Ecology and Environment ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (8): 1599-1606.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.08.006
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
QI Xuelian1( ), GE Xiaomin2, QIAN Zhuangzhuang1, ZHANG Kang1, ZHENG Xu1, QIAN Qi1, DING Hui2, TANG Luozhong1,*(
), GE Xiaomin2, QIAN Zhuangzhuang1, ZHANG Kang1, ZHENG Xu1, QIAN Qi1, DING Hui2, TANG Luozhong1,*( )
)
Received:2021-03-03
Online:2021-08-18
Published:2021-11-03
Contact:
TANG Luozhong
祁雪连1( ), 葛晓敏2, 钱壮壮1, 张康1, 郑旭1, 钱琦1, 丁晖2, 唐罗忠1,*(
), 葛晓敏2, 钱壮壮1, 张康1, 郑旭1, 钱琦1, 丁晖2, 唐罗忠1,*( )
)
通讯作者:
唐罗忠
作者简介:祁雪连(1996年生),女,硕士,主要开展森林生态系统土壤学研究。E-mail: 1479674671@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
QI Xuelian, GE Xiaomin, QIAN Zhuangzhuang, ZHANG Kang, ZHENG Xu, QIAN Qi, DING Hui, TANG Luozhong. Differences of Soil Properties between Natural Mixed Coniferous and Broad-leaved Forest and Moso Bamboo Plantation in Wuyi Mountains[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(8): 1599-1606.
祁雪连, 葛晓敏, 钱壮壮, 张康, 郑旭, 钱琦, 丁晖, 唐罗忠. 武夷山天然针阔混交林与毛竹人工林土壤性质差异[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1599-1606.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.08.006
| 土层 Soil layer/ cm | 林分类型 Stand type | pH | 电导率Conductivity γ/(μs∙cm-1) | 碳质量分数w(C)/ (g∙kg-1) | 全氮 质量分数 w(total nitrogen)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(C)/ w(N) | 全磷 质量分数 w(total phosphorus)/ (g∙kg-1) | 全钾 质量分数 w(total potassium)/ (g∙kg-1) | 有效磷 质量分数 w(available phosphorus)/ (mg∙kg-1) | 速效钾 质量分数 w(available potassium)/ (mg∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0-10 | 针阔混交林MCB | 4.37±0.07a | 99.5±1.7a | 121.62±0.02a | 4.03±0.01a | 30.18±0.59a | 0.68±0.01a | 3.53±0.01b | 3.19±0.01a | 110.60±0.47b |
| 毛竹林MB | 3.82±0.03b | 87.8±0.4b | 111.23±0.07b | 3.22±0.02b | 34.54±2.53a | 0.56±0.01b | 4.89±0.02a | 2.88±0.10b | 121.55±0.77a | |
| 10-20 | 针阔混交林MCB | 4.43±0.01a | 53.8±1.7a | 70.38±0.10a | 2.42±0.03a | 29.08±3.93a | 0.50±0.01a | 3.57±0.01b | 1.04±0.20a | 68.99±0.08a |
| 毛竹林MB | 4.24±0.01b | 50.9±0.5a | 60.76±0.03b | 2.03±0.01b | 29.93±1.95a | 0.43±0.01b | 6.21±0.01a | 0.89±0.05a | 70.23±1.05a |
Table 1 Soil properties in mixed coniferous and broad-leaved forest and moso bamboo plantation
| 土层 Soil layer/ cm | 林分类型 Stand type | pH | 电导率Conductivity γ/(μs∙cm-1) | 碳质量分数w(C)/ (g∙kg-1) | 全氮 质量分数 w(total nitrogen)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(C)/ w(N) | 全磷 质量分数 w(total phosphorus)/ (g∙kg-1) | 全钾 质量分数 w(total potassium)/ (g∙kg-1) | 有效磷 质量分数 w(available phosphorus)/ (mg∙kg-1) | 速效钾 质量分数 w(available potassium)/ (mg∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0-10 | 针阔混交林MCB | 4.37±0.07a | 99.5±1.7a | 121.62±0.02a | 4.03±0.01a | 30.18±0.59a | 0.68±0.01a | 3.53±0.01b | 3.19±0.01a | 110.60±0.47b |
| 毛竹林MB | 3.82±0.03b | 87.8±0.4b | 111.23±0.07b | 3.22±0.02b | 34.54±2.53a | 0.56±0.01b | 4.89±0.02a | 2.88±0.10b | 121.55±0.77a | |
| 10-20 | 针阔混交林MCB | 4.43±0.01a | 53.8±1.7a | 70.38±0.10a | 2.42±0.03a | 29.08±3.93a | 0.50±0.01a | 3.57±0.01b | 1.04±0.20a | 68.99±0.08a |
| 毛竹林MB | 4.24±0.01b | 50.9±0.5a | 60.76±0.03b | 2.03±0.01b | 29.93±1.95a | 0.43±0.01b | 6.21±0.01a | 0.89±0.05a | 70.23±1.05a |
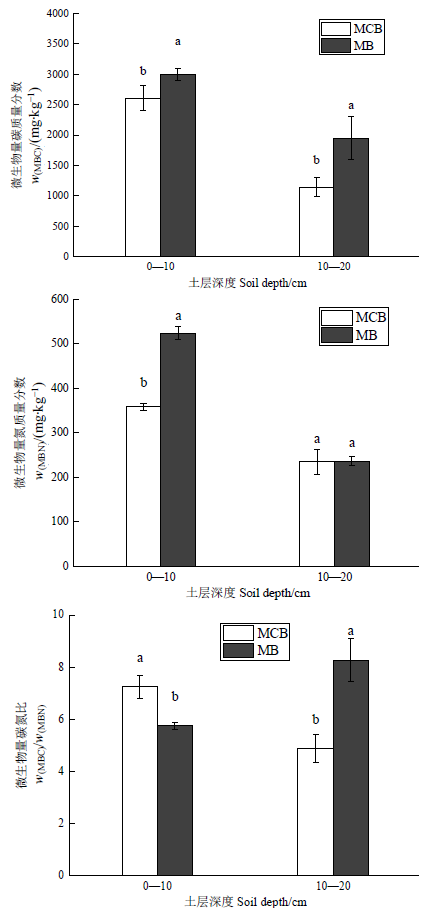
Fig. 2 Mass fractions of soil microbial carbon and nitrogen in mixed coniferous and broad-leaved forest and moso bamboo plantation The error line represents the standard deviation (n=3). MCB stands for mixed coniferous and broad-leaved forest, MB stands for moso bamboo plantation. Different lowercase letters in the figure indicate the difference between different forest in the same soil layer reach a significant level (P<0.05). The same as below
| pH | 电导率Conductivity | 碳含量Carbon content | 全氮 含量 Total nitrogen content | 全磷含量 Total phosphorus content | 全钾含量Total potassium content | 土壤C/N比Soil C/N ratio | 微生物碳含量MBC | 微生物氮含量MBN | 微生物 C/N比MBC/ MBN ratio | 铵态氮 含量Ammonium nitrogen content | 硝态氮 含量 Nitrate nitrogen content | 有效磷含量Available phosphorus content | 速效钾 含量Available potassium content | 脲酶 活性Urease activity | 过氧化氢酶 活性Catalase activity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| 电导率 Conductivity | -0.319 | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| 碳含量 Carbon content | -0.342 | 0.995** | 1 | |||||||||||||
| 全氮含量 Total nitrogen content | -0.104 | 0.974* | 0.970* | 1 | ||||||||||||
| 全磷含量 Total phosphorus content | 0.028 | 0.931 | 0.930 | 0.990* | 1 | |||||||||||
| 全钾含量 Total potassium content | -0.439 | -0.429 | -0.475 | -0.594 | -0.690 | 1 | ||||||||||
| 土壤C/N比 Soil C/N ratio | -0.970* | 0.514 | 0.544 | 0.323 | 0.201 | 0.220 | 1 | |||||||||
| 微生物碳含量 MBC | -0.726 | 0.815 | 0.794 | 0.666 | 0.553 | 0.154 | 0.802 | 1 | ||||||||
| 微生物氮含量 MBN | -0.842 | 0.755 | 0.783 | 0.608 | 0.506 | -0.049 | 0.946 | 0.877 | 1 | |||||||
| 微生物C/N比 MBC/MBN ratio | 0.087 | 0.015 | -0.082 | -0.030 | -0.075 | 0.600 | -0.188 | 0.270 | -0.215 | 1 | ||||||
| 铵态氮含量 Ammonium nitrogen content | -0.049 | 0.925 | 0.941 | 0.976* | 0.985* | -0.739 | 0.287 | 0.542 | 0.580 | -0.236 | 1 | |||||
| 硝态氮含量 Nitrate nitrogen content | -0.230 | -0.822 | -0.827 | -0.929 | -0.972* | 0.825 | -0.008 | -0.342 | -0.330 | 0.171 | -0.960* | 1 | ||||
| 有效磷含量 Available phosphorus content | -0.400 | 0.996** | 0.996** | 0.953* | 0.901 | -0.395 | 0.590 | 0.845 | 0.812 | -0.024 | 0.907 | -0.780 | 1 | |||
| 速效钾含量 Available potassium content | -0.636 | 0.933 | 0.942 | 0.833 | 0.752 | -0.216 | 0.789 | 0.920 | 0.939 | -0.071 | 0.784 | -0.592 | 0.961* | 1 | ||
| 脲酶活性 Urease activity | -0.236 | 0.959* | 0.979* | 0.968* | 0.952* | -0.638 | 0.462 | 0.662 | 0.723 | -0.250 | 0.982* | -0.890 | 0.957* | 0.882 | 1 | |
| 过氧化氢酶活性 Catalase activity | -0.355 | 0.994** | 0.998** | 0.966* | 0.925 | -0.471 | 0.557 | 0.798 | 0.793 | -0.092 | 0.938 | -0.820 | 0.996** | 0.946 | 0.979* | 1 |
Table 2 Correlation analysis among different properties of soil in mixed coniferous and broad-leaved forest and moso bamboo plantation
| pH | 电导率Conductivity | 碳含量Carbon content | 全氮 含量 Total nitrogen content | 全磷含量 Total phosphorus content | 全钾含量Total potassium content | 土壤C/N比Soil C/N ratio | 微生物碳含量MBC | 微生物氮含量MBN | 微生物 C/N比MBC/ MBN ratio | 铵态氮 含量Ammonium nitrogen content | 硝态氮 含量 Nitrate nitrogen content | 有效磷含量Available phosphorus content | 速效钾 含量Available potassium content | 脲酶 活性Urease activity | 过氧化氢酶 活性Catalase activity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| 电导率 Conductivity | -0.319 | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| 碳含量 Carbon content | -0.342 | 0.995** | 1 | |||||||||||||
| 全氮含量 Total nitrogen content | -0.104 | 0.974* | 0.970* | 1 | ||||||||||||
| 全磷含量 Total phosphorus content | 0.028 | 0.931 | 0.930 | 0.990* | 1 | |||||||||||
| 全钾含量 Total potassium content | -0.439 | -0.429 | -0.475 | -0.594 | -0.690 | 1 | ||||||||||
| 土壤C/N比 Soil C/N ratio | -0.970* | 0.514 | 0.544 | 0.323 | 0.201 | 0.220 | 1 | |||||||||
| 微生物碳含量 MBC | -0.726 | 0.815 | 0.794 | 0.666 | 0.553 | 0.154 | 0.802 | 1 | ||||||||
| 微生物氮含量 MBN | -0.842 | 0.755 | 0.783 | 0.608 | 0.506 | -0.049 | 0.946 | 0.877 | 1 | |||||||
| 微生物C/N比 MBC/MBN ratio | 0.087 | 0.015 | -0.082 | -0.030 | -0.075 | 0.600 | -0.188 | 0.270 | -0.215 | 1 | ||||||
| 铵态氮含量 Ammonium nitrogen content | -0.049 | 0.925 | 0.941 | 0.976* | 0.985* | -0.739 | 0.287 | 0.542 | 0.580 | -0.236 | 1 | |||||
| 硝态氮含量 Nitrate nitrogen content | -0.230 | -0.822 | -0.827 | -0.929 | -0.972* | 0.825 | -0.008 | -0.342 | -0.330 | 0.171 | -0.960* | 1 | ||||
| 有效磷含量 Available phosphorus content | -0.400 | 0.996** | 0.996** | 0.953* | 0.901 | -0.395 | 0.590 | 0.845 | 0.812 | -0.024 | 0.907 | -0.780 | 1 | |||
| 速效钾含量 Available potassium content | -0.636 | 0.933 | 0.942 | 0.833 | 0.752 | -0.216 | 0.789 | 0.920 | 0.939 | -0.071 | 0.784 | -0.592 | 0.961* | 1 | ||
| 脲酶活性 Urease activity | -0.236 | 0.959* | 0.979* | 0.968* | 0.952* | -0.638 | 0.462 | 0.662 | 0.723 | -0.250 | 0.982* | -0.890 | 0.957* | 0.882 | 1 | |
| 过氧化氢酶活性 Catalase activity | -0.355 | 0.994** | 0.998** | 0.966* | 0.925 | -0.471 | 0.557 | 0.798 | 0.793 | -0.092 | 0.938 | -0.820 | 0.996** | 0.946 | 0.979* | 1 |
| [1] | ASHAGRIE Y, ZECH W, 2010. Dynamics of dissolved nutrients in forest floor leachates: Comparison of a natural forest ecosystem with monoculture tree species plantations in south-east Ethiopia[J]. Ecohydrology & Hydrobiology, 10(2): 183-190. |
| [2] |
CHERUBIN M R, FRANCO A L C, CERRI C E P, et al., 2015. Sugarcane expansion in Brazilian tropical soils-effects of land use change on soil chemical attributes[J]. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 211: 173-184.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
DEMESSIE A, SINGH B R, LAL R, 2011. Soil carbon and nitrogen stocks under plantations in Gambo District, Southern Ethiopia[J]. Journal of Sustainable Forestry, 30(6): 496-517.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
FERNANDEZ-ROMERO M L, LOZANO-GARCIA B, PARRAS- ALCANTARA L, 2014. Topography and land use change effects on the soil organic carbon stock of forest soils in Mediterranean natural areas[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 195: 1-9.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
GE X M, DENG S P, ZHU L, et al., 2018. Response of nitrogen mineralization dynamics and biochemical properties to litter amendments to soils of a poplar plantation[J]. Journal of Forestry Research, 29(4): 915-924.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
KASEL S, BENNETT L T, 2007. Land-use history, forest conversion, and soil organic carbon in pine plantations and native forests of south eastern Australia[J]. Geoderma, 137(3-4): 401-413.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
MARCOS J A, MARCOS E, TABOADA A, et al., 2007. Comparison of community structure and soil characteristics in different aged Pinus sylvestris plantations and a natural pine forest[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 247(1-3): 35-42.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
ZHOU Z C, ZHANG X Y, GAN Z T, 2015. Changes in soil organic carbon and nitrogen after 26 years of farmland management on the Loess Plateau of China[J]. Journal of Arid Land, DOI: 10.1007/s40333-015-0051-y.
DOI |
| [9] | 陈涵兮, 海龙, 黄利民, 等, 2019. 坡向对毛竹林土壤养分及其生态化学计量特征的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 30(9): 2915-2922. |
| CHEN H X, HAI L, HUANG L M, et al., 2019. Effects of slope direction on soil nutrient and its ecological stoichiometry in bamboo forest[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 30(9): 2915-2922. | |
| [10] |
陈钦程, 徐福利, 王渭玲, 等, 2015. 秦岭北麓华北落叶松林地土壤有效性钾含量变化[J]. 植物学报, 50(4): 482-489.
DOI |
| CHEN Q C, XU F L, WANG W L, et al., 2015. Seasonal dynamics in soil content of effective potassium for different ages of larix principis-rupprechtii in the northern foot of the Qinling Mountains[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 50(4): 482-489. | |
| [11] | 董国涛, 杨胜天, 白娟, 等, 2012. 海南岛中部山区热带天然林与人工橡胶林土壤特性对比研究[J]. 热带地理, 32(1): 11-15. |
| DONG G T, YANG S T, BAI J, et al., 2012. Comparison of soil properties between tropical natural forest and rubber plantation in the central mountainous areas of Hainan island[J]. Tropical Geography, 32(1): 11-15. | |
| [12] | 杜红霞, 刘增文, 潘开文, 等, 2016. 外源性C、N干扰对森林土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 西北林学院学报, 21(2): 35-38. |
| DU H X, LIU Z W, PAN K W, et al., 2016. Effects of external source C, N disturbances on enzymes activities of forest soil[J]. Journal of Northwest forestry university, 21(2): 35-38. | |
| [13] | 方丽娜, 杨效东, 杜杰, 2011. 土地利用方式对西双版纳热带森林土壤微生物生物量碳的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 22(4): 837-844. |
| FANG L N, YANG X D, DU J, 2011. Effects of land use pattern on soil microbial biomass carbon in Xishuangbanna[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 22(4): 837-844. | |
| [14] | 龚伟, 胡庭兴, 王景燕, 等, 2011. 川南天然常绿阔叶林人工更新后土壤氮库与微生物的季节变化[J]. 生态学报, 31(7): 1763-1771. |
| GONG W, HU T X, WANG J X, et al., 2011. Seasonal variation of soil nitrogen pools and microbes under natural evergreen broadleaved forest and its artificial regeneration forests in Southern Sichuan Province, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31(7): 1763-1771. | |
| [15] | 龚珊珊, 廖善刚, 2009. 桉树人工林与天然林土壤养分的对比研究[J]. 江苏林业科技, 36(3): 1-4. |
| GONG S S, LIAO S G, 2009. Soil nutrient characteristics in eucalypt plantation and natural forest[J]. Journal of Jiangsu Forestry Science & Technology, 36(3): 1-4. | |
| [16] | 惠亚梅, 巨天珍, 贾丽, 等, 2015. 秦岭西段北坡森林土壤微生物群落及生境特征[J]. 江苏农业科学, 43(1): 322-326. |
| HUI Y M, JU T Z, JIA L, et al., 2015. Characteristics of forest soil microbial communities and habitats on the Northern Slope of the western Qinling Mountains[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 43(1): 322-326. | |
| [17] | 马晓雪, 龚伟, 胡庭兴, 等, 2010. 天然林及坡耕地转变为巨桉林后土壤养分含量变化[J]. 四川农业大学学报, 28(1): 56-60. |
| MA X X, GONG W, HU T X, et al., 2010. Effects of conversion of natural forest and slope farmland to eucalyptus grandis plantation on soil nutrients[J]. Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University, 28(1): 56-60. | |
| [18] | 彭舜磊, 王得祥, 赵辉, 等, 2008. 我国人工林现状与近自然经营途径探讨[J]. 西北林学院学报, 23(2): 184-188. |
| PENG S L, WANG D Y, ZHAO H, et al., 2008. Discussion the status quality of plantation and near nature forestry management in China[J]. Journal of Northwest forestry university, 23(2): 184-188. | |
| [19] | 商素云, 李永夫, 姜培坤, 等, 2012. 天然灌木林改造成板栗林对土壤碳库和氮库的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 23(3): 659-665. |
| SHANG S Y, LI Y F, JIANG P S, et al., 2012. Effects of the conversion from native shrub forest to Chinese chestnut plantation on soil carbon and nitrogen pools[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 23(3): 659-665. | |
| [20] | 施政, 汪家社, 何容, 等, 2008. 武夷山不同海拔土壤呼吸及其主要调控因子[J]. 生态学杂志, 27(4): 563-568. |
| SHI Z, WANG J S, HE R, et al., 2008. Soil respiration and its regulating factor along an elevation gradient in Wuyi Mountain of Southeast China[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 27(4): 563-568. | |
| [21] | 孙凤霞, 张伟华, 徐明岗, 等, 2010. 长期施肥对红壤微生物生物量碳氮和微生物碳源利用的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 21(11): 2792-2798. |
| SUN F X, ZHANG W H, XU M G, et al., 2010. Effects of long-term fertilization on microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen and on carbon source utilization of microbes in a red soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 21(11): 2792-2798. | |
| [22] | 王国兵, 郭娇娇, 曹国华, 等, 2016. 不同施肥模式对杨树人工林土壤微生物生物量C、N、P的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 40(5): 9-13. |
| WANG G B, GUO J J, CAO G H, et al., 2016. Effects of different fertilization regimes on soil microbial biomass C, N, P under poplar plantation[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 40(5): 9-13. | |
| [23] | 王莹, 王彦梅, 陈龙池, 2010. 湖南会同地区森林植被转变对土壤微生物生物量碳和酶活性的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 29(5): 905-909. |
| WANG Y, WANG Y M, CHEN L C, 2010. Effects of forest vegetation change on soil microbial biomass carbon and enzyme activities in Huitong, Hunan Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 29(5): 905-909. | |
| [24] | 吴秀坤, 李永梅, 李朝丽, 等, 2013. 纳版河流域土地利用方式对土壤总有机碳以及活性有机碳的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 22(1): 6-11. |
| WU X K, LI Y M, LI Z L, et al., 2013. Effects of land use type on soil total organic carbon and soil labile organic carbon in Naban River watershed[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 22(1): 6-11. | |
| [25] | 肖鹏, 李永夫, 姜培坤, 等, 2012. 常绿阔叶林改造成雷竹林对土壤活性碳库与氮库的影响[J]. 湖北农业科学, 51(21): 4739-4744. |
| XIAO P, LI Y F, JIANG P K, et al., 2012. Effect of Conversion from Evergreen Broad-leaved Forest to Phyllostachys violascens cv. Prevernalis Forest on Soil Labile Carbon and Nitrogen Pools[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 51(21): 4739-4744. | |
| [26] | 杨萌, 岳天, 李永夫, 等, 2017. 常绿阔叶林改造为板栗林对土壤氮磷钾库及酶活性的影响[J]. 自然资源学报, 32(5): 765-777. |
| YANG M, YUE T, LI Y F, et al., 2017. Effects of converting evergreen broad-leaved forests to Chinese chestnut forests on soil nitrogen, phosphorous and potassium pools and enzyme activity[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 32(5): 765-777. | |
| [27] | 杨玉盛, 董彬, 谢锦升, 等, 2004. 森林土壤呼吸及其对全球变化的响应[J]. 生态学报, 24(3): 583-591. |
| YANG Y S, DONG B, XIE J S, et al., 2004. Soil respiration of forest ecosystems and its respondence to global change[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 24(3): 583-591. | |
| [28] | 杨玉盛, 郭剑芬, 林鹏, 等, 2005. 格氏栲天然林与人工林粗木质残体碳库及养分库[J]. 林业科学, 41(3): 7-11. |
| YANG Y S, GUO J F, LIN P, et al., 2005. Carbon and nutrient pools of coarse woody debris in a natural forest and plantation in subtropical China[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 41(3): 7-11. | |
| [29] | 闫美芳, 张新时, 江源, 等, 2010. 主要管理措施对人工林土壤碳的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 29(11): 2265-2271. |
| YAN M F, ZHANG X S, JIANG Y, et al., 2010. Effects of management practices on forest plantation soil carbon: A review[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 29(11): 2265-2271. | |
| [30] | 岳天, 李永夫, 肖永恒, 等, 2016. 天然常绿阔叶林改造为板栗林对土壤有机碳库的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 27(7): 2181-2188. |
| YUE T, LI Y F, XIAO Y H, et al., 2016. Effects of conversion of evergreen broad-leaved forest to Chinese chestnut plantation on soil organic carbon pools[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 27(7): 2181-2188. | |
| [31] | 张彪, 高人, 杨玉盛, 等, 2010. 万木林自然保护区不同林分土壤可溶性有机氮含量[J]. 应用生态学报, 21(7): 1635-1640. |
| ZHANG B, GAO R, YANG Y S, et al., 2010. Soil soluble organic nitrogen content in different forest stands in Wanmulin Nature Reserve[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 21(7): 1635-1640. | |
| [32] | 张佳奇, 余坤勇, 刘健, 等, 2019. 毛竹叶片重要营养元素的光谱敏感波段分析[J]. 西北林学院学报, 34(1): 77-82. |
| ZHANG J Q, YU K Y, LIU J, et al., 2019. Spectral sensitive band analysis of important nutrient elements of Phyllostachys pubescens leaves[J]. Journal of Northwest forestry university, 34(1): 77-82. | |
| [33] | 张凯, 郑华, 陈法霖, 等, 2015. 桉树取代马尾松对土壤养分和酶活性的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 52(3): 646-653. |
| ZHANG K, ZHENG H, CHEN F L, et al., 2015. Impacts of replacement of pinus with eucalyptus on soil nutrients and enzyme activities[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 52(3): 646-653. | |
| [34] | 张涛, 李永夫, 姜培坤, 等, 2012. 长期集约经营对雷竹林土壤碳氮磷库特征的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 49(6): 1170-1177. |
| ZHANG T, LI Y F, JIANG P S, et al., 2012. Effect of long-term intensive management of phyllostachys praecox stands on carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus pools in the soil[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 49(6): 1170-1177. | |
| [35] | 章宪, 钟羡芳, 2014. 天然林转换为竹林对土壤碳氮含量及物理性质的影响[J]. 聊城大学学报(自然科学版), 27(2): 60-63. |
| ZHANG X, ZHONG X F, 2014. Study on carbon, nitrogen and physical properties of natural forest (Castanopsis Carlesii) and bamboo plantation[J]. Journal of Liaocheng University (Natural Sciences Edition), 27(2): 60-63. | |
| [36] | 张希彪, 上官周平, 2006. 黄土丘陵区油松人工林与天然林养分分布和生物循环比较[J]. 生态学报, 26(2): 373-382. |
|
ZHANG X B, SHANGGUAN Z P, 2006. Nutrient distributions and bio-cycle patterns in both natural and artificial Pinus tabulaeformis forests in Hilly Loess Regions[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 26(2): 373-382.
DOI URL |
|
| [37] | 张洋洋, 邓智文, 荣俊冬, 等, 2019. 毛竹林施肥研究进展[J]. 世界竹藤通讯, 17(5): 58-62. |
| ZHANG Y Y, DENG Z W, RONG J D, et al., 2019. Research progressin fertilization of phyllostachys edulis forest[J]. World Bamboo and Rattan, 17(5): 58-62. | |
| [38] | 张洋洋, 凡莉莉, 徐文达, 等, 2020. 带状采伐后不同时期毛竹林恢复和土壤养分特征[J]. 西北植物学报, 40(8): 1407-1413. |
| ZHANG Y Y, FAN L L, XU W D, et al., 2020. Restoration characteristics and soil nutrient content of Phyllostachys edulis forests after strip clear cutting[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 40(8): 1407-1413. | |
| [39] | 周焱, 徐宪根, 阮宏华, 等, 2008. 武夷山不同海拔高度土壤有机碳矿化速率的比较[J]. 生态学杂志, 27(11): 1901-1907. |
| ZHOU Y, XU X G, RUAN H H, et al., 2008. Mineralization rates of soil organic carbon along an elevation gradient in Wuyi Mountain of Southeast China[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 27(11): 1901-1907. |
| [1] | CHEN Keyi, LIN Tianmiao, WANG Jianjun, HE Youjun, ZHANG Liwen. Effects of Natural Forest Conservation Project on Forest Carbon Pool of Key State-Owned Forest Region of Daxing’anling, Heilongjiang Province in the Past 20 Years [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1016-1025. |
| [2] | WANG Lei, WEN Yuanguang, ZHOU Xiaoguo, ZHU Hongguang, SUN Dongjing. Effects of Mixing Eucalyptus urophylla×E. grandis with Castanopsis hystrix on Understory Vegetation and Soil Properties [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(7): 1340-1349. |
| [3] | XIA Enlong, NONG Junqing, WEI Songpo, LIU Xizhen, LIU Guanglu. Changes in Soil Nutrient Characteristics in Moso Bamboo Forest Expanding into Broadleaved Forest [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(6): 1110-1117. |
| [4] | YU Yanghua, WU Yingu, SONG Yanping, LI Yitong. Stoichiometric Characteristics of Soil Microbial Concentration and Biomass in Zanthoxylum planispinum var. Dintanensis Plantations of Different Ages [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(6): 1160-1168. |
| [5] | DUAN Wenjun, LI Da, LI Chong. Comparison and Determinant Factors Analysis of Understory Plant Diversity of 5 different Ages Eucalyptus urophylla×E. grandis Plantation [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(5): 857-864. |
| [6] | YAN Mingjuan, CHEN Xianyu, CAO Rongbin, LIN Cheng, WU Yiqun, HUANG Dingyi, WU Hailing, CHEN Zicong. The Distribution Characteristics of Soil Mn and Zn in Typical White Tea Plantation in Fujian Province [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(5): 885-895. |
| [7] | LIANG Lei, MA Xiuzhi, HAN Xiaorong, LI Changsheng, ZHANG Zhijie. Effects of Litter on Soil Greenhouse Gas Flux of Pinus tabulaeformis Plantation in Daqing Mountain under Simulated Warming [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 478-486. |
| [8] | SONG Ruipeng, YANG Qifan, ZHENG Zhiheng, XI Dan. Effects of Three Understory Vegetation Types on Soil Organic Carbon and Its Components in Cunninghamia lanceolata Plantation [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(12): 2283-2291. |
| [9] | XIAO Jun, LEI Lei, ZENG Lixiong, LI Zhaochen, MA Chenggong, XIAO Wenfa. Effects of Different Management Regimes on Carbon Stock of Pinus tabulaeformis Plantations in Northern China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(11): 2134-2142. |
| [10] | SONG Xianchong, CAI Xuemei, CHEN Tao, PAN Wen, SHI Yuanyuan, TANG Jian, CAO Jizhao. Variation Characteristics of Rhizosphere and Non-rhizosphere Soil Nutrient in Successive Eucalyptus Plantation [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(9): 1814-1820. |
| [11] | YAN Dongfeng, ZHANG Yanyan, LV Kangting, ZHOU Mengli, WANG Ting, ZHAO Ning. Niche Characteristics of Dominant Tree Species in Natural Forests at Different Altitudes in the South of Taihang Mountains [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(8): 1571-1580. |
| [12] | ZHAO Li, GUO Chunyan, ZHANG Wenjun, WANG Xiaojiang, LIU Pingsheng. Community Characteristics and Their Correlation Analysis of Typical Natural Forest in Zhalantun [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(7): 1353-1359. |
| [13] | WANG Yiquan, ZHOU Zhang, LI Yide, CHEN Dexiang, ZHANG Tao, YANG Fan. The Spatial-temporal Pattern and Influencing Factors of Negative Air Ions in Tropical Forests, Hainan, China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(5): 898-906. |
| [14] | ZHOU Dixuan, LIN Yongbiao, WANG Yanjia, LIU Zhanfeng, ZHOU Lixia. Assessment of Main Ecosystem Services in Subtropical Plantations [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(5): 907-919. |
| [15] | WANG Haoyue, GUO Yuefeng, XU Yajie, QI Wei, BU Fanjing, QI Huijuan. Coupling Relationship between Vegetation and Soil System in Ecological Restoration of Different Stand Types in Jiufeng Mountain [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(12): 2309-2316. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
