生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (10): 2010-2025.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.10.008
收稿日期:2021-04-30
出版日期:2021-10-18
发布日期:2021-12-21
通讯作者:
* 方锋(1977年生),高级工程师。E-mail: fangfeng0802@126.com作者简介:王静(1978年生),女,副研究员,博士,主要从事农业灾害风险评估工作。E-mail: wangjing1102@126.com
基金资助:
WANG Jing1( ), FANG Feng2,*(
), FANG Feng2,*( ), WANG Ying1
), WANG Ying1
Received:2021-04-30
Online:2021-10-18
Published:2021-12-21
摘要:
利用历史统计资料,以西南和华南5个省份/自治区[四川、云南、贵州、广东省和广西壮族自治区 (简称“广西”)]为代表区,探讨了多种粮食作物播种面积的时序变化特征,并分析了其变化的影响因素。结果表明,广东、广西和四川粮食播种面积逐渐减少,相较上世纪50年代,近10年分别减少了62.0%、13.9%和36.1%,贵州和云南省粮食播种面积则扩大明显,近10年分别扩大了41.4%和49.2%。其次,广东冬小麦、玉米和马铃薯播种面积呈增加趋势;广西稻谷、早稻、冬小麦、谷子、高粱和大豆播种面积呈先增后减趋势,玉米和马铃薯播种面积波动增加;四川冬小麦播种面积也呈先增后减趋势,玉米、豆类和薯类播种面积较为稳定,贵州谷物、稻谷、玉米、早稻、双季晚稻和豆类播种面积保持稳定,冬小麦播种面积呈先增后减趋势,高粱、大豆、薯类和马铃薯播种面积则持续增加,云南谷物、稻谷、豆类播种面积变化不大,双季晚稻和冬小麦播种面积呈先增后减趋势,玉米、谷子、大豆、薯类和马铃薯播种面积总体呈波动增加趋势。除此之外,各省/自治区其他粮食作物品种播种面积则呈逐渐减少趋势。分析了各粮食作物播种面积变化影响因素的效应,发现大多数影响因素与播种面积变化都有显著相关性,但具体到省份/自治区、作物品种,不同的因素效应不同。总体而言,社会经济因素中人口数量指标,以及个别农业技术指标对西南和华南粮食作物播种面积变化有重要影响。
中图分类号:
王静, 方锋, 王莺. 中国西南和华南粮食作物播种面积时序变化特征及其影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(10): 2010-2025.
WANG Jing, FANG Feng, WANG Ying. Temporal Variation Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Sown Area Variation of Grain Crops in Southwest and South China[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(10): 2010-2025.
| 农作物类型 Crop types | 粮食作物类型 Grain crop types | 谷物作物类型 Cereal crop types | 作物 Crop |
|---|---|---|---|
| 粮食作物 Grain crop (夏收作物 summer grain crop; 秋收作物 autumn grain crop) (1949-2018) | 谷物 Cereal crop (1991-2018) | 稻谷 Rice (1949-2018) | 早稻 Early rice (1949-2018) |
| 中稻和一季晚稻 Middle season rice and one season late rice (1980-2018) | |||
| 双季晚稻 Double cropping late rice (1980-2018) | |||
| 小麦 Wheat (1949-2018) | 冬小麦 Winter wheat (1949-2018) | ||
| 玉米 Maize (1949-2018) | 玉米 Maize (1949-2018) | ||
| 谷子 Millet (1970-2018) | 谷子 Millet (1970-2018) | ||
| 高粱 Sorghum (1970-2018) | 高粱 Sorghum (1970-2018) | ||
| 豆类 Beans crop (1991-2018) | 大豆 Soybean (1949-2018) | ||
| 薯类 Tuber crop (1949-2018) | 马铃薯 Potato (1982-2018) |
表1 待分析的粮食作物
Table 1 The analyzed grain crops
| 农作物类型 Crop types | 粮食作物类型 Grain crop types | 谷物作物类型 Cereal crop types | 作物 Crop |
|---|---|---|---|
| 粮食作物 Grain crop (夏收作物 summer grain crop; 秋收作物 autumn grain crop) (1949-2018) | 谷物 Cereal crop (1991-2018) | 稻谷 Rice (1949-2018) | 早稻 Early rice (1949-2018) |
| 中稻和一季晚稻 Middle season rice and one season late rice (1980-2018) | |||
| 双季晚稻 Double cropping late rice (1980-2018) | |||
| 小麦 Wheat (1949-2018) | 冬小麦 Winter wheat (1949-2018) | ||
| 玉米 Maize (1949-2018) | 玉米 Maize (1949-2018) | ||
| 谷子 Millet (1970-2018) | 谷子 Millet (1970-2018) | ||
| 高粱 Sorghum (1970-2018) | 高粱 Sorghum (1970-2018) | ||
| 豆类 Beans crop (1991-2018) | 大豆 Soybean (1949-2018) | ||
| 薯类 Tuber crop (1949-2018) | 马铃薯 Potato (1982-2018) |
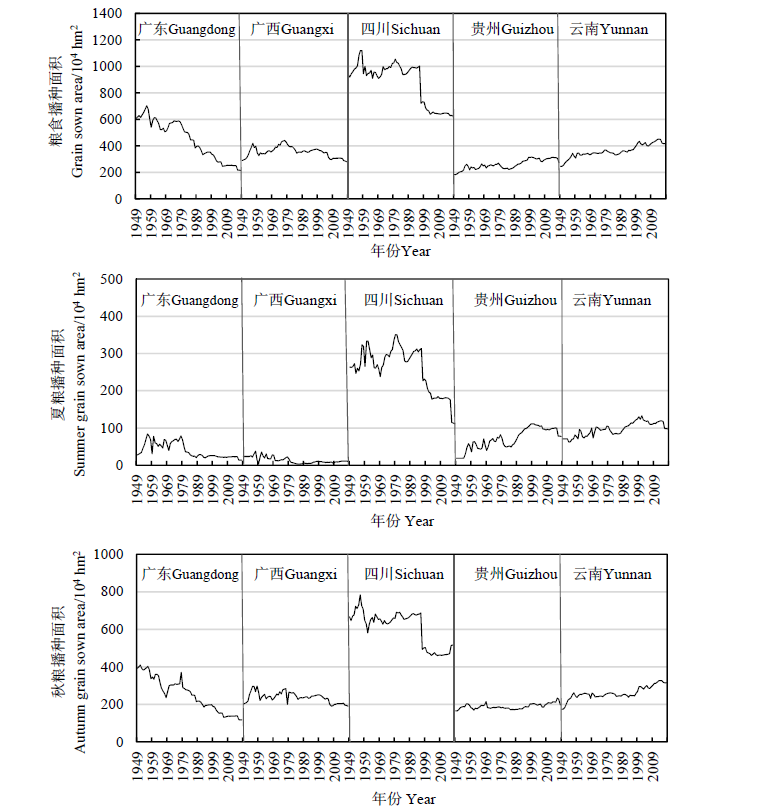
图3 中国西南和华南粮食、夏粮和秋粮播种面积时序变化特征
Fig. 3 Temporal variation characteristics of sown area for grain, summer grain and autumn grain in Southwest and South China
| 指标Index | 农作物 Crop | 粮食 Grain | 夏粮 Summer grain | 秋粮Autumn grain | 谷物 Cereal | 稻谷 Rice | 早稻 Early rice | 中稻和一季晚稻 Middle season rice and one season late rice | 双季晚稻 Double cropping late rice | 小麦Wheat | 冬小麦Winter wheat | 玉米Maize | 谷子Millet | 高粱Sorghum | 豆类Beans | 大豆Soybean | 薯类Tubers | 马铃薯Potato |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | -0.90** | -0.94** | -0.59** | -0.93** | -0.96** | -0.95** | -0.94** | -0.64** | -0.95** | -0.61** | -0.60** | 0.86** | -0.61** | -0.80** | -0.94** | -0.98** | -0.93** | 0.77** |
| X2 | 0.85** | 0.91** | 0.51** | 0.88** | 0.86** | 0.94** | 0.92** | 0.67** | 0.94** | 0.60** | 0.59** | -.92** | 0.56** | 0.79** | 0.67** | 0.88** | 0.84** | -0.79** |
| X3 | 0.84** | 0.91** | 0.52** | 0.88** | 0.85** | 0.93** | 0.91** | 0.64** | 0.93** | 0.62** | 0.61** | -0.91** | 0.58** | 0.79** | 0.66** | 0.87** | 0.83** | -0.78** |
| X4 | 0.76** | 0.79** | 0.54** | 0.77** | 0.59** | 0.79** | 0.79** | 0.56** | 0.78** | 0.50** | 0.50** | -0.61** | 0.57** | 0.68** | 0.78** | 0.87** | 0.75** | -0.68** |
| X5 | -0.90** | -0.92** | -0.58** | -0.91** | -0.93** | -0.92** | -0.91** | -0.59** | -0.92** | -0.58** | -0.56** | 0.78** | -0.61** | -0.78** | -0.98** | -0.98** | -0.92** | 0.67** |
| X6 | -0.88** | -0.91** | -0.58** | -0.91** | -0.93** | -0.91** | -0.90** | -0.59** | -0.91** | -0.57** | -0.57** | 0.80** | -0.59** | -0.76** | -0.97** | -0.98** | -0.93** | 0.70** |
| X7 | -0.78** | -0.80** | -0.45** | -0.79** | -0.93** | -0.79** | -0.81** | -0.49** | -0.80** | -0.44** | -0.40* | 0.69** | -0.45** | -0.62** | -0.99** | -0.95** | -0.86** | 0.55** |
| X8 | -0.84** | -0.87** | -0.55** | -0.86** | -0.75** | -0.89** | -0.87** | -0.61** | -0.88** | -0.59** | -0.58** | 0.83** | -0.64** | -0.79** | -0.83** | -0.93** | -0.84** | 0.71** |
| X9 | -0.82** | -0.85** | -0.41** | -0.83** | -0.88** | -0.87** | -0.89** | -0.65** | -0.90** | -0.48** | -0.45** | 0.88** | -0.48** | -0.68** | -0.74** | -0.90** | -0.84** | 0.66** |
| X10 | -0.68** | -0.73** | -0.41** | -0.71** | -0.23 | -0.75** | -0.74** | -0.61** | -0.74** | -0.45** | -0.44** | 0.67** | -0.45** | -0.63** | 0.09 | -0.59** | -0.67** | 0.69** |
| X11 | -0.71** | -0.73** | -0.43** | -0.72** | -0.82** | -0.72** | -0.74** | -0.43** | -0.72** | -0.39* | -0.37* | 0.60** | -0.40** | -0.56** | -0.94** | -0.89** | -0.80** | 0.55** |
| X12 | -0.76** | -0.79** | -0.41* | -0.77** | -0.90** | -0.78** | -0.81** | -0.45** | -0.80** | -0.41* | -0.37* | 0.67** | -0.39* | -0.62** | -0.99** | -0.96** | -0.84** | 0.55** |
| X13 | -0.67** | -0.69** | -0.41** | -0.68** | -0.79** | -0.67** | -0.70** | -0.40* | -0.68** | -0.36* | -0.34* | 0.55** | -0.37* | -0.52** | -0.92** | -0.86** | -0.77** | 0.52** |
| X14 | -0.73** | -0.75** | -0.44** | -0.74** | -0.85** | -0.74** | -0.76** | -0.45** | -0.75** | -0.40** | -0.38* | 0.62** | -0.42** | -0.57** | -0.96** | -0.91** | -0.82** | 0.55** |
| X15 | -0.74** | -0.76** | -0.44** | -0.75** | -0.87** | -0.76** | -0.78** | -0.47** | -0.76** | -0.41** | -0.38* | 0.64** | -0.43** | -0.59** | -0.98** | -0.93** | -0.82** | 0.56** |
| X16 | -0.81** | -0.84** | -0.51** | -0.83** | -0.86** | -0.84** | -0.85** | -0.55** | -0.84** | -0.49** | -0.49** | 0.73** | -0.52** | -0.68** | -0.96** | -0.96** | -0.87** | 0.67** |
| X17 | 0.54** | 0.57** | 0.54** | 0.55** | -0.42* | 0.59** | 0.51** | 0.44** | 0.49** | 0.56** | 0.59** | -0.41** | 0.60** | 0.63** | -0.69** | 0.28 | 0.43** | -0.47** |
| X18 | -0.92** | -0.95** | -0.64** | -0.94** | -0.92** | -0.95** | -0.93** | -0.61** | -0.95** | -0.65** | -0.64** | 0.82** | -0.70** | -0.85** | -0.97** | -0.98** | -0.93** | 0.76** |
| X19 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.17 | 0.03 | -0.72** | 0.05 | -0.02 | 0.14 | -0.04 | 0.19 | 0.24 | 0.03 | 0.23 | 0.18 | -0.92** | -0.30 | -0.09 | -0.09 |
| X20 | -0.81** | -0.82** | -0.79** | -0.81** | 0.39* | -0.82** | -0.72** | -0.50** | -0.78** | -0.78** | -0.78** | 0.58** | -0.89** | -0.91** | 0.28 | -0.62** | -0.71** | 0.74** |
| X21 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.26 | 0.03 | -0.69** | 0.06 | -0.01 | 0.17 | -0.11 | 0.30 | 0.38* | 0.01 | 0.31* | 0.24 | -0.87** | -0.28 | -0.09 | 0.04 |
| X22 | -0.85** | -0.89** | -0.64** | -0.87** | -0.47* | -0.89** | -0.85** | -0.59** | -0.88** | -0.64** | -0.64** | 0.70** | -0.74** | -0.86** | -0.68** | -0.84** | -0.83** | 0.80** |
| X23 | -0.92** | -0.95** | -0.59** | -0.94** | -0.94** | -0.96** | -0.94** | -0.65** | -0.96** | -0.62** | -0.60** | 0.86** | -0.65** | -0.82** | -0.85** | -0.95** | -0.94** | 0.74** |
| X24 | -0.94** | -0.97** | -0.69** | -0.96** | -0.89** | -0.96** | -0.90** | -0.58** | -0.96** | -0.71** | -0.69** | 0.75** | -0.73** | -0.91** | -0.96** | -0.94** | -0.91** | 0.77** |
| X25 | -0.83** | -0.86** | -0.49** | -0.85** | -0.96** | -0.86** | -0.87** | -0.56** | -0.87** | -0.49** | -0.47** | 0.77** | -0.49** | -0.68** | -0.97** | -0.97** | -0.90** | 0.63** |
| X26 | 0.30 | 0.33* | 0.44** | 0.33* | -0.08 | 0.33* | 0.23 | 0.19 | 0.16 | 0.55** | 0.59** | -0.39* | 0.50** | 0.39* | -0.32 | 0.12 | 0.22 | -0.08 |
| X27 | -0.72** | -0.74** | -0.43** | -0.73** | -0.82** | -0.74** | -0.75** | -0.44** | -0.74** | -0.42** | -0.38* | 0.67** | -0.44** | -0.59** | -0.95** | -0.91** | -0.80** | 0.53** |
| X28 | 0.50** | 0.48** | 0.37* | 0.52** | 0.59** | 0.47** | 0.38* | 0.21 | 0.42** | 0.40** | 0.36* | -0.51** | 0.39* | 0.42** | 0.63** | 0.54** | 0.54** | -0.33* |
| X29 | 0.28 | 0.31 | 0.04 | 0.30 | 0.40* | 0.33* | 0.38* | 0.22 | 0.41* | 0.07 | 0.07 | -0.38* | 0.04 | 0.15 | 0.41* | 0.41* | 0.31 | -0.32 |
| X30 | 0.43** | 0.44** | 0.12 | 0.43** | 0.53** | 0.46** | 0.49** | 0.34* | 0.48** | 0.16 | 0.11 | -0.58** | 0.18 | 0.37* | 0.51** | 0.54** | 0.50** | -0.46** |
| X31 | 0.68** | 0.65** | 0.78** | 0.73** | 0.70** | 0.61** | 0.37* | 0.60** | 0.69** | 0.82** | 0.81** | -0.49** | 0.81** | 0.69** | 0.51** | 0.49** | 0.61** | -0.56** |
| X32 | 0.30 | 0.25 | 0.22 | 0.32* | 0.56** | 0.23 | 0.13 | 0.08 | 0.18 | 0.25 | 0.20 | -0.31* | 0.21 | 0.20 | 0.61** | 0.34* | 0.35* | -0.2 |
| X33 | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.03 | 0.15 | 0.35 | 0.16 | 0.19 | 0.07 | 0.19 | 0.06 | 0.06 | -0.22 | -0.03 | 0.02 | 0.39* | 0.25 | 0.18 | -0.16 |
| X34 | 0.33* | 0.32* | 0.04 | 0.33* | 0.55** | 0.33* | 0.36* | 0.26 | 0.36* | 0.09 | 0.05 | -0.51** | 0.08 | 0.25 | 0.53** | 0.44** | 0.42** | -0.37* |
| X35 | 0.57** | 0.52** | 0.67** | 0.62** | 0.73** | 0.49** | 0.23 | 0.63** | 0.56** | 0.71** | 0.70** | -0.38* | 0.69** | 0.55** | 0.54** | 0.39* | 0.50** | -0.45** |
表2 广东省粮食作物播种面积和影响因素的相关性分析
Table 2 Correlation analysis of sown area and influencing factors of grain crops in Guangdong Province
| 指标Index | 农作物 Crop | 粮食 Grain | 夏粮 Summer grain | 秋粮Autumn grain | 谷物 Cereal | 稻谷 Rice | 早稻 Early rice | 中稻和一季晚稻 Middle season rice and one season late rice | 双季晚稻 Double cropping late rice | 小麦Wheat | 冬小麦Winter wheat | 玉米Maize | 谷子Millet | 高粱Sorghum | 豆类Beans | 大豆Soybean | 薯类Tubers | 马铃薯Potato |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | -0.90** | -0.94** | -0.59** | -0.93** | -0.96** | -0.95** | -0.94** | -0.64** | -0.95** | -0.61** | -0.60** | 0.86** | -0.61** | -0.80** | -0.94** | -0.98** | -0.93** | 0.77** |
| X2 | 0.85** | 0.91** | 0.51** | 0.88** | 0.86** | 0.94** | 0.92** | 0.67** | 0.94** | 0.60** | 0.59** | -.92** | 0.56** | 0.79** | 0.67** | 0.88** | 0.84** | -0.79** |
| X3 | 0.84** | 0.91** | 0.52** | 0.88** | 0.85** | 0.93** | 0.91** | 0.64** | 0.93** | 0.62** | 0.61** | -0.91** | 0.58** | 0.79** | 0.66** | 0.87** | 0.83** | -0.78** |
| X4 | 0.76** | 0.79** | 0.54** | 0.77** | 0.59** | 0.79** | 0.79** | 0.56** | 0.78** | 0.50** | 0.50** | -0.61** | 0.57** | 0.68** | 0.78** | 0.87** | 0.75** | -0.68** |
| X5 | -0.90** | -0.92** | -0.58** | -0.91** | -0.93** | -0.92** | -0.91** | -0.59** | -0.92** | -0.58** | -0.56** | 0.78** | -0.61** | -0.78** | -0.98** | -0.98** | -0.92** | 0.67** |
| X6 | -0.88** | -0.91** | -0.58** | -0.91** | -0.93** | -0.91** | -0.90** | -0.59** | -0.91** | -0.57** | -0.57** | 0.80** | -0.59** | -0.76** | -0.97** | -0.98** | -0.93** | 0.70** |
| X7 | -0.78** | -0.80** | -0.45** | -0.79** | -0.93** | -0.79** | -0.81** | -0.49** | -0.80** | -0.44** | -0.40* | 0.69** | -0.45** | -0.62** | -0.99** | -0.95** | -0.86** | 0.55** |
| X8 | -0.84** | -0.87** | -0.55** | -0.86** | -0.75** | -0.89** | -0.87** | -0.61** | -0.88** | -0.59** | -0.58** | 0.83** | -0.64** | -0.79** | -0.83** | -0.93** | -0.84** | 0.71** |
| X9 | -0.82** | -0.85** | -0.41** | -0.83** | -0.88** | -0.87** | -0.89** | -0.65** | -0.90** | -0.48** | -0.45** | 0.88** | -0.48** | -0.68** | -0.74** | -0.90** | -0.84** | 0.66** |
| X10 | -0.68** | -0.73** | -0.41** | -0.71** | -0.23 | -0.75** | -0.74** | -0.61** | -0.74** | -0.45** | -0.44** | 0.67** | -0.45** | -0.63** | 0.09 | -0.59** | -0.67** | 0.69** |
| X11 | -0.71** | -0.73** | -0.43** | -0.72** | -0.82** | -0.72** | -0.74** | -0.43** | -0.72** | -0.39* | -0.37* | 0.60** | -0.40** | -0.56** | -0.94** | -0.89** | -0.80** | 0.55** |
| X12 | -0.76** | -0.79** | -0.41* | -0.77** | -0.90** | -0.78** | -0.81** | -0.45** | -0.80** | -0.41* | -0.37* | 0.67** | -0.39* | -0.62** | -0.99** | -0.96** | -0.84** | 0.55** |
| X13 | -0.67** | -0.69** | -0.41** | -0.68** | -0.79** | -0.67** | -0.70** | -0.40* | -0.68** | -0.36* | -0.34* | 0.55** | -0.37* | -0.52** | -0.92** | -0.86** | -0.77** | 0.52** |
| X14 | -0.73** | -0.75** | -0.44** | -0.74** | -0.85** | -0.74** | -0.76** | -0.45** | -0.75** | -0.40** | -0.38* | 0.62** | -0.42** | -0.57** | -0.96** | -0.91** | -0.82** | 0.55** |
| X15 | -0.74** | -0.76** | -0.44** | -0.75** | -0.87** | -0.76** | -0.78** | -0.47** | -0.76** | -0.41** | -0.38* | 0.64** | -0.43** | -0.59** | -0.98** | -0.93** | -0.82** | 0.56** |
| X16 | -0.81** | -0.84** | -0.51** | -0.83** | -0.86** | -0.84** | -0.85** | -0.55** | -0.84** | -0.49** | -0.49** | 0.73** | -0.52** | -0.68** | -0.96** | -0.96** | -0.87** | 0.67** |
| X17 | 0.54** | 0.57** | 0.54** | 0.55** | -0.42* | 0.59** | 0.51** | 0.44** | 0.49** | 0.56** | 0.59** | -0.41** | 0.60** | 0.63** | -0.69** | 0.28 | 0.43** | -0.47** |
| X18 | -0.92** | -0.95** | -0.64** | -0.94** | -0.92** | -0.95** | -0.93** | -0.61** | -0.95** | -0.65** | -0.64** | 0.82** | -0.70** | -0.85** | -0.97** | -0.98** | -0.93** | 0.76** |
| X19 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.17 | 0.03 | -0.72** | 0.05 | -0.02 | 0.14 | -0.04 | 0.19 | 0.24 | 0.03 | 0.23 | 0.18 | -0.92** | -0.30 | -0.09 | -0.09 |
| X20 | -0.81** | -0.82** | -0.79** | -0.81** | 0.39* | -0.82** | -0.72** | -0.50** | -0.78** | -0.78** | -0.78** | 0.58** | -0.89** | -0.91** | 0.28 | -0.62** | -0.71** | 0.74** |
| X21 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.26 | 0.03 | -0.69** | 0.06 | -0.01 | 0.17 | -0.11 | 0.30 | 0.38* | 0.01 | 0.31* | 0.24 | -0.87** | -0.28 | -0.09 | 0.04 |
| X22 | -0.85** | -0.89** | -0.64** | -0.87** | -0.47* | -0.89** | -0.85** | -0.59** | -0.88** | -0.64** | -0.64** | 0.70** | -0.74** | -0.86** | -0.68** | -0.84** | -0.83** | 0.80** |
| X23 | -0.92** | -0.95** | -0.59** | -0.94** | -0.94** | -0.96** | -0.94** | -0.65** | -0.96** | -0.62** | -0.60** | 0.86** | -0.65** | -0.82** | -0.85** | -0.95** | -0.94** | 0.74** |
| X24 | -0.94** | -0.97** | -0.69** | -0.96** | -0.89** | -0.96** | -0.90** | -0.58** | -0.96** | -0.71** | -0.69** | 0.75** | -0.73** | -0.91** | -0.96** | -0.94** | -0.91** | 0.77** |
| X25 | -0.83** | -0.86** | -0.49** | -0.85** | -0.96** | -0.86** | -0.87** | -0.56** | -0.87** | -0.49** | -0.47** | 0.77** | -0.49** | -0.68** | -0.97** | -0.97** | -0.90** | 0.63** |
| X26 | 0.30 | 0.33* | 0.44** | 0.33* | -0.08 | 0.33* | 0.23 | 0.19 | 0.16 | 0.55** | 0.59** | -0.39* | 0.50** | 0.39* | -0.32 | 0.12 | 0.22 | -0.08 |
| X27 | -0.72** | -0.74** | -0.43** | -0.73** | -0.82** | -0.74** | -0.75** | -0.44** | -0.74** | -0.42** | -0.38* | 0.67** | -0.44** | -0.59** | -0.95** | -0.91** | -0.80** | 0.53** |
| X28 | 0.50** | 0.48** | 0.37* | 0.52** | 0.59** | 0.47** | 0.38* | 0.21 | 0.42** | 0.40** | 0.36* | -0.51** | 0.39* | 0.42** | 0.63** | 0.54** | 0.54** | -0.33* |
| X29 | 0.28 | 0.31 | 0.04 | 0.30 | 0.40* | 0.33* | 0.38* | 0.22 | 0.41* | 0.07 | 0.07 | -0.38* | 0.04 | 0.15 | 0.41* | 0.41* | 0.31 | -0.32 |
| X30 | 0.43** | 0.44** | 0.12 | 0.43** | 0.53** | 0.46** | 0.49** | 0.34* | 0.48** | 0.16 | 0.11 | -0.58** | 0.18 | 0.37* | 0.51** | 0.54** | 0.50** | -0.46** |
| X31 | 0.68** | 0.65** | 0.78** | 0.73** | 0.70** | 0.61** | 0.37* | 0.60** | 0.69** | 0.82** | 0.81** | -0.49** | 0.81** | 0.69** | 0.51** | 0.49** | 0.61** | -0.56** |
| X32 | 0.30 | 0.25 | 0.22 | 0.32* | 0.56** | 0.23 | 0.13 | 0.08 | 0.18 | 0.25 | 0.20 | -0.31* | 0.21 | 0.20 | 0.61** | 0.34* | 0.35* | -0.2 |
| X33 | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.03 | 0.15 | 0.35 | 0.16 | 0.19 | 0.07 | 0.19 | 0.06 | 0.06 | -0.22 | -0.03 | 0.02 | 0.39* | 0.25 | 0.18 | -0.16 |
| X34 | 0.33* | 0.32* | 0.04 | 0.33* | 0.55** | 0.33* | 0.36* | 0.26 | 0.36* | 0.09 | 0.05 | -0.51** | 0.08 | 0.25 | 0.53** | 0.44** | 0.42** | -0.37* |
| X35 | 0.57** | 0.52** | 0.67** | 0.62** | 0.73** | 0.49** | 0.23 | 0.63** | 0.56** | 0.71** | 0.70** | -0.38* | 0.69** | 0.55** | 0.54** | 0.39* | 0.50** | -0.45** |
| 指标Index | 农作物 Crop | 粮食 Grain | 夏粮 Summer grain | 秋粮Autumn grain | 谷物 Cereal | 稻谷 Rice | 早稻 Early rice | 中稻和一季晚稻 Middle season rice and one season late rice | 双季晚稻 Double cropping late rice | 小麦Wheat | 冬小麦Winter wheat | 玉米Maize | 谷子Millet | 高粱Sorghum | 豆类Beans | 大豆Soybean | 薯类Tubers | 马铃薯Potato |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 0.75** | -0.86** | 0.11 | -0.69** | -0.93** | -0.95** | -0.81** | -0.86** | -0.93** | -0.61** | -0.62** | 0.28 | -0.50** | 0.69** | -0.76** | -0.47** | 0.45** | 0.71** |
| X2 | -0.88** | 0.63** | -0.23 | 0.53** | 0.50** | 0.76** | 0.59** | 0.87** | 0.72** | 0.45** | 0.49** | -0.36* | 0.41** | -0.64** | 0.30 | 0.28 | -0.51** | -0.41* |
| X3 | 0.09 | -0.27 | 0.11 | -0.24 | -0.30 | -0.32* | -0.23 | -0.10 | -0.30 | -0.09 | 0.49** | 0.17 | 0.10 | 0.26 | -0.20 | -0.21 | 0.03 | 0.27 |
| X4 | 0.32* | -0.22 | -0.56** | 0.06 | 0.85** | -0.24 | -0.36* | -0.45** | 0.02 | -0.58** | -0.64** | -0.29 | -0.56** | -0.04 | 0.71** | 0.37* | 0.63** | -0.54** |
| X5 | 0.63** | -0.87** | 0.26 | -0.80** | -0.93** | -0.92** | -0.75** | -0.65** | -0.94** | -0.49** | -0.46** | 0.35* | -0.36* | 0.66** | -0.85** | -0.71** | 0.20 | 0.82** |
| X6 | 0.84** | -0.78** | 0.22 | -0.68** | -0.75** | -0.88** | -0.70** | -0.85** | -0.85** | -0.53** | -0.56** | 0.34* | -0.48** | 0.65** | -0.60** | -0.45** | 0.39* | 0.55** |
| X7 | 0.51** | -0.88** | 0.29 | -0.83** | -0.97** | -0.91** | -0.73** | -0.52** | -0.93** | -0.44** | -0.42** | 0.38* | -0.28 | 0.65** | -0.86** | -0.78** | 0.03 | 0.87** |
| X8 | 0.49** | -0.87** | 0.27 | -0.83** | -0.94** | -0.87** | -0.72** | -0.48** | -0.91** | -0.44** | -0.39* | 0.31 | -0.31* | 0.60** | -0.89** | -0.81** | 0.01 | 0.85** |
| X9 | 0.89** | -0.60** | 0.48** | -0.62** | -0.55** | -0.73** | -0.47** | -0.83** | -0.75** | -0.25 | -0.29 | 0.45** | -0.27 | 0.67** | -0.38* | -0.44** | 0.34* | 0.45** |
| X10 | -0.21 | 0.60** | -0.26 | 0.67** | 0.81** | 0.5** | 0.41** | 0.13 | 0.58** | 0.22 | 0.22 | -0.17 | 0.20 | -0.23 | 0.81** | 0.76** | 0.46** | -0.62** |
| X11 | 0.31 | -0.82** | 0.28 | -0.73** | -0.92** | -0.91** | -0.69** | -0.31 | -0.92** | -0.41* | -0.36 | 0.42* | -0.17 | 0.69** | -0.76** | -0.72** | -0.06 | 0.92** |
| X12 | 0.43** | -0.78** | 0.32* | -0.71** | -0.88** | -0.86** | -0.69** | -0.43** | -0.87** | -0.37* | -0.33* | 0.47** | -0.14 | 0.75** | -0.72** | -0.69** | 0.11 | 0.92** |
| X13 | 0.44** | -0.82** | 0.29 | -0.75** | -0.92** | -0.88** | -0.71** | -0.43** | -0.89** | -0.41* | -0.36* | 0.45** | -0.20 | 0.73** | -0.79** | -0.74** | 0.07 | 0.95** |
| X14 | 0.48** | -0.84** | 0.32* | -0.77** | -0.94** | -0.90** | -0.72** | -0.48** | -0.91** | -0.41** | -0.37* | 0.46** | -0.21 | 0.74** | -0.79** | -0.74** | 0.10 | 0.93** |
| X15 | 0.45** | -0.75** | 0.26 | -0.68** | -0.89** | -0.80** | -0.64** | -0.40* | -0.85** | -0.37* | -0.34* | 0.37* | -0.31 | 0.65** | -0.77** | -0.71** | 0.04 | 0.96** |
| X16 | 0.55** | -0.86** | 0.32* | -0.79** | -0.95** | -0.92** | -0.74** | -0.54** | -0.93** | -0.44** | -0.41** | 0.44** | -0.26 | 0.73** | -0.81** | -0.74** | 0.13 | 0.91** |
| X17 | 0.72** | -0.66** | 0.45** | -0.63** | -0.83** | -0.79** | -0.57** | -0.70** | -0.80** | -0.27 | -0.25 | 0.54** | -0.11 | 0.76** | -0.68** | -0.55** | 0.26 | 0.70** |
| X18 | 0.65** | -0.88** | 0.29 | -0.79** | -0.95** | -0.94** | -0.77** | -0.64** | -0.95** | -0.50** | -0.49** | 0.43** | -0.34* | 0.74** | -0.82** | -0.70** | 0.2 | 0.88** |
| X19 | 0.23 | -0.47** | 0.27 | -0.40* | -0.66** | -0.56** | -0.47** | -0.10 | -0.59** | -0.20 | -0.22 | 0.50** | -0.01 | 0.58** | -0.44* | -0.44** | 0.05 | 0.73** |
| X20 | 0.71** | -0.84** | 0.19 | -0.68** | -0.84** | -0.95** | -0.80** | -0.76** | -0.93** | -0.56** | -0.55** | 0.46** | -0.38* | 0.76** | -0.67** | -0.52** | 0.41** | 0.84** |
| X21 | 0.15 | -0.48** | 0.48** | -0.54** | -0.86** | -0.50** | -0.36* | -0.09 | -0.62** | -0.04 | 0.06 | 0.49** | 0.15 | 0.55** | -0.77** | -0.72** | -0.27 | 0.89** |
| X22 | 0.74** | -0.77** | 0.21 | -0.66** | -0.69** | -0.84** | -0.68** | -0.74** | -0.79** | -0.51** | -0.54** | 0.30 | -0.46** | 0.57** | -0.62** | -0.50** | 0.21 | 0.55** |
| X23 | 0.57** | -0.85** | 0.33* | -0.82** | -0.95** | -0.88** | -0.70** | -0.54** | -0.90** | -0.43** | -0.40* | 0.39* | -0.31* | 0.62** | -0.87** | -0.78** | -0.01 | 0.83** |
| X24 | 0.78** | -0.85** | 0.24 | -0.75** | -0.91** | -0.93** | -0.76** | -0.77** | -0.92** | -0.55** | -0.55** | 0.37* | -0.45** | 0.69** | -0.80** | -0.58** | 0.30 | 0.72** |
| X25 | 0.60** | -0.84** | 0.31* | -0.75** | -0.91** | -0.94** | -0.75** | -0.60** | -0.93** | -0.45** | -0.45** | 0.47** | -0.25 | 0.78** | -0.72** | -0.65** | 0.24 | 0.87** |
| X26 | -0.65** | 0.60** | 0.26 | 0.37* | -0.25 | 0.66** | 0.62** | 0.86** | 0.58** | 0.70** | 0.74** | 0.01 | 0.71** | -0.36* | -0.26 | 0.01 | -0.64** | -0.12 |
| X27 | 0.37* | -0.80** | 0.27 | -0.75** | -0.92** | -0.83** | -0.68** | -0.36* | -0.86** | -0.37* | -0.31 | 0.38* | -0.17 | 0.63** | -0.81** | -0.78** | -0.01 | 0.92** |
| X28 | 0.06 | 0.25 | -0.20 | 0.27 | 0.56** | 0.27 | 0.19 | -0.05 | 0.33* | 0.04 | -0.06 | -0.24 | 0.03 | -0.28 | 0.44* | 0.28 | 0.03 | -0.52** |
| X29 | -0.24 | 0.25 | -0.31* | 0.33* | 0.42* | 0.32* | 0.16 | 0.23 | 0.38* | 0.07 | 0.01 | -0.26 | 0.14 | -0.50** | 0.27 | 0.23 | -0.15 | -0.50** |
| X30 | 0.27 | 0.15 | -0.14 | 0.21 | 0.55** | 0.08 | 0.07 | -0.32* | 0.17 | -0.09 | -0.15 | -0.14 | -0.19 | -0.03 | 0.55** | 0.39* | 0.39* | -0.40* |
| X31 | -0.47** | 0.51** | -0.11 | 0.30 | 0.60** | 0.55** | 0.61** | 0.42** | 0.53** | 0.39* | 0.39* | -0.16 | 0.29 | -0.40* | 0.45* | 0.34* | -0.17 | -0.42* |
| X32 | 0.09 | 0.25 | -0.29 | 0.29 | 0.64** | 0.25 | 0.18 | -0.14 | 0.32* | -0.01 | -0.11 | -0.25 | -0.04 | -0.30 | 0.53** | 0.39* | 0.17 | -0.56** |
| X33 | -0.14 | 0.18 | -0.27 | 0.23 | 0.38* | 0.24 | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.28 | 0.06 | -0.01 | -0.19 | 0.14 | -0.45** | 0.22 | 0.17 | -0.11 | -0.42* |
| X34 | 0.22 | 0.13 | -0.16 | 0.2 | 0.50** | 0.06 | 0.05 | -0.28 | 0.15 | -0.09 | -0.13 | -0.15 | -0.16 | 0.01 | 0.52** | 0.37* | 0.40** | -0.36* |
| X35 | -0.46** | 0.48** | -0.16 | 0.33* | 0.63** | 0.52** | 0.53** | 0.40* | 0.52** | 0.31 | 0.31 | -0.19 | 0.22 | -0.40* | 0.52** | 0.35* | -0.16 | -0.38* |
表3 广西壮族自治区粮食作物播种面积和影响因素的相关性分析
Table 3 Correlation analysis of sown area and influencing factors of grain crops in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region
| 指标Index | 农作物 Crop | 粮食 Grain | 夏粮 Summer grain | 秋粮Autumn grain | 谷物 Cereal | 稻谷 Rice | 早稻 Early rice | 中稻和一季晚稻 Middle season rice and one season late rice | 双季晚稻 Double cropping late rice | 小麦Wheat | 冬小麦Winter wheat | 玉米Maize | 谷子Millet | 高粱Sorghum | 豆类Beans | 大豆Soybean | 薯类Tubers | 马铃薯Potato |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 0.75** | -0.86** | 0.11 | -0.69** | -0.93** | -0.95** | -0.81** | -0.86** | -0.93** | -0.61** | -0.62** | 0.28 | -0.50** | 0.69** | -0.76** | -0.47** | 0.45** | 0.71** |
| X2 | -0.88** | 0.63** | -0.23 | 0.53** | 0.50** | 0.76** | 0.59** | 0.87** | 0.72** | 0.45** | 0.49** | -0.36* | 0.41** | -0.64** | 0.30 | 0.28 | -0.51** | -0.41* |
| X3 | 0.09 | -0.27 | 0.11 | -0.24 | -0.30 | -0.32* | -0.23 | -0.10 | -0.30 | -0.09 | 0.49** | 0.17 | 0.10 | 0.26 | -0.20 | -0.21 | 0.03 | 0.27 |
| X4 | 0.32* | -0.22 | -0.56** | 0.06 | 0.85** | -0.24 | -0.36* | -0.45** | 0.02 | -0.58** | -0.64** | -0.29 | -0.56** | -0.04 | 0.71** | 0.37* | 0.63** | -0.54** |
| X5 | 0.63** | -0.87** | 0.26 | -0.80** | -0.93** | -0.92** | -0.75** | -0.65** | -0.94** | -0.49** | -0.46** | 0.35* | -0.36* | 0.66** | -0.85** | -0.71** | 0.20 | 0.82** |
| X6 | 0.84** | -0.78** | 0.22 | -0.68** | -0.75** | -0.88** | -0.70** | -0.85** | -0.85** | -0.53** | -0.56** | 0.34* | -0.48** | 0.65** | -0.60** | -0.45** | 0.39* | 0.55** |
| X7 | 0.51** | -0.88** | 0.29 | -0.83** | -0.97** | -0.91** | -0.73** | -0.52** | -0.93** | -0.44** | -0.42** | 0.38* | -0.28 | 0.65** | -0.86** | -0.78** | 0.03 | 0.87** |
| X8 | 0.49** | -0.87** | 0.27 | -0.83** | -0.94** | -0.87** | -0.72** | -0.48** | -0.91** | -0.44** | -0.39* | 0.31 | -0.31* | 0.60** | -0.89** | -0.81** | 0.01 | 0.85** |
| X9 | 0.89** | -0.60** | 0.48** | -0.62** | -0.55** | -0.73** | -0.47** | -0.83** | -0.75** | -0.25 | -0.29 | 0.45** | -0.27 | 0.67** | -0.38* | -0.44** | 0.34* | 0.45** |
| X10 | -0.21 | 0.60** | -0.26 | 0.67** | 0.81** | 0.5** | 0.41** | 0.13 | 0.58** | 0.22 | 0.22 | -0.17 | 0.20 | -0.23 | 0.81** | 0.76** | 0.46** | -0.62** |
| X11 | 0.31 | -0.82** | 0.28 | -0.73** | -0.92** | -0.91** | -0.69** | -0.31 | -0.92** | -0.41* | -0.36 | 0.42* | -0.17 | 0.69** | -0.76** | -0.72** | -0.06 | 0.92** |
| X12 | 0.43** | -0.78** | 0.32* | -0.71** | -0.88** | -0.86** | -0.69** | -0.43** | -0.87** | -0.37* | -0.33* | 0.47** | -0.14 | 0.75** | -0.72** | -0.69** | 0.11 | 0.92** |
| X13 | 0.44** | -0.82** | 0.29 | -0.75** | -0.92** | -0.88** | -0.71** | -0.43** | -0.89** | -0.41* | -0.36* | 0.45** | -0.20 | 0.73** | -0.79** | -0.74** | 0.07 | 0.95** |
| X14 | 0.48** | -0.84** | 0.32* | -0.77** | -0.94** | -0.90** | -0.72** | -0.48** | -0.91** | -0.41** | -0.37* | 0.46** | -0.21 | 0.74** | -0.79** | -0.74** | 0.10 | 0.93** |
| X15 | 0.45** | -0.75** | 0.26 | -0.68** | -0.89** | -0.80** | -0.64** | -0.40* | -0.85** | -0.37* | -0.34* | 0.37* | -0.31 | 0.65** | -0.77** | -0.71** | 0.04 | 0.96** |
| X16 | 0.55** | -0.86** | 0.32* | -0.79** | -0.95** | -0.92** | -0.74** | -0.54** | -0.93** | -0.44** | -0.41** | 0.44** | -0.26 | 0.73** | -0.81** | -0.74** | 0.13 | 0.91** |
| X17 | 0.72** | -0.66** | 0.45** | -0.63** | -0.83** | -0.79** | -0.57** | -0.70** | -0.80** | -0.27 | -0.25 | 0.54** | -0.11 | 0.76** | -0.68** | -0.55** | 0.26 | 0.70** |
| X18 | 0.65** | -0.88** | 0.29 | -0.79** | -0.95** | -0.94** | -0.77** | -0.64** | -0.95** | -0.50** | -0.49** | 0.43** | -0.34* | 0.74** | -0.82** | -0.70** | 0.2 | 0.88** |
| X19 | 0.23 | -0.47** | 0.27 | -0.40* | -0.66** | -0.56** | -0.47** | -0.10 | -0.59** | -0.20 | -0.22 | 0.50** | -0.01 | 0.58** | -0.44* | -0.44** | 0.05 | 0.73** |
| X20 | 0.71** | -0.84** | 0.19 | -0.68** | -0.84** | -0.95** | -0.80** | -0.76** | -0.93** | -0.56** | -0.55** | 0.46** | -0.38* | 0.76** | -0.67** | -0.52** | 0.41** | 0.84** |
| X21 | 0.15 | -0.48** | 0.48** | -0.54** | -0.86** | -0.50** | -0.36* | -0.09 | -0.62** | -0.04 | 0.06 | 0.49** | 0.15 | 0.55** | -0.77** | -0.72** | -0.27 | 0.89** |
| X22 | 0.74** | -0.77** | 0.21 | -0.66** | -0.69** | -0.84** | -0.68** | -0.74** | -0.79** | -0.51** | -0.54** | 0.30 | -0.46** | 0.57** | -0.62** | -0.50** | 0.21 | 0.55** |
| X23 | 0.57** | -0.85** | 0.33* | -0.82** | -0.95** | -0.88** | -0.70** | -0.54** | -0.90** | -0.43** | -0.40* | 0.39* | -0.31* | 0.62** | -0.87** | -0.78** | -0.01 | 0.83** |
| X24 | 0.78** | -0.85** | 0.24 | -0.75** | -0.91** | -0.93** | -0.76** | -0.77** | -0.92** | -0.55** | -0.55** | 0.37* | -0.45** | 0.69** | -0.80** | -0.58** | 0.30 | 0.72** |
| X25 | 0.60** | -0.84** | 0.31* | -0.75** | -0.91** | -0.94** | -0.75** | -0.60** | -0.93** | -0.45** | -0.45** | 0.47** | -0.25 | 0.78** | -0.72** | -0.65** | 0.24 | 0.87** |
| X26 | -0.65** | 0.60** | 0.26 | 0.37* | -0.25 | 0.66** | 0.62** | 0.86** | 0.58** | 0.70** | 0.74** | 0.01 | 0.71** | -0.36* | -0.26 | 0.01 | -0.64** | -0.12 |
| X27 | 0.37* | -0.80** | 0.27 | -0.75** | -0.92** | -0.83** | -0.68** | -0.36* | -0.86** | -0.37* | -0.31 | 0.38* | -0.17 | 0.63** | -0.81** | -0.78** | -0.01 | 0.92** |
| X28 | 0.06 | 0.25 | -0.20 | 0.27 | 0.56** | 0.27 | 0.19 | -0.05 | 0.33* | 0.04 | -0.06 | -0.24 | 0.03 | -0.28 | 0.44* | 0.28 | 0.03 | -0.52** |
| X29 | -0.24 | 0.25 | -0.31* | 0.33* | 0.42* | 0.32* | 0.16 | 0.23 | 0.38* | 0.07 | 0.01 | -0.26 | 0.14 | -0.50** | 0.27 | 0.23 | -0.15 | -0.50** |
| X30 | 0.27 | 0.15 | -0.14 | 0.21 | 0.55** | 0.08 | 0.07 | -0.32* | 0.17 | -0.09 | -0.15 | -0.14 | -0.19 | -0.03 | 0.55** | 0.39* | 0.39* | -0.40* |
| X31 | -0.47** | 0.51** | -0.11 | 0.30 | 0.60** | 0.55** | 0.61** | 0.42** | 0.53** | 0.39* | 0.39* | -0.16 | 0.29 | -0.40* | 0.45* | 0.34* | -0.17 | -0.42* |
| X32 | 0.09 | 0.25 | -0.29 | 0.29 | 0.64** | 0.25 | 0.18 | -0.14 | 0.32* | -0.01 | -0.11 | -0.25 | -0.04 | -0.30 | 0.53** | 0.39* | 0.17 | -0.56** |
| X33 | -0.14 | 0.18 | -0.27 | 0.23 | 0.38* | 0.24 | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.28 | 0.06 | -0.01 | -0.19 | 0.14 | -0.45** | 0.22 | 0.17 | -0.11 | -0.42* |
| X34 | 0.22 | 0.13 | -0.16 | 0.2 | 0.50** | 0.06 | 0.05 | -0.28 | 0.15 | -0.09 | -0.13 | -0.15 | -0.16 | 0.01 | 0.52** | 0.37* | 0.40** | -0.36* |
| X35 | -0.46** | 0.48** | -0.16 | 0.33* | 0.63** | 0.52** | 0.53** | 0.40* | 0.52** | 0.31 | 0.31 | -0.19 | 0.22 | -0.40* | 0.52** | 0.35* | -0.16 | -0.38* |
| 指标Index | 农作物 Crop | 粮食 Grain | 夏粮 Summer grain | 秋粮Autumn grain | 谷物 Cereal | 稻谷 Rice | 早稻 Early rice | 中稻和一季晚稻 Middle season rice and one season late rice | 双季晚稻 Double cropping late rice | 小麦Wheat | 冬小麦Winter wheat | 玉米Maize | 高粱Sorghum | 豆类Beans | 大豆Soybean | 薯类Tubers | 马铃薯Potato |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | -0.59** | -0.73** | -0.74** | -0.68** | -0.35 | -0.74** | -0.87** | -0.69** | -0.91** | -0.59** | -0.56** | -0.40* | -0.78** | -0.46** | 0.33* | -0.67** | 0.07 |
| X2 | 0.83** | 0.82** | 0.76** | 0.84** | 0.92** | 0.82** | 0.46** | 0.83** | 0.68** | 0.80** | 0.85** | 0.62** | 0.76** | 0.05 | -0.50** | 0.80** | -0.04 |
| X3 | 0.83** | 0.82** | 0.76** | 0.83** | 0.93** | 0.82** | 0.46** | 0.83** | 0.68** | 0.80** | 0.84** | 0.59** | 0.76** | 0.06 | -0.52** | 0.79** | -0.07 |
| X4 | 0.77** | 0.78** | 0.81** | 0.74** | 0.88** | 0.81** | 0.33* | 0.86** | 0.63** | 0.91** | 0.88** | 0.28 | 0.72** | -0.02 | -0.84** | 0.68** | -0.43** |
| X5 | -0.76** | -0.89** | -0.92** | -0.82** | -0.81** | -0.89** | -0.77** | -0.88** | -0.88** | -0.88** | -0.87** | -0.37* | -0.86** | -0.29 | 0.75** | -0.78** | 0.44** |
| X6 | -0.77** | -0.88** | -0.90** | -0.82** | -0.78** | -0.88** | -0.71** | -0.87** | -0.85** | -0.89** | -0.88** | -0.40** | -0.84** | -0.15 | 0.74** | -0.78** | 0.37* |
| X7 | -0.73** | -0.82** | -0.88** | -0.74** | -0.77** | -0.82** | -0.55** | -0.83** | -0.69** | -0.93** | -0.90** | -0.23 | -0.77** | -0.12 | 0.90** | -0.70** | 0.55** |
| X8 | -0.84** | -0.91** | -0.87** | -0.89** | -0.87** | -0.89** | -0.60** | -0.90** | -0.79** | -0.88** | -0.94** | -0.55** | -0.83** | -0.22 | 0.73** | -0.84** | 0.40* |
| X9 | -0.83** | -0.84** | -0.77** | -0.86** | -0.83** | -0.82** | -0.41** | -0.85** | -0.74** | -0.80** | -0.89** | -0.70** | -0.75** | -0.03 | 0.46** | -0.80** | -0.06 |
| X10 | 0.51** | 0.69** | 0.73** | 0.61** | 0.32 | 0.69** | 0.73** | 0.65** | 0.79** | 0.66** | 0.63** | 0.23 | 0.75** | 0.41* | -0.64** | 0.56** | -0.52** |
| X11 | -0.58** | -0.67** | -0.78** | -0.56** | -0.61** | -0.70** | -0.45** | -0.71** | -0.57** | -0.85** | -0.77** | 0.03 | -0.64** | -0.09 | 0.95** | -0.54** | 0.68** |
| X12 | -0.53** | -0.62** | -0.70** | -0.54** | -0.57** | -0.64** | -0.42** | -0.66** | -0.52** | -0.77** | -0.70** | -0.02 | -0.61** | -0.12 | 0.92** | -0.49** | 0.71** |
| X13 | -0.55** | -0.64** | -0.75** | -0.54** | -0.59** | -0.67** | -0.43** | -0.68** | -0.54** | -0.82** | -0.73** | 0.03 | -0.62** | -0.11 | 0.95** | -0.51** | 0.72** |
| X14 | -0.61** | -0.70** | -0.80** | -0.60** | -0.63** | -0.73** | -0.47** | -0.73** | -0.60** | -0.86** | -0.80** | -0.02 | -0.67** | -0.10 | 0.95** | -0.57** | 0.67** |
| X15 | -0.62** | -0.71** | -0.79** | -0.62** | -0.65** | -0.73** | -0.48** | -0.74** | -0.60** | -0.85** | -0.78** | -0.07 | -0.69** | -0.14 | 0.94** | -0.58** | 0.68** |
| X16 | -0.70** | -0.80** | -0.86** | -0.70** | -0.71** | -0.81** | -0.56** | -0.81** | -0.70** | -0.90** | -0.86** | -0.15 | -0.77** | -0.15 | 0.91** | -0.66** | 0.61** |
| X17 | 0.75** | 0.75** | 0.61** | 0.81** | 0.50** | 0.71** | 0.59** | 0.66** | 0.72** | 0.48** | 0.71** | 0.87** | 0.62** | 0.43* | 0.08 | 0.80** | 0.59** |
| X18 | -0.73** | -0.83** | -0.89** | -0.75** | -0.75** | -0.84** | -0.62** | -0.84** | -0.75** | -0.91** | -0.88** | -0.22 | -0.80** | -0.20 | 0.88** | -0.71** | 0.57** |
| X19 | -0.48** | -0.55** | -0.59** | -0.50** | -0.57** | -0.56** | -0.32* | -0.59** | -0.41** | -0.67** | -0.65** | -0.10 | -0.53** | -0.22 | 0.86** | -0.44** | 0.68** |
| X20 | 0.36* | 0.22 | 0.17 | 0.28 | 0.82** | 0.29 | -0.38* | 0.54** | 0.17 | 0.33* | 0.35* | 0.16 | 0.27 | -0.38* | -0.28 | 0.16 | -0.16 |
| X21 | -0.22 | -0.21 | -0.29 | -0.15 | -0.54** | -0.24 | 0.10 | -0.34* | -0.03 | -0.45** | -0.35* | 0.25 | -0.20 | 0.04 | 0.73** | -0.11 | 0.70** |
| X22 | 0.03 | 0.18 | 0.24 | 0.12 | -0.30 | 0.12 | 0.36* | 0.05 | 0.39* | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.07 | 0.04 | -0.15 | 0.13 | -0.12 |
| X23 | -0.71** | -0.79** | -0.85** | -0.71** | -0.75** | -0.81** | -0.52** | -0.82** | -0.67** | -0.91** | -0.87** | -0.18 | -0.76** | -0.13 | 0.91** | -0.67** | 0.59** |
| X24 | -0.56** | -0.72** | -0.72** | -0.67** | -0.30 | -0.73** | -0.83** | -0.69** | -0.88** | -0.61** | -0.62** | -0.36* | -0.83** | -0.41* | 0.46** | -0.62** | 0.33* |
| X25 | -0.79** | -0.89** | -0.93** | -0.82** | -0.83** | -0.91** | -0.69** | -0.90** | -0.84** | -0.93** | -0.91** | -0.33* | -0.87** | -0.20 | 0.81** | -0.78** | 0.45** |
| X26 | 0.69** | 0.77** | 0.70** | 0.77** | 0.45* | 0.73** | 0.81** | 0.69** | 0.85** | 0.55** | 0.67** | 0.71** | 0.68** | 0.35 | -0.12 | 0.78** | 0.37* |
| X27 | -0.53** | -0.60** | -0.72** | -0.53** | -0.57** | -0.64** | -0.42** | -0.66** | -0.52** | -0.78** | -0.69** | 0.03 | -0.61** | -0.14 | 0.94** | -0.49** | 0.74** |
| X28 | 0.54** | 0.54** | 0.59** | 0.48** | 0.68** | 0.56** | 0.40* | 0.56** | 0.36* | 0.63** | 0.53** | 0.05 | 0.46** | 0.15 | -0.59** | 0.50** | -0.38* |
| X29 | 0.40* | 0.41** | 0.46** | 0.36* | 0.51** | 0.43** | 0.45** | 0.41** | 0.19 | 0.46** | 0.38* | 0.03 | 0.39* | 0.16 | -0.42** | 0.41** | -0.35* |
| X30 | 0.28 | 0.23 | 0.27 | 0.21 | 0.47* | 0.24 | -0.11 | 0.34* | 0.25 | 0.36* | 0.26 | -0.02 | 0.12 | -0.03 | -0.39* | 0.18 | -0.21 |
| X31 | 0.62** | 0.60** | 0.57** | 0.59** | 0.75** | 0.64** | 0.34* | 0.64** | 0.49** | 0.59** | 0.56** | 0.30 | 0.57** | 0.12 | -0.42** | 0.56** | -0.11 |
| X32 | 0.47** | 0.46** | 0.52** | 0.41** | 0.66** | 0.48** | 0.28 | 0.49** | 0.33* | 0.57** | 0.48** | 0.02 | 0.38* | -0.02 | -0.59** | 0.40** | -0.42** |
| X33 | 0.27 | 0.29 | 0.34* | 0.24 | 0.43* | 0.32* | 0.25 | 0.30 | 0.14 | 0.37* | 0.29 | -0.04 | 0.30 | -0.10 | -0.42** | 0.25 | -0.39* |
| X34 | 0.30 | 0.26 | 0.30 | 0.23 | 0.55** | 0.25 | -0.08 | 0.34* | 0.24 | 0.39* | 0.32* | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.01 | -0.43** | 0.21 | -0.25 |
| X35 | 0.57** | 0.57** | 0.57** | 0.55** | 0.75** | 0.57** | 0.42** | 0.56** | 0.44** | 0.56** | 0.53** | 0.29 | 0.46** | 0.30 | -0.37* | 0.56** | -0.054 |
表4 四川省粮食作物播种面积和影响因素的相关性分析
Table 4 Correlation analysis of sown area and influencing factors of grain crops in Sichuan Province
| 指标Index | 农作物 Crop | 粮食 Grain | 夏粮 Summer grain | 秋粮Autumn grain | 谷物 Cereal | 稻谷 Rice | 早稻 Early rice | 中稻和一季晚稻 Middle season rice and one season late rice | 双季晚稻 Double cropping late rice | 小麦Wheat | 冬小麦Winter wheat | 玉米Maize | 高粱Sorghum | 豆类Beans | 大豆Soybean | 薯类Tubers | 马铃薯Potato |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | -0.59** | -0.73** | -0.74** | -0.68** | -0.35 | -0.74** | -0.87** | -0.69** | -0.91** | -0.59** | -0.56** | -0.40* | -0.78** | -0.46** | 0.33* | -0.67** | 0.07 |
| X2 | 0.83** | 0.82** | 0.76** | 0.84** | 0.92** | 0.82** | 0.46** | 0.83** | 0.68** | 0.80** | 0.85** | 0.62** | 0.76** | 0.05 | -0.50** | 0.80** | -0.04 |
| X3 | 0.83** | 0.82** | 0.76** | 0.83** | 0.93** | 0.82** | 0.46** | 0.83** | 0.68** | 0.80** | 0.84** | 0.59** | 0.76** | 0.06 | -0.52** | 0.79** | -0.07 |
| X4 | 0.77** | 0.78** | 0.81** | 0.74** | 0.88** | 0.81** | 0.33* | 0.86** | 0.63** | 0.91** | 0.88** | 0.28 | 0.72** | -0.02 | -0.84** | 0.68** | -0.43** |
| X5 | -0.76** | -0.89** | -0.92** | -0.82** | -0.81** | -0.89** | -0.77** | -0.88** | -0.88** | -0.88** | -0.87** | -0.37* | -0.86** | -0.29 | 0.75** | -0.78** | 0.44** |
| X6 | -0.77** | -0.88** | -0.90** | -0.82** | -0.78** | -0.88** | -0.71** | -0.87** | -0.85** | -0.89** | -0.88** | -0.40** | -0.84** | -0.15 | 0.74** | -0.78** | 0.37* |
| X7 | -0.73** | -0.82** | -0.88** | -0.74** | -0.77** | -0.82** | -0.55** | -0.83** | -0.69** | -0.93** | -0.90** | -0.23 | -0.77** | -0.12 | 0.90** | -0.70** | 0.55** |
| X8 | -0.84** | -0.91** | -0.87** | -0.89** | -0.87** | -0.89** | -0.60** | -0.90** | -0.79** | -0.88** | -0.94** | -0.55** | -0.83** | -0.22 | 0.73** | -0.84** | 0.40* |
| X9 | -0.83** | -0.84** | -0.77** | -0.86** | -0.83** | -0.82** | -0.41** | -0.85** | -0.74** | -0.80** | -0.89** | -0.70** | -0.75** | -0.03 | 0.46** | -0.80** | -0.06 |
| X10 | 0.51** | 0.69** | 0.73** | 0.61** | 0.32 | 0.69** | 0.73** | 0.65** | 0.79** | 0.66** | 0.63** | 0.23 | 0.75** | 0.41* | -0.64** | 0.56** | -0.52** |
| X11 | -0.58** | -0.67** | -0.78** | -0.56** | -0.61** | -0.70** | -0.45** | -0.71** | -0.57** | -0.85** | -0.77** | 0.03 | -0.64** | -0.09 | 0.95** | -0.54** | 0.68** |
| X12 | -0.53** | -0.62** | -0.70** | -0.54** | -0.57** | -0.64** | -0.42** | -0.66** | -0.52** | -0.77** | -0.70** | -0.02 | -0.61** | -0.12 | 0.92** | -0.49** | 0.71** |
| X13 | -0.55** | -0.64** | -0.75** | -0.54** | -0.59** | -0.67** | -0.43** | -0.68** | -0.54** | -0.82** | -0.73** | 0.03 | -0.62** | -0.11 | 0.95** | -0.51** | 0.72** |
| X14 | -0.61** | -0.70** | -0.80** | -0.60** | -0.63** | -0.73** | -0.47** | -0.73** | -0.60** | -0.86** | -0.80** | -0.02 | -0.67** | -0.10 | 0.95** | -0.57** | 0.67** |
| X15 | -0.62** | -0.71** | -0.79** | -0.62** | -0.65** | -0.73** | -0.48** | -0.74** | -0.60** | -0.85** | -0.78** | -0.07 | -0.69** | -0.14 | 0.94** | -0.58** | 0.68** |
| X16 | -0.70** | -0.80** | -0.86** | -0.70** | -0.71** | -0.81** | -0.56** | -0.81** | -0.70** | -0.90** | -0.86** | -0.15 | -0.77** | -0.15 | 0.91** | -0.66** | 0.61** |
| X17 | 0.75** | 0.75** | 0.61** | 0.81** | 0.50** | 0.71** | 0.59** | 0.66** | 0.72** | 0.48** | 0.71** | 0.87** | 0.62** | 0.43* | 0.08 | 0.80** | 0.59** |
| X18 | -0.73** | -0.83** | -0.89** | -0.75** | -0.75** | -0.84** | -0.62** | -0.84** | -0.75** | -0.91** | -0.88** | -0.22 | -0.80** | -0.20 | 0.88** | -0.71** | 0.57** |
| X19 | -0.48** | -0.55** | -0.59** | -0.50** | -0.57** | -0.56** | -0.32* | -0.59** | -0.41** | -0.67** | -0.65** | -0.10 | -0.53** | -0.22 | 0.86** | -0.44** | 0.68** |
| X20 | 0.36* | 0.22 | 0.17 | 0.28 | 0.82** | 0.29 | -0.38* | 0.54** | 0.17 | 0.33* | 0.35* | 0.16 | 0.27 | -0.38* | -0.28 | 0.16 | -0.16 |
| X21 | -0.22 | -0.21 | -0.29 | -0.15 | -0.54** | -0.24 | 0.10 | -0.34* | -0.03 | -0.45** | -0.35* | 0.25 | -0.20 | 0.04 | 0.73** | -0.11 | 0.70** |
| X22 | 0.03 | 0.18 | 0.24 | 0.12 | -0.30 | 0.12 | 0.36* | 0.05 | 0.39* | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.07 | 0.04 | -0.15 | 0.13 | -0.12 |
| X23 | -0.71** | -0.79** | -0.85** | -0.71** | -0.75** | -0.81** | -0.52** | -0.82** | -0.67** | -0.91** | -0.87** | -0.18 | -0.76** | -0.13 | 0.91** | -0.67** | 0.59** |
| X24 | -0.56** | -0.72** | -0.72** | -0.67** | -0.30 | -0.73** | -0.83** | -0.69** | -0.88** | -0.61** | -0.62** | -0.36* | -0.83** | -0.41* | 0.46** | -0.62** | 0.33* |
| X25 | -0.79** | -0.89** | -0.93** | -0.82** | -0.83** | -0.91** | -0.69** | -0.90** | -0.84** | -0.93** | -0.91** | -0.33* | -0.87** | -0.20 | 0.81** | -0.78** | 0.45** |
| X26 | 0.69** | 0.77** | 0.70** | 0.77** | 0.45* | 0.73** | 0.81** | 0.69** | 0.85** | 0.55** | 0.67** | 0.71** | 0.68** | 0.35 | -0.12 | 0.78** | 0.37* |
| X27 | -0.53** | -0.60** | -0.72** | -0.53** | -0.57** | -0.64** | -0.42** | -0.66** | -0.52** | -0.78** | -0.69** | 0.03 | -0.61** | -0.14 | 0.94** | -0.49** | 0.74** |
| X28 | 0.54** | 0.54** | 0.59** | 0.48** | 0.68** | 0.56** | 0.40* | 0.56** | 0.36* | 0.63** | 0.53** | 0.05 | 0.46** | 0.15 | -0.59** | 0.50** | -0.38* |
| X29 | 0.40* | 0.41** | 0.46** | 0.36* | 0.51** | 0.43** | 0.45** | 0.41** | 0.19 | 0.46** | 0.38* | 0.03 | 0.39* | 0.16 | -0.42** | 0.41** | -0.35* |
| X30 | 0.28 | 0.23 | 0.27 | 0.21 | 0.47* | 0.24 | -0.11 | 0.34* | 0.25 | 0.36* | 0.26 | -0.02 | 0.12 | -0.03 | -0.39* | 0.18 | -0.21 |
| X31 | 0.62** | 0.60** | 0.57** | 0.59** | 0.75** | 0.64** | 0.34* | 0.64** | 0.49** | 0.59** | 0.56** | 0.30 | 0.57** | 0.12 | -0.42** | 0.56** | -0.11 |
| X32 | 0.47** | 0.46** | 0.52** | 0.41** | 0.66** | 0.48** | 0.28 | 0.49** | 0.33* | 0.57** | 0.48** | 0.02 | 0.38* | -0.02 | -0.59** | 0.40** | -0.42** |
| X33 | 0.27 | 0.29 | 0.34* | 0.24 | 0.43* | 0.32* | 0.25 | 0.30 | 0.14 | 0.37* | 0.29 | -0.04 | 0.30 | -0.10 | -0.42** | 0.25 | -0.39* |
| X34 | 0.30 | 0.26 | 0.30 | 0.23 | 0.55** | 0.25 | -0.08 | 0.34* | 0.24 | 0.39* | 0.32* | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.01 | -0.43** | 0.21 | -0.25 |
| X35 | 0.57** | 0.57** | 0.57** | 0.55** | 0.75** | 0.57** | 0.42** | 0.56** | 0.44** | 0.56** | 0.53** | 0.29 | 0.46** | 0.30 | -0.37* | 0.56** | -0.054 |
| 指标Index | 农作物 Crop | 粮食 Grain | 夏粮 Summer grain | 秋粮Autumn grain | 谷物 Cereal | 稻谷 Rice | 早稻 Early rice | 中稻和一季晚稻 Middle season rice and one season late rice | 双季晚稻 Double cropping late rice | 小麦Wheat | 冬小麦Winter wheat | 玉米Maize | 谷子Millet | 高粱Sorghum | 豆类Beans | 大豆Soybean | 薯类Tubers | 马铃薯Potato |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 0.82** | 0.84** | 0.86** | 0.58** | -0.03 | -0.59** | -0.57** | -0.57** | -0.34* | 0.24 | 0.32* | 0.33* | -0.63** | 0.51** | 0.78** | 0.43** | 0.79** | 0.72** |
| X2 | -0.81** | -0.62** | -0.42** | -0.71** | 0.63** | 0.81** | 0.57** | 0.69** | 0.52** | 0.52** | 0.46** | -0.59** | 0.90** | -0.80** | -0.42* | -0.56** | -0.89** | -0.89** |
| X3 | -0.82** | -0.64** | -0.45** | -0.71** | 0.61** | 0.80** | 0.59** | 0.68** | 0.47** | 0.47** | 0.42** | -0.59** | 0.88** | -0.80** | -0.37 | -0.57** | -0.89** | -0.89** |
| X4 | 0.44** | 0.56** | 0.72** | 0.19 | 0.08 | -0.33* | -0.44** | -0.33* | -0.11 | 0.41** | 0.38* | 0.01 | -0.39* | 0.09 | 0.16 | -0.02 | 0.45** | 0.27 |
| X5 | 0.72** | 0.47** | 0.28 | 0.58** | -0.12 | -0.57** | -0.38* | -0.49** | -0.34* | -0.24 | -0.02 | 0.44** | -0.37* | 0.80** | 0.11 | 0.82** | 0.58** | 0.52** |
| X6 | 0.97** | 0.79** | 0.59** | 0.83** | -0.40* | -0.78** | -0.49** | -0.70** | -0.43** | -0.24 | -0.06 | 0.63** | -0.74** | 0.90** | 0.46* | 0.79** | 0.92** | 0.91** |
| X7 | 0.83** | 0.55** | 0.25 | 0.79** | -0.55** | -0.77** | -0.32* | -0.69** | -0.45** | -0.61** | -0.50** | 0.70** | -0.72** | 0.94** | 0.30 | 0.77** | 0.83** | 0.86** |
| X8 | 0.82** | 0.59** | 0.31* | 0.78** | -0.44* | -0.80** | -0.35* | -0.67** | -0.44** | -0.57** | -0.49** | 0.70** | -0.77** | 0.91** | 0.24 | 0.75** | 0.84** | 0.81** |
| X9 | 0.86** | 0.73** | 0.50** | 0.82** | -0.57** | -0.81** | -0.29 | -0.74** | -0.52** | -0.46** | -0.39* | 0.69** | -0.91** | 0.83** | 0.47* | 0.60** | 0.94** | 0.96** |
| X10 | -0.22 | 0.05 | 0.34* | -0.35* | 0.25 | 0.3 | -0.06 | 0.21 | 0.06 | 0.67** | 0.60** | -0.43** | 0.18 | -0.56** | 0.15 | -0.44** | -0.20 | -0.36* |
| X11 | 0.79** | 0.58** | 0.25 | 0.85** | -0.41* | -0.67** | -0.29 | -0.54** | -0.39* | -0.54** | -0.46** | 0.86** | -0.65** | 0.92** | 0.19 | 0.79** | 0.76** | 0.77** |
| X12 | 0.73** | 0.50** | 0.24 | 0.70** | -0.19 | -0.68** | -0.26 | -0.49** | -0.35* | -0.50** | -0.42** | 0.57** | -0.65** | 0.86** | 0.14 | 0.74** | 0.70** | 0.70** |
| X13 | 0.78** | 0.49** | 0.17 | 0.76** | -0.42* | -0.70** | -0.28 | -0.60** | -0.39* | -0.59** | -0.48** | 0.66** | -0.62** | 0.94** | 0.21 | 0.81** | 0.74** | 0.77** |
| X14 | 0.78** | 0.49** | 0.17 | 0.76** | -0.45* | -0.69** | -0.28 | -0.61** | -0.39* | -0.58** | -0.46** | 0.67** | -0.60** | 0.93** | 0.24 | 0.81** | 0.74** | 0.77** |
| X15 | 0.73** | 0.59** | 0.47** | 0.70** | -0.48* | -0.77** | -0.32 | -0.67** | -0.40* | -0.32 | -0.32 | 0.75** | -0.88** | 0.86** | 0.28 | 0.39* | 0.87** | 0.82** |
| X16 | 0.79** | 0.50** | 0.20 | 0.76** | -0.41* | -0.66** | -0.29 | -0.59** | -0.37* | -0.53** | -0.38* | 0.67** | -0.55** | 0.91** | 0.26 | 0.83** | 0.72** | 0.76** |
| X17 | 0.87** | 0.68** | 0.44** | 0.80** | -0.47* | -0.82** | -0.37* | -0.72** | -0.46** | -0.46** | -0.35* | 0.66** | -0.81** | 0.89** | 0.25 | 0.74** | 0.90** | 0.87** |
| X18 | 0.87** | 0.64** | 0.38* | 0.80** | -0.49** | -0.84** | -0.37* | -0.71** | -0.47** | -0.55** | -0.46** | 0.67** | -0.84** | 0.94** | 0.28 | 0.75** | 0.90** | 0.89** |
| X19 | 0.71** | 0.52** | 0.27 | 0.69** | -0.20 | -0.76** | -0.32* | -0.57** | -0.40* | -0.56** | -0.55** | 0.64** | -0.77** | 0.89** | 0.11 | 0.65** | 0.77** | 0.72** |
| X20 | 0.94** | 0.74** | 0.50** | 0.83** | -0.33 | -0.74** | -0.43** | -0.66** | -0.42** | -0.30 | -0.1 | 0.63** | -0.68** | 0.93** | 0.39* | 0.85** | 0.87** | 0.87** |
| X21 | 0.33* | 0.26 | -0.07 | 0.61** | -0.12 | -0.28 | 0.07 | -0.16 | -0.23 | -0.58** | -0.61** | 0.74** | -0.43** | 0.42** | 0.19 | 0.38* | 0.40** | 0.58** |
| X22 | 0.88** | 0.75** | 0.48** | 0.88** | -0.35 | -0.75** | -0.32* | -0.60** | -0.43** | -0.39* | -0.33* | 0.81** | -0.79** | 0.93** | 0.29 | 0.76** | 0.89** | 0.87** |
| X23 | 0.71** | 0.40** | 0.08 | 0.70** | -0.41* | -0.61** | -0.23 | -0.54** | -0.34* | -0.59** | -0.47** | 0.62** | -0.50** | 0.90** | 0.20 | 0.80** | 0.65** | 0.69** |
| X24 | 0.97** | 0.86** | 0.65** | 0.83** | -0.39* | -0.86** | -0.84** | -0.78** | -0.48** | -0.25 | -0.15 | 0.65** | -0.84** | 0.85** | 0.50** | 0.69** | 0.98** | 0.95** |
| X25 | 0.80** | 0.56** | 0.28 | 0.75** | -0.41* | -0.69** | -0.32* | -0.60** | -0.39* | -0.47** | -0.32* | 0.64** | -0.61** | 0.90** | 0.28 | 0.75** | 0.76** | 0.77** |
| X26 | -0.73** | -0.71** | -0.74** | -0.48** | -0.02 | 0.57** | 0.71** | 0.54** | 0.24 | -0.17 | -0.22 | -0.25 | 0.60** | -0.49** | -0.75** | -0.42** | -0.70** | -0.64** |
| X27 | 0.74** | 0.47** | 0.15 | 0.75** | -0.38* | -0.70** | -0.27 | -0.57** | -0.38* | -0.62** | -0.53** | 0.67** | -0.65** | 0.90** | 0.15 | 0.78** | 0.73** | 0.74** |
| X28 | -0.08 | 0.04 | 0.19 | -0.17 | 0.17 | -0.02 | -0.06 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.28 | 0.16 | -0.22 | -0.01 | -0.20 | -0.33 | -0.25 | -0.05 | -0.15 |
| X29 | -0.15 | -0.11 | -0.02 | -0.20 | 0.03 | -0.03 | 0.04 | -0.03 | -0.06 | 0.04 | -0.06 | -0.20 | 0.01 | -0.09 | -0.28 | -0.21 | -0.10 | -0.11 |
| X30 | 0.15 | 0.28 | 0.42** | 0.03 | 0.60** | 0.10 | -0.23 | 0.20 | 0.25 | 0.57** | 0.55** | -0.12 | 0.07 | -0.11 | -0.33 | 0.05 | 0.04 | -0.21 |
| X31 | -0.23 | -0.08 | 0.08 | -0.27 | 0.37 | 0.29 | 0.09 | 0.29 | 0.37* | 0.49** | 0.46** | -0.27 | 0.43** | -0.30 | -0.30 | -0.22 | -0.31 | -0.31 |
| X32 | -0.03 | 0.06 | 0.18 | -0.11 | 0.12 | -0.06 | -0.09 | -0.01 | 0.01 | 0.21 | 0.11 | -0.18 | -0.06 | -0.13 | -0.28 | -0.18 | 0.01 | -0.09 |
| X33 | -0.11 | -0.09 | -0.06 | -0.11 | -0.04 | -0.08 | 0.03 | -0.05 | -0.10 | -0.08 | -0.17 | -0.11 | -0.08 | -0.02 | -0.20 | -0.16 | -0.03 | -0.03 |
| X34 | 0.22 | 0.36* | 0.51** | 0.07 | 0.58** | 0.05 | -0.19 | 0.11 | 0.19 | 0.63** | 0.63** | -0.1 | 0.07 | -0.08 | -0.3 | 0.06 | 0.09 | -0.11 |
| X35 | -0.10 | -0.01 | 0.16 | -0.21 | 0.37* | 0.26 | -0.13 | 0.32* | 0.21 | 0.52** | 0.51** | -0.31* | 0.34* | -0.22 | -0.14 | -0.02 | -0.21 | -0.30 |
表5 贵州省粮食作物播种面积和影响因素的相关性分析
Table 5 Correlation analysis of sown area and influencing factors of grain crops in Guizhou Province
| 指标Index | 农作物 Crop | 粮食 Grain | 夏粮 Summer grain | 秋粮Autumn grain | 谷物 Cereal | 稻谷 Rice | 早稻 Early rice | 中稻和一季晚稻 Middle season rice and one season late rice | 双季晚稻 Double cropping late rice | 小麦Wheat | 冬小麦Winter wheat | 玉米Maize | 谷子Millet | 高粱Sorghum | 豆类Beans | 大豆Soybean | 薯类Tubers | 马铃薯Potato |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 0.82** | 0.84** | 0.86** | 0.58** | -0.03 | -0.59** | -0.57** | -0.57** | -0.34* | 0.24 | 0.32* | 0.33* | -0.63** | 0.51** | 0.78** | 0.43** | 0.79** | 0.72** |
| X2 | -0.81** | -0.62** | -0.42** | -0.71** | 0.63** | 0.81** | 0.57** | 0.69** | 0.52** | 0.52** | 0.46** | -0.59** | 0.90** | -0.80** | -0.42* | -0.56** | -0.89** | -0.89** |
| X3 | -0.82** | -0.64** | -0.45** | -0.71** | 0.61** | 0.80** | 0.59** | 0.68** | 0.47** | 0.47** | 0.42** | -0.59** | 0.88** | -0.80** | -0.37 | -0.57** | -0.89** | -0.89** |
| X4 | 0.44** | 0.56** | 0.72** | 0.19 | 0.08 | -0.33* | -0.44** | -0.33* | -0.11 | 0.41** | 0.38* | 0.01 | -0.39* | 0.09 | 0.16 | -0.02 | 0.45** | 0.27 |
| X5 | 0.72** | 0.47** | 0.28 | 0.58** | -0.12 | -0.57** | -0.38* | -0.49** | -0.34* | -0.24 | -0.02 | 0.44** | -0.37* | 0.80** | 0.11 | 0.82** | 0.58** | 0.52** |
| X6 | 0.97** | 0.79** | 0.59** | 0.83** | -0.40* | -0.78** | -0.49** | -0.70** | -0.43** | -0.24 | -0.06 | 0.63** | -0.74** | 0.90** | 0.46* | 0.79** | 0.92** | 0.91** |
| X7 | 0.83** | 0.55** | 0.25 | 0.79** | -0.55** | -0.77** | -0.32* | -0.69** | -0.45** | -0.61** | -0.50** | 0.70** | -0.72** | 0.94** | 0.30 | 0.77** | 0.83** | 0.86** |
| X8 | 0.82** | 0.59** | 0.31* | 0.78** | -0.44* | -0.80** | -0.35* | -0.67** | -0.44** | -0.57** | -0.49** | 0.70** | -0.77** | 0.91** | 0.24 | 0.75** | 0.84** | 0.81** |
| X9 | 0.86** | 0.73** | 0.50** | 0.82** | -0.57** | -0.81** | -0.29 | -0.74** | -0.52** | -0.46** | -0.39* | 0.69** | -0.91** | 0.83** | 0.47* | 0.60** | 0.94** | 0.96** |
| X10 | -0.22 | 0.05 | 0.34* | -0.35* | 0.25 | 0.3 | -0.06 | 0.21 | 0.06 | 0.67** | 0.60** | -0.43** | 0.18 | -0.56** | 0.15 | -0.44** | -0.20 | -0.36* |
| X11 | 0.79** | 0.58** | 0.25 | 0.85** | -0.41* | -0.67** | -0.29 | -0.54** | -0.39* | -0.54** | -0.46** | 0.86** | -0.65** | 0.92** | 0.19 | 0.79** | 0.76** | 0.77** |
| X12 | 0.73** | 0.50** | 0.24 | 0.70** | -0.19 | -0.68** | -0.26 | -0.49** | -0.35* | -0.50** | -0.42** | 0.57** | -0.65** | 0.86** | 0.14 | 0.74** | 0.70** | 0.70** |
| X13 | 0.78** | 0.49** | 0.17 | 0.76** | -0.42* | -0.70** | -0.28 | -0.60** | -0.39* | -0.59** | -0.48** | 0.66** | -0.62** | 0.94** | 0.21 | 0.81** | 0.74** | 0.77** |
| X14 | 0.78** | 0.49** | 0.17 | 0.76** | -0.45* | -0.69** | -0.28 | -0.61** | -0.39* | -0.58** | -0.46** | 0.67** | -0.60** | 0.93** | 0.24 | 0.81** | 0.74** | 0.77** |
| X15 | 0.73** | 0.59** | 0.47** | 0.70** | -0.48* | -0.77** | -0.32 | -0.67** | -0.40* | -0.32 | -0.32 | 0.75** | -0.88** | 0.86** | 0.28 | 0.39* | 0.87** | 0.82** |
| X16 | 0.79** | 0.50** | 0.20 | 0.76** | -0.41* | -0.66** | -0.29 | -0.59** | -0.37* | -0.53** | -0.38* | 0.67** | -0.55** | 0.91** | 0.26 | 0.83** | 0.72** | 0.76** |
| X17 | 0.87** | 0.68** | 0.44** | 0.80** | -0.47* | -0.82** | -0.37* | -0.72** | -0.46** | -0.46** | -0.35* | 0.66** | -0.81** | 0.89** | 0.25 | 0.74** | 0.90** | 0.87** |
| X18 | 0.87** | 0.64** | 0.38* | 0.80** | -0.49** | -0.84** | -0.37* | -0.71** | -0.47** | -0.55** | -0.46** | 0.67** | -0.84** | 0.94** | 0.28 | 0.75** | 0.90** | 0.89** |
| X19 | 0.71** | 0.52** | 0.27 | 0.69** | -0.20 | -0.76** | -0.32* | -0.57** | -0.40* | -0.56** | -0.55** | 0.64** | -0.77** | 0.89** | 0.11 | 0.65** | 0.77** | 0.72** |
| X20 | 0.94** | 0.74** | 0.50** | 0.83** | -0.33 | -0.74** | -0.43** | -0.66** | -0.42** | -0.30 | -0.1 | 0.63** | -0.68** | 0.93** | 0.39* | 0.85** | 0.87** | 0.87** |
| X21 | 0.33* | 0.26 | -0.07 | 0.61** | -0.12 | -0.28 | 0.07 | -0.16 | -0.23 | -0.58** | -0.61** | 0.74** | -0.43** | 0.42** | 0.19 | 0.38* | 0.40** | 0.58** |
| X22 | 0.88** | 0.75** | 0.48** | 0.88** | -0.35 | -0.75** | -0.32* | -0.60** | -0.43** | -0.39* | -0.33* | 0.81** | -0.79** | 0.93** | 0.29 | 0.76** | 0.89** | 0.87** |
| X23 | 0.71** | 0.40** | 0.08 | 0.70** | -0.41* | -0.61** | -0.23 | -0.54** | -0.34* | -0.59** | -0.47** | 0.62** | -0.50** | 0.90** | 0.20 | 0.80** | 0.65** | 0.69** |
| X24 | 0.97** | 0.86** | 0.65** | 0.83** | -0.39* | -0.86** | -0.84** | -0.78** | -0.48** | -0.25 | -0.15 | 0.65** | -0.84** | 0.85** | 0.50** | 0.69** | 0.98** | 0.95** |
| X25 | 0.80** | 0.56** | 0.28 | 0.75** | -0.41* | -0.69** | -0.32* | -0.60** | -0.39* | -0.47** | -0.32* | 0.64** | -0.61** | 0.90** | 0.28 | 0.75** | 0.76** | 0.77** |
| X26 | -0.73** | -0.71** | -0.74** | -0.48** | -0.02 | 0.57** | 0.71** | 0.54** | 0.24 | -0.17 | -0.22 | -0.25 | 0.60** | -0.49** | -0.75** | -0.42** | -0.70** | -0.64** |
| X27 | 0.74** | 0.47** | 0.15 | 0.75** | -0.38* | -0.70** | -0.27 | -0.57** | -0.38* | -0.62** | -0.53** | 0.67** | -0.65** | 0.90** | 0.15 | 0.78** | 0.73** | 0.74** |
| X28 | -0.08 | 0.04 | 0.19 | -0.17 | 0.17 | -0.02 | -0.06 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.28 | 0.16 | -0.22 | -0.01 | -0.20 | -0.33 | -0.25 | -0.05 | -0.15 |
| X29 | -0.15 | -0.11 | -0.02 | -0.20 | 0.03 | -0.03 | 0.04 | -0.03 | -0.06 | 0.04 | -0.06 | -0.20 | 0.01 | -0.09 | -0.28 | -0.21 | -0.10 | -0.11 |
| X30 | 0.15 | 0.28 | 0.42** | 0.03 | 0.60** | 0.10 | -0.23 | 0.20 | 0.25 | 0.57** | 0.55** | -0.12 | 0.07 | -0.11 | -0.33 | 0.05 | 0.04 | -0.21 |
| X31 | -0.23 | -0.08 | 0.08 | -0.27 | 0.37 | 0.29 | 0.09 | 0.29 | 0.37* | 0.49** | 0.46** | -0.27 | 0.43** | -0.30 | -0.30 | -0.22 | -0.31 | -0.31 |
| X32 | -0.03 | 0.06 | 0.18 | -0.11 | 0.12 | -0.06 | -0.09 | -0.01 | 0.01 | 0.21 | 0.11 | -0.18 | -0.06 | -0.13 | -0.28 | -0.18 | 0.01 | -0.09 |
| X33 | -0.11 | -0.09 | -0.06 | -0.11 | -0.04 | -0.08 | 0.03 | -0.05 | -0.10 | -0.08 | -0.17 | -0.11 | -0.08 | -0.02 | -0.20 | -0.16 | -0.03 | -0.03 |
| X34 | 0.22 | 0.36* | 0.51** | 0.07 | 0.58** | 0.05 | -0.19 | 0.11 | 0.19 | 0.63** | 0.63** | -0.1 | 0.07 | -0.08 | -0.3 | 0.06 | 0.09 | -0.11 |
| X35 | -0.10 | -0.01 | 0.16 | -0.21 | 0.37* | 0.26 | -0.13 | 0.32* | 0.21 | 0.52** | 0.51** | -0.31* | 0.34* | -0.22 | -0.14 | -0.02 | -0.21 | -0.30 |
| 指标Index | 农作物 Crop | 粮食 Grain | 夏粮 Summer grain | 秋粮Autumn grain | 谷物 Cereal | 稻谷 Rice | 早稻 Early rice | 中稻和一季晚稻 Middle season rice and one season late rice | 双季晚稻 Double cropping late rice | 小麦Wheat | 冬小麦Winter wheat | 玉米Maize | 谷子Millet | 高粱Sorghum | 豆类Beans | 大豆Soybean | 薯类Tubers | 马铃薯Potato |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 0.97** | 0.88** | 0.62** | 0.83** | 0.46* | -0.16 | -0.46** | -0.51** | -0.09 | -0.37* | -0.28 | 0.77** | 0.60** | -0.57** | 0.36 | 0.90** | 0.92** | 0.95** |
| X2 | -0.92** | -0.86** | -0.47** | -0.88** | -0.36 | -0.02 | 0.51** | 0.34* | 0.22 | 0.52** | 0.47** | -0.81** | -0.54** | 0.51** | -0.31 | -0.85** | -0.92** | -0.95** |
| X3 | -0.90** | -0.84** | -0.45** | -0.86** | -0.38* | -0.02 | 0.54** | 0.33* | 0.20 | 0.51** | 0.47** | -0.79** | -0.54** | 0.52** | -0.31 | -0.84** | -0.90** | -0.94** |
| X4 | 0.65** | 0.60** | 0.77** | 0.41** | -0.19 | -0.18 | -0.20 | -0.35* | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.03 | 0.24 | 0.38* | -0.64** | 0.30 | 0.56** | 0.66** | 0.53** |
| X5 | 0.93** | 0.78** | 0.36* | 0.83** | 0.40* | -0.16 | -0.65** | -0.60** | -0.06 | -0.58** | -0.48** | 0.88** | 0.63** | -0.49** | 0.17 | 0.90** | 0.81** | 0.84** |
| X6 | 0.95** | 0.84** | 0.35* | 0.91** | 0.48* | -0.10 | -0.58** | -0.51** | -0.13 | -0.61** | -0.50** | 0.95** | 0.61** | -0.41** | 0.2 | 0.92** | 0.86** | 0.90** |
| X7 | 0.89** | 0.78** | 0.22 | 0.90** | 0.46* | -0.08 | -0.60** | -0.47** | -0.16 | -0.69** | -0.59** | 0.97** | 0.58** | -0.35* | 0.16 | 0.89** | 0.80** | 0.86** |
| X8 | 0.96** | 0.86** | 0.40* | 0.91** | 0.46* | -0.07 | -0.59** | -0.52** | -0.11 | -0.55** | -0.45** | 0.92** | 0.61** | -0.43** | 0.23 | 0.92** | 0.87** | 0.90** |
| X9 | 0.96** | 0.92** | 0.53** | 0.92** | 0.44* | -0.01 | -0.39* | -0.35* | -0.24 | -0.49** | -0.41** | 0.84** | 0.52** | -0.46** | 0.31 | 0.89** | 0.97** | 0.99** |
| X10 | -0.65** | -0.62** | -0.15 | -0.72** | -0.45* | 0.01 | 0.31 | 0.39* | 0.05 | 0.41** | 0.24 | -0.80** | -0.40** | 0.14 | 0.06 | -0.63** | -0.56** | -0.71** |
| X11 | 0.83** | 0.70** | 0.15 | 0.83** | 0.48** | -0.17 | -0.59** | -0.53** | -0.07 | -0.65** | -0.52** | 0.96** | 0.58** | -0.27 | 0.09 | 0.85** | 0.70** | 0.76** |
| X12 | 0.85** | 0.76** | 0.25 | 0.86** | 0.49** | 0.09 | -.60** | -0.46** | -0.07 | -0.60** | -0.51** | 0.89** | 0.54** | -0.30 | 0.09 | 0.81** | 0.73** | 0.77** |
| X13 | 0.85** | 0.73** | 0.19 | 0.85** | 0.49** | -0.09 | -0.61** | -0.53** | -0.05 | -0.64** | -0.52** | 0.95** | 0.57** | -0.28 | 0.08 | 0.85** | 0.72** | 0.77** |
| X14 | 0.87** | 0.74** | 0.20 | 0.86** | 0.49** | -0.14 | -0.59** | -0.53** | -0.08 | -0.64** | -0.51** | 0.97** | 0.59** | -0.3 | 0.12 | 0.87** | 0.74** | 0.80** |
| X15 | 0.89** | 0.78** | 0.24 | 0.89** | 0.48* | -0.06 | -0.62** | -0.51** | -0.10 | -0.64** | -0.54** | 0.96** | 0.59** | -0.33* | 0.14 | 0.87** | 0.78** | 0.82** |
| X16 | 0.90** | 0.78** | 0.26 | 0.88** | 0.49** | -0.13 | -0.58** | -0.53** | -0.09 | -0.62** | -0.50** | 0.97** | 0.61** | -0.33* | 0.14 | 0.89** | 0.78** | 0.83** |
| X17 | 0.98** | 0.90** | 0.56** | 0.89** | 0.50** | -0.17 | -0.46** | -0.52** | -0.08 | -0.42** | -0.29 | 0.87** | 0.63** | -0.48** | 0.33 | 0.93** | 0.91** | 0.94** |
| X18 | 0.96** | 0.87** | 0.42** | 0.92** | 0.51** | -0.06 | -0.56** | -0.50** | -0.11 | -0.55** | -0.45** | 0.93** | 0.61** | -0.43** | 0.21 | 0.92** | 0.89** | 0.91** |
| X19 | 0.79** | 0.72** | 0.24 | 0.83** | 0.43* | 0.26 | -0.58** | -0.34* | -0.14 | -0.60** | -0.60** | 0.84** | 0.47** | -0.28 | 0.12 | 0.76** | 0.74** | 0.73** |
| X20 | 0.95** | 0.89** | 0.73** | 0.80** | 0.55** | -0.15 | -0.40* | -0.53** | -0.01 | -0.22 | -0.15 | 0.71** | 0.58** | -0.54** | 0.40* | 0.88** | 0.90** | 0.88** |
| X21 | 0.66** | 0.58** | -0.02 | 0.76** | 0.49** | 0.07 | -0.54** | -0.37* | -0.09 | -0.64** | -0.55** | 0.87** | 0.45** | -0.08 | 0.06 | 0.67** | 0.55** | 0.65** |
| X22 | 0.98** | 0.90** | 0.50** | 0.93** | 0.51** | 0.04 | -0.53** | -0.45** | -0.11 | -0.49** | -0.43** | 0.93** | 0.59** | -0.43** | 0.25 | 0.92** | 0.91** | 0.92** |
| X23 | 0.89** | 0.79** | 0.24 | 0.90** | 0.50** | -0.09 | -0.59** | -0.50** | -0.10 | -0.64** | -0.52** | 0.98** | 0.59** | -0.3 | 0.15 | 0.88** | 0.78** | 0.84** |
| X24 | 0.59** | 0.49** | -0.13 | 0.70** | 0.47* | 0.15 | -0.62** | -0.16 | -0.28 | -0.81** | -0.77** | 0.75** | 0.35* | -0.16 | 0.25 | 0.63** | 0.57** | 0.61** |
| X25 | 0.94** | 0.84** | 0.36* | 0.91** | 0.51** | -0.12 | -0.55** | -0.52** | -0.09 | -0.57** | -0.45** | 0.96** | 0.56** | -0.38* | 0.18 | 0.92** | 0.84** | 0.89** |
| X26 | -0.76** | -0.70** | -0.51** | -0.66** | -0.39* | -0.04 | 0.42** | 0.12 | 0.3 | 0.37* | 0.37* | -0.49** | -0.31* | 0.58** | -0.27 | -0.69** | -0.82** | -0.86** |
| X27 | 0.80** | 0.69** | 0.12 | 0.83** | 0.47* | -0.04 | -0.62** | -0.50** | -0.08 | -0.66** | -0.56** | 0.92** | 0.56** | -0.26 | 0.09 | 0.83** | 0.67** | 0.72** |
| X28 | 0.25 | 0.28 | 0.40* | 0.17 | -0.25 | 0.07 | -0.04 | -0.06 | -0.01 | 0.06 | -0.13 | -0.02 | 0.04 | -0.33* | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.37* | 0.26 |
| X29 | 0.19 | 0.23 | 0.24 | 0.18 | -0.14 | 0.12 | -0.11 | -0.03 | -0.06 | -0.03 | -0.18 | 0.02 | -0.02 | -0.26 | 0.10 | 0.13 | 0.29 | 0.25 |
| X30 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.49** | -0.17 | -0.30 | -0.25 | 0.10 | -0.16 | 0.26 | 0.46** | 0.44** | -0.23 | 0.16 | -0.23 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.01 | -0.23 |
| X31 | 0.06 | 0.10 | 0.30 | -0.02 | -0.23 | 0.19 | 0.25 | 0.24 | 0.01 | 0.23 | 0.15 | -0.18 | 0.06 | -0.19 | 0.26 | 0.05 | 0.13 | -0.01 |
| X32 | 0.30 | 0.35* | 0.39* | 0.25 | -0.17 | 0.06 | -0.05 | -0.07 | -0.08 | 0.01 | -0.13 | 0.08 | 0.12 | -0.31* | 0.20 | 0.24 | 0.42** | 0.33* |
| X33 | 0.23 | 0.28 | 0.21 | 0.25 | -0.06 | 0.13 | -0.14 | 0.01 | -0.15 | -0.10 | -0.22 | 0.11 | 0.03 | -0.23 | 0.10 | 0.17 | 0.34* | 0.3 |
| X34 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.48** | -0.17 | -0.26 | -0.27 | 0.17 | -0.21 | 0.29 | 0.48** | 0.48** | -0.20 | 0.19 | -0.21 | -0.02 | 0.02 | -0.01 | -0.21 |
| X35 | 0.14 | 0.19 | 0.42** | 0.04 | -0.21 | 0.06 | 0.28 | 0.11 | 0.08 | 0.30 | 0.28 | -0.09 | 0.20 | -0.19 | 0.37 | 0.12 | 0.18 | 0.07 |
表6 云南省粮食作物播种面积和影响因素的相关性分析
Table 6 Correlation analysis of sown area and influencing factors of grain crops in Yunnan Province
| 指标Index | 农作物 Crop | 粮食 Grain | 夏粮 Summer grain | 秋粮Autumn grain | 谷物 Cereal | 稻谷 Rice | 早稻 Early rice | 中稻和一季晚稻 Middle season rice and one season late rice | 双季晚稻 Double cropping late rice | 小麦Wheat | 冬小麦Winter wheat | 玉米Maize | 谷子Millet | 高粱Sorghum | 豆类Beans | 大豆Soybean | 薯类Tubers | 马铃薯Potato |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 0.97** | 0.88** | 0.62** | 0.83** | 0.46* | -0.16 | -0.46** | -0.51** | -0.09 | -0.37* | -0.28 | 0.77** | 0.60** | -0.57** | 0.36 | 0.90** | 0.92** | 0.95** |
| X2 | -0.92** | -0.86** | -0.47** | -0.88** | -0.36 | -0.02 | 0.51** | 0.34* | 0.22 | 0.52** | 0.47** | -0.81** | -0.54** | 0.51** | -0.31 | -0.85** | -0.92** | -0.95** |
| X3 | -0.90** | -0.84** | -0.45** | -0.86** | -0.38* | -0.02 | 0.54** | 0.33* | 0.20 | 0.51** | 0.47** | -0.79** | -0.54** | 0.52** | -0.31 | -0.84** | -0.90** | -0.94** |
| X4 | 0.65** | 0.60** | 0.77** | 0.41** | -0.19 | -0.18 | -0.20 | -0.35* | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.03 | 0.24 | 0.38* | -0.64** | 0.30 | 0.56** | 0.66** | 0.53** |
| X5 | 0.93** | 0.78** | 0.36* | 0.83** | 0.40* | -0.16 | -0.65** | -0.60** | -0.06 | -0.58** | -0.48** | 0.88** | 0.63** | -0.49** | 0.17 | 0.90** | 0.81** | 0.84** |
| X6 | 0.95** | 0.84** | 0.35* | 0.91** | 0.48* | -0.10 | -0.58** | -0.51** | -0.13 | -0.61** | -0.50** | 0.95** | 0.61** | -0.41** | 0.2 | 0.92** | 0.86** | 0.90** |
| X7 | 0.89** | 0.78** | 0.22 | 0.90** | 0.46* | -0.08 | -0.60** | -0.47** | -0.16 | -0.69** | -0.59** | 0.97** | 0.58** | -0.35* | 0.16 | 0.89** | 0.80** | 0.86** |
| X8 | 0.96** | 0.86** | 0.40* | 0.91** | 0.46* | -0.07 | -0.59** | -0.52** | -0.11 | -0.55** | -0.45** | 0.92** | 0.61** | -0.43** | 0.23 | 0.92** | 0.87** | 0.90** |
| X9 | 0.96** | 0.92** | 0.53** | 0.92** | 0.44* | -0.01 | -0.39* | -0.35* | -0.24 | -0.49** | -0.41** | 0.84** | 0.52** | -0.46** | 0.31 | 0.89** | 0.97** | 0.99** |
| X10 | -0.65** | -0.62** | -0.15 | -0.72** | -0.45* | 0.01 | 0.31 | 0.39* | 0.05 | 0.41** | 0.24 | -0.80** | -0.40** | 0.14 | 0.06 | -0.63** | -0.56** | -0.71** |
| X11 | 0.83** | 0.70** | 0.15 | 0.83** | 0.48** | -0.17 | -0.59** | -0.53** | -0.07 | -0.65** | -0.52** | 0.96** | 0.58** | -0.27 | 0.09 | 0.85** | 0.70** | 0.76** |
| X12 | 0.85** | 0.76** | 0.25 | 0.86** | 0.49** | 0.09 | -.60** | -0.46** | -0.07 | -0.60** | -0.51** | 0.89** | 0.54** | -0.30 | 0.09 | 0.81** | 0.73** | 0.77** |
| X13 | 0.85** | 0.73** | 0.19 | 0.85** | 0.49** | -0.09 | -0.61** | -0.53** | -0.05 | -0.64** | -0.52** | 0.95** | 0.57** | -0.28 | 0.08 | 0.85** | 0.72** | 0.77** |
| X14 | 0.87** | 0.74** | 0.20 | 0.86** | 0.49** | -0.14 | -0.59** | -0.53** | -0.08 | -0.64** | -0.51** | 0.97** | 0.59** | -0.3 | 0.12 | 0.87** | 0.74** | 0.80** |
| X15 | 0.89** | 0.78** | 0.24 | 0.89** | 0.48* | -0.06 | -0.62** | -0.51** | -0.10 | -0.64** | -0.54** | 0.96** | 0.59** | -0.33* | 0.14 | 0.87** | 0.78** | 0.82** |
| X16 | 0.90** | 0.78** | 0.26 | 0.88** | 0.49** | -0.13 | -0.58** | -0.53** | -0.09 | -0.62** | -0.50** | 0.97** | 0.61** | -0.33* | 0.14 | 0.89** | 0.78** | 0.83** |
| X17 | 0.98** | 0.90** | 0.56** | 0.89** | 0.50** | -0.17 | -0.46** | -0.52** | -0.08 | -0.42** | -0.29 | 0.87** | 0.63** | -0.48** | 0.33 | 0.93** | 0.91** | 0.94** |
| X18 | 0.96** | 0.87** | 0.42** | 0.92** | 0.51** | -0.06 | -0.56** | -0.50** | -0.11 | -0.55** | -0.45** | 0.93** | 0.61** | -0.43** | 0.21 | 0.92** | 0.89** | 0.91** |
| X19 | 0.79** | 0.72** | 0.24 | 0.83** | 0.43* | 0.26 | -0.58** | -0.34* | -0.14 | -0.60** | -0.60** | 0.84** | 0.47** | -0.28 | 0.12 | 0.76** | 0.74** | 0.73** |
| X20 | 0.95** | 0.89** | 0.73** | 0.80** | 0.55** | -0.15 | -0.40* | -0.53** | -0.01 | -0.22 | -0.15 | 0.71** | 0.58** | -0.54** | 0.40* | 0.88** | 0.90** | 0.88** |
| X21 | 0.66** | 0.58** | -0.02 | 0.76** | 0.49** | 0.07 | -0.54** | -0.37* | -0.09 | -0.64** | -0.55** | 0.87** | 0.45** | -0.08 | 0.06 | 0.67** | 0.55** | 0.65** |
| X22 | 0.98** | 0.90** | 0.50** | 0.93** | 0.51** | 0.04 | -0.53** | -0.45** | -0.11 | -0.49** | -0.43** | 0.93** | 0.59** | -0.43** | 0.25 | 0.92** | 0.91** | 0.92** |
| X23 | 0.89** | 0.79** | 0.24 | 0.90** | 0.50** | -0.09 | -0.59** | -0.50** | -0.10 | -0.64** | -0.52** | 0.98** | 0.59** | -0.3 | 0.15 | 0.88** | 0.78** | 0.84** |
| X24 | 0.59** | 0.49** | -0.13 | 0.70** | 0.47* | 0.15 | -0.62** | -0.16 | -0.28 | -0.81** | -0.77** | 0.75** | 0.35* | -0.16 | 0.25 | 0.63** | 0.57** | 0.61** |
| X25 | 0.94** | 0.84** | 0.36* | 0.91** | 0.51** | -0.12 | -0.55** | -0.52** | -0.09 | -0.57** | -0.45** | 0.96** | 0.56** | -0.38* | 0.18 | 0.92** | 0.84** | 0.89** |
| X26 | -0.76** | -0.70** | -0.51** | -0.66** | -0.39* | -0.04 | 0.42** | 0.12 | 0.3 | 0.37* | 0.37* | -0.49** | -0.31* | 0.58** | -0.27 | -0.69** | -0.82** | -0.86** |
| X27 | 0.80** | 0.69** | 0.12 | 0.83** | 0.47* | -0.04 | -0.62** | -0.50** | -0.08 | -0.66** | -0.56** | 0.92** | 0.56** | -0.26 | 0.09 | 0.83** | 0.67** | 0.72** |
| X28 | 0.25 | 0.28 | 0.40* | 0.17 | -0.25 | 0.07 | -0.04 | -0.06 | -0.01 | 0.06 | -0.13 | -0.02 | 0.04 | -0.33* | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.37* | 0.26 |
| X29 | 0.19 | 0.23 | 0.24 | 0.18 | -0.14 | 0.12 | -0.11 | -0.03 | -0.06 | -0.03 | -0.18 | 0.02 | -0.02 | -0.26 | 0.10 | 0.13 | 0.29 | 0.25 |
| X30 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.49** | -0.17 | -0.30 | -0.25 | 0.10 | -0.16 | 0.26 | 0.46** | 0.44** | -0.23 | 0.16 | -0.23 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.01 | -0.23 |
| X31 | 0.06 | 0.10 | 0.30 | -0.02 | -0.23 | 0.19 | 0.25 | 0.24 | 0.01 | 0.23 | 0.15 | -0.18 | 0.06 | -0.19 | 0.26 | 0.05 | 0.13 | -0.01 |
| X32 | 0.30 | 0.35* | 0.39* | 0.25 | -0.17 | 0.06 | -0.05 | -0.07 | -0.08 | 0.01 | -0.13 | 0.08 | 0.12 | -0.31* | 0.20 | 0.24 | 0.42** | 0.33* |
| X33 | 0.23 | 0.28 | 0.21 | 0.25 | -0.06 | 0.13 | -0.14 | 0.01 | -0.15 | -0.10 | -0.22 | 0.11 | 0.03 | -0.23 | 0.10 | 0.17 | 0.34* | 0.3 |
| X34 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.48** | -0.17 | -0.26 | -0.27 | 0.17 | -0.21 | 0.29 | 0.48** | 0.48** | -0.20 | 0.19 | -0.21 | -0.02 | 0.02 | -0.01 | -0.21 |
| X35 | 0.14 | 0.19 | 0.42** | 0.04 | -0.21 | 0.06 | 0.28 | 0.11 | 0.08 | 0.30 | 0.28 | -0.09 | 0.20 | -0.19 | 0.37 | 0.12 | 0.18 | 0.07 |
| 省份/自治区 Province/Autono-mous region | 关联度Correlation degree | 关联度分布频率 Frequency distribution of correlation degree | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最大值MAX | 最小值 MIN | 平均值Average | 标准差 Std. Deviation | [0.0, 0.3] | [0.3,0.4] | [0.4,0.5] | [0.5,0.6] | [0.6,0.7] | [0.7,0.8] | [0.8,0.9] | [0.9,1.0] | ||
| 广东 Guangdong | 0.94 | 0.32 | 0.62 | 0.14 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.17 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.17 | 0.08 | 0.02 | |
| 广西 Guangxi | 0.99 | 0.67 | 0.84 | 0.07 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.27 | 0.50 | 0.21 | |
| 四川 Sichuan | 0.86 | 0.23 | 0.49 | 0.14 | 0.02 | 0.30 | 0.23 | 0.21 | 0.12 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 0.00 | |
| 贵州 Guizhou | 0.93 | 0.29 | 0.56 | 0.12 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.30 | 0.26 | 0.23 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.00 | |
| 云南 Yunnan | 0.93 | 0.3 | 0.56 | 0.13 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.23 | 0.31 | 0.22 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.01 | |
表7 西南和华南各省粮食作物播种面积变化和影响因素的灰色关联度统计特征
Table 7 Statistical characteristics of grey correlation degree between sown area and influencing factors of grain crops in Southwest and South China
| 省份/自治区 Province/Autono-mous region | 关联度Correlation degree | 关联度分布频率 Frequency distribution of correlation degree | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最大值MAX | 最小值 MIN | 平均值Average | 标准差 Std. Deviation | [0.0, 0.3] | [0.3,0.4] | [0.4,0.5] | [0.5,0.6] | [0.6,0.7] | [0.7,0.8] | [0.8,0.9] | [0.9,1.0] | ||
| 广东 Guangdong | 0.94 | 0.32 | 0.62 | 0.14 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.17 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.17 | 0.08 | 0.02 | |
| 广西 Guangxi | 0.99 | 0.67 | 0.84 | 0.07 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.27 | 0.50 | 0.21 | |
| 四川 Sichuan | 0.86 | 0.23 | 0.49 | 0.14 | 0.02 | 0.30 | 0.23 | 0.21 | 0.12 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 0.00 | |
| 贵州 Guizhou | 0.93 | 0.29 | 0.56 | 0.12 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.30 | 0.26 | 0.23 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.00 | |
| 云南 Yunnan | 0.93 | 0.3 | 0.56 | 0.13 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.23 | 0.31 | 0.22 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.01 | |
| 关联序 Correlation order | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | X12 | X13 | X14 | X15 | X16 | X17 | X18 | X19 | X20 | X21 | X22 | X23 | X24 | X25 | X26 | X27 | X28 | X29 | X30 | X31 | X32 | X33 | X34 | X35 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 农作物 Crop | 3 | 6 | 15 | 2 | 9 | 13 | 29 | 25 | 8 | 4 | 31 | 34 | 33 | 30 | 32 | 27 | 1 | 18 | 23 | 5 | 22 | 11 | 28 | 7 | 26 | 14 | 35 | 10 | 21 | 16 | 19 | 12 | 24 | 17 | 20 |
| 粮食 Grain | 3 | 5 | 10 | 1 | 11 | 18 | 29 | 25 | 13 | 2 | 30 | 34 | 32 | 31 | 33 | 27 | 4 | 22 | 24 | 6 | 21 | 14 | 28 | 8 | 26 | 12 | 35 | 7 | 20 | 15 | 16 | 9 | 23 | 17 | 19 |
| 夏粮 Summer grain | 4 | 5 | 12 | 1 | 10 | 16 | 29 | 25 | 11 | 2 | 30 | 34 | 32 | 31 | 33 | 27 | 3 | 22 | 24 | 6 | 21 | 13 | 28 | 8 | 26 | 14 | 35 | 7 | 20 | 15 | 18 | 9 | 23 | 17 | 19 |
| 秋粮 Autumn grain | 3 | 5 | 11 | 1 | 9 | 18 | 30 | 25 | 12 | 4 | 29 | 34 | 32 | 31 | 33 | 27 | 2 | 21 | 24 | 6 | 22 | 14 | 28 | 8 | 26 | 13 | 35 | 7 | 20 | 15 | 16 | 10 | 23 | 17 | 19 |
| 谷物 Cereal | 2 | 4 | 11 | 1 | 8 | 15 | 27 | 23 | 12 | 3 | 31 | 34 | 33 | 29 | 32 | 25 | 6 | 16 | 30 | 5 | 28 | 10 | 26 | 7 | 20 | 13 | 35 | 9 | 22 | 17 | 19 | 14 | 24 | 18 | 21 |
| 稻谷 Rice | 5 | 3 | 7 | 1 | 12 | 20 | 31 | 25 | 14 | 2 | 29 | 34 | 33 | 30 | 32 | 27 | 4 | 22 | 24 | 8 | 21 | 13 | 28 | 11 | 26 | 9 | 35 | 6 | 19 | 15 | 16 | 10 | 23 | 17 | 18 |
| 早稻 Early rice | 8 | 1 | 5 | 2 | 18 | 24 | 33 | 25 | 15 | 3 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 32 | 35 | 28 | 4 | 23 | 22 | 12 | 21 | 20 | 27 | 17 | 26 | 6 | 34 | 7 | 11 | 13 | 10 | 9 | 16 | 19 | 14 |
| 中稻和一季晚稻 Middle season rice and one season late rice | 4 | 3 | 11 | 1 | 14 | 21 | 30 | 26 | 18 | 2 | 29 | 34 | 32 | 31 | 33 | 27 | 5 | 23 | 24 | 7 | 22 | 19 | 28 | 15 | 25 | 10 | 35 | 8 | 17 | 13 | 6 | 12 | 20 | 16 | 9 |
| 双季晚稻 Double cropping late rice | 8 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 17 | 23 | 35 | 25 | 19 | 4 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 32 | 34 | 27 | 5 | 24 | 22 | 11 | 21 | 20 | 26 | 15 | 28 | 7 | 33 | 6 | 14 | 10 | 13 | 9 | 18 | 16 | 12 |
| 小麦 Wheat | 7 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 18 | 22 | 31 | 26 | 19 | 3 | 29 | 33 | 32 | 30 | 34 | 27 | 9 | 24 | 23 | 14 | 21 | 20 | 28 | 16 | 25 | 12 | 35 | 5 | 15 | 11 | 6 | 10 | 17 | 13 | 8 |
| 冬小麦 Winter wheat | 7 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 18 | 22 | 31 | 26 | 19 | 3 | 29 | 33 | 32 | 30 | 34 | 27 | 9 | 24 | 23 | 14 | 21 | 20 | 28 | 16 | 25 | 12 | 35 | 6 | 15 | 11 | 5 | 10 | 17 | 13 | 8 |
| 玉米 Maize | 1 | 9 | 16 | 3 | 5 | 11 | 29 | 21 | 6 | 4 | 31 | 33 | 34 | 30 | 32 | 28 | 2 | 15 | 26 | 8 | 17 | 10 | 25 | 7 | 22 | 14 | 35 | 12 | 24 | 18 | 19 | 13 | 27 | 20 | 23 |
| 谷子 Millet | 14 | 1 | 6 | 9 | 13 | 15 | 34 | 27 | 23 | 8 | 30 | 31 | 33 | 29 | 32 | 24 | 11 | 22 | 12 | 19 | 10 | 20 | 28 | 25 | 26 | 7 | 35 | 5 | 16 | 17 | 2 | 4 | 18 | 21 | 3 |
| 高粱 Sorghum | 8 | 1 | 5 | 4 | 16 | 19 | 29 | 25 | 13 | 3 | 30 | 34 | 33 | 31 | 32 | 27 | 2 | 22 | 21 | 6 | 23 | 15 | 28 | 7 | 26 | 10 | 35 | 9 | 18 | 12 | 11 | 14 | 24 | 17 | 20 |
| 豆类 Beans | 1 | 7 | 15 | 3 | 12 | 10 | 27 | 23 | 8 | 2 | 31 | 34 | 33 | 30 | 32 | 25 | 4 | 18 | 29 | 5 | 28 | 11 | 26 | 6 | 21 | 14 | 35 | 9 | 22 | 16 | 19 | 13 | 24 | 17 | 20 |
| 大豆 Soybean | 2 | 9 | 16 | 4 | 3 | 13 | 29 | 24 | 5 | 7 | 30 | 34 | 32 | 31 | 33 | 27 | 1 | 17 | 22 | 6 | 23 | 11 | 28 | 8 | 26 | 19 | 35 | 10 | 20 | 14 | 18 | 12 | 25 | 15 | 21 |
| 薯类 Tubers | 6 | 8 | 16 | 3 | 11 | 12 | 29 | 24 | 4 | 7 | 31 | 34 | 33 | 30 | 32 | 27 | 1 | 15 | 20 | 2 | 21 | 9 | 28 | 5 | 26 | 18 | 35 | 10 | 19 | 14 | 22 | 13 | 25 | 17 | 23 |
| 马铃薯 Potato | 5 | 20 | 21 | 10 | 7 | 6 | 25 | 12 | 2 | 11 | 28 | 32 | 29 | 26 | 27 | 17 | 4 | 9 | 23 | 3 | 18 | 8 | 14 | 1 | 16 | 19 | 34 | 13 | 30 | 22 | 35 | 15 | 33 | 24 | 31 |
| 平均关联序Average correlation order | 5 | 5 | 10 | 3 | 12 | 17 | 30 | 24 | 12 | 4 | 30 | 33 | 32 | 30 | 33 | 26 | 4 | 20 | 23 | 8 | 21 | 14 | 27 | 10 | 25 | 12 | 35 | 8 | 19 | 15 | 15 | 11 | 22 | 17 | 17 |
表8 中国西南和华南各粮食作物播种面积变化和影响因素的灰色关联分析
Table 8 Grey correlation analysis on sown area and influencing factors of grain crops in Southwest and South China
| 关联序 Correlation order | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | X12 | X13 | X14 | X15 | X16 | X17 | X18 | X19 | X20 | X21 | X22 | X23 | X24 | X25 | X26 | X27 | X28 | X29 | X30 | X31 | X32 | X33 | X34 | X35 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 农作物 Crop | 3 | 6 | 15 | 2 | 9 | 13 | 29 | 25 | 8 | 4 | 31 | 34 | 33 | 30 | 32 | 27 | 1 | 18 | 23 | 5 | 22 | 11 | 28 | 7 | 26 | 14 | 35 | 10 | 21 | 16 | 19 | 12 | 24 | 17 | 20 |
| 粮食 Grain | 3 | 5 | 10 | 1 | 11 | 18 | 29 | 25 | 13 | 2 | 30 | 34 | 32 | 31 | 33 | 27 | 4 | 22 | 24 | 6 | 21 | 14 | 28 | 8 | 26 | 12 | 35 | 7 | 20 | 15 | 16 | 9 | 23 | 17 | 19 |
| 夏粮 Summer grain | 4 | 5 | 12 | 1 | 10 | 16 | 29 | 25 | 11 | 2 | 30 | 34 | 32 | 31 | 33 | 27 | 3 | 22 | 24 | 6 | 21 | 13 | 28 | 8 | 26 | 14 | 35 | 7 | 20 | 15 | 18 | 9 | 23 | 17 | 19 |
| 秋粮 Autumn grain | 3 | 5 | 11 | 1 | 9 | 18 | 30 | 25 | 12 | 4 | 29 | 34 | 32 | 31 | 33 | 27 | 2 | 21 | 24 | 6 | 22 | 14 | 28 | 8 | 26 | 13 | 35 | 7 | 20 | 15 | 16 | 10 | 23 | 17 | 19 |
| 谷物 Cereal | 2 | 4 | 11 | 1 | 8 | 15 | 27 | 23 | 12 | 3 | 31 | 34 | 33 | 29 | 32 | 25 | 6 | 16 | 30 | 5 | 28 | 10 | 26 | 7 | 20 | 13 | 35 | 9 | 22 | 17 | 19 | 14 | 24 | 18 | 21 |
| 稻谷 Rice | 5 | 3 | 7 | 1 | 12 | 20 | 31 | 25 | 14 | 2 | 29 | 34 | 33 | 30 | 32 | 27 | 4 | 22 | 24 | 8 | 21 | 13 | 28 | 11 | 26 | 9 | 35 | 6 | 19 | 15 | 16 | 10 | 23 | 17 | 18 |
| 早稻 Early rice | 8 | 1 | 5 | 2 | 18 | 24 | 33 | 25 | 15 | 3 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 32 | 35 | 28 | 4 | 23 | 22 | 12 | 21 | 20 | 27 | 17 | 26 | 6 | 34 | 7 | 11 | 13 | 10 | 9 | 16 | 19 | 14 |
| 中稻和一季晚稻 Middle season rice and one season late rice | 4 | 3 | 11 | 1 | 14 | 21 | 30 | 26 | 18 | 2 | 29 | 34 | 32 | 31 | 33 | 27 | 5 | 23 | 24 | 7 | 22 | 19 | 28 | 15 | 25 | 10 | 35 | 8 | 17 | 13 | 6 | 12 | 20 | 16 | 9 |
| 双季晚稻 Double cropping late rice | 8 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 17 | 23 | 35 | 25 | 19 | 4 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 32 | 34 | 27 | 5 | 24 | 22 | 11 | 21 | 20 | 26 | 15 | 28 | 7 | 33 | 6 | 14 | 10 | 13 | 9 | 18 | 16 | 12 |
| 小麦 Wheat | 7 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 18 | 22 | 31 | 26 | 19 | 3 | 29 | 33 | 32 | 30 | 34 | 27 | 9 | 24 | 23 | 14 | 21 | 20 | 28 | 16 | 25 | 12 | 35 | 5 | 15 | 11 | 6 | 10 | 17 | 13 | 8 |
| 冬小麦 Winter wheat | 7 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 18 | 22 | 31 | 26 | 19 | 3 | 29 | 33 | 32 | 30 | 34 | 27 | 9 | 24 | 23 | 14 | 21 | 20 | 28 | 16 | 25 | 12 | 35 | 6 | 15 | 11 | 5 | 10 | 17 | 13 | 8 |
| 玉米 Maize | 1 | 9 | 16 | 3 | 5 | 11 | 29 | 21 | 6 | 4 | 31 | 33 | 34 | 30 | 32 | 28 | 2 | 15 | 26 | 8 | 17 | 10 | 25 | 7 | 22 | 14 | 35 | 12 | 24 | 18 | 19 | 13 | 27 | 20 | 23 |
| 谷子 Millet | 14 | 1 | 6 | 9 | 13 | 15 | 34 | 27 | 23 | 8 | 30 | 31 | 33 | 29 | 32 | 24 | 11 | 22 | 12 | 19 | 10 | 20 | 28 | 25 | 26 | 7 | 35 | 5 | 16 | 17 | 2 | 4 | 18 | 21 | 3 |
| 高粱 Sorghum | 8 | 1 | 5 | 4 | 16 | 19 | 29 | 25 | 13 | 3 | 30 | 34 | 33 | 31 | 32 | 27 | 2 | 22 | 21 | 6 | 23 | 15 | 28 | 7 | 26 | 10 | 35 | 9 | 18 | 12 | 11 | 14 | 24 | 17 | 20 |
| 豆类 Beans | 1 | 7 | 15 | 3 | 12 | 10 | 27 | 23 | 8 | 2 | 31 | 34 | 33 | 30 | 32 | 25 | 4 | 18 | 29 | 5 | 28 | 11 | 26 | 6 | 21 | 14 | 35 | 9 | 22 | 16 | 19 | 13 | 24 | 17 | 20 |
| 大豆 Soybean | 2 | 9 | 16 | 4 | 3 | 13 | 29 | 24 | 5 | 7 | 30 | 34 | 32 | 31 | 33 | 27 | 1 | 17 | 22 | 6 | 23 | 11 | 28 | 8 | 26 | 19 | 35 | 10 | 20 | 14 | 18 | 12 | 25 | 15 | 21 |
| 薯类 Tubers | 6 | 8 | 16 | 3 | 11 | 12 | 29 | 24 | 4 | 7 | 31 | 34 | 33 | 30 | 32 | 27 | 1 | 15 | 20 | 2 | 21 | 9 | 28 | 5 | 26 | 18 | 35 | 10 | 19 | 14 | 22 | 13 | 25 | 17 | 23 |
| 马铃薯 Potato | 5 | 20 | 21 | 10 | 7 | 6 | 25 | 12 | 2 | 11 | 28 | 32 | 29 | 26 | 27 | 17 | 4 | 9 | 23 | 3 | 18 | 8 | 14 | 1 | 16 | 19 | 34 | 13 | 30 | 22 | 35 | 15 | 33 | 24 | 31 |
| 平均关联序Average correlation order | 5 | 5 | 10 | 3 | 12 | 17 | 30 | 24 | 12 | 4 | 30 | 33 | 32 | 30 | 33 | 26 | 4 | 20 | 23 | 8 | 21 | 14 | 27 | 10 | 25 | 12 | 35 | 8 | 19 | 15 | 15 | 11 | 22 | 17 | 17 |
| [1] |
LIU Z J, YANG X G, CHEN F, et al., 2013. The effects of past climate change on the northern limits of maize planting in Northeast China[J]. Climatic Change, 117(4):891-902.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
XIA T, WU W B, ZHOU Q B, et al., 2014. Spatio-temporal changes in the rice planting area and their relationship to climate change in northeast China: A model-based analysis[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 13(7):1575-1585.
DOI URL |
| [3] | 安悦, 谭雪兰, 谭杰扬, 等, 2021. 湖南省农作物种植结构演变及影响因素[J]. 经济地理, 41(2):156-166. |
| AN Y, TAN X L, TAN J Y, et al., 2021. Evolution of crop planting structure in traditional agricultural areas and its influence factors: A case study in Hunan Province[J]. Economic Geography, 41(2):156-166. | |
| [4] | 陈有禄, 周强, 陈琼, 等, 2018. 近20年河湟谷地粮食作物种植结构对气候变化的响应[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 36(5):223-229. |
| CHEN Y L, ZHOU Q, CHEN Q, et al., 2018. The response of grain crops in Hehuang valley to the climate change nearly 20 years[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 36(5):223-229. | |
| [5] | 程叶青, 2009. 东北地区粮食单产空间格局变化及其动因分析[J]. 自然资源学报, 24(9):1541-1549. |
| CHENG Y Q, 2009. Spatial pattern change and its driving factors of grain per unit area yield in Northeast China[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 24(9):1541-1549. | |
| [6] | 邓聚龙, 1987. 灰色系统基本方法[M]. 武汉: 华中理工大学出版社: 74-106. |
| DENG J L, 1987. Basic methods of grey system[M]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Technology Press: 74-106. | |
| [7] | 高永道, 乔荣荣, 季树新, 等. 2021. 内蒙古河套灌区作物种植结构变化及其驱动因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 41(3):110-117. |
| GAO Y D, QIAO R R, JI S X, et al., 2021. Changes and driving factors of crops planting structure in Hetao Irrigation Region in Inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 41(3):110-117. | |
| [8] | 耿仲钟, 肖海峰, 2016. 我国粮食播种面积的动态演变: 1985—2013[J]. 华南理工大学学报(社会科学版), 18(2):9-16. |
| GENG Z Z, XIAO H F, 2016. The dynamic evolution of grain sown area in China: 1985-2013[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Social Science Edition), 18(2):9-16. | |
| [9] | 胡琼, 吴文斌, 宋茜, 等, 2015. 农作物种植结构遥感提取研究进展[J]. 中国农业科学, 48(10):1900-1914. |
| HU Q, WU W B, SONG Q, et al., 2015. Recent Progresses in Research of Crop Patterns Mapping by Using Remote Sensing[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 48(10):1900-1914. | |
| [10] | 胡忆雨, 朱颖璇, 杨雨豪, 等. 2019. 1951—2015年中国主要粮食与油料作物种植结构变化分析[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 24(11):183-196. |
| HU Y Y, ZHU Y X, YANG Y H, et al., 2019. Changes of the planting structure of major food and oil crops in China from 1995 to 2015[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 24(11):183-196. | |
| [11] | 黄玛兰, 李晓云, 2019. 农业劳动力价格上涨对农作物种植结构变化的省际差异性影响[J]. 经济地理, 39(6):172-182. |
| HUANG M L, LI X Y, 2019. The Impacts of Rural Labor Price Rising on Crop Structure among Provinces[J]. Economic Geography, 39(6):172-182. | |
| [12] | 柯映明, 沈占锋, 李均力, 等, 2019. 1994—2018年新疆塔河干流农作物播种面积时空变化及影响因素分析[J]. 农业工程学报, 35(18):180-188. |
| KE Y M, SHEN Z F, LI J L, et al., 2019. Temporal and spatial change of sown area of crop and its influencing factors in main stream of Tarim River from 1994 to 2018[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 35(18):180-188. | |
| [13] | 李晨曦, 2019. 吉林省粮食生产结构演变及其现状分析[D]. 长春: 吉林农业大学: 12-16. |
| LI C X, 2019. The development and current situation of grain production structure in Jilin Province[D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University: 12-16. | |
| [14] | 李明, 甄善继, 高祺, 等, 2018. 黑龙江省作物种植结构演变特点与调整对策研究[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 39(5):46-53. |
| LI M, ZHEN S J, GAO Q, et al., 2018. Research on the evolution characteristics of crop planting structure and adjustment counter measures in Heilongjiang Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 39(5):46-53. | |
| [15] | 林兰稳, 朱立安, 曾清苹, 2020. 广东省农业面源污染时空变化及其防控对策[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(6):1245-1250. |
| LIN L W, ZHU L A, ZENG Q P, 2020. Spatial and temporal changes of agricultural non-point source pollution in Guangdong Province and its prevention and control measures[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29(6):1245-1250. | |
| [16] |
刘珍环, 杨鹏, 吴文斌, 等, 2016. 近30年中国农作物种植结构时空变化分析[J]. 地理学报, 71(5):840-851.
DOI |
| LIU Z H, YANG P, WU W B, et al., 2016. Spatio-temporal changes in Chinese crop patterns over the past three decades[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 71(5):840-851. | |
| [17] | 米胜渊, 谭雪兰, 谭杰扬, 等, 2020. 近30年来洞庭湖地区水稻种植面积演变的影响因素分析[J]. 自然资源学报, 35(10):2499-2510. |
| MI S Y, TAN X L, TAN J Y, et al., 2020. Analysis of influencing factors of rice planting area evolution in Dongting LakeArea during 1987-2017[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 35(10):2499-2510. | |
| [18] | 彭继权, 张利国, 2020. 农业机械化对农户主粮种植面积的影响[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 25(9):227-238. |
| PENG J Q, ZHANG L G, 2020. Influence of agricultural machinery on the planting area of farmers’ main grains[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 25(9):227-238. | |
| [19] | 平怡, 2019. 农业生产风险对区域经济的影响分析[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 40(4):103-110. |
| PING Y, 2019. Analysis on the effect of the risk of agricultural production on the regional economy[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 40(4):103-110. | |
| [20] | 曲衍波, 王世磊, 朱伟亚, 等, 2021. 黄河三角洲国土空间演变的时空分异特征与驱动力分析[J]. 农业工程学报, 37(6):252-263. |
| QU Y B, WANG S L, ZHU W Y, et al., 2021. Spatial-temporal differentiation characteristics and driving force of territorial space evolution in the Yellow River Delta[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 37(6):252-263. | |
| [21] | 尚永辉, 2019. 我国农业劳动力结构变动对粮食生产的影响研究[D]. 荆州: 长江大学: 27-32. |
| SHANG Y H, 2019. Research on the impact of the change of agricultural labor force structure on grain production in China[D]. Jingzhou: Yangtze University: 27-32. | |
| [22] | 宋喜芳, 姚海荣, 张小飞, 等, 2020. 陕西省粮食产量影响因素的灰色关联分析—基于面板数据的实证研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 36(28):158-164. |
| SONG X F, YAO H R, ZHANG X F, et al., 2020. Grey correlation analysis of the influence factors of grain yield in Shaanxi: empirical research based on panel data[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 36(28):158-164. | |
| [23] | 王卫东, 曹旭, 2020. 陕西省主要粮食作物种植结构时空变化特征分析[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 41(9):155-162. |
| WANG W D, CAO X, 2020. Temporal and spatial variation characteristics of main grain crop planting structures in Shaanxi Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 41(9):155-162. | |
| [24] | 王学, 李秀彬, 辛良杰, 2013. 河北平原冬小麦播种面积收缩及由此节省的水资源量估算[J]. 地理学报, 68(5):694-707. |
| WANG X, LI X B, XIN L J, 2013. Impact of the shrinking winter wheat sowing area on agricultural water consumption in the Hebei Plain[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 68(5):694-707. | |
| [25] | 吴美琼, 2015. 基于主成分分析的广西甘蔗种植面积时空变化及驱动力研究[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 36(3):103-111. |
| WU M Q, 2015. Study of spacial and temporal evolution of sugarcane planting area and its driving force in Guangxi[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 36(3):103-111. | |
| [26] | 熊吉峰, 2005. 农户模型的偏最小二乘回归研究[J]. 华中农业大学学报(社会科学版), 56(2):5-6. |
| XIONG J F, 2005. Study on partial least squares regression of farmers’ model[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University (Social Sciences Edition), 56(2):5-6. | |
| [27] | 许婧雪, 曹银贵, 2016. 区域城市化阶段划分与粮食播种面积变化驱动力分区关系研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 32(36):188-197. |
| XU J X, CAO Y G, 2016. Relationship between the division of regional urbanization stage and the driving forces of grain sowing area[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 32(36):188-197. | |
| [28] | 杨玮, 孙红, 郑立华, 等, 2013. 基于土壤参数的冬小麦产量预测模型[J]. 农业工程学报, 29(23):118-123. |
| YANG W, SUN H, ZHENG L H, et al., 2013. Prediction model of winter wheat yield based on soil parameters[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 29(23):118-123. | |
| [29] | 姚成胜, 杨一单, 殷伟, 2020. 中国非主粮生产的地理集聚特征及其空间演化机制[J]. 经济地理, 40(12):155-165. |
| YAO C S, YANG Y D, YIN W, 2020. Geographical agglomeration characteristics of China's non-primary grain production and its spatial evolution mechanism[J]. Economic Geography, 40(12):155-165. | |
| [30] | 于翔, 2020. 中国区域粮食生产优势度及影响因素研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学: 34-43. |
| YU X, 2020. Evaluation on regional grain production superiority and influencing factors in China[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University: 34-43. | |
| [31] | 邹军, 朱颖璇, 杨雨豪, 等, 2019. 1981—2015年华北地区种植结构演变及其驱动机制分析[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 24(12):23-32. |
| ZOU J, ZHU Y X, YANG Y H, et al., 2019. Analysis of planting structure evolution and its driving mechanism in North China from 1981 to 2015[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 24(12):23-32. | |
| [32] | 张红军, 2021. 安徽省粮食作物种植结构演变及粮食安全评价[J]. 云南农业大学学报(社会科学), 15(2):87-93. |
| ZHANG H J, 2021. Evolution of Grain Crop Planting Structure and Evaluation of Food Security in Anhui Province[J]. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University (Social Science), 15(2):87-93. |
| [1] | 巫晨煜, 许帆帆, 魏士博, 樊晶晶, 刘观鹏, 王坤. 渭河流域地表植被覆盖对气候变化的响应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 835-844. |
| [2] | 陈文裕, 夏丽华, 徐国良, 余世钦, 陈行, 陈金凤. 2000—2020年珠江流域NDVI动态变化及影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1306-1316. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
