生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (8): 1629-1636.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.08.015
李秀华1,2( ), 赵玲1, 滕应1,*(
), 赵玲1, 滕应1,*( ), 骆永明1, 黄标1, 刘冲1, 刘本乐1,2, 赵其国1,*(
), 骆永明1, 黄标1, 刘冲1, 刘本乐1,2, 赵其国1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-12-09
出版日期:2022-08-18
发布日期:2022-10-10
通讯作者:
赵其国,E-mail: qgzhao@issas.ac.cn作者简介:李秀华(1983年生),女,博士研究生,主要从事土壤污染治理与修复研究。E-mail: xhli@issas.ac.cn
基金资助:
LI Xiuhua1,2( ), ZHAO Ling1, TENG Ying1,*(
), ZHAO Ling1, TENG Ying1,*( ), LUO Yongming1, HUANG Biao1, LIU Chong1, LIU Benle1,2, ZHAO Qiguo1,*(
), LUO Yongming1, HUANG Biao1, LIU Chong1, LIU Benle1,2, ZHAO Qiguo1,*( )
)
Received:2021-12-09
Online:2022-08-18
Published:2022-10-10
摘要:
贵州汞矿开采和冶炼活动产生的“三废”,带来矿区周边农田土壤重金属污染问题,引起了国家及地方环保部门的高度关注。为探明研究区重金属污染分布,该研究采集了铜仁市敖寨乡农田表层土壤样品350个,双层样品19个,研究区剖面和对照剖面各1个,测定了土壤pH值、有机质(SOM)、总汞(Hg)和总镉(Cd)的含量;采用克里格插值法分析了空间分布特征;依据土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准(GB 15618—
中图分类号:
李秀华, 赵玲, 滕应, 骆永明, 黄标, 刘冲, 刘本乐, 赵其国. 贵州汞矿区周边农田土壤汞镉复合污染特征空间分布及风险评估[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1629-1636.
LI Xiuhua, ZHAO Ling, TENG Ying, LUO Yongming, HUANG Biao, LIU Chong, LIU Benle, ZHAO Qiguo. Characteristics, Spatial Distribution and Risk Assessment of Combined Mercury and Cadmium Pollution in Farmland Soils Surrounding Mercury Mining Areas in Guizhou[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(8): 1629-1636.
| 符号Symbol | 含义 Meaning | 取值 Values | 单位 Unit | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 儿童 Child | 成人 Adult | |||
| Igc/Iga | 摄入土壤的频率 | 200 | 100 | mg∙d-1 |
| Ihc/Iha | 呼吸频率 | 7.5 | 14.5 | m3∙d-1 |
| mc/ma | 平均体质量 | 15.9 | 56.8 | kg |
| Sc/Sa | 暴露皮肤表面积 | 2247.56 | 5074.98 | cm2 |
| Yc/Ya | 暴露年限 | 6 | 24 | a |
| P | 颗粒物排放因子 | 1.36×109 | 1.36×109 | m3∙kg-1 |
| Lc/La | 皮肤黏着度 | 0.2 | 0.07 | mg∙cm-2∙d -1 |
| Ac/Aa | 皮肤吸收因子 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 无量纲 |
| F | 暴露频率 | 350 | 350 | d∙a-1 |
| tc/ta | 平均暴露时间 | 2190(非致癌物) 26280(致癌物) | d | |
表1 重金属暴露参数
Table 1 Exposure parameters of heavy metals
| 符号Symbol | 含义 Meaning | 取值 Values | 单位 Unit | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 儿童 Child | 成人 Adult | |||
| Igc/Iga | 摄入土壤的频率 | 200 | 100 | mg∙d-1 |
| Ihc/Iha | 呼吸频率 | 7.5 | 14.5 | m3∙d-1 |
| mc/ma | 平均体质量 | 15.9 | 56.8 | kg |
| Sc/Sa | 暴露皮肤表面积 | 2247.56 | 5074.98 | cm2 |
| Yc/Ya | 暴露年限 | 6 | 24 | a |
| P | 颗粒物排放因子 | 1.36×109 | 1.36×109 | m3∙kg-1 |
| Lc/La | 皮肤黏着度 | 0.2 | 0.07 | mg∙cm-2∙d -1 |
| Ac/Aa | 皮肤吸收因子 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 无量纲 |
| F | 暴露频率 | 350 | 350 | d∙a-1 |
| tc/ta | 平均暴露时间 | 2190(非致癌物) 26280(致癌物) | d | |
| 项目 Content | 表层土壤 Surface soil | 亚表层土壤Subsurface soil | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | w(SOM)/(g∙kg-1) | w(Hg)/(mg∙kg-1) | w(Cd)/(mg∙kg-1) | pH | w(SOM)/(g∙kg-1) | w(Hg)/(mg∙kg-1) | w(Cd)/(mg∙kg-1) | ||
| 最大值 Max | 8.38 | 57.50 | 128.00 | 5.39 | 8.19 | 32.51 | 47.7 | 2.11 | |
| 最小值 Min | 4.89 | 9.00 | 0.07 | 0.23 | 5.78 | 13.50 | 0.51 | 0.49 | |
| 中值 Median | 7.59 | 34.50 | 13.7 | 1.01 | 7.68 | 26.00 | 6.50 | 0.88 | |
| 均值 Average | 7.41±0.73 | 34.80±7.50 | 20.20±19.31 | 1.17±0.33 | 7.55±0.60 | 24.41±5.90 | 12.66±12.98 | 1.03±0.46 | |
表2 研究区表层和亚表层土壤pH值、有机质、总汞及总镉含量
Table 2 Surface and subsurface soil pH, SOM, Hg and Cd contents in the study area
| 项目 Content | 表层土壤 Surface soil | 亚表层土壤Subsurface soil | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | w(SOM)/(g∙kg-1) | w(Hg)/(mg∙kg-1) | w(Cd)/(mg∙kg-1) | pH | w(SOM)/(g∙kg-1) | w(Hg)/(mg∙kg-1) | w(Cd)/(mg∙kg-1) | ||
| 最大值 Max | 8.38 | 57.50 | 128.00 | 5.39 | 8.19 | 32.51 | 47.7 | 2.11 | |
| 最小值 Min | 4.89 | 9.00 | 0.07 | 0.23 | 5.78 | 13.50 | 0.51 | 0.49 | |
| 中值 Median | 7.59 | 34.50 | 13.7 | 1.01 | 7.68 | 26.00 | 6.50 | 0.88 | |
| 均值 Average | 7.41±0.73 | 34.80±7.50 | 20.20±19.31 | 1.17±0.33 | 7.55±0.60 | 24.41±5.90 | 12.66±12.98 | 1.03±0.46 | |
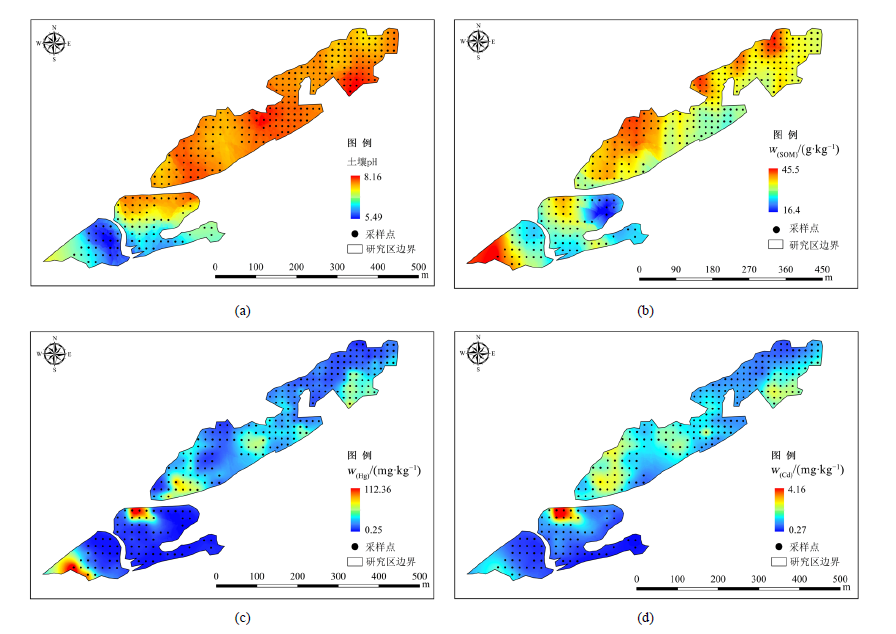
图2 土壤pH值、有机质、汞和镉含量空间分布 (a)土壤中pH值空间分布 Distribution of pH in soil;(b)土壤有机质空间分布Distribution of SOM in soil; (c)土壤中汞含量空间分布Distribution of Hg in soil;(d)土壤中镉含量空间分布Distribution of Cd in soil
Figure 2 Spatial distribution of pH,SOM,Hg and Cd in soil
| 项目 Content | 农田剖面 Farmland soil profile/ cm | 自然林地剖面 Natural woodland profile/ cm | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0-10 | 10-20 | 20-40 | 40-60 | 0-10 | 10-20 | 20-40 | 40-60 | ||
| pH | 7.96 | 7.98 | 8.42 | 8.45 | 5.30 | 5.48 | 5.25 | 5.19 | |
| w(SOM)/(g∙kg-1) | 3.03 | 2.33 | 1.82 | 1.92 | 3.46 | 1.72 | 2.00 | 1.96 | |
| w(Hg)/(mg∙kg-1) | 9.65 | 2.55 | 2.48 | 6.26 | 5.18 | 0.28 | 0.17 | 0.32 | |
| w(Cd)/(mg∙kg-1) | 0.90 | 0.53 | 0.53 | 0.46 | 0.30 | 0.19 | ND | ND | |
表3 剖面土壤pH值、有机质、总汞及总镉含量
Table 3 pH, SOM, Hg and Cd contents in profile soils
| 项目 Content | 农田剖面 Farmland soil profile/ cm | 自然林地剖面 Natural woodland profile/ cm | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0-10 | 10-20 | 20-40 | 40-60 | 0-10 | 10-20 | 20-40 | 40-60 | ||
| pH | 7.96 | 7.98 | 8.42 | 8.45 | 5.30 | 5.48 | 5.25 | 5.19 | |
| w(SOM)/(g∙kg-1) | 3.03 | 2.33 | 1.82 | 1.92 | 3.46 | 1.72 | 2.00 | 1.96 | |
| w(Hg)/(mg∙kg-1) | 9.65 | 2.55 | 2.48 | 6.26 | 5.18 | 0.28 | 0.17 | 0.32 | |
| w(Cd)/(mg∙kg-1) | 0.90 | 0.53 | 0.53 | 0.46 | 0.30 | 0.19 | ND | ND | |
| 重金属 Heavy metals | pH | SOM | Hg |
|---|---|---|---|
| SOM | 0.239** | ||
| Hg | 0.484** | 0.328** | |
| Cd | 0.540** | 0.341** | 0.792** |
表4 土壤pH值、有机质含量、总汞含量、总镉含量的皮尔逊相关系数
Table 4 Pearson correlation coefficient for soil pH, SOM, Hg and Cd
| 重金属 Heavy metals | pH | SOM | Hg |
|---|---|---|---|
| SOM | 0.239** | ||
| Hg | 0.484** | 0.328** | |
| Cd | 0.540** | 0.341** | 0.792** |
| 重金属 Heavy metals | Ci≤a | a<Ci≤b | Ci>b | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 点位数 Number of points | 占比 Proportion/% | 点位数 Number of points | 占比 Proportion/% | 点位数 Number of points | 占比 Proportion/% | |||
| Hg | 1 | 0.29 | 39 | 11.14 | 310 | 88.57 | ||
| Cd | 3 | 0.86 | 344 | 98.28 | 3 | 0.86 | ||
表5 研究区农田土壤重金属安全评估结果
Table 5 Safety assessment results of heavy metals in farmland soils of the study area
| 重金属 Heavy metals | Ci≤a | a<Ci≤b | Ci>b | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 点位数 Number of points | 占比 Proportion/% | 点位数 Number of points | 占比 Proportion/% | 点位数 Number of points | 占比 Proportion/% | |||
| Hg | 1 | 0.29 | 39 | 11.14 | 310 | 88.57 | ||
| Cd | 3 | 0.86 | 344 | 98.28 | 3 | 0.86 | ||
| 危害指数 Hazard index | 分布范围 distribution range | 平均值 Average value | 潜在生态风险比例 Potential ecological risk ratio/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 轻微Low | 中Moderate | 强Considerable | 很强High | 极强Very high | ||||
| | Hg | 5.36-10240 | 1610.28 | 0.28 | 0.86 | 5.43 | 5.71 | 87.72 |
| Cd | 23-539 | 116.90 | 3.14 | 23.43 | 55.72 | 15.71 | 2.00 | |
表6 研究区土壤中重金属的潜在生态风险指数
Table 6 Potential ecological risk index of heavy metals in soils of the study area
| 危害指数 Hazard index | 分布范围 distribution range | 平均值 Average value | 潜在生态风险比例 Potential ecological risk ratio/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 轻微Low | 中Moderate | 强Considerable | 很强High | 极强Very high | ||||
| | Hg | 5.36-10240 | 1610.28 | 0.28 | 0.86 | 5.43 | 5.71 | 87.72 |
| Cd | 23-539 | 116.90 | 3.14 | 23.43 | 55.72 | 15.71 | 2.00 | |
| 重金属 Heavy metals | 指标Index | 儿童 Child | 成人 Adult | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 经口摄入 Ingestion | 呼吸吸入 Inhalation | 皮肤接触 Skin contact | 经口摄入 Ingestion | 呼吸吸入 Inhalation | 皮肤接触 Skin contact | |||
| Hg | 最大值 Max | 8.02 | 1.75×10-3 | 0.58 | 2.88 | 1.20×10-3 | 0.15 | |
| 最小值 Min | 4.39×10-3 | 9.62×10-7 | 3.18×10-4 | 1.57×10-3 | 6.58×10-7 | 7.99×10-5 | ||
| 平均值 Average | 1.26 | 2.77×10-4 | 9.17×10-2 | 0.45 | 1.89×10-4 | 2.30×10-2 | ||
| Cd | 最大值 Max | 0.34 | 7.41×10-5 | 2.46×10-2 | 0.12 | 5.06×10-5 | 6.15×10-4 | |
| 最小值 Min | 1.44×10-2 | 3.16×10-6 | 1.05×10-3 | 5.18×10-3 | 2.16×10-6 | 2.63×10-4 | ||
| 平均值 Average | 0.073 | 1.61×10-5 | 5.33×10-3 | 2.63×10-2 | 1.10×10-5 | 1.34×10-3 | ||
表7 研究区土壤中重金属的非致癌健康风险指数
Table 7 Non-carcinogenic health risk index of heavy metals in soils of the study area
| 重金属 Heavy metals | 指标Index | 儿童 Child | 成人 Adult | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 经口摄入 Ingestion | 呼吸吸入 Inhalation | 皮肤接触 Skin contact | 经口摄入 Ingestion | 呼吸吸入 Inhalation | 皮肤接触 Skin contact | |||
| Hg | 最大值 Max | 8.02 | 1.75×10-3 | 0.58 | 2.88 | 1.20×10-3 | 0.15 | |
| 最小值 Min | 4.39×10-3 | 9.62×10-7 | 3.18×10-4 | 1.57×10-3 | 6.58×10-7 | 7.99×10-5 | ||
| 平均值 Average | 1.26 | 2.77×10-4 | 9.17×10-2 | 0.45 | 1.89×10-4 | 2.30×10-2 | ||
| Cd | 最大值 Max | 0.34 | 7.41×10-5 | 2.46×10-2 | 0.12 | 5.06×10-5 | 6.15×10-4 | |
| 最小值 Min | 1.44×10-2 | 3.16×10-6 | 1.05×10-3 | 5.18×10-3 | 2.16×10-6 | 2.63×10-4 | ||
| 平均值 Average | 0.073 | 1.61×10-5 | 5.33×10-3 | 2.63×10-2 | 1.10×10-5 | 1.34×10-3 | ||
| [1] |
ADLANE B, XU Z D, XU X H, et al., 2020. Evaluation of the potential risks of heavy metal contamination in rice paddy soils around an abandoned Hg mine area in Southwest China[J]. Acta Geochimica, 39(1): 85-95.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
AVIGLIANO E, SCHENONE N F, 2015. Human health risk assessment and environmental distribution of trace elements, glyphosate, fecal coliform and total coliform in Atlantic Rainforest mountain rivers (South America)[J]. Microchemical Journal, 122: 149-158.
DOI URL |
| [3] | CHEN H Y, TENG Y G, LU S J, et al., 2015. Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 512: 143-153. |
| [4] |
HAKANSON L, 1980. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution-control-a sedimentological approach[J]. Water Research, 14(8): 975-1001.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
HE Y B, HUANG D Y, ZHU Q H, et al., 2017. A three-season field study on the in-situ remediation of Cd-contaminated paddy soil using lime, two industrial by-products, and a low-Cd-accumulation rice cultivar[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 136: 135-141.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
LI P, DU B Y, CHAN H M, et al., 2015. Human inorganic mercury exposure, renal effects and possible pathways in Wanshan mercury mining area, China[J]. Environmental Research, 140(1): 198-204
DOI URL |
| [7] |
LI P, FENG X B, SHANG L H, et al., 2008. Mercury pollution from artisanal mercury mining in Tongren, Guizhou, China[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 23(8): 2055-2064.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
LIU X M, ZHONG L B, MENG J, et al., 2018. A multi-medium chain modeling approach to estimate the cumulative effects of cadmium pollution on human health[J]. Environmental Pollution, 239: 308-317.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
OBRIST D, KIRK J L, ZHANG L, et al., 2018. A review of global environmental mercury processes in response to human and natural perturbations: Changes of emissions, climate, and land use[J]. Ambio, 47(2): 116-140.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
WANG B, CHEN M, DING L, et al., 2021. Fish, rice, and human hair mercury concentrations and health risks in typical Hg-contaminated areas and fish-rich areas, China[J]. Environment International, DOI: 10.1016/j.envint.2021.106561.
DOI |
| [11] |
WANG X Y, LI Y F, LI B, et al., 2011. Multielemental contents of foodstuffs from the Wanshan (China) mercury mining area and the potential health risks[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 26(2): 182-187.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
WU S, PENG S Q, ZHANG X X, et al., 2015. Levels and health risk assessments of heavy metals in urban soils in Dongguan, China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 148: 71-78.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
YANG S C, WANG B, QIN C Y, et al., 2021. Compound-specific stable isotope analysis provides new insights for tracking human monomethylmercury exposure sources[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 55(18): 12493-12503.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
YUAN W, WANG X, LIN C J, et al., 2021. Quantification of atmospheric mercury deposition to and legacy re-emission from a subtropical forest floor by mercury isotopes[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 55(18): 12352-12361.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
ZHANG H, FENG X B, LARSSEN T, et al., 2010. Fractionation, distribution and transport of mercury in rivers and tributaries around Wanshan Hg mining district, Guizhou province, southwestern China: Part 1-Total mercury[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 25(5): 633-641.
DOI URL |
| [16] | ZHANG W L, DU Y, ZHAI M M, et al., 2014. Cadmium exposure and its health effects: A 19-year follow-up study of a polluted area in China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 470: 224-228. |
| [17] |
ZHAO F J, MA Y, ZHU Y G, et al., 2015. Soil contamination in China: Current status and mitigation strategies[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 49(2): 750-759.
DOI URL |
| [18] | 曹雪莹, 2019. 污染农田休耕修复中土壤镉有效性及肥力变化研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南师范大学. |
| CAO X Y, 2019. Study on the cadmium availability and fertilities of soils in fallow system integrated with soil remediation of contaminated farmland[D]. Changsha: Hunan Normal University. | |
| [19] | 常慧, 2019. 贵州省典型污染区镉的空间分布和来源识别[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学 (北京). |
| CHANG H, 2019. Spatial distribution and source identification of cadmium in typical polluted areas of Guizhou province: A case study of Wanshan mercury mine[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, Beijing. | |
| [20] | 陈欢, 白晓永, 李阳兵, 等, 2020. 铜仁市万山喀斯特地区石漠化演变及其对土地利用变化的响应[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 37(1): 24-35. |
| CHEN H, BAI X Y, LI Y B, et al., 2020. The evolution of rocky desertification and its response to land use changes in Wanshan Karst area, Tongren City, Guizhou Province, China[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 37(1): 24-35 | |
| [21] | 陈晓晨, 黄艺佳, 赵桐, 等, 2021. 中国典型土壤中镉的生物可给性影响因素研究及其健康风险评估[J]. 环境化学, 40(10): 3015-3023. |
| CHEN X C, HUANG Y J, ZHAO T, et al., 2021. Influencing factors of Cd bioaccessibility in China’s representative soils and the human health risk assessment[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 40(10): 3015-3023. | |
| [22] | 冯新斌, 史建波, 李平, 等, 2020. 我国汞污染研究与履约进展[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 35(11): 1344-1350. |
| FENG X B, SHI J B, LI P, et al., 2020. Progress of mercury pollution research and implementation of minamata convention in China[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 35(11): 1344-1350. | |
| [23] | 冯新斌, 尹润生, 俞奔, 等, 2012. 贵州不同汞污染区表层土壤汞同位素组成变化[J]. 科学通报, 57(33): 3119-3124. |
| FENG X B, YIN R S, YU B, et al., 2012. Mercury isotope variations in surface soils in different contaminated areas in Guizhou Province, China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 57(33): 3119-3124. | |
| [24] | 李福燕, 李许明, 吴鹏飞, 等, 2009. 海南省农用地土壤重金属含量与土壤有机质及pH的相关性[J]. 土壤, 41(1): 49-53. |
| LI F Y, LI X M, WU P F, et al., 2009. Correlation between heavy metal pollution and basic properties of agricultural soils in Hainan Province[J]. Soils, 41(1): 49-53. | |
| [25] | 李平, 冯新斌, 仇广乐, 2011. 贵州汞矿区居民食用大米的甲基汞暴露及健康风险评价[J]. 生态学杂志, 30(5): 914-921. |
| LI P, FENG X B, QIU G L, 2011. Methyl mercury exposure through rice consumption and its health risk assessment for the residents in Guizhou mercury mining areas[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 30(5): 914-921. | |
| [26] | 梁俊, 赵政阳, 樊明涛, 2008. 陕西渭北苹果园土壤中汞、镉污染与分布特征研究[J]. 农业工程学报, 24(3): 209-213. |
| LIANG J, ZHAO Z Y, FAN M T, et al., 2008. Spatial distribution and pollution of mercury and cadmium in Weibei apple orchard soils of Shaanxi Province[J]. Transactions of the Chineses Society of Agricultural Engineering, 24(3): 209-213. | |
| [27] | 刘冲, 赵玲, 李秀华, 等, 2020. 苎麻对农田土壤中汞、镉的吸收累积特征研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 39(5): 1034-1042. |
| LIU C, ZHAO L, LI X H, et al., 2020. Accumulation and transfer of mercury and cadmium in ramie from agricultural soils[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 39(5): 1034-1042. | |
| [28] | 鲁如坤, 2000. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社. |
| LU R K, 2000. Soil agricultural chemical analysis method[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press. | |
| [29] | 骆永明, 滕应, 2018. 我国土壤污染的区域差异与分区治理修复策略[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 33(2): 45-152. |
| LUO Y M, TENG Y, 2018. Regional difference in soil pollution and strategy of soil zonal governance and remediation in China[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 33(2): 145-152. | |
| [30] | 王道涵, 杨亚利, 任鹏, 等, 2015. 内蒙古某电厂周围土壤汞分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 环境工程学报, 9(12): 6135-6140. |
| WANG D H, YANG Y L, REN P, et al., 2015. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of mercury in soil around some coal-fired power plant of Inner Mongolia[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 9(12): 6135-6140. | |
| [31] | 王锐, 邓海, 贾中民, 等, 2020. 汞矿区周边土壤重金属空间分布特征、污染与生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 42(6): 3018-3027. |
|
WANG R, DENG H, JIA Z M, et al., 2020. Spatial distribution characteristics, pollution, and ecological risk assessment of soil heavy metals around mercury mining areas[J]. Environmental Science, 42(6): 3018-3027.
DOI URL |
|
| [32] | 魏复盛, 陈静生, 吴燕玉, 等, 1991. 中国土壤环境背景值研究[J]. 环境科学, 12(4):12-19, 94. |
|
WEI F S, CHEN J S, WU Y Y, et al., 1991. Study on the background contents on elements of soil in China[J]. Environmental Science, 12(4): 12-19, 94.
DOI URL |
|
| [33] | 夏吉成, 胡平, 王建旭, 等, 2016. 贵州省铜仁汞矿区汞污染特征研究[J]. 生态毒理学报, 11(1): 231-238. |
| XIA J C, HU P, WANG J X, et al., 2016. Mercury pollution characteristics in Tongren mercury mining area,Guizhou Province, China[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 11(1): 231-238 | |
| [34] | 尹伊梦, 赵委托, 黄庭, 等, 2018. 电子垃圾拆解区土壤-水稻系统重金属分布特征及健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 39(2): 916-926. |
| YIN Y M, ZHAO W T, HUANG T, et al., 2018. Distribution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in a soil-rice system in an E-waste dismantling area[J]. Environmental Science, 39(2): 916-926. | |
| [35] | 湛天丽, 2017. 贵州铜仁汞矿区农田土壤重金属污染风险评估和紫花苜蓿修复效果[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学. |
| ZHAN T L, 2017. Risk assessment and Medicago sativa remediation of agricultural soil contaminated with heavy metal in mercury mine area in Tongren, Guizhou Province[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University. | |
| [36] | 张莉, 周康, 2005. 贵州省土壤重金属污染现状与对策[J]. 贵州农业科学, 33(5): 114-115. |
| ZHANG L, ZHOU K, 2005. Current status and countermeasures for heavy metal contamination in soil in Guizhou[J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 33(5): 114-115. | |
| [37] | 赵慧芳, 闫海鱼, 王训, 等, 2016. 中国南方稻田土壤汞含量及潜在危害评价[J]. 生态毒理学报, 11(6): 252-258. |
| ZHAO H F, YAN H Y, WANG X, et al., 2016. Mercury concentrations and potential risk assessment of paddy soil in South China[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 11(6): 252-258. | |
| [38] | 赵金璇, 2009. 食物和儿童体内重金属含量及对健康影响的研究[D]. 淄博: 山东理工大学. |
| ZHAO J X, 2009. Studies on concentration of heavy metals in selected food stuffs and samples from children and their effects on health[D]. Zibo: Shandong University of Technology. | |
| [39] | 赵金璇, 李玉锋, 梁佳, 等, 2009. 贵阳和万山地区部分蔬菜中的重金属含量及其健康风险[J]. 生态毒理学报, 4(3): 392-398. |
| ZHAO J X, LI Y F, LIANG J, et al., 2009. Contents of heavy metals in some vegetables and their potential risks to human health in Guiyang and Wanshan areas[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 4(3): 392-398. | |
| [40] | 赵其国, 沈仁芳, 滕应, 等, 2017. 中国重金属污染区耕地轮作休耕制度试点进展、问题及对策建议[J]. 生态环境学报, 26(12): 2003-2007. |
| ZHAO Q G, SHEN R F, TENG Y, et al., 2017. Pilot progress, problems and countermeasures on farmland rotation and fallow system in the heavy metal polluted region of China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 26(12): 2003-2007. | |
| [41] | 中华人民共和国环保部. 2014. 污染场地风险评估技术导则:HJ25.3-2014[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| Environmental Protection Department of the People 's Republic of China. 2014. Technical guidelines for risk assessment of contaminated sites:HJ25.3-2014[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. | |
| [42] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部, 国家市场监督管理总局. 2018. 土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准:GB15618-2018[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation. 2018. Soil environmental quality-Risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land: GB 15618-2018[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China. |
| [1] | 董智今, 张呈春, 展秀丽, 张维福. 宁夏河东沙地生物土壤结皮及其下伏土壤养分的空间分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 910-919. |
| [2] | 杨春亮, 刘旻霞, 王千月, 苗乐乐, 肖音迪, 王敏. 单户与联户放牧经营下草玉梅与嵩草种群空间格局及其关联性[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 651-659. |
| [3] | 陈敏毅, 朱航海, 佘伟铎, 尹光彩, 黄祖照, 杨巧玲. 珠三角某遗留造船厂场地土壤重金属人体健康风险评估及源解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 794-804. |
| [4] | 杨耀东, 陈玉梅, 涂鹏飞, 曾清如. 经济作物轮作模式下镉污染农田修复潜力[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 627-634. |
| [5] | 吴胜义, 王飞, 徐干君, 马浩, 党禹杰, 吴菲. 川西北高山峡谷区森林碳储量及空间分布研究--以四川洛须自然保护区为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1735-1744. |
| [6] | 朱立安, 张会化, 程炯, 李婷, 林梓, 李俊杰. 珠江三角洲林业用地土壤重金属潜在生态风险格局分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1253-1262. |
| [7] | 温智峰, 魏识广, 李林, 叶万辉, 练琚愉. 南亚热带常绿阔叶林植物不同分类水平上的空间分布格局及空间关联[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 440-450. |
| [8] | 上官宇先, 尹宏亮, 徐懿, 钟红梅, 何明江, 秦鱼生, 郭松, 喻华. 不同钝化剂对水稻小麦籽粒镉吸收的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 370-379. |
| [9] | 刘娣, 苏超, 张红, 秦冠宇. 典型煤炭产业聚集区土壤重金属污染特征与风险评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 391-399. |
| [10] | 张楷悦, 刘增辉, 王颜昊, 王敬宽, 崔德杰, 柳新伟. 黄河三角洲自然保护区土壤PAHs的风险评估和空间特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2198-2205. |
| [11] | 刘志坚, 董元华, 张琇, 卿成实. 卫宁平原农用地土壤重金属污染特征与生态风险研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2216-2224. |
| [12] | 周椿富, 于锐, 王翔, 闯绍闯, 杨洪杏, 谢越. 抗生素对不同土壤中酶活性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2234-2241. |
| [13] | 王海鹤, 孙媛媛, 张帅, 徐小蓉, 商成梅, 黎春想. 贵阳市集中式饮用水源地重金属污染特征及健康风险评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 2039-2047. |
| [14] | 刘畅, 罗艳丽, 刘晨通, 郑玉红, 晁博, 董乐乐. 奎屯河下游区域地下水和农田土壤砷的空间分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 2070-2078. |
| [15] | 任丽江, 张妍, 张鑫, 山泽萱, 张成前. 渭河流域关中段地表水重金属的污染特征与健康风险评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 131-141. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
