生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (8): 1634-1641.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.08.010
李欣1,2( ), 陈小华2, 顾海蓉2, 钱晓雍2,*(
), 陈小华2, 顾海蓉2, 钱晓雍2,*( ), 沈根祥2,*(
), 沈根祥2,*( ), 赵庆节2, 白玉杰2
), 赵庆节2, 白玉杰2
收稿日期:2021-03-09
出版日期:2021-08-18
发布日期:2021-11-03
通讯作者:
沈根祥,E-mail: shengx@saes.sh.cn作者简介:李欣(1995年生),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为农田土壤健康评价。E-mail: 18862394452@163.com
基金资助:
LI Xin1,2( ), CHEN Xiaohua2, GU Hairong2, QIAN Xiaoyong2,*(
), CHEN Xiaohua2, GU Hairong2, QIAN Xiaoyong2,*( ), SHEN Genxiang2,*(
), SHEN Genxiang2,*( ), ZHAO Qingjie2, BAI Yujie2
), ZHAO Qingjie2, BAI Yujie2
Received:2021-03-09
Online:2021-08-18
Published:2021-11-03
摘要:
土壤酶是参与有机物分解和养分循环的关键成分,其活性可以用作衡量土壤健康的指标。了解土壤酶活性对农田利用方式的响应,对评价土壤健康状况、建立可持续耕作管理模式具有重要意义。为探究不同农田生产方式下农田土壤酶活性分布及主要环境影响因素,以果园、蔬菜大棚、水田3种农田利用方式为研究对象,采用野外监测和室内分析相结合的方法,探讨了农田土壤中过氧化氢酶活性(S-CAT)、脲酶活性(S-UE)、水解酶活性(FDA)、中性磷酸酶活性(S-NP)分布特征与生物和非生物因子间的响应关系。结果表明,农田土壤酶活性因耕作管理方式不同,存在较大差异(P<0.05)。土壤过氧化氢酶活性表现为蔬菜大棚<果园<水田,土壤脲酶活性表现为蔬菜大棚<水田<果园,水解酶活性在不同耕作管理方式下无显著差异(P>0.05),中性磷酸酶活性表现为水田<蔬菜大棚<果园。前3种土壤酶活性的变异系数大于16%,为中等变异,中性磷酸酶为强变异。冗余分析(RDA)表明,影响土壤酶活性的关键因子是土壤全钾TK(P=0.002)、水解性氮HN(P=0.002)、呼吸通量SR(P=0.002)、pH(P=0.008)、有效磷AP(P=0.016)、全氮TN(P=0.002)和阳离子交换量CEC(P=0.040)。在上海农田的主要耕作模式下,土壤养分、呼吸通量、pH和阳离子交换量是影响农田土壤酶活性的主要因素。因此,在对不同类型农田土壤进行土壤健康评价时,应合理选择针对性的酶活性指标。
中图分类号:
李欣, 陈小华, 顾海蓉, 钱晓雍, 沈根祥, 赵庆节, 白玉杰. 典型农田土壤酶活性分布特征及影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1634-1641.
LI Xin, CHEN Xiaohua, GU Hairong, QIAN Xiaoyong, SHEN Genxiang, ZHAO Qingjie, BAI Yujie. Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Enzyme Activities in Typical Farmland Soils[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(8): 1634-1641.
| 农田利用类型 Type of farmland use | 样地 Sample | 生产模式 Production model | 肥料投入Fertilizer input quantity | 翻耕次数 Number of tillage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 化肥 Chemical fertilizer/(kg∙hm-2) | 有机肥 Organic fertilizer/(kg∙hm-2) | ||||
| 果园 Orchard | 3 | 立架栽植 Rack cultivation | 410-1500 | 7500-28800 | 0 |
| 蔬菜大棚 Plastic shed vegetable field | 4 | 一年4—6茬 4-6 crops per year | 859-1199 | 10645-59970 | 4-6 |
| 水田 Paddy field | 3 | 水旱轮作 Water-dry rotation | 262-324 | 7496-13493 | 1 |
表1 典型农田2020年田间管理情况
Table 1 Field management of typical farmlands in 2020
| 农田利用类型 Type of farmland use | 样地 Sample | 生产模式 Production model | 肥料投入Fertilizer input quantity | 翻耕次数 Number of tillage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 化肥 Chemical fertilizer/(kg∙hm-2) | 有机肥 Organic fertilizer/(kg∙hm-2) | ||||
| 果园 Orchard | 3 | 立架栽植 Rack cultivation | 410-1500 | 7500-28800 | 0 |
| 蔬菜大棚 Plastic shed vegetable field | 4 | 一年4—6茬 4-6 crops per year | 859-1199 | 10645-59970 | 4-6 |
| 水田 Paddy field | 3 | 水旱轮作 Water-dry rotation | 262-324 | 7496-13493 | 1 |
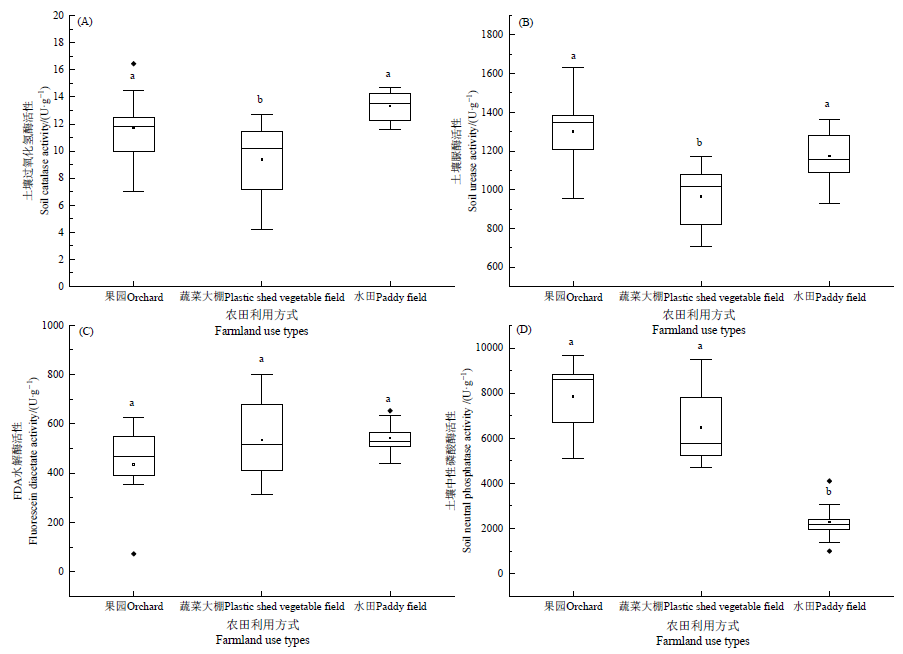
图2 典型农田利用类型的土壤酶活性分布 n=3,小写字母代表在0.05水平下有显著差异
Fig. 2 Distribution of soil enzyme activity of typical farmland use types Data (n=3), lowercase letters represent significant differences at the 0.05 level
| 项目 Item | 指标 Indicator | 单位 Unit | 果园 Orchard | 蔬菜大棚 Plastic shed vegetable field | 水田 Paddy field |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 理化性质 Physicochemical property | pH值 pH value (pH) | ‒ | 7.08±0.91b | 5.86±0.89c | 7.86±0.09a |
| 有机质 Soil organic matter (SOM) | g∙kg-1 | 35.8±15.3b | 48.4±16.6a | 24.4±1.8b | |
| 阳离子交换量 Cation exchange capacity (CEC) | cmol(+)∙kg-1 | 17.8±3.9a | 17.8±2.7a | 12.8±0.5b | |
| 全盐量 Total salt content (TS) | g∙kg-1 | 3.72±5.14a | 3.17±2.29ab | 0.52±0.14b | |
| 全磷 Total phosphorus (TP) | g∙kg-1 | 2.00±1.27a | 2.31±0.36a | 0.79±0.10b | |
| 有效磷 Available phosphorus (AP) | mg∙kg-1 | 320±261a | 310±79a | 23±11b | |
| 总氮 Total nitrogen (TN) | g∙kg-1 | 2.5±0.9b | 3.27±0.97a | 1.41±0.12c | |
| 水解性氮 Hydrolysable nitrogen (HN) | mg∙kg-1 | 445±464a | 418±163a | 99±5b | |
| 全钾 Total potassium (TK) | g∙kg-1 | 18.3±1.1a | 17.7±0.7a | 15.4±0.4b | |
| 速效钾Available potassium (AK) | mg∙kg-1 | 625±431a | 618±375a | 105±16b | |
| 粘粒质量分数 w(<0.002mm, clay) | % | 28.7±0.61a | 24.2±0.65a | 24.3±1.0a | |
| 生物特性 Biological characteristic | 呼吸通量 Soil respiration efflux (SR) | mg∙m-2∙h-1 | 1.59±0.5b | 3.70±1.68a | 2.05±0.71b |
| 孔平均颜色变化率 Average well color development (AWCD) | ‒ | 0.33±0.08b | 0.41±0.07b | 0.56±0.61a |
表2 不同农田利用类型环境因子的多重比较
Table 2 Multiple comparisons of environmental factors of different farmland use types
| 项目 Item | 指标 Indicator | 单位 Unit | 果园 Orchard | 蔬菜大棚 Plastic shed vegetable field | 水田 Paddy field |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 理化性质 Physicochemical property | pH值 pH value (pH) | ‒ | 7.08±0.91b | 5.86±0.89c | 7.86±0.09a |
| 有机质 Soil organic matter (SOM) | g∙kg-1 | 35.8±15.3b | 48.4±16.6a | 24.4±1.8b | |
| 阳离子交换量 Cation exchange capacity (CEC) | cmol(+)∙kg-1 | 17.8±3.9a | 17.8±2.7a | 12.8±0.5b | |
| 全盐量 Total salt content (TS) | g∙kg-1 | 3.72±5.14a | 3.17±2.29ab | 0.52±0.14b | |
| 全磷 Total phosphorus (TP) | g∙kg-1 | 2.00±1.27a | 2.31±0.36a | 0.79±0.10b | |
| 有效磷 Available phosphorus (AP) | mg∙kg-1 | 320±261a | 310±79a | 23±11b | |
| 总氮 Total nitrogen (TN) | g∙kg-1 | 2.5±0.9b | 3.27±0.97a | 1.41±0.12c | |
| 水解性氮 Hydrolysable nitrogen (HN) | mg∙kg-1 | 445±464a | 418±163a | 99±5b | |
| 全钾 Total potassium (TK) | g∙kg-1 | 18.3±1.1a | 17.7±0.7a | 15.4±0.4b | |
| 速效钾Available potassium (AK) | mg∙kg-1 | 625±431a | 618±375a | 105±16b | |
| 粘粒质量分数 w(<0.002mm, clay) | % | 28.7±0.61a | 24.2±0.65a | 24.3±1.0a | |
| 生物特性 Biological characteristic | 呼吸通量 Soil respiration efflux (SR) | mg∙m-2∙h-1 | 1.59±0.5b | 3.70±1.68a | 2.05±0.71b |
| 孔平均颜色变化率 Average well color development (AWCD) | ‒ | 0.33±0.08b | 0.41±0.07b | 0.56±0.61a |
| 排序轴Axis | 第Ⅰ轴Axis 1 | 第Ⅱ轴Axis 2 | 第Ⅲ轴Axis 3 | 第Ⅳ轴Axis 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤酶活性特征解释量 Soil enzyme activities eigenvalues/% | 50.7 | 20.4 | 7.5 | 1.6 |
| 土壤酶活性特征与环境因子相关性 Enzymes-environmental factors correlations | 0.924 | 0.904 | 0.805 | 0.636 |
| 土壤酶活性特征累计解释量 Cumulative explained amount of soil enzyme activity characteristics/% | 50.7 | 71.1 | 78.6 | 80.2 |
| 土壤酶活性特征-环境因子关系累计解释量 Cumulative percentage variance of enzymes-environmental factors/% | 63.1 | 88.6 | 98.0 | 100.0 |
| 典范特征值 Sum of all eigenvalues | 1.000 | |||
| 总特征值 Sum of all canonical eigenvalues | 0.802 | |||
表3 土壤酶活性特征值与解释量的RDA排序分析
Table 3 Redundancy analysis of the characteristic values of soil enzyme activity and the amount of explanation
| 排序轴Axis | 第Ⅰ轴Axis 1 | 第Ⅱ轴Axis 2 | 第Ⅲ轴Axis 3 | 第Ⅳ轴Axis 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤酶活性特征解释量 Soil enzyme activities eigenvalues/% | 50.7 | 20.4 | 7.5 | 1.6 |
| 土壤酶活性特征与环境因子相关性 Enzymes-environmental factors correlations | 0.924 | 0.904 | 0.805 | 0.636 |
| 土壤酶活性特征累计解释量 Cumulative explained amount of soil enzyme activity characteristics/% | 50.7 | 71.1 | 78.6 | 80.2 |
| 土壤酶活性特征-环境因子关系累计解释量 Cumulative percentage variance of enzymes-environmental factors/% | 63.1 | 88.6 | 98.0 | 100.0 |
| 典范特征值 Sum of all eigenvalues | 1.000 | |||
| 总特征值 Sum of all canonical eigenvalues | 0.802 | |||
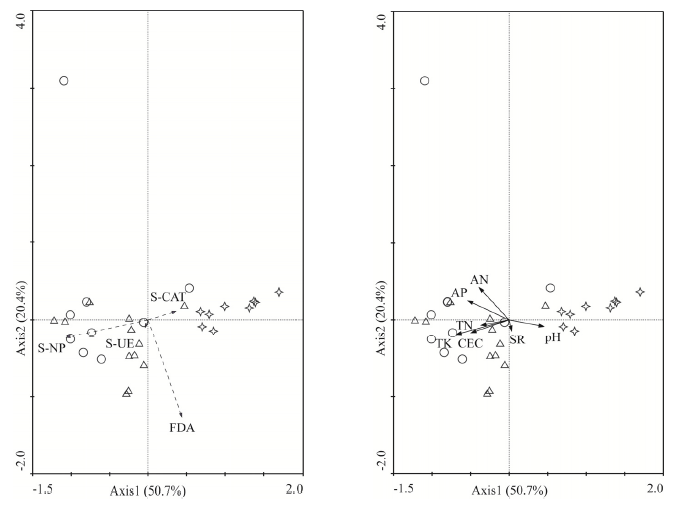
图4 土壤样方分布与酶活性关系/环境因子的RDA排序 图中空白圆圈表示果园,三角形代表蔬菜大棚,星形代表水田,n=3
Fig. 4 RDA ranking of soil sample distribution and enzyme activity/environmental factors Blank circles in the figure represent orchards, triangles represent plastic shed vegetable fields, stars represent paddy fields, n=3
| [1] |
ANANBEH H, STOJANOVIĆ M, POMPEIANO A, et al., 2019. Use of soil enzyme activities to assess the recovery of soil functions in abandoned coppice forest systems[J]. Science of The Total Environment, DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133692.
DOI |
| [2] |
BAI X J, ZENG Q C, FAKHER A, et al., 2018. Characteristics of soil enzyme activities and microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen under different vegetation zones on the Loess Plateau, China[J]. Arid Land Research And Management, 32(4): 438-454.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
CHANG F, JIA F G, LV R, et al., 2021. Soil bacterial communities reflect changes in soil properties during the tillage years of newly created farmland on the Loess Plateau[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, DOI: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2020.103853.
DOI |
| [4] |
FISHER K A, YARWOOD S A, JAMES B R, 2017. Soil urease activity and bacterial ureC gene copy numbers: Effect of pH[J]. Geoderma, 285: 1-8.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
FLOCH C, CAPOWIEZ Y, CRIQUET S, 2009. Enzyme activities in apple orchard agroecosystems: How are they affected by management strategy and soil properties[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 41(1): 61-68.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
GOHARA D W, DI CERA E, 2016. Molecular Mechanisms of Enzyme Activation by Monovalent Cations[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 291(40): 20840-20848.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
GOMEZ E J, DELGADO J A, GONZALEZ J M, 2020. Environmental factors affect the response of microbial extracellular enzyme activity in soils when determined as a function of water availability and temperature[J]. Ecology And Evolution, 10(18): 10105-10115.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
JING X, YANG X X, REN F, et al., 2016. Neutral effect of nitrogen addition and negative effect of phosphorus addition on topsoil extracellular enzymatic activities in an alpine grassland ecosystem[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 107: 205-213.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
KELTING D L, BURGER J A, EDWARDS G S, 1998. Estimating root respiration, microbial respiration in the rhizosphere, and root-free soil respiration in forest soils[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 30(7): 961-968.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
LI T, BU Z J, LIU W Y, et al., 2019. Weakening of the ‘enzymatic latch’ mechanism following long-term fertilization in a minerotrophic peatland[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, DOI: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2019.107528.
DOI |
| [11] |
LIU G L, ZHANG L C, ZHANG Q, et al., 2015. The response of grain production to changes in quantity and quality of cropland in Yangtze River Delta, China[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 95(3): 480-489.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
LUO L, MENG H, GU J D, 2017. Microbial extracellular enzymes in biogeochemical cycling of ecosystems[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 197: 539-549.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
PAUSCH J, KUZYAKOV Y, 2018. Carbon input by roots into the soil: Quantification of rhizodeposition from root to ecosystem scale[J]. Global Change Biology, 24(1): 1-12.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
SALAZAR S, SANCHEZ L E, ALVAREZ J, et al., 2011. Correlation among soil enzyme activities under different forest system management practices[J]. Ecological Engineering, 37(8): 1123-1131.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
SINGH K, 2016. Microbial and Enzyme Activities of Saline and Sodic Soils[J]. Land Degradation & Development, 27(3): 706-718.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
SONG Z Z, MA R J, YU M L, 2015. Genome-wide analysis and identification of KT/HAK/KUP potassium transporter gene family in peach (Prunus persica)[J]. Genetics and Molecular Research, 14(1): 774-787.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
TAN X P, NIE Y X, MA X M, et al., 2021. Soil chemical properties rather than the abundance of active and potentially active microorganisms control soil enzyme kinetics[J]. Science of The Total Environment, DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144500.
DOI |
| [18] |
XU H W, QU Q, CHEN Y H, et al., 2021. Responses of soil enzyme activity and soil organic carbon stability over time after cropland abandonment in different vegetation zones of the Loess Plateau of China[J]. Catena, DOI: 10.1016/j.catena.2020.104812.
DOI |
| [19] |
XU M, SHANG H, 2016. Contribution of soil respiration to the global carbon equation[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 203: 16-28.
DOI URL |
| [20] | 陈林生, 鲍鑫培, 2019. 现代都市农业背景下农业产业融合水平测度及评价研究--以上海为例[J]. 经济问题 (12): 89-95. |
| CHEN L S, BAO X P, 2019. Research on measurement and evaluation of shanghai agricultural industry integration level under the background of modern urban agriculture[J]. On Economic Problems (12): 89-95. | |
| [21] | 贡璐, 张雪妮, 冉启洋, 2015. 基于最小数据集的塔里木河上游绿洲土壤质量评价[J]. 土壤学报, 52(3): 682-689. |
| GONG L, ZHANG X N, RAN Q Y, 2015. Quality assessment of oasis soil in the upper reaches of Tarim river based on minimum data set[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 52(3): 682-689. | |
| [22] | 关松荫, 张德生, 张志明, 1986. 土壤酶及其研究法[M]. 北京: 农业出版社. |
| GUAN S Y, ZHANG D S, ZHANG Z M, 1986. Soil enzyme and its research methods[M]. Beijing: Agricultural Press. | |
| [23] | 管孝艳, 王少丽, 高占义, 等, 2012. 盐渍化灌区土壤盐分的时空变异特征及其与地下水埋深的关系[J]. 生态学报, 32(4): 198-206. |
|
GUAN X Y, WANG S L, GAO Z Y, et al., 2012. Spatio-temporal variability of soil salinity and its relationship with the depth to groundwater in salinization irrigation district[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32(4): 198-206.
DOI URL |
|
| [24] | 郭鹏飞, 葛新伟, 王锐, 等, 2020. 有机肥对酿酒葡萄土壤微生物、酶活性及产量的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 38(3): 145-154. |
| GUO P F, GE X W, WANG R, et al., 2020. Effects of organic manure on soil microbial community, enzyme activity and yield of wine grape[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 38(3): 145-154. | |
| [25] | 胡尧, 李懿, 侯雨乐, 2018. 岷江流域不同土地利用方式对土壤有机碳组分及酶活性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 27(9): 1617-1624. |
| HU Y, LI Y, HOU Y L, 2018. The variation of soil organic carbon fractions and soil enzyme activity of different land use types in minjiang river valley[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 27(9): 1617-1624. | |
| [26] | 李琦, 裴怀弟, 马忠明, 等, 2020. 钾肥与有机肥配施对食用百合根际土壤酶活性、养分含量及鳞茎产量的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料 (1): 91-99. |
| LI Q, PEI H D, MA Z M, et al., 2020. Effects of potassium fertilizer and organic fertilizer on rhizosphere soil enzyme activity, nutrient content and bulb yield of Lily[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China (1): 91-99. | |
| [27] | 刘爽, 王雅, 刘兵兵, 等, 2019. 晋西北不同土地管理方式对土壤碳氮、酶活性及微生物的影响[J]. 生态学报, 39(12): 4376-4389. |
| LIU S, WANG Y, LIU B B, et al., 2019. Effects of different land management practices on soil carbon and nitrogen, enzyme activities, and microbial diversities northwest of Shanxi[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(12): 4376-4389. | |
| [28] | 鲁如坤, 2000. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社. |
| LU R K, 2000. Methods for agricultural chemical analysis of soil[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press. | |
| [29] | 王文锋, 李春花, 黄绍文, 等, 2016. 不同施肥模式对设施秋冬茬芹菜生育期间土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 22(3): 676-686. |
| WANG W F, LI C H, HUANG S W, et al., 2016. Effects of different fertilization patterns on soil enzyme activities during growing period of autumn-winter season celery in greenhouse[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 22(3): 676-686. | |
| [30] | 杨东伟, 章明奎, 刘千千, 等, 2019. 土壤理化性质和微生物活性对水田改果园的动态响应[J]. 水土保持通报, 39(2): 48-55. |
| YANG D W, ZHANG M K, LIU Q Q, et al., 2019. Response of soil physicochemical properties and microbial activity on land-use conversion from paddy field to orchard farm[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 39(2): 48-55. | |
| [31] | 杨敏, 李岩, 王红斌, 等, 2008. 除草剂草甘膦对土壤过氧化氢酶活性的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 39(6): 1380-1383. |
| YANG M, LI Y, WANG H B, et al., 2008. Effects of glyphosate on catalase activities in soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 39(6): 1380-1383. | |
| [32] | 张华勇, 尹睿, 黄锦法, 等, 2005. 稻麦轮作田改为菜地后生化指标的变化[J]. 土壤, 37(2): 182-186. |
| ZHANG H Y, YIN R, HUANG J F, et al., 2005. Changes in soil biochemical properties caused by cropping system alteration from rice-wheat rotation to vegetable cultivation[J]. Soils, 37(2): 182-186. | |
| [33] | 张静, 高云华, 张池, 等, 2013. 不同土地利用方式下赤红壤生物学性状及其与土壤肥力的关系[J]. 应用生态学报, 24(12): 3423-3430. |
| ZHANG J, GAO Y H, ZHANG C, et al., 2013. Biological properties of lateritic red soil and their relationships with soil fertility in southern China under different land use types[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 24(12): 3423-3430. | |
| [34] | 张文学, 王少先, 夏文建, 等, 2019. 脲酶抑制剂与硝化抑制剂对稻田土壤硝化, 反硝化功能菌的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 25(6): 897-909. |
| ZHANG W X, WANG S X, XIA W J, et al., 2019. Effects of urease inhibitor and nitrification inhibitor on functional nitrifier and denitrifier in paddy soil[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 25(6): 897-909. | |
| [35] | 赵海燕, 徐福利, 王渭玲, 等, 2015. 秦岭地区华北落叶松人工林地土壤养分和酶活性变化[J]. 生态学报, 35(4): 1086-1094. |
| ZHAO H Y, XU F L, WANG W L, et al., 2015. Soil nutrients and enzyme activities in Larix principis-rupprechtii plantations in the Qinling Mountains, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35(4): 1086-1094. | |
| [36] | 钟泽坤, 杨改河, 任成杰, 等, 2021. 黄土丘陵区撂荒农田土壤酶活性及酶化学计量变化特征[J]. 环境科学, 42(1): 411-421. |
| ZHONG Z K, YANG G H, REN C J, et al., 2021. Effects of farmland abandonment on soil enzymatic activity and enzymatic stoichiometry in the Loess Hilly Region, China[J]. Environmental Science, 42(1): 411-421. | |
| [37] | 周际海, 郜茹茹, 魏倩, 等, 2020. 旱地红壤不同土地利用方式对土壤酶活性及微生物多样性的影响差异[J]. 水土保持学报, 34(1): 327-332. |
| ZHOU J H, GAO R R, WEI Q, et al., 2020. Effects of different land use patterns on enzyme activities and microbial diversity in upland red soil[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 34(1): 327-332. | |
| [38] | 朱英, 沈根祥, 钱晓雍, 等, 2015. 上海市郊不同耕地类型土壤微生物活性研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 38(1): 15-18. |
| ZHU Y, SHEN G X, QIAN X Y, et al., 2015. Study on soil microbial activity of different types of farmland in Shanghai suburban areas[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 38(1): 15-18. |
| [1] | 张露, 何雨霏, 陈坦, 杨婷, 张冰, 金军. 2011—2020年汾渭平原农田生态系统碳足迹的时空格局演变[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1149-1162. |
| [2] | 杨耀东, 陈玉梅, 涂鹏飞, 曾清如. 经济作物轮作模式下镉污染农田修复潜力[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 627-634. |
| [3] | 盛美君, 李胜君, 杨昕玥, 王蕊, 李洁, 李刚, 修伟明. 华北潮土农田土壤酶活性对土地利用强度的响应特征探讨[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 299-308. |
| [4] | 张贝儿, 吴建强, 王敏, 熊丽君, 谭娟, 沈城, 黄波涛, 黄沈发. 耕地生态保育工程的土壤健康度评价方法初探[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 388-396. |
| [5] | 肖国举, 李秀静, 郭占强, 胡延斌, 王静. 贺兰山东麓土壤有机碳对玉米生长发育及水分利用的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1754-1764. |
| [6] | 郝贝贝, 王楠, 吴昊平, 周智鑫, 张思毅, 贺斌. 生态沟渠对珠三角稻田径流污染的削减功能研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1856-1864. |
| [7] | 李秀华, 赵玲, 滕应, 骆永明, 黄标, 刘冲, 刘本乐, 赵其国. 贵州汞矿区周边农田土壤汞镉复合污染特征空间分布及风险评估[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1629-1636. |
| [8] | 周椿富, 于锐, 王翔, 闯绍闯, 杨洪杏, 谢越. 抗生素对不同土壤中酶活性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2234-2241. |
| [9] | 刘畅, 罗艳丽, 刘晨通, 郑玉红, 晁博, 董乐乐. 奎屯河下游区域地下水和农田土壤砷的空间分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 2070-2078. |
| [10] | 王飞, 赵颖. 太原市污灌区农田土壤中多环芳烃污染特征及生态风险评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 160-169. |
| [11] | 李春环, 王攀, 韩翠, 许艺馨, 黄菊莹. 硫氮沉降下西北荒漠煤矿区周边土壤性质的变化特点[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 170-180. |
| [12] | 王瑞, 宋祥云, 柳新伟. 黄河三角洲不同植被类型土壤酶活性的季节变化[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 62-69. |
| [13] | 邹旭东, 蔡福, 李荣平, 米娜, 赵胡笳, 王笑影, 张云海, 汪宏宇, 贾庆宇. 玉米农田水热通量及能量变化研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1642-1653. |
| [14] | 梁姗姗, 王建佳, 黄锦树, 陈彬, 刘文华, 郑新庆, 胡文佳. 近岸多源环境因素影响下珊瑚群落的生态脆弱性评价研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(12): 2360-2369. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
