生态环境学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (2): 268-278.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2025.02.009
翁雷霆1( ), 王鹏1,*(
), 王鹏1,*( ), 肖荣波1,2,3, 白晋晶1, 钟俊宏2
), 肖荣波1,2,3, 白晋晶1, 钟俊宏2
收稿日期:2024-10-24
出版日期:2025-02-18
发布日期:2025-03-03
通讯作者:
*王鹏。E-mail: wangpengdili@163.com作者简介:翁雷霆(2000年生),男,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为环境生态学。E-mail: 13922031586@163.com
基金资助:
WENG Leiting1( ), WANG Peng1,*(
), WANG Peng1,*( ), XIAO Rongbo1,2,3, BAI Jinjing1, ZHONG Junhong2
), XIAO Rongbo1,2,3, BAI Jinjing1, ZHONG Junhong2
Received:2024-10-24
Online:2025-02-18
Published:2025-03-03
摘要:
掌握PM2.5和O3复合污染的时空特征,对于支撑新形势下PM2.5与O3污染的协同控制具有重要意义。利用Mann-Kendall趋势和小波分析法分析了珠三角城市群2000-2022年PM2.5和O3数据,探讨了PM2.5和O3的变化趋势、周期、时空特征及其影响因素。结果表明:2000-2022年,珠三角地区PM2.5浓度呈下降趋势,但O3浓度呈升高趋势;珠三角PM2.5和O3浓度具有显著的季节性,PM2.5污染主要发生在冬季,而夏季浓度相对较低;O3污染则在秋季较严重,冬季浓度最低。PM2.5和O3浓度变化存在10个月左右的周期,在较短时间尺度上呈正相关,长时间尺度上为负相关,表明在年尺度上具有关联性。珠三角人口、GDP、温度、湿度等与PM2.5浓度呈现较强的负相关,但与O3浓度变化呈正相关,表明珠三角推行的节能减排政策对于PM2.5污染控制具有明显效果,但是O3污染问题应引起重视。低温有利于PM2.5生成,高温有利于O3生成;相对湿度太大时,PM2.5浓度随相对湿度的升高而降低;风速越低越不利于PM2.5和O3扩散,其浓度越高。PM2.5-O3的协同污染控制需要综合考虑自然和社会因素影响。
中图分类号:
翁雷霆, 王鹏, 肖荣波, 白晋晶, 钟俊宏. 2000-2022年珠三角城市群PM2.5与O3时空分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(2): 268-278.
WENG Leiting, WANG Peng, XIAO Rongbo, BAI Jinjing, ZHONG Junhong. Spatial-Temporal Distribution Characteristics of PM2.5 and O3 in the Pearl River Delta Urban Agglomeration and Corresponding Influence Factors[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2025, 34(2): 268-278.
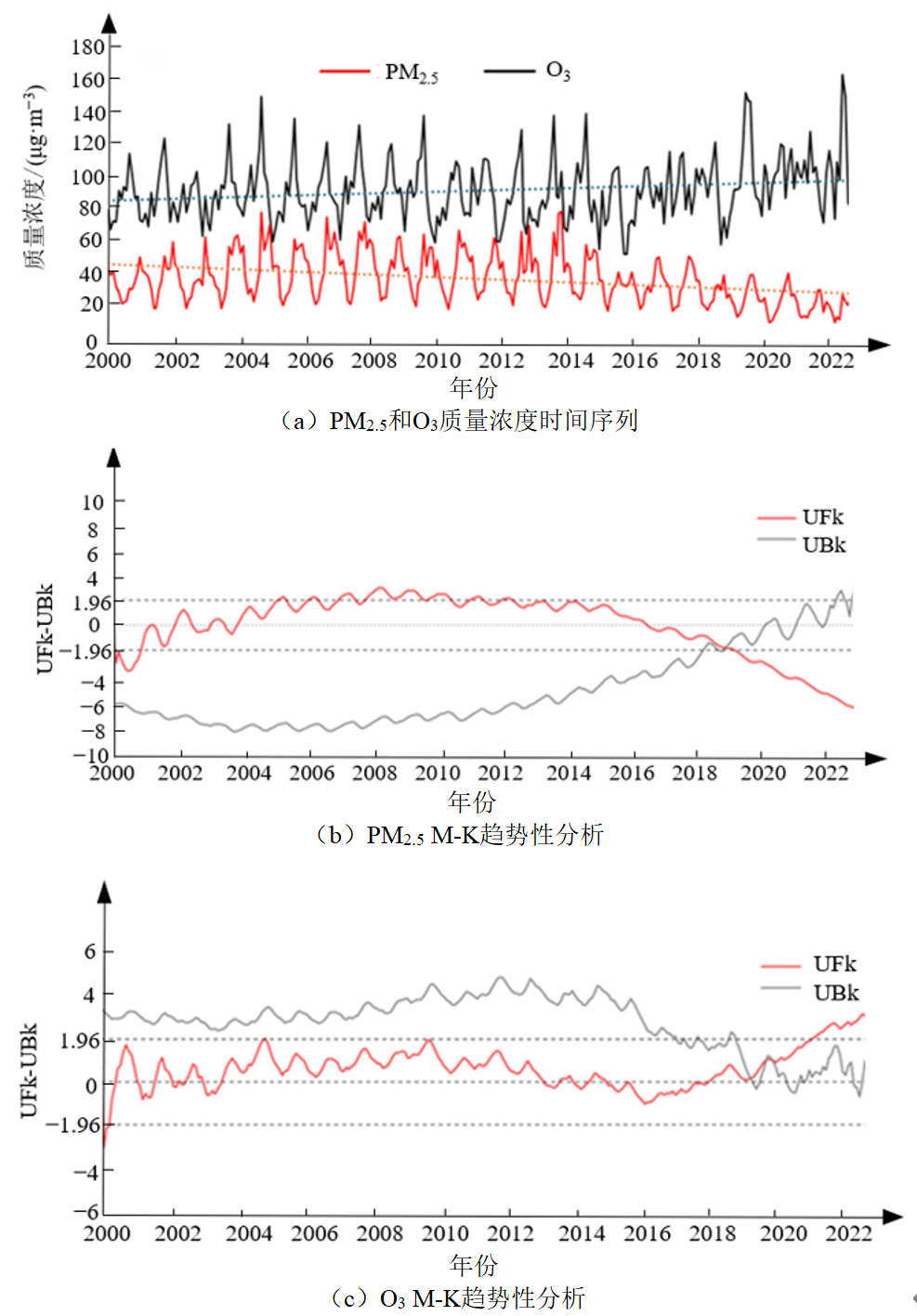
图2 2000-2022年珠三角区域PM2.5和O3质量浓度年均值变化及M-K趋势性分析
Figure 2 Time series and Mann-Kendall Trend Test of annual average concentrations of PM2.5 and O3 in the Pearl River Delta region from 2000?2022
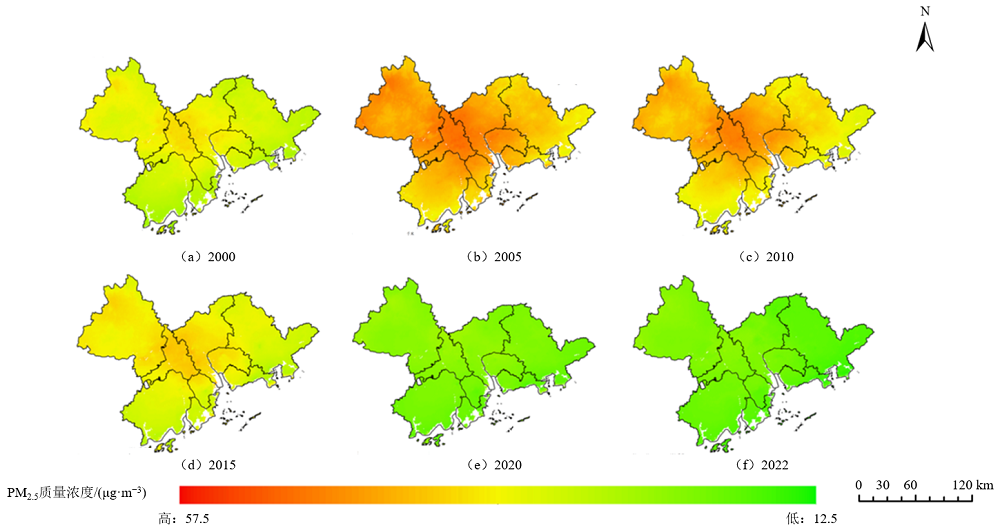
图3 2000-2022 年珠三角区域PM2.5质量浓度年均值的空间分布特征
Figure 3 Spatial distribution characteristics of annual average PM2.5 concentrations in the Pearl River Delta region from 2000 to 2022
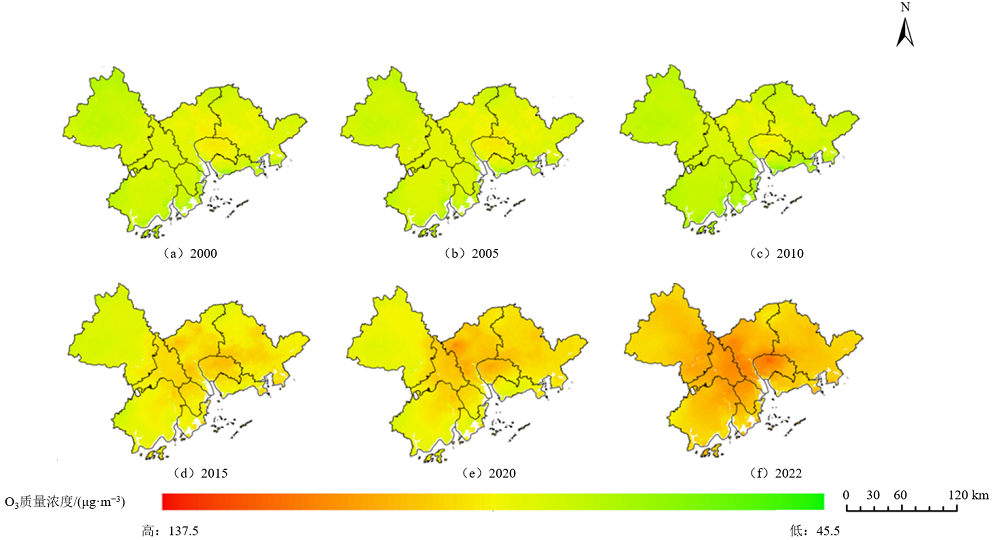
图4 2000-2022年珠三角区域O3质量浓度年均值的空间分布特征
Figure 4 Spatial distribution characteristics of annual average O3 concentrations in the Pearl River Delta region from 2000 to 2022
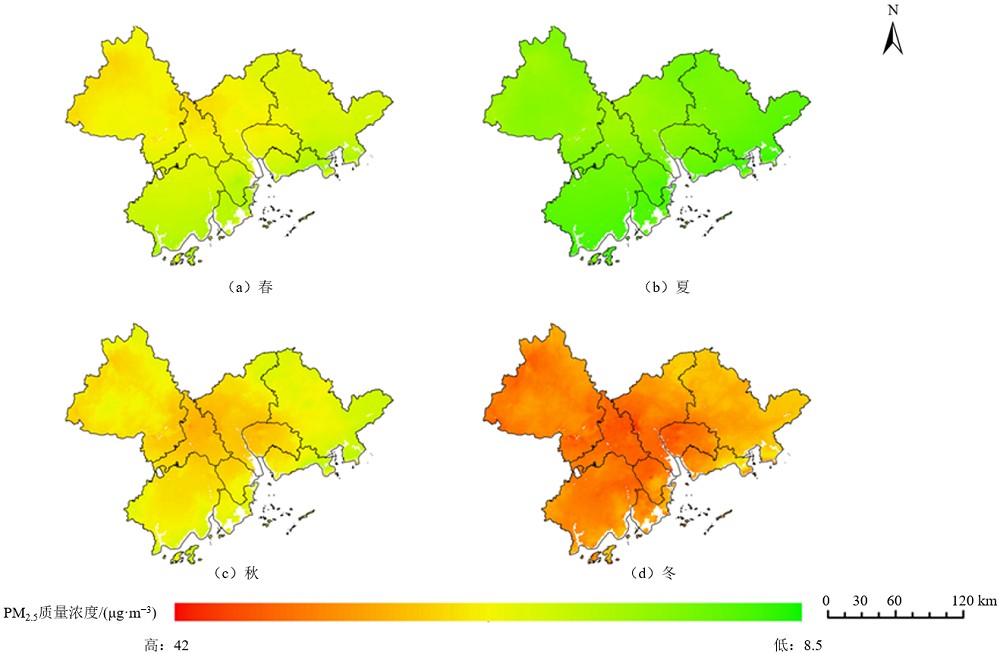
图6 2000-2022年珠三角区域PM2.5质量浓度季节的空间分布特征
Figure 6 Spatial distribution characteristics of seasonal PM2.5 concentrations in the Pearl River Delta region from 2000 to 2022
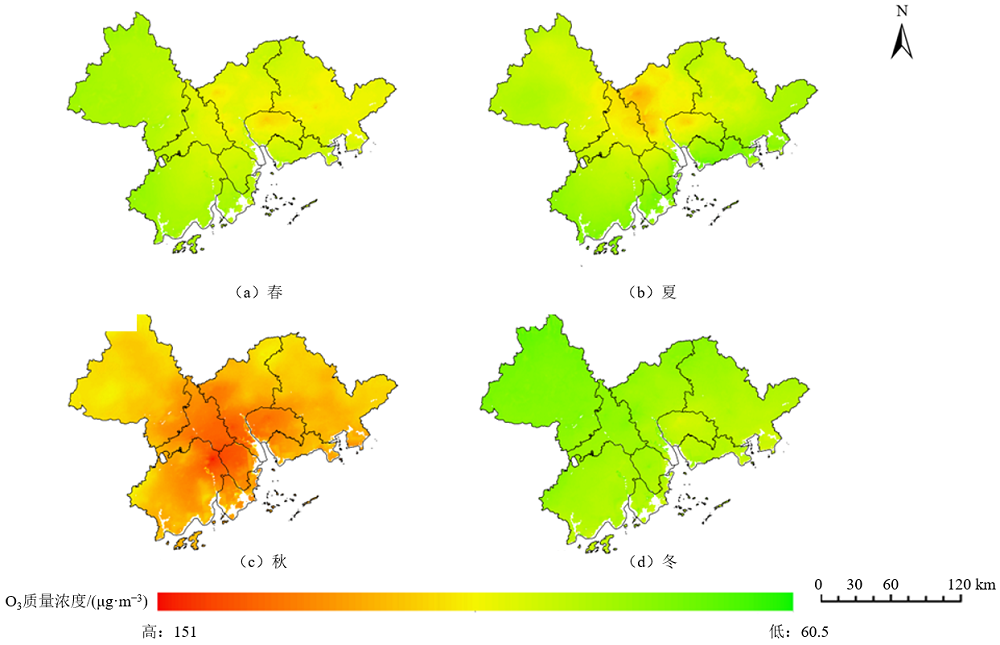
图7 2000-2022年珠三角区域O3质量浓度季节的空间分布特征
Figure 7 Spatial distribution characteristics of seasonal O3 concentrations in the Pearl River Delta region from 2000 to 2022
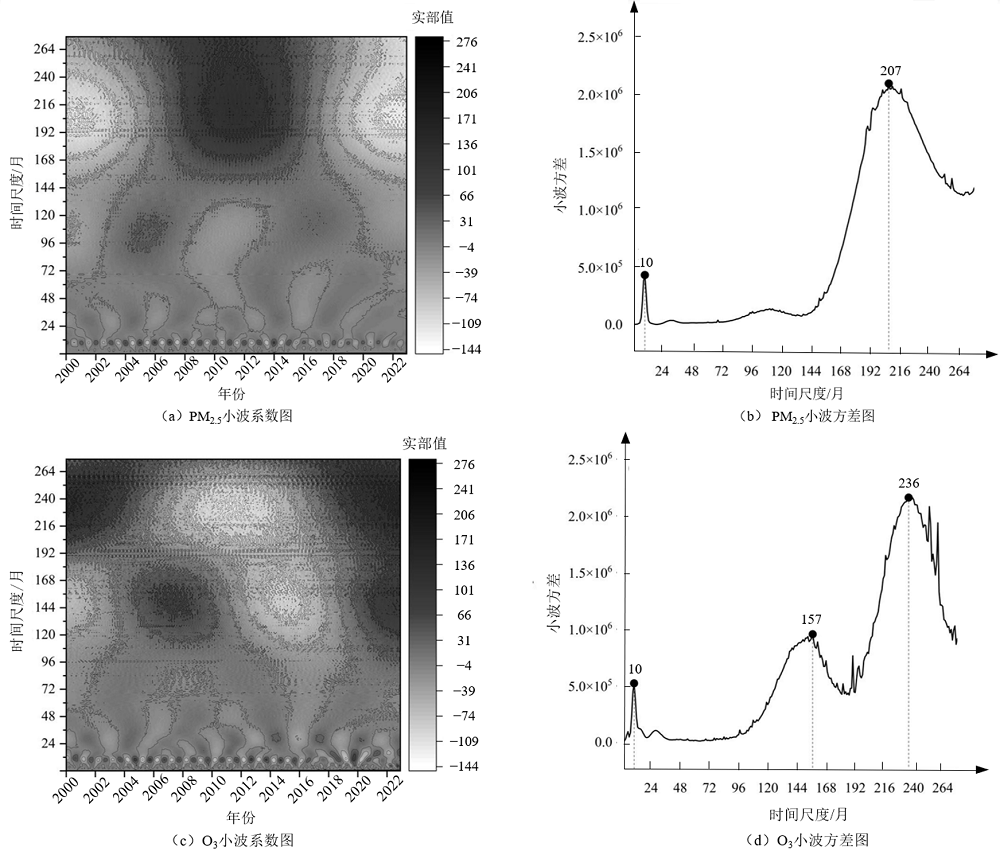
图8 2000-2022年珠三角区域PM2.5和O3小波系数分布图 实部值是反映信号变化的相位正负性的系数,由正到负再到正代表信号变化的一个周期
Figure 8 Wavelet real part plot of PM2.5 and O3 in the Pearl River Delta region from 2000 to 2022
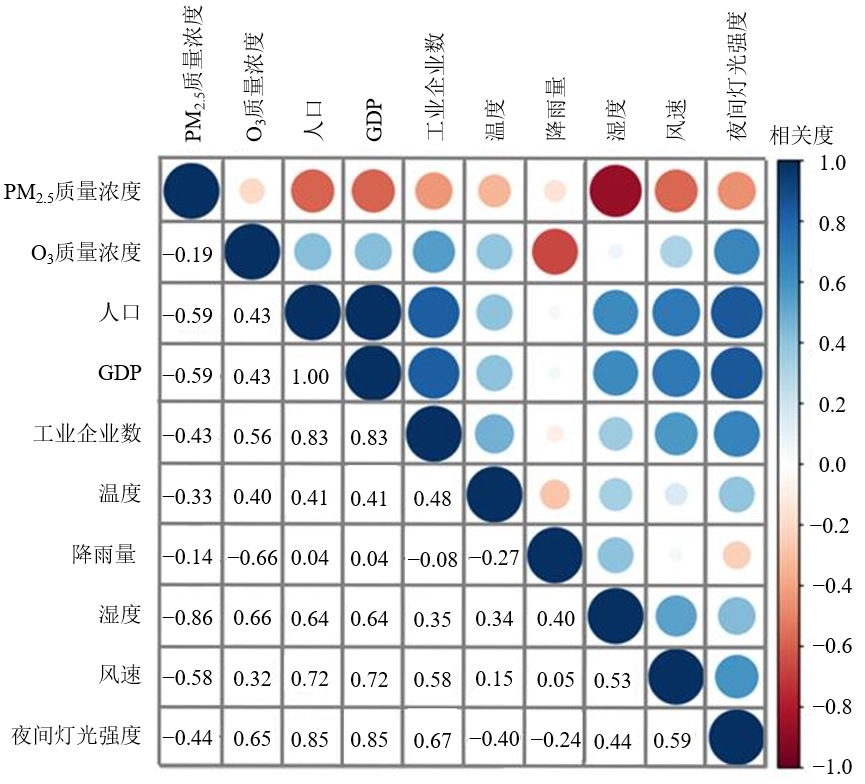
图10 2000-2022年珠三角区域PM2.5和O3影响因素的相关性分析热图
Figure 10 Heatmap of correlation analysis of influencing factors of PM2.5 and O3 in the Pearl River Delta region from 2000 to 2022
| [1] | CHEN L, ZHU J, LIAO H, et al., 2020. Meteorological influences on PM2.5 and O3 trends and associated health burden since China’s clean air actions[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 744: 140837. |
| [2] | GUAN T J, YAO M S, WANG J X, et al., 2014. Airborne endotoxin in fine particulate matter in Beijing[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 97: 35-42. |
| [3] | WANG J J, LU X M, YAN Y T, et al., 2020. Spatiotemporal characteristics of PM2.5 concentration in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration, China on the application of big data and wavelet analysis[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 724: 138134. |
| [4] | YANG Y, LI J, ZHU G B, et al., 2019. Spatio-Temporal relationship and evolvement of socioeconomic factors and PM2.5 in China During 1998-2016[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(7): 071149. |
| [5] | ZHAO H, ZHENG Y F, LI C, 2018. Spatiotemporal distribution of PM2.5 and O3 and their interaction during the summer and winter seasons in Beijing, China[J]. Sustainability, 10(12): 124519. |
| [6] | 蔡清楠, 车扬子, 孙凌瑜, 等, 2021. 珠三角地区PM2.5浓度估算及其健康效应评估[J]. 生态学报, 41(22): 8977-8990. |
| CAI Q N, CHE Y Z, SUN L Y, et al., 2021. PM2.5 concentration prediction and its health effect in the Pearl River Delta of China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(22): 8977-8990. | |
| [7] | 曹阳, 杨红刚, 张莉, 等, 2021. 武汉市汉阳区大气污染特征及气象影响分析[J]. 环境科学与技术, 44(7): 30-39. |
| CAO Y, YANG H G, ZHANG L, et al., 2021. Analysis of air pollution characteristics and meteorological impact in Hanyang District, Wuhan City[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 44(7): 30-39. | |
| [8] | 陈多宏, 沈劲, 陈瑶瑶, 等, 2022. 2020年珠三角O3污染特征及主要成因[J]. 中国环境科学, 42(11): 5000-5007. |
| CHEN D H, SHEN J, CHEN Y Y, et al., 2022. Characteristics and main causes of ozone pollution in the Pearl River Delta in 2020[J]. China Environmental Science, 42(11): 5000-5007. | |
| [9] | 陈伟, 徐学哲, 刘文清, 等, 2022. 2017-2021年苏皖鲁PM2.5和O3时空变化特征及影响因素[J]. 环境科学, 48(6): 60-65. |
| CHEN W, XU X Z, LIU W Q, et al., 2022. Spatial-temporal Characteristics and Influencing Factors of PM2.5 and Ozone in the Border Area of Jiangsu, Anhui, Shangdong and Henan from 2017 to 2021[J]. Environmental Science, 48(6): 60-65. | |
| [10] | 代园园, 龚绍琦, 张存杰, 2022. 粤港澳大湾区空气污染物的时空分布及其影响因素[J]. 环境工程学报, 16(12): 4001-4017. |
| DAI Y Y, GONG S Q, ZHANG C J, 2022. Analysis on the temporal and spatial distribution and influencing factors of air pollutants in Gunagdong-Hong Kong-Marco Greater Bay Area[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 16(12): 4001-4017. | |
| [11] | 代园园, 龚绍琦, 张存杰, 等, 2024. 粤港澳大湾区大气PM2.5浓度的遥感估算模型[J]. 环境科学, 45(1): 8-22. |
| DAI Y Y, GONG S Q, ZHANG C J, et al., 2024. Remote sensing model for estimating atmospheric PM2.5concentration in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area[J]. Environmental Science, 45(1): 8-22. | |
| [12] | 邓涛, 吴兑, 邓雪娇, 等, 2012. 珠江三角洲一次典型复合型污染过程的模拟研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 32(2): 193-199. |
| DENG T, WU D, DENG X J, et al., 2012. Simulation of a typical complex pollution process over Pearl River Delta area[J]. China Environmental Science, 32(2): 193-199. | |
| [13] | 丁成亮, 郑洪波, 2024. 大连市PM2.5-O3复合污染特征及潜在源区分析[J]. 环境科学与技术, 47(1): 95-101. |
| DING C L, ZHENG H B, 2024. Composite pollution characteristics and potential source area analysis of PM2.5-O3 in Dalian City[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 47(S1): 95-101. | |
| [14] | 丁娟, 梁财, 2023. 空气PM2.5污染分析以及环境治理研究[J]. 能源与环保, 45(3): 105-117. |
| DING J, LIANG C, 2023. Analysis of air PM2.5 pollution and research on environmental treatment[J]. China Energy and Environmental Protection, 45(3): 105-117. | |
| [15] | 费冬冬, 侯雪伟, 魏蕾, 等, 2021. 全球近地层臭氧时空分布特征及其来源解析[J]. 中国环境科学, 41(7): 3004-3016. |
| FEI D D, HOU X W, WEI L, et al., 2021. Quantitative sources of global surface ozone and spatial and temporal distribution characteristics[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 41(7): 3004-3016. | |
| [16] | 郭成, 刘薇, 王沁, 等, 2021. 山东省弥河流域历史降雨统计规律分析[J]. 水利规划与设计, (11): 52-56. |
| GUO C, LIU W, WANG Q, et al., 2021. Statistical analysis of historical rainfall in Miheriver basin of Shandong Province[J]. Water Resources Planning and Design, (11): 52-56. | |
| [17] | 黄春桃, 林锦眉, 张馨予, 2021. 2016-2020年珠三角地区PM2.5时空变化特征分析[J]. 山东化工, 50(15): 263-265, 269. |
| HUANG C T, LIN J M, ZHANG X Y, 2021. Analysis of the Characteristics of the Temporal and Spatial Changes of PM2.5 in the Pearl River Delta from 2016 to 2020[J]. Shandong Chemical Industry, 50(15): 263-265, 269. | |
| [18] | 栗泽苑, 杨雷蜂, 华道柱, 等, 2021. 2013-2018年中国近地面臭氧浓度空间分布特征及其与气象因子的关系[J]. 环境科学研究, 34(9): 2094-2104. |
| JIA Z Y, YANG L F, HUA D Z, et al., 2021. Spatial Pattern of surface ozone and its relationship with meteorological variables in China during 2013−2018[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 34(9): 2094-2104. | |
| [19] | 赖安琪, 陈晓阳, 刘一鸣, 等, 2018. 珠江三角洲高质量浓度PM2.5和O3复合污染特征[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 57(4): 30-36. |
| LAI A Q, CHEN X Y, LIU Y M, et al., 2018. Characteristics of complex pollution with high concentrations of PM2.5 and O3 over the Pearl River Delta, China[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 57(4): 30-36. | |
| [20] | 李方杰, 2022. 北京城市地区非甲烷烃来源及其对O3和SOA生成影响研究[D]. 大连: 辽宁大学: 3-8. |
| LI F J, 2022. Sources of Non-Methane Hydrocarbons and their impacts on O3 and SOA formation in urban areas of Beijing[D]. Dalian: Liaoning University: 3-8. | |
| [21] | 李红, 彭良, 毕方, 等, 2019. 我国PM2.5与臭氧污染协同控制策略研究[J]. 环境科学研究, 32(10): 1763-1778. |
| LI H, PENG L, BI F, et al., 2019. Strategy of coordinated control of PM2.5 and Ozone in China[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 32(10): 1763-1778. | |
| [22] | 李文强, 2022. 基于小波变换的水文时间序列分析[J]. 地下水, 48(6): 60-65. |
| LI W Q, 2022. Analysis of hydrological time series based on wavelet transform[J]. Ground water, 48(6): 60-65. | |
| [23] | 刘南希, 何成, 刘晨曦, 等, 2023. 2015-2021年广州市臭氧和PM2.5复合污染特征及天气分型研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 43(1): 42-53. |
| LIU N X, HE C, LIU C X, et al., 2023. Study on characteristics and weather classification of ozone and PM2.5 complex pollution in Guangzhou from 2015 to 2021[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 43(1): 42-53. | |
| [24] | 刘贤赵, 张国桥, 杨文涛, 等, 2022. 长株潭城市群PM2.5和O3时空分布特征及影响因素分析[J]. 环境科学, 43(12): 5354-5366. |
| LIU X Z, ZHANG G Q, YANG W T, et al., 2022. Analysis of spatiotemporal distribution characteristics and influencing factors of PM2.5 and O3 in Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan Urban Agglomeration, China[J]. Environmental Science, 43(12): 5354-5366. | |
| [25] |
潘光, 苗亚茹, 谷树茂, 等, 2024. 济南市不同类型燃煤供暖企业废气组分特征及排放估算[J]. 生态环境学报, 33(6): 919-926.
DOI |
| PAN G, MIAO Y R, GU S M, et al., 2024. Component characteristics and emission estimation of exhaust gas from different types of coal-fired heating enterprises in Ji’nan, China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 33(6): 919-926. | |
| [26] | 逄妮妮, 赵旭辉, 王含月, 等, 2024. 2018-2021年安徽省PM2.5和O3时空分布特征及其健康风险分析[J]. 中国环境监测, 40(2): 132-140. |
| PANG N, ZHAO X H, WANG H Y, et al., 2024. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics and health risk analysis of PM2.5and O3 in Anhui Province from 2018 to 2021[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 40(2): 132-140. | |
| [27] | 苏涛, 2022. 基于同位素的珠三角大气硝酸根溯源及其在PM2.5源解析中的应用[D]. 北京: 中国科学院: 145-146. |
| SU T, 2022. Isotope based source apportionment of atmospheric nitrate and its application to source apportionment of PM2.5 in the Pearl River Delta[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Sciences: 145-146. | |
| [28] | 王建华, 薛燕妮, 王仁桃, 等, 2023. 山西省近地面O3时空分布特征及防治研究[J]. 环境科学与管理, 45(3): 56-61. |
| WANG J H, XUE Y N, WANG R T, et al., 2023. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of near-surface ozone concentration and prevention countermeasures in Shanxi Province[J]. Environmental Science and management, 45(3): 56-61. | |
| [29] |
温丽容, 林勃机, 李婷婷, 等, 2023. 基于多同位素的珠三角PM2.5中二次无机气溶胶来源解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 32(9): 1654-1662.
DOI |
| WEN L R, LIN B J, LI T T, et al., 2023. Source apportionment of ammonium in atmospheric PM2.5 in the Pearl River Delta based on nitrogen isotope[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 32(9): 1654-1662. | |
| [30] | 肖致美, 李源, 孔君, 等, 2018. 天津市PM2.5-O3复合污染特征及气象影响分析[J]. 环境科学, 43(6): 2928-2936. |
| XIAO Z M, LI Y, KONG J, et al., 2018. Characteristics and Meteorological Factors of PM2.5-O3 Compound Pollution in Tianjin[J]. Environmental Science, 43(6): 2928-2936. | |
| [31] | 姚青, 丁净, 杨旭, 等, 2024. 基于时间序列分解的京津冀区PM2.5和O3空间分布特征[J]. 环境科学, 45(5): 2487-2496. |
| YAO Q, DING J, YANG X, et al., 2024. Spatial distribution characteristics of PM2.5 and O3 in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region based on time series decomposition[J]. Environmental Science, 45(5): 2487-2496. | |
| [32] | 姚青, 马志强, 郝天依, 等, 2021. 京津冀区域臭氧时空分布特征及其背景浓度估算[J]. 中国环境科学, 41(11): 4999-5008. |
| YAO Q, MA Z Q, HAO T Y, et al., 2021. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics and background concentration estimation of ozone in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region[J]. China Environmental Science, 41(11): 4999-5008. | |
| [33] | 姚懿娟, 王美园, 曾春玲, 等, 2021. 广州不同站点类型PM2.5与O3污染特征及相互作用[J]. 中国环境科学, 41(10): 4495-4506. |
| YAO Y J, WANG M Y, ZENG C L, et al., 2021. Pollution characteristics and interaction between PM2.5 and O3 at different types of stations in Guangzhou[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 41(10): 4495-4506. | |
| [34] | 颜丰华, 陈伟华, 常鸣, 等, 2024. 珠江三角洲大气光化学氧化剂O3和PM2.5复合超标污染特征及气象影响因素[J]. 环境科学, 42(4): 1600-1614. |
| YAN F H, CHEN W H, CHANG M, et al., 2024. Spatial distribution characteristics of PM2.5 and O3 in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region Based on Time Series Decomposition[J]. Environmental Science, 42(4): 1600-1614. | |
| [35] | 阳欢, 陈佰满, 李建维, 等, 2023. 东莞市PM2.5浓度时间变化特征及影响因素研究[J]. 环境科学与管理, 48(6): 60-65. |
| YANG H, CHEN B M, LI J W, et al., 2023. Time variation characteristics and influencing factors of PM2.5 concentration in Donguan[J]. Environmental Science and Management, 48(6): 60-65. | |
| [36] | 杨绍康, 2021. 天津市大气污染特征及气象因素影响分析[J]. 环境与可持续发展, 46(5): 144-150. |
| YANG S K, 2021. Analysis of air pollution characteristics and meteorological factors in Tianjin[J]. Environment and Sustainable Development, 46(5): 144-150. | |
| [37] | 杨云芸, 胡燕, 肖童觉, 等, 2021. 湖南省长株潭城市群臭氧分布特征研究及分析[J]. 灾害学, 36(2): 97-103 |
| YANG Y Y, HU Y, XIAO T J, et al., 2021. Distribution characteristics of ozone in Chang Zhu Tan Urban agglomeration of Hunan Province[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 36(2): 97-103. | |
| [38] |
叶深, 王鹏, 黄祎, 等, 2023. 长三角城市群城市空间形态对PM2.5与O3污染空间异质性特征的影响研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 32(10): 1771-1784.
DOI |
| YE S, WANG P, HUANG Y, et al., 2023. Urban morphology and the influence of the spatial heterogeneity of PM2.5and O3 pollution: The case of the Yangtze River Delta[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 32(10): 1771-1784. | |
| [39] | 余益军, 孟晓艳, 王振, 等, 2020. 京津冀地区城市臭氧污染趋势及原因探讨[J]. 环境科学, 41(1): 106-114. |
| YU Y J, MENG X Y, WANG Z, et al., 2020. Driving factors of the significant increase in surface ozone in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region, China, during 2013−2018[J]. Environmental Science, 41(1): 106-114. | |
| [40] | 袁鑫, 黄志炯, 陆梦华, 等, 2023. 基于观测和机器学习的珠三角臭氧污染季节特征演变及成因分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 43(8): 214-225. |
| YUAN X, HUANG Z J, LU M H, et al, 2023. Seasonal evolution and cause analysis of ozone pollution in the Pearl River Delta based on observation and machine learning[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 43(8): 214-225. | |
| [41] | 赵梦珂, 王玲玲, 马双良, 等, 2024. 2015-2022年春季豫北地区PM2.5-O3复合污染特征及影响因素分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 44(8):12-21. |
| ZHAO M K, WANG L L, MA S L, et al., 2024. Analysis of PM2.5-O3 compound pollution characteristics and influencing factors in the spring from 2015 to 2022 in northern HenanActa[J]. Scientiae Circumstantiae, 44(8): 12-21. | |
| [42] | 张运林, 睢晋玲, 吴娴, 等, 2021. 粤港澳大湾区PM2.5时空分布特征及其与气象要素的关系[J]. 生态学报, 41(6): 2272-2281. |
| ZHANG Y L, SUI J L, WU X, et al., 2021. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of PM2.5 and its relationship with meteorological factors in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(6): 2272-2281. | |
| [43] | 郑晶, 刘晓秋, 刘芳, 等, 2018. 哈尔滨市大气污染与居民循环系统疾病死亡风险的相关分析[J]. 环境与职业医学, 35(10): 885-891. |
| ZHENG J, LIU X Q, LIU F, et al., 2018. Correlation analysis between air pollution and risk of death from circulatory diseases of residents in Harbin[J]. Journal of Environmental and Occupational Medicine, 35(10): 885-891. | |
| [44] | 中华人民共和国环境保护部, 2013. 国务院关于印发大气污染防治行动计划的通知[EB/OL]. (2013-9-12) [2023-11-12]. https://www.gov.cn/zwgk/2013-09/12/content_2486773.htm. |
| Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China. Under the state council concerning the action plan for the control of air pollution[EB/OL]. (2013-9-12)[2023-11-12]. https://www.gov.cn/zwgk/2013-09/12/content_2486773.htm. | |
| [45] | 中华人民共和国环境保护部, 2018. 国务院关于印发打赢蓝天保卫战三年行动计划的通知[EB/OL]. (2018-7-3) [2023-11-12]. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2018-07/03/content_5303158.htm. |
| Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China, 2018. Three-year action plan to fight air pollution[EB/OL]. (2018-7-3) [2023-11-12]. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2018-07/03/content_5303158.htm. | |
| [46] | 周胜, 黄报远, 陈慧英, 等, 2020. 珠三角城市群PM2.5和O3污染特征及VOCs组分敏感性分析[J]. 环境工程, 38(1): 42-47. |
| ZHOU S, HUANG B Y, CHEN H Y, et al., 2020. Pollution charateristics of PM2.5 and O3 in the pearl river delta and the sensitivity analysis of VOCs components[J]. Environmental Engineering, 38(1): 42-47. | |
| [47] | 周志衡, 周廷刚, 刘文清, 等, 2022. 中原城市群PM2.5驱动因子联动效应及非线性影响[J]. 环境科学, 45(4): 1950-1962. |
| ZHOU Z H, ZHOU T G, LIU W Q, et al., 2022. Linkage effect and nonlinear impact of PM2.5 concentration driving factors in Central Plains urban agglomeration[J]. Environmental Science, 45(4): 1950-1962. |
| [1] | 尤琪, 杨艺, 张寅清, 祝凌燕. 纳米银颗粒在水环境中的化学转化及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(1): 156-166. |
| [2] | 王薇, 夏宇轩. 基于遥感技术和机器学习的城市街区PM2.5空间分布特征研究——以合肥市滨湖新区为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(9): 1426-1437. |
| [3] | 王聪聪, 张小玲, 雷雨, 黄小娟, 王婧怡, 尹黎昊, 王传扬. 基于WRF-CMAQ模型的四川盆地春季持续臭氧污染过程中PM2.5组分解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(8): 1214-1226. |
| [4] | 张维琛, 王惺琪, 王博杰. 塔布河流域生态系统服务时空格局及影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(7): 1142-1152. |
| [5] | 潘光, 苗亚茹, 谷树茂, 唐厚全, 毛书帅, 张桂芹, 闫学军. 济南市不同类型燃煤供暖企业废气组分特征及排放估算[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(6): 919-926. |
| [6] | 李程, 程志鹏, 刘育金, 姚义鸣, 李春雷. 全(多)氟烷基化合物生态风险及其管控政策研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(6): 980-996. |
| [7] | 李彩虹. 基因技术生态风险的伦理治理探析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(5): 824-830. |
| [8] | 张淼, 王桂霞, 王昌伟, 贺艳云, 许艳芳, 李琪, 许杨, 张俊骁, 张桂芹. 济南市区黑碳污染变化特征及来源解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(4): 560-572. |
| [9] | 梁燕, 刘家齐, 肖凡, 潘民萍, 韦凯文, 张楚雯, 段敏. 氮沉降形态对西南岩溶区森林土壤有效磷来源的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(2): 192-201. |
| [10] | 罗小玲, 刘军, 王琦, 刘同旭, 梁耀杰, 谢志宜, 王中伟, 陈多宏. 2016年以来广东省不同土地利用类型土壤pH和有机质时空变化及其影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(12): 1849-1861. |
| [11] | 邹耀, 张凯, 张兆威. 广东省典型淡水水产养殖尾水治理技术模式污染物去除效果对比研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(12): 1923-1930. |
| [12] | 赵琼, 胡溪, 张伟, 张增凯, 薛文博, 赵静. 京津冀区域燃煤小锅炉清洁改造环境效益评估[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(10): 1554-1562. |
| [13] | 袁茜, 傅开道, 陶雨晨, 张年, 杨丽莎. 澜沧江(云南段)水-气界面氧化亚氮释放通量时空分布特征及其影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(1): 54-61. |
| [14] | 王薇, 代萌萌. 基于颗粒物时空分布的街道峡谷空间形态研究——以合肥市同安街道为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(9): 1632-1643. |
| [15] | 温丽容, 林勃机, 李婷婷, 张子洋, 张正恩, 江明, 周炎, 张涛, 李军, 张干. 基于多同位素的珠三角PM2.5中二次无机气溶胶来源解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(9): 1654-1662. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
