Ecology and Environment ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (10): 1794-1801.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.10.008
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHOU Jiacheng1,2( ), SONG Zhibin1, MIAO Peng1,2, TAN Lu1, TANG Tao1,2,*(
), SONG Zhibin1, MIAO Peng1,2, TAN Lu1, TANG Tao1,2,*( )
)
Received:2023-06-27
Online:2023-10-18
Published:2024-01-16
Contact:
TANG Tao
周佳诚1,2( ), 宋志斌1, 苗芃1,2, 谭路1, 唐涛1,2,*(
), 宋志斌1, 苗芃1,2, 谭路1, 唐涛1,2,*( )
)
通讯作者:
唐涛
作者简介:周佳诚(1998年生),男,博士研究生,主要从事流域生态学研究。E-mail: zhoujiacheng@ihb.ac.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
ZHOU Jiacheng, SONG Zhibin, MIAO Peng, TAN Lu, TANG Tao. Differences in Benthic Macroinvertebrate Communities and Their Driving Forces between the Edge and Center Positions of the Liujiang River Network[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(10): 1794-1801.
周佳诚, 宋志斌, 苗芃, 谭路, 唐涛. 柳江不同河网位置大型底栖动物群落特征及其影响因子差异比较研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(10): 1794-1801.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.10.008
| 环境因子 | 均值 (取值范围) | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 河网边缘 | 河网中心 | ||
| 电导率Cond/(μS∙cm−1) | 110.4 (20.8‒465.7) | 152.5 (26.1‒311.4) | 0.004 |
| 浊度Turb/NTU | 3.91 (0.7‒28.4) | 3.09 (0.6‒11.1) | 0.397 |
| 溶解氧DO/(mg∙L−1) | 9.78 (6.9‒14.7) | 8.98 (6.17‒12.24) | 0.018 |
| 化学需氧量COD/(mg∙L−1) | 0.94 (0.39‒2.15) | 2.19 (0.02‒8.48) | <0.001 |
| 总氮TN/(mg∙L−1) | 0.64 (0.10‒1.79) | 0.91 (0.41‒1.88) | <0.001 |
| 总磷TP/(mg∙L−1) | 0.02 (0.01‒0.06) | 0.02 (0.01‒0.03) | 0.074 |
| 流速/(m∙s−1) | 0.51 (0.1‒1.3) | 0.31 (0.1‒0.92) | 0.001 |
| 水深/m | 0.35 (0.18‒0.47) | 0.46 (0.19‒0.55) | 0.019 |
Table 1 Statistics and differences in environmental factors between the edge and center positions of the Liujiang River network
| 环境因子 | 均值 (取值范围) | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 河网边缘 | 河网中心 | ||
| 电导率Cond/(μS∙cm−1) | 110.4 (20.8‒465.7) | 152.5 (26.1‒311.4) | 0.004 |
| 浊度Turb/NTU | 3.91 (0.7‒28.4) | 3.09 (0.6‒11.1) | 0.397 |
| 溶解氧DO/(mg∙L−1) | 9.78 (6.9‒14.7) | 8.98 (6.17‒12.24) | 0.018 |
| 化学需氧量COD/(mg∙L−1) | 0.94 (0.39‒2.15) | 2.19 (0.02‒8.48) | <0.001 |
| 总氮TN/(mg∙L−1) | 0.64 (0.10‒1.79) | 0.91 (0.41‒1.88) | <0.001 |
| 总磷TP/(mg∙L−1) | 0.02 (0.01‒0.06) | 0.02 (0.01‒0.03) | 0.074 |
| 流速/(m∙s−1) | 0.51 (0.1‒1.3) | 0.31 (0.1‒0.92) | 0.001 |
| 水深/m | 0.35 (0.18‒0.47) | 0.46 (0.19‒0.55) | 0.019 |
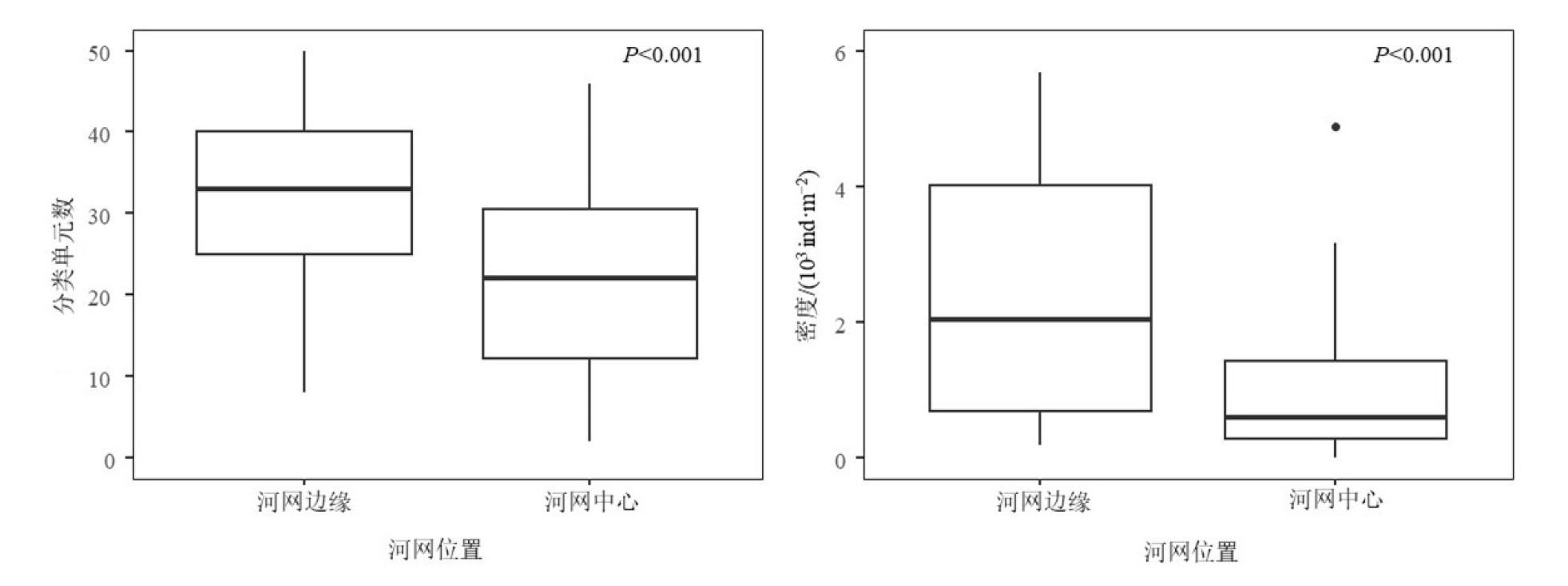
Figure 2 Boxplots displaying differences in taxonomic units and density of benthic macroinvertebrates between the edge and center positions of the Liujiang River network
| 分类单元 | 河网边缘 | 河网中心 |
|---|---|---|
| 四节蜉属 Baetis sp. | 19.80 | 14.03 |
| 直突摇蚊亚科 Orthocladiinae | 15.15 | 19.22 |
| 宽基蜉属 Choroterpes sp. | 7.81 | 6.15 |
| 扁蜉属 Heptagenia sp. | 5.59 | 5.46 |
| 蚋 Simulium sp. | 5.33 | 1.35 |
| 长足摇蚊亚科 Tanypodinae | 5.15 | 13.91 |
| 摇蚊亚科 Chironominae | 4.65 | 6.36 |
| 细蜉属 Caenis sp. | 3.78 | 2.19 |
| 锯形蜉属 Serrattella sp. | 3.55 | 2.38 |
| 朝大蚊属 Antocha sp. | 1.66 | 1.79 |
| 花翅蜉属 Baetiella sp. | 1.60 | |
| 高翔蜉属 Epeorus sp. | 1.38 |
Table 2 Relative abundance of dominant taxonomic units of benthic macroinvertebrates between the edge and center positions of the Liujiang River network %
| 分类单元 | 河网边缘 | 河网中心 |
|---|---|---|
| 四节蜉属 Baetis sp. | 19.80 | 14.03 |
| 直突摇蚊亚科 Orthocladiinae | 15.15 | 19.22 |
| 宽基蜉属 Choroterpes sp. | 7.81 | 6.15 |
| 扁蜉属 Heptagenia sp. | 5.59 | 5.46 |
| 蚋 Simulium sp. | 5.33 | 1.35 |
| 长足摇蚊亚科 Tanypodinae | 5.15 | 13.91 |
| 摇蚊亚科 Chironominae | 4.65 | 6.36 |
| 细蜉属 Caenis sp. | 3.78 | 2.19 |
| 锯形蜉属 Serrattella sp. | 3.55 | 2.38 |
| 朝大蚊属 Antocha sp. | 1.66 | 1.79 |
| 花翅蜉属 Baetiella sp. | 1.60 | |
| 高翔蜉属 Epeorus sp. | 1.38 |
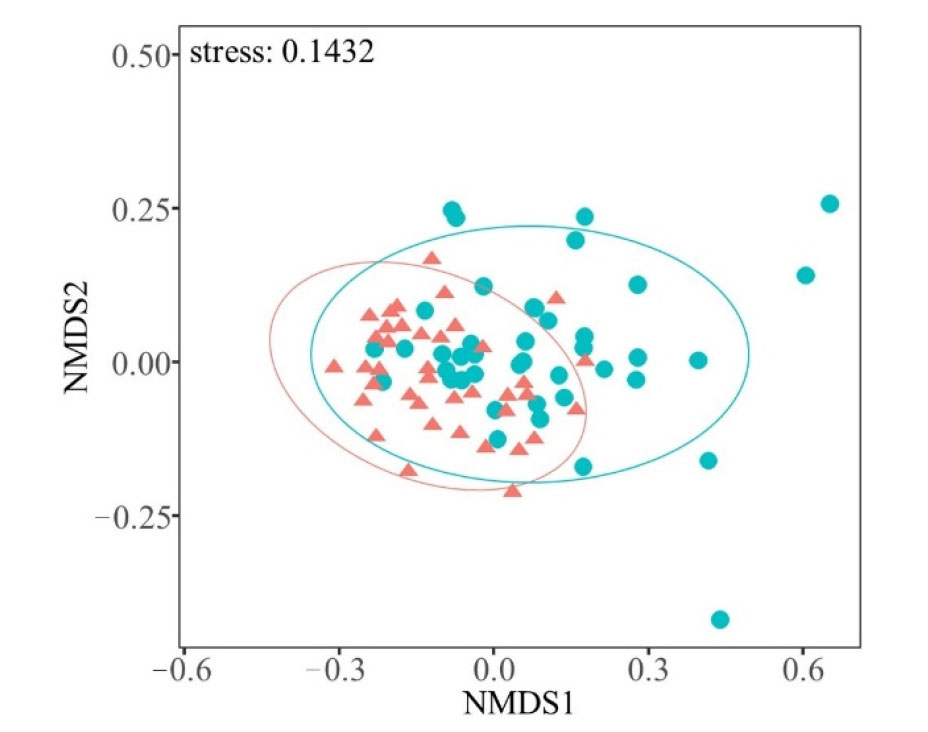
Figure 3 Non-metric Multidimensional Scaling (NMDS) plot based on inter-site Bray-Curtis dissimilarity of benthic macroinvertebrate communities in the Liujiang River network
| 检验 | 因子 | 控制因子 | 河网边缘 | 河网中心 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | r | |||
| Mantel 检验 | 陆上距离 | ‒ | 0.197* 1) | 0.126* |
| 河道距离 | ‒ | 0.164* | 0.028 | |
| 环境 | ‒ | 0.419*** 2) | 0.250* | |
| 偏Mantel 检验 | 陆上距离 | 环境 | 0.157* | 0.069 |
| 河道距离 | 环境 | 0.139* | 0.20 | |
| 环境 | 陆上距离 | 0.274* | 0.245* | |
| 环境 | 河道距离 | 0.287* | 0.247* | |
| 环境因子 | ‒ | ‒ | 溶解氧; 化学需氧量; 水深 | 溶解氧; 总氮 流速; 水深 |
Table 3 The correlations between benthic macroinvertebrate beta diversity and spatial distances (Overland, Watercourse) and environmental distances with Mantel test and partial Mantel test
| 检验 | 因子 | 控制因子 | 河网边缘 | 河网中心 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | r | |||
| Mantel 检验 | 陆上距离 | ‒ | 0.197* 1) | 0.126* |
| 河道距离 | ‒ | 0.164* | 0.028 | |
| 环境 | ‒ | 0.419*** 2) | 0.250* | |
| 偏Mantel 检验 | 陆上距离 | 环境 | 0.157* | 0.069 |
| 河道距离 | 环境 | 0.139* | 0.20 | |
| 环境 | 陆上距离 | 0.274* | 0.245* | |
| 环境 | 河道距离 | 0.287* | 0.247* | |
| 环境因子 | ‒ | ‒ | 溶解氧; 化学需氧量; 水深 | 溶解氧; 总氮 流速; 水深 |
| [1] |
ALTERMATT F, SEYMOUR M, MARTINEZ N, 2013. River network properties shape α-diversity and community similarity patterns of aquatic insect communities across major drainage basins[J]. Journal of Biogeography, 40(12): 2249-2260.
DOI URL |
| [2] | ANDERSON M J, 2001. A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance[J]. Austral Ecology, 26(1): 32-46. |
| [3] |
ARCE P, PALT M, SCHLETTERER M, et al., 2023. Has riparian woody vegetation a positive effect on dispersal and distribution of mayfly, stonefly and caddisfly species?[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 879: 163137.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
ASTORGA A, OKSANEN J, LUOTO M, et al., 2012. Distance decay of similarity in freshwater communities: Do macro- and microorganisms follow the same rules?[J]. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 21(3): 365-375.
DOI URL |
| [5] | BELMAR O, VELASCO J, GUTIERREZ-CANOVAS C, et al., 2013. The influence of natural flow regimes on macroinvertebrate assemblages in a semiarid Mediterranean basin[J]. Ecohydrology, 6(3): 363-379. |
| [6] |
BROWN B L, SWAN C M, 2010. Dendritic network structure constrains metacommunity properties in riverine ecosystems[J]. Journal of Animal Ecology, 79(3): 571-580.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
BROWN B L, SWAN C M, AUERBACH D A, et al., 2011. Metacommunity theory as a multispecies, multiscale framework for studying the influence of river network structure on riverine communities and ecosystems[J]. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 30(1): 310-327.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
CALAPEZ A R, SERRA S R Q, RIVAES R, et al., 2021. Influence of river regulation and instream habitat on invertebrate assemblage' structure and function[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 794: 148696.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
CANEDO-ARGUEELLES M, BOERSMA K S, BOGAN M T, et al., 2015. Dispersal strength determines meta-community structure in a dendritic riverine network[J]. Journal of Biogeography, 42(4): 778-790.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
CHAPUT-BARDY A, ALCALA N, SECONDI J, et al., 2017. Network analysis for species management in rivers networks: Application to the Loire River[J]. Biological Conservation, 210(Part A): 26-36.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
CLARKE A, MAC NALLY R, BOND N, et al., 2008. Macroinvertebrate diversity in headwater streams: A review[J]. Freshwater Biology, 53(9): 1707-1721.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
CLARKE K R, AINSWORTH M, 1993. A method of linking multivariate community structure to environmental variables[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 92: 205-219.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
COTTENIE K, 2005. Integrating environmental and spatial processes in ecological community dynamics[J]. Ecology Letters, 8(11): 1175-1182.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
DODDS W K, 2006. Eutrophication and trophic state in rivers and streams[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 51(1): 671-680.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
GAUTHIER M, LAUNAY B, LE GOFF G, et al., 2020. Fragmentation promotes the role of dispersal in determining 10 intermittent headwater stream metacommunities[J]. Freshwater Biology, 65(12): 2169-2185.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
GOTHE E, ANGELER D G, SANDIN L, 2013. Metacommunity structure in a small boreal stream network[J]. Journal of Animal Ecology, 82(2): 449-458.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
GRÖNROOS M, HEINO J, SIQUEIRA T, et al., 2013. Metacommunity structuring in stream networks: Roles of dispersal mode, distance type, and regional environmental context[J]. Ecology and Evolution, 3(13): 4473-4487.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
HE S W, WANG B X, CHEN K, et al., 2023. Patterns in aquatic metacommunities are associated with environmental and trait heterogeneity[J]. Freshwater Biology, 68(1): 91-102.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
HE S W, SOININEN J, CHEN K, et al., 2020. Environmental factors override dispersal-related factors in shaping diatom and macroinvertebrate communities within stream networks in China[J]. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 8: 141.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
HEINO J, MELO A S, SIQUEIRA T, et al., 2015. Metacommunity organisation, spatial extent and dispersal in aquatic systems: Patterns, processes and prospects[J]. Freshwater Biology, 60(5): 845-869.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
HENRIQUES-SILVA R, LOGEZ M, REYNAUD N, et al., 2019. A comprehensive examination of the network position hypothesis across multiple river metacommunities[J]. Ecography, 42(2): 284-294.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
HITT N P, ANGERMEIER P L, 2011. Fish community and bioassessment responses to stream network position[J]. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 30(1): 296-309.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
KARNA O-M, GRONROOS M, ANTIKAINEN H, et al., 2015. Inferring the effects of potential dispersal routes on the metacommunity structure of stream insects: As the crow flies, as the fish swims or as the fox runs?[J]. Journal of Animal Ecology, 84(5): 1342-1353.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
KHALAF M A, KOCHZIUS M, 2002. Changes in trophic community structure of shore fishes at an industrial site in the Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 239: 287-299.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
LANSAC-TOHA F M, BINI L M, HEINO J, et al., 2021. Scale-dependent patterns of metacommunity structuring in aquatic organisms across floodplain systems[J]. Journal of Biogeography, 48(4): 872-885.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
LI Z F, CHEN X, JIANG X M, et al., 2021. Distance decay of benthic macroinvertebrate communities in a mountain river network: Do dispersal routes and dispersal ability matter?[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 758: 143630.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
MASESE F O, ACHIENG A O, O'BRIEN G C, et al., 2021. Macroinvertebrate taxa display increased fidelity to preferred biotopes among disturbed sites in a hydrologically variable tropical river[J]. Hydrobiologia, 848: 321-343.
DOI |
| [28] |
MAZOR R D, REHN A C, ODE P R et al., 2016. Bioassessment in complex environments: Designing an index for consistent meaning in different settings[J]. Freshwater Science, 35(1): 249-71.
DOI URL |
| [29] | MERRITT R W, CUMMINS K W, BERG M B, 2019. An introduction to the aquatic insects of North America[M]. Fifth Edition. Dibuque county: Kendall Hunt. |
| [30] |
MEYER J L, STRAYER D L, WALLACE J B, et al., 2007. The contribution of headwater streams to biodiversity in river networks[J]. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 43(1): 86-103.
DOI URL |
| [31] | MORSE J C, YANG L F, TIAN L, 1994. Aquatic insects of China useful for monitoring water quality[M]. Nanjing: Hohai University. |
| [32] |
MRUZEK J L, BUDNICK W R, LARSON C A, et al., 2022. Stronger niche than dispersal effects on α- and β-diversity of stream algae, insects, and fish across latitudes in the United States[J]. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 31(12): 2453-2462.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
OESTER R, OLIVEIRA P C D, MORETTI M S, et al., 2023. Leaf-associated macroinvertebrate assemblage and leaf litter breakdown in headwater streams depend on local riparian vegetation[J]. Hydrobiologia, 850(15): 3359-3374.
DOI PMID |
| [34] |
POFF N, LEROY O, JULIAN D, et.al., 2006. Functional trait niches of North American lotic insects: Traits-based ecological applications in light of phylogenetic relationships[J]. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 25(4): 730-755.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
QUANZ M E, WALKER T R, OAKES K, et al., 2021. Effects of industrial effluent on wetland macroinvertebrate community structures near a wastewater treatment facility[J]. Ecological Indicators, 127: 107709.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
RICHARDSON J S, 2019. Biological diversity in headwater streams[J]. Water, 11(2): 366.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
SARREMEJANE R, MYKRA H, BONADA N, et al., 2017. Habitat connectivity and dispersal ability drive the assembly mechanisms of macroinvertebrate communities in river networks[J]. Freshwater Biology, 62(6): 1073-1082.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
STRAHLER A N, 1957. Quantitative analysis of watershed geomorphology[J]. Eos, Transactions American Geophysical Union, 38: 913-920.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
TRIGAL C, DEGERMAN E, 2015. Multiple factors and thresholds explaining fish species distributions in lowland streams[J]. Global Ecology and Conservation, 4: 589-601.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
TURUNEN J, AROVIITA J, MARTTILA H, et al., 2017. Differential responses by stream and riparian biodiversity to in-stream restoration of forestry-impacted streams[J]. Journal of Applied Ecology, 54(5): 1505-1514.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
WANG X G, WIEGAND T, ANDERSON-TEIXEIRA K J, et al., 2018. Ecological drivers of spatial community dissimilarity, species replacement and species nestedness across temperate forests[J]. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 27(5): 581-592.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
WILLIAMS-SUBIZA E A, BRAND C, MISERENDINO M L, 2020. Metacommunity structure analysis reveals nested patterns in deconstructed macroinvertebrates assemblages[J]. Ecological Entomology, 45(6): 1284-1295.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
ZHENG B, YIN X W, 2023. Assembly mechanism of macroinvertebrate metacommunities and ecological factors of multiple aspects of beta diversity in a boreal river basin, China[J]. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 11: 1131403.
DOI URL |
| [44] | 李佳静, 刘威, 邓培雁, 2020. 柳江流域不同水文季节水质对附生硅藻群落的影响研究[J]. 生态科学, 39(1): 10-19. |
| LI J J, LIU W, DENG P Y, 2020. The effects of water quality on epilithic diatom community in different hydrological seasons in Liujiang River Basin[J]. Ecological Science, 39(1): 10-19. | |
| [45] | 李鑫, 邓培雁, 刘威, 2021. 柳江流域大型底栖动物群落结构及其与水质因子的关系[J]. 华南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 53(5): 53-61. |
| LI X, DENG P Y, LIU W, 2021. The Macrobenthos community structure and its relationships with water quality factors in the Liujiang River basin[J]. Journal of South China Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 53(5): 53-61. | |
| [46] | 刘建康, 1999. 高级水生生物学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 241. |
| LIU J K, 1999. Advanced hydrobiology[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 241. | |
| [47] | 卢玉典, 张盛, 莫飞龙, 等, 2023. 广西柳江鱼类资源调查[J]. 农业与技术, 43(6): 102-107. |
| LU Y D, ZHANG S, MO F L, et al., 2023. Investigation of fish resources in Liujiang River, Guangxi[J]. Agriculture and Technology, 43(6): 102-107. | |
| [48] | 国家环境保护总局, 2002. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 第4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| State Environmental Protection Administration, 2002. Water and wastewater monitoring and analysis method[M]. The fourth edition. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. | |
| [49] | 国家环境保护总局, 国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 2002. 地表水环境质量标准: GB 3838—2002 [S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| State Environmental Protection Administration, General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine, 2002. Environmental quality standards for surface water: GB 3838—2002 [S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. | |
| [50] | 杨钙仁, 张秀清, 蔡德所, 等, 2012. 广西主要人工林凋落物分解过程及其对淋溶水质的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 23(1): 9-16. |
| YANG G R, ZHANG X Q, CAI D S, et al., 2012. Litter decomposition of dominant plantations in Guangxi and its effects on leachate quality[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 23(1): 9-16. | |
| [51] | 杨昆, 贺磊, 许乃中, 等, 2016. 柳江流域生态系统服务价值的影响研究[J]. 生态科学, 35(4): 148-156. |
| YANG K, HE L, XU N Z, et al., 2016. The study of ecosystem service values of Liujiang River basin[J]. Ecological Science, 35(4): 148-156. | |
| [52] | 张婉军, 辛存林, 于奭, 等, 2021. 柳江流域河流溶解态重金属时空分布及污染评价[J]. 环境科学, 42(9): 4234-4245. |
| ZHANG W J, XIN C L, YU S, et al., 2021. Spatial and temporal distribution and pollution evaluation of soluble heavy metals in Liujiang River basin[J]. Environmental Science, 42(9): 4234-4245. | |
| [53] | 周长发, 归鸿, 周开亚, 2003. 中国蜉蝣目稚虫科检索表 (昆虫纲)[J]. 南京师大学报 (自然科学版), 26(3): 65-68. |
| ZHOU C F, GUI H, ZHOU K Y, 2003. Larval Key to Families of Ephemeroptera from China (Insecta)[J]. Journal of Nanjing Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 26(3): 65-68. |
| [1] | JIANG Yongwei, DING Zhenjun, YUAN Junbin, ZHANG Zheng, LI Yang, WEN Qingchun, WANG Yeyao, JIN Xiaowei. Study on Benthic Macroinvertebrates Community Structure and Water Quality Evaluation in Main Rivers of Liaoning Province [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 969-979. |
| [2] | WANG Yun, ZHENG Xilai, CAO Min, LI Lei, SONG Xiaoran, LIN Xiaolei, GUO Kai. Study on Denitrification Performance and Control Factors in Brackish-Freshwater Transition Zone of Coastal Aquifer [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 980-988. |
| [3] | KOU Zhu, QING Chun, YUAN Changguo, LI Ping. Diversity and Distribution of Sulfur Oxidizing Bacteria in Hot Springs of Northeast Tibet, China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 989-1000. |
| [4] | WANG Xinyu, GAO Dengzhou, LIU Bolin, WANG Bin, ZHENG Yanling, LI Xiaofei, HOU Lijun. The Tidal-cycle Variation and Influencing Factors of Dark Carbon Fixation Process in the Yangtze Estuary [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 733-743. |
| [5] | LI Shanjia, WANG Xingmin, LIU Haifeng, SUN Mengge, LEI Yuxin. Diversity of Desert Plants in Hexi Corridor and Its Response to Environmental Factors [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 429-438. |
| [6] | CHEN Le, WEI Wei. Spatiotemporal Changes in Land Use and Habitat Quality in A Typical Dryland Watershed of Northwest China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(9): 1909-1918. |
| [7] | CAI Guojun, YUAN Guixiang, FU Hui. Status and Trends on Ecological Networks Research: A Review Based on Bibliometric Analysis [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(8): 1690-1699. |
| [8] | WANG Lei, WEN Yuanguang, ZHOU Xiaoguo, ZHU Hongguang, SUN Dongjing. Effects of Mixing Eucalyptus urophylla×E. grandis with Castanopsis hystrix on Understory Vegetation and Soil Properties [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(7): 1340-1349. |
| [9] | JIANG Nihao, ZHANG Shihao, ZHANG Shihan. Interspecific Associations and Environmental Interpretation of the Dominant Species of the Communities Invaded by Ageratina adenophora in Ailao Mountains [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(7): 1370-1382. |
| [10] | XIA Kai, DENG Pengfei, MA Ruihao, WANG Fei, WEN Zhengyu, XU Xiaoniu. Changes of Soil Bacterial Community Structure and Diversity from Conversion of Masson Pine Secondary Forest to Slash Pine and Chinese Fir Plantations [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 460-469. |
| [11] | XUE Wenkai, ZHU Pan, DE Ji, GUO Xiaofang. Study on the Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of the Dominant Species of Cultivable Filamentous Fungi in Nam Co Lake [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(12): 2331-2340. |
| [12] | LI Cong, LÜ Jinghua, LU Mei, YANG Zhidong, LIU Pan, REN Yulian, DU Fan. Responses of Soil Bacterial Communities to Vertical Vegetarian Zone Changes in the Subtropical Forests, Southeastern Yunnan [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(10): 1971-1983. |
| [13] | LIU Xiaoju, CHU Jiangtao, ZHANG Yue, SHAN Qi. Effects of Environmental Factors and Fire Disturbance Factors on Distribution of Chamerion angustifolium in Kanas Taiga [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(1): 37-43. |
| [14] | CAI Xi'an, HUANG Juan, WU Tong, LIU Juxiu, JIANG Fen, WANG Senhao. Study on Methane Emission from Tree Leaves [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(9): 1842-1847. |
| [15] | ZONG Ning, SHI Peili, ZHU Juntao. Changes of Plant Community Composition and Niche Characteristics during Desertification Process in An Alpine Steppe [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(8): 1561-1570. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
