生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (5): 1051-1059.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.05.018
张兵兵( ), 杨照, 薛斌, 丁小艳, 娄金分, 王盛, 陈蔚洁, 徐国敏*(
), 杨照, 薛斌, 丁小艳, 娄金分, 王盛, 陈蔚洁, 徐国敏*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-12-10
出版日期:2021-05-18
发布日期:2021-08-06
通讯作者:
* 徐国敏,女,研究员。E-mail:410034801@qq.com作者简介:张兵兵(1992年生),男(苗族),助理研究员,硕士,主要从事水体污染治理方向。E-mail:1591505377@qq.com
基金资助:
ZHANG Bingbing( ), YANG Zhao, XUE Bin, DING Xiaoyan, LOU Jinfen, WANG Sheng, CHEN Weijie, XU Guomin*(
), YANG Zhao, XUE Bin, DING Xiaoyan, LOU Jinfen, WANG Sheng, CHEN Weijie, XU Guomin*( )
)
Received:2020-12-10
Online:2021-05-18
Published:2021-08-06
摘要:
农业废弃物资源化利用和无害化处理是实现农业可持续发展和发展循环经济的有效途径,对薏仁米(Semen Coicis)秸秆制备生物炭吸附剂,实现有机固体废弃物资源化利用,解决重金属废水处理难题,以薏仁米秸秆为原料,采用快速热解法制备生物炭。为探明不同温度下制备的薏仁米秸秆生物炭对重金属Hg2+的去除机制及机理,并用扫描电子镜-能谱分析法(SEM-EDS)、傅立叶变换红外光谱法(FT-IR)、氮吸附法(BET)、X射线光电子能谱法(XPS)脱附对制备的生物炭进行了表征,研究其对水中Hg2+的吸附特性及机制。通过结果表明,随裂解温度的升高,生物炭的孔径尺寸逐渐增大,表面极性官能团逐渐减少,比表面积、孔隙容积呈现先增加后减小的趋势。薏仁米秸秆生物炭具有丰富的蜂窝状孔结构和-COOH、-OH等表面活性基团。生物炭对质量浓度小于100 mg∙L-1溶液中Hg2+的去除率大于92%,且生物炭对Hg2+的去除率主要发生在前1 h吸附时间内,然后趋于平衡;随添加量的增加,生物炭对Hg2+去除效率呈现先增加后减小的趋势,含量为2 g∙L-1时生物炭对水中Hg2+的去除效率最高,且700 ℃制备的生物炭对Hg2+的去除效率最高,最大吸附量可达235.3 mg∙g-1。吸附平衡等温线和吸附动力学结果表明,薏仁米秸秆生物炭对Hg2+的吸附过程符合Langmuir等温吸附模型和准二级动力学吸附模型,其对Hg2+的吸附为单层吸附;结合X射线光电子能谱和立叶变换红外光谱,吸附作用机制主要以共沉淀和表面络合为主,Hg-π非共价相互作用为辅的形式结合机理。
中图分类号:
张兵兵, 杨照, 薛斌, 丁小艳, 娄金分, 王盛, 陈蔚洁, 徐国敏. 薏仁米秸秆生物炭对水中Hg2+的吸附特性及机制[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(5): 1051-1059.
ZHANG Bingbing, YANG Zhao, XUE Bin, DING Xiaoyan, LOU Jinfen, WANG Sheng, CHEN Weijie, XU Guomin. Adsorption of Aquatic Hg2+ by Biochar Obtained from Coix Straw[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(5): 1051-1059.
| 生物炭 Biochar | 元素含量 Element content | 元素比 Element ratio | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | K | Si | Ca | O/C | ||
| BC500 | 73.59 | 20.05 | 4.88 | 0.18 | 1.31 | 0.272 | |
| BC600 | 84.22 | 9.07 | 3.40 | 1.08 | ‒ | 0.108 | |
| BC700 | 88.79 | 8.87 | 0.80 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.100 | |
| BC800 | 88.04 | 7.23 | 2.10 | 0.70 | ‒ | 0.082 | |
表1 不同温度制备生物炭的元素组成
Table 1 Chemical contents of BCs surface
| 生物炭 Biochar | 元素含量 Element content | 元素比 Element ratio | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | K | Si | Ca | O/C | ||
| BC500 | 73.59 | 20.05 | 4.88 | 0.18 | 1.31 | 0.272 | |
| BC600 | 84.22 | 9.07 | 3.40 | 1.08 | ‒ | 0.108 | |
| BC700 | 88.79 | 8.87 | 0.80 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.100 | |
| BC800 | 88.04 | 7.23 | 2.10 | 0.70 | ‒ | 0.082 | |
| 吸附剂 Adsorbent | 比表面积 Specific surface area/ (m2∙g-1) | 孔容积 Pore volume/ (cm3∙g-1) | 平均孔径 Average pore size/ nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| BC500 | 78.127 | 0.073 | 15.352 |
| BC600 | 119.126 | 0.085 | 15.405 |
| BC700 | 293.632 | 0.119 | 15.454 |
| BC800 | 25.262 | 0.014 | 15.328 |
表2 不同裂解温度制备生物炭N2吸附-脱附结构参数
Table 2 Structure parameters of BCs
| 吸附剂 Adsorbent | 比表面积 Specific surface area/ (m2∙g-1) | 孔容积 Pore volume/ (cm3∙g-1) | 平均孔径 Average pore size/ nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| BC500 | 78.127 | 0.073 | 15.352 |
| BC600 | 119.126 | 0.085 | 15.405 |
| BC700 | 293.632 | 0.119 | 15.454 |
| BC800 | 25.262 | 0.014 | 15.328 |
| 吸附剂 Adsorbent | Freundlich模型 Freundlich model | Langmuir模型 Langmuir model | 实际吸附量 Actual adsorption capacity qamax/(mg∙g-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kf /(mg1-n∙Ln∙g-1) | R2 | q0/(mg∙g-1) | R2 | |||
| BC500 | 8.05 | 0.9359 | 138.13 | 0.9827 | 113.1 | |
| BC600 | 8.23 | 0.9002 | 167.09 | 0.9787 | 171.9 | |
| BC700 | 14.29 | 0.8323 | 243.29 | 0.9570 | 222.9 | |
| BC800 | 10.18 | 0.8559 | 209.27 | 0.9642 | 183.7 | |
表3 Freundlich 和Langmuir等温吸附模型参数
Table 3 Parameters of Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms models for BCs at 303K
| 吸附剂 Adsorbent | Freundlich模型 Freundlich model | Langmuir模型 Langmuir model | 实际吸附量 Actual adsorption capacity qamax/(mg∙g-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kf /(mg1-n∙Ln∙g-1) | R2 | q0/(mg∙g-1) | R2 | |||
| BC500 | 8.05 | 0.9359 | 138.13 | 0.9827 | 113.1 | |
| BC600 | 8.23 | 0.9002 | 167.09 | 0.9787 | 171.9 | |
| BC700 | 14.29 | 0.8323 | 243.29 | 0.9570 | 222.9 | |
| BC800 | 10.18 | 0.8559 | 209.27 | 0.9642 | 183.7 | |
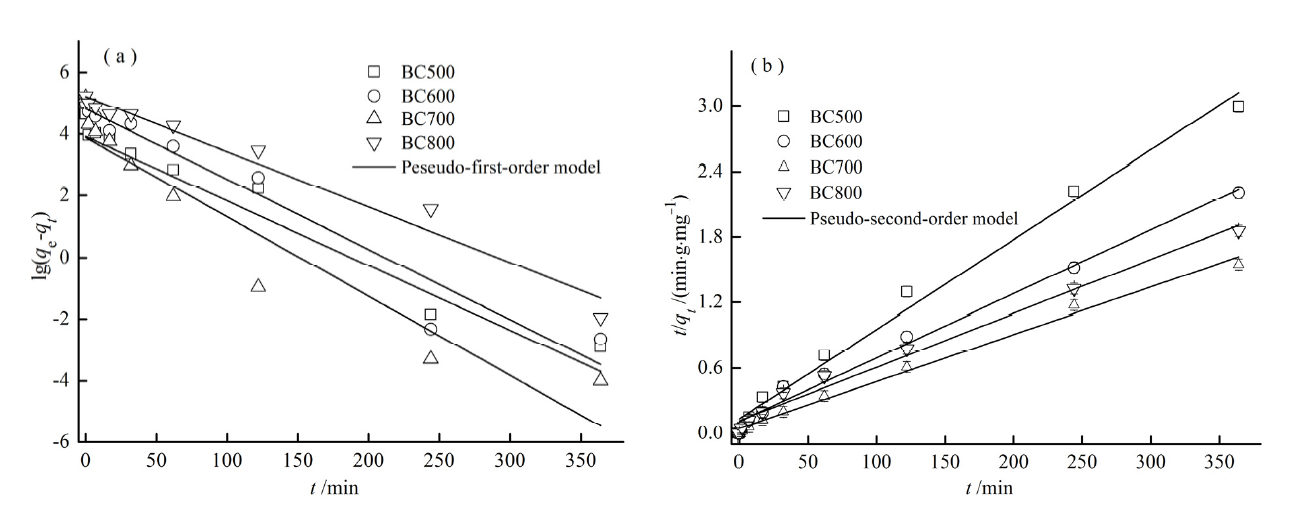
图8 (a)吸附Hg2+的准一级模型的线性拟合;(b)吸附Hg2+的准二级模型的线性拟合
Fig. 8 Pseudo-first-order (a)and pseudo-second-order (b) kinetics fitting plots for Hg2+ onto BCs at 303 K
| 吸附剂 Adsorbent | 准一级吸附模型 Quasi-first kinetic adsorption model | 准二级吸附模型 Quasi- secondary kinetic adsorption model | 实际吸附 Actual adsorption qbmax | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qt /(mg∙g-1) | r2 | k1∙10-3/(min)-1) | qt /(mg∙g-1) | r2 | k2∙10-3/[g∙(mg·min)-1] | |||
| BC500 | 103.46 | 0.7250 | 1.39 | 121.8 | 0.9883 | 1.11 | 121.6 | |
| BC600 | 150.60 | 0.8484 | 2.02 | 170.7 | 0.9884 | 1.37 | 164.7 | |
| BC700 | 189.05 | 0.7731 | 2.97 | 231.54 | 0.9922 | 1.81 | 235.3 | |
| BC800 | 180.53 | 0.8837 | 1.19 | 203.10 | 0.9834 | 1.65 | 196.1 | |
表4 准一级动力学及准二级动力学吸附模型参数
Table 4 Quasi-first and Quasi-secondary kinetic adsorption model parameters
| 吸附剂 Adsorbent | 准一级吸附模型 Quasi-first kinetic adsorption model | 准二级吸附模型 Quasi- secondary kinetic adsorption model | 实际吸附 Actual adsorption qbmax | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qt /(mg∙g-1) | r2 | k1∙10-3/(min)-1) | qt /(mg∙g-1) | r2 | k2∙10-3/[g∙(mg·min)-1] | |||
| BC500 | 103.46 | 0.7250 | 1.39 | 121.8 | 0.9883 | 1.11 | 121.6 | |
| BC600 | 150.60 | 0.8484 | 2.02 | 170.7 | 0.9884 | 1.37 | 164.7 | |
| BC700 | 189.05 | 0.7731 | 2.97 | 231.54 | 0.9922 | 1.81 | 235.3 | |
| BC800 | 180.53 | 0.8837 | 1.19 | 203.10 | 0.9834 | 1.65 | 196.1 | |
| [1] | AHMAD M, LEE S S, OH S E, et al., 2013. Modeling adsorption kinetics of trichloroethylene onto biochars derived from soybean stover and peanut shell wastes[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 12: 8364-8373. |
| [2] |
BRAADBAART F, BOON J J, VELD H, et al., 2004. Laboratory simulations of the transformation of peas as a result of heat treatment: changes of the physical and chemical properties[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 31(6): 821-833.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
LIU P, CAROL P L, DAVID B W, et al., 2016. Mechanisms of mercury removal by biochars produced from different feedstocks determined using X-ray absorption spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 308: 233-242.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
DING Z H, HU X, WAN Y S, et al., 2016. Removal of lead, copper, cadmium, zinc, and nickel from aqueous solutions by alkali-modified biochar: Batch and column tests[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 33: 239-245.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
DONG L J, WU S Y, LI S B, et al., 2020. Sorption Behaviors and Mechanisms of Eu(III) on Rice Straw-derived Biochar[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, DOI:10.15541/jim20190314.
DOI |
| [6] |
FU F L, WANG Q, 2011. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 92(3): 407-418.
DOI URL |
| [7] | HASSAN S S, AWWAD N S, ABOTERIKA A H, ,2016. Removal of mercury(II) from wastewater using camel bone charcoal [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 154(1-3): 992-997. |
| [8] |
KEILUWEIT M, KLEBER M, 2009. Molecular-Level Interactions in Soils and Sediments: The Role of Aromatic π-Systems[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 43(10): 3421-3429.
DOI URL |
| [9] | LI M L, ZHANG Z Q, LI R H, et al., 2016. Removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions from aqueous solution by thiosemicarbazide modified chitosan [J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 86: 876-884. |
| [10] |
DINESH M, KUMAR H, SARSWAT A, et al., 2014. Cadmium and Lead Remediation using Magnetic Oak Wood and Oak Bark Fast Pyrolysis Bio-chars[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 236: 513-528.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
TENG D Y, ZHANG B B, XU G M, et al., 2020. Efficient removal of Cd(II) from aqueous solution by pinecone biochar: Sorption performance and governing mechanisms [J]. Environmental Pollution, DOI:10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115001.
DOI |
| [12] |
VU T M, TRINH V T, DOAN D P, et al., 2017. Removing ammonium from water using modified corncob-biochar[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 579: 612-619.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
WU Q H, ZHOU H, TAM N F Y, et al., 2016. Contamination, toxicity and speciation of heavy metals in an industrialized urban river: Implications for the dispersal of heavy metals[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 104(1-2): 153-161.
DOI URL |
| [14] | WU J Z, HUANG D, LIU X M, et al., 2018. Remediation of As(III) and Cd(II) co-contamination and its mechanism in aqueous systems by a novel calcium-based magnetic biochar [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 348: 10-19. |
| [15] | XU X Y, ARIETTE S, XU N, et al., 2018. Comparison of the characteristics and mechanisms of Hg(II) sorption by biochars and activated carbon [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 463: 55-60. |
| [16] | ZHU Q F, WANG L T, AN Z H, et al., 2016. Hydrothermal synthesis of silico-manganese nanohybrid for Cu(II) adsorption from aqueous solution [J]. Applied Surface Science, 371: 102-111. |
| [17] | ZHU Q F, ZHANG B B, WANG T T, et al., 2019. Synthesis and properties of porous δ-MnO2/polymer millimeter-sized beads for Ni(II) removal [J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 273: 90-98. |
| [18] | 毕景望, 单锐, 韩静, 等, 2020. 改性西瓜皮生物炭的制备及其对Pb(Ⅱ) 的吸附特性[J]. 环境科学, 41(4): 1770-1778. |
| BI J W, SHAN R, HAN J, et al., 2020. Preparation of Modified Watermelon Biochar and Its Adsorption Properties for Pb(Ⅱ)[J]. Environmental Science, 41(4): 1770-1779. | |
| [19] | 段浩楠, 吕宏虹, 王夫美, 等, 2020. 生物炭/铁复合材料的制备及其在环境修复中的应用研究进展[J]. 环境化学, 39(3): 774-790. |
| DUAN H N, LU H H, WANG F M, et al., 2020. Preparation of biochar/iron composite and its application in environmental remediation[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 39(3): 774-790. | |
| [20] | 牛淑娟, 王朝旭, 贺国华, 等, 2020. 玉米秸秆生物炭和碳骨架的制备及对农田土壤CO2排放的影响[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 36(1): 95-105. |
| NIU S J, WANG C X, HE G H, et al., 2020. Preparation of maize straw-derived biochars and corresponding carbon skeletons and their effects on CO2 emissions from farmland soil[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 36(1): 95-105. | |
| [21] | 闫奇, 郑乾送, 周江敏, 等, 2020. 生物炭负载羧甲基纤维素钠稳定化纳米铁对水中六价铬的去除[J]. 环境工程学报, 14(3): 579-587. |
| YAN Q, ZHENG Q S, ZHOU J M, et al., 2020. Removal of hexavalent chromium from water by biochar supported with sodium carboxymethyl cellulose-stabilized nano-iron[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 14(3): 579-587. | |
| [22] | 王桂仙, 张启伟, 2008. 竹炭对水体中重金属离子的吸附规律研究[J]. 化学与生物工程, 25(3): 66-68. |
| WANG G X, ZHANG Q W, 2008. Adsorption law of bamboo-charcoalfor heavy metal ions in aqueous solution[J]. Chemistry & Bioengineering, 25(3): 66-68. | |
| [23] | 张兵兵, 朱秋锋, 王婷婷, 等, 2019. MnO2基复合吸附剂制备及去除水中重金属性能[J]. 水处理技术, 45(4): 53-58. |
| ZHANG B B, ZHU Q F, WANG T T, et al., 2019. Preparation of silico-manganese based composite adsorbents and its performance for heavy metal ions removal from water[J]. Technology of Water Treatment, 45(4): 53-58. | |
| [24] | 张杏锋, 聂小奇, 姚航, 等, 2020. 羊粪生物炭对Pb、Zn、Cd和Cu吸附特性及机制[J]. 水处理技术, 46(5): 24-29. |
| ZHANG X F, NIE X Q, YAO H, et al., 2020. Adsorption characteristic and mechanism of Pb, Zn, Cd and Cu by sheep manure biochar[J]. Technology of Water Treatment, 46(5): 24-29. | |
| [25] | 朱秋锋, 王丽婷, 安泽欢, 等, 2016. 不同形态氧化锰的水热制备及吸附重金属离子性能[J]. 化工新型材料, 44(6): 184-186. |
| ZHU Q F, WANG L T, AN Z H, et al., 2016. Hydrothermal preparation of different forms of manganese oxide and the adsorption performance of heavy metal ions[J]. New Chemical Materials, 44(6): 184-186. | |
| [26] | 赵益华, 贾凯悦, 季民, 等, 2020. 壳聚糖改性硅藻土除藻性能及生态安全性评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(12): 2441-2448. |
| ZHAO Y H, JIA K Y, JI M, et al., 2020. Algae removal performance and ecological safety evaluation of diatomite modified by chitosan[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29(12): 2441-2448. |
| [1] | 赵维彬, 唐丽, 王松, 刘玲玲, 王树凤, 肖江, 陈光才. 两种生物炭对滨海盐碱土的改良效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 678-686. |
| [2] | 游宏建, 张文文, 兰正芳, 马兰, 张宝娣, 穆晓坤, 李文慧, 曹云娥. 蚯蚓原位堆肥与生物炭对黄瓜根结线虫及根际微生物的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 99-109. |
| [3] | 郝贝贝, 王楠, 吴昊平, 周智鑫, 张思毅, 贺斌. 生态沟渠对珠三角稻田径流污染的削减功能研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1856-1864. |
| [4] | 李晓晖, 艾仙斌, 李亮, 王玺洋, 辛在军, 孙小艳. 新型改性稻壳生物炭材料对镉污染土壤钝化效果的研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1901-1908. |
| [5] | 陶玲, 黄磊, 周怡蕾, 李中兴, 任珺. 污泥-凹凸棒石共热解生物炭对矿区土壤重金属生物有效性和环境风险的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1637-1646. |
| [6] | 房献宝, 张智钧, 赖阳晴, 叶脉, 刁增辉. 新型污泥生物炭对土壤重金属Cr和Cd的修复研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1647-1656. |
| [7] | 钱莲文, 余甜甜, 梁旭军, 王义祥, 陈永山. 茶园土壤酸化改良中生物炭应用5 a后的稳定性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1442-1447. |
| [8] | 张慧琦, 李子忠, 秦艳. 玉米秸秆生物炭用量对砂土孔隙和持水性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1272-1277. |
| [9] | 邓晓, 武春媛, 杨桂生, 李怡, 李勤奋. 椰壳生物炭对海南滨海土壤的改良效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 723-731. |
| [10] | 魏岚, 黄连喜, 李翔, 王泽煌, 陈伟盛, 黄庆, 黄玉芬, 刘忠珍. 生物炭基质可显著地促进香蕉幼苗生长[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 732-739. |
| [11] | 赵超凡, 周丹丹, 孙建财, 钱坤鹏, 李芳芳. 生物炭中可溶性组分对其吸附镉的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 814-823. |
| [12] | 程文远, 李法云, 吕建华, 吝美霞, 王玮. 碱改性向日葵秸秆生物炭对多环芳烃菲吸附特性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 824-834. |
| [13] | 刘美, 马志良. 增温和植物去除对青藏高原东部高寒灌丛土壤不同形态氮的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 470-477. |
| [14] | 苏焱, 全妍红, 宦紫嫣, 姚佳, 苏小娟. 磷改性生物炭对云南某铅锌矿周边农田铅锌污染土壤修复效果的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 593-602. |
| [15] | 刘沙沙, 陈诺, 杨晓茵. 微塑料对有机污染物的吸附-解吸特性及其复合毒性效应研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 610-620. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
