生态环境学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (7): 1263-1274.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.07.009
童永杰1( ), 汪毅1, 华玉妹1,*(
), 汪毅1, 华玉妹1,*( ), 赵建伟1, 刘广龙1, 蒋永参2
), 赵建伟1, 刘广龙1, 蒋永参2
收稿日期:2023-06-16
出版日期:2023-07-18
发布日期:2023-09-27
通讯作者:
* 华玉妹。E-mail: ymhua@mail.hzau.edu.cn作者简介:童永杰(1999年生),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为水环境污染研究。E-mail: 1114797026@qq.com
基金资助:
TONG Yongjie1( ), WANG Yi1, HUA Yumei1,*(
), WANG Yi1, HUA Yumei1,*( ), ZHAO Jianwei1, LIU Guanglong1, JIANG Yongcan2
), ZHAO Jianwei1, LIU Guanglong1, JIANG Yongcan2
Received:2023-06-16
Online:2023-07-18
Published:2023-09-27
摘要:
磷是湖泊的关键生源要素,其转化受多种生物化学反应的驱动。在富营养化后期,藻类在厌氧条件下衰败所产生的乙酸盐可作为反硝化过程的有机电子供体,铁可作为反硝化过程的电子供体和能量来源,它们会通过影响氮的转化而直接或间接对磷转化产生影响。本研究取武汉市墨水湖的样品构建了沉积物-上覆水体系,通过向上覆水中输入硝酸盐、铁和乙酸盐以探明有机电子供体(乙酸盐)影响下铁和氮对磷转化的驱动作用。在不同乙酸盐浓度下,研究上覆水和间隙水中氮、磷与铁质量浓度随时间的变化,确定沉积物中反硝化酶活性与硝酸盐型亚铁氧化菌(NDFOB)丰度,分析沉积物中的磷形态以明晰铁结合态磷的存在形式。结果表明,(1)乙酸盐增加了沉积物中NDFOB丰度和反硝化酶活性,使硝态氮(NO3--N)去除效率提高22.6%。(2)总磷(TP)浓度与总铁(TFe)浓度之间显著正相关(P=0.001),易还原铁氧化物(Feox1)和可还原铁氧化物(Feox2)是沉积物中对磷吸附能力最强的铁形态,占沉积物总铁质量的43.8%-54.1%。(3)乙酸盐促进了沉积物中Fe(Ⅲ) 的还原,由于沉积物中Feox1和Feox2还原作用而产生较高质量分数Fe(Ⅱ),铁结合态磷质量分数明显降低。(4)最终沉积物中易还原铁结合态磷(P-Feox1)质量分数比NO3-处理组低0.250 mg·g-1,同时乙酸盐抑制沉积物中Feox2生成过程,可还原铁结合态磷(P-Feox2)质量分数比NO3-处理组低0.010 mg·g-1,上覆水和间隙水总磷浓度显著高于NO3-处理组(P=0.000)。研究结果通过明确不同介导作用下沉积物磷与铁结合形式的转变,有助于加深对湖泊内源污染理论的认识。
中图分类号:
童永杰, 汪毅, 华玉妹, 赵建伟, 刘广龙, 蒋永参. 有机电子供体影响下硝酸盐和铁对磷转化的驱动作用[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1263-1274.
TONG Yongjie, WANG Yi, HUA Yumei, ZHAO Jianwei, LIU Guanglong, JIANG Yongcan. Transformation of Phosphorus in Sediments Driven by Nitrate and Iron in the Presence of Organic Electron Donor[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(7): 1263-1274.
| 步骤 | 提取 | 提取目标相 |
|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 10 mL 1 mol·L-1 Na2CO3; pH值4.5, 24 h | 碳酸盐铁 (Fecarb), 碳酸盐铁结合态磷 (P-Fecarb) |
| Ⅱ | 10 mL 1 mol·L-1盐酸羟胺 (25%乙酸), 48 h | 易还原铁氧化物 (Feox1), 易还原铁氧化物铁结合态磷 (P-Feox1) |
| Ⅲ | 10 mL 50 g·L-1连二亚硫酸钠 (0.35 mol·L-1乙酸/0.2 mol·L-1柠檬酸三钠) 2 h | 可还原铁氧化物 (Feox2), 可还原铁结合态磷 (P-Feox2) |
| Ⅳ | 10 mL 0.2 mol·L-1草酸/0.17 mol·L-1草酸铵 (pH值3.26 h) | 磁铁矿 (Femag), 磁铁矿结合态磷 (P-Femag) |
| Ⅴ | 5 mL 12 mol·L-1盐酸, 煮沸1 min | 片状硅酸盐铁 (Feprs), 片状硅酸盐铁结合态磷 (P-Feprs) |
表1 沉积物铁结合磷同步分级提取过程
Table 1 The iron bound phosphorus simultaneous extraction process of sediments
| 步骤 | 提取 | 提取目标相 |
|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 10 mL 1 mol·L-1 Na2CO3; pH值4.5, 24 h | 碳酸盐铁 (Fecarb), 碳酸盐铁结合态磷 (P-Fecarb) |
| Ⅱ | 10 mL 1 mol·L-1盐酸羟胺 (25%乙酸), 48 h | 易还原铁氧化物 (Feox1), 易还原铁氧化物铁结合态磷 (P-Feox1) |
| Ⅲ | 10 mL 50 g·L-1连二亚硫酸钠 (0.35 mol·L-1乙酸/0.2 mol·L-1柠檬酸三钠) 2 h | 可还原铁氧化物 (Feox2), 可还原铁结合态磷 (P-Feox2) |
| Ⅳ | 10 mL 0.2 mol·L-1草酸/0.17 mol·L-1草酸铵 (pH值3.26 h) | 磁铁矿 (Femag), 磁铁矿结合态磷 (P-Femag) |
| Ⅴ | 5 mL 12 mol·L-1盐酸, 煮沸1 min | 片状硅酸盐铁 (Feprs), 片状硅酸盐铁结合态磷 (P-Feprs) |
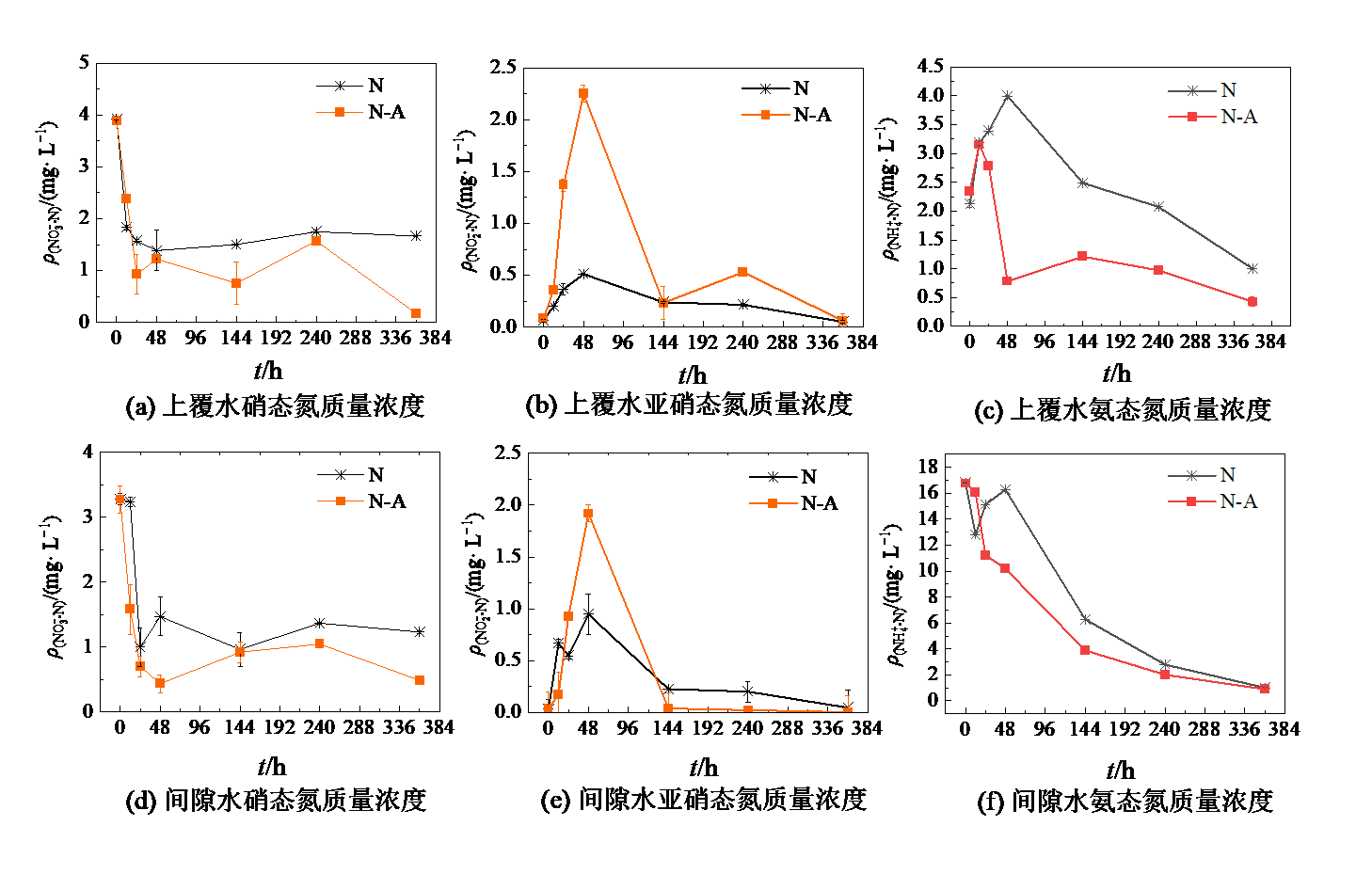
图3 上覆水(a、b、c)和间隙水(d、e、f)NO3-、NO2-和NH4+质量浓度的变化
Figure 3 Change of NO3-, NO2- and NH4+ concentration in overlying water (a, b, c) and pore water (d, e, f)
| t/d | N组TP质量分数 | N-A组TP质量分数 |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2.27±0.03 | 2.26±0.01 |
| 0.5 | 2.19±0.03 | 2.13±0.02 |
| 1 | 2.21±0.03 | 2.14±0.02 |
| 2 | 2.20±0.06 | 1.99±0.20 |
| 6 | 2.07±0.23 | 2.02±0.07 |
| 10 | 2.12±0.06 | 2.01±0.01 |
| 15 | 2.12±0.07 | 2.00±0.01 |
表2 沉积物TP质量分数的变化
Table 2 Change in sediment TP concentrations mg·g-1
| t/d | N组TP质量分数 | N-A组TP质量分数 |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2.27±0.03 | 2.26±0.01 |
| 0.5 | 2.19±0.03 | 2.13±0.02 |
| 1 | 2.21±0.03 | 2.14±0.02 |
| 2 | 2.20±0.06 | 1.99±0.20 |
| 6 | 2.07±0.23 | 2.02±0.07 |
| 10 | 2.12±0.06 | 2.01±0.01 |
| 15 | 2.12±0.07 | 2.00±0.01 |
| [1] |
BONGOUA-DEVISME A J, CEBRON A, KASSIN K E, et al., 2013. Microbial communities involved in Fe reduction and mobility during soil organic matter (SOM) mineralization in two contrasted paddy soils[J]. Geomicrobiology Journal, 30(4): 347-361.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BRYCE C, BLACKWELL N, SCHMIDT C, et al., 2018. Microbial anaerobic Fe(II) oxidation - ecology, mechanisms and environmental implications: Microbial anaerobic Fe(II) oxidation[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 20(10): 3462-3483.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
CORZO A, BERGEIJK S A V, GARCIA-ROBLEDO E, 2009. Effects of green macroalgal blooms on intertidal sediments: net metabolism and carbon and nitrogen contents[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 380: 81-93.
DOI URL |
| [4] | DAI J W, HE S B, ZHOU W L, et al., 2018. Integrated ecological floating bed treating wastewater treatment plant effluents: effects of influent nitrogen forms and sediments[J]. Environmental Science & Pollution Research, 25(19): 18793-18801. |
| [5] | DANIEL P, JIRI J, DAGMARA S, et al., 2018. Iron and nitrogen cycling, bacterioplankton community composition and mineral transformations involving phosphorus stabilisation in the ferruginous hypolimnion of a post-mining lake[J]. Environmental science. Processes & impacts, 20(10): 1414-1426. |
| [6] |
GIBNEY B P, NUSSLEIN K, 2007. Arsenic sequestration by nitrate respiring microbial communities in urban lake sediments[J]. Chemosphere, 70(2): 329-336.
PMID |
| [7] |
HAYAKAWA A, HATAKEYAMA M, ASANO R, et al., 2013. Nitrate reduction coupled with pyrite oxidation in the surface sediments of a sulfide-rich ecosystem[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Biogeosciences, 118(2): 639-649.
DOI URL |
| [8] | HEINRICH L, ROTHE M, BRAUN B, et al., 2020. Transformation of redox-sensitive to redox-stable iron-bound phosphorus in anoxic lake sediments under laboratory conditions[J]. Water Research, 89: 116609. |
| [9] |
HENDERSON R K, BAKER A, PARSONS S A, et al., 2008. Characterisation of algogenic organic matter extracted from cyanobacteria, green algae and diatoms[J]. Water Research, 42(13): 3435-3445.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
HEPBURN L E, BUTLER I B, BOYCE A, et al., 2020. The use of operationally-defined sequential Fe extraction methods for mineralogical applications: A cautionary tale from Mssbauer spectroscopy[J]. Chemical Geology, 543: 119584.
DOI URL |
| [11] | HOWARTH R, CHAN F, CONLEY D J, et al., 2011. Coupled biogeochemical cycles: eutrophication and hypoxia in temperate estuaries and coastal marine ecosystems[J]. Frontiers in Ecology & the Environment, 9(1): 18-26. |
| [12] |
KANAPARTHI D, CONRAD R, 2015. Role of humic substances in promoting autotrophic growth in nitrate-dependent iron-oxidizing bacteria[J]. Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 38(3): 184-188.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
KANG M X, PENG S, TIAN Y M, et al., 2018. Effects of dissolved oxygen and nutrient loading on phosphorus fluxes at the sediment-water interface in the Hai River Estuary, China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 130: 132-139.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
KLUEGLEIN N, KAPPLER A, 2013. Abiotic oxidation of Fe(II) by reactive nitrogen species in cultures of the nitrate-reducing Fe(II) oxidizer Acidovorax sp. BoFeN1-questioning the existence of enzymatic Fe(II) oxidation[J]. Geobiology, 11(2): 180-190.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
KUYPERS M M, MARCHANT H K, KARTAL B, 2018. The microbial nitrogen-cycling network[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 16(5): 263.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
LARESE-CASANOVA P, HADERLEIN S B, KAPPLER A, 2010. Biomineralization of lepidocrocite and goethite by nitrate-reducing Fe(II)-oxidizing bacteria: Effect of pH, bicarbonate, phosphate, and humic acids[J]. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 74(13): 3721-3734.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
LI H X, LI D P, ZHANG L, et al., 2019. Fundamental aspects of the corrosion of N80 steel in a formation water system under high CO2 partial pressure at 100 degrees C[J]. RSC advances, 9(21): 11641-11648.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
LI S J, LIN Z G, LIU M, et al., 2020. Effect of ferric chloride on phosphorus immobilization and speciation in Dianchi Lake sediments[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 197: 110637.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
LI Y Y, CHAPMAN S J, NICOL G W, et al., 2018. Nitrification and nitrifiers in acidic soils[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 116: 290-301.
DOI URL |
| [20] | MA H, ZHAO B Y, LI L, et al., 2019. Fractionation trends of phosphorus associating with iron fractions: An explanation by the simultaneous extraction procedure[J]. Soil & Tillage Research, 190: 41-49. |
| [21] |
MARCEL M M, MARCHANT H, KARTAL B, 2018. The microbial nitrogen-cycling network[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 16(5): 263.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
MEJIA J, RODEN E E, GINDER-VOGEL M, 2016. Influence of Oxygen and Nitrate on Fe (Hydr)oxide Mineral Transformation and Soil Microbial Communities during Redox Cycling[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 50(7): 3580-3588.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
MELTON E D, SWANNER E D, BEHRENS S, et al., 2014. The interplay of microbially mediated and abiotic reactions in the biogeochemical Fe cycle[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 12(12): 797-808.
DOI PMID |
| [24] | MOLINUEVO B, GARCIA M C, KARAKASHEV D, et al., 2009. Anammox for ammonia removal from pig manure effluents: Effect of organic matter content on process performance[J]. Bioresource Technology, 99(7): 2171-2175. |
| [25] |
ORIHEL D M, BAULCH H M, CASSON N J, et al., 2017. Internal phosphorus loading in Canadian fresh waters: a critical review and data analysis[J]. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 74(12): 2005-2029.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
PAIPA C, MATEO M, GODOY I, et al., 2005. Comparative study of alternative methods for the simultaneous determination of Fe3+ and Fe2+ in leaching solutions and in acid mine drainages[J]. Minerals Engineering, 18(11): 1116-1119.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
POULTON S W, CANFIELD D E, 2005. Development of a sequential extraction procedure for iron: implications for iron partitioning in continentally derived particulates[J]. Chemical Geology, 214(3-4): 209-221.
DOI URL |
| [28] | ROH Y, ZHANG C L, VALI H, et al., 2003. Biogeochemical and environmental factors in Fe biomineralization: Magnetite and siderite formation[J]. Clays & Clay Minerals, 51(1): 83-95. |
| [29] |
RUBAN V, LÓPEZ-SÁNCHEZ J F, PARDO P, et al., 1999. Selection and evaluation of sequential extraction procedures for the determination of phosphorus forms in lake sediment[J]. Journal of Environmental Monitoring Jem, 1(1): 51-6.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
RUTTENBERG K C, 1992. Development of a sequential extraction method for different forms of phosphorus in marine sediments[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 37(7): 1460-1482.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
SCHÄDLER S, BURKHARDT C, HEGLER F, et al., 2009. Formation of Cell-Iron-Mineral Aggregates by Phototrophic and Nitrate-Reducing Anaerobic Fe(II)-Oxidizing Bacteria[J]. Geomicrobiology Journal, 26(2): 93-103.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
SMITH M S, TIEDJE J M, 1979. Phases of denitrification following oxygen depletion in soil[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 11(3): 261-267.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
WANG J F, CHEN J A, DING S M, et al., 2015. Effects of temperature on phosphorus release in sediments of Hongfeng Lake, southwest China: an experimental study using diffusive gradients in thin-films (DGT) technique[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 74(7): 5885-5894.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
WEBER K A, HEDRICK D B, PEACOCK A D, et al., 2009. Physiological and taxonomic description of the novel autotrophic, metal oxidizing bacterium, Pseudogulbenkiania sp. strain 2002[J]. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 83(3): 555-565.
DOI PMID |
| [35] |
XIONG Y J, GUILBAUD R, PEACOCK C L, et al., 2019. Phosphorus cycling in Lake Cadagno, Switzerland: A low sulfate euxinic ocean analogue[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 251: 116-135.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
YUAN H Z, TAI Z Q, LI Q, et al., 2020. In-situ, high-resolution evidence from water-sediment interface for significant role of iron bound phosphorus in eutrophic lake[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 706: 136040.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
ZHOU Y, OEHMEN A, LIM M, et al., 2011. The role of nitrite and free nitrous acid (FNA) in wastewater treatment plants[J]. Water Research, 45(15): 4672-4682.
DOI PMID |
| [38] | 李奔运, 匡帅, 王臻宇, 等, 2020. 东巢湖沉积物水界面氮,磷,氧迁移特征及意义[J]. 湖泊科学, 32(3): 688-700. |
| LI B Y, KUANG S, WANG Z Y, et al., 2020. Migration characteristics and significance of nitrogen, phosphorus, and oxygen at the sediment water interface of Dongchao Lake[J]. Lake Science, 32(3): 688-700. | |
| [39] | 李子阳, 陆东亮, 华天予, 等, 2020. 蓝藻发酵液中氮磷回收及其作为反硝化碳源研究[J]. 环境化学, 39(12): 3562-3573. |
| LI Z Y, LU D L, HUA T Y, et al., 2020. Recovery of nitrogen and phosphorus from blue-green algae fermentation broth and its use as a denitrification carbon source[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 39(12): 3562-3573. | |
| [40] | 李敏, 韦鹤平, 王光谦, 等, 2004. 长江口、杭州湾水域沉积物中磷的化学形态分布特征[J]. 海洋学报, 26(2): 125-131. |
| LI M, WEI H P, WANG G Q, et al., 2004. Environmental science distribution characteristics of chemical forms of phosphorus in sediments of Yangtze Estuary and Hangzhou Bay Waters[J]. Journal of Oceanography, 26(2): 125-131. | |
| [41] | 王睿喆, 王沛芳, 任凌霄, 等, 2015. 营养盐输入对太湖水体中磷形态转化及藻类生长的影响[J]. 环境科学, 36(4): 1301-1308. |
| WANG R Z, WANG P F, REN L X, et al., 2015. Effects of nutrient input on phosphorus speciation transformation and algae growth in the Taihu Lake Lake[J]. Environmental Science, 36(4): 1301-1308. | |
| [42] | 余芬芳, 2013. 外源硫酸盐对武汉墨水湖沉积物营养盐和重金属的作用[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学. |
| YU F F, 2013. Effects of exogenous sulfates on nutrients and heavy metals in sediments of Wuhan Ink Lake[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University | |
| [43] | 杨文斌, 唐皓, 韩超, 等, 2016. 太湖沉积物铁形态分布特征及磷铁相关性分析[J]. 中国环境科学, 36(4): 1145-1156. |
| YANG W B, TANG H, HAN C, et al., 2016. Distribution characteristics of iron forms and correlation analysis of phosphorus and iron in the Taihu Lake Lake sediments[J]. China Environmental Science, 36(4): 1145-1156. |
| [1] | 梁燚彤, 李泽敏, 吴宇伦, 邱光磊, 吴海珍, 韦朝海. 亚硝酸盐对厌氧氨氧化耦合系统的脱氮效能及微生物群落的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1275-1284. |
| [2] | 王家一, 孙亭亭, 沙润钰, 谌婷红, 邢冉, 秦伯强, 施文卿. 富营养化湖泊蓝藻打捞减污降碳效果模拟研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1108-1114. |
| [3] | 王超, 杨倩楠, 张池, 刘同旭, 张晓龙, 陈静, 刘科学. 丹霞山不同土地利用方式土壤磷组分特征及其有效性[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 889-897. |
| [4] | 王云, 郑西来, 曹敏, 李磊, 宋晓冉, 林晓宇, 郭凯. 滨海含水层咸-淡水过渡带反硝化性能与控制因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 980-988. |
| [5] | 王铁铮, 瞿心悦, 刘春香, 李有志. 东江湖水质时空变化规律及其与流域土地利用的关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 722-732. |
| [6] | 张广毅, 张嘉涛, 王晓伟. 湖泊底泥微生物燃料电池中磷形态分布及释放研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 590-598. |
| [7] | 杨奇丽, 窦韦丽, 刘之文, 郭景, 吕刚. 正构烷烃示源的阜新细河河道石油烃类污染特征及其影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 599-608. |
| [8] | 樊慧琳, 张佳敏, 李欢, 王艳玲. 坡耕地稻田剖面磷的储存格局与流失风险研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 283-291. |
| [9] | 杨瑞, 孙蔚旻, 李永斌, 郭丽芳, 焦念元. 尾矿先锋植物根际溶磷菌的分离鉴定与其促生研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 166-174. |
| [10] | 黄伟佳, 刘春, 刘岳, 黄斌, 李定强, 袁再健. 南岭山地不同海拔土壤生态化学计量特征及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 80-89. |
| [11] | 李晓晖, 艾仙斌, 李亮, 王玺洋, 辛在军, 孙小艳. 新型改性稻壳生物炭材料对镉污染土壤钝化效果的研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1901-1908. |
| [12] | 吉冰静, 刘艺, 吴杨, 高淑涛, 曾祥英, 于志强. 长江口及邻近东海沉积物中多环芳烃和含氧多环芳烃的分布特征、来源及生态风险[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1400-1408. |
| [13] | 魏岚, 黄连喜, 李翔, 王泽煌, 陈伟盛, 黄庆, 黄玉芬, 刘忠珍. 生物炭基质可显著地促进香蕉幼苗生长[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 732-739. |
| [14] | 贺斌, 胡茂川. 广东省各区县农业面源污染负荷估算及特征分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 771-776. |
| [15] | 苏焱, 全妍红, 宦紫嫣, 姚佳, 苏小娟. 磷改性生物炭对云南某铅锌矿周边农田铅锌污染土壤修复效果的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 593-602. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
