生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 1260-1268.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.06.017
陈思( ), 王灿, 李想, 李明锐, 湛方栋, 李元, 祖艳群, 何永美(
), 王灿, 李想, 李明锐, 湛方栋, 李元, 祖艳群, 何永美( )
)
收稿日期:2021-01-28
出版日期:2021-06-18
发布日期:2021-09-10
通讯作者:
* 何永美,E-mail: heyongmei06@126.com作者简介:陈思(1996年生),女,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为紫外辐射生态学。E-mail: 1204035029@qq.com
基金资助:
CHEN Si( ), WANG Can, LI Xiang, Li Mingrui, ZHAN Fangdong, LI Yuan, ZU Yanquan, HE Yongmei(
), WANG Can, LI Xiang, Li Mingrui, ZHAN Fangdong, LI Yuan, ZU Yanquan, HE Yongmei( )
)
Received:2021-01-28
Online:2021-06-18
Published:2021-09-10
摘要:
UV-B辐射增强对整个农业生态系统产生不同程度的影响,为探讨不同UV-B辐射增幅对稻田土壤碳转化和温室气体排放的影响,在元阳梯田稻田原位种植农家水稻品种白脚老粳,通过人工模拟不同UV-B辐射增幅(0、2.5、5.0、7.5 kJ∙m-2),研究不同UV-B辐射增幅对水稻生长期稻田土壤碳转化酶活性、活性有机碳含量和CH4、CO2、N2O排放的影响。结果表明,5.0 kJ∙m-2 UV-B辐射处理导致稻田土壤纤维素酶活性显著增加,增幅范围为15.4%—37.7%;而7.5 kJ∙m-2 UV-B辐射导致土壤碳转化酶(纤维素酶、β-葡萄糖苷酶、多酚氧化酶和蔗糖酶)活性显著降低。UV-B辐射增强导致土壤溶解性有机碳含量显著增加,而易氧化有机碳和微生物量碳含量减少。3个强度的UV-B辐射增幅处理均使稻田CH4排放量显著减少,降幅范围为7.5%—30.6%;5.0 kJ∙m-2 UV-B辐射处理显著增加稻田CO2、N2O排放量,而7.5 kJ∙m-2 UV-B辐射导致稻田CO2、N2O排放降低;综合而言,UV-B辐射增强导致稻田3种温室气体的全球增温潜能降低。此外,土壤中多酚氧化酶活性与微生物量碳、易氧化有机碳含量呈显著正相关(P<0.05),CH4排放通量与微生物量碳含量呈极显著正相关(P<0.01)。可见,随UV-B辐射增强稻田土壤多酚氧化酶活性降低,进而减少易氧化有机碳和微生物量碳含量,最终导致稻田CH4排放减少、CO2和N2O排放增加。
中图分类号:
陈思, 王灿, 李想, 李明锐, 湛方栋, 李元, 祖艳群, 何永美. 不同UV-B辐射增幅对稻田土壤酶活性、活性有机碳含量及温室气体排放的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1260-1268.
CHEN Si, WANG Can, LI Xiang, Li Mingrui, ZHAN Fangdong, LI Yuan, ZU Yanquan, HE Yongmei. Effects of Different UV-B Radiation Levels on Soil Enzyme Activities, Active Organic Carbon Content and Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Paddy Fields[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(6): 1260-1268.
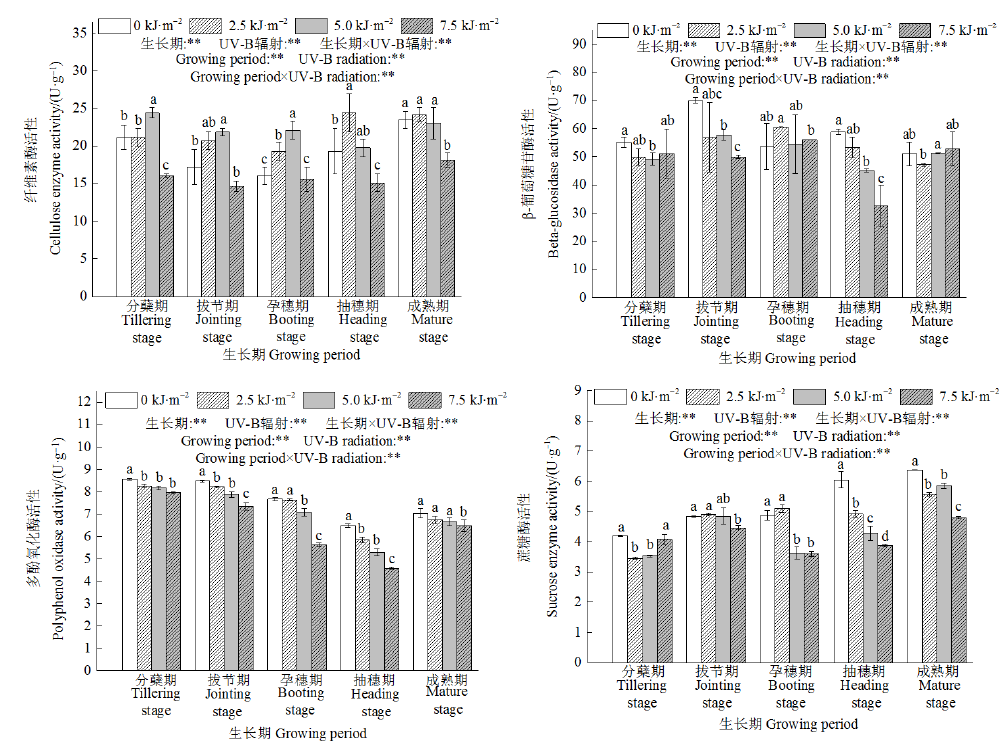
图1 不同UV-B辐射增幅对稻田土壤碳转化酶活性的影响 不同小写字母表示同一时期不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。下同
Fig. 1 Effects of different UV-B radiation levels on the activity of soil carbon invertase in the rice paddy Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments during the same period (P<0.05). The same below
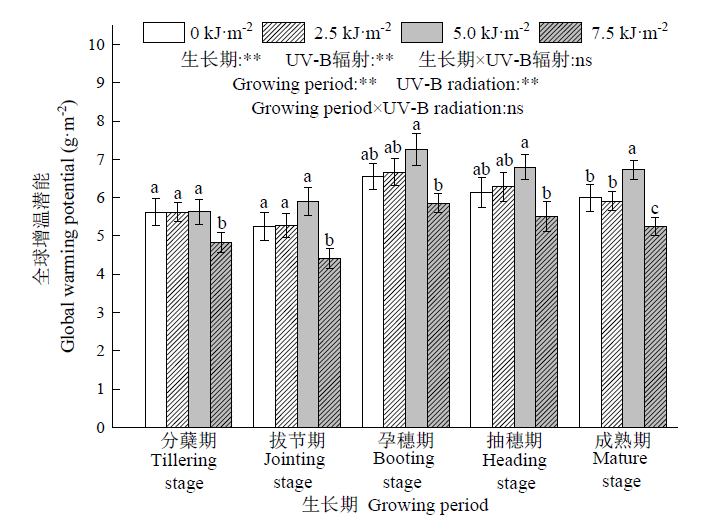
图4 不同UV-B辐射增幅对稻田3种温室气体增温潜能的影响
Fig. 4 Effects of different UV-B radiation levels on the global warming potential of three greenhouse gases in the rice paddy
| 多酚氧化酶 Polyphenol oxidase activity | β-葡萄糖苷酶 Beta-glucosidase activity | 蔗糖酶 Sucrose enzyme activity | 纤维素酶 Cellulose enzyme activity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解性有机碳Dissolved organic carbon | -0.681* | -0.439 | -0.139 | -0.179 |
| 微生物量碳Microbial biomass carbon | 0.769* | -0.470 | 0.288 | -0.059 |
| 易氧化有机碳Labile organic carbon | 0.633* | -0.549 | -0.196 | -0.162 |
表1 水稻生育期稻田土壤碳转化酶活性与活性有机碳含量的相关性
Table 1 Correlation coefficients between carbon invertase activities and active organic carbon contents in the rice paddy
| 多酚氧化酶 Polyphenol oxidase activity | β-葡萄糖苷酶 Beta-glucosidase activity | 蔗糖酶 Sucrose enzyme activity | 纤维素酶 Cellulose enzyme activity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解性有机碳Dissolved organic carbon | -0.681* | -0.439 | -0.139 | -0.179 |
| 微生物量碳Microbial biomass carbon | 0.769* | -0.470 | 0.288 | -0.059 |
| 易氧化有机碳Labile organic carbon | 0.633* | -0.549 | -0.196 | -0.162 |
| 溶解性有机碳 Dissolved organic carbon | 微生物量碳 Microbial biomass carbon | 易氧化有机碳 Labile organic carbon | CH4 | CO2 | N2O | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解性有机碳Dissolved organic carbon | 1 | |||||
| 微生物量碳Microbial biomass carbon | -0.366 | 1 | ||||
| 易氧化有机碳Labile organic carbon | -0.136 | 0.752* | 1 | |||
| CH4 | -0.681* | 0.881** | 0.538 | 1 | ||
| CO2 | -0.128 | -0.212 | -0.129 | -0.125 | 1 | |
| N2O | 0.022 | -0.566 | -0.602 | -0.229 | 0.071 | 1 |
表2 水稻生育期土壤活性有机碳含量与碳排放通量的相关性
Table 2 Correlation coefficients between soil active organic carbon contents with carbon gas emissions in the rice paddy
| 溶解性有机碳 Dissolved organic carbon | 微生物量碳 Microbial biomass carbon | 易氧化有机碳 Labile organic carbon | CH4 | CO2 | N2O | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解性有机碳Dissolved organic carbon | 1 | |||||
| 微生物量碳Microbial biomass carbon | -0.366 | 1 | ||||
| 易氧化有机碳Labile organic carbon | -0.136 | 0.752* | 1 | |||
| CH4 | -0.681* | 0.881** | 0.538 | 1 | ||
| CO2 | -0.128 | -0.212 | -0.129 | -0.125 | 1 | |
| N2O | 0.022 | -0.566 | -0.602 | -0.229 | 0.071 | 1 |
| [1] |
BALL W T, ALSING J, MORTLOVCK D J, et al., 2018. Evidence for a continuous decline in lower stratospheric ozone offsetting ozone layer recovery[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 18(2): 1379-1394.
DOI URL |
| [2] | BAO T, ZHU R, WANG P, et al., 2018. Potential effects of ultraviolet radiation reduction on tundra nitrous oxide and methane fluxes in maritime Antarctica[J]. Scientific Reports, 8(1): 1-11. |
| [3] |
BERND M, KARSTEN K, 2003. Controls of bioavailability and biodegradability of dissolved organic matter in soils[J]. Geoderma, 113(3): 211-235.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
BHATTACHARYYA P, DASH P K, SWAIN C K, et al., 2019. Mechanism of plant mediated methane emission in tropical lowland rice[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 651(Part 1): 84-92
DOI URL |
| [5] |
BLAIR G J, LEFROY R D B, LISLE L, 1995. Soil carbon fractions based on their degree of oxidation, and the development of a carbon management index for agricultural systems[J]. Australian Journal of Agricultural Research, 46(7): 1459-1466.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
BURNS R G, DEFOREST J L, MARXSEN J, et al., 2013. Soil enzymes in a changing environment: current knowledge and future directions[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 58: 216-234.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
BURNS R G, DEFOREST J L, MARXSEN J, et al., 2013. Soil enzymes in a changing environment: current knowledge and future directions[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 58: 216-234.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
CHEN Z D, ZHANG H, XUE J, et al., 2021. A nine-year study on the effects of tillage on net annual global warming potential in double rice-cropping systems in Southern China[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 206: 104797.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
ERICKSON D J, SULZBERGER B, ZEPP R G, et al., 2015. Effects of stratospheric ozone depletion, solar UV radiation, and climate change on biogeochemical cycling: interactions and feedbacks[J]. Photochemical and Photobiological Sciences, 14(1): 127-148.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
GAO L, LIU Y, WANG X, et al., 2019. Lower levels of UV-B light trigger the adaptive responses by inducing plant antioxidant metabolism and flavonoid biosynthesis in Medicago sativa seedlings[J]. Functional Plant Biology, 46(10): 896-906.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
GU Y, WANG P, KONG C H, 2009. Urease, invertase, dehydrogenase and polyphenoloxidase activities in paddy soil influenced by allelopathic rice variety[J]. European Journal of Soil Biology, 45(5-6): 436-441.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
HE Y M, ZHAN F D, LI Y, et al., 2016. Effect of enhanced UV-B radiation on methane emission in a paddy field and rice root exudation of low-molecular-weight organic acids[J]. Photochemical and Photobiological Sciences, 15(6): 735-743.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
HENNING N, BECKER J N, GUILLAUME T, et al., 2021. Riparian wetland properties counter the effect of land-use change on soil carbon stocks after rainforest conversion to plantations[J]. Catena, 196: 104941.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
HOU P F, LI G H, WANG S H, et al., 2013. Methane emissions from rice fields under continuous straw return in the middle-lower reaches of the Yangtze River[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 25(9): 1874-1881.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
HU Z H, JIANG J Y, CHEN S T, et al., 2010. Enhanced UV-B radiation reduced soil-soybean ecosystem respiration and nitrous oxide emissions[J]. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 87(1): 71-79.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
KIMBERLY M. GERBER J S, MUELLER N D, et al., 2017. Greenhouse gas emissions intensity of global croplands[J]. Nature Climate Change, 7(1): 63-68.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
KIRSCHKE S, BOUSQUET P, CIAIS P, et al., 2013. Three decades of global methane sources and sinks[J]. Nature Geoscience, 6(10): 813-823.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
KÖGEL-KNABNER I, AMELUNG W, CAO Z H, et al., 2010. Biogeochemistry of paddy soils[J]. Geoderma, 157(1-2): 1-14.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
KOU T J, CHENG X H, ZHU J G, et al., 2015. The influence of ozone pollution on CO2, CH4, and N2O emissions from a Chinese subtropical rice-wheat rotation system under free-air O3 exposure[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 204: 72-81.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
LI T G, LI X, LIANG Y, et al., 2020. Effects of UV-B radiation on soil carbon conversion and greenhouse gas emission in paddy soil[J]. Greenhouse Gases: Science and Technology, 10(5): 965-979.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
LOU Y S, MENG Y, REN L X, et al., 2016. Silicate application decreased methane emission from paddy soil under elevated UV-B radiation[J]. Greenhouse Gases: Science and Technology, 6(5): 662-669.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
LOU Y S, ZHOU W L, REN L X, et al., 2012. Elevated UV-B radiation increased CH4 emission in transgenic rice from a paddy soil[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 151: 16-20.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
MAHMOOD K, KHAN M B, SONG Y Y, et al., 2013. UV-irradiation enhances rice allelopathic potential in rhizosphere soil[J]. Plant Growth Regulation, 71(1): 21-29.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
NIEMI R, MARTIKAINEN P J, SILVOLA J, et al., 2010. Elevated UV-B radiation alters fluxes of methane and carbon dioxide in peatland microcosms[J]. Global Change Biology, 8(4): 361-371.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
ROBSON T M, KLEM K, URBAN O, et al., 2015. Re-interpreting plant morphological responses to UV-B radiation[J]. Plant, Cell and Environment, 38(5): 856-866.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
ROBSON T M, PANCOTTO V A, BALLARE C L, et al., 2004. Reduction of solar UV-B mediates changes in the Sphagnum capitulum microenvironment and the peatland microfungal community[J]. Oecologia, 140(3): 480-490.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
SATO T, OKU N, IIDA E, et al., 1996. Differential effect of UV-B and UV-C on DNA damage in L-132 cells[J]. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 19(5): 721-725.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
SINSABAUGH R L, 2010. Phenol oxidase, peroxidase and organic matter dynamics of soil[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 42(3): 391-404.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
SONG Y Y, SONG C C, YANG G S, et al., 2012. Changes in labile organic carbon fractions and soil enzyme activities after marshland reclamation and restoration in the Sanjiang Plain in Northeast China[J]. Environmental Management, 50(3): 418-426.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
STRAHAN S E, DOUGLASS A R, 2018. Decline in antarctic ozone depletion and lower stratospheric chlorine determined from Aura Microwave Limb Sounder observations[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 45(1): 382-290.
DOI URL |
| [31] | WAGH Y S, NANDINI K, 2019. Changes in Morpho-physiological and yield parameters of rice (Oryza sativa L.) in response to ultraviolet-B (UV-B) radiation[J]. International Journal of Environment and Climate Change, 9(12): 862-877. |
| [32] |
WANG X W, SONG C C, SUN X X, et al., 2013. Soil carbon and nitrogen across wetland types in discontinuous permafrost zone of the Xiao Xing'an Mountains, northeastern China[J]. Catena, 101: 31-37.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
WARGENT J J, JOEDAN B R, 2013. From ozone depletion to agriculture: understanding the role of UV radiation in sustainable crop production[J]. New Phytologist, 197(4): 1058-1076.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
WICKINGS K, GRANDY A S, REED S C, et al., 2012. The origin of litter chemical complexity during decomposition[J]. Ecology Letters, 15(10): 1180-1188.
DOI URL |
| [35] | WU J, LIN Q, HUANG Q, et al., 2006. Measurement method and application of soil microbial biomass[M]. Beijing: China Meteorological Press. |
| [36] | YANG W, ZHAO H, CHEN X L, et al., 2013. Consequences of short-term C4 plant Spartina alterniflora invasions for soil organic carbon dynamics in a coastal wetland of Eastern China[J]. Ecological Engineering, 61(Part A): 50-57. |
| [37] |
ZHAN M, CAO C G, WANG J P, et al., 2011. Dynamics of methane emission, active soil organic carbon and their relationships in wetland integrated rice-duck systems in Southern China[J]. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 89(1): 1-13.
DOI URL |
| [38] | 褚润, 陈年来, 2017. UV-B辐射增强对芦苇光合生理及叶绿体超微结构的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 28(11): 3515-3520. |
| CHU R, CGEN N L, 2017. Effects of enhanced UV-B radiation on photosynthetic physiology and chloroplast ultrastructure of Phragmites australis[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 28(11): 3515-3520. | |
| [39] | 耿玉清, 王冬梅, 2012. 土壤水解酶活性测定方法的研究进展[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 20(4): 387-394. |
|
GENG Y Q, WANG D M, 2012. Research advances on the measurement methods for soil hydrolytic enzymes activities[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 20(4): 387-394
DOI URL |
|
| [40] | 关松荫, 1986. 土壤酶及其研究方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社. |
| GUAN S Y, 1986. Soil enzyme and its research method[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Press. | |
| [41] | 何永美, 湛方栋, 高召华, 等, 2012. 水稻对UV-B辐射响应的敏感性差异[J]. 生态环境学报, 21(3): 489-495. |
| HE Y M, ZHAN F D, GAO S H, et al., 2012. Differences of UV-B radiation sensitivity of rice[J]. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 21(3): 489-495. | |
| [42] | 何永美, 湛方栋, 吴炯, 等, 2016. UV-B辐射对元阳梯田水稻根系LMWOAs分泌量和根际微生物数量的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 35(4): 613-619. |
| HE Y M, ZHAN F D, WU J, et al., 2016. Effects of UV-B radiation on rice root exudation LMWOAs and rhizospheric microorganism quantities in a paddy field of Yuanyang Terraces, Yunnan Province[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 35(4): 613-619. | |
| [43] | 胡正华, 凌慧, 陈书涛, 等, 2011. UV-B增强对稻田呼吸速率、CH4和N2O排放的影响[J]. 环境科学, 32(10): 3018-3022. |
| HU Z H, LING H, CHEN S T, et al., 2011. Impacts of enhanced UV-B radiation on respiration rate, CH4 and N2O emission fluxes from rice paddy[J]. Environmental Science, 32(10): 3018-3022. | |
| [44] | 蒋静艳, 牛传坡, 胡正华, 等, 2006. 地表UV-B辐射增强对土壤-冬小麦系统N2O排放的影响机理研究[J]. 环境科学, 27(9): 1712-1716. |
| JIANG J Y, NIU C P, HU Z H, et al., 2006. Study on mechanism of enhanced UV-B radiation influencing on N2O emission from soil-winter wheat system[J]. Environmental Science, 27(9): 1712-1716. | |
| [45] | 李海防, 夏汉平, 熊燕梅, 等, 2007. 土壤温室气体产生与排放影响因素研究进展[J]. 生态环境, 16(6): 1781-1788. |
| LI H F, XIA H P, XIONG Y M, et al., 2007. Mechanism of greenhouse gases fluxes from soil and its controlling factors: A review[J]. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 16(6): 1781-1788. | |
| [46] | 李想, 谢春梅, 何永美, 等, 2018. UV-B辐射与稻瘟病菌复合胁迫对元阳梯田水稻生长和光合特性的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 37(4): 613-620. |
| LI X, XIE C M, HE Y M, et al., 2018. Effects of complex UV-B radiation and Magnaporthe oryzae stresses on the growth and photosynthetic characteristics of rice in Yuanyang Terrace, China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 37(4): 613-620. | |
| [47] | 李元, 杨济龙, 王勋陵, 1999. 紫外辐射增加对春小麦根际土壤微生物种群数量的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 19(2): 157-160. |
| LI Y, YANG J H, WANG X L, 1999. The effect of UV-B radiation on the population quantity of spring wheat rhizosphere microorganisms[J]. China Environmental Science, 19(2): 157-160. | |
| [48] | 李增强, 张贤, 王建红, 等, 2018. 紫云英施用量对土壤活性有机碳和碳转化酶活性的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料 (4): 14-20. |
| LI Z Q, ZHANG X, WANG J H, 2018. Effects of Chinese milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus L.) application rate on soil labile organic carbon and C-transformation enzyme activities[J]. Soils and Fertilizers Sciences in China (4): 14-20 | |
| [49] | 李振高, 骆永明, 滕应, 2008. 土壤与环境微生物研究法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| LI Z G, LUO Y M, TENG Y, 2008. Soil and environmental microbiological research method[M]. Beijing: Science Press. | |
| [50] | 柳淑蓉, 胡荣桂, 蔡高潮, 2012. UV-B辐射增强对陆地生态系统碳循环的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 23(7): 1992-1998. |
| LIU S R, HU R G, CAI G C, 2012. Effects of enhanced UV-B radiation on terrestrial ecosystem carbon cycle: A review[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 23(7): 1992-1998. | |
| [51] | 娄运生, 周文鳞, 2012. UV-B辐射增强对抗除草剂转基因水稻CH4排放的影响[J]. 生态学报, 32(15): 4731-4736. |
|
LOU Y S, ZHOU W L, 2012. Effect of elevated ultraviolet-B radiation on CH4 emission in herbicide resistant transgenic rice from a paddy soil[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32(15): 4731-4736.
DOI URL |
|
| [52] | 盛浩, 宋迪思, 王翠红, 等, 2015. 土壤溶解性有机碳四种测定方法的对比和转换[J]. 土壤, 47(6): 1049-1053. |
| SHENG H, SONG D S, WANG C H, et al., 2015. Comparison and transform of soil dissolved organic carbon measured by four methods[J]. Soils, 47(6): 1049-1053. | |
| [53] | 王灿, 李虹茹, 湛方栋, 等, 2018. UV-B辐射对元阳梯田稻田土壤活性有机碳含量与温室气体排放的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 37(2): 383-391. |
| WANG C, LI H R, ZHAN F D, et al., 2018. Effects of enhanced UV-B radiation on the content of soil active organic carbon and greenhouse gas emission from a rice paddy in Yuanyang Terraces[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 37(2): 383-391. | |
| [54] | 吴家梅, 纪雄辉, 霍莲杰, 等, 2013. 稻田土壤氧化态有机碳组分变化及其与甲烷排放的关联性[J]. 生态学报, 33(15): 4599-4607. |
|
WU J M, JI X H, HUO L J, et al., 2013. Fraction changes of oxidation organic carbon in paddy soil and its correlation with CH4 emission fluxes[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33(15): 4599-4607.
DOI URL |
|
| [55] | 吴家梅, 霍莲杰, 纪雄辉, 等, 2017. 不同施肥处理对土壤活性有机碳和甲烷排放的影响[J]. 生态学报, 37(18): 6167-6175. |
| WU J M, HUO L J, JI X H, et al., 2017. Effects of organic manure application on active soil organic carbon and methane emission in paddy soils[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37(18): 6167-6175. | |
| [56] | 徐渭渭, 何永美, 湛方栋, 等, 2015. UV-B辐射增强对元阳哈尼梯田稻田CH4排放规律的影响[J]. 生态学报, 35(5): 1329-1336. |
| XU W W, HE Y M, ZHAN F D, 2015. Effect of enhanced UV-B radiation on CH4 emission from paddy field in Yuanyang Hani Terraces[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35(5): 1329-1336. | |
| [57] | 张彦雪, 何永美, 李想, 等, 2020. UV-B辐射增强对稻田土壤氮转化的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 39(3): 656-664. |
| ZAHNG Y X, HE Y M, LI X, et al., 2020. Effects of enhanced UV-B radiation on nitrogen transformation in paddy soil[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 39(3): 656-664. | |
| [58] | 赵炳梓, 陈吉, 张佳宝, 等, 2011. 风干土保存时间和湿土培育时间对黄淮海平原潮土酶活性的影响[J]. 土壤, 43(3): 418-425. |
| ZHAO B Z, CHEN J, ZHANG J B, et al., 2011. Effect of storage time of air-drying soil and incubation period following rewetting on soil enzyme activities in North China Plain[J]. Soils, 43(3): 418-425. | |
| [59] | 肇思迪, 娄运生, 张祎玮, 等, 2017. UV-B增强下施硅对稻田CH4和N2O排放及其增温潜势的影响[J]. 生态学报, 37(14): 4715-4724. |
| ZHAO S D, LOU Y S, ZHANG Y W, et al., 2017. Effect of silicate supply on CH4 and N2O emissions and their global warming potentials in a Chinese paddy soil under enhanced UV-B radiation[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37(14): 4715-4724. | |
| [60] | 郑有飞, 张金恩, 吴荣军, 等, 2011. UV-B辐射增强与O3胁迫对冬小麦光合特征的影响[J]. 环境科学, 32(10): 3023-3032. |
| ZHENG Y F, ZHANG J E, WU R J, et al., 2011. Combination effects of enhanced UV-B radiation and O3 stress on photosynthetic characteristics of winter wheat[J]. Environmental Science, 32(10): 3023-3032. |
| [1] | 贺晓佳, 冯书华, 蒋明, 李明锐, 湛方栋, 李元, 何永美. UV-B辐射对水稻根际土壤活性有机碳转化和产甲烷潜力的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 556-564. |
| [2] | 郝小雨, 王晓军, 高洪生, 毛明艳, 孙磊, 马星竹, 周宝库, 迟凤琴, 李伟群. 松嫩平原不同秸秆还田方式下农田温室气体排放及碳足迹估算[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 318-325. |
| [3] | 宋瑞朋, 杨起帆, 郑智恒, 习丹. 3种林下植被类型对杉木人工林土壤有机碳及其组分特征的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2283-2291. |
| [4] | 李梦丽, 徐墨馨, 陈永山, 叶丽丽, 蒋金平. 石灰性土壤添加不同量碳酸钙对秸秆有机碳矿化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 2002-2009. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
