生态环境学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (9): 1416-1425.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.09.009
吴东阳1,2( ), 吴家欢1,2, 李伟志3, 黄志杰1,2, 杨春亚1,2, 陈火君1,2,*(
), 吴家欢1,2, 李伟志3, 黄志杰1,2, 杨春亚1,2, 陈火君1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-03-15
出版日期:2024-09-18
发布日期:2024-10-18
通讯作者:
*陈火君。E-mail: hjchen@scau.edu.cn作者简介:吴东阳(1999生),男,硕士研究生,主要从事农业资源安全利用。E-mail: ayuan2316@outlook.com
基金资助:
WU Dongyang1,2( ), WU Jiahuan1,2, LI Weizhi3, HUANG Zhijie1,2, YANG Chunya1,2, CHEN Huojun1,2,*(
), WU Jiahuan1,2, LI Weizhi3, HUANG Zhijie1,2, YANG Chunya1,2, CHEN Huojun1,2,*( )
)
Received:2024-03-15
Online:2024-09-18
Published:2024-10-18
摘要:
粪肥还田是常见畜禽粪污资源化无害化的处理手段之一。深入讨论粪肥还田在特定农业生态系统中的应用效果,针对辣椒产地土壤结构破坏、肥力下降和辣椒减产的问题,同时比较蚯蚓粪和猪粪的施肥还田效果差异,开展田间试验探究猪粪、蚯蚓粪配施化肥对土壤质量、辣椒生长及品质的影响,以期为粪肥还田利用和培肥土壤提供数据支撑。试验设计6个不同处理:CK(不施肥处理)、CF1(农户习惯施肥)、OF(优化配方施肥)、VC1(蚯蚓粪+优化施肥85% N)、VC2(蚯蚓粪+优化施肥70% N)和PM(猪粪+优化施肥85% N)。主要结果如下:与不施肥和单施化肥相比,粪肥与化肥配施能有效改善土壤结构、显著优化土壤肥力,促进辣椒生长发育和品质。结合主成分分析,以隶属函数得分值最高的VC2处理改善土壤效果最好,使土壤容重降低了1.81%,土壤pH提高了7.20%,土壤有机质含量增加了101%,土壤铵态氮、硝态氮、有效磷和速效钾含量分别增加了60.2%、209%、152%和192%。蚯蚓粪配施化肥明显促进了辣椒的生长发育,与CK相比VC2处理辣椒产量显著提高达到13.4 t∙hm−2,而且显著提高辣椒维生素C和可溶性糖含量。不同施肥处理对辣椒可溶性固形物含量变化无显著性影响(p>0.05)。蚯蚓粪替代30%化肥处理改善土壤质量、提高辣椒生长和品质的综合效果最佳。该研究为粤西地区的农业生产实践提供科学依据和理论基础,探究出同时兼顾土壤综合肥力、辣椒生长及品质的合理施肥方式,对提升农业生产效率、促进农业绿色发展具有重要作用。
中图分类号:
吴东阳, 吴家欢, 李伟志, 黄志杰, 杨春亚, 陈火君. 蚓粪、猪粪配施化肥对土壤质量、辣椒生长及品质的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(9): 1416-1425.
WU Dongyang, WU Jiahuan, LI Weizhi, HUANG Zhijie, YANG Chunya, CHEN Huojun. Effects of Vermicompost and Pig manure Combined with Chemical Fertilizers on Soil Quality, Growth and Quality of Peppers[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(9): 1416-1425.
| 粪肥 | pH | w(OM)/% | w(N)/% | w(P2O5)/% | w(K2O)/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 蚯蚓粪 | 7.08±0.11 | 17.5±0.9 | 1.72±0.03 | 1.98±0.04 | 1.41±0.02 |
| 猪粪 | 7.54±0.13 | 39.8±1.4 | 1.91±0.09 | 4.81±0.09 | 1.77±0.04 |
表1 粪肥主要养分指标
Table 1 The main nutrient index of manure fertilizer
| 粪肥 | pH | w(OM)/% | w(N)/% | w(P2O5)/% | w(K2O)/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 蚯蚓粪 | 7.08±0.11 | 17.5±0.9 | 1.72±0.03 | 1.98±0.04 | 1.41±0.02 |
| 猪粪 | 7.54±0.13 | 39.8±1.4 | 1.91±0.09 | 4.81±0.09 | 1.77±0.04 |
| 处理 | 化肥用量/(kg∙hm−2) | 粪肥用量/ (kg∙hm−2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P2O5 | K2O | ||
| CK | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| CF | 300 | 150 | 200 | 0 |
| OF | 203 | 105 | 188 | 0 |
| VC1 | 172 | 70 | 163 | 1766 |
| VC2 | 142 | 35 | 138 | 3532 |
| PM | 172 | 29 | 159 | 1590 |
表2 试验处理与肥料用量
Table 2 Treatment and fertilizer amount of the experiment
| 处理 | 化肥用量/(kg∙hm−2) | 粪肥用量/ (kg∙hm−2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P2O5 | K2O | ||
| CK | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| CF | 300 | 150 | 200 | 0 |
| OF | 203 | 105 | 188 | 0 |
| VC1 | 172 | 70 | 163 | 1766 |
| VC2 | 142 | 35 | 138 | 3532 |
| PM | 172 | 29 | 159 | 1590 |
| 处理 | w(NH4+)/ (mg∙kg−1) | w(NO3−)/ (mg∙kg−1) | w(AP)/ (mg∙kg−1) | w(AK)/ (mg∙kg−1) | w(OM)/ (g∙kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 10.8±0.6c | 1.57±0.06b | 4.60±0.30c | 17.0±1.6c | 6.84±1.14c |
| CF | 11.9±1.6c | 1.75±0.55b | 8.50±0.10b | 29.0±3.7bc | 7.16±1.21c |
| OF | 12.1±2.5c | 2.12±0.38b | 10.5±0.9ab | 42.7±4.3ab | 7.81±0.43c |
| VC1 | 12.9±1.2bc | 4.21±0.15a | 11.5±1.8a | 40.8±3.4ab | 10.4±1.1b |
| VC2 | 17.3±0.9a | 4.86±0.08a | 11.6±0.5a | 49.6±7.3a | 13.7±0.8b |
| PM | 15.6±1.1ab | 5.00±0.44a | 12.1±0.4a | 47.2±6.7a | 14.3±0.9a |
表3 不同施肥方式对土壤养分含量的影响
Table 3 Effects of different fertilization methods on soil nutrient content
| 处理 | w(NH4+)/ (mg∙kg−1) | w(NO3−)/ (mg∙kg−1) | w(AP)/ (mg∙kg−1) | w(AK)/ (mg∙kg−1) | w(OM)/ (g∙kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 10.8±0.6c | 1.57±0.06b | 4.60±0.30c | 17.0±1.6c | 6.84±1.14c |
| CF | 11.9±1.6c | 1.75±0.55b | 8.50±0.10b | 29.0±3.7bc | 7.16±1.21c |
| OF | 12.1±2.5c | 2.12±0.38b | 10.5±0.9ab | 42.7±4.3ab | 7.81±0.43c |
| VC1 | 12.9±1.2bc | 4.21±0.15a | 11.5±1.8a | 40.8±3.4ab | 10.4±1.1b |
| VC2 | 17.3±0.9a | 4.86±0.08a | 11.6±0.5a | 49.6±7.3a | 13.7±0.8b |
| PM | 15.6±1.1ab | 5.00±0.44a | 12.1±0.4a | 47.2±6.7a | 14.3±0.9a |
| 处理 | 维生素C质量分数/ (mg∙100 g−1) | 可溶性糖质量分数/ (mg∙g−1) | 可溶性固形物 质量分数/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 155±11c | 3.23±0.31b | 6.33±0.31ab |
| CF | 165±4c | 3.66±0.13ab | 6.47±0.40ab |
| OF | 171±11bc | 3.69±0.20ab | 6.37±0.25ab |
| VC1 | 187±17ab | 3.61±0.20ab | 6.12±0.33b |
| VC2 | 190±8ab | 3.98±0.36a | 6.60±0.81ab |
| PM | 193±8a | 3.86±0.28a | 7.21±0.70a |
表4 不同施肥方式对辣椒品质的影响
Table 4 Effects of different fertilization methods on pepper quality
| 处理 | 维生素C质量分数/ (mg∙100 g−1) | 可溶性糖质量分数/ (mg∙g−1) | 可溶性固形物 质量分数/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 155±11c | 3.23±0.31b | 6.33±0.31ab |
| CF | 165±4c | 3.66±0.13ab | 6.47±0.40ab |
| OF | 171±11bc | 3.69±0.20ab | 6.37±0.25ab |
| VC1 | 187±17ab | 3.61±0.20ab | 6.12±0.33b |
| VC2 | 190±8ab | 3.98±0.36a | 6.60±0.81ab |
| PM | 193±8a | 3.86±0.28a | 7.21±0.70a |
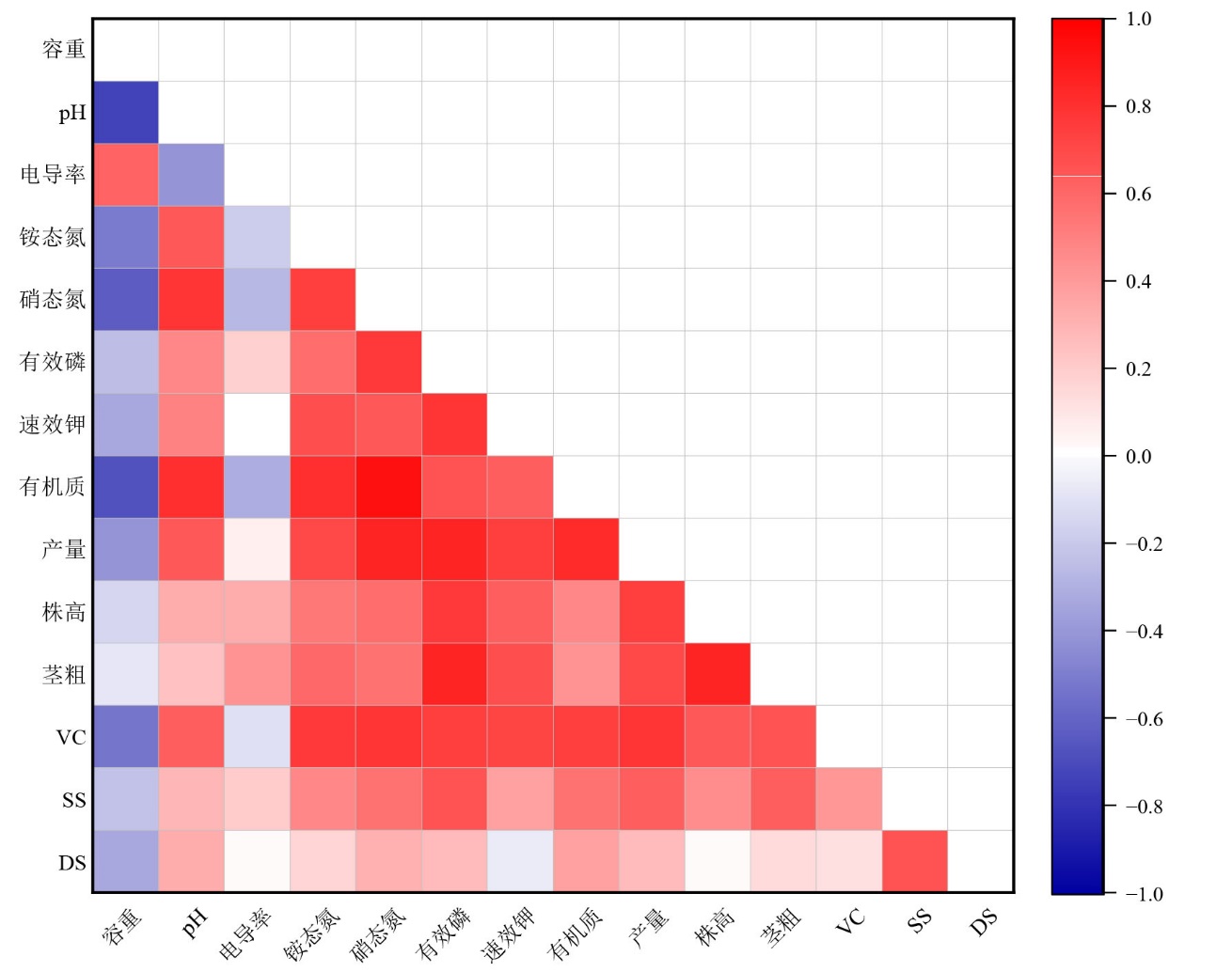
图7 不同施肥方式各指标Pearson相关性热图 VC:维生素C;SS:可溶性糖;DS:可溶性固形物。颜色渐变表示相关系数,红色表示正相关,蓝色色表示负相关;*表示显著相关性(* p≤0.05,** p≤0.01)
Figure 7 Pearson correlation heat map of various indicators for different fertilization methods
| 处理 | F1 | F2 | F3 | U1 | U2 | U3 | D | 排序 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | −1.00 | −1.75 | 0.11 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.55 | 0.14 | 6 |
| CF | −0.87 | 0.78 | −1.34 | 0.06 | 0.89 | 0.00 | 0.23 | 5 |
| OF | −0.71 | 1.10 | 0.69 | 0.13 | 1.00 | 0.77 | 0.51 | 4 |
| VC1 | 0.28 | 0.14 | 1.28 | 0.58 | 0.67 | 1.00 | 0.84 | 3 |
| VC2 | 1.07 | 0.02 | 0.27 | 0.93 | 0.62 | 0.62 | 1.00 | 1 |
| PM | 1.23 | −0.30 | −1.00 | 1.00 | 0.51 | 0.13 | 0.91 | 2 |
表6 不同施肥方式主成分值,隶属函数值,综合评价得分及排序
Table 6 Principal component value,subordinate function value,comprehensive evaluation score and ranking of different fertilization methods
| 处理 | F1 | F2 | F3 | U1 | U2 | U3 | D | 排序 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | −1.00 | −1.75 | 0.11 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.55 | 0.14 | 6 |
| CF | −0.87 | 0.78 | −1.34 | 0.06 | 0.89 | 0.00 | 0.23 | 5 |
| OF | −0.71 | 1.10 | 0.69 | 0.13 | 1.00 | 0.77 | 0.51 | 4 |
| VC1 | 0.28 | 0.14 | 1.28 | 0.58 | 0.67 | 1.00 | 0.84 | 3 |
| VC2 | 1.07 | 0.02 | 0.27 | 0.93 | 0.62 | 0.62 | 1.00 | 1 |
| PM | 1.23 | −0.30 | −1.00 | 1.00 | 0.51 | 0.13 | 0.91 | 2 |
| [1] | ATIYEH R M, SUBLER S, EDWARDS C A, et al., 2000. Effects of vermicomposts and composts on plant growth in horticultural container media and soil[J]. Pedobiologia, 44(5): 579-590. |
| [2] | BRUTO M, PRIGENT-COMBARET C, MULLER D, et al., 2014. Analysis of genes contributing to plant-beneficial functions in plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria and related Proteobacteria[J]. Scientific Reports, 6261: 4-6. |
| [3] | CAI Z J, WANG B R, XU M G, et al., 2015. Intensified soil acidification from chemical N fertilization and prevention by manure in an 18-year field experiment in the red soil of southern China[J]. Journal of soils and sediments, 15(2): 260-270. |
| [4] | CHEN L D, ZHOU W, LUO L, et al., 2022. Short-term responses of soil nutrients, heavy metals and microbial community to partial substitution of chemical fertilizer with spent mushroom substrates (SMS)[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 844: 7-9. |
| [5] | GUO Z C, ZHANG Z B, ZHOU H, et al., 2018. Long-term animal manure application promoted biological binding agents but not soil aggregation in a Vertisol[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 180: 232-237. |
| [6] | HADAS A, AGASSI M, ZHEVELEV H, et al., 2004. Mulching with composted municipal solid wastes in the Central Negev, Israel[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 78(1): 115-128. |
| [7] |
RAVINDRAN B, LEE S R, CHANG S W, et al., 2019. Positive effects of compost and vermicompost produced from tannery waste-animal fleshing on the growth and yield of commercial crop-tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum L.) plant[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 234: 154-158.
DOI PMID |
| [8] | SHI Y J, WANG Z Y, WANG Y R, 2020. Optimizing the amount of pig manure in the vermicomposting of spent mushroom (Lentinula) substrate[J]. PEERJ, 8: 11-14. |
| [9] | WANG H X, XU J L, LIU X J, et al., 2019. Effects of long-term application of organic fertilizer on improving organic matter content and retarding acidity in red soil from China[J]. Soil & Tillage Research, 195: 5-7. |
| [10] | WANG L, BUTTERLY C R, TIAN W, et al., 2016. Effects of fertilization practices on aluminum fractions and species in a wheat soil[J]. Journal of soils and sediments, 16(7): 1933-1943. |
| [11] | ZHAO H T, LI T P, ZHANG Y, et al., 2017. Effects of vermicompost amendment as a basal fertilizer on soil properties and cucumber yield and quality under continuous cropping conditions in a greenhouse[J]. Journal of Soils & Sediments, 17(12): 2718-2730. |
| [12] | ZUO Y N, ZHANG J X, ZHAO R, et al., 2018. Application of vermicompost improves strawberry growth and quality through increased photosynthesis rate, free radical scavenging and soil enzymatic activity[J]. Scientia Horticulturae, 233: 132-140. |
| [13] | 陈吉, 赵炳梓, 张佳宝, 等, 2010. 主成分分析方法在长期施肥土壤质量评价中的应用[J]. 土壤, 42(3): 415-420. |
| CHEN J, ZHAO B Z, ZAHNG J B, et al., 2010. Application of principal component analysis in evaluation of soil quality under different long-term fertilization[J]. Soils, 42(3): 415-420. | |
| [14] | 陈小娟, 2017. 腐殖酸类肥料的生产应用研究进展[J]. 现代盐化工, 44(5): 1-3. |
| CHEN X J, 2017. Advances in production and application of humic acid fertilizers[J]. Modern Salt and Chemical Industry, 44(5): 1-3. | |
| [15] | 冯棣, 张俊鹏, 孙池涛, 等, 2014. 长期咸水灌溉对土壤理化性质和土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 28(3): 171-176. |
| FENG D, ZHANG J P, SUN C T, et al., 2014. Effects of long-term irrigation with saline water on soil physical-chemical properties and activities of soil enzyme[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 28(3): 171-176. | |
| [16] | 冯腾腾, 2017. 蚯蚓粪和秸秆生物炭对大棚多年连作黄瓜的调控效果[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学: 34-35. |
| FENG T T, 2017. The effect of earthworm manure and straw biochar to control greenhouse continuous cropping cucumber[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University: 34-35. | |
| [17] | 韩顺斌, 马丽君, 华军, 等, 2020. 蚯蚓粪和化肥配施对日光温室番茄产量和品质的影响[J]. 农业科技与信息 (13): 19-21. |
| HAN S B, MA L J, HUA J, et al., 2020. Effects of vermicompost and chemical fertilizer application on tomato yield and quality in solar greenhouse[J]. Agricultural Science-technology and Lnformation (13): 19-21. | |
| [18] | 何小霞, 曾思坚, 2005. 科学施肥与农业生产可持续发展[J]. 生态环境, 14(3): 443-444. |
| HE X X, ZENG S J, 2005. Scientific application of fertilizers and sustainable development of agricultural production[J]. Ecology and Environment, 14(3): 443-444. | |
| [19] | 胡艳霞, 孙振钧, 程文玲, 2003. 蚯蚓养殖及蚓粪对植物土传病害抑制作用的研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 14(2): 296-300. |
| HU Y X, SUN Z J, CHENG W L, 2003. Advances in vermiculture and inhibition of vermicompost to soil-borne disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 14(2): 296-300. | |
| [20] | 胡艳霞, 孙振钧, 王东辉, 等, 2004. 蚯蚓粪中拮抗微生物分析[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 10(1): 99-103. |
| HU Y X, SUN Z J, WANG D H, et al., 2004. Anlalysis of antagomistic microorganism in vermicompost[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied & Environmental Biology, 10(1): 99-103. | |
| [21] | 胡哲伟, 金淑, 应蓉蓉, 等, 2021. 蚓粪和益生菌配施对土壤微生物生物量及酶活性的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 49(11): 201-207. |
| HU Z W, JIN S, YING R R, et al., 2021. Effects of combined application of vermicompost and probiotics on soil microbial biomass and enzyme activity[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 49(11): 201-207. | |
| [22] | 黄志鹏, 吴海宁, 唐秀梅, 等, 2020. 化肥减施对花生根际土壤细菌群落结构和多样性的影响[J]. 花生学报, 49(3): 8-13, 31. |
| HUANG Z P, WU H N, TANG X M, et al., 2020. Effects of reduced chemical fertilizer application on bacterial community structure and diversity in peanut rhizosphere soil[J]. Journal of Peanut Science, 49(3): 8-13, 31. | |
| [23] | 孔涛, 李勃, 柯杨, 等, 2017. 蔬菜废弃物堆肥对设施蔬菜产量和土壤生物特性的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料 (5): 157-160. |
| KONG T, LI B, KE Y, et al., 2017. Effect of vegetables waste compost on protected vegetable yield and soil microbial property[J]. Soils and Fertilizers Sciences in China (5): 157-160. | |
| [24] | 李丽贤, 张平显, 石艳梅, 等, 2020. 烤烟化肥减施对烟株农艺和经济性状的影响[J]. 云南农业 (7): 63-69. |
| LI L X, ZAHNG P X, SHI Y M, et al., 2020. Effects of reducing chemical fertilizer application on flue-cured tobacco on agronomic and economic traits of tobacco plants[J]. Yunnan Agriculture (7): 63-69. | |
| [25] | 李颖, 王恒明, 徐小万, 等, 2020. 华南地区辣椒品种选育及育种技术研究进展[J]. 广东农业科学, 47(11): 60-69. |
| LI Y, WANG H M, XU X W, et al., 2020. Breeding of pepper cultivars in south China and research progress in pepper breeding technology[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 47(11): 60-69. | |
| [26] |
李玉涛, 李博文, 马理, 等, 2016. 不同种植年限设施番茄土壤理化性质变化规律的研究[J]. 河北农业大学学报, 39(1): 63-68.
DOI |
| LI Y T, LI B W, MA L, et al., 2016. A Study of physicochemical properties variation in the surface soil of facilities tomatoes under different cultivation years[J]. Journal of Agricultural University of Hebei, 39(1): 63-68. | |
| [27] |
刘丽, 郭宝贝, 刘娟桃, 等, 2019. 蚯蚓粪肥对 ‘玉露香梨’ 果实品质及土壤理化性状和酶活性的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 35(20): 38-43.
DOI |
| LIU L, GUO B B, LIU J T, et al., 2019. Effects of vermicompost fertilizer on fruit quality, soil physical and chemical properties and enzyme activity of ‘Yulu Xiang’ Pear[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 35(20): 38-43. | |
| [28] | 刘学方, 仇美华, 郁洁, 等, 2022. 秸秆及生物炭部分替代化肥对温室连作黄瓜生长与土壤性质的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学, 50(23): 144-150. |
| LIU X F, QIU M H, YU J, et al., 2022. Effects of straw biochar partially replacing chemical fertilizer on growth of continuous cropping cucumber and soil properties in greenhouse[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 50(23): 144-150. | |
| [29] | 鲁如坤, 2000. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社: 1-57. |
| LU R S, 2000. Soil agrichemical analysis methods[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Science and Technology Press: 1-57. | |
| [30] | 罗希榕, 罗银, 李唐燕, 等, 2018. 生物有机肥不同施肥配方对连作辣椒生长发育及产量的影响[J]. 耕作与栽培 (6): 5-8. |
| LUO X R, LUO Y, LI T Y, et al., 2018. Effect of different fertilization formulas of bio-organic fertilizer on growth development and yield of continuous planting pepper[J]. Tillage and Cultivation (6): 5-8. | |
| [31] | 邱江平, 2000. 蚯蚓及其在环境保护上的应用III. 蚯蚓在处理有机废弃物和生活污水上的应用[J]. 上海农学院学报, 18(1): 53-58. |
| QIU J P, 2000. Earthworms and their application in environment protection III∙ Application of earthworms in the treatment of organic waste and urban sewage[J]. Journal of Shanghai Agricultural College, 18(1): 53-58. | |
| [32] | 单颖, 赵凤亮, 林艳, 等, 2017. 蚯蚓粪对土壤环境质量和作物生长影响的研究现状与展望[J]. 热带农业科学, 37(6): 11-17. |
| SHAN Y, ZHAO F L, LIN Y, et al., 2017. Research Advances and prospective on effects of vermicomposton soil environment quality and crop production[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Agriculture, 37(6): 11-17. | |
| [33] | 邵孝候, 张宇杰, 常婷婷, 等, 2018. 生物有机肥对盐渍土壤水盐动态及番茄产量的影响[J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版), 46(2): 153-160. |
| SHAO X H, ZHANG Y J, CHANG T T, et al., 2018. Effects of different fertilizer treatments on soil water, salt and crop yield formation in saline soils[J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences), 46(2): 153-160. | |
| [34] | 孙喜军, 吕爽, 高莹, 等, 2020. 蚯蚓粪对作物连作障碍抑制作用研究进展①[J]. 土壤, 52(4): 676-684. |
| SUN X J, LÜ S, GAO Y, et al., 2020. Research progresses on inhibition effect of vermicompost to continuous cropping obstacles[J]. Soils, 52(4): 676-684. | |
| [35] | 汪洋, 盛海, 刘晓娇, 等, 2023. 日光温室蚯蚓粪不同配比对番茄生长及品质影响[J]. 农业工程技术, 43(24): 36-39. |
| WANG Y, SHENG H, LIU X J, et al., 2023. Effects of different ratios of vermicompost in solar greenhouse on tomato growth and quality[J]. Agricultural Engineering Technology, 43(24): 36-39. | |
| [36] | 王贺, 邓明江, 王旋, 等, 2020. 减施化肥对京津地区苹果生长发育的影响[J]. 果树学报, 37(2): 196-203. |
| WANG H, DENG M J, WANG X, et al., 2020. Effects of reducing chemical fertilizer use on apple tree growth and development in Beijing and Tianjin orchards[J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 37(2): 196-203. | |
| [37] | 王婧, 王盼忠, 徐惠云, 2019. 西北地区农业生产中土壤污染现状及防治措施[J]. 农业科技通讯 (9): 200-202. |
| WANG J, WANG P Z, XU H Y, 2019. Current status and prevention measures of soil pollution in agricultural production in northwest China[J]. Bulletin of Agricultural Science and Technology (9): 200-202. | |
| [38] |
王宁, 南宏宇, 冯克云, 2020. 化肥减量配施有机肥对棉田土壤微生物生物量、酶活性和棉花产量的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 31(1): 173-181.
DOI |
| WANG N, NAN H Y, FENG K Y, 2020. Effects of reduced chemical fertilizer with organic fertilizer application on soil microbial biomass, enzyme activity and cotton yield[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 31(1): 173-181. | |
| [39] | 王晓莉, 张文文, 尹翠, 等, 2020. 设施土壤处理方式对辣椒生长发育及土壤特性的影响[J]. 河南农业大学学报, 54(1): 38-43. |
| WANG X L, ZAHNG W W, YIN C, et al., 2020. Effects of different soil treatments on growth of pepper and Effects of different soil treatments on growth of pepper and soil properties[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural University, 54(1): 38-43. | |
| [40] | 徐立明, 1984. 蚯蚓在环境保护中的作用[J]. 农业环境科学学报 (4): 23-25. |
| XU L M, 1984. The role of earthworms in environmental protection[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science (4): 23-25. | |
| [41] | 赵海涛, 李天鹏, 赵子笑, 等, 2015. 蚓粪基质中添加蛭石和氮磷钾肥对黄瓜幼苗生长的影响[J]. 上海农业学报, 31(5): 13-20. |
| ZHAO H T, LI T P, ZHAO Z X, et al., 2015. Cucumber seedling growth as influenced by worm cast medium added with vermiculite and nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium fertilizers[J]. Acta Agriculturae Shanghai, 31(5): 13-20. | |
| [42] | 赵洪宝, 蒋冬梅, 李岳, 等, 2023. 河曲露天矿排土场不同复垦区土壤质量评价[J]. 矿业科学学报, 8(3): 419-427. |
| ZHAO H B, JIANG D M, LI Y, et al., 2023. Evaluation of soil quality in different reclamation areas of Hequ open-pit mine dump[J]. Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 8(3): 419-427. |
| [1] | 庞波, 海香, 张海芳, 张艳军, 王慧, 刘红梅, 杨殿林. 藜芦扩散对山地草甸草地植被特征和土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(8): 1174-1181. |
| [2] | 罗庆, 何清, 吴慧秋, 寇力月, 方旭, 张鑫雨, 李缘, 柴育廷, 张瑞生, 代文举. 辽河口湿地土壤有机碳组分特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(3): 333-340. |
| [3] | 张腾云, 王静, 高健磊, 葛文静, 王宗耀, 韩龙. 碱性农田土壤冬小麦不同生育期镉的迁移转化研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(3): 450-459. |
| [4] | 冯自贤, 佘璐, 王秀慧, 杨璐, 杨晨. 基于改进遥感生态指数的宁夏生态环境质量时空变化[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(1): 131-143. |
| [5] | 宋思梦, 林冬梅, 周恒宇, 罗宗志, 张丽丽, 易超, 林辉, 林兴生, 刘斌, 苏德伟, 郑丹, 余世葵, 林占熺. 种植巨菌草对乌兰布和沙漠植物物种多样性与土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(9): 1595-1605. |
| [6] | 王源哲, 华春林, 赵丽, 樊敏, 梁晓盈, 周乐乐, 蔡璨, 姚婧. 山地城市主要河流水质评价及预测研究——以四川省绵阳市为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(8): 1465-1477. |
| [7] | 王玉琴, 宋梅玲, 周睿, 王宏生. 黄帚橐吾扩散对高寒草甸土壤理化特性及酶活性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(8): 1384-1391. |
| [8] | 杜丹丹, 高瑞忠, 房丽晶, 谢龙梅. 旱区盐湖盆地土壤重金属空间变异及对土壤理化因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1123-1132. |
| [9] | 王敬, 孟珂, 陈璇, 章家恩, 向慧敏, 钟嘉文, 石兆基. 酸雨对生菜和上海青的产量、品质及生理特性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1098-1107. |
| [10] | 胡启瑞, 吉春容, 李迎春, 王雪姣, 杨明凤, 郭燕云. 膜下滴灌棉花蕾期干旱胁迫对光合特性及产量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1045-1052. |
| [11] | 陈敏毅, 朱航海, 佘伟铎, 尹光彩, 黄祖照, 杨巧玲. 珠三角某遗留造船厂场地土壤重金属人体健康风险评估及源解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 794-804. |
| [12] | 徐兰青, 程冰徐, 王传洗. 叶面喷施生物质碳点对玉米光合及产量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(12): 2166-2173. |
| [13] | 袁佳宝, 宋艳宇, 刘桢迪, 朱梦圆, 程小峰, 马秀艳, 陈宁, 李晓宇. 松嫩平原芦苇湿地土壤酶活性剖面分布特征及其微生物养分限制指示作用[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(12): 2141-2153. |
| [14] | 赵蔓, 张晓曼, 杨明洁. 林火干扰对栓皮栎-辽东栎混交林植物多样性与土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(10): 1732-1740. |
| [15] | 王礼霄, 刘晋仙, 柴宝峰. 华北亚高山土壤细菌群落及氮循环对退耕还草的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1537-1546. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
