生态环境学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (11): 2072-2082.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.11.017
• 综述 •
上一篇
周永康1,2( ), 余圣品3,4, 李佳乐1,2,*(
), 余圣品3,4, 李佳乐1,2,*( ), 董一慧1,2, 王萌1,2, 赵齐灵1,2, 李烨余1,2
), 董一慧1,2, 王萌1,2, 赵齐灵1,2, 李烨余1,2
收稿日期:2023-08-01
出版日期:2023-11-18
发布日期:2024-01-17
通讯作者:
* 李佳乐。E-mail: lijiale@ecut.edu.cn作者简介:周永康(1998年生),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为环境有机污染。E-mail: 1115268271@qq.com
基金资助:
ZHOU Yongkang1,2( ), YU Shengpin3,4, LI Jiale1,2,*(
), YU Shengpin3,4, LI Jiale1,2,*( ), DONG Yihui1,2, WANG Meng1,2, ZHAO Qiling1,2, LI Yeyu1,2
), DONG Yihui1,2, WANG Meng1,2, ZHAO Qiling1,2, LI Yeyu1,2
Received:2023-08-01
Online:2023-11-18
Published:2024-01-17
摘要:
抗生素进入土壤后会发生一系列环境行为,造成环境污染。该文梳理了土壤中抗生素的来源、污染现状和环境行为,系统总结抗生素的官能团和分子结构以及土壤的类型、pH、共存离子和有机质影响抗生素在土壤中吸附的基本规律以及作用机制。土壤中抗生素主要来源于畜牧和医疗产生的废弃物;主要有四环素类、磺胺类、大环内酯类和喹诺酮类;通过生物蓄积和吸附作用残留在土壤中,诱导抗性基因产生或与其他污染物交叉污染造成生态风险。具有羟基、羧基、胺基等可电离基团和不同分子结构的抗生素,存在不同酸解离常数,通过H键作用、π-π相互作用、金属离子络合作用、去质子化作用和阳离子交换等机制被土壤吸附;颗粒细小,质地细腻,具有较大比表面积和孔隙体积的土壤会暴露更多吸附位点,更容易吸附抗生素;土壤存在可变电荷,土壤电荷与抗生素的价态相同会抑制抗生素吸附,反之则促进;有机质通过羟基、羧基等官能团增强抗生素吸附,或与抗生素竞争土壤吸附位点抑制抗生素吸附;Al3+、Fe3+等酸性金属离子,作为抗生素与土壤颗粒联结的桥梁促进抗生素吸附;K+、Na+、Ca2+和Mg2+等碱性金属离子,竞争吸附位点抑制抗生素吸附。此外,土壤中能产生β-内酰胺酶、氨基糖苷类水解酶等胞外酶的微生物可以分解抗生素;植物根系可以分泌有机酸和糖类与抗生素相互作用。未来可利用有机质、离子含量较高的腐殖土研发污染土壤改良剂用于污染土壤原位修复,或利用矿物研发高效低成本的吸附材料;并加强多重复合污染体系与多机制预测模型研究。
中图分类号:
周永康, 余圣品, 李佳乐, 董一慧, 王萌, 赵齐灵, 李烨余. 土壤中抗生素的吸附行为与机理研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(11): 2072-2082.
ZHOU Yongkang, YU Shengpin, LI Jiale, DONG Yihui, WANG Meng, ZHAO Qiling, LI Yeyu. Research Progress on Adsorption Behavior and Mechanism of Antibiotics in Soil[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(11): 2072-2082.
| 样品类型 | 采样地点 | 主要污染物 | 检出率/% | 质量分数/(μg∙kg−1) | 参考文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤 | 重庆市开州区 | 四环素类 (TCs) | 土霉素 (OTC) | 46.15 | 0‒42.88 | 方林发等, |
| 喹诺酮类 (FQs) | 诺氟沙星 (NOR) | 100 | 1.75‒32.23 | |||
| 环丙沙星 (CIP) | 66.67 | 1.31‒264.70 | ||||
| 恩诺沙星 (ENR) | 50 | 0‒120.35 | ||||
| 洛美沙星 (LOM) | 25 | 0‒37.41 | ||||
| 诺氟沙星 (NOR) | 50 | 0‒48.63 | ||||
| 浙江省宁波市海曙区 | 四环素类 (TCs) | 金霉素 (CTC) | ‒ | 0‒324.70 | 赵方凯等, | |
| 江苏省、上海市 和云南省 | 四环素类 (TCs) | 四环素 (TC) | 100 | 1.30‒249 | Zhang et al., | |
| 土霉素 (OTC) | 100 | 1‒ | ||||
| 多西环素 (DOC) | 100 | 1.10‒256 | ||||
| 喹诺酮类 (FQs) | 诺氟沙星 (NOR) | 100 | 1.50‒102 | |||
| 恩诺沙星 (ENR) | 100 | 0.20‒92 | ||||
| 珠江三角洲 | 四环素类 (TCs) | 四环素 (TC) | 54 | 0‒90.42 | Gu et al., | |
| 土霉素 (OTC) | 81 | 0‒406.70 | ||||
| 金霉素 (CTC) | 77 | 0‒134.30 | ||||
| 山西省汾河沿岸 | 喹诺酮类 (FQs) | 诺氟沙星 (NOR) | 100 | 0‒27.21 | Zhu et al., | |
| 新加坡 | 大环内酯类 (MLs) | 红霉素 (ERY) | 93 | 18.80‒80.60 | Yi et al., | |
| 河流沉积物 | 丹江口水库 | 磺胺类 (SAs) | ‒ | 7.18 | 0‒8.94 | Li et al., |
| 大环内酯类 (MLs) | ‒ | 54.5 | 0‒4.34 | |||
| 四环素类 (TCs) | ‒ | 13.3 | 0‒12.10 | |||
| 广东省珠江沿岸 | 磺胺类 (SAs) | 磺胺二甲嘧啶 (SMZ) | 78 | 0‒248 | Yang et al., | |
| 四环素类 (TCs) | 土霉素 (OTC) | 71 | 0‒196 | |||
| 喹诺酮类 (FQs) | 诺氟沙星 (NOR) | 57 | 0‒1120 | |||
| 氧氟沙星 (OFL) | 57 | 0‒1560 | ||||
| 大环内酯类 (MLs) | 罗红霉素 (RTM) | 86 | 0‒133 | |||
| 莱州湾东岸 | 磺胺类 (SAs) | 磺胺二甲嘧啶 (SMZ) | ‒ | 0‒1369.61 | Han et al., | |
| 甲氧苄氨嘧啶 (TMP) | ‒ | 0‒4533.83 | ||||
| 喹诺酮类 (FQs) | 氧氟沙星 (OFL) | ‒ | 0‒2007.84 | |||
| 恩诺沙星 (ENR) | ‒ | 0‒1778.12 | ||||
| 环丙沙星 (CIP) | ‒ | 0‒752.11 | ||||
| 波兰海岸波罗的海南部 | 磺胺类 (SAs) | 磺胺甲噁唑 (SMX) | 58 | 0‒419 | Siedlewicz et al., | |
表1 土壤及沉积物中抗生素污染水平现状
Table 1 Current status of antibiotic pollution in soil environment
| 样品类型 | 采样地点 | 主要污染物 | 检出率/% | 质量分数/(μg∙kg−1) | 参考文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤 | 重庆市开州区 | 四环素类 (TCs) | 土霉素 (OTC) | 46.15 | 0‒42.88 | 方林发等, |
| 喹诺酮类 (FQs) | 诺氟沙星 (NOR) | 100 | 1.75‒32.23 | |||
| 环丙沙星 (CIP) | 66.67 | 1.31‒264.70 | ||||
| 恩诺沙星 (ENR) | 50 | 0‒120.35 | ||||
| 洛美沙星 (LOM) | 25 | 0‒37.41 | ||||
| 诺氟沙星 (NOR) | 50 | 0‒48.63 | ||||
| 浙江省宁波市海曙区 | 四环素类 (TCs) | 金霉素 (CTC) | ‒ | 0‒324.70 | 赵方凯等, | |
| 江苏省、上海市 和云南省 | 四环素类 (TCs) | 四环素 (TC) | 100 | 1.30‒249 | Zhang et al., | |
| 土霉素 (OTC) | 100 | 1‒ | ||||
| 多西环素 (DOC) | 100 | 1.10‒256 | ||||
| 喹诺酮类 (FQs) | 诺氟沙星 (NOR) | 100 | 1.50‒102 | |||
| 恩诺沙星 (ENR) | 100 | 0.20‒92 | ||||
| 珠江三角洲 | 四环素类 (TCs) | 四环素 (TC) | 54 | 0‒90.42 | Gu et al., | |
| 土霉素 (OTC) | 81 | 0‒406.70 | ||||
| 金霉素 (CTC) | 77 | 0‒134.30 | ||||
| 山西省汾河沿岸 | 喹诺酮类 (FQs) | 诺氟沙星 (NOR) | 100 | 0‒27.21 | Zhu et al., | |
| 新加坡 | 大环内酯类 (MLs) | 红霉素 (ERY) | 93 | 18.80‒80.60 | Yi et al., | |
| 河流沉积物 | 丹江口水库 | 磺胺类 (SAs) | ‒ | 7.18 | 0‒8.94 | Li et al., |
| 大环内酯类 (MLs) | ‒ | 54.5 | 0‒4.34 | |||
| 四环素类 (TCs) | ‒ | 13.3 | 0‒12.10 | |||
| 广东省珠江沿岸 | 磺胺类 (SAs) | 磺胺二甲嘧啶 (SMZ) | 78 | 0‒248 | Yang et al., | |
| 四环素类 (TCs) | 土霉素 (OTC) | 71 | 0‒196 | |||
| 喹诺酮类 (FQs) | 诺氟沙星 (NOR) | 57 | 0‒1120 | |||
| 氧氟沙星 (OFL) | 57 | 0‒1560 | ||||
| 大环内酯类 (MLs) | 罗红霉素 (RTM) | 86 | 0‒133 | |||
| 莱州湾东岸 | 磺胺类 (SAs) | 磺胺二甲嘧啶 (SMZ) | ‒ | 0‒1369.61 | Han et al., | |
| 甲氧苄氨嘧啶 (TMP) | ‒ | 0‒4533.83 | ||||
| 喹诺酮类 (FQs) | 氧氟沙星 (OFL) | ‒ | 0‒2007.84 | |||
| 恩诺沙星 (ENR) | ‒ | 0‒1778.12 | ||||
| 环丙沙星 (CIP) | ‒ | 0‒752.11 | ||||
| 波兰海岸波罗的海南部 | 磺胺类 (SAs) | 磺胺甲噁唑 (SMX) | 58 | 0‒419 | Siedlewicz et al., | |
| 抗生素类型 | 化学结构式 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 磺胺类 | 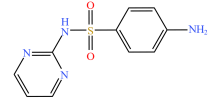 | 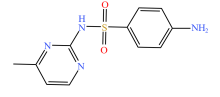 | 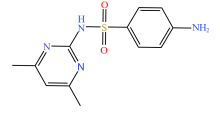 | 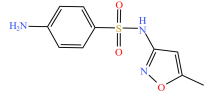 |
| 磺胺嘧啶 | 磺胺甲基嘧啶 | 磺胺二甲嘧啶 | 磺胺甲噁唑 | |
| 四环素类 | 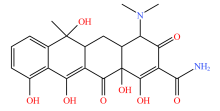 | 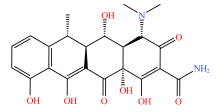 | 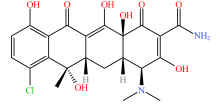 | 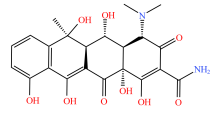 |
| 四环素 | 多西环素 | 金霉素 | 土霉素 | |
| 喹诺酮类 | 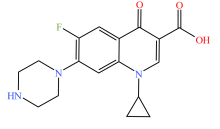 | 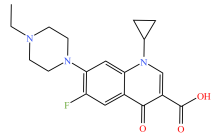 | 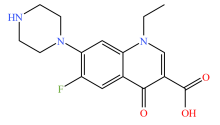 | 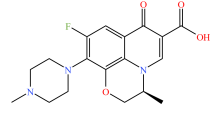 |
| 环丙沙星 | 恩诺沙星 | 诺氟沙星 | 左氧氟沙星 | |
| 大环内酯类 | 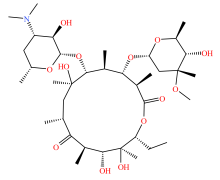 | 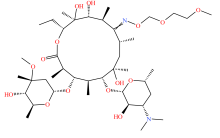 | 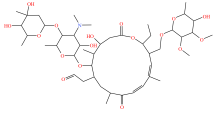 | 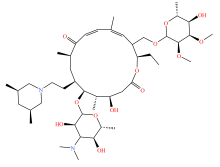 |
| 红霉素 | 罗红霉素 | 泰乐菌素 | 替米考星 | |
表2 土壤中检测到的抗生素类型及其分子结构
Table 2 Types and molecular structure of antibiotics detected in soil
| 抗生素类型 | 化学结构式 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 磺胺类 | 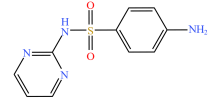 | 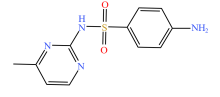 |  |  |
| 磺胺嘧啶 | 磺胺甲基嘧啶 | 磺胺二甲嘧啶 | 磺胺甲噁唑 | |
| 四环素类 |  |  |  |  |
| 四环素 | 多西环素 | 金霉素 | 土霉素 | |
| 喹诺酮类 |  |  |  |  |
| 环丙沙星 | 恩诺沙星 | 诺氟沙星 | 左氧氟沙星 | |
| 大环内酯类 |  |  |  |  |
| 红霉素 | 罗红霉素 | 泰乐菌素 | 替米考星 | |
| 吸附机制 | 主要原子 | 主要官能团 |
|---|---|---|
| H键作用 | N、H、O | -OH、-NH2和C=O |
| π-π相互作用 | C、H | 苯环 |
| 金属离子配位络合作用 | N、H、O | -NH2、-COOH和-OH |
| 去质子化作用 | C、H、O | -COOH |
| 阳离子交换 | N、H、O | -OH、-NH2和-COOH |
表3 吸附机制及涉及的主要原子和官能团
Table 3 Adsorption mechanism and the main atoms and functional groups involved
| 吸附机制 | 主要原子 | 主要官能团 |
|---|---|---|
| H键作用 | N、H、O | -OH、-NH2和C=O |
| π-π相互作用 | C、H | 苯环 |
| 金属离子配位络合作用 | N、H、O | -NH2、-COOH和-OH |
| 去质子化作用 | C、H、O | -COOH |
| 阳离子交换 | N、H、O | -OH、-NH2和-COOH |
| 抗生素类型 | 溶解性/ (mg∙L−1) | pKa1 | pKa2 | pKa3 | logKow | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 磺胺类 | 磺胺甲噁唑 (Chen et al., | 610 | 1.7 | 5.6 | ‒ | 0.89 |
| 磺胺嘧啶 (杜鹃, | 77 | 2.0 | 7.0 | ‒ | 0.25 | |
| 磺胺二甲嘧啶 (杜鹃, | 1500 | 2.7 | 7.7 | ‒ | 0.89 | |
| 四环 素类 | 四环素 (Rivera-Utrilla et al., | 22 | 3.3 | 7.8 | 9.6 | −1.30 |
| 土霉素 (Rivera-Utrilla et al., | 17 | 3.2 | 7.5 | 9.0 | −0.90 | |
| 金霉素 (Rivera-Utrilla et al., | 4.2 | 3.3 | 7.6 | 9.3 | −0.62 | |
| 多西环素 (Gao et al., | ‒ | 3.5 | 7.7 | 9.5 | ‒ | |
| 大环 内酯类 | 罗红霉素 (杜鹃, | 0.02 | ‒ | ‒ | 9.1 | 1.7 |
| 红霉素 (杜鹃, | 4.2 | ‒ | ‒ | 8.4 | 2.37 | |
| 喹诺 酮类 | 环丙沙星 (杜鹃, | 30000 | ‒ | 6.1 | 8.7 | 0.28 |
| 恩诺沙星 (杜鹃, | 3430 | ‒ | 5.5 | 8.6 | −0.2 | |
| 诺氟沙星 (杜鹃, | 17800 | ‒ | 6.3 | 8.7 | 0.46 | |
表4 抗生素的基本性质
Table 4 Basic properties of antibiotics
| 抗生素类型 | 溶解性/ (mg∙L−1) | pKa1 | pKa2 | pKa3 | logKow | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 磺胺类 | 磺胺甲噁唑 (Chen et al., | 610 | 1.7 | 5.6 | ‒ | 0.89 |
| 磺胺嘧啶 (杜鹃, | 77 | 2.0 | 7.0 | ‒ | 0.25 | |
| 磺胺二甲嘧啶 (杜鹃, | 1500 | 2.7 | 7.7 | ‒ | 0.89 | |
| 四环 素类 | 四环素 (Rivera-Utrilla et al., | 22 | 3.3 | 7.8 | 9.6 | −1.30 |
| 土霉素 (Rivera-Utrilla et al., | 17 | 3.2 | 7.5 | 9.0 | −0.90 | |
| 金霉素 (Rivera-Utrilla et al., | 4.2 | 3.3 | 7.6 | 9.3 | −0.62 | |
| 多西环素 (Gao et al., | ‒ | 3.5 | 7.7 | 9.5 | ‒ | |
| 大环 内酯类 | 罗红霉素 (杜鹃, | 0.02 | ‒ | ‒ | 9.1 | 1.7 |
| 红霉素 (杜鹃, | 4.2 | ‒ | ‒ | 8.4 | 2.37 | |
| 喹诺 酮类 | 环丙沙星 (杜鹃, | 30000 | ‒ | 6.1 | 8.7 | 0.28 |
| 恩诺沙星 (杜鹃, | 3430 | ‒ | 5.5 | 8.6 | −0.2 | |
| 诺氟沙星 (杜鹃, | 17800 | ‒ | 6.3 | 8.7 | 0.46 | |
| [1] |
ADEYINKA G C, MOODLEY B, 2019. Kinetic and thermodynamic studies on partitioning of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) between aqueous solution and modeled individual soil particle grain sizes[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences (China), 76: 100-110.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
ÁLVAREZ-ESMORÍS C, RODRÍGUEZ-LÓPEZ, NÚÑEZ-DELGADO A, et al., 2022. Influence of pH on the adsorption-desorption of doxycycline, enrofloxacin, and sulfamethoxypyridazine in soils with variable surface charge[J]. Environmental Research, 214(Part 4): 114071.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
ALVAREZ-ESMORIS C, CONDE-CID M, FERNANDEZ-CALVINO D, et al., 2020. Adsorption-desorption of doxycycline in agricultural soils: Batch and stirred-flow-chamber experiments[J]. Environmental Research, 186: 109565.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
BADSHA M A H, KHAN M, WU B, et al., 2021. Role of surface functional groups of hydrogels in metal adsorption: From performance to mechanism[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 408: 124463.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
BHATT P, BHANDARI G, BILAL M, 2022. Occurrence, toxicity impacts and mitigation of emerging micropollutants in the aquatic environments: Recent tendencies and perspectives[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 10(3): 107598.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
CHEN J G, ZHU B, ZHANG Y H, 2023. A meta-analysis on the responses of soil microbial biomass and community structure to antibiotics[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 184: 104786.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
CHEN K L, LIU L C, CHEN W R, 2017. Adsorption of sulfamethoxazole and sulfapyridine antibiotics in high organic content soils[J]. Environmental Pollution, 231(Part 1): 1163-1171.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
CHENG J, YE Q, LU Z J, et al., 2021. Quantification of the sorption of organic pollutants to minerals via an improved mathematical model accounting for associations between minerals and soil organic matter[J]. Environmental Pollution, 280: 116991.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
CONDE-CID M, FERREIRA-COELHO G, ARIAS-ESTEVEZ M, et al., 2020. Adsorption/desorption of three tetracycline antibiotics on different soils in binary competitive systems[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 262: 110337.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
CONDE-CID M, FERREIRA-COELHO G, NUNEZ-DELGADO A, et al., 2019. Competitive adsorption of tetracycline, oxytetracycline and chlortetracycline on soils with different pH value and organic matter content[J]. Environmental Research, 178: 108669.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
GAO Y, LI Y, ZHANG L, et al., 2012. Adsorption and removal of tetracycline antibiotics from aqueous solution by graphene oxide[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 368(1): 540-546.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
GONZALEZ-GAYA B, GARCIA-BUENO N, BUELOW E, et al., 2022. Effects of aquaculture waste feeds and antibiotics on marine benthic ecosystems in the Mediterranean Sea[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 806(Part 2): 151190.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
GU J Y, CHEN C Y, HUANG X Y, et al., 2021. Occurrence and risk assessment of tetracycline antibiotics in soils and vegetables from vegetable fields in Pearl River Delta, South China[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 776(4): 145959.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
HACIOSMANOGLU G G, MEJIAS C, MARTIN J, et al., 2022. Antibiotic adsorption by natural and modified clay minerals as designer adsorbents for wastewater treatment: A comprehensive review[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 317: 115397.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
HAIDER F U, WANG X K, ZULFIQAR U, et al., 2022. Biochar application for remediation of organic toxic pollutants in contaminated soils; An update[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 248: 114322.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
HAN Q F, ZHANG X R, XU X Y, et al., 2021. Antibiotics in marine aquaculture farms surrounding Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea: Distribution characteristics considering various culture modes and organism species[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 760: 143863.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
HOMEM V, SANTOS L, 2011. Degradation and removal methods of antibiotics from aqueous matrices: A review[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 92(10): 2304-2347.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
HUI K L, XI B D, TAN W B, et al., 2022. Long-term application of nitrogen fertilizer alters the properties of dissolved soil organic matter and increases the accumulation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons[J]. Environmental Research, 215(Part 2): 114267.
DOI URL |
| [19] | JIA W L, SONG C, HE L Y, et al., 2022. Antibiotics in soil and water: occurrence, fate, and risk[J]. Current Opinion in Environmental Science & Health, 32: 100437. |
| [20] |
JING K, LI Y, YAO C, et al., 2023. Towards the fate of antibiotics and the development of related resistance genes in stream biofilms[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 898: 165554.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
KOOPAL L, TAN W F, AVENA M, 2020. Equilibrium mono- and multicomponent adsorption models: From homogeneous ideal to heterogeneous non-ideal binding[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 280: 102138.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
LI F F, CHEN L J, CHEN W D, et al., 2020. Antibiotics in coastal water and sediments of the East China Sea: Distribution, ecological risk assessment and indicators screening[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 151(1-2): 110810.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
LI J P, LI W, LIU K, et al., 2022a. Global review of macrolide antibiotics in the aquatic environment: Sources, occurrence, fate, ecotoxicity, and risk assessment[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 439: 129628.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
LI M, YANG L, YEN H, et al., 2023. Occurrence, spatial distribution and ecological risks of antibiotics in soil in urban agglomeration[J]. Journal Environmental Sciences (China), 125: 678-690.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
LI S, SHI W Z, LIU W, et al., 2018. A duodecennial national synthesis of antibiotics in China’s major rivers and seas (2005-2016)[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 615: 906-917.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
LI S, SHI W Z, YOU M T, et al., 2019. Antibiotics in water and sediments of Danjiangkou Reservoir, China: Spatiotemporal distribution and indicator screening[J]. Environmental Pollution, 246: 435-442.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
LI Y, WEI M L, LIU L, 2022b. Evaluation on adsorption capacity of low organic matter soil for hydrophobic organic pollutant[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 10(3): 107561.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
LU Y, LI Y L, LIU D Q, et al., 2020. Adsorption of benzene vapor on natural silicate clay minerals under different moisture contents and binary mineral mixtures[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 585: 124072.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
MA W J, XU X Y, AN B Y, et al., 2021. Single and ternary competitive adsorption-desorption and degradation of amphenicol antibiotics in three agricultural soils[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 297: 113366.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
MANGALGIRI K P, IBITOYE T, BLANEY L, 2022. Molar absorption coefficients and acid dissociation constants for fluoroquinolone, sulfonamide, and tetracycline antibiotics of environmental concern[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 835: 155508.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
NOVIKAU R, LUJANIENE G, 2022. Adsorption behaviour of pollutants: Heavy metals, radionuclides, organic pollutants, on clays and their minerals (raw, modified and treated): A review[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 309: 114685.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
OKOYE C O, NYARUABA R, ITA R E, et al., 2022. Antibiotic resistance in the aquatic environment: Analytical techniques and interactive impact of emerging contaminants[J]. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 96: 103995.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
QU C C, CHEN W L, HU X P, et al., 2019. Heavy metal behaviour at mineral-organo interfaces: Mechanisms, modelling and influence factors[J]. Environment International, 131: 104995.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
RATH S, FOSTIER A H, PEREIRA L A, et al., 2019. Sorption behaviors of antimicrobial and antiparasitic veterinary drugs on subtropical soils[J]. Chemosphere, 214: 111-122.
DOI PMID |
| [35] |
RIVERA-UTRILLA J, GOMEZ-PACHECO C V, SANCHEZ-POLO M, et al., 2013. Tetracycline removal from water by adsorption/bioadsorption on activated carbons and sludge-derived adsorbents[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 131: 16-24.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
ROUT D R, JENA H M, BAIGENZHENOV O, et al., 2023. Graphene-based materials for effective adsorption of organic and inorganic pollutants: A critical and comprehensive review[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 863: 160871.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
SHAIKH S M R, NASSER M S, HUSSEIN I, et al., 2017. Influence of polyelectrolytes and other polymer complexes on the flocculation and rheological behaviors of clay minerals: A comprehensive review[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 187: 137-161.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
SHEN C, HE M Y, ZHANG J H, et al., 2023. Effects of the coexistence of antibiotics and heavy metals on the fate of antibiotic resistance genes in chicken manure and surrounding soils[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 263: 115367.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
SIEDLEWICZ G, BORECKA M, BIAŁK-BIELIŃSKA A, et al., 2016. Determination of antibiotic residues in southern Baltic Sea sediments using tandem solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Oceanologia, 58(3): 221-234.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
SRINIVASAN P, SARMAH A K, MANLEY-HARRIS M, 2014. Sorption of selected veterinary antibiotics onto dairy farming soils of contrasting nature[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 472: 695-703.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
TANG J P, WANG S, FAN J J, et al., 2019. Predicting distribution coefficients for antibiotics in a river water-sediment using quantitative models based on their spatiotemporal variations[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 655: 1301-1310.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
TIAN C H, SUN M, QUAN J, 2021. Molecular chirality of Macrolide antibiotics[J]. Chemical Physics, 545: 111120.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
WANG W B, ZHAO W T, ZHANG H, et al., 2021. Mesoporous polymetallic silicate derived from naturally abundant mixed clay: A potential robust adsorbent for removal of cationic dye and antibiotic[J]. Powder Technology, 390: 303-314.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
WANG Y T, YU W F, CHANG Z F, et al., 2022. Effects of dissolved organic matter on the adsorption of norfloxacin on a sandy soil (fraction) from the Yellow River of Northern China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 848: 157495.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
WU M, ZHAO S F, JING R S, et al., 2019. Competitive adsorption of antibiotic tetracycline and ciprofloxacin on montmorillonite[J]. Applied Clay Science, 180: 105175.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
XU L Y, ZHANG H, XIONG P, et al., 2021. Occurrence, fate, and risk assessment of typical tetracycline antibiotics in the aquatic environment: A review[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 753: 141975.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
XU Y F, ZHU L, CHEN S G, et al., 2023. Risk assessment and dissemination mechanism of antibiotic resistance genes in compost[J]. Environment International, 178: 108126.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
YANG H R, DONG H, HUANG Y R, et al., 2022. Interactions of microplastics and main pollutants and environmental behavior in soils[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 821: 153511.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
YANG J F, YING G G, ZHAO J L, et al., 2010. Simultaneous determination of four classes of antibiotics in sediments of the Pearl Rivers using RRLC-MS/MS[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 408(16): 3424-3432.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
YI X Z, LIN C H, ONG E J L, et al., 2019. Occurrence and distribution of trace levels of antibiotics in surface waters and soils driven by non-point source pollution and anthropogenic pressure[J]. Chemosphere, 216: 213-223.
DOI PMID |
| [51] |
ZHANG H B, ZHOU Y, HUANG Y J, et al., 2016. Residues and risks of veterinary antibiotics in protected vegetable soils following application of different manures[J]. Chemosphere, 152: 229-237.
DOI PMID |
| [52] |
ZHAO F K, CHEN L D, YEN H, et al., 2020. An innovative modeling approach of linking land use patterns with soil antibiotic contamination in peri-urban areas[J]. Environment International, 134: 105327.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
ZHAO F K, YANG L, CHEN L D, et al., 2019. Soil contamination with antibiotics in a typical peri-urban area in eastern China: Seasonal variation, risk assessment, and microbial responses[J]. Journal of environmental sciences (China), 79: 200-212.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
ZHAO Y P, TAN Y Y, GUO Y, et al., 2013. Interactions of tetracycline with Cd (II), Cu (II) and Pb (II) and their cosorption behavior in soils[J]. Environmental Pollution, 180: 206-213.
DOI PMID |
| [55] |
ZHI D, YANG D X, ZHENG Y X, et al., 2019. Current progress in the adsorption, transport and biodegradation of antibiotics in soil[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 251: 109598.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
ZHU Y, MIAO J R, WEN H X, et al., 2019. The occurrence and spatial distribution of typical antibiotics in soils along the Fenhe River in Shanxi Province[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 20(2): 889-899.
DOI |
| [57] | 陈宇, 许亚南, 庞燕, 2021. 抗生素赋存、来源及风险评估研究进展[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 11(03): 562-570. |
| CHEN Y, XU Y N, PANG Y, 2021. Advances in research on the occurrence, source and risk assessment of antibiotics[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 11(3): 562-570. | |
| [58] |
丛鑫, 王宇, 李瑶, 等, 2022. 生物炭及氧化石墨烯/生物炭复合材料对水中抗生素吸附性能研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 31(2): 326-334.
DOI |
| CONG X, WANG Y, LI Y, et al., 2022. Adsorption characteristics of biochars and graphene oxide/biochar composites for antibiotics from aqueous solution[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 31(2): 326-334. | |
| [59] | 杜鹃, 2021. 黄渤海部分区域近岸海域中抗生素的分布、分配及释放动力学[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学:18-107. |
| DU J, 2021. Occurence, distribution and desorption kinetics of antibiotics in regional coastal areas of the Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology:18-107. | |
| [60] | 方林发, 叶苹苹, 方标, 等, 2022. 重庆开州区菜地土壤抗生素污染特征及潜在生态环境风险评估[J]. 环境科学, 43(11): 5244-5252. |
| FANG L F, YE P P, FANG B, et al., 2022. Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of antibiotics in vegetable field in Kaizhou District, Chongqing[J]. Environmental Science, 43(11): 5244-5252. | |
| [61] | 郭欣妍, 王娜, 许静, 等, 2013. 5种磺胺类抗生素在土壤中的吸附和淋溶特性[J]. 环境科学学报, 33(11): 3083-3091. |
| GUO X Y, WANG N, XU J, et al., 2013. Adsorption and leaching behavior of five sulfonamide in soil[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 33(11): 3083-3091. | |
| [62] | 黄利玲, 2012. 氮肥施用对紫色土酸化及表面电化学性质的影响研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学:11-55. |
| HUANG L L, 2012. Study on the influence of nitrogen fertilization on purple soil acidification and surface electrochemical Properties[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University:11-55. | |
| [63] | 李佳乐, 王萌, 胡发旺, 等, 2022a. 江西锦江流域抗生素污染特征与生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 43(8): 4064-4073. |
| LI J L, WANG M, HU F W, et al., 2022a. Antibiotic pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment in Jinjiang River Basin, Jiangxi province[J]. Environmental Science, 43(8): 4064-4073. | |
| [64] | 李佳乐, 王瑶, 董一慧, 等, 2022b. 鄱阳湖流域袁河水体典型抗生素分布特征及生态风险评价[J]. 生态毒理学报, 17(4): 563-574. |
| LI J L, WANG Y, DONG Y H, et al., 2022b. Distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of typical antibiotics in Yuanhe River of Poyang Lake Basin[J]. Journal of Ecotoxicology, 17(4): 563-574. | |
| [65] | 李威, 李佳熙, 李吉平, 等, 2020. 我国不同环境介质中的抗生素污染特征研究进展[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 44(1): 205-214. |
| LI W, LI J X, LI J P, et al., 2020. Pollution characteristics of antibiotics in different environment media in China: A review[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 44(1): 205-214. | |
| [66] | 李艳丹, 2017. 典型氟喹诺酮类抗生素在高岭土上吸附特征的实验研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学:13-90. |
| LI Y D, 2017. Sorption behavior of typical fluoroquinolone antibiotics on kaolinite: Batch experiments[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences:13-90. | |
| [67] | 李余杰, 2020. 畜禽粪污中FQs类抗生素的污染水平及在紫色土中迁移转化研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学:14-122. |
| LI Y J, 2020. Pollution of fluoroquinolone antibiotics in livestock and poultry wastes and its migration-transformation in purple soil[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University:14-122. | |
| [68] | 林吟萱, 于娇, 吴玲玲, 2023. 抗生素和重金属复合污染现状及其生态效应研究进展[J]. 应用化工, 52(2): 504-510. |
| LIN Y X, YU J, WU L L, 2023. The status and ecological effects of antibiotics and heavy metals combined pollution: A review[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 52(2): 504-510. | |
| [69] | 秦晓鹏, 刘菲, 王广才, 等, 2015. 抗生素在土壤/沉积物中吸附行为的研究进展[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 42(3): 142-148. |
| QIN X P, LIU F, WANG G C, et al., 2015. Adsorption of antibiotics in soils/sediments: A review[J]. Hydrogeology Engineering Geology, 42(3): 142-148. | |
| [70] | 宋豆豆, 2021. 底泥对磺胺类抗生素的吸附-解吸特性研究[D]. 长春: 吉林农业大学:7-36. |
| SONG D D, 2021. Study on the adsorption-desorption characteristics of sulfonamide antibiotics in sediment[D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University:7-36. | |
| [71] | 提清清, 高增文, 季慧慧, 等, 2017. 抗生素在土壤中的吸附行为研究进展[J]. 土壤, 49(3): 437-445. |
| TI Q Q, GAO Z W, JI H H, et al., 2017. Adsorption of Antibiotics in Soils: A Review[J]. Soil, 49(3): 437-445. | |
| [72] | 王晓洁, 赵蔚, 张志超, 等, 2021. 兽用抗生素在土壤中的环境行为、生态毒性及危害调控[J]. 中国科学: 技术科学, 51(6): 615-636. |
| WANG X J, ZHAO W, ZHANG Z C, et al., 2021. Veterinary antibiotics in soils:Environmental processes, ecotoxicity, and risk mitigation[J]. China Science: Technical Sciences, 51(6): 615-636. | |
| [73] | 王新爽, 2017. 不同类型土壤对磺胺甲恶唑的吸附/解吸特性研究[D]. 长春: 吉林农业大学:8-42. |
| WANG X S, 2017. The characteristic study of different type of soils absorption/desorption for sulfamethoxazole[D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University:8-42. | |
| [74] | 卫承芳, 2022. 典型抗生素在污水塘土壤中的吸附、迁移特性[D]. 南昌: 东华理工大学:13-86. |
| WEI C F, 2022. Adsorption and migration characteristics of typical antibiotics in sewage pond soil[D]. Nanchang: East China University of Technology:13-86. | |
| [75] | 夏敏, 2021. 赤铁矿与黏土矿物相互作用对有机污染物归趋的影响[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学:17-70. |
| XIA M, 2021. Impact of the interaction between hematite and clay on environmental fate of organic pollutants[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology:17-70. | |
| [76] | 张步迪, 2017. 磺胺嘧啶在土壤及组分中的吸附迁移特征及模拟[D]. 青岛: 青岛大学:10-114. |
| ZHANG B D, 2017. Adsorption and migration characteristics and simulation of sulfadiazine in soil and its components[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao University:10-114. | |
| [77] | 张焕军, 王席席, 李轶, 2022. 水体中抗生素污染现状及其对氮转化过程的影响研究进展[J]. 环境化学, 41(4): 1168-1181. |
| ZHANG H J, WANG X X, LI Y, 2022. Progress in current pollution status of antibiotics and their influences on the nitrogen transformation in water[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 41(4): 1168-1181. | |
| [78] | 张平, 2020. 东营凹陷泥页岩中有机质与无机矿物相互作用及孔隙特征研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学:11-96. |
| ZHANG P, 2020. Study on the interaction between organic matter and inorganic minerals and pore characteristcs in shale of Dongying depression[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum:11-96. | |
| [79] | 章明奎, 王丽平, 郑顺安, 2008. 两种外源抗生素在农业土壤中的吸附与迁移特性[J]. 生态学报, 28(2): 761-766. |
| ZHANG M K, WANG L P, ZHENG S A, 2008. Adsorption and migration characteristics of two exogenous antibiotics in agricultural soils[J]. Ecology, 28(2): 761-766. | |
| [80] | 赵方凯, 陈利顶, 杨磊, 等, 2017. 长三角典型城郊不同土地利用土壤抗生素组成及分布特征[J]. 环境科学, 38(12): 5237-5246. |
| ZHAO F K, CHEN L D, YANG L, et al., 2017. Composition and distribution of antibiotics in soils with different land use types in a typical peri-urban area of the Yangtze River Delta[J]. Environmental Sciences, 38(12): 5237-5246. | |
| [81] | 周琪琪, 2022. 巢湖流域抗生素的分布、来源、风险评估及其去除方法研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学:17-132. |
| ZHOU Q Q, 2022. Study on the distribution, source, risk assessment and removal methods of antibiotics in Chaohu Lake Basin[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China:17-132. |
| [1] | 唐志伟, 翁颖, 朱夏童, 蔡洪梅, 代雯慈, 王捧娜, 郑宝强, 李金才, 陈翔. 秸秆还田下中国农田土壤微生物生物量碳变化及其影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(9): 1552-1562. |
| [2] | 李航, 陈金平, 丁兆华, 舒洋, 魏江生, 赵鹏武, 周梅, 王宇轩, 梁驰昊, 张轶超. 火干扰对兴安落叶松林土壤氮组分及土壤中氮循环功能基因的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(9): 1563-1573. |
| [3] | 房园, 梁中, 张毓涛, 师庆东, 孙雪娇, 李吉玫, 李翔, 董振涛. 天山云杉森林生态系统的水源涵养能力海拔梯度变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(9): 1574-1584. |
| [4] | 宋思梦, 林冬梅, 周恒宇, 罗宗志, 张丽丽, 易超, 林辉, 林兴生, 刘斌, 苏德伟, 郑丹, 余世葵, 林占熺. 种植巨菌草对乌兰布和沙漠植物物种多样性与土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(9): 1595-1605. |
| [5] | 梁鑫, 韩亚峰, 郑柯, 王旭刚, 陈志怀, 杜鹃. 磁铁矿对稻田土壤碳矿化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(9): 1615-1622. |
| [6] | 刘晗, 王萍, 孙鲁沅, 秦文婧, 陈晓芬, 陈金, 周国朋, 梁婷, 刘佳, 李燕丽. 种植冬绿肥对红壤幼龄橘园土壤微生物量碳、氮和酶活的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(9): 1623-1631. |
| [7] | 宁健, 程晓波, 苏超丽, 汤泽平, 余泽峰. 广东省伴生放射性矿周围土壤放射性水平分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(9): 1692-1699. |
| [8] | 姜懿珊, 孙迎韬, 张干, 罗春玲. 中国不同气候类型森林土壤微生物群落结构及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(8): 1355-1364. |
| [9] | 王玉琴, 宋梅玲, 周睿, 王宏生. 黄帚橐吾扩散对高寒草甸土壤理化特性及酶活性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(8): 1384-1391. |
| [10] | 刘晨, 白雪冬, 赵海超, 黄智鸿, 刘松涛, 卢海博, 刘子刚, 刘雪玲. 寒旱区春玉米秸秆还田方式对土壤DOM光谱特征的影响机制[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(8): 1419-1432. |
| [11] | 李佳蔓, 王晓明, 胡欣蕊, 谢莹莹, 文震. 铁硫比对施氏矿物微观结构及吸附铬性能的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(8): 1478-1486. |
| [12] | 刘炳妤, 王一佩, 姚作芳, 杨钙仁, 徐晓楠, 邓羽松, 黄钰涵. 沼液还田下不同种植模式的重金属风险评价及安全消纳量分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(8): 1507-1515. |
| [13] | 范婉仪, 涂晨, 王顺扬, 吴昕优, 李烜桢, 骆永明. 不同品种烟草对轻度污染耕地土壤中镉的累积特征与减量修复潜力[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(8): 1516-1524. |
| [14] | 陈懂懂, 霍莉莉, 赵亮, 陈昕, 舒敏, 贺福全, 张煜坤, 张莉, 李奇. 青海高寒草地水热因子对土壤微生物生物量碳、氮空间变异的贡献——基于增强回归树模型[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1207-1217. |
| [15] | 赵旭丽, 姚宇阗, 陈超, 黄新琦, 孟天竹. 土壤pH和SO42-含量对设施菜地土壤障碍强还原处理修复的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1218-1225. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
