生态环境学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (9): 1452-1462.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2025.09.012
蒋凯1,2( ), 柯常栋2,3,*(
), 柯常栋2,3,*( ), 王丽萍4, 李朋辉5, 赖迪智4, 张杨2, 吴永洁2, 吴仁人2, 肖利平1,*(
), 王丽萍4, 李朋辉5, 赖迪智4, 张杨2, 吴永洁2, 吴仁人2, 肖利平1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2025-01-16
出版日期:2025-09-18
发布日期:2025-09-05
通讯作者:
*柯常栋。E-mail: ke.cd@foxmail.com;肖利平。E-mail: xiaoliping@xtu.edu.cn
作者简介:蒋凯(2000年生),男,硕士研究生,从事微生物污染源解析研究。E-mail: Jkai2000@126.com
基金资助:
JIANG Kai1,2( ), KE Changdong2,3,*(
), KE Changdong2,3,*( ), WANG Liping4, LI Penghui5, LAI Dizhi4, ZHANG Yang2, WU Yongjie2, WU Renren2, XIAO Liping1,*(
), WANG Liping4, LI Penghui5, LAI Dizhi4, ZHANG Yang2, WU Yongjie2, WU Renren2, XIAO Liping1,*( )
)
Received:2025-01-16
Online:2025-09-18
Published:2025-09-05
摘要: 准确识别粪便污染与溶解有机质(DOM)污染的来源对于水质管理和生态环境健康至关重要。采用荧光定量聚合酶链式反应(qPCR)、三维荧光光谱(3D-EEM)结合平行因子分析法(PARAFAC)解析了珠江广州河段的粪便污染与DOM的来源和分布特征,以及它们之间的潜在联系。结果发现珠江广州河段人源拟杆菌标记物(BacHum)和噬菌体标记物(CPQ_064)的平均检测浓度分别为 (4.56±0.58)、(4.18±0.56) log10(gene copies/100 mL),未检测出其他宿主来源的粪便污染标记物,表明珠江广州河段的粪便污染以人源粪便污染为主。3D-EEM-PARAFAC确定了3种主要DOM组分,即微生物类腐殖质(C1),类色氨酸(C2),陆源类腐殖质(C3);DOM在枯水期和平水期主要来源于内源输入,丰水期以外源输入为主。在丰水期时粪便和DOM污染更为严重,且均沿珠江广州河段的流向呈现先递增后降低的变化趋势。利用Pearson相关性分析,发现BacHum、CPQ_064与C1、C2和C3呈强显著正相关(p<0.001),总磷(TP)、氨氮(NH3-N)与BacHum和CPQ_064均呈正相关性(p<0.05),表明它们具有污染同源性,可以利用3D-EEM分析作为粪便污染的预检测手段,能够经济、有效和及时地评估水体的粪便污染。该研究可为水体污染控制与管理提供有力的技术指导。
中图分类号:
蒋凯, 柯常栋, 王丽萍, 李朋辉, 赖迪智, 张杨, 吴永洁, 吴仁人, 肖利平. 珠江广州河段粪便污染和溶解有机质的来源解析及分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(9): 1452-1462.
JIANG Kai, KE Changdong, WANG Liping, LI Penghui, LAI Dizhi, ZHANG Yang, WU Yongjie, WU Renren, XIAO Liping. Source Analysis and Distribution Characteristics of Fecal Pollution and Dissolved Organic Matter in the Guangzhou Section of the Pearl River[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2025, 34(9): 1452-1462.
| 标记物 | 引物 | 序列(5’→3’) | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| AllBac | AllBac296f | GAGAGGAAGGTCCCCCAC | Layton et al., |
| AllBac412r | CGCTACTTGGCTGGTTCAG | ||
| E.coli | EC23S857F | GGTAGAGCACTGTTTTGGCA | Chern et al., |
| EC23S857R | TGTCTCCCGTGATAACTTTCTC | ||
| BacHum | BacHum-160-f | TGAGTTCACATGTCCGCATGA | Zhang et al., |
| BacHum-241-r | CGTTACCCCGCCTACTATCTAATG | ||
| CPQ_064 | 064F1 | TGTATAGATGCTGCTGCAACTGTACTC | Stachler et al., |
| 064R1 | CGTTGTTTTCATCTTTATCTTGTCCAT | ||
| P.ND5 | P.ND5-f | ACAGCTGCACTACAAGCAATGC | Zhang et al., |
| P.ND5-r | GGATGTAGTCCGAATTGAGCTGATTAT | ||
| Rum-2-Bac | BacB2-590-f | ACAGCCCGCGATTGATACTGGTAA | Zhang et al., |
| Bac708Rm | CAATCGGAGTTCTTCGTGAT | ||
| GFD | GFD-f | TCGGCTGAGCACTCTAGGG | Zhang et al., |
| GFD-r | GCGTCTCTTTGTACATCCCA |
表1 粪便污染标记物的引物信息
Table 1 Primer information for the fecal pollution markers
| 标记物 | 引物 | 序列(5’→3’) | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| AllBac | AllBac296f | GAGAGGAAGGTCCCCCAC | Layton et al., |
| AllBac412r | CGCTACTTGGCTGGTTCAG | ||
| E.coli | EC23S857F | GGTAGAGCACTGTTTTGGCA | Chern et al., |
| EC23S857R | TGTCTCCCGTGATAACTTTCTC | ||
| BacHum | BacHum-160-f | TGAGTTCACATGTCCGCATGA | Zhang et al., |
| BacHum-241-r | CGTTACCCCGCCTACTATCTAATG | ||
| CPQ_064 | 064F1 | TGTATAGATGCTGCTGCAACTGTACTC | Stachler et al., |
| 064R1 | CGTTGTTTTCATCTTTATCTTGTCCAT | ||
| P.ND5 | P.ND5-f | ACAGCTGCACTACAAGCAATGC | Zhang et al., |
| P.ND5-r | GGATGTAGTCCGAATTGAGCTGATTAT | ||
| Rum-2-Bac | BacB2-590-f | ACAGCCCGCGATTGATACTGGTAA | Zhang et al., |
| Bac708Rm | CAATCGGAGTTCTTCGTGAT | ||
| GFD | GFD-f | TCGGCTGAGCACTCTAGGG | Zhang et al., |
| GFD-r | GCGTCTCTTTGTACATCCCA |
| 时期 | 溶解氧 | 化学需氧量 | 氨氮 | 总磷 | 总氮 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 枯水期 | 5.20±0.70a | 11.93±1.49a | 0.17±0.12b | 0.12±0.03a | 5.16±0.56a |
| 丰水期 | 4.95±1.28a | 8.85±2.38b | 0.47±0.30a | 0.13±0.04a | 2.81±0.49c |
| 平水期 | 5.17±0.42a | 9.07±1.64b | 0.15±0.12b | 0.13±0.03a | 3.85±0.62b |
表2 不同时期的水质变化情况
Table 2 Changes in water quality over time mg·L?1
| 时期 | 溶解氧 | 化学需氧量 | 氨氮 | 总磷 | 总氮 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 枯水期 | 5.20±0.70a | 11.93±1.49a | 0.17±0.12b | 0.12±0.03a | 5.16±0.56a |
| 丰水期 | 4.95±1.28a | 8.85±2.38b | 0.47±0.30a | 0.13±0.04a | 2.81±0.49c |
| 平水期 | 5.17±0.42a | 9.07±1.64b | 0.15±0.12b | 0.13±0.03a | 3.85±0.62b |
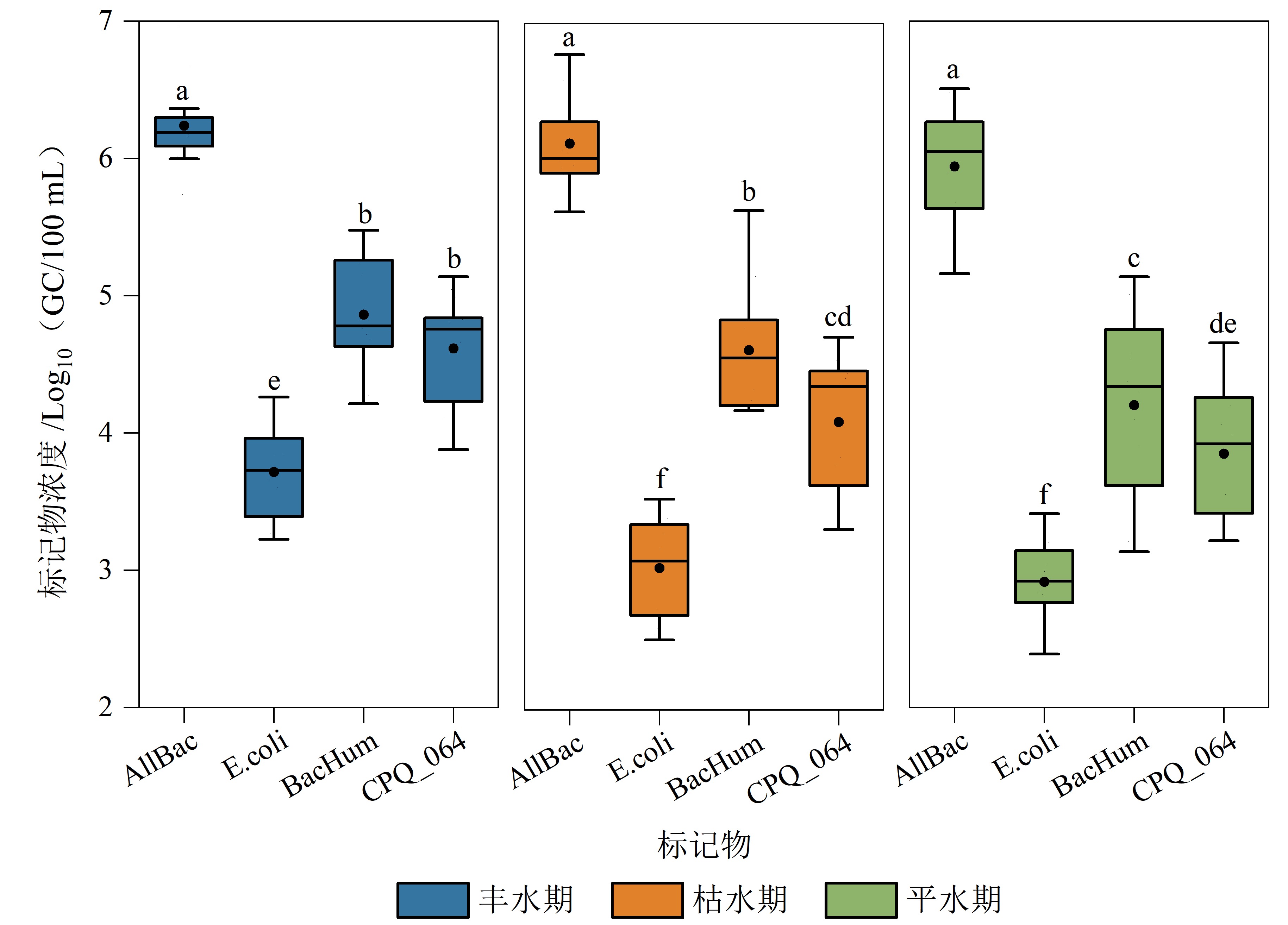
图3 珠江广州河段不同水文时期的标记物浓度差异 不同小写字母之间表示标记物浓度存在显著差异(p<0.05)
Figure 3 Differences in marker concentrations during different hydrological periods in the Guangzhou section of the Pearl River
| 时期 | 荧光指数 | 生物指数 | 腐殖化指数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 枯水期 | 1.93±0.04a | 1.13±0.13a | 1.46±0.24c |
| 丰水期 | 1.64±0.03c | 0.85±0.06c | 3.14±0.55a |
| 平水期 | 1.78±0.09b | 0.98±0.04b | 2.12±0.52b |
表3 不同时期的DOM荧光指数
Table 3 DOM fluorescence index at different times
| 时期 | 荧光指数 | 生物指数 | 腐殖化指数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 枯水期 | 1.93±0.04a | 1.13±0.13a | 1.46±0.24c |
| 丰水期 | 1.64±0.03c | 0.85±0.06c | 3.14±0.55a |
| 平水期 | 1.78±0.09b | 0.98±0.04b | 2.12±0.52b |
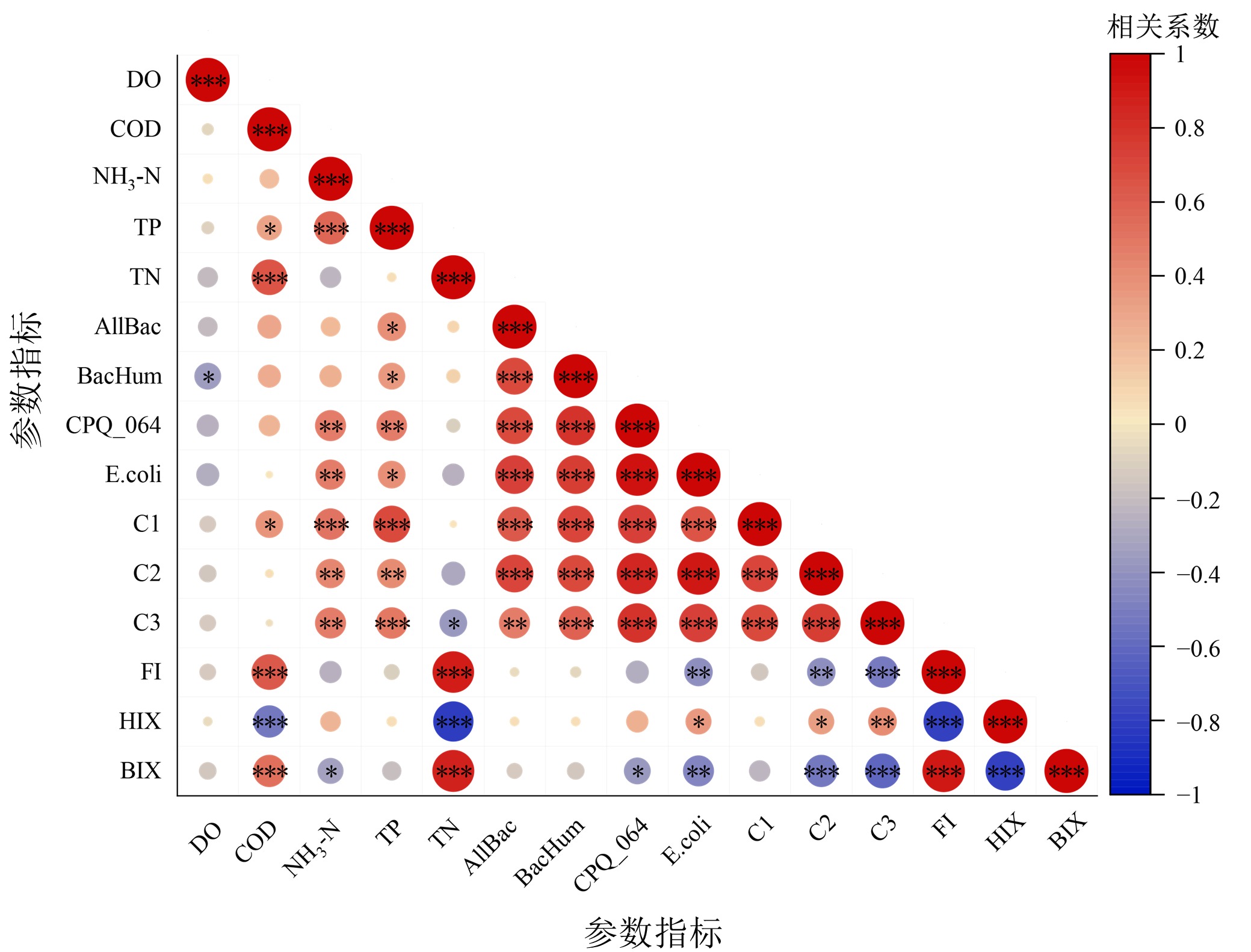
图7 DOM、粪便污染标记物与各项环境因子之间的相关性分析 *、**和***分别表示p<0.05、p<0.01和p<0.001水平相关性显著
Figure 7 Correlation analysis between DOM, fecal pollution markers and various environmental factors
| [1] | AHMED W, KORAJKIC A, GABREWOLD M, et al., 2024. Assessing the nucleic acid decay of human wastewater markers and enteric viruses in estuarine waters in Sydney, Australia[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 926: 171389. |
| [2] | ANDERSSON C A, BRO R, 2000. The N-way Toolbox for MATLAB[J]. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 52(1): 1-4. |
| [3] | BAKER A, CUMBERLAND S A, BRADLEY C, et al., 2015. To what extent can portable fluorescence spectroscopy be used in the real-time assessment of microbial water quality?[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 532: 14-19. |
| [4] | BOWEN M, FARAG IBRAHIM F, MAIN CHRISTOPHER R, et al., 2023. Reference library for microbial source tracking in the mid-Atlantic United States[J]. Microbiology Resource Announcements, 13(1): e00674-23. |
| [5] | BRANDT A M, SENKBEIL J K, LOBOS A E, et al., 2025. Fecal indicator bacteria and sewage-associated marker genes are associated with nitrate and environmental parameters in two Florida freshwater systems[J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 136(2): lxaf030. |
| [6] | CHERN E, SIEFRING S, PAAR J, et al., 2011. Comparison of quantitative PCR assays for Escherichia coli targeting ribosomal RNA and single copy genes[J]. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 52(3): 298-306. |
| [7] | DERX J, KILIÇ H S, LINKE R, et al., 2023. Probabilistic fecal pollution source profiling and microbial source tracking for an urban river catchment[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 857(Part 2): 159533. |
| [8] | DUAN Q N, ZHANG Q, QUAN X D, et al., 2024. Innovations of water pollution traceability technology with artificial intelligence[J]. Earth Critical Zone, 1(1): 100009. |
| [9] | FELLMAN J B, HOOD E, SPENCER R G J L, et al., 2010. Fluorescence spectroscopy opens new windows into dissolved organic matter dynamics in freshwater ecosystems: A review[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 55(6): 2452-2462. |
| [10] |
FIELD K G, SAMADPOUR M J W R, 2007. Fecal source tracking, the indicator paradigm, and managing water quality[J]. Water Research, 41(16): 3517-3538.
DOI PMID |
| [11] | HAJJ-MOHAMAD M, HACHAD M, DESCHAMPS G, et al., 2019. Fecal contamination of storm sewers: Evaluating wastewater micropollutants, human-specific Bacteroides 16S rRNA, and mitochondrial DNA genetic markers as alternative indicators of sewer cross connections[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 659: 548-560. |
| [12] | HE C J, HE X W, YUAN R, et al., 2023b. Binding characteristics of Pb and Zn to low-temperature feces-based biochar-derived DOM revealed by EEM-PARAFAC combined with general and moving-window two-dimensional correlation analyses[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30(10): 27525-27538. |
| [13] | HE J, JIAO L X, ZHI G Q, et al., 2023a. Heterogeneity of molecular-level and photochemical of dissolved organic matter derived from decomposing submerged macrophyte and algae[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 334: 117420. |
| [14] | HOU X S, QIN L, WANG F L, et al., 2024. Faecal contamination in China: Trends, sources, and driving mechanisms[J]. Water Research, 261: 122017. |
| [15] | HU T C, ZHENG K X, LUO M, et al., 2024. Probing the optical and molecular properties of sedimentary dissolved organic matter in the laminated diatom mats from the southern Mariana Trench[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 234: 104386. |
| [16] |
LAYTON A, MCKAY L, WILLIAMS D, et al., 2006. Development of Bacteroides 16S rRNA gene TaqMan-based real-time PCR assays for estimation of total, human, and bovine fecal pollution in water[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 72(6): 4214-4224.
DOI PMID |
| [17] | LI J K, LI H, SHEN B, et al., 2011. Effect of non-point source pollution on water quality of the Weihe River[J]. International Journal of Sediment Research, 26(1): 50-61. |
| [18] | LI S Y, LUO J C, XU Y J, et al., 2022. Hydrological seasonality and nutrient stoichiometry control dissolved organic matter characterization in a headwater stream[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 807(Part 2): 150843. |
| [19] | LIN H, GUO L D, 2020. Variations in colloidal DOM composition with molecular weight within individual water samples as characterized by flow field-flow fractionation and EEM-PARAFAC analysis[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 54(3): 1657-1667. |
| [20] | LIN L, ZUO L Z, PENG J P, et al., 2018. Occurrence and distribution of microplastics in an urban river: A case study in the Pearl River along Guangzhou City, China[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 644: 375-381. |
| [21] | LIU Y C, YE Q H, HUANG W L, et al., 2020. Spectroscopic and molecular-level characteristics of dissolved organic matter in the Pearl River Estuary, South China[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 710: 136307. |
| [22] | LIU Z J, YUAN J L, LIN Y Y, et al., 2024. Integrating fecal pollution markers and fluorescence analysis for water quality assessment of urban river[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 909: 168492. |
| [23] |
MA K, SHEN H D, ZHOU T H, et al., 2023. Water quality characteristics and evaluation of Qilian Mountain National Park section in Heihe River Basin based on water quality indices and 3D fluorescence technology[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 45: 4373-4387.
DOI PMID |
| [24] | MADONIA A, CARUSO G, PIAZZOLLA D, et al., 2020. Chromophoric Dissolved Organic Matter as a Tracer of Fecal Contamination for Bathing Water Quality Monitoring in the Northern Tyrrhenian Sea (Latium, Italy)[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 8(6): 430. |
| [25] |
MENG F A, HUANG G C, YANG X, et al., 2013. Identifying the sources and fate of anthropogenically impacted dissolved organic matter (DOM) in urbanized rivers[J]. Water Research, 47(14): 5027-5039.
DOI PMID |
| [26] | NOWICKA-KRAWCZYK P, ŻELAZNA-WIECZOREK J, 2017. Dynamics in cyanobacterial communities from a relatively stable environment in an urbanised area (ambient springs in Central Poland)[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 579: 420-429. |
| [27] | OHNO T, 2002. Fluorescence Inner-Filtering Correction for Determining the Humification Index of Dissolved Organic Matter[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 36(4): 742-746. |
| [28] |
PARUCH L, PARUCH A M, 2021. Cross-tracking of faecal pollution origins, macronutrients, pharmaceuticals and personal care products in rural and urban watercourses[J]. Water Science and Technology, 83(3): 610-621.
DOI PMID |
| [29] | RODRÍGUEZ-VIDAL F J, GARCíA-VALVERDE M, ORTEGA-AZABACHE B, et al., 2020. Characterization of urban and industrial wastewaters using excitation-emission matrix (EEM) fluorescence: Searching for specific fingerprints[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 263: 110396. |
| [30] | SHANKS O C, DIEDRICH A, SIVAGANESAN M, et al., 2024. Quantitative fecal source characterization of urban municipal storm sewer system outfall ‘wet’ and ‘dry’ weather discharges[J]. Water Research, 259: 121857. |
| [31] | SHEIKH M, HARAMI H R, REZAKAZEMI M, et al., 2023. Towards a sustainable transformation of municipal wastewater treatment plants into biofactories using advanced NH3-N recovery technologies: A review[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 904: 166077. |
| [32] |
SHUTOVA Y, BAKER A, BRIDGEMAN J, et al., 2014. Spectroscopic characterisation of dissolved organic matter changes in drinking water treatment: From PARAFAC analysis to online monitoring wavelengths[J]. Water Research, 54: 159-169.
DOI PMID |
| [33] |
SORENSEN J P R, LAPWORTH D J, MARCHANT B P, et al., 2015. In-situ tryptophan-like fluorescence: A real-time indicator of faecal contamination in drinking water supplies[J]. Water Research, 81: 38-46.
DOI PMID |
| [34] | STACHLER E, AKYON B, DE CARVALHO N A, et al., 2018. Correlation of crAssphage qPCR Markers with Culturable and Molecular Indicators of Human Fecal Pollution in an Impacted Urban Watershed[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 52(13): 7505-7512. |
| [35] | STEDMON C A, BRO R, 2008. Characterizing dissolved organic matter fluorescence with parallel factor analysis: A tutorial[J]. Limnology and Oceanography: Methods, 6(11): 572-579. |
| [36] | SUN C Z, WANG S M, WANG H W, et al., 2022. Internal nitrogen and phosphorus loading in a seasonally stratified reservoir: Implications for eutrophication management of deep-water ecosystems[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 319: 115681. |
| [37] | TYRE K N, BREWTON R A, KREIGER L B, et al., 2023. Widespread human waste pollution in surface waters observed throughout the urbanized, coastal communities of Lee County, Florida, USA[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 879: 162716. |
| [38] | WU Z S, WANG X L, CHEN Y W, et al., 2018. Assessing river water quality using water quality index in Lake Taihu Basin, China[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 612: 914-922. |
| [39] | XIE R R, QI J B, SHI C C, et al., 2023. Changes of dissolved organic matter following salinity invasion in different seasons in a nitrogen rich tidal reach[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 880: 163251. |
| [40] | YANG L Y, CHEN L W, ZHUANG W E, et al., 2024. Unveiling changes in the complexation of dissolved organic matter with Pb(II) by photochemical and microbial degradation using fluorescence EEMs-PARAFAC[J]. Environmental Pollution, 341: 122982. |
| [41] |
YI X H, ZHANG C, LIU H B, et al., 2019. Occurrence and distribution of neonicotinoid insecticides in surface water and sediment of the Guangzhou section of the Pearl River, South China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 251: 892-900.
DOI PMID |
| [42] | ZEKI S, ASLAN A, BURAK S, et al., 2021. Occurrence of a human‐associated microbial source tracking marker and its relationship with faecal indicator bacteria in an urban estuary[J]. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 72(2): 167-177. |
| [43] | ZHANG X Y, ZHI X S, CHEN L, et al., 2020b. Spatiotemporal variability and key influencing factors of river fecal coliform within a typical complex watershed[J]. Water Research, 178: 115835. |
| [44] | ZHANG Y, WU R R, LI W J, et al., 2021. Occurrence and distributions of human-associated markers in an impacted urban watershed[J]. Environmental Pollution, 275: 116654. |
| [45] | ZHANG Y, WU R R, LIN K R, et al., 2020a. Performance of host-associated genetic markers for microbial source tracking in China[J]. Water Research, 175: 115670. |
| [46] | ZHAO Y P, SONG Y M, CUI J L, et al., 2020. Assessment of water quality evolution in the Pearl River Estuary (south Guangzhou) from 2008 to 2017[J]. Water, 12(1): 59. |
| [47] | 陈慧敏, 胡洋, 俞晓琴, 等, 2022. 兴凯湖有色可溶性有机物来源与组成特征——中国境内特大型界湖[J]. 中国环境科学, 42(5): 2238-2249. |
| CHEN H M, HU Y, YU X Q, et al., 2022. Characterizing sources and optical composition of chromophoric dissolved organic matter in Lake Xingkai, a large boundary lake in China[J]. China Environmental Science, 42(5): 2238-2249. | |
| [48] | 黄全佳, 2021. El Niño事件对河流入海COD的调控机制-基于高分辨率时间序列观测的证据[J]. 海洋学报, 43(6): 62-70. |
| HUANG Q J, 2021. Regulation of El Niño event on riverine COD export: Evidence from high frequency time-series buoy monitoring[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 43(6): 62-70. | |
| [49] | 国家环境保护总局, 2002a. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 第4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社: 210-285. |
| State Environmental Protection Agency, 2002a. Monitoring and analysis methods of water and wastewater[M]. 4th edition. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press: 210-285. | |
| [50] | 国家环境保护总局, 2002b. 地表水环境质量标准: GB 3838—2002[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社: 2-3. |
| State Environmental Protection Agency, 2002b. Environmental quality standard for surface water: GB 3838—2002[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press: 2-3. | |
| [51] | 李丛杨, 史宸菲, 方家琪, 等, 2021. 太湖入湖河流氮磷时空分布特征[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 37(2): 182-187. |
| LI C Y, SHI C F, FANG J Q, et al., 2021. Spatio-temporal distribution characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus in the typical inflow river of Taihu Lake[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 37(2): 182-187. | |
| [52] | 李东蔚, 明红霞, 苏洁, 等, 2023. 降雨降低非点源污染海水浴场粪便指示细菌丰度[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 29(5): 1203-1210. |
| LI D W, MING H X, SU J, et al., 2023. Rainfall decreases non-point source polluted beach feces indicator bacterial abundance[J]. Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 29(5): 1203-1210. | |
| [53] | 龙云川, 王龙燕, 胡菁, 等, 2024. 基于UV-Vis和EEM-PARAFAC的草海沉积物DOM时空分布特征[J]. 环境科学研究, 37(12): 2698-2709. |
| LONG Y C, WANG L Y, HU J, et al., 2024. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of DOM in sediments from Guizhou Caohai based on UV-Vis and EEM-PARAFAC[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 37(12): 2698-2709. | |
| [54] | 罗月萱, 吕泽兰, 晏彩霞, 等, 2024. 袁河流域沉积物中溶解性有机质的光谱特征[J]. 环境科学, 45(8): 4553-4564. |
| LUO Y X, LÜ Z L, YAN C X, et al., 2024. Spectral characteristics of dissolved organic matter in sediments from Yuanhe River basin[J]. Environmental Science, 45(8): 4553-4564. | |
| [55] |
吕伟伟, 姚昕, 张保华, 2018. 太湖水体有机质荧光特征及其来源解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 27(8): 1512-1521.
DOI |
| LÜ W W, YAO X, ZHANG B H, 2018. Fluorescent characteristics and sources of organic matter in Lake Taihu[J]. Journal of Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 27(8): 1512-1521. | |
| [56] |
马飞扬, 樊团团, 孙小平, 等, 2021. 洞庭湖不同湖区水体DOM的荧光特征及来源[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(12): 2370-2379.
DOI |
| MA F Y, FAN T T, SUN X P, et al., 2021. DOM Fluorescence Characteristics and Sources in Different Regions of Dongting Lake[J]. Journal of Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(12): 2370-2379. | |
| [57] | 宋照风, 方战强, 2013. 珠江广州河段水体中溶解性有机质的特性[J]. 轻工科技, 29(5): 118-120, 156. |
| SONG Z F, FANG Z Q, 2013. Characteristics of dissolved organic matter in the waters of the Pearl River in Guangzhou[J]. Light Industry Science and Technology, 29(5): 118-120, 156. | |
| [58] | 张华, 全桂军, 黄健, 等, 2017. 废水DOM荧光强度与COD总氮的相关分析[J]. 环境科学与技术, 40(10): 157-162. |
| ZHANG H, QUAN G J, HUANG J, et al., 2017. Analysis of the correlation between the fluorescence intensity of the dissolved organic matter and COD and total nitrogen in wastewater[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 40(10): 157-162. | |
| [59] | 张柳青, 彭凯, 周蕾, 等, 2019. 南水北调东线中游枢纽湖泊有色可溶性有机物来源组成特征[J]. 环境科学, 40(7): 3018-3029. |
| ZHANG L Q, PENG K, ZHOU L, et al., 2019. Characterizing chromophoric dissolved organic matter in key lakes in the middle reaches of the east route of the south-north water diversion project[J]. Environmental Science, 40(7): 3018-3029. | |
| [60] | 张杨, 郑前兴, 吴仁人, 等, 2022. 有氧和厌氧环境下指示微生物的稳定性特征[J]. 中国环境科学, 42(3): 1327-1334. |
| ZHANG Y, ZHENG Q X, WU R R, et al., 2022. The stability of microbiological indicators in aerobic and anaerobic environment[J]. China Environmental Science, 42(3): 1327-1334. |
| [1] | 田蜜, 廖日权, 张健, 董凤凤, 唐建辉. 钦州湾全氟/多氟烷基化合物的污染特征及生态风险评估[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(7): 1020-1028. |
| [2] | 贺环, 周丹丹, 马芷萱, 李芳芳, 秦珊珊, 豆思娴. 钙改性对生物炭中溶解性有机质与Cd(Ⅱ)结合的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(7): 1121-1132. |
| [3] | 翁雷霆, 王鹏, 肖荣波, 白晋晶, 钟俊宏. 2000-2022年珠三角城市群PM2.5与O3时空分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(2): 268-278. |
| [4] | 欧阳美凤, 尹宇莹, 张金谌, 刘清霖, 谢意南, 方平. 洞庭湖典型水域重金属含量的空间分布与来源解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(8): 1269-1278. |
| [5] | 王文静, 翟水晶, 王赛. 闽江下游湿地土壤硅的沿程分布特征及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(8): 1182-1191. |
| [6] | 吴文伟, 沈城, 沙晨燕, 林匡飞, 吴健, 谢雨晴, 周璇. 城市工业地块土壤重金属污染风险评价与源解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(5): 791-801. |
| [7] | 何艺, 秦欣欣, 张翔, 孙楠, 杨雅淋, 连军锋. 微塑料断面分布的不均一性——以赣江水域赣州段为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(4): 626-632. |
| [8] | 张瑞东, 吴富勤, 李坤冀, 金彦杉, 刘程霞, 申仕康. 云南九大高原湖泊湖滨带入侵植物物种组成与分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(3): 351-361. |
| [9] | 唐舒娅, 王春辉, 宋靖, 李刚. 环象山港区域土壤重金属污染特征及风险评估[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(11): 1768-1781. |
| [10] | 董智今, 张呈春, 展秀丽, 张维福. 宁夏河东沙地生物土壤结皮及其下伏土壤养分的空间分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 910-919. |
| [11] | 李文菁, 黄月群, 黄亮亮, 李向通, 苏琼源, 孙扬言. 北部湾海洋鱼类微塑料污染特征及其风险评估[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(11): 1913-1921. |
| [12] | 何文宣, 李垒, 孙思宇, 李昌, 李久义, 田秀君. 北运河水体、沉积物和鱼类中微塑料的分布特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(11): 1901-1912. |
| [13] | 谢晨敏, 隆楚月, 黎大宁, 朱春友, 彭先芝, 孙毓鑫, 罗孝俊, 张黎, 麦碧娴. 南海永兴岛和东岛土壤中微塑料和卤代阻燃剂的分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 1008-1014. |
| [14] | 许冬雪, 李兴, 王勇, 勾芒芒. 冰封期乌梁素海不同形态氮、磷和叶绿素a的空间分布特征及其响应关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(9): 1855-1864. |
| [15] | 邓慧颖, 陈立新, 余永江, 王宏. 武夷山市臭氧分布特征及其与气象要素关系分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(7): 1428-1435. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
