Ecology and Environment ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (2): 272-281.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.02.011
• Research Article [Environmental Sciences] • Previous Articles Next Articles
LAN Jun1,2( ), CHEN Guanhong2,*(
), CHEN Guanhong2,*( ), ZHANG Juntao3, HEMMAT-JOU Mohammad Hossein2, SHU Xiaohua1, FANG Liping2, LI Fangbai2
), ZHANG Juntao3, HEMMAT-JOU Mohammad Hossein2, SHU Xiaohua1, FANG Liping2, LI Fangbai2
Received:2023-12-03
Online:2024-02-18
Published:2024-04-03
蓝浚1,2( ), 陈冠虹2,*(
), 陈冠虹2,*( ), 张俊涛3, Hemmat-Jou Mohammad Hossein2, 舒小华1, 方利平2, 李芳柏2
), 张俊涛3, Hemmat-Jou Mohammad Hossein2, 舒小华1, 方利平2, 李芳柏2
通讯作者:
陈冠虹。E-mail: 作者简介:蓝浚(2000年生),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为土壤锑污染控制。E-mail: lanjun9527@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
LAN Jun, CHEN Guanhong, ZHANG Juntao, HEMMAT-JOU Mohammad Hossein, SHU Xiaohua, FANG Liping, LI Fangbai. Microbial Mechanism of Electron Shuttle-mediated Antimony Reduction and Mineralization by Soil Microorganism[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(2): 272-281.
蓝浚, 陈冠虹, 张俊涛, Hemmat-Jou Mohammad Hossein, 舒小华, 方利平, 李芳柏. 电子穿梭体介导土壤锑还原成矿的微生物机制[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(2): 272-281.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.02.011
| 目的基因 | 引物名称 | 引物序列 (5′-3′) | 扩增条件 |
|---|---|---|---|
| gyrB | gyrB-F | GGCGGTACACACGAATTTGG | 95 ℃预变性 2 min; 95 ℃ 10 s, 60 ℃ 20 s, 40个循环 |
| gyrB-R | CTTCACGCACGTCTTCTCCT | ||
| dmsB | dmsB-F | CCAGATCACGGATGAGGGCG | |
| dmsB-R | CGCGTCACTTGGGCAAACAG | ||
| nrfC | nrfC-F | GTAAGTGTCTGCCCGACCAA | |
| nrfC-R | TACCTTCTGCGACCAACTCG | ||
| nasA | nasA-F | CCTGCTACAACATGGGCAGA | |
| nasA-R | CTGGCCTTTACCGAGACGTT | ||
| fdnG | fdnG F | CATCCCACCAAATGACAGCC | |
| fdnG-R | GCAAGAACCGCTCCAAGAAC | ||
| arsC | arsC-F | AGGCGATGAATGAGGTGGGA | |
| arsC-R | GTTACCGGGCAGTGCTCATC |
Table 1 Details of primer pairs and thermal cycling parameters for qPCR
| 目的基因 | 引物名称 | 引物序列 (5′-3′) | 扩增条件 |
|---|---|---|---|
| gyrB | gyrB-F | GGCGGTACACACGAATTTGG | 95 ℃预变性 2 min; 95 ℃ 10 s, 60 ℃ 20 s, 40个循环 |
| gyrB-R | CTTCACGCACGTCTTCTCCT | ||
| dmsB | dmsB-F | CCAGATCACGGATGAGGGCG | |
| dmsB-R | CGCGTCACTTGGGCAAACAG | ||
| nrfC | nrfC-F | GTAAGTGTCTGCCCGACCAA | |
| nrfC-R | TACCTTCTGCGACCAACTCG | ||
| nasA | nasA-F | CCTGCTACAACATGGGCAGA | |
| nasA-R | CTGGCCTTTACCGAGACGTT | ||
| fdnG | fdnG F | CATCCCACCAAATGACAGCC | |
| fdnG-R | GCAAGAACCGCTCCAAGAAC | ||
| arsC | arsC-F | AGGCGATGAATGAGGTGGGA | |
| arsC-R | GTTACCGGGCAGTGCTCATC |
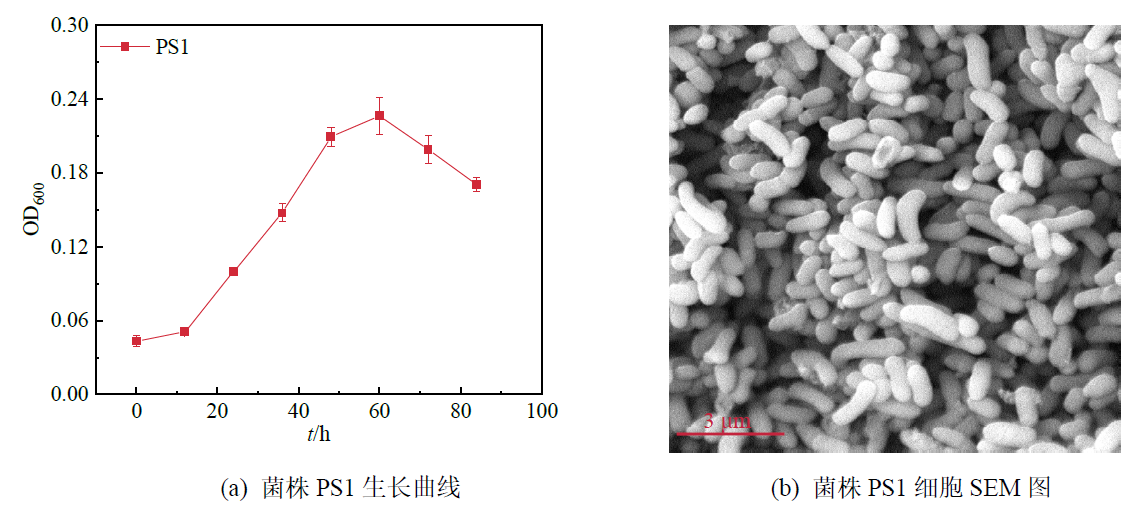
Figure 1 Growth curve and SEM image of antimonate-reducing strain PS1 in the medium supplemented with lactate and Sb(V) as electron donor and acceptor
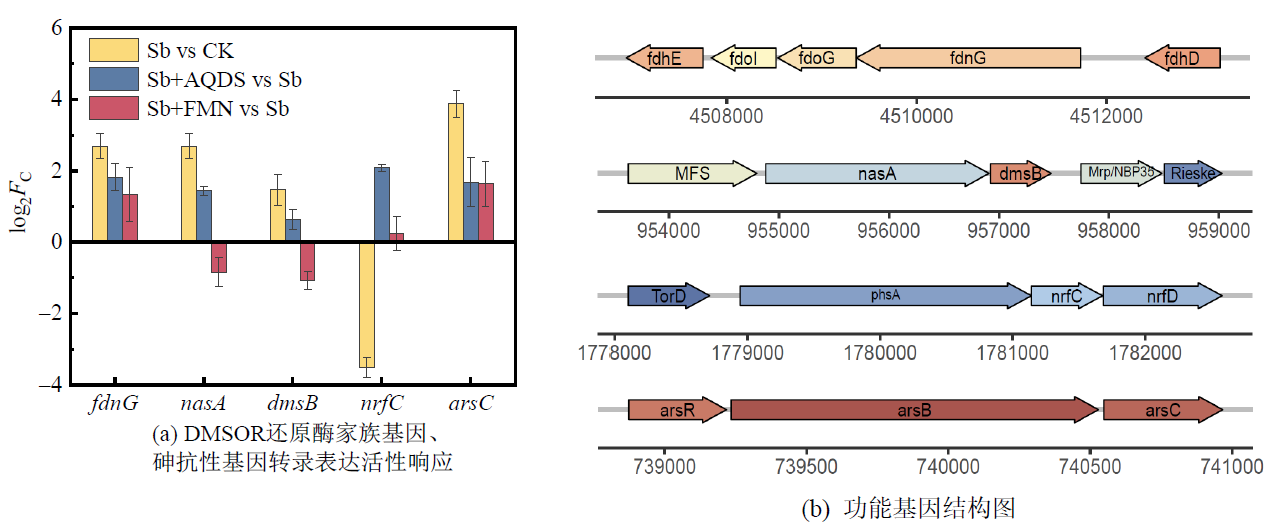
Figure 7 Transcriptional responses of DMSOR family genes and arsenic resistance genes in strain PS1 under different treatments (Fc is the variance multiplier)
| [1] |
ABIN C A, HOLLIBAUGH J T, 2013. Dissimilatory antimonate reduction and production of antimony trioxide microcrystals by a novel microorganism[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 48(1): 681-688.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
ABIN C A, HOLLIBAUGH J T, 2019. Transcriptional response of the obligate anaerobe Desulfuribacillus stibiiarsenatis MLFW-2T to growth on antimonate and other terminal electron acceptors[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 21(2): 618-630.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
BOLAN N, KUMAR M, SINGH E, et al., 2022. Antimony contamination and its risk management in complex environmental settings: A review[J]. Environment International, 158: 106908.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
BUTCHER BRONWYN G, DEANE SHELLY M, RAWLINGS DOUGLAS E, 2000. The chromosomal arsenic resistance genes of thiobacillus ferrooxidans have an unusual arrangement and confer increased arsenic and antimony resistance to Escherichia coli[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 66(5): 1826-1833.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
FILELLA M, BELZILE N, CHEN Y W, 2002. Antimony in the environment: a review focused on natural waters: II. Relevant solution chemistry[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 59(1): 265-285.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
GUO X J, WU Z J, HE M C, et al., 2014. Adsorption of antimony onto iron oxyhydroxides: Adsorption behavior and surface structure[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 276: 339-345.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
HARSHITHA R, ARUNRAJ D R, 2021. Real-time quantitative PCR: A tool for absolute and relative quantification[J]. Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Education, 49(5): 800-812.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
HE M C, YANG J R, 1999. Effects of different forms of antimony on rice during the period of germination and growth and antimony concentration in rice tissue[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 243-244: 149-155.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
JORMAKKA M, TöRNROTH S, BYRNE B, et al., 2002. Molecular basis of proton motive force generation: Structure of formate dehydrogenase-N[J]. Science, 295(5561): 1863-1868.
PMID |
| [10] | KIELKOPF C L, BAUER W, URBATSCH I L, 2020. Bradford assay for determining protein concentration[M]. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols, (4): 102269. |
| [11] |
KLÜPFEL L, PIEPENBROCK A, KAPPLER A, et al., 2014. Humic substances as fully regenerable electron acceptors in recurrently anoxic environments[J]. Nature Geoscience, 7(3): 195-200.
DOI |
| [12] |
LI Q, HUANG M H, SHU S H, et al., 2022. Quinone-mediated Sb removal from sulfate-rich wastewater by anaerobic granular sludge: Performance and mechanisms[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 838(Part 3): 156217.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
MENG Y L, LIU Z J, ROSEN B P, 2004. As(III) and Sb(III) uptake by GlpF and efflux by ArsB in Escherichia coli[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279(18): 18334-18341.
DOI URL |
| [14] | MORENO-VIVIáN C, FLORES E, 2007. Chapter 17 - nitrate assimilation in bacteria[M]// Biology of the Nitrogen Cycle. Amsterdam: Elsevier: 263-282. |
| [15] |
MURCIEGO A M, SÁNCHEZ A G, GONZÁLEZ M A R, et al., 2007. Antimony distribution and mobility in topsoils and plants (Cytisus striatus, Cistus ladanifer and Dittrichia viscosa) from polluted Sb-mining areas in Extremadura (Spain)[J]. Environmental Pollution, 145(1): 15-21.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
NGUYEN V K, PARK Y, LEE T, 2019. Microbial antimonate reduction with a solid-state electrode as the sole electron donor: A novel approach for antimony bioremediation[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 377: 179-185.
DOI PMID |
| [17] | OKAMOTO A, SAITO K, INOUE K, et al., 2014. Uptake of self-secreted flavins as bound cofactors for extracellular electron transfer in Geobacter species[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 7(4): 1357-1361. |
| [18] |
PAT-ESPADAS A M, RAZO-FLORES E, RANGEL-MENDEZ J R, et al., 2014. Direct and quinone-mediated palladium reduction by geobacter sulfurreducens: Mechanisms and modeling[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 48(5): 2910-2919.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
SAINI G, CHAN C S, 2012. Near-neutral surface charge and hydrophilicity prevent mineral encrustation of Fe-oxidizing micro-organisms[J]. Geobiology, 11(2): 191-200.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
SCHEINOST A C, ROSSBERG A, VANTELON D, et al., 2006. Quantitative antimony speciation in shooting-range soils by EXAFS spectroscopy[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 70(13): 3299-3312.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
SHI L D, WANG M, HAN Y L, et al., 2019. Multi-omics reveal various potential antimonate reductases from phylogenetically diverse microorganisms[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 103(21): 9119-9129.
DOI |
| [22] |
SUN W M, SUN X X, HAGGBLOM M M, et al., 2021. Identification of antimonate reducing bacteria and their potential metabolic traits by the combination of stable isotope probing and metagenomic-pangenomic analysis[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 55(20): 13902-13912.
DOI URL |
| [23] | THÖNY-MEYER L, 1997. Biogenesis of respiratory cytochromes in bacteria[J]. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 61(3): 337-376. |
| [24] | TOLAR JOE G, LI S, AJO-FRANKLIN CAROLINE M, 2022. The differing roles of flavins and quinones in extracellular electron transfer in lactiplantibacillus plantarum[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 89(1): e01313-01322. |
| [25] |
WANG L Y, YE L, JING C Y, 2020. Genetic identification of antimonate respiratory reductase in Shewanella sp. ANA-3[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 54(21): 14107-14113.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
WANG L Y, YE L, YU Y Q, et al., 2018. Antimony redox biotransformation in the subsurface: Effect of indigenous Sb(V) respiring microbiota[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 52(3): 1200-1207.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
WANG S S, XING Z H, CHEN G Y, et al., 2016. Cuboctahedral Sb2O3 mesocrystals organized from octahedral building blocks: More than self-similarity[J]. Crystal Growth & Design, 16(7): 3613-3617.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
WANG X M, WANG L, CHEN L, et al., 2022. AQDS activates extracellular synergistic biodetoxification of copper and selenite via altering the coordination environment of outer-membrane proteins[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 56(19): 13786-13797.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
WANG X Q, LI F B, YUAN C L, et al., 2019. The translocation of antimony in soil-rice system with comparisons to arsenic: Alleviation of their accumulation in rice by simultaneous use of Fe(II) and NO3-[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 650(Part 1): 633-641.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
WU Y, LUO X, QIN B, et al., 2020. Enhanced current production by exogenous electron mediators via synergy of promoting biofilm formation and the electron shuttling process[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 54(12): 7217-7225.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
YAMAMURA S, IIDA C, KOBAYASHI Y, et al., 2021. Production of two morphologically different antimony trioxides by a novel antimonate-reducing bacterium, Geobacter sp. SVR[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 411: 125100.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
YANG Z R, HOSOKAWA H, SADAKANE T, et al., 2020. Isolation and characterization of facultative-anaerobic antimonate-reducing bacteria[J]. Microorganisms, 8(9): 1435.
DOI URL |
| [33] | YING Z Y, CHEN H, HE Z, et al., 2022. Redox mediator-regulated microbial electrolysis cell to boost coulombic efficiency and degradation activity during gaseous chlorobenzene abatement[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 528: 231314. |
| [34] |
YU H, YAN X Z, WENG W L, et al., 2022. Extracellular proteins of Desulfovibrio vulgaris as adsorbents and redox shuttles promote biomineralization of antimony[J]. J Hazard Mater, 426: 127795.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
YU Y S, CHEN J C, LI Y P, et al., 2021. Identification of a MarR subfamily that regulates arsenic resistance genes[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 87(24): e0158821.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
ZHANG Y D, BOYANOV M I, O’LOUGHLIN E J, et al., 2024. Reaction pathways and Sb(III) minerals formation during the reduction of Sb(V) by Rhodoferax ferrireducens strain YZ-1[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 465: 133240.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
ZHOU J Z, WU C Y, PANG S, et al., 2022a. Dissimilatory and cytoplasmic antimonate reductions in a hydrogen-based membrane biofilm reactor[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 56(20): 14808-14816.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
ZHOU J Z, WU C Y, PANG S, et al., 2022b. Dissimilatory and cytoplasmic antimonate reductions in a hydrogen-based membrane biofilm reactor[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 56(20): 14808-14816.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
ZOTOV A V, SHIKINA N D, AKINFIEV N N, 2003. Thermodynamic properties of the Sb(III) hydroxide complex Sb(OH)3(aq) at hydrothermal conditions[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 67(10): 1821-1836.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
阳涅, 孙晓旭, 孔天乐, 等, 2023. 微生物群落对河流底泥中锑含量变化的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 32(3): 609-618.
DOI |
| YANG N, SUN X X, KONG T L, et al.., 2023. Response of microbial communities to changes in antimony content in river sediments[J]. Journal of Ecology and Environment, 32(3): 609-618. |
| [1] | DING Hao, LI Changxin, DING Jing, LAN Hao. Genetic and Functional Diversity of N-damo Bacteria in Different Environments [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(2): 202-211. |
| [2] | LI Jiahui, TONG Hui, CHEN Manjia, LIU Chengshuai, JIANG Qi, YI Xiu. Formation of Fe(Ⅲ) Minerals by Microaerophilic Fe(Ⅱ)-oxidizing Bacteria and Its Effect on Immobilization of Heavy Metals: A Review [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(2): 310-320. |
| [3] | MA Yuan, TIAN Lulu, LÜ Jie, LIU Pei, ZHANG Xu, LI Eryang, ZHANG Qinghang. Soil Microbial Communities and Influencing Factors of Picea schrenkiana Forest on the Northern Slope of Tianshan Mountains [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(1): 1-11. |
| [4] | YANG Zhengqiao, ZOU Qi, WEI Hang, ZHOU Kai, CHEN Zhiliang. Research Progress on the Adaptation and Regulation Mechanism of Micro-organisms in Metal Tailings [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(1): 156-166. |
| [5] | YUAN Jiabao, SONG Yanyu, LIU Zhendi, ZHU Mengyuan, CHENG Xiaofeng, MA Xiuyan, CHEN Ning, LI Xiaoyu. Profile Distribution Characteristics of Soil Enzyme Activity and Its Indicative Function of Microbial Nutrient Restriction in Reed Wetlands of Songnen Plain [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(12): 2141-2153. |
| [6] | LI Chengtao, WU Wanqing, CHEN Chen, ZHANG Yong, ZHANG Kai. Effects of Biodegradable PBAT Microplastics on Soil Physical and Chemical Properties and Physiological Indicators of Brassica chinensis [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(11): 1964-1977. |
| [7] | LI Xuan, QIAN Xiuwen, HUANG Juan, WANG Mingyu, XIAO Jun. Responses of Operating Performance and Microbial Community in Constructed Wetlands to NiO NPs Exposure [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(10): 1833-1841. |
| [8] | LIANG Chuan, YANG Yanfang, YU Shanshan, ZHOU Li, ZHANG Jingwei, ZHANG Xiujuan. Differences of Microbial Biomass and Community Structure Characteristics in Sediments under Net-pen and Pond Fish Farming [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(10): 1802-1810. |
| [9] | TANG Zhiwei, WENG Ying, ZHU Xiatong, CAI Hongmei, DAI Wenci, WANG Pengna, ZHENG Baoqiang, LI Jincai, CHEN Xiang. Meta-analysis of Soil Microbial Mass Carbon and Its Influencing Factors in Farmland in China under Straw Return [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(9): 1552-1562. |
| [10] | LIANG Chuan, YANG Yanfang, YU Shanshan, ZHOU Li, ZHANG Jingwei, ZHANG Xiujuan. Differences of Microbial Biomass and Community Structure Characteristics in Sediments under Net-pen and Pond Fish Farming [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(8): 1487-1495. |
| [11] | JIANG Yishan, SUN Yingtao, ZHANG Gan, LUO Chunling. Pattern and Influencing Factors of Forest Soil Microbial Communities in Different Climate Types in China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(8): 1355-1364. |
| [12] | ZHU Yiwen, YIN Dan, HU Min, DU Yanhong, HONG Zebin, CHENG Kuan, YU Huanyun. Research Progress on Coupling of Nitrogen Cycle and Arsenic Speciation Transformation in Paddy Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(7): 1344-1354. |
| [13] | CHEN Dongdong, HUO Lili, ZHAO Liang, CHEN Xin, SHU Min, HE Fuquan, ZHANG Yukun, ZHANG Li, LI Qi. Contribution of Water and Heat Factors to Spatial Variability of Soil Microbial Biomass Carbon and Nitrogen in Qinghai Alpine Grassland: Based on Enhanced Regression Tree Model [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(7): 1207-1217. |
| [14] | LI Guiying, LIU Jianying, AN Taicheng. The Formation and Resuscitation Mechanisms of Viable But Nonculturable Bacteria during Water Disinfection Processes [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(7): 1333-1343. |
| [15] | KOU Zhu, QING Chun, YUAN Changguo, LI Ping. Diversity and Distribution of Sulfur Oxidizing Bacteria in Hot Springs of Northeast Tibet, China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 989-1000. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
