Ecology and Environment ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (9): 1362-1371.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.09.004
• Papers on Carbon Cycling and Carbon Emission Reduction • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Yanlin*( ), CHEN Yangyang, YANG Shuangrong, LIU Jumei
), CHEN Yangyang, YANG Shuangrong, LIU Jumei
Received:2024-05-11
Online:2024-09-18
Published:2024-10-18
Contact:
LI Yanlin
通讯作者:
李彦林
作者简介:李彦林(1990年生),女,副教授,博士,主要研究方向为环境生物学。E-mail: ygzzfyhlyl@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
LI Yanlin, CHEN Yangyang, YANG Shuangrong, LIU Jumei. Study on the Effects of Organic Acids in Plant Root Exudates on Soil Organic Carbon and Nitrogen Mineralization[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(9): 1362-1371.
李彦林, 陈杨洋, 杨霜溶, 刘菊梅. 植物根系分泌的有机酸对土壤碳氮矿化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(9): 1362-1371.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.09.004
| 有机酸 | pH | 总氮质量分数/ (g·kg−1) | 速效氮质量分数/ (mg·kg−1) | 总磷质量分数/ (g·kg−1) | 速效磷质量分数/ (mg·kg−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 种类 | 质量浓度/(mg·L−1) | |||||
| 乙酸 | 0 | 7.16±0.05a | 0.80±0.03a | 147.00±3.50c | 0.14±0.01a | 8.17±0.21d |
| 5 | 6.77±0.01b | 0.81±0.01a | 259.00±3.50b | 0.15±0.00a | 20.14±0.22b | |
| 10 | 6.45±0.02c | 0.78±0.01a | 277.67±5.35a | 0.15±0.02a | 28.43±0.50a | |
| 20 | 6.12±0.03d | 0.79±0.01a | 266.00±3.50b | 0.15±0.01a | 17.40±0.32c | |
| 乳酸 | 0 | 7.16±0.05a | 0.80±0.03a | 147.00±3.50d | 0.14±0.01a | 8.17±0.21c |
| 5 | 6.37±0.02b | 1.02±0.07a | 266.00±3.50c | 0.14±0.01a | 14.91±0.21b | |
| 10 | 6.20±0.01c | 1.00±0.17a | 295.75±11.48b | 0.15±0.01a | 17.33±0.38a | |
| 15 | 6.08±0.02d | 1.02±0.02a | 311.50±7.00a | 0.15±0.00a | 14.59±0.28b | |
| 富马酸 | 0 | 7.16±0.05a | 0.80±0.03a | 147.00±3.50c | 0.14±0.01a | 8.17±0.21c |
| 0.2 | 6.01±0.03b | 0.77±0.07a | 278.83±14.15b | 0.15±0.01a | 16.49±1.39a | |
| 0.3 | 5.94±0.01c | 0.78±0.09a | 288.17±22.50b | 0.15±0.01a | 10.38±0.48b | |
| 0.4 | 5.80±0.02d | 0.80±0.09a | 318.50±6.06a | 0.15±0.01a | 9.61±0.32b | |
Table 1 Soil physicochemical properties under different treatments
| 有机酸 | pH | 总氮质量分数/ (g·kg−1) | 速效氮质量分数/ (mg·kg−1) | 总磷质量分数/ (g·kg−1) | 速效磷质量分数/ (mg·kg−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 种类 | 质量浓度/(mg·L−1) | |||||
| 乙酸 | 0 | 7.16±0.05a | 0.80±0.03a | 147.00±3.50c | 0.14±0.01a | 8.17±0.21d |
| 5 | 6.77±0.01b | 0.81±0.01a | 259.00±3.50b | 0.15±0.00a | 20.14±0.22b | |
| 10 | 6.45±0.02c | 0.78±0.01a | 277.67±5.35a | 0.15±0.02a | 28.43±0.50a | |
| 20 | 6.12±0.03d | 0.79±0.01a | 266.00±3.50b | 0.15±0.01a | 17.40±0.32c | |
| 乳酸 | 0 | 7.16±0.05a | 0.80±0.03a | 147.00±3.50d | 0.14±0.01a | 8.17±0.21c |
| 5 | 6.37±0.02b | 1.02±0.07a | 266.00±3.50c | 0.14±0.01a | 14.91±0.21b | |
| 10 | 6.20±0.01c | 1.00±0.17a | 295.75±11.48b | 0.15±0.01a | 17.33±0.38a | |
| 15 | 6.08±0.02d | 1.02±0.02a | 311.50±7.00a | 0.15±0.00a | 14.59±0.28b | |
| 富马酸 | 0 | 7.16±0.05a | 0.80±0.03a | 147.00±3.50c | 0.14±0.01a | 8.17±0.21c |
| 0.2 | 6.01±0.03b | 0.77±0.07a | 278.83±14.15b | 0.15±0.01a | 16.49±1.39a | |
| 0.3 | 5.94±0.01c | 0.78±0.09a | 288.17±22.50b | 0.15±0.01a | 10.38±0.48b | |
| 0.4 | 5.80±0.02d | 0.80±0.09a | 318.50±6.06a | 0.15±0.01a | 9.61±0.32b | |
| 有机酸 种类 | 总氮质量分数/ (g·kg−1) | 总磷质量分数/ (g·kg−1) | 速效氮质量分数/ (mg·kg−1) | 速效磷质量分数/ (mg·kg−1) | pH | 净氮矿化速率/ (mg·kg−1·d−1) | 净氨化速率/ (mg·kg−1·d−1) | 净硝化速率/ (mg·kg−1·d−1) | 累积碳矿化量/(mg·g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乙酸 | −0.311 | 0.130 | 0.694* | 0.394 | −0.974** | −0.785* | 0.758* | −0.818* | −0.796* |
| 乳酸 | 0.591*2) | 0.479 | 0.903**1) | 0.713** | −0.902** | 0.822* | 0.332 | 0.672 | −0.542 |
| 富马酸 | −0.005 | 0.372 | 0.944** | 0.110 | −0.934** | 0.613 | 0.665 | 0.216 | −0.225 |
Table 2 Correlation analysis of organic acids with soil carbon and nitrogen mineralization and soil physicochemical factors
| 有机酸 种类 | 总氮质量分数/ (g·kg−1) | 总磷质量分数/ (g·kg−1) | 速效氮质量分数/ (mg·kg−1) | 速效磷质量分数/ (mg·kg−1) | pH | 净氮矿化速率/ (mg·kg−1·d−1) | 净氨化速率/ (mg·kg−1·d−1) | 净硝化速率/ (mg·kg−1·d−1) | 累积碳矿化量/(mg·g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乙酸 | −0.311 | 0.130 | 0.694* | 0.394 | −0.974** | −0.785* | 0.758* | −0.818* | −0.796* |
| 乳酸 | 0.591*2) | 0.479 | 0.903**1) | 0.713** | −0.902** | 0.822* | 0.332 | 0.672 | −0.542 |
| 富马酸 | −0.005 | 0.372 | 0.944** | 0.110 | −0.934** | 0.613 | 0.665 | 0.216 | −0.225 |
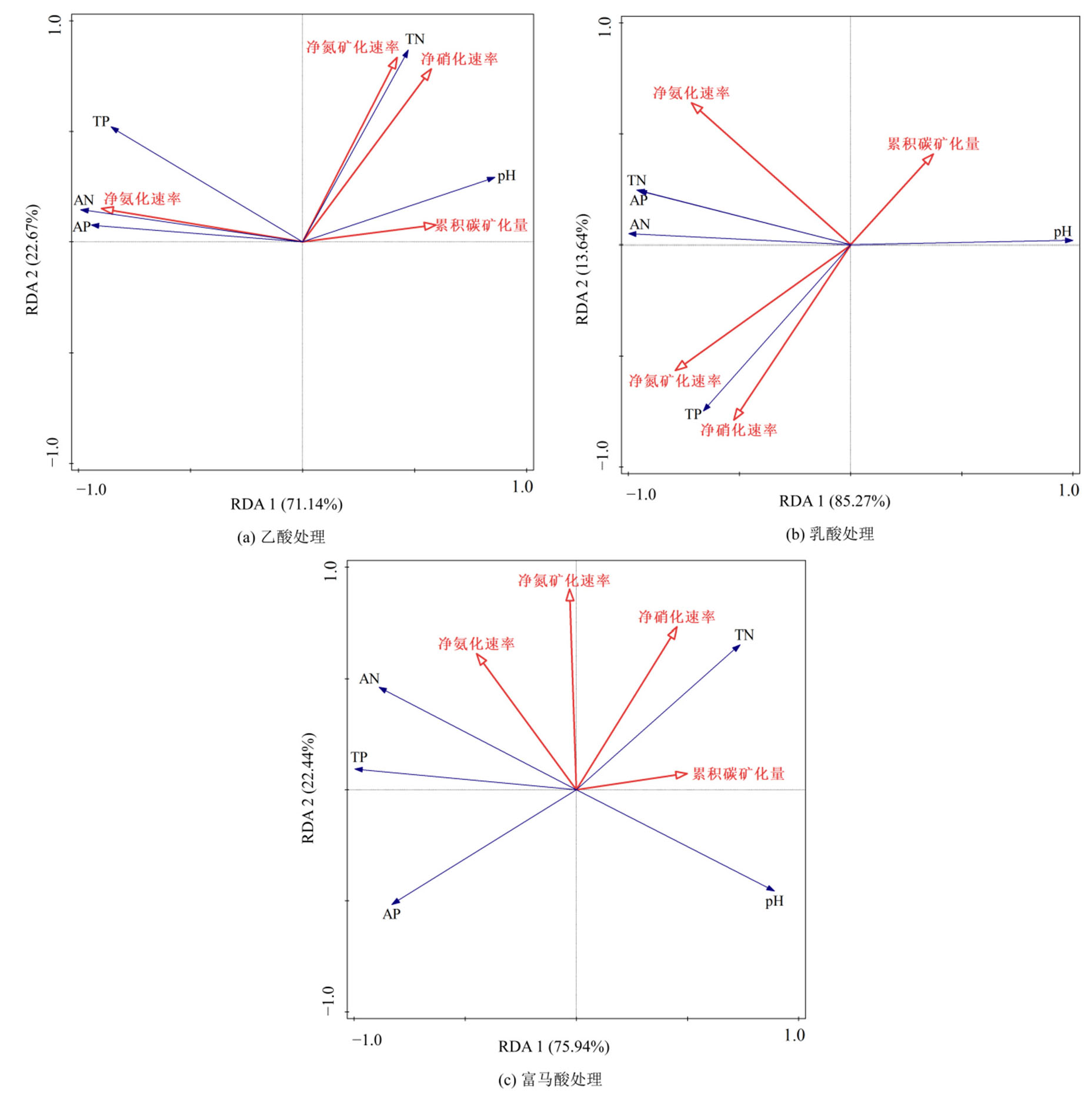
Figure 6 RDA analysis of the relationship between soil physical and chemical properties and soil cumulative carbon mineralization, net ammonification rate, net nitrification rate, and net nitrogen mineralization rate
| [1] | CHEN H, JU P, ZHU Q, et al., 2022. Carbon and nitrogen cycling on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 3(10): 701-716. |
| [2] | GUO W J, ZHANG Z L, LIU Q, et al., 2021. Seasonal variations in plant a)nitrogen acquisition in an ectomycorrhizal alpine forest on the eastern Tibetan Plateau, China[J]. Plant and Soil, 459(1): 79-91. |
| [3] | GIARDINA C P, RYAN M G, HUBBARD R M, et al., 2001. Tree species and soil textural controls on carbon and nitrogen mineralization rates[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 65(4): 1272-1279. |
| [4] | JIANG Z H, LIU Y Z, YANG J P, et al., 2021. Rhizosphere priming regulates soil organic carbon and nitrogen mineralization: The significance of abiotic mechanisms[J]. Geoderma, 385(1): 114877. |
| [5] | LIANG Y, LIU J, JIN Z J, et al., 2024. Effects of low-molecular-weight organic acids on the transformation and phosphate retention of iron (hydr) oxides[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 940: 173667. |
| [6] | LI J Y, CHEN P, LI Z G, et al., 2023. Soil aggregate-associated organic carbon mineralization and its driving factors in rhizosphere soil[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 186: 109182. |
| [7] | LIU Y, EVANS S E, Friesen M L, et al., 2022. Root exudates shift how N mineralization and N fixation contribute to the plant-available N supply in low fertility soils[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 165: 108541. |
| [8] | LIU Y H, SHAHBAZ M, GE T D, et al., 2020. Effects of root exudate stoichiometry on CO2 emission from paddy soil[J]. European Journal of Soil Biology, 101: 103247. |
| [9] |
LUO Y Q, ZHAO X Y, ANDREN O, et al., 2014. Artificial root exudates and soil organic carbon mineralization in a degraded sandy grassland in northern China[J]. Journal of Arid Land, 6(4): 423-431.
DOI |
| [10] | MO F, REN C J, YU K L, et al., 2022. Global pattern of soil priming effect intensity and its environmental drivers[J]. Ecology, 103(11): e3790. |
| [11] | PANCHAL P, PREECE C, PENUELAS J, et al., 2022. Soil carbon sequestration by root exudates[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 27(8): 749-757. |
| [12] | YUAN Y S, ZHAO W Q, ZHANG Z L, et al., 2018. Impacts of oxalic acid and glucose additions on N transformation in microcosms via artificial roots[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 121: 16-23. |
| [13] | ZHAO M L, ZHAO J, YIAN J, et al., 2021. Root exudates drive soil‐microbe‐nutrient feedbacks in response to plant growth[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 44(2): 613-628. |
| [14] | 蔡银美, 张成富, 赵庆霞, 等, 2021. 模拟根系分泌物输入对森林土壤氮转化的影响研究综述[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 38(5): 916-925. |
| CAI Y M, ZHANG C F, ZHAO Q X, et al., 2021. Effect of simulated root exudates input on soil nitrogen transformation: A review[J]. Journal of Zhejiang A & F University, 38(5): 916-925. | |
| [15] | 陈懂懂, 2010. 青藏高原东北缘高寒草甸土壤养分、微生物量碳氮及氮矿化潜力的研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学: 22-58. |
| CHEN D D, 2010. Research about the soil nutrients, microbial biomass C and N mineralization potential of an alpine meadow on the northeastern Tibetan Plateau[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University: 22-58. | |
| [16] | 杜思垚, 方娅婷, 鲁剑巍, 2023. 根系分泌物对作物养分吸收利用的影响研究进展[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 42(2): 147-157. |
| DU S Y, FANG Y T, LU J W, 2023. Advance in effect of different root exudates on plant nutrient uptake[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 42(2): 147-157. | |
| [17] |
高雪峰, 贾渊, 2020. 荒漠草原植物根系分泌物中有机酸组分分析及其生态效应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(10): 1927-1934.
DOI |
| GAO X F, JIA Y, 2020. Analysis of organic acid components in root exudates and their ecological effects of the plants in desert steppe of Inner Mongolia[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29(10): 1927-1934. | |
| [18] | 高雪峰, 韩国栋, 2021. 短花针茅根系分泌物对荒漠草原土壤细菌群落及土壤养分的影响[J]. 中国草地学报, 43(6): 76-84. |
| GAO X F, HAN G D, 2021. Effects of Stipa breviflora root exudates on soil bacterial community and soil nutrients in desert steppe[J]. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 43(6): 76-84. | |
| [19] | 耿贵, 2011. 作物根系分泌物对土壤碳、氮含量、微生物数量和酶活性的影响[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学: 21-59. |
| GENG G, 2011. Effect of grop root exudates on carbon and nitrogen contents, microorganisms quatity and enzyme activities in soil[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University: 21-59. | |
| [20] | 李彦林, 贺怀鹏, 刘菁, 等, 2024. 不同根系分泌有机酸组分分析及其对土壤养分、酶活性的影响[J]. 北方园艺 (12): 73-79. |
| LI Y L, HE H P, LIU J, et al., 2024. Analysis of organic acid components in root exudates and their effects on soil nutrients and enzyme activities[J]. Northern Horticulture (12): 73-79. | |
| [21] | 鲁如坤, 2000. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社: 146-180. |
| LU R K, 2000. Analytical Methods of Soil Agrochemistry[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: 146-180. | |
| [22] | 王兰鸽, 张前前, 赵明水, 等, 2023. 毛竹和阔叶林凋落物浸提液对土壤微生物及氮矿化的影响[J]. 农业生物技术学报, 31(5): 1053-1063. |
| WANG L G, ZHANG Q Q, ZHAO M S, et al., 2023. Effects of litter extracts from moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) and broadleaved forests on soil microbes and nitrogen mineralization[J]. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 31(5): 1053-1063. | |
| [23] | 王秀英, 周秉荣, 苏淑兰, 等, 2023. 青藏高原高寒草甸和荒漠碳交换特征及其气象影响机制[J]. 生态学报, 43(3): 1194-1208. |
| WANG X Y, ZHOU B R, SU S L, et al., 2023. Carbon exchange characteristics and mechanism of Alpine Meadow and desert in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 43(3): 1194-1208. | |
| [24] | 文启孝, 1984. 土壤有机质研究法[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社: 273-284. |
| WEN Q X, 1984. Soil Organic Matter Research Method[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press: 273-284. | |
| [25] | 袁胜南, 商雨晴, 王俊, 2020. 不同温度下添加绿肥对旱作农田土壤有机碳矿化的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 38(5): 45-50. |
| YUAN S N, SHANG Y Q, WANG J, 2020. Effects of green manure on soil organic carbon mineralization in dry land soil under different temperature[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 38(5): 45-50. | |
| [26] | 张根柱, 2011. 外源柠檬酸对塿土养分, 酶活性及微生物活性的影响[D]. 榆林: 西北农林科技大学: 8-34. |
| ZHANG G Z, 2011. Effects of exogenous citric on soil nutrients and enzyme activities and microbial activity of old manured loessal soil[D]. Yulin: Northwest A&F University:8-34. | |
| [27] | 章晴, 2016. 杨-桤混交林根系碳分泌及其对根际土壤氮转化的影响[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学: 24-46. |
| ZHANG Q, 2016. Root exuduation and effect of root exduate to soil nitrogen transformation in poplar and alder mixed plantation[D]. Nanjing: Nan jing Forestry University: 24-46. | |
| [28] | 赵媛, 周旺明, 王守乐, 等, 2017. 冻融对温带森林土壤碳、氮矿化作用的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 36(6): 1548-1554. |
| ZHAO Y, ZHOU W M, WANG S L, et al., 2017. Effects of freezing-thawing on soil carbon and nitrogen mineralization in temperate forest ecosystems[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 36(6): 1548-1554. | |
| [29] |
周祉蕴, 王奕钧, 杨艳丽, 等, 2024. 脉冲降水和凋落物对温性草原土壤碳矿化激发效应的影响[J]. 草地学报, 32(3):879-888.
DOI |
| ZHOU Z Y, WANG Y J, YANG Y L, et al., 2024. Influence of pulsed precipitation and litteron the priming effects of soil carbon mineralization in temperate steppe[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 32(3): 879-888. | |
| [30] | 朱灵, 2021. 西藏忍冬 (Lonicera thibetica) 根系分泌物有机酸组成及其对土壤碳氮矿化的影响[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学: 41-76. |
| ZHU L, 2021. Organic acid composition of Lonicera thibetica root exudates and its effect on soil carbon and nitrogen mineralization[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences: 41-76. |
| [1] | LI Chengyang, LIANG Zhihui, LI Zhenming, CAI Min, XU Ruiyao, CHEN Xiuyu, DING Jiayin, XU Qiuyun, PENG Fei. Plant Community Characteristics and Soil Characteristics of Degraded Alpine Meadows in the Beilu River Basin of the Yangtze River Source Area [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(7): 1063-1071. |
| [2] | WANG Yuqin, SONG Meiling, ZHOU Rui, WANG Hongsheng. Effects of Spread of Ligularia virgaurea on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Enzyme Activities in Alpine Meadow [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(8): 1384-1391. |
| [3] | YANG Chunliang, LIU Minxia, WANG Qianyue, MIAO Lele, XIAO Yindi, WANG Min. Spatial Pattern and Correlation of Populations of Anemone rivularis and Kobresia myosuroides under Single-household Management and Multi-household Management Grazing Patterns [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 651-659. |
| [4] | ZHOU Xuanbo, WANG Xiaoli, MA Yushou, WANG Yanlong, LUO Shaohui, XIE Lele. Niche of Main Plant Populations in Alpine Meadow Under the Rest-grazing in the Green-Up Period [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(8): 1547-1555. |
| [5] | GONG Lingxuan, WANG Lili, ZHAO Jianning, LIU Hongmei, YANG Dianlin, ZHANG Guilong. Effects of Different Cover Crop Patterns on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Organic Carbon Mineralization in Tea Gardens [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(6): 1141-1150. |
| [6] | WANG Yingcheng, YAO Shiting, JIN Xin, YU Wenzhen, LU Guangxin, WANG Junbang. Comparative Study on Soil Bacterial Diversity of Degraded Alpine Meadow in the Sanjiangyuan Region [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(4): 695-703. |
| [7] | HE Xiaojia, FENG Shuhua, JIANG Ming, LI Mingrui, ZHAN Fangdong, LI Yuan, HE Yongmei. Effects of UV-B Radiation on Conversion of Active Organic Carbon and Methane Production Potential of Rice Rhizosphere Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 556-564. |
| [8] | LI Mengli, XU Moxin, CHEN Yongshan, YE Lili, JIANG Jinping. Effects of Different Amounts of Calcium Carbonate on the Mineralization of Straw Organic Carbon in Calcareous Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(10): 2002-2009. |
| [9] | YAO Shiting, LU Guangxin, DENG Ye, DANG Ning, WANG Yingcheng, ZHANG Haijuan, YAN Huilin. Effects of Simulated Warming on Soil Fungal Community Composition and Diversity [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(7): 1404-1411. |
| [10] | XIA Zitai, CHENG Weiwei, ZHAO Jixia, LI Yongmei, FAN Maopan. Effects of Different Planting Patterns on Maize Root System and Soil Aggregate Stability [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(12): 2331-2338. |
| [11] | XU Wenyin, ZHANG Yupeng, DUAN Chengwei, CHAI Yu, SONG Xian, LI Xilai. Spatial Variability of Soil Nutrients in Degraded Alpine Meadows in Different Regions of the Yellow River [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(10): 1968-1975. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
