, 33(1): 1-11. |
| [5] | JIANG Yongwei, DING Zhenjun, YUAN Junbin, ZHANG Zheng, LI Yang, WEN Qingchun, WANG Yeyao, JIN Xiaowei. Study on Benthic Macroinvertebrates Community Structure and Water Quality Evaluation in Main Rivers of Liaoning Province [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2023, 32(5): 969-979. |
| [6] | WANG Yun, ZHENG Xilai, CAO Min, LI Lei, SONG Xiaoran, LIN Xiaolei, GUO Kai. Study on Denitrification Performance and Control Factors in Brackish-Freshwater Transition Zone of Coastal Aquifer [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2023, 32(5): 980-988. |
| [7] | KOU Zhu, QING Chun, YUAN Changguo, LI Ping. Diversity and Distribution of Sulfur Oxidizing Bacteria in Hot Springs of Northeast Tibet, China [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2023, 32(5): 989-1000. |
| [8] | WANG Xinyu, GAO Dengzhou, LIU Bolin, WANG Bin, ZHENG Yanling, LI Xiaofei, HOU Lijun. The Tidal-cycle Variation and Influencing Factors of Dark Carbon Fixation Process in the Yangtze Estuary [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2023, 32(4): 733-743. |
| [9] | ZHOU Jiacheng, SONG Zhibin, MIAO Peng, TAN Lu, TANG Tao. Differences in Benthic Macroinvertebrate Communities and Their Driving Forces between the Edge and Center Positions of the Liujiang River Network [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2023, 32(10): 1794-1801. |
| [10] | JIANG Nihao, ZHANG Shihao, ZHANG Shihan. Interspecific Associations and Environmental Interpretation of the Dominant Species of the Communities Invaded by Ageratina adenophora in Ailao Mountains [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2022, 31(7): 1370-1382. |
| [11] | XIA Kai, DENG Pengfei, MA Ruihao, WANG Fei, WEN Zhengyu, XU Xiaoniu. Changes of Soil Bacterial Community Structure and Diversity from Conversion of Masson Pine Secondary Forest to Slash Pine and Chinese Fir Plantations [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2022, 31(3): 460-469. |
| [12] | XUE Wenkai, ZHU Pan, DE Ji, GUO Xiaofang. Study on the Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of the Dominant Species of Cultivable Filamentous Fungi in Nam Co Lake [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2022, 31(12): 2331-2340. |
| [13] | LI Cong, LÜ Jinghua, LU Mei, YANG Zhidong, LIU Pan, REN Yulian, DU Fan. Responses of Soil Bacterial Communities to Vertical Vegetarian Zone Changes in the Subtropical Forests, Southeastern Yunnan [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2022, 31(10): 1971-1983. |
| [14] | LIU Xiaoju, CHU Jiangtao, ZHANG Yue, SHAN Qi. Effects of Environmental Factors and Fire Disturbance Factors on Distribution of Chamerion angustifolium in Kanas Taiga [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2022, 31(1): 37-43. |
| [15] | CAI Xi'an, HUANG Juan, WU Tong, LIU Juxiu, JIANG Fen, WANG Senhao. Study on Methane Emission from Tree Leaves [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2021, 30(9): 1842-1847. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
