Ecology and Environment ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (1): 1-11.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.01.001
• Research Article • Next Articles
MA Yuan1,2( ), TIAN Lulu1,2, LÜ Jie3,*(
), TIAN Lulu1,2, LÜ Jie3,*( ), LIU Pei1,2, ZHANG Xu4, LI Eryang1,2, ZHANG Qinghang1,2
), LIU Pei1,2, ZHANG Xu4, LI Eryang1,2, ZHANG Qinghang1,2
Received:2023-07-10
Online:2024-01-18
Published:2024-03-19
Contact:
Lü Jie
马媛1,2( ), 田路露1,2, 吕杰3,*(
), 田路露1,2, 吕杰3,*( ), 柳沛1,2, 张旭4, 李二阳1,2, 张清航1,2
), 柳沛1,2, 张旭4, 李二阳1,2, 张清航1,2
通讯作者:
吕杰
作者简介:马媛(1977年生),女,副教授,主要从事土壤微生物方面的研究。E-mail: xjmyuan@sina.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
MA Yuan, TIAN Lulu, LÜ Jie, LIU Pei, ZHANG Xu, LI Eryang, ZHANG Qinghang. Soil Microbial Communities and Influencing Factors of Picea schrenkiana Forest on the Northern Slope of Tianshan Mountains[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(1): 1-11.
马媛, 田路露, 吕杰, 柳沛, 张旭, 李二阳, 张清航. 天山北坡雪岭云杉森林土壤微生物群落及影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(1): 1-11.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.01.001
| 类群 | 区域 | Richness指数 | Chao1指数 | ACE指数 | Pielou指数 | Shannon 指数 | Simpson指数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 古菌 | TW | 770.6±37.04b | 981.95±55.62a | 1014.05±64.84a | 0.79±0.01a | 5.26±0.06a | 0.99±0a |
| TM | 823.33±57.17a | 1045.4±97a | 1080.66±100.45a | 0.78±0.02a | 5.24±0.07a | 0.99±0a | |
| TE | 781.44±45.16ab | 1003.05±53.68a | 1044.69±49.08a | 0.79±0.01a | 5.25±0.03a | 0.99±0a | |
| 细菌 | TW | 14010.93±352.42a | 16000.54±592.88a | 16049.53±618.06a | 0.80±0.01b | 7.68±0.10b | 1±0b |
| TM | 14386.42±525.86a | 16654.17±916.42a | 16715.64±945.73a | 0.81±0.01a | 7.79±0.08a | 1±0a | |
| TE | 14227.89±421.68a | 16360.28±432.21a | 16404.91±462.63a | 0.81±0.01ab | 7.72±0.08ab | 1±0a | |
| 真菌 | TW | 1599.33±199.69b | 2409.73±510.61b | 2559.33±578.9b | 0.79±0.05a | 5.84±0.32a | 0.99±0.02a |
| TM | 1848±258.26a | 3010.62±587.34a | 3271.16±739.05a | 0.79±0.01a | 5.95±0.02a | 1±0a | |
| TE | 1818.89±314.98ab | 2759.54±561.59ab | 2924.43±631.94ab | 0.79±0.03a | 5.93±0.1a | 1±0a |
Table 1 Soil microbial alpha diversity under P. schrenkiana forest on the northern slope of Tianshan Mountains
| 类群 | 区域 | Richness指数 | Chao1指数 | ACE指数 | Pielou指数 | Shannon 指数 | Simpson指数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 古菌 | TW | 770.6±37.04b | 981.95±55.62a | 1014.05±64.84a | 0.79±0.01a | 5.26±0.06a | 0.99±0a |
| TM | 823.33±57.17a | 1045.4±97a | 1080.66±100.45a | 0.78±0.02a | 5.24±0.07a | 0.99±0a | |
| TE | 781.44±45.16ab | 1003.05±53.68a | 1044.69±49.08a | 0.79±0.01a | 5.25±0.03a | 0.99±0a | |
| 细菌 | TW | 14010.93±352.42a | 16000.54±592.88a | 16049.53±618.06a | 0.80±0.01b | 7.68±0.10b | 1±0b |
| TM | 14386.42±525.86a | 16654.17±916.42a | 16715.64±945.73a | 0.81±0.01a | 7.79±0.08a | 1±0a | |
| TE | 14227.89±421.68a | 16360.28±432.21a | 16404.91±462.63a | 0.81±0.01ab | 7.72±0.08ab | 1±0a | |
| 真菌 | TW | 1599.33±199.69b | 2409.73±510.61b | 2559.33±578.9b | 0.79±0.05a | 5.84±0.32a | 0.99±0.02a |
| TM | 1848±258.26a | 3010.62±587.34a | 3271.16±739.05a | 0.79±0.01a | 5.95±0.02a | 1±0a | |
| TE | 1818.89±314.98ab | 2759.54±561.59ab | 2924.43±631.94ab | 0.79±0.03a | 5.93±0.1a | 1±0a |
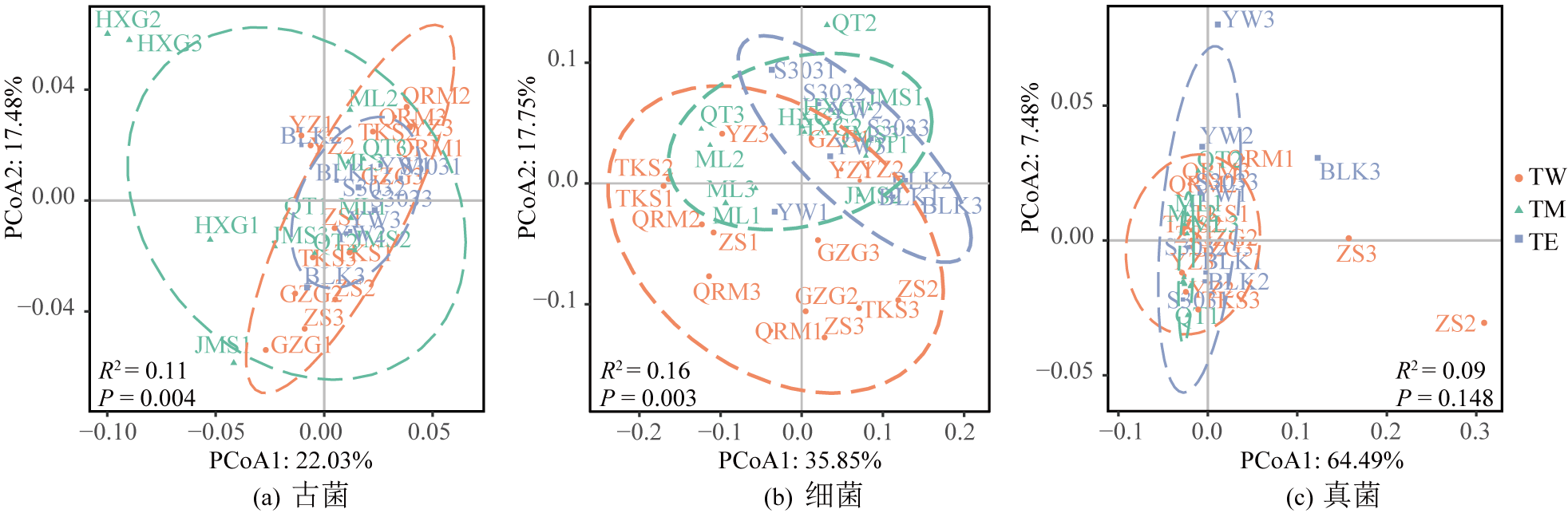
Figure 5 Principal coordinate analysis of soil microbial community structure in P. schrenkiana forest on the northern slopes of Tianshan Mountains in different regions

Figure 6 Correlation analysis between soil microbial community structure and environmental factors of P. schrenkiana forest soils in Tianshan Mountains
| 类群 | 多样性指数 | 有机碳 | 总氮 | 总磷 | 总钾 | 硝态氮 | 铵态氮 | 微生物碳 | 微生物氮 | pH | 年均降水量 | 年均摄氏温度 | 土壤湿度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 古菌 | Richness | −0.450** 2) | −0.377* | −0.157 | 0.149 | −0.180 | −0.196 | −0.173 | −0.135 | 0.085 | −0.079 | −0.236 | −0.028 |
| Chao1 | −0.301 | −0.258 | −0.322 | 0.193 | −0.050 | −0.126 | −0.079 | −0.018 | 0.289 | 0.078 | −0.094 | 0.198 | |
| ACE | −0.336* 1) | −0.433** | −0.245 | 0.081 | −0.156 | −0.081 | −0.215 | −0.179 | 0.225 | −0.105 | −0.296 | 0.081 | |
| Shannon | −0.033 | 0.172 | 0.225 | −0.003 | 0.038 | −0.053 | −0.066 | 0.172 | −0.648*** 3) | −0.061 | 0.032 | −0.372* | |
| Simpson | 0.054 | 0.252 | 0.172 | 0.082 | 0.069 | −0.040 | 0.095 | 0.170 | −0.371* | −0.196 | 0.139 | −0.413* | |
| Pielou | 0.125 | 0.286 | 0.258 | −0.056 | 0.097 | 0.019 | −0.001 | 0.203 | −0.617*** | −0.030 | 0.109 | −0.330* | |
| 细菌 | Richness | −0.150 | −0.054 | 0.340* | −0.147 | −0.167 | −0.038 | 0.037 | 0.022 | −0.256 | −0.055 | −0.585*** | 0.068 |
| Chao1 | −0.176 | −0.125 | 0.213 | −0.012 | −0.122 | −0.111 | 0.086 | 0.002 | −0.016 | −0.031 | −0.535*** | 0.189 | |
| ACE | −0.178 | −0.096 | 0.252 | −0.045 | −0.143 | −0.106 | 0.088 | 0.012 | −0.067 | −0.041 | −0.547*** | 0.146 | |
| Shannon | −0.300 | −0.359* | 0.055 | −0.142 | −0.349* | 0.009 | −0.243 | −0.278 | −0.002 | −0.308 | −0.377* | −0.253 | |
| Simpson | −0.099 | −0.360* | −0.127 | −0.061 | −0.348* | 0.158 | −0.050 | −0.518** | 0.534*** | −0.393* | −0.137 | −0.084 | |
| Pielou | −0.299 | −0.386* | −0.016 | −0.125 | −0.350* | 0.019 | −0.279 | −0.314 | 0.056 | −0.330* | −0.286 | −0.296 | |
| 真菌 | Richness | −0.169 | 0.124 | 0.202 | 0.218 | 0.109 | −0.326 | 0.429** | 0.255 | 0.213 | −0.159 | −0.540*** | 0.226 |
| Chao1 | −0.285 | −0.027 | 0.125 | 0.157 | −0.019 | −0.300 | 0.292 | 0.179 | 0.200 | −0.122 | −0.546*** | 0.239 | |
| ACE | −0.256 | −0.049 | 0.128 | 0.110 | −0.054 | −0.257 | 0.265 | 0.155 | 0.193 | −0.108 | −0.544*** | 0.245 | |
| Shannon | 0.024 | −0.045 | 0.088 | 0.052 | 0.032 | −0.167 | −0.009 | 0.080 | −0.093 | −0.125 | −0.418* | −0.127 | |
| Simpson | 0.013 | −0.027 | 0.094 | 0.090 | 0.026 | −0.178 | 0.025 | 0.095 | −0.058 | −0.130 | −0.362* | −0.135 | |
| Pielou | 0.098 | −0.089 | 0.000 | −0.032 | −0.014 | −0.032 | −0.188 | −0.021 | −0.189 | −0.054 | −0.172 | −0.229 |
Table 2 Correlation coefficients between soil microbial diversity index and environmental factors
| 类群 | 多样性指数 | 有机碳 | 总氮 | 总磷 | 总钾 | 硝态氮 | 铵态氮 | 微生物碳 | 微生物氮 | pH | 年均降水量 | 年均摄氏温度 | 土壤湿度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 古菌 | Richness | −0.450** 2) | −0.377* | −0.157 | 0.149 | −0.180 | −0.196 | −0.173 | −0.135 | 0.085 | −0.079 | −0.236 | −0.028 |
| Chao1 | −0.301 | −0.258 | −0.322 | 0.193 | −0.050 | −0.126 | −0.079 | −0.018 | 0.289 | 0.078 | −0.094 | 0.198 | |
| ACE | −0.336* 1) | −0.433** | −0.245 | 0.081 | −0.156 | −0.081 | −0.215 | −0.179 | 0.225 | −0.105 | −0.296 | 0.081 | |
| Shannon | −0.033 | 0.172 | 0.225 | −0.003 | 0.038 | −0.053 | −0.066 | 0.172 | −0.648*** 3) | −0.061 | 0.032 | −0.372* | |
| Simpson | 0.054 | 0.252 | 0.172 | 0.082 | 0.069 | −0.040 | 0.095 | 0.170 | −0.371* | −0.196 | 0.139 | −0.413* | |
| Pielou | 0.125 | 0.286 | 0.258 | −0.056 | 0.097 | 0.019 | −0.001 | 0.203 | −0.617*** | −0.030 | 0.109 | −0.330* | |
| 细菌 | Richness | −0.150 | −0.054 | 0.340* | −0.147 | −0.167 | −0.038 | 0.037 | 0.022 | −0.256 | −0.055 | −0.585*** | 0.068 |
| Chao1 | −0.176 | −0.125 | 0.213 | −0.012 | −0.122 | −0.111 | 0.086 | 0.002 | −0.016 | −0.031 | −0.535*** | 0.189 | |
| ACE | −0.178 | −0.096 | 0.252 | −0.045 | −0.143 | −0.106 | 0.088 | 0.012 | −0.067 | −0.041 | −0.547*** | 0.146 | |
| Shannon | −0.300 | −0.359* | 0.055 | −0.142 | −0.349* | 0.009 | −0.243 | −0.278 | −0.002 | −0.308 | −0.377* | −0.253 | |
| Simpson | −0.099 | −0.360* | −0.127 | −0.061 | −0.348* | 0.158 | −0.050 | −0.518** | 0.534*** | −0.393* | −0.137 | −0.084 | |
| Pielou | −0.299 | −0.386* | −0.016 | −0.125 | −0.350* | 0.019 | −0.279 | −0.314 | 0.056 | −0.330* | −0.286 | −0.296 | |
| 真菌 | Richness | −0.169 | 0.124 | 0.202 | 0.218 | 0.109 | −0.326 | 0.429** | 0.255 | 0.213 | −0.159 | −0.540*** | 0.226 |
| Chao1 | −0.285 | −0.027 | 0.125 | 0.157 | −0.019 | −0.300 | 0.292 | 0.179 | 0.200 | −0.122 | −0.546*** | 0.239 | |
| ACE | −0.256 | −0.049 | 0.128 | 0.110 | −0.054 | −0.257 | 0.265 | 0.155 | 0.193 | −0.108 | −0.544*** | 0.245 | |
| Shannon | 0.024 | −0.045 | 0.088 | 0.052 | 0.032 | −0.167 | −0.009 | 0.080 | −0.093 | −0.125 | −0.418* | −0.127 | |
| Simpson | 0.013 | −0.027 | 0.094 | 0.090 | 0.026 | −0.178 | 0.025 | 0.095 | −0.058 | −0.130 | −0.362* | −0.135 | |
| Pielou | 0.098 | −0.089 | 0.000 | −0.032 | −0.014 | −0.032 | −0.188 | −0.021 | −0.189 | −0.054 | −0.172 | −0.229 |
| [1] |
BARDGETT R D, VAN DER PUTTEN W H, 2013. Belowground biodiversity and ecosystem functioning[J]. Nature, 515(7528): 505-511.
DOI |
| [2] |
BUEE M, REICH M, MURAT C, et al., 2009. Pyrosequencing analyses of forest soils reveal an unexpectedly high fungal diversity[J]. New Phytologist, 184(2): 449-456.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
EDWARDS K A, MCCULLOCH J, KERSHAW G P, et al., 2006. Soil microbial and nutrient dynamics in a wet arctic sedge meadow in latewinter and early spring[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 38(9): 2843-2851.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
GREEN J L, HOLMES A J, WESTOBY M, et al., 2004. Spatial scaling of microbial eukaryote diversity[J]. Nature, 432(7018): 747-750.
DOI |
| [5] |
JENKINSON D S, POWLSON D S, 1976. The effects of biocidal treatments on metabolism in soil-V: A method for measuring soil biomass[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 8(3): 179-188.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
JONES D L, WILLETT V B, 2006. Experimental evaluation of methods to quantify dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) and dissolved organic carbon (DOC) in soil[J]. Soil Biology & Biochemistry. 38(5): 991-999.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
KACHURINA O M, ZHANG H L, RAUN W R, et al., 2000. Simultaneous determination of soil aluminum, ammonium‐ and nitrate‐nitrogen using 1 M potassium chloride extraction[J]. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis. 31(7-8): 893-903.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
LI J Q, ZHU T, SINGH B K, et al., 2021. Key microorganisms mediate soil carbon-climate feedbacks in forest ecosystems[J]. Science Bulletin, 66(19): 2036-2044.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
NACHIMUTHU G, KING K, KRISTIANSEN P, et al., 2007. Comparison of methods for measuring soil microbial activity using cotton strips and a respirometer[J]. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 69(2): 322-329.
PMID |
| [10] |
PREEM J K, TRUU J, TRUU M, et al., 2012. Bacterial community structure and its relationship to soil physico-chemical characteristics in alder stands with different management histories[J]. Ecological Engineering, 49: 10-17.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
SICILIANO S D, PALMERA S, WINSLEY T, et al., 2014. Soil fertility is associated with fungal and bacterial richness, whereas pH is associated with community composition in polar soil microbial communities[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 78: 10-20.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
TAN H, BARRET M, MOOIJ M J, et al., 2013. Long-term phosphorus fertilisation increased the diversity of the total bacterial community and the phoD phosphorus mineraliser group in pasture soils[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 49(6): 661-672.
DOI URL |
| [13] | WOOD D E, SALZBERG S L, 2014. Kraken: Ultrafast metagenomic sequence classification using exact alignments[J]. Genome Biology, 15(3): 1-12. |
| [14] |
WU L W, ZHANG Y, GUO X, et al., 2022. Reduction of microbial diversity in grassland soil is driven by long-term climate warming[J]. Nature Microbiology, 7(7): 1054-1062.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
XIA Z W, BAI E, WANG Q K, et al., 2016. Biogeographic distribution patterns of bacteria in typical Chinese forest soils[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 7: 1106.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
ZHANG B P, ZHOU C H, CHAN S P, 2003. The geo-info-spectrum of montane altitudinal belts in China[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 58(2): 163-171.
DOI |
| [17] | 陈曦, 许文强, 罗格平, 等, 2008. 天山北坡不同环境条件下雪岭云杉 (Picea schrenkiana) 林限土壤属性[J]. 生态学报, 28(1): 53-61. |
| CHEN X, XU W Q, LUO G P, et al., 2008. Soil properties at the tree limits of Picea schrenkiana forests in response to varying environmental conditions on the northern slope of Tianshan mountains[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 28(1): 53-61. | |
| [18] | 陈新, 2019. 季节性雪被下新疆天山雪岭云杉林凋落物分解与土壤微生物的关系[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆大学. |
| CHEN X, 2019. Relationship between litter decomposition and soil microbes of Schrenk sprucein forest under seasonal snowfall in Tianshan Mountains[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang University. | |
| [19] | 丛微, 于晶晶, 喻海茫, 等, 2022. 不同气候带森林土壤微生物多样性和群落构建特征[J]. 林业科学, 58(2): 70-79. |
| CONG W, YU J J, YU H M, et al., 2022. Diversity and community assembly of forest soil microorganisms in different climatic zones[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 58(2): 70-79. | |
| [20] | 高本强, 齐瑞, 赵阳, 等, 2022. 洮河上游不同海拔紫果云杉根际与非根际土壤细菌多样性及影响因子[J]. 微生物学通报, 49(9): 3604-3616. |
| GAO B Q, QI R, ZHAO Y, et al., 2022. Diversity and influencing factors of bacteria in rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soil of Picea purpurea at different altitudes in the upstream of Taohe River[J]. Microbiology China, 49(9): 3604-3616. | |
| [21] | 胡波, 张会兰, 王彬, 等, 2015. 重庆缙云山地区森林土壤酸化特征[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 24(2): 300-309. |
| HU B, ZHANG H L, WANG B, et al., 2015. Analysis on the forest soil acidification and mechanisms in Chongqing Jinyun Mountain[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 24(2): 300-309. | |
| [22] | 李宝, 常顺利, 孙雪娇, 等, 2022. 天山北坡雪岭云杉森林的蒸腾耗水规律[J]. 西部林业科学, 51(5): 106-112. |
| LI B, CHANG S L, SUN X J, et al., 2022. Transpiration and water consumption patterns of Picea schrenkiana forests in northern Tianshan[J]. Journal of West China Forestry Science, 51(5): 106-112. | |
| [23] | 罗明, 庞峻峰, 李叙勇, 等, 1997. 新疆天山云杉林区森林土壤微生物学特性及酶活性[J]. 生态学杂志 (1): 27-31. |
| LUO M, PANG J F, LI X Y, et al., 1997. Microbiological characteristics and enzymes activity of the forest-soil in Picea schrenkiana var·tianshanican in Xinjiang[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology (1): 27-31. | |
| [24] | 罗庆辉, 徐泽源, 许仲林, 等, 2020. 天山雪岭云杉林生物量估测及空间格局分析[J]. 生态学报, 40(15): 5288-5297. |
| LUO Q H, XU Z Y, XU Z L, et al., 2020. Estimation and spatial pattern analysis of biomass of Picea schrenkiana forests[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(15): 5288-5297. | |
| [25] | 国家林业局, 2015. 森林土壤钾的测定: LY/T 1234—2015[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社: 1-8. |
| State Forestry Administration, 2015, Potassium determination methods of forest soil: LY/T 1234—2015[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China: 1-8. | |
| [26] | 毛克彪, 2021. 中国土壤水分数据集 (2002-2018)[DB/OL]. 北京: 国家青藏高原科学数据中心, [2020-09-26]. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4738556. |
| MAO K B, 2021. Soil Moisture in China dataset (2002-2018)[DB/OL]. Beijing: National Tibetan Plateau Data Center, [2020-09-26]. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4738556. . | |
| [27] | 王瑞琨, 2018. 用电位法测定土壤pH值[J]. 山西化工, 38(3): 64-65, 76. |
| WANG R K, 2018. Determination of soil pH by potentiometry[J]. Shanxi Chemical Industry, 38(3): 64-65, 76. | |
| [28] | 吴尊凤, 史应武, 娄恺, 等, 2012. 天山北坡垂直自然带土壤古菌多样性分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 49(3): 488-495. |
| WU Z F, SHI Y W, LOU K, et al., 2012. Archaeal diversity along vertical natural belt in the northern slope of Tianshain Mountain[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 49(3): 488-495. | |
| [29] | 向仕敏, 陆梅, 徐柳斌, 等, 2008. 5种林分类型林地土壤氮含量与其土壤微生物学性质的研究[J]. 西部林业科学, 37(1): 41-45. |
| XIANG S M, LU M, XU L B, et al., 2008. Nitrogen content and microbial characteristics of forest soil of 5 stands[J]. Journal of West China Forestry Science, 37(1): 41-45. | |
| [30] | 向晓黎, 马小宁, 魏向利, 等, 2015. 土壤全磷测定方法要点分析[J]. 农业灾害研究, 5(5): 30-31. |
| XIANG X L, MA X N, WEI X L, et al., 2015. Analysis of essentials for the determination of soil total phosphorus[J]. Journal of Agricultural Catastrophology, 5(5): 30-31. | |
| [31] | 许光辉, 郑洪元, 1986. 土壤微生物分析方法手册[M]. 北京: 农业出版社. |
| XU G H, ZHENG H Y, 1986. Methods manual for soil microbiological analysis[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press. | |
| [32] | 于天仁, 1988. 中国土壤的酸度特点和酸化问题[J]. 土壤通报, 18(2): 49-51. |
| YU T R, 1988. Acidity characteristics and acidification problems of soil in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 18(2): 49-51. | |
| [33] | 郑拴丽, 2016. 新疆天山雪岭云杉和阿尔泰山西伯利亚落叶松生物量、碳储量及空间分布格局研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆大学. |
| ZHENG S L, 2016. Research on biomass, carbon storage and spatial distribution of Picea schrenkiana and Larix sibirica in Xinjiang Tianshan and altay mountains[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang University. | |
| [34] | 周虹, 2020. 典型沙区生物土壤结皮微生物群落结构与功能研究[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院. |
| ZHOU H, 2020. The microbial community structure and function of biological soil crusts in typical sandland areas[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry. | |
| [35] |
周煜杰, 贾夏, 赵永华, 等, 2020. 森林生态系统土壤真菌群落及其影响因素研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(8): 1703-1712.
DOI |
| ZHOU Y J, JIA X, ZHAO Y H, et al., 2020. A review on soil fungal community and its affecting factors in forest ecosystem[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29(8): 1703-1712. |
| [1] | KOU Zhu, QING Chun, YUAN Changguo, LI Ping. Diversity and Distribution of Sulfur Oxidizing Bacteria in Hot Springs of Northeast Tibet, China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 989-1000. |
| [2] | WANG Yun, ZHENG Xilai, CAO Min, LI Lei, SONG Xiaoran, LIN Xiaolei, GUO Kai. Study on Denitrification Performance and Control Factors in Brackish-Freshwater Transition Zone of Coastal Aquifer [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 980-988. |
| [3] | JIANG Yongwei, DING Zhenjun, YUAN Junbin, ZHANG Zheng, LI Yang, WEN Qingchun, WANG Yeyao, JIN Xiaowei. Study on Benthic Macroinvertebrates Community Structure and Water Quality Evaluation in Main Rivers of Liaoning Province [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 969-979. |
| [4] | WANG Xinyu, GAO Dengzhou, LIU Bolin, WANG Bin, ZHENG Yanling, LI Xiaofei, HOU Lijun. The Tidal-cycle Variation and Influencing Factors of Dark Carbon Fixation Process in the Yangtze Estuary [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 733-743. |
| [5] | ZHOU Jiacheng, SONG Zhibin, MIAO Peng, TAN Lu, TANG Tao. Differences in Benthic Macroinvertebrate Communities and Their Driving Forces between the Edge and Center Positions of the Liujiang River Network [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(10): 1794-1801. |
| [6] | JIANG Nihao, ZHANG Shihao, ZHANG Shihan. Interspecific Associations and Environmental Interpretation of the Dominant Species of the Communities Invaded by Ageratina adenophora in Ailao Mountains [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(7): 1370-1382. |
| [7] | XIA Kai, DENG Pengfei, MA Ruihao, WANG Fei, WEN Zhengyu, XU Xiaoniu. Changes of Soil Bacterial Community Structure and Diversity from Conversion of Masson Pine Secondary Forest to Slash Pine and Chinese Fir Plantations [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 460-469. |
| [8] | XUE Wenkai, ZHU Pan, DE Ji, GUO Xiaofang. Study on the Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of the Dominant Species of Cultivable Filamentous Fungi in Nam Co Lake [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(12): 2331-2340. |
| [9] | LI Cong, LÜ Jinghua, LU Mei, YANG Zhidong, LIU Pan, REN Yulian, DU Fan. Responses of Soil Bacterial Communities to Vertical Vegetarian Zone Changes in the Subtropical Forests, Southeastern Yunnan [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(10): 1971-1983. |
| [10] | LIU Xiaoju, CHU Jiangtao, ZHANG Yue, SHAN Qi. Effects of Environmental Factors and Fire Disturbance Factors on Distribution of Chamerion angustifolium in Kanas Taiga [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(1): 37-43. |
| [11] | CAI Xi'an, HUANG Juan, WU Tong, LIU Juxiu, JIANG Fen, WANG Senhao. Study on Methane Emission from Tree Leaves [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(9): 1842-1847. |
| [12] | SUN Xuejiao, LI Jimei, ZHANG Yutao, LI Xiang, LU Jianjiang, SHE Fei. Characteristics and Influence of Runoff and Sediment Yield in Mountain Forest on the North Slope of Tianshan Mountains [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(9): 1821-1830. |
| [13] | YAO Shiting, LU Guangxin, DENG Ye, DANG Ning, WANG Yingcheng, ZHANG Haijuan, YAN Huilin. Effects of Simulated Warming on Soil Fungal Community Composition and Diversity [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(7): 1404-1411. |
| [14] | Xue Liyuan, Liu Zhiliang, Song Wei, An Ying, Yuan Xiaobo, Chen Xiao. Spatial Distribution of Aurelia sp. Ephyrae and Its Relationship with Environmental Factors in the Coastal Waters of Qinhuangdao in Spring, 2020 [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(6): 1240-1248. |
| [15] | ZHENG Shiyu, ZHANG Lvshui, GUO Xiaomin, HUANG Zijun, XIAO Yihua. Spatial and Temporal Variations of Negative Oxygen Ions in the Air and Environmental Influencing Factors in Forest Environment with Different Canopy Densities: A Case Study of Maofeng Mountain in Guangzhou [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(11): 2204-2212. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
