生态环境学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (7): 1249-1262.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.07.008
周宏光1( ), 甘艳平1, 伍德权3, 杨延梅1,*(
), 甘艳平1, 伍德权3, 杨延梅1,*( ), 张扬2, 王璐瑶2
), 张扬2, 王璐瑶2
收稿日期:2023-03-12
出版日期:2023-07-18
发布日期:2023-09-27
通讯作者:
* 杨延梅。Email: yymeicq@163.com作者简介:周宏光(1987年生),男,副教授,博士,主要从事环境功能材料研制及水污染控制。Email: hgzhou@cqjtu.edu.cn
基金资助:
ZHOU Hongguang1( ), GAN Yanping1, WU Dequan3, YANG Yanmei1,*(
), GAN Yanping1, WU Dequan3, YANG Yanmei1,*( ), ZHANG Yang2, WANG Luyao2
), ZHANG Yang2, WANG Luyao2
Received:2023-03-12
Online:2023-07-18
Published:2023-09-27
摘要:
水库消落带因受到交替淹没与暴露的问题,其底泥As释放、迁移和转化受到影响,此外,腐殖酸(HA)作为底泥的主要有机成分,其对As的作用机制尚存在争议,因此通过钝化剂来稳定底泥中的As,对底泥资源化利用具有重要意义。采用改进的共沉淀法制备FeMnMg-LDH,在人工培养的As(Ⅴ)污染底泥上模拟淹水和落干试验,同时考虑HA的影响,以FeMnMg-LDH作为钝化剂对消落带地区的底泥进行稳定化处理,研究As的形态转化特征及浸出毒性变化,并分析两者的相关性。结果表明:淹水条件下HA促进As向上覆水体释放且HA水平越高释放量越多,60 mg·kg-1和250 mg·kg-1污染底泥向上覆水体释放的As质量浓度最高分别可达4.81×103 μg·L-1和1.22×104 μg·L-1,添加FeMnMg-LDH后有效抑制As由底泥向上覆水体释放;随FeMnMg-LDH添加水平的增加,淹水和落干条件下60 mg·kg-1污染底泥中弱酸提取态砷(MASF-As)百分比降至0.06%和0.07%,250 mg·kg-1污染底泥中MASF-As百分比均降至0.13%,MASF-As向更稳定的形态转变;随FeMnMg-LDH添加水平的增加,底泥中As的浸出质量浓度逐渐降低,稳定化效率逐渐升高,60 mg·kg-1和250 mg·kg-1污染底泥在淹水期稳定化效率高达到76.0%和74.1%,在落干期高达75.9%和73.3%;落干期底泥中As的浸出毒性风险高于淹水期;淹水及落干条件下HA的添加影响FeMnMg-LDH对污染底泥中As的稳定化作用,表现为正效应。相关性分析结果表明,由于淹水过程中底泥向上覆水体释放As,部分底泥As的浸出毒性与MASF-As和可还原态砷(RF-As)的相关性不显著;落干条件下底泥As的浸出毒性与MASF-As呈正相关,与RF-As呈负相关。综上所述,FeMnMg-LDH材料在消落带As污染底泥钝化修复工作中,具有一定的实践意义。
中图分类号:
周宏光, 甘艳平, 伍德权, 杨延梅, 张扬, 王璐瑶. 淹水-落干条件下FeMnMg-LDH对污染底泥中砷迁移转化的调控研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1249-1262.
ZHOU Hongguang, GAN Yanping, WU Dequan, YANG Yanmei, ZHANG Yang, WANG Luyao. Regulation of Arsenic Transport and Transformation in Contaminated Sediment by FeMnMg-LDH under Flooding-drying Conditions[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(7): 1249-1262.
| 样品 | pH | w(total Pb)/(mg·kg-1) | w(total Cd)/(mg·kg-1) | w(total Fe)/(mg·kg-1) | w(total Mn)/(mg·kg-1) | w(total As)/(mg·kg-1) | CEC/(cmol·kg-1) | w有机质/(mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 底泥 | 8.76 | 342 | 5.27 | 9.37 | 3.71×102 | 6.10 | 22.4 | 1.45×104 |
表1 供试底泥基本理化性质
Table 1 Basic physicochemical properties of sediment samples
| 样品 | pH | w(total Pb)/(mg·kg-1) | w(total Cd)/(mg·kg-1) | w(total Fe)/(mg·kg-1) | w(total Mn)/(mg·kg-1) | w(total As)/(mg·kg-1) | CEC/(cmol·kg-1) | w有机质/(mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 底泥 | 8.76 | 342 | 5.27 | 9.37 | 3.71×102 | 6.10 | 22.4 | 1.45×104 |
| As污染水平 (mg·kg-1) | HA添加水平 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | 2% | 5% | |
| 60 | As-60 | As-60-2% | As-60-5% |
| 250 | As-250 | As-250-2% | As-250-5% |
表2 试验设计
Table 2 Experimental design
| As污染水平 (mg·kg-1) | HA添加水平 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | 2% | 5% | |
| 60 | As-60 | As-60-2% | As-60-5% |
| 250 | As-250 | As-250-2% | As-250-5% |
| 形态 | 提取试剂 | 提取条件 |
|---|---|---|
| 弱酸提取态 (MASF-As) | 0.11 mol·L-1 HAc | 加入40 mL提取剂, 室温 (22±5) ℃振荡16 h, 3000 r·min-1离心20 min, 倾析液体保存待测 |
| 可还原态 (RF-As) | 0.50 mol·L-1 NH2OH·HCl | 加入40 mL提取剂, 室温 (22±5) ℃振荡16 h, 3000 r·min-1离心20 min, 倾析液体保存待测 |
| 可氧化态 (OF-As) | 1.00 mol·L-1 NH4Ac (pH=2), H2O2 (pH=2-3) | 按标准操作多次加入H2O2对试样进行消化, 然后加入50 mL NH4Ac, 室温 (22±5) ℃振荡16 h, 3000 r·min-1离心20 min, 倾析液体保存待测 |
| 残渣态 (ResF-As) | 王水水浴消解 | 加入10 mL王水 (1+1), 加塞于水浴锅中煮沸2 h, 期间摇动3-4次, 摇匀静置后取上清液待测 |
表3 As元素形态顺序提取试剂及提取条件
Table 3 As element morphological order extraction reagents and extraction conditions
| 形态 | 提取试剂 | 提取条件 |
|---|---|---|
| 弱酸提取态 (MASF-As) | 0.11 mol·L-1 HAc | 加入40 mL提取剂, 室温 (22±5) ℃振荡16 h, 3000 r·min-1离心20 min, 倾析液体保存待测 |
| 可还原态 (RF-As) | 0.50 mol·L-1 NH2OH·HCl | 加入40 mL提取剂, 室温 (22±5) ℃振荡16 h, 3000 r·min-1离心20 min, 倾析液体保存待测 |
| 可氧化态 (OF-As) | 1.00 mol·L-1 NH4Ac (pH=2), H2O2 (pH=2-3) | 按标准操作多次加入H2O2对试样进行消化, 然后加入50 mL NH4Ac, 室温 (22±5) ℃振荡16 h, 3000 r·min-1离心20 min, 倾析液体保存待测 |
| 残渣态 (ResF-As) | 王水水浴消解 | 加入10 mL王水 (1+1), 加塞于水浴锅中煮沸2 h, 期间摇动3-4次, 摇匀静置后取上清液待测 |
| 风险等级 | 无风险 | 低风险 | 中等风险 | 高风险 | 非常高风险 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MASF所占比例/% | <1 | 1-10 | 11-30 | 31-50 | >50 |
表4 风险评价准则
Table 4 Risk assessment criteria
| 风险等级 | 无风险 | 低风险 | 中等风险 | 高风险 | 非常高风险 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MASF所占比例/% | <1 | 1-10 | 11-30 | 31-50 | >50 |
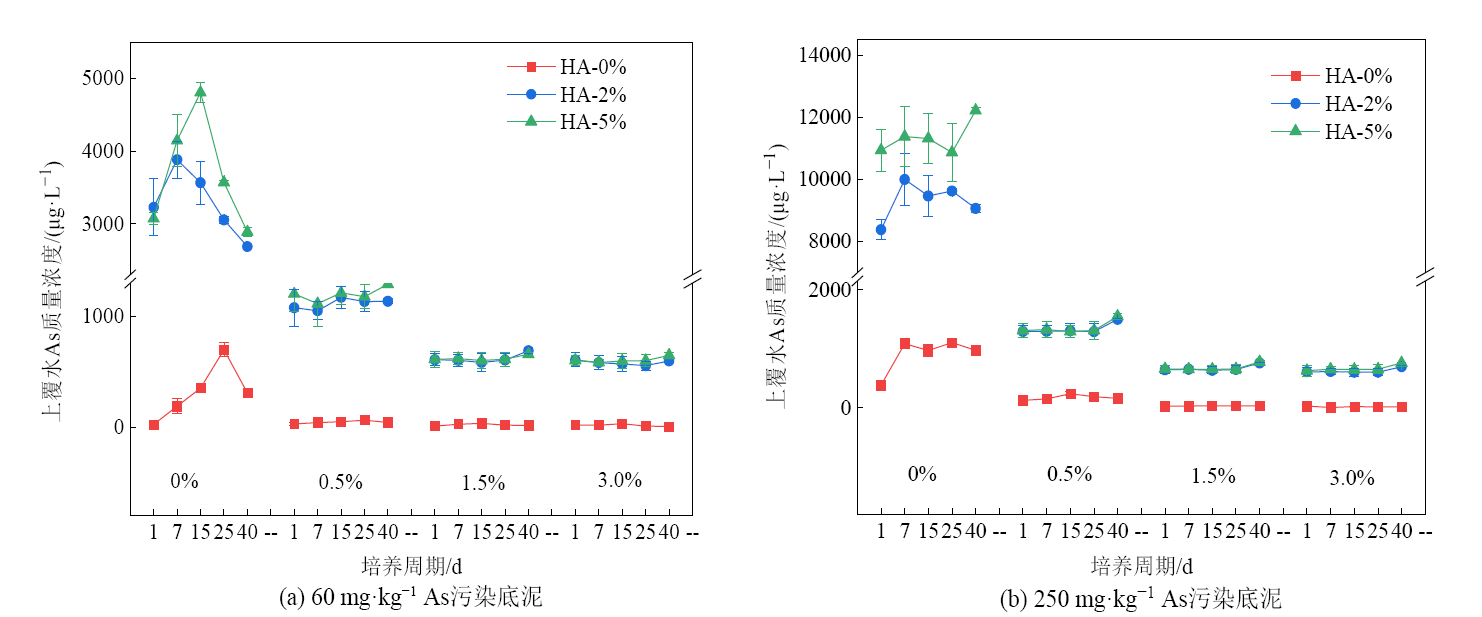
图2 HA添加下FeMnMg-LDH材料对底泥上覆水As质量浓度的影响
Figure 2 Effect of FeMnMg-LDH material on As mass concentration in overlying water of sediment under the influence of HA addition
| 赋存 形态 | 浸出毒性 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As-60 | As-60-2% | As-60-5% | As-250 | As-250-2% | As-250-5% | |
| MASF-As | 0.982* 1) | 0.891 | 0.849 | 0.994** 2) | 0.999** | 0.997** |
| RF-As | -0.979* | -0.892 | -0.927 | -0.840 | -0.929 | -0.996** |
| OF-As | -0.807 | -0.963* | -0.885 | -0.872 | -0.999** | -0.943 |
| ResF-As | 0.879 | 0.919 | 0.929 | 0.667 | 0.956* | 0.996** |
表5 淹水条件下污染底泥中As的赋存形态与浸出毒性质量分数的Pearson相关性
Table 5 Pearson correlation between As fugacity pattern and leaching toxicity mass fraction in contaminated sediments under flooding conditions
| 赋存 形态 | 浸出毒性 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As-60 | As-60-2% | As-60-5% | As-250 | As-250-2% | As-250-5% | |
| MASF-As | 0.982* 1) | 0.891 | 0.849 | 0.994** 2) | 0.999** | 0.997** |
| RF-As | -0.979* | -0.892 | -0.927 | -0.840 | -0.929 | -0.996** |
| OF-As | -0.807 | -0.963* | -0.885 | -0.872 | -0.999** | -0.943 |
| ResF-As | 0.879 | 0.919 | 0.929 | 0.667 | 0.956* | 0.996** |
| 赋存形态 | 浸出毒性 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As-60 | As-60-2% | As-60-5% | As-250 | As-250-2% | As-250-5% | |
| MASF-As | 0.996** | 0.999** | 0.999** | 0.999** | 0.956* | 0.975* |
| RF-As | -0.972* | -0.958* | -0.963* | -0.974* | -0.988* | -0.963* |
| OF-As | 0.106 | 0.772 | -0.685 | -0.088 | 0.835 | 0.840 |
| ResF-As | 0.702 | 0.977* | 0.844 | 0.994** | 0.987* | 0.995** |
表6 落干条件下污染底泥中As的赋存形态与浸出毒性质量分数的Pearson相关性
Table 6 Pearson correlation between As fugacity pattern and leaching toxicity mass fraction in contaminated sediments under drying conditions
| 赋存形态 | 浸出毒性 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As-60 | As-60-2% | As-60-5% | As-250 | As-250-2% | As-250-5% | |
| MASF-As | 0.996** | 0.999** | 0.999** | 0.999** | 0.956* | 0.975* |
| RF-As | -0.972* | -0.958* | -0.963* | -0.974* | -0.988* | -0.963* |
| OF-As | 0.106 | 0.772 | -0.685 | -0.088 | 0.835 | 0.840 |
| ResF-As | 0.702 | 0.977* | 0.844 | 0.994** | 0.987* | 0.995** |
| [1] |
AL-MAKISHAH N H, ABU TALEB M, BARAKAT M A, 2020. Arsenic bioaccumulation in arsenic-contaminated soil: A review[J]. Chemical Papers, 74(9): 2743-2757.
DOI |
| [2] |
BALALI-MOOD M, NASERI K, TAHERGORABI Z, et al., 2021. Toxic mechanisms of five heavy metals: mercury, lead, chromium, cadmium, and arsenic[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 12: 643972.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
BYEON E, KANG H M, YOON C, et al., 2021. Toxicity mechanisms of arsenic compounds in aquatic organisms[J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 237: 105901.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
CHENG X, HUANG X, WANG X, et al., 2010. Influence of calcination on the adsorptive removal of phosphate by Zn-Al layered double hydroxides from excess sludge liquor[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 177(1-3): 516-523.
DOI PMID |
| [5] |
CAVANI F, TRIFIRÒ F, VACCARI A, 1991. Hydrotalcite-type anionic clays: preparation, properties and applications[J]. Catalysis Today, 11(2): 173-301.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
FAKOUR H, LIN T F, 2014. Experimental determination and modeling of arsenic complexation with humic and fulvic acids[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 279: 569-578.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
GAO M S, SU Y, GAO J B, et al., 2022. Arsenic speciation transformation in soils with high geological background: new insights from the governing role of Fe[J]. Chemosphere, 302: 134860.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
GRAF W L, 2006. Downstream hydrologic and geomorphic effects of large dams on American rivers[J]. Geomorphology, 79(3-4): 336-360.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
GUO Y W, ZHU Z L, QIU Y L, et al., 2013. Synthesis of mesoporous Cu/Mg/Fe layered double hydroxide and its adsorption performance for arsenate in aqueous solutions[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 25(5): 944-953.
PMID |
| [10] |
GUPTA S, NAYEK S, SAHA R N, 2010. Temporal changes and depth wise variations in pit pond hydrochemistry contaminated with industrial effluents with special emphasis on metal distribution in water-sediment system[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 183(1-3): 125-131.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
HONG J, ZHU Z L, LU H T, et al., 2014. Synthesis and arsenic adsorption performances of ferric-based layered double hydroxide with α-alanine intercalation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 252: 267-274.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
HU Y Y, ZHENG X H, LIU S S, et al., 2021. Prediction and optimization of adsorption performance of MC@MgAl-LDH for the removal of humic acid from aqueous solution: BBD model and mechanism[J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 302: 122377.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
JAIN C K, 2004. Metal fractionation study on bed sediments of River Yamuna, India[J]. Water Research, 38(3): 569-578.
PMID |
| [14] |
JI L P, LI S T, XU H M, et al., 2022. Morphology control enables [SnS4]4- clusters and MgFe-LDHs dual active sites for the adsorption of mercury and arsenic ions[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 433(3): 133761-133769.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
JUNG K W, LEE S Y, CHOI J W, et al., 2021. Synthesis of Mg-Al layered double hydroxides-functionalized hydrochar composite via an in situ one-pot hydrothermal method for arsenate and phosphate removal: structural characterization and adsorption performance[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 420(1): 129775.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
KARRI V, SCHUHMACHER M, KUMAR V, 2016. Heavy metals (Pb, Cd, As and MeHg) as risk factors for cognitive dysfunction: A general review of metal mixture mechanism in brain[J]. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 48: 203-213.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
KOWALIK P, KONKOL M, KONDRACKA M, et al., 2013. Memory effect of the CuZnAl-LDH derived catalyst precursor-In situ XRD studies[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 464-465: 339-347.
DOI URL |
| [18] | LALAS S, ATHANASIADIS V, DOURTOGLOU V G, 2018. Humic and fulvic acids as potentially toxic metal reducing agents in water[J]. CLEAN - Soil, Air, Water, 46(2): 1-6. |
| [19] |
LI J P, DING Y, WANG K L, et al., 2020. Comparison of humic and fulvic acid on remediation of arsenic contaminated soil by electrokinetic technology[J]. Chemosphere, 241(2): 125038.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
LIU J Q, WU P X, LI S S, et al., 2019. Synergistic deep removal of As(III) and Cd(II) by a calcined multifunctional MgZnFe-CO3 layered double hydroxide: photooxidation, precipitation and adsorption[J]. Chemosphere, 225: 115-125.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
LÜ P, LI L F, HUANG X Y, et al., 2022. Pre-magnetic bamboo biochar cross-linked CaMgAl layered double-hydroxide composite: high- efficiency removal of As(III) and Cd(II) from aqueous solutions and insight into the mechanism of simultaneous purification[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 823: 153743.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
MANDAL S K, RAY R, CHOWDHURY C, et al., 2013. Implication of organic matter on arsenic and antimony sequestration in sediment: evidence from Sundarban mangrove forest, India[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 90: 451-455.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
MATUSIK J, HYLA J, MAZIARZ P, et al., 2019. Performance of halloysite-Mg/Al LDH materials for aqueous As(V) and Cr(VI) removal[J]. Materials (Basel), 12(21): 3569.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
MAZIARZ P, MATUSIK J, STRĄCZEK T, et al., 2019. Highly effective magnet-responsive LDH-Fe oxide composite adsorbents for As(V) removal[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 362: 207-216.
DOI URL |
| [25] | NIU Y D, CHEN F L, LI Y Z, et al., 2021. Trends and sources of heavy metal pollution in global river and lake sediments from 1970 to 2018[J]. Reviews of Environmental Contamination Toxicology, 257: 1-35. |
| [26] | OTGONJARGAL E, KIM Y S, PARK S M, et al., 2012. Mn-Fe layered double hydroxides for adsorption of As(III) and As(V)[J]. Separation Science and Technology, 47(15): 2192-2198. |
| [27] |
PRIYA V N, RAJKUMAR M, MOBIKA J, et al., 2020. Removal of As(V) in water using β-Cyclodextrin intercalated Fe-Al layered double hydroxide/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites[J]. Synthetic Metals, 270: 116595-116610.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
QIAN G R, XU L, LI N, et al., 2022. Enhanced arsenic migration in tailings soil with the addition of humic acid, fulvic acid and thiol-modified humic acid[J]. Chemosphere, 286(Part 2): 131784.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
QIAO J T, LI X M, LI F B, et al., 2019. Humic substances facilitate arsenic reduction and release in flooded paddy soil[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 53(9): 5034-5042.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
QUIROGA M M B, JUNCA M I, MERINO N A, 2021. Study of the effect of the LDH cations precursors in the removal of arsenic in aqueous solution[J]. Water Science and Technology, 83(10): 2518-2525.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
RYBKA K, MATUSIK J, MARZEC M, 2022. Mg/Al and Mg/Fe layered double hydroxides derived from magnesite and chemicals: the effect of adsorbent features and anions chemistry on their removal efficiency[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 332(15): 130084.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
SANTOS-ECHEANDIA J, VALE C, CAETANO M, et al., 2010. Effect of tidal flooding on metal distribution in pore waters of marsh sediments and its transport to water column (Tagus estuary, Portugal)[J]. Marine Environmental Research, 70(5): 358-367.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
SARKAR A, PAUL B, 2016. The global menace of arsenic and its conventional remediation-a critical review[J]. Chemosphere, 158: 37-49.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
SHI X F, KANG L, HONG J M, et al., 2021. Strong selectivity and high capacity in the adsorption of As(V) from wastewater by glycine-modified Fe/Cu-layered double hydroxides[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 865: 158956-158965.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
WANG J Y, ZHANG T P, LI M, et al., 2018. Arsenic removal from water/wastewater using layered double hydroxide derived adsorbents, a critical review[J]. RSC Advances, 8: 22694-22709.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
WANG Q W, LIN Q H, LI Q Z, et al., 2021a. As(III) removal from wastewater and direct stabilization by in-situ formation of Zn-Fe layered double hydroxides[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 403: 123920.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
WANG S, ZHENG K, LI H P, et al., 2021b. Arsenopyrite weathering in acidic water: Humic acid affection and arsenic transformation[J]. Water Research, 194: 116917.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
XU W H, WANG J, WANG L, et al., 2013. Enhanced arsenic removal from water by hierarchically porous CeO2-ZrO2 nanospheres: Role of surface- and structure-dependent properties[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 260: 498-507.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
XU Y F, WU Y, HAN J G, et al., 2017. The current status of heavy metal in lake sediments from China: pollution and ecological risk assessment[J]. Ecology and Evolution, 7(14): 5454-5466.
DOI PMID |
| [40] |
YE C, DENG J, HUAI L Y, et al., 2022. Multifunctional capacity of CoMnFe-LDH/LDO activated peroxymonosulfate for parsanilic acid removal and inorganic arsenic immobilization: Performance and surface-bound radical mechanism[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 806(Part 1): 150379.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
ZHANG C, YU Z G, ZENG G M, et al., 2014. Effects of sediment geochemical properties on heavy metal bioavailability[J]. Environment International, 73: 270-281.
DOI PMID |
| [42] | ZHANG J, LU W J, ZHAN S Y, et al., 2021. Adsorption and mechanistic study for humic acid removal by magnetic biochar derived from forestry wastes functionalized with Mg/Al-LDH[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 276(3-4): 119296. |
| [43] |
ZHAO X J, GAO B, XU D Y, et al., 2017. Heavy metal pollution in sediments of the largest reservoir (Three Gorges Reservoir) in China: A review[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24: 20844-20858.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
ZHOU H G, JIANG Z M, WEI S Q, 2018a. A new hydrotalcite-like absorbent FeMnMg-LDH and its adsorption capacity for Pb2+ ions in water[J]. Applied Clay Science, 153: 29-37.
DOI URL |
| [45] | ZHOU H G, JIANG Z M, WEI S Q, et al., 2018b. Adsorption of Cd(II) from aqueous solutions by a novel layered double hydroxide FeMnMg-LDH[J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 229(3): 1-16. |
| [46] |
ZHOU Y L, ZHANG Y B, LI G H, et al., 2016. Effects of metal cations on the fulvic acid (FA) adsorption onto natural iron oxide in iron ore pelletizing process[J]. Powder Technology, 302: 90-99.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
ZHU Y G, YOSHINAGA M, ZHAO F J, et al., 2014. Earth abides arsenic biotransformations[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 42: 443-467.
DOI |
| [48] | 董丽华, 李亚男, 常素云, 等, 2009. 沉积物中重金属的形态分析及风险评价[J]. 天津大学学报, 42(12): 1112-1117. |
| DONG L H, LI Y L, CHANG S Y, et al., 2009. Fraction distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments[J]. Journal of Tianjin University, 42(12): 1112-1117. | |
| [49] | 国家环境保护总局科技标准司,2007. 固体废物浸出毒性浸出方法醋酸缓冲溶液法: HJ/T 300-2007[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社: 2-4. |
| Science and Technology Standards Department of State Environmental Protection Administration,2007. Solid waste- Extraction procedure for leaching toxicity-Acetic acid buffer solution method: HJ/T 300-2007[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press: 2-4. | |
| [50] | 韩冬雅, 2020. 间歇性灌溉下土壤外源砷的结合形态转化研究[D]. 石家庄: 河北地质大学:45-46. |
| HAN D Y, 2020. Study on the fractionation of exogenous arsenic under intermittent irrigation[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei GEO University:45-46. | |
| [51] | 环境保护部科技标准司. 2013. 土壤和沉积物汞, 砷, 硒, 铋, 锑的测定微波消解/原子荧光法: HJ 680-2013[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社: 1-6. |
| Department of Science and Technology Standards, Ministry of Environmental Protection, 2013. Soil and sediment-Determination of mercury, arsenic, selenium, bismuth, antimony-Microwave dissolution/ Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry: HJ 680-2013[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press: 1-6. | |
| [52] | 黄桂云, 蔡玉鹏, 徐敏, 等, 2023. 三峡水库近坝段消落区土壤重金属分布特征及污染评价[J/OL]. 水生态学杂志: 1-9[2023-08-01]. http://libvpn.cqjtu.edu.cn:80/rwt/CNKI/https/MSYXTLUQPJUB/10.15928/j. |
| HUANG G Y, CAI Y P, XU M, et al., 2023. Distribution characteristics and pollution assessment of soil heavy metals in the water-level-fluctuating zone near the dam section of Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Journal of Water Ecology: 1-9 [2023-08-01]. http://libvpn.cqjtu.edu.cn:80/rwt/CNKI/https/MSYXTLUQPJUB/10.15928/j. | |
| [53] | 江维薇, 杨楠, 肖衡林, 2023. 三峡库区与西南库区消落带植物多样性及群落构建比较[J]. 湖泊科学, 35(2): 564-579. |
|
JIANG W W, YANG N, XIAO H L, 2023. Comparison of plant diversity and community assembly between drawdown zone of Three Gorges Reservoir and its southwest reservoir area[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 35(2): 564-579.
DOI URL |
|
| [54] | 廖玉梅, 余杰, 魏世强, 等, 2021. FeMnNi-LDHs对水中As(Ⅲ)的吸附性能与机制[J]. 环境科学, 42(1): 293-304. |
| LIAO Y M, YU J, WEI S Q, et al., 2021. Adsorption effect and mechanism of aqueous arsenic on FeMnNi-LDHs[J]. Environmental Science, 42(1): 293-304. | |
| [55] | 林海兰, 朱日龙, 于磊, 等, 2020. 水浴消解-原子荧光光谱法测定土壤和沉积物中砷、汞、硒、锑和铋[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 40(5): 1528-1533. |
| LIN H L, ZHU R L, YU L, et al., 2020. Determination of arsenic, mercury, selenium, antimony and bismuth in soil and sediments by water bath digestion-atomic fluorescence spectrometry[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 40(5): 1528-1533. | |
| [56] | 乔敏敏, 季宏兵, 朱先芳, 等, 2013. 密云水库沉积物中重金属形态分析及风险评价[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 32(7): 1423-1431. |
| QIAO M M, JI H B, ZHU X F, et al., 2013. Fraction distribution and risk assessment of heavy metal in sediments of Miyun Reservoir[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 32(7): 1423-1431. | |
| [57] | 生态环境部土壤环境管理司、科技标准司, 2018. 土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准 (试行): GB 15618-2018[S]. 北京: 中国环境出版集团: 2. |
| Department of Soil Environmental Management, Department of Science and Technology Standards,Ministry of Ecology and Environment, 2018. Soil environmental quality-Risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land: GB 15618-2018[S]. Beijing: China Environment Publishing Group: 2. | |
| [58] | 张雨婷, 朱奇宏, 黄道友, 等, 2022. 落干过程对土壤-水稻系统镉和砷形态及有效性的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 60(2): 446-457. |
| ZHANG Y T, ZHU H Q, HUANG D Y, et al., 2023. Effects of drying and oxidation stage on the forms and availability of Cd and As in the soil-rice system[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 60(2): 446-457. | |
| [59] | 中华人民共和国国土资源部,2010. 土壤和沉积物 13个微量元素形态顺序提取程序: GB/T 25282-2010[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社: 1-6. |
| Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China,2010. Soil and sediment-Sequential extraction procedure of speciation of 13 trace elements: GB/T 25282-2010[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press: 1-6. |
| [1] | 朱忆雯, 尹丹, 胡敏, 杜衍红, 洪泽彬, 程宽, 于焕云. 稻田土壤氮循环与砷形态转化耦合的研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1344-1354. |
| [2] | 阳涅, 孙晓旭, 孔天乐, 孙蔚旻, 陈泉源, 高品. 微生物群落对河流底泥中锑含量变化的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 609-618. |
| [3] | 杨宇, 邓仁健, 隆佩, 黄中杰, 任伯帜, 王政华. 砷氧化菌Pseudomonas sp. AO-1的分离鉴定及其对As(Ⅲ)的氧化性能研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 619-626. |
| [4] | 尹浩均, 龙明亮, 刘维, 倪春林, 李芳柏, 吴云当. 溶氧浓度调控嗜水气单胞菌的砷还原:效应与机制[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 381-387. |
| [5] | 高鹏, 高品, 孙蔚旻, 孔天乐, 黄端仪, 刘华清, 孙晓旭. 蜈蚣草根际及内生微生物群落对砷污染胁迫的响应机制研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1225-1234. |
| [6] | 徐梅华, 顾明华, 王骋臻, 雷静, 韦燕燕, 沈方科. 锰对土壤砷形态转化及水稻吸收砷的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 802-813. |
| [7] | 刘畅, 罗艳丽, 刘晨通, 郑玉红, 晁博, 董乐乐. 奎屯河下游区域地下水和农田土壤砷的空间分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 2070-2078. |
| [8] | 丛超, 杨宁柯, 王海娟, 王宏镔. 吲哚乙酸和激动素配合施用提高蜈蚣草和龙葵对砷、镉富集的田间试验[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1299-1309. |
| [9] | 张晋龙, 黄颖, 吴丽芳, 龚云辉, 刘云根, 王妍, 杨思林. 砷胁迫对狭叶香蒲生理生态及砷亚细胞分布的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(5): 1042-1050. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
