Ecology and Environment ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (11): 1756-1767.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.11.010
• Research Article [Environmental Science] • Previous Articles Next Articles
YAN Siyao1,2( ), YANG Guang1,2, BAI Yan1,2, GAO Yifan1,2, LIANG Luyu1,2, GONG Feng1,2, HUANG Guoyong1,2, PAN Dandan1,2, LI Xiaomin1,2,*(
), YANG Guang1,2, BAI Yan1,2, GAO Yifan1,2, LIANG Luyu1,2, GONG Feng1,2, HUANG Guoyong1,2, PAN Dandan1,2, LI Xiaomin1,2,*( )
)
Received:2024-06-29
Online:2024-11-18
Published:2024-12-06
Contact:
LI Xiaomin
颜思瑶1,2( ), 杨光1,2, 白艳1,2, 高一帆1,2, 梁露予1,2, 龚凤1,2, 黄国勇1,2, 潘丹丹1,2, 李晓敏1,2,*(
), 杨光1,2, 白艳1,2, 高一帆1,2, 梁露予1,2, 龚凤1,2, 黄国勇1,2, 潘丹丹1,2, 李晓敏1,2,*( )
)
通讯作者:
李晓敏
作者简介:颜思瑶(1999年生),女,硕士,研究方向为土壤重金属转化的生物调控研究。E-mail: 2249538170@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
YAN Siyao, YANG Guang, BAI Yan, GAO Yifan, LIANG Luyu, GONG Feng, HUANG Guoyong, PAN Dandan, LI Xiaomin. Effect of Rice on Arsenic Transformation in Paddy Soil under Flooded Conditions[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(11): 1756-1767.
颜思瑶, 杨光, 白艳, 高一帆, 梁露予, 龚凤, 黄国勇, 潘丹丹, 李晓敏. 淹水条件下水稻对土壤砷转化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(11): 1756-1767.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.11.010
| 参数 | 单位 | 处理 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soil LAs | Soil HAs | ||
| pH | - | 5.47 | 4.99 |
| 总砷 | mg·kg-1 | 15.5 | 52.1 |
| 总铁 | g·kg-1 | 16.3 | 16.8 |
| 总钙 | mg·kg-1 | 999 | 440 |
| 总镁 | mg·kg-1 | 997 | 195 |
| 总钾 | g·kg-1 | 32.9 | 15.0 |
| 总磷 | mg·kg-1 | 409 | 894 |
| 总有机质 | g·kg-1 | 20.2 | 24.3 |
Table 1 Physicochemical properties of the tested soils
| 参数 | 单位 | 处理 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soil LAs | Soil HAs | ||
| pH | - | 5.47 | 4.99 |
| 总砷 | mg·kg-1 | 15.5 | 52.1 |
| 总铁 | g·kg-1 | 16.3 | 16.8 |
| 总钙 | mg·kg-1 | 999 | 440 |
| 总镁 | mg·kg-1 | 997 | 195 |
| 总钾 | g·kg-1 | 32.9 | 15.0 |
| 总磷 | mg·kg-1 | 409 | 894 |
| 总有机质 | g·kg-1 | 20.2 | 24.3 |
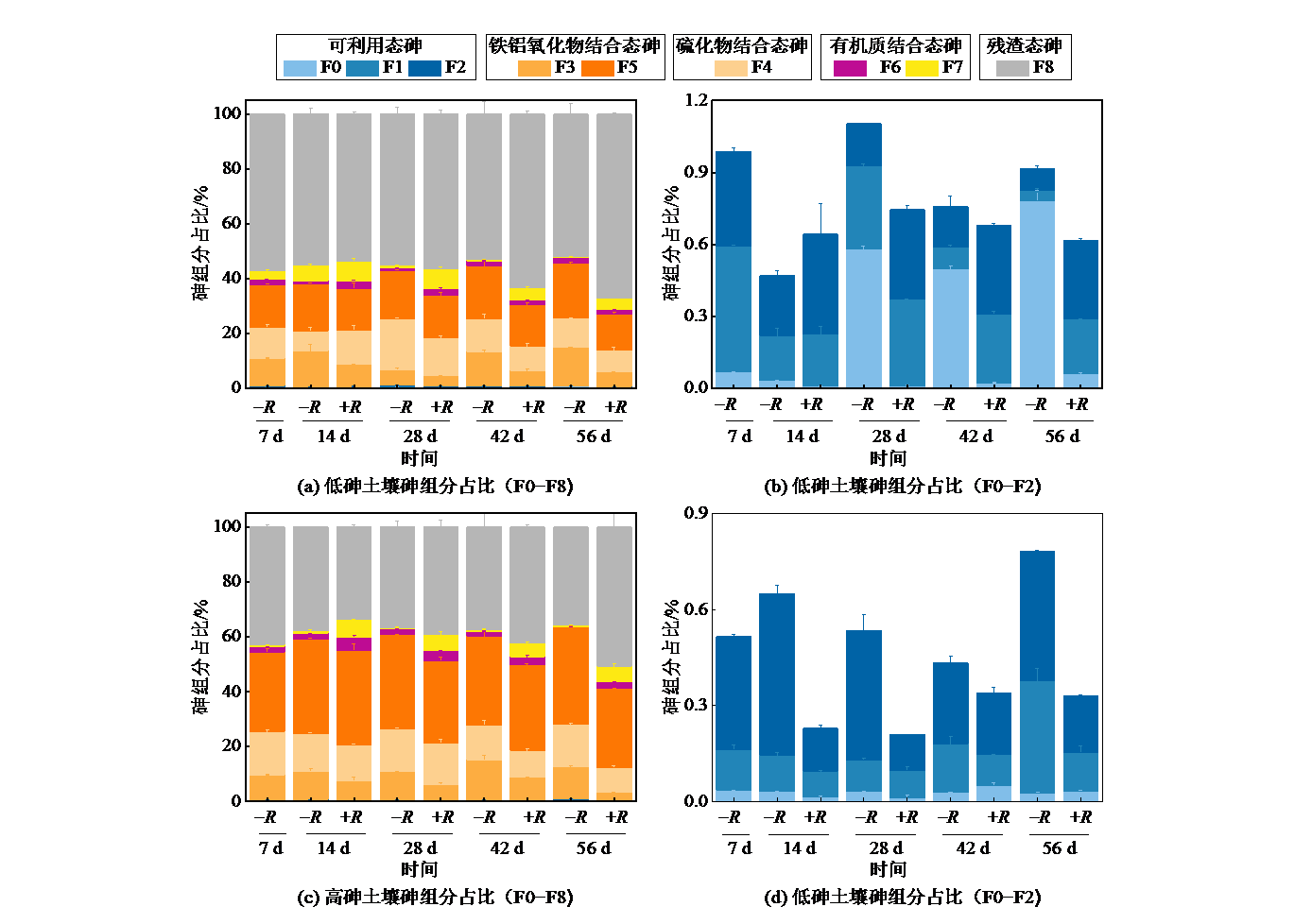
Figure 1 Changes in soil arsenic fraction of non-rice cultivation treatment (-R) and rice cultivation treatment (+R) with low arsenic and high arsenic soils
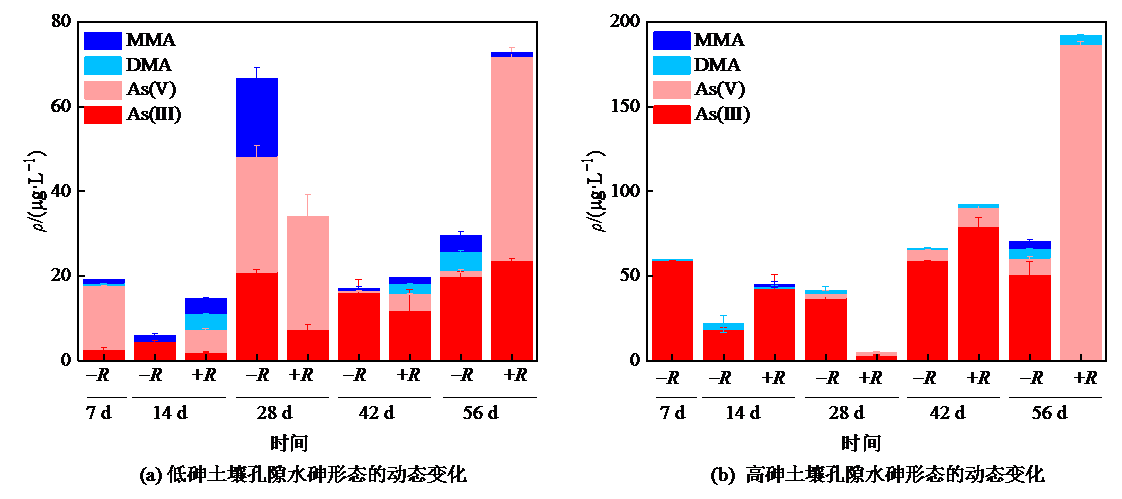
Figure 2 Changes in arsenic speciation in soil pore water of non-rice cultivation treatment (-R) and rice cultivation treatment (+R) with low arsenic and high arsenic soils
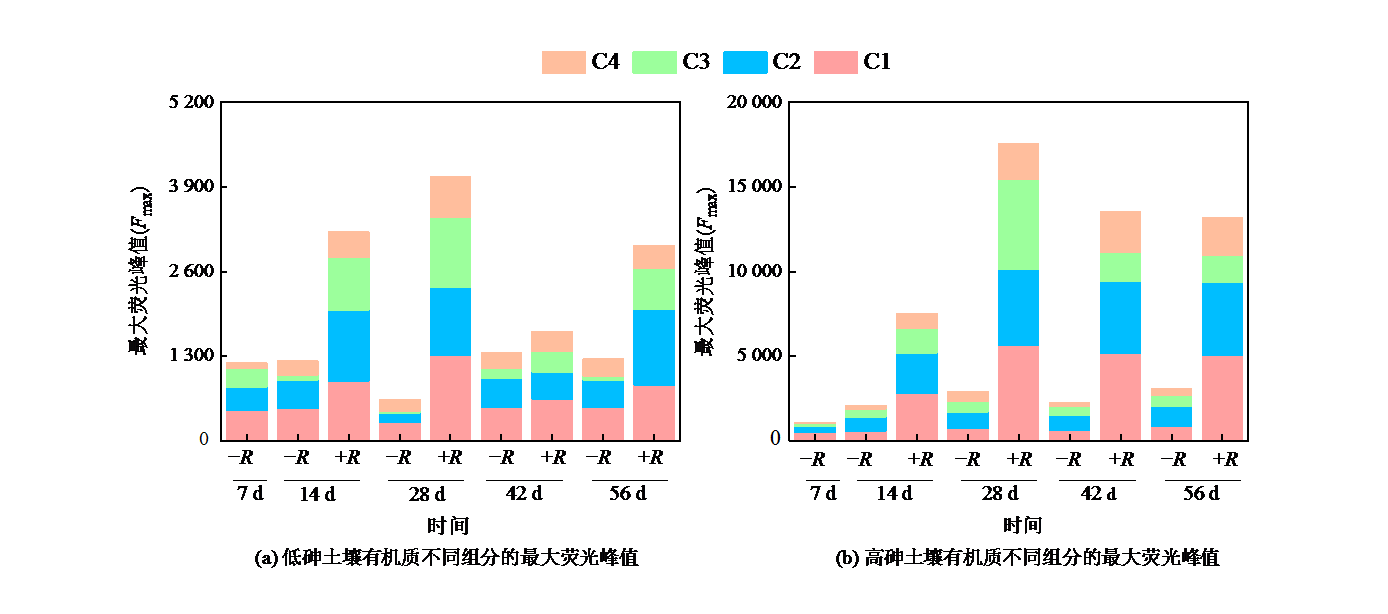
Figure 4 Changes in maximum intensity of fluorescence peak of different soil dissolved organic matter components in low arsenic and high arsenic soils
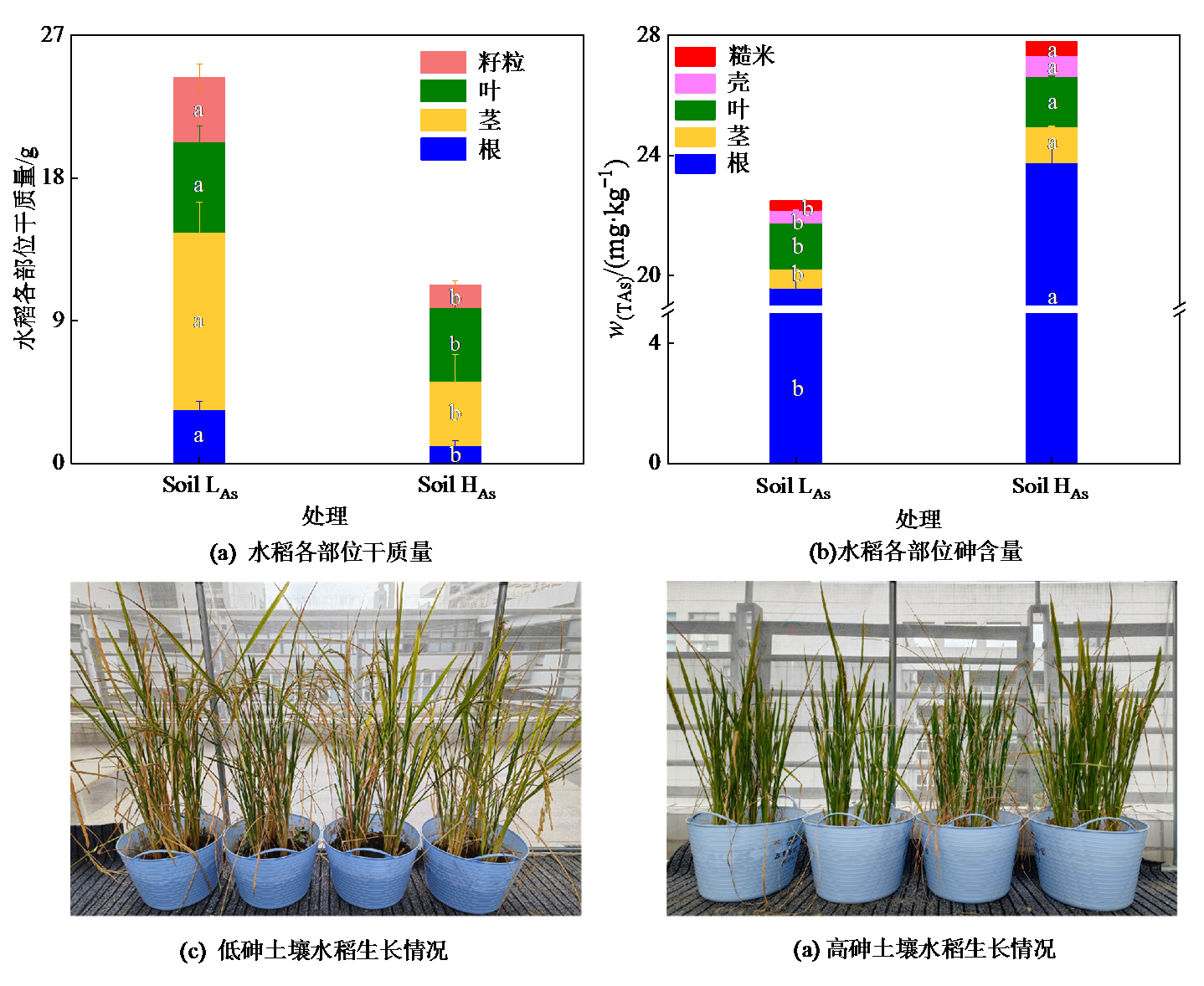
Figure 6 Dry weight and arsenic concentration in each part of rice plants, and rice growth in low arsenic (Soil LAs+R) and high arsenic (Soil HAs+R) soils at maturity stage
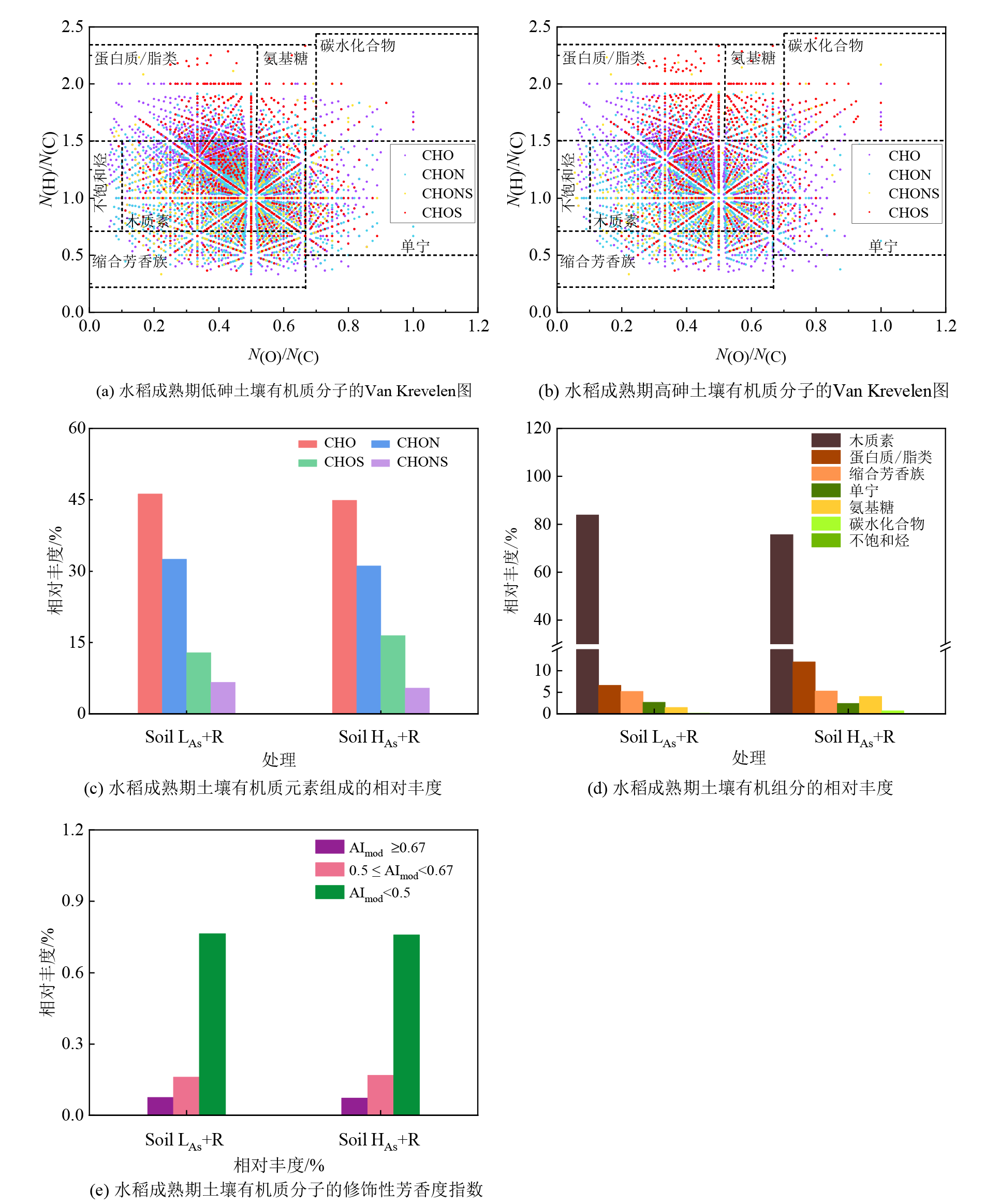
Figure 7 Van Krevelen diagram of organic matter molecules in low arsenic and high arsenic soils after rice cultivation at maturity stage, relative abundance of elemental components, relative abundance of major components, modified aromatics index
| [1] | AMARAL D C, LOPES G, GUILHERME L R, et al., 2017. A new approach to sampling intact Fe plaque reveals Si-induced changes in Fe mineral composition and shoot As in rice[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 51(1): 38-45. |
| [2] | AULAKH M S, WASSMANN R, BUENO C, et al., 2001. Characterization of root exudates at different growth stages of ten rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars[J]. Plant Biology, 3(2): 139-148. |
| [3] | BAO Y P, BOLAN N S, LAI J H, et al., 2021. Interactions between organic matter and Fe(hydr)oxides and their influences on immobilization and remobilization of metal(loid)s: A review[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 52(22): 4016-4037. |
| [4] |
BAUER M, BLODAU C, 2006. Mobilization of arsenic by dissolved organic matter from iron oxides, soils and sediments[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 354(2-3): 179-190.
PMID |
| [5] |
BOSE P, SHARMA A, 2002. Role of iron in controlling speciation and mobilization of arsenic in subsurface environment[J]. Water Research, 36(19): 4916-4926.
PMID |
| [6] | BUSCHMANN J, KAPPELER A, LINDAUER U, et al., 2006. Arsenite and arsenate binding to dissolved humic acids: Influence of pH, type of humic acid, and aluminum[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 40(19): 6015-6020. |
| [7] | CHEN C, LI L Y, HUANG K, et al., 2019. Sulfate-reducing bacteria and methanogens are involved in arsenic methylation and demethylation in paddy soils[J]. The ISME Journal, 13(10): 2523-2535. |
| [8] | CHEN W, WESTERHOFF P, LEENHEER J A, et al., 2003. Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 37(24): 5701-5710. |
| [9] |
CHEN Z, WANG Y P, XIA D, et al., 2016. Enhanced bioreduction of iron and arsenic in sediment by biochar amendment influencing microbial community composition and dissolved organic matter content and composition[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 311: 20-29.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | DING Y, SHI Z Q, YE Q T, et al., 2020. Chemodiversity of soil dissolved organic matter[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 54(10): 6174-6184. |
| [11] |
DUAN G L, SHAO G S, TANG Z, et al., 2017. Genotypic and environmental variations in grain cadmium and arsenic concentrations among a panel of high yielding rice cultivars[J]. Rice, 10(1): 9.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
FITZ W J, WENZEL W W, 2002. Arsenic transformations in the soil-rhizosphere-plant system: Fundamentals and potential application to phytoremediation[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 99(3): 259-278.
PMID |
| [13] | GAO A X, CHEN C, GAO Z Y, et al., 2024. Soil redox status governs within-field spatial variation in microbial arsenic methylation and rice straighthead disease[J]. The ISME Journal, 18(1): wrae057. |
| [14] | GAO A X, CHEN C, ZHANG H H, et al., 2023. Multi-site field trials demonstrate the effectiveness of silicon fertilizer on suppressing dimethylarsenate accumulation and mitigating straighthead disease in rice[J]. Environmental Pollution, 316(Part 1): 120515. |
| [15] | HOFFMANN M, MIKUTTA C, KRETZSCHMAR R, 2013. Arsenite binding to natural organic matter: Spectroscopic evidence for ligand exchange and ternary complex formation[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 47(21): 12165-12173. |
| [16] | HONG Z B, HU S W, YANG Y, et al., 2023. The key roles of Fe oxyhydroxides and humic substances during the transformation of exogenous arsenic in a redox-alternating acidic paddy soil[J]. Water Research, 242: 120286. |
| [17] | HOU D Y, O’CONNOR D, IGALAVITHANA A D, et al., 2020. Metal contamination and bioremediation of agricultural soils for food safety and sustainability[J]. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 1(7): 366-381. |
| [18] | HU S W, LIANG Y Z, LIU T X, et al., 2020. Kinetics of As(V) and carbon sequestration during Fe(II)-induced transformation of ferrihydrite-As(V)-fulvic acid coprecipitates[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 272: 160-176. |
| [19] | HU S W, LU Y, PENG L F, et al., 2018. Coupled kinetics of ferrihydrite transformation and As(V) sequestration under the effect of humic acids: A mechanistic and quantitative study[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 52(20): 11632-11641. |
| [20] | HUANG B Y, ZHAO F J, WANG P, et al., 2022. The relative contributions of root uptake and remobilization to the loading of Cd and As into rice grains: Implications in simultaneously controlling grain Cd and As accumlation using a segmented water management strategy[J]. uEnvironmental Pollution, 293: 118497. |
| [21] | HUANG H, JIA Y, SUN G X, et al., 2012. Arsenic speciation and volatilization from flooded paddy soils amended with different organic matters[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 46(4): 2163-2168. |
| [22] | JIA Y, HUANG H, CHEN Z, et al., 2014. Arsenic uptake by rice is influenced by microbe-mediated arsenic redox changes in the rhizosphere[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 48(2): 1001-1007. |
| [23] |
JIANG O Y, LI L Y, DUAN G L, et al., 2023. Root exudates increased arsenic mobility and altered microbial community in paddy soils[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 127: 410-420.
DOI PMID |
| [24] | JONES D L, WILLETT V B, 2006. Experimental evaluation of methods to quantify dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) and dissolved organic carbon (DOC) in soil[J]. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 8(5): 991-999. |
| [25] |
KAPPLER A, BRYCE C, MANSOR M, et al., 2021. An evolving view on biogeochemical cycling of iron[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 19(6): 360-374.
DOI PMID |
| [26] | KLUEGLEIN N, KAPPLER A, 2013. Abiotic oxidation of Fe(II) by reactive nitrogen species in cultures of the nitrate-reducing Fe(II) oxidizer Acidovorax sp. BoFeN1-questioning the existence of enzymatic Fe(II) oxidation[J]. Geobiology, 11(4): 396-396. |
| [27] | KUMARATHILAKA P, SENEWEERA S, MEHARG A, et al., 2018. Arsenic speciationdynamics in paddy rice soil-water environment: Sources, physico-chemical, and biological factors: A review[J]. Water Research, 140: 403-414 |
| [28] |
LI G, SUN G X, WILLIAMS P N, et al., 2011. Inorganic arsenic in Chinese food and its cancer risk[J]. Environment International, 37(7): 1219-1225.
DOI PMID |
| [29] | LI X M, CHEN Q L, HE C, et al., 2019. Organic carbon amendments affect the chemodiversity of soil dissolved organic matter and its associations with soil microbial communities[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 53(1): 50-59. |
| [30] | LIU C J, HU C Y, XIAO S F, et al., 2024. Insoluble-phytate improves plant growth and arsenic accumulation in As-hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata: Phytase activity, nutrient uptake, and As-metabolism[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 58(8): 3858-3868. |
| [31] | LIU L, YANG Y P, DUAN G, et al., 2022. The chemical-microbial release and transformation of arsenic induced by citric acid in paddy soil[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 421: 126731. |
| [32] | LIU X, FU J W, GUAN D X, et al., 2016. Arsenic induced phytate exudation, and promoted FeAsO4 dissolution and plant growth in As-hyperaccumulator pteris vittata[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 50(17): 9070. |
| [33] | LIU Y, DING Y, SHENG A, et al., 2023. Fe(II)-catalyzed transformation of ferrihydrite with different degrees of crystallinity[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 57(17): 6934-6943. |
| [34] | MAISCH M, LUEDER U, KAPPLER A, et al., 2019. Iron lung: How rice roots induce iron redox changes in the rhizosphere and create niches for microaerophilic Fe (II)-oxidizing bacteria[J]. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 6(10): 600-605. |
| [35] |
MATERA V, LE HÉCHO I, LABOUDIGUE A, et al., 2003. A methodological approach for the identification of arsenic bearing phases in polluted soils[J]. Environmental Pollution, 126(1): 51-64.
PMID |
| [36] | MEHARG A A, RAHMAN M, 2003. Arsenic contamination of Bangladesh paddy field soils: Implications for rice contribution to arsenic consumption[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 37(2): 229-234. |
| [37] | MEI K, LIU J C, FAN J, et al., 2021. Low-level arsenite boosts rhizospheric exudation of low-molecular-weight organic acids from mangrove seedlings (Avicennia marina): Arsenic phytoextraction, removal, and detoxification[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 775: 145685. |
| [38] | MIKUTTA C, FROMMER J, VOEGELIN A, et al., 2010. Effect of citrate on the local Fe coordination in ferrihydrite, arsenate binding, and ternary arsenate complex formation[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 74(19): 5574-5592. |
| [39] | MIKUTTA C, KRETZSCHMAR R, 2011. Spectroscopic evidence for ternary complex formation between arsenate and ferric iron complexes of humic substances[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 45(22): 9550-9557. |
| [40] | MLADENOV N, ZHENG Y, MILLER M P, et al., 2010. Dissolved organic matter sources and consequences for iron and arsenic mobilization in Bangladesh aquifers[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 44(1): 123-128. |
| [41] | MLADENOV N, ZHENG Y, SIMONE B, et al., 2015. Dissolved organic matter quality in a shallow aquifer of Bangladesh: Implications for arsenic mobility[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 49(18): 10815-10824. |
| [42] | NIAZI N K, SINGH B, SHAH P, et al., 2011. Arsenic speciation and phytoavailability in contaminated soils using a sequential extraction procedure and XANES spectroscopy[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 45(17): 7135-7142. |
| [43] |
NORTON G J, ADOMAKO E E, DEACON C M et al., 2013. Effect of organic matter amendment, arsenic amendment and water management regime on rice grain arsenic species[J]. Environmental Pollution, 177: 38-47.
DOI PMID |
| [44] | OHNO T, HE Z Q, TAZISONG I A, et al., 2009. Influence of tillage, cropping, and nitrogen source on the chemical characteristics of humic acid, fulvic acid, and water-soluble soil organic matter fractions of a long-term cropping system study[J]. Soil Science, 174(12): 652-660. |
| [45] |
PAN D D, YI J C, LI F B, et al., 2020. Dynamics of gene expression associated with arsenic uptake and transport in rice during the whole growth period[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 20(1): 133.
DOI PMID |
| [46] |
PODGORSKI J, BERG M, 2020. Global threat of arsenic in groundwater[J]. Science, 368(6493): 845-850.
DOI PMID |
| [47] | QIAO J T, LI X M, HU M, et al., 2018. Transcriptional activity of arsenic-reducing bacteria and genes regulated by lactate and biochar during arsenic transformation in flooded paddy soil[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 52(1): 61-70. |
| [48] | QIAO J T, LI X M, LI F B, et al., 2019. Humic substances facilitate arsenic reduction and release in flooded paddy soil[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 53(9): 5034-5042. |
| [49] | RINKLEBE J, SHAHEEN S M, YU K, 2016. Release of As, Ba, Cd, Cu, Pb, and Sr under pre-definite redox conditions in different rice paddy soils originating from the USA and Asia[J]. Geoderma, 270(15): 21-32. |
| [50] | ROTH V N, DITTMAR T, GAUPP R, et al., 2015. The molecular composition of dissolved organic matter in forest soils as a function of pH and temperature[J]. PloS One, 10(3): e0119188. |
| [51] | SI D F, WU S, WU H T, et al., 2024. Activated carbon application simultaneously alleviates paddy soil arsenic mobilization and carbon emission by decreasing porewater dissolved organic matter[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 58(18): 7880-7890. |
| [52] | TAKAHASHI Y, MINAMIKAWA R, HATTORI K H, et al., 2004. Arsenic behavior in paddy fields during the cycle of flooded and non-flooded periods[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 38(4): 1038-1044. |
| [53] |
TANG Z, WANG Y J, GAO A X et al., 2020. Dimethylarsinic acid is the causal agent inducing rice straighthead disease[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 71(18): 5631-5644.
DOI PMID |
| [54] | TU S X, MA L, LUONGO T, 2004. Root exudates and arsenic accumulation in arsenic hyperaccumulating Pteris vittata and non-hyperaccumulating Nephrolepis exaltata[J]. Plant and Soil, 258(1-2): 9-19. |
| [55] | TUFANO K J, REYES C, SALTIKOV C W, et al., 2008. Reductive processes controlling arsenic retention: Revealing the relative importance of iron and arsenic reduction[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 42(22): 8283-8289. |
| [56] | WANG D M, MAI L W, YU Z, et al., 2024. Deciphering the bioavailability of dissolved organic matter in thermophilic compost and vermicompost at the molecular level[J]. Bioresource Technology, 391(Part A): 129947. |
| [57] | WANG X Q, YU H Y, LI F B, et al., 2019. Enhanced immobilization of arsenic and cadmium in a paddy soil by combined applications of woody peat and Fe(NO3)3: Possible mechanisms and environmental implications[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 649: 535-543. |
| [58] | WEBER F A, HOFACKER A F, VOEGELIN A, et al., 2010. Temperature dependence and coupling of iron and arsenic reduction and release during flooding of a contaminated soil[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 44(1): 116-122. |
| [59] | WELLS M J M, MULLINS G A, BELL K Y, et al., 2017. Fluorescence and quenching assessment (EEM-PARAFAC) of de facto potable reuse in the Neuse River, North Carolina, United States[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 51(23): 13592-13602. |
| [60] | WILLIAMS P N, VILLADA A, DEACON C, et al., 2007. Greatly enhanced arsenic shoot assimilation in rice leads to elevated grain levels compared to wheat and barley[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 41(19): 6854-6859. |
| [61] | WISAWAPIPAT W, CHOOAIEM N, ARAMRAK S, et al., 2021. Sulfur amendments to soil decrease inorganic arsenic accumulation in rice grain under flooded and nonflooded conditions: insights from temporal dynamics of porewater chemistry and solid-phase arsenic solubility[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 779: 146352. |
| [62] | XU Y, HE Y, FENG X L, et al., 2014. Enhanced abiotic and biotic contributions to dechlorination of pentachlorophenol during Fe(III) reduction by an iron-reducing bacterium clostridium beijerinckii[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 473-474: 215-223. |
| [63] | ZHAI W W, MA Y Y, YANG S, et al., 2023. Synchronous response of arsenic methylation and methanogenesis in paddy soils with rice straw amendment[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 445: 130380. |
| [64] | ZHANG G Q, YUAN Z D, LEI L, et al., 2019. Arsenic redistribution and transformation during Fe(II)-catalyzed recrystallization of As-adsorbed ferrihydrite under anaerobic conditions[J]. Chemical Geology, 525: 380-389. |
| [65] | ZHANG S Y, ZHANG J J, NIU L L, et al., 2024. Escalating arsenic contamination throughout Chinese soils[J]. Nature Sustainability, 7: 766-775. |
| [66] | ZHONG R L, PAN D D, HUANG G Y, et al., 2024. Colloidal fraction on pomelo peel-derived biochar plays a dual role as electron shuttle and adsorbent in controlling arsenic transformation in anoxic paddy soil[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 934: 173340. |
| [67] | ZHU Y G, XUE X M, KAPPLER A, et al., 2017. Linking genes to microbial biogeochemical cycling: Lessons from arsenic[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 51(13): 7326-7339. |
| [68] | 鲍士旦, 2000. 土壤农化分析[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社. |
| BAO S D, 2000. Soil agrochemical analysis[M]. 3 edition. Beijing: China Agriculture Press. | |
| [69] | 田晓庆, 王星皓, 徐昊, 等, 2024. 稻田土壤淹水期As/Sb释放的动态过程及因素探究[J]. 环境科学学报, 44(4): 324-332. |
| TIAN X Q, WANG X H, XU H, et al., 2024. Study on the dynamic process and factors of As/Sb release in paddy soil during flooding period[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 44(4): 324-332. | |
| [70] | 霍丽娟, 王美玲, 赵慧超, 等, 2022. 不同组成有机质对土壤中砷迁移行为的影响[J]. 地球与环境, 50(2): 184-191. |
| HUO L J, WANG M L, ZHAO H C, et al., 2022. Effects of different organic matter on arsenic migration behavior in soil[J]. Earth and Enviroment, 50(2): 184-191. | |
| [71] | 钟松雄, 何宏飞, 陈志良, 等, 2018. 水淹条件下水稻土中砷的生物化学行为研究进展[J]. 土壤学报, 55(1): 1-17. |
| ZHONG S X, HE H F, CHEN Z L, et al., 2018. Research progress on the biochemical behavior of arsenic in paddy soil under flooding conditions[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 55(1): 1-17. |
| [1] | LI Yucai, YANG Lei, LIANG Xian, MENG Hongyan, LIU Huanhuan, SHI Hui, REN Yongxiang. Transcriptomics Analysis Reveals the Impact of Humic Acid on the Toxicity of Nano-Cr2O3 to Chlorella sp. [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(8): 1289-1297. |
| [2] | CHEN Wenzhe, HUANG Qiuxiang, MENG Fande, GAO Jinyan, LI Min, ZHANG Enjun, YUAN Guodong. Impacts of Oxalic and Tartaric Acids on Arsenic Desorption from a Paddy Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(8): 1298-1305. |
| [3] | XIE Jie, CHEN Yuanhua, XU Changxu, YANG Tao, LI Jianguo, DONG Aiqin. Effects of Long-term Returning of Astragalus sinicus L. on Content and Forms of DOM and Cd in Paddy Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(7): 1096-1106. |
| [4] | JIANG Runhai, WEN Shaofu, ZHU Chengqiang, ZHANG Mei, YANG Runling, WANG Chunxue, HOU Xiuli. Research on the Promotion of Maize Growth and Immobilization of Pb in the Rhizosphere by Pb-tolerant Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria in Pb-contaminated Mining Areas [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(2): 291-300. |
| [5] | LI Qiang, TANG Qing, WU Rui. Influence of Antibiotic Addition on Priming Effect of Soil Organic Matter from Different Successional Stages in Karst Ecosystems [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(11): 1717-1726. |
| [6] | LIU Sujie, LIU Chuanping, FANG Liping, CHEN Guanhong, LI Fangbai. Arsenic Methylation Process and the Associated Microbial Mechanisms in Paddy Soil Butyrate-degrading Methanogenic Communities [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(10): 1580-1589. |
| [7] | LIANG Xin, HAN Yafeng, ZHENG Ke, WANG Xugang, CHEN Zhihuai, DU Juan. Effects of Fe3O4 on Soil Carbon Mineralization in Paddy Field [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(9): 1615-1622. |
| [8] | ZHOU Hongguang, GAN Yanping, WU Dequan, YANG Yanmei, ZHANG Yang, WANG Luyao. Regulation of Arsenic Transport and Transformation in Contaminated Sediment by FeMnMg-LDH under Flooding-drying Conditions [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(7): 1249-1262. |
| [9] | ZHU Yiwen, YIN Dan, HU Min, DU Yanhong, HONG Zebin, CHENG Kuan, YU Huanyun. Research Progress on Coupling of Nitrogen Cycle and Arsenic Speciation Transformation in Paddy Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(7): 1344-1354. |
| [10] | YANG Yu, DENG Renjian, LONG Pei, HUANG Zhongjie, Ren Bozhi, WANG Zhenghua. Isolation and Identification of Arsenic-oxidizing Bacterium Pseudomonas sp. AO-1 and Its Oxidation Properties for As(Ⅲ) [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 619-626. |
| [11] | YIN Haojun, LONG Mingliang, LIU Wei, NI Chunlin, LI Fangbai, WU Yundang. Dissolved Oxygen Concentration Regulates Arsenic Reduction in Aeromonas hydrophila: Effects and Mechanisms [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(2): 381-387. |
| [12] | YANG Xiaoli, MAO Jiaxuan, MA Luran, XU Qijing, LIU Xue. Nanomaterial-immobilized Phytase: Preparation, Catalytic Efficiency and Influencing Factors [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(10): 1889-1900. |
| [13] | LI Shaoning, LI Tingting, TAO Xueying, ZHAO Na, XU Xiaotian, LU Shaowei. Comparative Study on the Release of Beneficial Volatile Organic Compounds from Four Deciduous Tree Species [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(1): 123-128. |
| [14] | MA Chuang, WANG Yuyang, ZHOU Tong, WU Longhua. Enrichment Characteristics and Desorption Behavior of Cadmium and Zinc in Particulate Organic Matter of Polluted Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(9): 1892-1900. |
| [15] | DONG Leheng, WANG Xugang, CHEN Manjia, WANG Zihao, SUN Lirong, SHI Zhaoyong, Wu Qiqi. Interaction of Iron Redox and Cu Activities in Calcareous Paddy Soil under Light and Dark Condition [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(7): 1448-1455. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
