生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (9): 1856-1864.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.09.016
郝贝贝1,2( ), 王楠1,2, 吴昊平3, 周智鑫4, 张思毅1,2, 贺斌1,2,*(
), 王楠1,2, 吴昊平3, 周智鑫4, 张思毅1,2, 贺斌1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-05-07
出版日期:2022-09-18
发布日期:2022-11-07
通讯作者:
*贺斌(1977年生),男,研究员,博士,研究方向为流域水循环与污染防治。E-mail: bhe@soil.gd.cn作者简介:郝贝贝(1985年生),女,副研究员,博士,研究方向为面源污染防治与水环境修复。E-mail: bbhao@soil.gd.cn
基金资助:
HAO Beibei1,2( ), WANG Nan1,2, WU Haoping3, ZHOU Zhixin4, ZHANG Siyi1,2, HE Bin1,2,*(
), WANG Nan1,2, WU Haoping3, ZHOU Zhixin4, ZHANG Siyi1,2, HE Bin1,2,*( )
)
Received:2022-05-07
Online:2022-09-18
Published:2022-11-07
摘要:
探讨不同类型生态沟渠在实际应用中的径流氮磷拦截效应,对农业面源污染防治具有重要意义。以广州增城生态农业基地内生态化改造后的4条沟渠为研究对象,分析比较不同构造类型和植物配置方式对稻田排水截留净化效果的影响。结果表明:受降雨事件影响,生态沟渠不同监测断面的水质变化特征在降雨前后发生显著变化。沟渠不同断面水体NH4+和NO3-含量,在降雨发生期间沿水流方向略有增加;而降雨结束后沿水流方向呈现降低趋势,表现出一定的污染物削减效果。单因素方差分析结果表明,构造类型和植物配置方式不同的4条生态沟渠对径流水体NH4+和DO的净化效果存在显著差异(P<0.05)。进一步选择植物配置方式相同但构造类型不同的两种生态沟渠(素土生态沟渠和多孔砖生态沟渠),深入比较其对氮、磷和COD等面源径流污染物的削减效果发现:由入口到出口断面,素土生态沟渠和多孔砖生态沟渠水体氮、磷和COD含量均呈逐步下降趋势,多孔砖生态沟渠对水体NH4+、NO3-、TN、TP和COD的平均削减率(28%、50%、30%、54%和41%)均高于素土生态沟渠(26%、25%、23%、33%和27%)。综上,相比素土生态沟渠而言,该研究中多孔砖生态沟渠对面源污染物净化效果更佳。因此在进行农田沟渠生态化改造时,因地制宜选择合适的生态沟渠类型,可有效提高其对面源径流污染物的拦截净化效果。
中图分类号:
郝贝贝, 王楠, 吴昊平, 周智鑫, 张思毅, 贺斌. 生态沟渠对珠三角稻田径流污染的削减功能研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1856-1864.
HAO Beibei, WANG Nan, WU Haoping, ZHOU Zhixin, ZHANG Siyi, HE Bin. Research on the Reduction Function of Ecological Ditches on Runoff Pollution from Rice Field in the Pearl River Delta[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(9): 1856-1864.
| 沟渠编号 Ditch number | 构造类型 Tectonic types | 断面尺寸 Cross-sectional size | 沟渠长度 Ditch length/m | 沟渠坡面植物配置 Plant configurations on slope | 沟渠底部植物配置 Plant configurations on bottom |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ED1 | 坡面素土夯实, 沟底挖平 | 底宽2.6 m, 高1.1 m, 坡度1:1.25 | 88 | 美人蕉 (C. indica) 和再力花 (T. dealbata), 种植密度16-18 plant∙m-2 | 苦草 (V. natans), 种植密度50-60 plant∙m-2 |
| ED2 | 坡面素土夯实, 沟底挖平 | 底宽2.6 m, 高1.0 m, 坡度1:1.25 | 120.5 | 美人蕉 (C. indica)和再力花 (T. dealbata), 种植密度16-18 plant∙m-2 | 荷花 (N. nucifera), 种植密度4-5 plant∙m-2 |
| ED3 | 坡面素土夯实后平铺菱形多孔砖, 沟底挖平 | 底宽2.6 m, 高1.1 m, 坡度1:1.25 | 92 | 美人蕉 (C. indica) 和再力花 (T. dealbata), 种植密度16-18 plant∙m-2 | 苦草 (V. natans), 种植密度50-60 plant∙m-2 |
| ED4 | 坡面素土夯实后平铺菱形多孔砖, 沟底挖平 | 底宽2.5 m, 高1.1 m, 坡度1:1.25 | 140 | 紫芋 (C. tonoimo) 和再力花 (T. dealbata), 种植密度16 plant∙m-2 | 黄花水龙 (J. stipulacea), 种植密度20-25 plant∙m-2 |
表1 本研究中4条生态沟渠的工程措施和植物配置方式
Table1 Engineering measures and plant configuration of four ecological ditches in this study
| 沟渠编号 Ditch number | 构造类型 Tectonic types | 断面尺寸 Cross-sectional size | 沟渠长度 Ditch length/m | 沟渠坡面植物配置 Plant configurations on slope | 沟渠底部植物配置 Plant configurations on bottom |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ED1 | 坡面素土夯实, 沟底挖平 | 底宽2.6 m, 高1.1 m, 坡度1:1.25 | 88 | 美人蕉 (C. indica) 和再力花 (T. dealbata), 种植密度16-18 plant∙m-2 | 苦草 (V. natans), 种植密度50-60 plant∙m-2 |
| ED2 | 坡面素土夯实, 沟底挖平 | 底宽2.6 m, 高1.0 m, 坡度1:1.25 | 120.5 | 美人蕉 (C. indica)和再力花 (T. dealbata), 种植密度16-18 plant∙m-2 | 荷花 (N. nucifera), 种植密度4-5 plant∙m-2 |
| ED3 | 坡面素土夯实后平铺菱形多孔砖, 沟底挖平 | 底宽2.6 m, 高1.1 m, 坡度1:1.25 | 92 | 美人蕉 (C. indica) 和再力花 (T. dealbata), 种植密度16-18 plant∙m-2 | 苦草 (V. natans), 种植密度50-60 plant∙m-2 |
| ED4 | 坡面素土夯实后平铺菱形多孔砖, 沟底挖平 | 底宽2.5 m, 高1.1 m, 坡度1:1.25 | 140 | 紫芋 (C. tonoimo) 和再力花 (T. dealbata), 种植密度16 plant∙m-2 | 黄花水龙 (J. stipulacea), 种植密度20-25 plant∙m-2 |
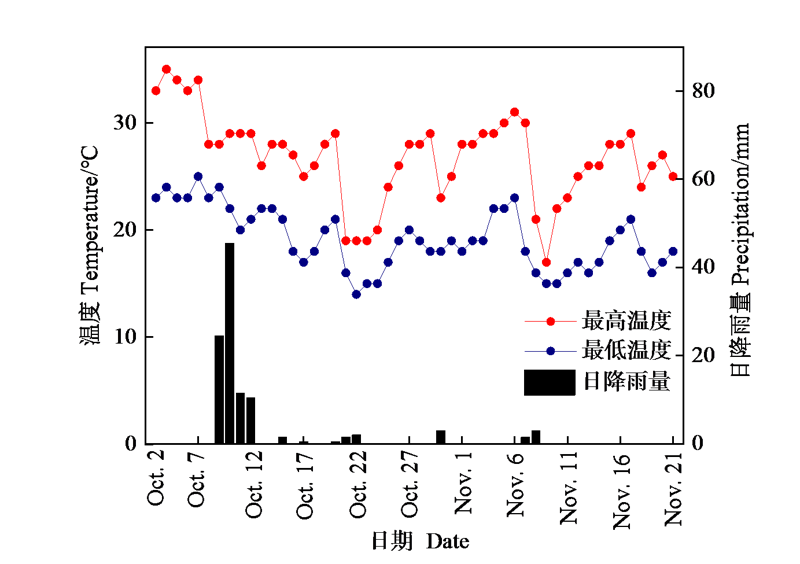
图2 试验期间温度(最高温度、最低温度)和日降雨量变化
Figure 2 Change of temperature (maximum temperature, minimum temperature) and daily precipitation during the experiment period
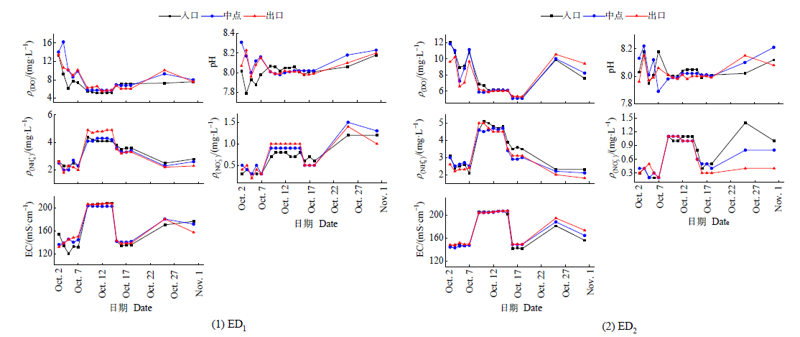
图3 两条素土生态沟渠(ED1和ED2)入口、中点、出口的水质监测情况
Figure 3 Water quality monitoring at entrance, midpoint and outlet of the two plain soil ecological ditches (ED1 and ED2)
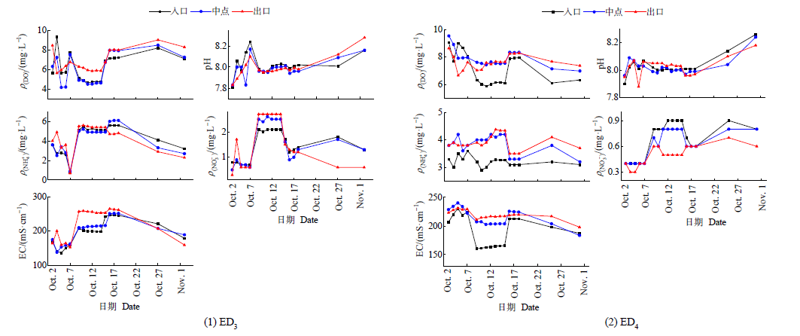
图4 两条多孔砖生态沟渠(ED3和ED4)入口、中点、出口的水质监测情况
Figure 4 Water quality monitoring at entrance, midpoint and outlet of the two ecological ditches with perforated bricks (ED3 and ED4)
| 指标 Indicators | 自由度 d.f. | F值 F value | P值 P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| r(DO) | 3 | 7.081 | 0.002 |
| r(NH4+) | 3 | 25.200 | <0.001 |
| r(NO3-) | 3 | 3.015 | 0.054 |
| r(pH) | 3 | 2.712 | 0.077 |
| r(EC) | 3 | 0.864 | 0.479 |
表2 单因素方差分析比较由入口到出口ρ(Do)、pH、ρ(NH4+)、ρ(NO3-)和EC的削减率在不同生态沟渠间是否存在差异
Table 2 One-way ANOVA compare the removal percentage of ρ(DO), pH, ρ(NH4+), ρ(NO3-) and EC among the four different ecological ditches
| 指标 Indicators | 自由度 d.f. | F值 F value | P值 P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| r(DO) | 3 | 7.081 | 0.002 |
| r(NH4+) | 3 | 25.200 | <0.001 |
| r(NO3-) | 3 | 3.015 | 0.054 |
| r(pH) | 3 | 2.712 | 0.077 |
| r(EC) | 3 | 0.864 | 0.479 |
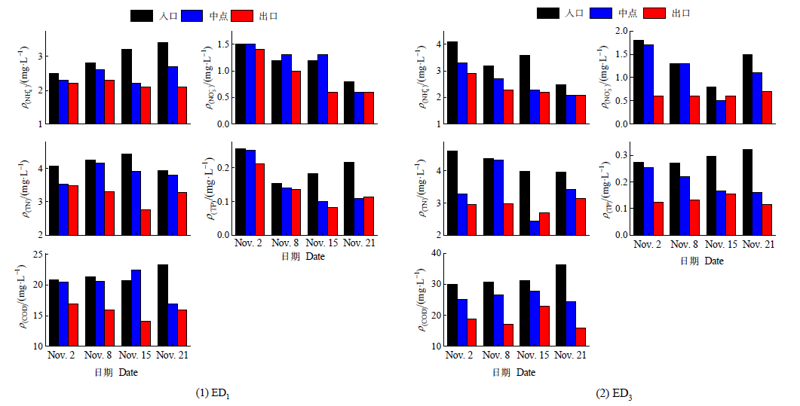
图5 两种不同生态沟渠(ED1和ED3)入口、中点、出口面源污染物含量的变化
Figure 5 Non-point source pollutant content at entrance, midpoint and outlet of two different ecological ditches (ED3 and ED4)
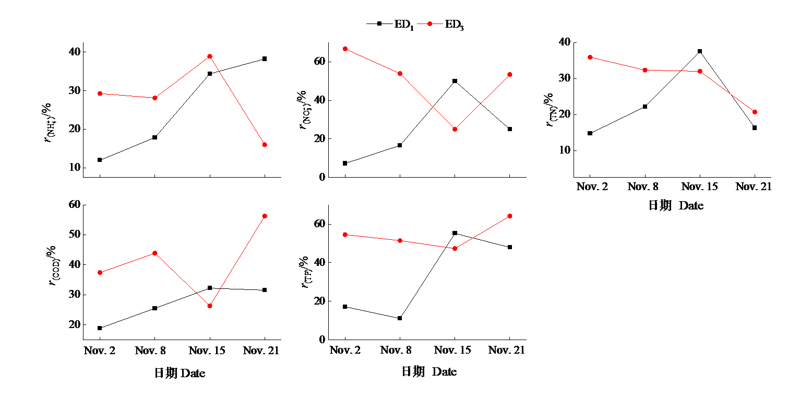
图6 两种不同生态沟渠(ED1和ED3)对水体NH4+、NO3-、TN、TP和COD的削减率对比
Figure 6 Comparison of removal percentage of NH4+, NO3-, TN, TP and COD in two different ecological ditches (ED3 and ED4)
| [1] |
CHEN Y, WEN Y, ZHOU Q, et al., 2014. Effects of plant biomass on denitrifying genes in subsurface-flow constructed wetlands[J]. Bioresource Technology, 157: 341-345.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
FU D F, GONG W J, XU Y, et al., 2014. Nutrient mitigation capacity of agricultural drainage ditches in Tai lake basin[J]. Ecological Engineering, 71: 101-107.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
LEVAVASSEUR F, BIARN S A, BAILLY J S, et al., 2014. Time-varying impacts of different management regimes on vegetation cover in agricultural ditches[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 140: 14-19.
DOI URL |
| [4] | LI X N, ZHANG W W, ZHAO C Q, et al., 2020. Nitrogen interception and fate in vegetated ditches using the isotope tracer method: A simulation study in northern China[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 228: 105893. |
| [5] |
LIN Y F, JING S R, WANG T W, et al., 2002. Effects of macrophytes and external carbon sources on nitrate removal from groundwater in constructed wetlands[J]. Environmental Pollution, 119(3): 413-420.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
STOTTMEISTER U, WIENER A, KUSCHK P, et al., 2003. Effects of plants and microorganisms in constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 22(1-2): 93-117.
PMID |
| [7] |
WATSON A M, ORMEROD S J, 2004. The distribution of three uncommon freshwater gastropods in the drainage ditches of British grazing marshes[J]. Biological Conservation, 118(4): 455-66.
DOI URL |
| [8] | WOLTEMADE C J. 2000. Ability of restored wetlands to reduce nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations in agricultural drainage water[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 55(3): 303-309. |
| [9] |
WU H L, WANG X Z, HE X J, et al., 2017. Effects of root exudates on denitrifier gene abundance, community structure and activity in a micro-polluted constructed wetland[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 598: 697-703.
DOI URL |
| [10] | 陈海生, 王光华, 刘建飞, 等, 2010. 模拟生态沟渠中盘培牧草降解农业面源污染效应的研究[J]. 江西农业学报, 22(9): 143-145, 151. |
| CHEN H S, WANG G H, LIU J F, et al., 2010. Research on effects of simulative ecological ditch on degradation of agricultural non-point pollution[J]. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 22(9): 143-145, 151. | |
| [11] | 段四喜, 张磊, 杨芳, 等, 2022. 典型生态拦截措施水质净化效果研究[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 39(3): 493-502. |
| DUAN S X, ZHANG L, YANG F, et al., 2022. Study on water purification effect of typical ecological interception measures[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 39(3): 493-502. | |
| [12] | 董晓亮, 陈克勤, 李正兵, 2021. 土地整治中生态沟渠建设研究[J]. 农业与技术, 41(22): 59-61. |
| DONG X L. CHEN K Q, LI Z B, 2021. Research on construction of ecological ditches in land consolidation[J]. Agriculture & Technology, 41(22): 59-61. | |
| [13] | 国家环境保护总局, 2002. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 第4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| State Environmental Protection Administration, 2002. Method for monitoring and analysis water and waste water[M]. Fourth Version. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. | |
| [14] | 韩例娜, 李裕元, 石辉, 等, 2012. 水生植物对农田排水沟渠氮磷迁移生态阻控效果比较研究[J]. 农业现代化研究, 33(1): 117-120. |
| HAN L N, LI Y Y, SHI H, et al., 2012. Study on comparison of different aquatic plant on nitrogen and phosphorus ecological control measures in drainage ditch of farmland in southern China[J]. Research of Agricultural Modernization, 33(1): 117-120. | |
| [15] | 何佳宁, 刘春敬, 李思安, 等, 2018. 烧结多孔砖基质Fe系改性脱氮除磷效果研究[J]. 河北农业大学学报, 41(6): 104-109. |
| HE J N, LIU C J, LI S A, et al., 2018. Study on nitrogen and phosphorus removal performance of sintered porous brick matrix modified by Fe system. Journal of Agricultural University of Hebei, 41(6): 104-109. | |
| [16] | 何元庆, 魏建兵, 胡远安, 等, 2012. 珠三角典型稻田生态沟渠型人工湿地的非点源污染削减功能[J]. 生态学杂志, 31(2): 394-398. |
| HE Y Q, WEI J B, HU Y A, et al., 2012. Non-point source pollution control functions of constructed wetland in the ditches of paddy field system in Pearl River Delta[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 31(2): 394-398. | |
| [17] | 姜翠玲, 崔广柏, 范晓秋, 等, 2004. 沟渠湿地对农业非点源污染物的净化能力研究[J]. 环境科学, 25(2): 125-128. |
| JIANG C L, CUI G B, FAN X Q, et al., 2004. Purification capacity of ditch wetland to agricultural non-point pollutants[J]. Environmental Science, 25(2): 125-128. | |
| [18] | 李强坤, 胡亚伟, 苏欣, 2017. 排水沟渠水-底泥-植物协同作用下非点源溶质氮运移模拟研究[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 25(3): 460-466. |
| LI Q K, HU Y W, SU X, 2017. Simulation of non-point source solute nitrogen transport in drainage ditches under water-sediment-aquatic plant synergy[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 25(3): 460-466 | |
| [19] | 刘福兴, 陈桂发, 付子轼, 等, 2019. 不同构造生态沟渠的农田面源污染物处理能力及实际应用效果[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 35(6): 787-794. |
| LIU F X, CHEN G F, FU Z S, et al., 2019. Comparison on effects of practical application of ecological ditches with different construction in treating agricultural non-point pollutants[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 35(6): 787-794. | |
| [20] | 刘泉, 李占斌, 李鹏, 等, 2016. 汉江水源区生态沟渠对径流氮、磷的生态拦截效应[J]. 水土保持通报, 36(2): 54-58, 64. |
| LIU Q, LI Z B, LI P, et al., 2016. Effects of Ecological Ditch Interception of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Water Source Area of Hanjiang River[J]. Bulletin of Soil And Water Conservation, 36(2): 54-58, 64. | |
| [21] | 田上, 沙之敏, 岳玉波, 等, 2016. 不同类型沟渠对农田氮磷流失的拦截效果[J]. 江苏农业科学, 44(4): 361-365. |
| TIAN S, SHA Z M, YUE Y B, et al., 2016. The interception effect of different types of ditches on nitrogen and phosphorus loss in farmland[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 44(4): 361-365. | |
| [22] | 徐德福, 李映雪, 2007. 用于污水处理的人工湿地的基质、植物及其配置[J]. 湿地科学, 5(1): 32-38. |
| XU D F, LI Y X, 2007. Screen plants and substrates of the constructed wetland for treatment of wastewater[J]. Wetland Science, 5(1): 32-38. | |
| [23] | 王迪, 李红芳, 刘锋, 等, 2016. 亚热带农区生态沟渠对农业径流中氮素迁移拦截效应研究[J]. 环境科学, 37(5): 1717-1723. |
| WANG D, LI H F, LIU F, et al., 2016. Interception effect of ecological ditch on nitrogen transport in agricultural runoff in subtropical China[J]. Environmental Science, 37(5): 1717-1723. | |
| [24] | 王晓玲, 乔斌, 李松敏, 等, 2015. 生态沟渠对水稻不同生长期降雨径流氮磷的拦截效应研究[J]. 水利学报, 46(12): 1406-1413. |
| WANG X L, QIAO B, LI S M, et al., 2015. Studies on the interception effects of ecological ditch on nitrogen and phosphorus in the rainfall runoff of different rice growth period[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 46(12): 1406-1413. | |
| [25] | 王晓玲, 涂佳敏, 李松敏, 等, 2014. 稻田沟渠施肥后降雨径流中氮素迁移规律研究[J]. 水利学报, 45(9): 1075-1081. |
| WANG X L, TU J M, LI S M, et al., 2014. Nitrogen transport mechanisms in ditches of rainfall-runoff after fertilizing[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 45(9): 1075-1081. | |
| [26] | 王岩, 王建国, 李伟, 等, 2010. 生态沟渠对农田排水中氮磷的去除机理初探[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 26(6): 586-590. |
| WANG Y, WANG J G, LI W, et al., 2010. Initial exploration of mechanism of ecological ditch intercepting nitrogen and phosphorus in drainage from farmland[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 26(6): 586-590. | |
| [27] | 杨林章, 周小平, 王建国, 等, 2005. 用于农田非点源污染控制的生态拦截型沟渠系统及其效果[J]. 生态学杂志, 24(11): 1371-1374. |
| YANG L Z, ZHOU X P, WANG J G, et al., 2005. Ecological ditch system with interception function and its effects on controlling farmland non-point pollution[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 24(11): 1371-1374. | |
| [28] | 杨继伟, 张辉, 曹秀清, 等, 2022. 农田排水沟渠生态化建设与管理[J]. 治淮, (3): 68-70. |
| YANG J W, ZHANG H, CAO X Q, et al., 2022. Ecological Construction and Management of Farmland Drainage Ditch[J]. Harnessing the Huaihe River, (3): 68-70. | |
| [29] | 于会彬, 席北斗, 郭旭晶, 等, 2009. 降水对农田排水沟渠中氮磷流失的影响[J]. 环境科学研究, 22(4): 409-414. |
| YU H B, XI B D, GUO X J, et al., 2009. Effect of Rainfall Runoff on Nitrogen and Phosphorus Loss in Farming Drainage Ditch[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 22(4): 409-414. | |
| [30] | 余红兵, 肖润林, 杨知建, 等, 2014. 灌溉和降雨条件下生态沟渠氮、磷输出特征研究[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 23(5): 686-692. |
| YU H B, XIAO R L, YANG Z J, et al., 2014. Study on the characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus transportation through ecological ditch during irrigation and rainfall[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 23(5): 686-692. | |
| [31] | 张树楠, 肖润林, 刘锋, 等, 2015. 生态沟渠对氮、磷污染物的拦截效应[J]. 环境科学, 36(12): 4516-4522. |
| ZHANG S N, XIAO R L, LIU F, et al., 2015. Interception effect of vegetated drainage ditch on nitrogen and phosphorus from drainage ditches[J]. Environmental Science, 36(12): 4516-4522. | |
| [32] | 张燕, 2013. 农田排水沟渠对氮磷的去除效应及管理措施[D]. 长春: 中国科学院研究生院 (东北地理与农业生态研究所). |
| ZHANG Y, 2013. Removal effect and management measures of nitrogen and phosphorus in agricultural drainage ditches[D]. Changchun: Northeast Institute of Geography and Agroecology, Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences. |
| [1] | 黄英梅, 钟松雄, 朱忆雯, 王向琴, 李芳柏. 单质硫抑制水稻植株甲基汞累积的效应与机制[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1115-1122. |
| [2] | 杜丹丹, 高瑞忠, 房丽晶, 谢龙梅. 旱区盐湖盆地土壤重金属空间变异及对土壤理化因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1123-1132. |
| [3] | 冯树娜, 吕家珑, 何海龙. KI淋洗对黄绵土汞污染的去除效果及土壤理化性状的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 776-783. |
| [4] | 代德敏, 蒋旭升, 刘杰, 王路洋, 陈诗奇, 韩庆坤. 3种有机改良剂对铅锌矿尾砂适生性改善的研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 784-793. |
| [5] | 陈敏毅, 朱航海, 佘伟铎, 尹光彩, 黄祖照, 杨巧玲. 珠三角某遗留造船厂场地土壤重金属人体健康风险评估及源解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 794-804. |
| [6] | 刘抗旱, 郑刘根, 张理群, 丁丹, 单士锋. 复合型植物源活化剂强化蜈蚣草修复砷污染土壤的效应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 635-642. |
| [7] | 杨宇, 邓仁健, 隆佩, 黄中杰, 任伯帜, 王政华. 砷氧化菌Pseudomonas sp. AO-1的分离鉴定及其对As(Ⅲ)的氧化性能研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 619-626. |
| [8] | 杨耀东, 陈玉梅, 涂鹏飞, 曾清如. 经济作物轮作模式下镉污染农田修复潜力[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 627-634. |
| [9] | 徐敏, 许超, 余光辉, 尹力初, 张泉, 朱捍华, 朱奇宏, 张杨珠, 黄道友. 地下水位和长期秸秆还田对土壤镉有效性及稻米镉含量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 150-157. |
| [10] | 谢洁芬, 章家恩, 危晖, 刘自强, 陈璇. 土壤中微塑料复合污染研究进展与展望[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2431-2440. |
| [11] | 任珺, 潘佳璇, 陶玲, 仝云龙, 王若安, 孙新妮. 氢氧化钠改性坡缕石对Cd污染土壤的钝化修复效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2422-2430. |
| [12] | 伍德, 彭鸥, 刘玉玲, 张朴心, 尹雪斐, 黄薪铭, 铁柏清. 螯合剂及组配对伴矿景天修复两种镉污染土壤的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2414-2421. |
| [13] | 秦秦, 段海芹, 宋科, 孙丽娟, 孙雅菲, 周斌, 薛永. 常规施肥对土壤水稳性团聚体镉吸附解吸特性及化学形态的影响研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2403-2413. |
| [14] | 张丽聪, 肖凯, 张鹏, 李海龙, 王俊坚, 李镇扬, 王芬芳, 徐华林, 郭跃华. 淤泥质潮滩重金属和溶解性有机质的潮汐变化特征及其环境影响评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2169-2179. |
| [15] | 张楷悦, 刘增辉, 王颜昊, 王敬宽, 崔德杰, 柳新伟. 黄河三角洲自然保护区土壤PAHs的风险评估和空间特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2198-2205. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
