生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (8): 1607-1616.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.08.007
郭佳琦( ), 陈俊辰, 黄旬, 黄佳乐, 赵丽娅, 李兆华*(
), 陈俊辰, 黄旬, 黄佳乐, 赵丽娅, 李兆华*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-04-20
出版日期:2021-08-18
发布日期:2021-11-03
通讯作者:
* 李兆华,教授,博士研究生导师,主要从事环境生态学研究。E-mail: zli@hubu.edu.cn作者简介:郭佳琦(1997年生),女,硕士研究生,主要从事入侵生态学研究。E-mail: 960221054@qq.com
基金资助:
GUO Jiaqi( ), CHEN Junchen, HUANG Xun, HUANG Jiale, ZHAO Liya, LI Zhaohua*(
), CHEN Junchen, HUANG Xun, HUANG Jiale, ZHAO Liya, LI Zhaohua*( )
)
Received:2021-04-20
Online:2021-08-18
Published:2021-11-03
摘要:
喜旱莲子草(Alternanthera philoxeroides)是中国危害最严重的入侵物种之一,为有效评估和预测入侵植物喜旱莲子草的危害程度,以喜旱莲子草入侵群落为研究对象,在野外调查的基础上,基于2×2列联表,测定生态位宽度、生态位相似性指数、生态位重叠指数,应用方差比率法(Rv)、χ 2检验、匹配系数Ochiai(IO)和贡献定律法,对群落中17个主要物种进行生态位、种间联结和群落稳定性分析,以期为喜旱莲子草植物群落的管理提供参考依据。结果表明,(1)群落中共发现草本植物18科38属41种,其中喜旱莲子草的重要值(IV =18.06)和生态位宽度(BL=0.80,BS=3.78)最大,占显著优势地位并且与多数物种产生较高的生态位重叠,禾本科(Amaranthaceae)植物狗牙根(Cynodon dactylon)、双穗雀稗(Paspalum paspaloides)、马唐(Digitaria sanguinalis)的优势地位次之。(2)群落整体呈现不显著负联结(Rv=0.92,W=45.82),关联性不显著的种对占95.24%,大部分物种间的联系并不紧密;喜旱莲子草与13个主要物种呈不同程度的负关联,这与其入侵性有关;与双穗雀稗、狗牙根、马唐存在高生态位重叠且紧密正关联,上述种对可能有相似的资源偏好而共存一定时期,另一方面说明其对喜旱莲子草的侵入有一定抵抗性。(3)模型方程与直线方程的交点坐标为(37.62,62.38),目前群落处于非稳定状态,大多数物种趋于独立,但主要物种存在一定的资源争夺。因此,建议考虑双穗雀稗、狗牙根和马唐用于喜旱莲子草群落入侵初期以及清除后的植被恢复。
中图分类号:
郭佳琦, 陈俊辰, 黄旬, 黄佳乐, 赵丽娅, 李兆华. 喜旱莲子草入侵群落主要物种生态位和种间联结研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1607-1616.
GUO Jiaqi, CHEN Junchen, HUANG Xun, HUANG Jiale, ZHAO Liya, LI Zhaohua. Niche Characteristics and Interspecific Associations of the Dominant Species of the Communities Invaded by Alternanthera philoxeroides[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(8): 1607-1616.
| 编号 No. | 科 Family | 物种名 Species | 重要值 Importance value/% | 生态位宽度 Niche breadth | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BL | BS | ||||
| 1 | 苋科 Amaranthaceae | *喜旱莲子草 Alternanthera philoxeroides | 18.06 | 0.80 | 3.78 |
| 2 | 禾本科 Poaceae | 狗牙根 Cynodon dactylon | 9.43 | 0.70 | 3.60 |
| 3 | 禾本科 Poaceae | 双穗雀稗 Paspalum paspaloides | 7.84 | 0.59 | 3.41 |
| 4 | 禾本科 Poaceae | 马唐 Digitaria sanguinalis | 7.24 | 0.44 | 3.19 |
| 5 | 禾本科 Poaceae | 结缕草 Zoysia japonica | 5.66 | 0.38 | 3.01 |
| 6 | 旋花科 Convolvulaceae | 圆叶牵牛 Ipomoea purpurea | 4.56 | 0.40 | 3.08 |
| 7 | 禾本科 Poaceae | 黑麦草 Lolium perenne | 4.43 | 0.26 | 1.93 |
| 8 | 禾本科 Poaceae | 狗尾草 Setaria viridis | 3.72 | 0.26 | 2.67 |
| 9 | 蓼科 Polygonaceae | 酸模 Rumex acetosa | 3.37 | 0.26 | 2.67 |
| 10 | 蓼科 Polygonaceae | 绵毛酸模叶蓼 Persicaria lapathifolia | 3.33 | 0.19 | 2.36 |
| 11 | 桑科 Moraceae | 葎草 Humulus scandens | 3.19 | 0.15 | 2.15 |
| 12 | 菊科 Asteraceae | 鳢肠 Eclipta prostrata | 3.15 | 0.23 | 2.56 |
| 13 | 菊科 Asteraceae | *小蓬草 Erigeron canadensis | 2.40 | 0.10 | 1.78 |
| 14 | 酢浆草科 Oxalidaceae | 酢浆草 Oxalis corniculata | 2.19 | 0.14 | 2.19 |
| 15 | 菊科 Asteraceae | 狼杷草 Bidens tripartita | 2.06 | 0.13 | 2.03 |
| 16 | 天门冬科 Asparagaceae | 麦冬 Ophiopogon japonicus | 2.00 | 0.11 | 1.91 |
| 17 | 雨久花科 Pontederiaceae | 鸭舌草 Monochoria vaginalis | 2.00 | 0.12 | 1.93 |
| 18 | ‒ | 其他24种 | 15.37 | ‒ | ‒ |
表1 喜旱莲子草群落植物的重要值和生态位宽度
Table 1 Importance value and niche breadth of plants in Alternanthera philoxeroides community
| 编号 No. | 科 Family | 物种名 Species | 重要值 Importance value/% | 生态位宽度 Niche breadth | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BL | BS | ||||
| 1 | 苋科 Amaranthaceae | *喜旱莲子草 Alternanthera philoxeroides | 18.06 | 0.80 | 3.78 |
| 2 | 禾本科 Poaceae | 狗牙根 Cynodon dactylon | 9.43 | 0.70 | 3.60 |
| 3 | 禾本科 Poaceae | 双穗雀稗 Paspalum paspaloides | 7.84 | 0.59 | 3.41 |
| 4 | 禾本科 Poaceae | 马唐 Digitaria sanguinalis | 7.24 | 0.44 | 3.19 |
| 5 | 禾本科 Poaceae | 结缕草 Zoysia japonica | 5.66 | 0.38 | 3.01 |
| 6 | 旋花科 Convolvulaceae | 圆叶牵牛 Ipomoea purpurea | 4.56 | 0.40 | 3.08 |
| 7 | 禾本科 Poaceae | 黑麦草 Lolium perenne | 4.43 | 0.26 | 1.93 |
| 8 | 禾本科 Poaceae | 狗尾草 Setaria viridis | 3.72 | 0.26 | 2.67 |
| 9 | 蓼科 Polygonaceae | 酸模 Rumex acetosa | 3.37 | 0.26 | 2.67 |
| 10 | 蓼科 Polygonaceae | 绵毛酸模叶蓼 Persicaria lapathifolia | 3.33 | 0.19 | 2.36 |
| 11 | 桑科 Moraceae | 葎草 Humulus scandens | 3.19 | 0.15 | 2.15 |
| 12 | 菊科 Asteraceae | 鳢肠 Eclipta prostrata | 3.15 | 0.23 | 2.56 |
| 13 | 菊科 Asteraceae | *小蓬草 Erigeron canadensis | 2.40 | 0.10 | 1.78 |
| 14 | 酢浆草科 Oxalidaceae | 酢浆草 Oxalis corniculata | 2.19 | 0.14 | 2.19 |
| 15 | 菊科 Asteraceae | 狼杷草 Bidens tripartita | 2.06 | 0.13 | 2.03 |
| 16 | 天门冬科 Asparagaceae | 麦冬 Ophiopogon japonicus | 2.00 | 0.11 | 1.91 |
| 17 | 雨久花科 Pontederiaceae | 鸭舌草 Monochoria vaginalis | 2.00 | 0.12 | 1.93 |
| 18 | ‒ | 其他24种 | 15.37 | ‒ | ‒ |
| 编号No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.72 | 0.69 | 0.55 | 0.53 | 0.55 | 0.56 | 0.41 | 0.48 | 0.38 | 0.28 | 0.36 | 0.31 | 0.36 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.19 | |
| 2 | 0.64 | 0.74 | 0.61 | 0.51 | 0.62 | 0.34 | 0.51 | 0.47 | 0.27 | 0.32 | 0.42 | 0.18 | 0.27 | 0.25 | 0.21 | 0.26 | |
| 3 | 0.58 | 0.67 | 0.48 | 0.59 | 0.40 | 0.41 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.21 | 0.19 | 0.31 | 0.25 | 0.24 | 0.32 | 0.24 | 0.23 | |
| 4 | 0.45 | 0.52 | 0.51 | 0.28 | 0.40 | 0.00 | 0.45 | 0.36 | 0.30 | 0.51 | 0.36 | 0.16 | 0.18 | 0.33 | 0.14 | 0.31 | |
| 5 | 0.38 | 0.41 | 0.47 | 0.28 | 0.22 | 0.44 | 0.22 | 0.26 | 0.11 | 0.17 | 0.32 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 0.39 | 0.36 | 0.40 | |
| 6 | 0.42 | 0.50 | 0.39 | 0.41 | 0.23 | 0.20 | 0.32 | 0.29 | 0.31 | 0.30 | 0.39 | 0.40 | 0.17 | 0.15 | 0.27 | 0.31 | |
| 7 | 0.34 | 0.25 | 0.31 | 0.00 | 0.36 | 0.17 | 0.08 | 0.19 | 0.24 | 0.04 | 0.15 | 0.00 | 0.32 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.05 | |
| 8 | 0.24 | 0.34 | 0.21 | 0.36 | 0.17 | 0.31 | 0.09 | 0.35 | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.40 | 0.28 | 0.23 | 0.16 | 0.10 | 0.26 | |
| 9 | 0.28 | 0.32 | 0.22 | 0.32 | 0.21 | 0.28 | 0.16 | 0.38 | 0.04 | 0.33 | 0.19 | 0.24 | 0.38 | 0.09 | 0.22 | 0.09 | |
| 10 | 0.21 | 0.17 | 0.14 | 0.22 | 0.07 | 0.26 | 0.18 | 0.15 | 0.05 | 0.19 | 0.13 | 0.08 | 0.23 | 0.40 | 0.22 | 0.00 | |
| 11 | 0.14 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.31 | 0.12 | 0.21 | 0.03 | 0.15 | 0.30 | 0.16 | 0.00 | 0.23 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.30 | |
| 12 | 0.22 | 0.28 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.30 | 0.36 | 0.15 | 0.34 | 0.19 | 0.12 | 0.00 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.07 | 0.19 | 0.23 | |
| 13 | 0.12 | 0.07 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.22 | 0.00 | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.06 | 0.22 | 0.13 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.28 | 0.00 | |
| 14 | 0.16 | 0.21 | 0.22 | 0.17 | 0.11 | 0.17 | 0.20 | 0.27 | 0.23 | 0.19 | 0.07 | 0.21 | 0.00 | 0.14 | 0.25 | 0.06 | |
| 15 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.16 | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.16 | 0.10 | 0.37 | 0.14 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.17 | 0.33 | 0.57 | |
| 16 | 0.09 | 0.10 | 0.12 | 0.09 | 0.22 | 0.17 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.20 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.30 | 0.19 | 0.27 | 0.37 | |
| 17 | 0.08 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.19 | 0.25 | 0.18 | 0.03 | 0.16 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.25 | 0.17 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.48 | 0.30 |
表2 喜旱莲子草群落主要物种生态位相似性指数(对角线左)和生态位重叠指数(对角线右)
Table 2 Niche similarity (diagonal to the left) and niche overlap (diagonal to the right) of main plant species in the Alternanthera philoxeroides community
| 编号No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.72 | 0.69 | 0.55 | 0.53 | 0.55 | 0.56 | 0.41 | 0.48 | 0.38 | 0.28 | 0.36 | 0.31 | 0.36 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.19 | |
| 2 | 0.64 | 0.74 | 0.61 | 0.51 | 0.62 | 0.34 | 0.51 | 0.47 | 0.27 | 0.32 | 0.42 | 0.18 | 0.27 | 0.25 | 0.21 | 0.26 | |
| 3 | 0.58 | 0.67 | 0.48 | 0.59 | 0.40 | 0.41 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.21 | 0.19 | 0.31 | 0.25 | 0.24 | 0.32 | 0.24 | 0.23 | |
| 4 | 0.45 | 0.52 | 0.51 | 0.28 | 0.40 | 0.00 | 0.45 | 0.36 | 0.30 | 0.51 | 0.36 | 0.16 | 0.18 | 0.33 | 0.14 | 0.31 | |
| 5 | 0.38 | 0.41 | 0.47 | 0.28 | 0.22 | 0.44 | 0.22 | 0.26 | 0.11 | 0.17 | 0.32 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 0.39 | 0.36 | 0.40 | |
| 6 | 0.42 | 0.50 | 0.39 | 0.41 | 0.23 | 0.20 | 0.32 | 0.29 | 0.31 | 0.30 | 0.39 | 0.40 | 0.17 | 0.15 | 0.27 | 0.31 | |
| 7 | 0.34 | 0.25 | 0.31 | 0.00 | 0.36 | 0.17 | 0.08 | 0.19 | 0.24 | 0.04 | 0.15 | 0.00 | 0.32 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.05 | |
| 8 | 0.24 | 0.34 | 0.21 | 0.36 | 0.17 | 0.31 | 0.09 | 0.35 | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.40 | 0.28 | 0.23 | 0.16 | 0.10 | 0.26 | |
| 9 | 0.28 | 0.32 | 0.22 | 0.32 | 0.21 | 0.28 | 0.16 | 0.38 | 0.04 | 0.33 | 0.19 | 0.24 | 0.38 | 0.09 | 0.22 | 0.09 | |
| 10 | 0.21 | 0.17 | 0.14 | 0.22 | 0.07 | 0.26 | 0.18 | 0.15 | 0.05 | 0.19 | 0.13 | 0.08 | 0.23 | 0.40 | 0.22 | 0.00 | |
| 11 | 0.14 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.31 | 0.12 | 0.21 | 0.03 | 0.15 | 0.30 | 0.16 | 0.00 | 0.23 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.30 | |
| 12 | 0.22 | 0.28 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.30 | 0.36 | 0.15 | 0.34 | 0.19 | 0.12 | 0.00 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.07 | 0.19 | 0.23 | |
| 13 | 0.12 | 0.07 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.22 | 0.00 | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.06 | 0.22 | 0.13 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.28 | 0.00 | |
| 14 | 0.16 | 0.21 | 0.22 | 0.17 | 0.11 | 0.17 | 0.20 | 0.27 | 0.23 | 0.19 | 0.07 | 0.21 | 0.00 | 0.14 | 0.25 | 0.06 | |
| 15 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.16 | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.16 | 0.10 | 0.37 | 0.14 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.17 | 0.33 | 0.57 | |
| 16 | 0.09 | 0.10 | 0.12 | 0.09 | 0.22 | 0.17 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.20 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.30 | 0.19 | 0.27 | 0.37 | |
| 17 | 0.08 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.19 | 0.25 | 0.18 | 0.03 | 0.16 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.25 | 0.17 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.48 | 0.30 |
| 方差比率 Variance ratio | 检验统计量 Statistic W | χ 2临界值 [ | 检验结果 Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.92 | 45.82 | 34.76, 67.50 | 不显著负关联 Non-significant negative association |
表3 种间总体关联性
Table 3 Overall interspecific associations among main plant species in the Alternanthera philoxeroides community
| 方差比率 Variance ratio | 检验统计量 Statistic W | χ 2临界值 [ | 检验结果 Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.92 | 45.82 | 34.76, 67.50 | 不显著负关联 Non-significant negative association |
| 编号 No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.38 | 0.06 | 0.00 | -0.03 | -0.01 | -0.19 | -0.19 | -0.19 | -0.47 | -0.71 | -0.24 | -1.40 | -0.57 | -0.88 | -1.10 | -1.10 | |
| 2 | + | 1.75 | 0.24 | -0.10 | 1.80 | -1.88 | 2.30 | -0.63 | -0.47 | -0.09 | -0.01 | -1.17 | -0.01 | -0.14 | -0.61 | -0.03 | |
| 3 | + | + | 0.65 | 0.76 | -0.02 | -0.26 | -0.26 | -0.26 | -2.66 | 0.00 | -0.01 | -0.49 | -0.05 | -0.13 | -0.02 | -0.02 | |
| 4 | + | + | + | -0.66 | 0.09 | -20.33 | 1.10 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 1.80 | 0.02 | 0.11 | -0.05 | 1.07 | 0.01 | 0.49 | |
| 5 | - | - | + | - | -1.54 | 0.02 | -1.27 | -0.25 | -2.15 | 0.04 | 0.16 | 0.00 | -0.25 | 0.01 | 1.66 | 1.66 | |
| 6 | - | + | - | + | - | -2.21 | 0.98 | 0.14 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 1.69 | 5.72 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 1.10 | 0.05 | |
| 7 | - | - | - | ▼ | + | - | -1.81 | 0.45 | 0.02 | 0.93 | 0.23 | 1.52 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 0.28 | 0.28 | |
| 8 | - | ◯ | - | + | - | + | - | 1.81 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.80 | 0.44 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.13 | |
| 9 | - | - | - | + | - | + | + | + | 1.80 | 2.09 | 0.23 | 0.44 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.28 | |
| 10 | - | - | - | + | - | + | + | + | + | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 2.63 | 0.00 | 1.05 | |
| 11 | - | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 2.74 | 2.59 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.06 | 0.06 | |
| 12 | - | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 0.03 | 0.30 | 0.40 | 0.24 | 0.17 | |
| 13 | - | - | - | + | + | △ | + | + | + | + | + | + | 0.58 | 0.30 | 4.33 | 0.18 | |
| 14 | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| 15 | - | - | - | + | + | ◯ | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 0.18 | 7.00 | |
| 16 | - | - | - | ◯ | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | △ | + | + | 0.37 | |
| 17 | - | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ▲ | + |
表4 主要物种种间关联性的χ 2统计量检验
Table 4 χ2 correlation test of main plant species in the Alternanthera philoxeroides community
| 编号 No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.38 | 0.06 | 0.00 | -0.03 | -0.01 | -0.19 | -0.19 | -0.19 | -0.47 | -0.71 | -0.24 | -1.40 | -0.57 | -0.88 | -1.10 | -1.10 | |
| 2 | + | 1.75 | 0.24 | -0.10 | 1.80 | -1.88 | 2.30 | -0.63 | -0.47 | -0.09 | -0.01 | -1.17 | -0.01 | -0.14 | -0.61 | -0.03 | |
| 3 | + | + | 0.65 | 0.76 | -0.02 | -0.26 | -0.26 | -0.26 | -2.66 | 0.00 | -0.01 | -0.49 | -0.05 | -0.13 | -0.02 | -0.02 | |
| 4 | + | + | + | -0.66 | 0.09 | -20.33 | 1.10 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 1.80 | 0.02 | 0.11 | -0.05 | 1.07 | 0.01 | 0.49 | |
| 5 | - | - | + | - | -1.54 | 0.02 | -1.27 | -0.25 | -2.15 | 0.04 | 0.16 | 0.00 | -0.25 | 0.01 | 1.66 | 1.66 | |
| 6 | - | + | - | + | - | -2.21 | 0.98 | 0.14 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 1.69 | 5.72 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 1.10 | 0.05 | |
| 7 | - | - | - | ▼ | + | - | -1.81 | 0.45 | 0.02 | 0.93 | 0.23 | 1.52 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 0.28 | 0.28 | |
| 8 | - | ◯ | - | + | - | + | - | 1.81 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.80 | 0.44 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.13 | |
| 9 | - | - | - | + | - | + | + | + | 1.80 | 2.09 | 0.23 | 0.44 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.28 | |
| 10 | - | - | - | + | - | + | + | + | + | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 2.63 | 0.00 | 1.05 | |
| 11 | - | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 2.74 | 2.59 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.06 | 0.06 | |
| 12 | - | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 0.03 | 0.30 | 0.40 | 0.24 | 0.17 | |
| 13 | - | - | - | + | + | △ | + | + | + | + | + | + | 0.58 | 0.30 | 4.33 | 0.18 | |
| 14 | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| 15 | - | - | - | + | + | ◯ | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 0.18 | 7.00 | |
| 16 | - | - | - | ◯ | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | △ | + | + | 0.37 | |
| 17 | - | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ▲ | + |
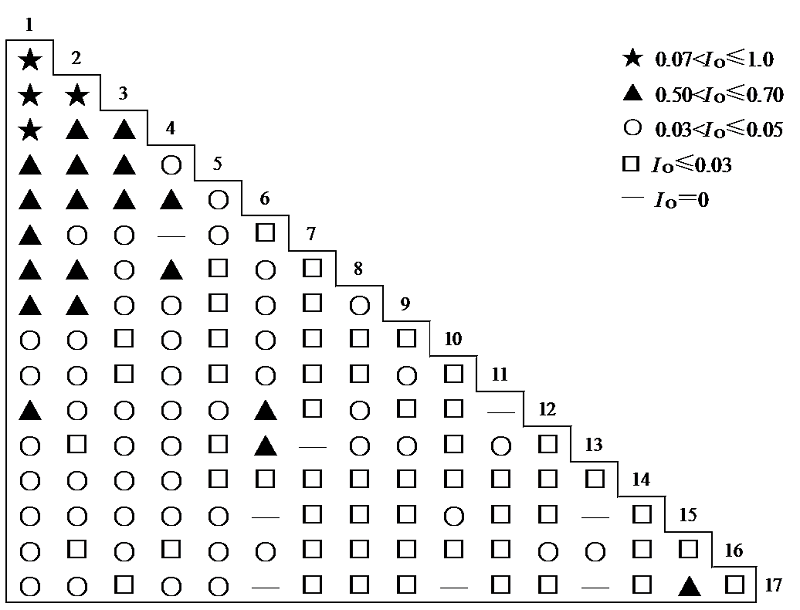
图2 主要物种种间匹配系数Ochiai(IO)半矩阵 物种编号含义见表1
Fig. 2 Semi-matrix diagram of Ochiai index (IO) of main species in the Alternanthera philoxeroides community Species codes are the same as in Table 1
| [1] |
CALLAWAY RM, MARON J, 2006. What have exotic plant invasions taught us over the past 20 years. Trends in Ecology and Evolution[J]. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 21(7): 369-374.
DOI URL |
| [2] | GREIG-SMITH P, 1983. Quantitative Plant Ecology[M]. 3rd ed. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications: 105-128. |
| [3] |
HU Y Y, LEI F, YU F Z, et al., 2020. Prediction of the spatial distribution of Alternanthera philoxeroides in China based on ArcGIS and MaxEnt[J]. Global Ecology and Conservation, DOI: 10.1016/j.gecco.2019.e00856.
DOI |
| [4] | LEGENDRE P L, LEGENDRE L, 1983. Numerical Ecology[J]. Ecology, 63(2): 853. |
| [5] | ROUSSET O, LEPART J, 2000. Positive and negative interactions at different life stages of a colonizing species[J]. Journal of Ecology, 88(3): 402-412. |
| [6] |
SCHLUTER D, 1984. A Variance test for detecting species associations, with some example applications[J]. Ecology, 65(3): 998-1005.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
WU H, ISMAIL M, DING J Q, 2017. Global warming increases the interspecific competitiveness of the invasive plant alligator weed, Alternanthera philoxeroides[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 575: 1415-1422.
DOI URL |
| [8] | 从春蕾, 刘天雷, 邹焓, 2016. 安顺市空心莲子草入侵对伴生杂草的组成及多样性的影响[J]. 南方农业, 10(22): 47-52. |
| CONG C L, LIU T L, ZOU H, 2016. Effects of invasion of Alternanthera philoxeroides on composition and diversity of associated weeds in Anshun City[J]. South China Agriculture, 10(22): 47-52. | |
| [9] | 邓贤兰, 曹裕松, 梁琴, 等, 2016. 井冈山山顶矮林乔木层优势种的生态位研究[J]. 植物资源与环境学报, 25(1): 88-93. |
| DENG H L, CAO Y S, LIANG Q, et al., 2016. Study on niche of dominant species at arbor layer in montane elfin forest of Jinggangshan[J]. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment, 25(1): 88-93. | |
| [10] | 丁文慧, 李秀珍, 姜俊彦, 等, 2016. 崇明东滩南部河口盐沼植物群落种间关系的数量分析[J]. 应用生态学报, 27(5): 1417-1426. |
| DING W H, LI X Z, JIANG J Y, et al., 2016. Numerical analysis of inter-specific relationships in the estuary salt marsh plant community of southern Chongming Dongtan, Shanghai[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 27(5): 1417-1426. | |
| [11] | 房飞, 胡玉昆, 张伟, 等, 2012. 高寒草原植物群落种间关系的数量分析[J]. 生态学报, 32(6): 1898-1907. |
| FANG F, HU Y K, ZHANG W, et al., 2012. Numerical analysis of inter-specific relationships in Alpine steppe community in Bayanbulak[J]. Acta Ecological Sinica, 32(6): 1898-1907. | |
| [12] | 郭连金, 王涛, 2009. 空心莲子草入侵对乡土植物群落种间联结性及稳定性的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 17(5): 851-856. |
|
GUO L J, WANG T, 2009. Impact of invasion of exotic plant Alternanthera philoxeroides on interspecies association and stability of native plant community[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 17(5): 851-856.
DOI URL |
|
| [13] | 郭连金, 2011. 苏门白酒草对乡土植物群落种间联结性及稳定性的影响[J]. 亚热带植物科学, 40(2): 18-23. |
| GUO L J, 2011. Impacts to the Interspecies Association and Stability of Native Community Invaded by an Exotic Plant Conyza sumatrensis [J]. Subtropical plant science, 40(2): 18-23. | |
| [14] | 郭志华, 卓正大, 陈洁, 等, 1997. 庐山常绿阔叶、落叶阔叶混交林乔木种群种间联结性研究[J]. 植物生态学报, 21(5): 424-432. |
| GUO Z H, ZHUO Z D, CHEN J, et al., 1997. Interspecific association of trees in mixed evergreen and deciduous broadleaved forest in Lushan Mountain[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 21(5): 424-432. | |
| [15] | 洪思思, 缪崇崇, 方本基, 等, 2008. 浙江省阔叶丰花草入侵群落物种多样性、生态位及种间联结研究[J]. 武汉植物学研究, 26(5): 501-508. |
| HONG S S, MIAO C C, FANG B J, et al., 2008. On Species Diversity Niche Breath and Interspecies Association in communities Invaded by Spermacoce latifolia Zhejjang Province[J]. Journal of Wuhan Botanical Research, 26(5): 501-508. | |
| [16] |
江焕, 张辉, 龙文兴, 等, 2019. 金钟藤入侵群落的种间联结及生态位特征[J]. 生物多样性, 27(4): 388-399.
DOI |
|
JIANG H, ZHANG H, LONG W X, et al., 2019. Interspecific associations and niche characteristics of communities invaded by Decalobanthus boisianus [J]. Biodiversity Science, 27(4): 388-399.
DOI URL |
|
| [17] | 李安定, 谢元贵, 张建利, 等, 2013. 异质生境空心莲子草植物群落组成及物种多样性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 22(8): 1322-1328. |
| LI A D, XIE Y G, ZHANG J L, et al., 2013. Impacts of the invasion of Alternathera philoxeroides on species composition and diversity of heterogeneous habitat in Caohai wetland[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 22(8): 1322-1328. | |
| [18] | 刘海, 杜如万, 王勇, 等, 2017. 紫茎泽兰对四川省凉山州共生植物种间联结性及稳定性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 37(15): 5031-5038. |
| LIU H, DU R W, WANG Y, et al., 2017. Effects of Eupatorium adenophorum on interspecific association and the stability of companion species in Liangshan Prefecture of Sichuan Province[J]. Acta Ecological Sinica, 37(15): 5031-5038. | |
| [19] | 刘建康, 张克斌, 王黎黎, 等, 2014. 半干旱区人工封育草场植被群落生态位研究--以宁夏盐池县长期定位监测点为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 23(5): 762-768. |
| LIU J K, ZHANG K B, WANG L L, et al., 2014. Vegetation niche of enclosed grassland in semi-arid area: Taking Yanchi of Ningxia as an example[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 23(5): 762-768. | |
| [20] | 刘润红, 陈乐, 涂洪润, 等, 2020. 桂林岩溶石山青冈群落灌木层主要物种生态位与种间联结[J]. 生态学报, 40(6): 2057-2071. |
| LIU R H, CHEN L, TU H R, et al., 2020. Niche and interspecific association of main species in shrub layer of Cyclobalanopsis glauca community in karst hills of Guilin,southwest China[J]. Acta Ecological Sinica, 40(6): 2057-2071. | |
| [21] | 柳剑丽, 王宗礼, 李平, 等, 2013. 锡林郭勒典型草原不同群落物种间关系的数量分析[J]. 中国草地学报, 35(5): 74-79. |
| LIU J L, WANG Z L, LI P, et al., 2013. Quantitative Analysis of Relationships among Species of Different Communities in Typical Steppe in Xilingol[J]. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 35(5): 74-79. | |
| [22] | 罗瑛, 冯伟瑜, 欧文军, 2017. 空心莲子草水浸提液对3种暖季型草坪草种子萌发与幼苗生长的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 33(25): 76-80. |
| LUO Y, FENG W Y, OU W J, 2017. Allelopathic Effects of Aquatic Lixivium and Extracts from Alternanthera philoxeroides on Seed Germination and Early Seedling Growth of Three Kinds of Warm-season Turf Grass, 33(25): 76-80. | |
| [23] | 潘高, 张合平, 潘登, 2015. 南方红壤丘陵区3种森林群落内主要草本植物种群生态位特征[J]. 草业科学, 32(12): 2094-2106. |
| PAN G, ZHANG H P, PAN D, 2015. Niche characteristics of herb populations within three forest types in hilly red soil region of southern China[J]. Pratacultural Science, 32(12): 2094-2106. | |
| [24] |
潘晓云, 耿宇鹏, 张文驹, 等, 2006. 喜旱莲子草沿河岸带不同生境的盖度变化及形态可塑性[J]. 植物生态学报, 30(5): 835-843.
DOI |
|
PAN X Y, GENG Y P, ZHANG W J, et al., 2006. Cover shift and morphological plasticity of invasive Alternathera philoxeroides along a riparian zone in south China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 30(5): 835-843.
DOI URL |
|
| [25] | 宋振, 张瑞海, 张国良, 等, 2018. 空心莲子草叶甲释放量对空心莲子草防控效果的研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 27(11): 2033-2038. |
| SONG Z, ZHANG R H, ZHANG G L, et al., 2018. The Effect of Agasicles hygrophila Release on the Control of Alternanthera philoxeroides[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 27(11): 2033-2038. | |
| [26] | 王颖, 李为花, 李丹, 等, 2015. 喜旱莲子草入侵机制及防治策略研究进展[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 32(4): 625-634. |
| WANG Y, LI W H, LI D, et al., 2015. Research progress on invasion mechanism and prevention strategy of Alternanthera philoxeroides [J]. Journal of Zhejiang A & F University, 32(4): 625-634. | |
| [27] | 吴昊, 蔡东章, 高靓文, 等, 2020. 信阳市入侵植物空心莲子草群落数量分类及功能群研究[J]. 信阳师范学院学报 (自然科学版), 33(2): 250-257. |
| WU H, CAI D Z, GAO L W, et al., 2020. Quantitative Classification and Functional Groups of Alien Plant Alternanthera philoxeroides Invaded Community in Xinyang City[J]. Journal of Xinyang Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 33(2): 250-257. | |
| [28] | 吴昊, 杜奎, 李万通, 等, 2019. 空心莲子草入侵对豫南草本植物群落多样性及稳定性的影响[J]. 草业科学, 36(2): 382-393. |
| WU H, DU K, LI W T, et al., 2019. Influence of Alternanthera philoxeroides invasion on species diversity and stability in the herbaceous community in southern Henan Province[J]. Pratacultural Science, 36(2): 382-393. | |
| [29] | 吴倩楠, 董建文, 郑宇, 等, 2017. 百里杜鹃国家森林公园优势种生态位研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报 (自然科学版), 41(2): 175-180. |
| WU Q N, DONG J W, ZHENG Y, et al., 2017. Niches of the main plant species in Baili Rhododendron National Forest Park[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 41(2): 175-180. | |
| [30] | 徐满厚, 刘敏, 翟大彤, 等, 2016. 植物种间联结研究内容与方法评述[J]. 生态学报, 36(24): 8224-8233. |
| XU M H, LIU M, ZHAI D T, et al., 2016. A review of contents and methods used to analyze various aspects of plant interspecific associations[J]. Acta Ecological Sinica, 36(24): 8224-8233. | |
| [31] | 张建利, 蔡国俊, 吴迪, 等, 2018. 贵州草海湿地空心莲子草入侵迹地植物群落结构数量特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 27(5): 827-833. |
| ZHANG J L, CAI G J, WU D, et al., 2018. The plant community structure and quantitative features after the invasion of Alternanthera philoxeroides in Caohai Wetland of Guizhou Province[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 27(5): 827-833. | |
| [32] | 张金屯, 2011. 数量生态学[M]. 第2版. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| ZHANG J T, 2011. Quantitative ecology[M]. 2nd Edition. Beijing: Science Press. | |
| [33] | 赵彩莉, 张峰, 庞春花, 等, 2013. 反枝苋群落优势种的种间关联性分析[J]. 植物研究, 33(4): 454-460. |
| ZHAO C L, ZHANG F, PANG C H, et al., 2013. Interspecific Association of Dominant Species of Amaranthus retroflexus L. Community[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 33(4): 454-460. | |
| [34] | 郑超超, 伊力塔, 张超, 等, 2015. 浙江江山公益林物种种间关系及CCA排序[J]. 生态学报, 35(22): 7511-7521. |
| ZHENG C C, YI L T, ZHANG C, et al., 2015. Interspecific relationship and canonical correspondence analysis of the dominant species in ecological service forest of Jiangshan City in Zhejiang Province[J]. Acta Ecological Sinica, 35(22): 7511-7521. | |
| [35] | 郑元润, 2000. 森林群落稳定性研究方法初探[J]. 林业科学, 36(5): 28-32. |
| ZHENG Y R, 2000. Comparison of methods for studying stability of forest community[J]. Forestry science, 36(5): 28-32. |
| [1] | 侯晖, 颜培轩, 谢沁宓, 赵宏亮, 庞丹波, 陈林, 李学斌, 胡杨, 梁咏亮, 倪细炉. 贺兰山蒙古扁桃灌丛根际土壤AM真菌群落多样性特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 857-865. |
| [2] | 姜永伟, 丁振军, 袁俊斌, 张峥, 李杨, 问青春, 王业耀, 金小伟. 辽宁省主要河流底栖动物群落结构及水质评价研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 969-979. |
| [3] | 王云, 郑西来, 曹敏, 李磊, 宋晓冉, 林晓宇, 郭凯. 滨海含水层咸-淡水过渡带反硝化性能与控制因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 980-988. |
| [4] | 寇祝, 卿纯, 袁昌果, 李平. 西藏东北部热泉水中硫氧化菌的多样性及分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 989-1000. |
| [5] | 周沁苑, 董全民, 王芳草, 刘玉祯, 冯斌, 杨晓霞, 俞旸, 张春平, 曹铨, 刘文亭. 放牧方式对高寒草地瑞香狼毒根际土壤团聚体及有机碳特征的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 660-667. |
| [6] | 胡芳, 刘聚涛, 温春云, 韩柳, 文慧. 抚河流域浮游植物群落结构特征及其水生态状况评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 744-755. |
| [7] | 于菲, 曾海龙, 房怀阳, 付玲芳, 林澍, 董家豪. 典型感潮河网浮游藻类功能群时空变化特征及水质评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 756-765. |
| [8] | 秦浩, 李蒙爱, 高劲, 陈凯龙, 张殷波, 张峰. 芦芽山不同海拔灌丛土壤细菌群落组成和多样性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 459-468. |
| [9] | 阳涅, 孙晓旭, 孔天乐, 孙蔚旻, 陈泉源, 高品. 微生物群落对河流底泥中锑含量变化的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 609-618. |
| [10] | 樊慧琳, 张佳敏, 李欢, 王艳玲. 坡耕地稻田剖面磷的储存格局与流失风险研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 283-291. |
| [11] | 周世强, Vanessa HULL, 张晋东, 刘巅, 谢浩, 黄金燕, 张和民. 野生大熊猫与放牧家畜利用生境的特征比较[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 309-319. |
| [12] | 向兴, 满百膺, 张俊忠, 罗洋, 毛小涛, 张超, 孙丙华, 王希. 黄山土壤细菌群落及氮循环功能群的垂向分布格局[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 56-69. |
| [13] | 李萍, 白小明, 陈鑫, 李娟霞, 冉福, 陈辉, 杨小妮, 康瑞卿. 白三叶入侵对禾本科草坪土壤特性和植物群落的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 70-79. |
| [14] | 王哲, 田胜尼, 张永梅, 张和禹, 周忠泽. 巢湖派河口滩涂植物群落特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1823-1831. |
| [15] | 陈小弯, 田华川, 常军军, 陈礼强, 舒兴权, 冯秀祥. 杞麓湖中河河口表流湿地净化河道污染水的效果及其微生物群落特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1865-1875. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
