Ecology and Environment ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (10): 2028-2038.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.10.011
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHEN Yang1( ), ZHANG Jinpu1, QIU Xiaonuan1, JU Hong1, HUANG Jun2
), ZHANG Jinpu1, QIU Xiaonuan1, JU Hong1, HUANG Jun2
Received:2022-06-08
Online:2022-10-18
Published:2022-12-09
作者简介:陈漾(1990年生),女,工程师,硕士,主要环境空气质量综合分析。E-mail: belindaychen@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
CHEN Yang, ZHANG Jinpu, QIU Xiaonuan, JU Hong, HUANG Jun. Characteristic of Ozone Pollution and Meteorological Factors Analysis in Guangzhou in 2021[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(10): 2028-2038.
陈漾, 张金谱, 邱晓暖, 琚鸿, 黄俊. 2021年广州市臭氧污染特征及气象因子影响分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 2028-2038.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.10.011
Figure 1 Location of air automatic monitoring sites in Guangzhou 1. GYQ; 2. YXLH; 3. HZBG; 4. HZCS; 5. LWXC; 6. THTYX; 7. BYJH; 8. BYZL; 9. HPDSD; 10. HPZL; 11. HPKXC; 12. HDXH; 13. HDTM; 14. PYSQ; 15. PYDXC; 16. NSHG; 17. NSJ; 18. CHLK; 19. CHJK; 20. ZCLC; 21. MFS; 22. HZSY; 23. HZH; 24. LWFC; 25. THAT; 26. THLD; 27. THWS; 28. BYJG; 29. BYSJ; 30. BYXS; 31. HPYH; 32. HPXQ; 33. HPWC; 34. HDHD; 35. HDCN; 36. PYDS; 37. PYSW; 38. PYYYC; 39. PYDFS; 40. PYNC; 41. NSPZ; 42. NSXK; 43. NSLH; 44. NSSLW; 45. ZCXT; 46. ZCPT; 47. ZCZX; 48. ZCST; 49. BYS; 50. FHS; 51. YJLBZ; 52. HSLBZ
| 气象因子 Meteorological factors | 全年 The whole year | 湿季 Wet season | 干季 Dry season | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 相关系数 Correlation coefficient (r) | 显著性水平 Significance level (P) | 样本量 Sample volume (n) | 相关系数 Correlation coefficient (r) | 显著性水平 Significance level (P) | 样本量 Sample volume (n) | 相关系数Correlation coefficient (r) | 显著性水平 Significance level (P) | 样本量 Sample volume (n) | |||||||||||||||
| 日照时数 Sunshine duration | 0.643** | 0.000 | 362 | 0.682** | 0.000 | 183 | 0.640** | 0.000 | 179 | ||||||||||||||
| 风速 Wind speed | -0.355** | 0.000 | 365 | -0.172* | 0.019 | 184 | -0.514** | 0.000 | 181 | ||||||||||||||
| 气温 Temperature | 0.332** | 0.000 | 365 | 0.310** | 0.000 | 184 | 0.458** | 0.000 | 181 | ||||||||||||||
| 降水量 Precipitation | -0.239** | 0.000 | 365 | -0.265** | 0.000 | 184 | -0.253** | 0.001 | 181 | ||||||||||||||
| 气压 Air pressure | -0.208** | 0.000 | 365 | -0.192** | 0.009 | 184 | -0.287** | 0.000 | 181 | ||||||||||||||
| 相对湿度Relative humidity | -0.139** | 0.008 | 365 | -0.469** | 0.000 | 184 | 0.041 | 0.584 | 181 | ||||||||||||||
| 日照时数/风速 Sunshine duration/ Wind speed | 0.745** | 0.000 | 362 | 0.752** | 0.000 | 183 | 0.782** | 0.000 | 179 | ||||||||||||||
Table 1 The correlations between the concentration of O3-8 h and meteorological factors in Guangzhou in 2021
| 气象因子 Meteorological factors | 全年 The whole year | 湿季 Wet season | 干季 Dry season | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 相关系数 Correlation coefficient (r) | 显著性水平 Significance level (P) | 样本量 Sample volume (n) | 相关系数 Correlation coefficient (r) | 显著性水平 Significance level (P) | 样本量 Sample volume (n) | 相关系数Correlation coefficient (r) | 显著性水平 Significance level (P) | 样本量 Sample volume (n) | |||||||||||||||
| 日照时数 Sunshine duration | 0.643** | 0.000 | 362 | 0.682** | 0.000 | 183 | 0.640** | 0.000 | 179 | ||||||||||||||
| 风速 Wind speed | -0.355** | 0.000 | 365 | -0.172* | 0.019 | 184 | -0.514** | 0.000 | 181 | ||||||||||||||
| 气温 Temperature | 0.332** | 0.000 | 365 | 0.310** | 0.000 | 184 | 0.458** | 0.000 | 181 | ||||||||||||||
| 降水量 Precipitation | -0.239** | 0.000 | 365 | -0.265** | 0.000 | 184 | -0.253** | 0.001 | 181 | ||||||||||||||
| 气压 Air pressure | -0.208** | 0.000 | 365 | -0.192** | 0.009 | 184 | -0.287** | 0.000 | 181 | ||||||||||||||
| 相对湿度Relative humidity | -0.139** | 0.008 | 365 | -0.469** | 0.000 | 184 | 0.041 | 0.584 | 181 | ||||||||||||||
| 日照时数/风速 Sunshine duration/ Wind speed | 0.745** | 0.000 | 362 | 0.752** | 0.000 | 183 | 0.782** | 0.000 | 179 | ||||||||||||||
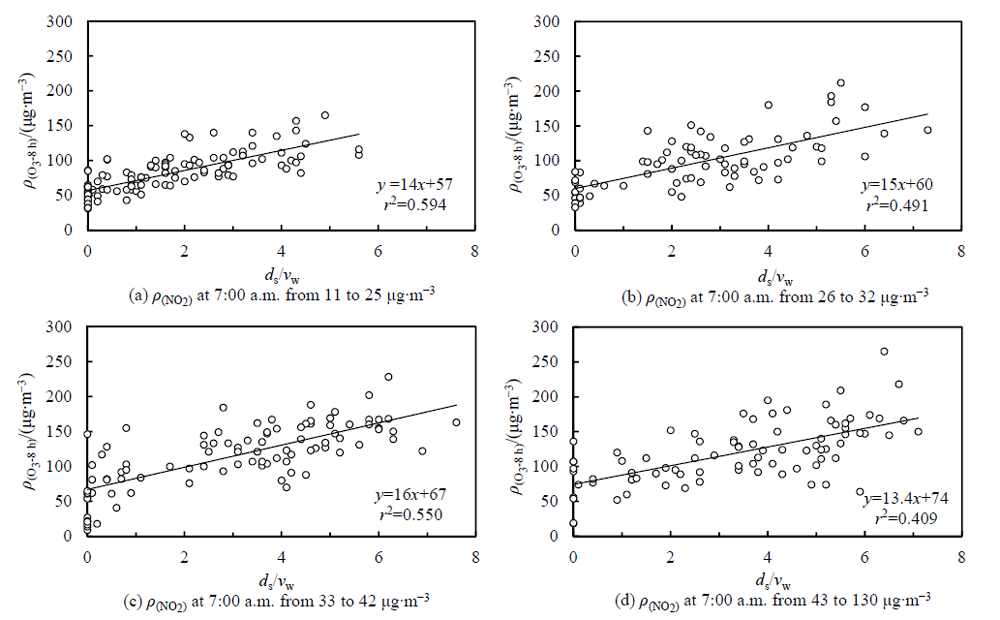
Figure 4 Linear fitting diagrams of the concentrations of O3-8 h and the ratio of sunshine duration/wind speed at different range of the concentrations of NO2 at 7:00 a.m.
| 气象因子 Meteorological factors | 范围 Range | ρ(O3-8 h)/ (μg·m-3) | O3-8 h超标率 Over-limit ratio of O3-8 h/% | 气象因子 Meteorological factors | 范围 Range | ρ(O3-8 h)/ (μg·m-3) | O3-8 h超标率 Over-limit ratio of O3-8 h/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 日照时数 Sunshine duration/(h·d-1) | 0-2.9 | 65 | 0.0 | 相对湿度 Relative humidity/% | ≤60 | 86 | 0.0 |
| 3.0-5.9 | 102 | 2.4 | 61-70 | 114 | 9.8 | ||
| 6.0-8.9 | 127 | 22.4 | 71-80 | 115 | 15.6 | ||
| 9.0-11.9 | 127 | 16.9 | ≥81 | 83 | 4.5 | ||
| 气温 Temperature/℃ | ≤10.0 | 60 | 0.0 | 降水量Precipitation/mm | 0.0 | 114 | 13.2 |
| 10.1-15.0 | 84 | 0.0 | 0.1-9.9 | 88 | 6.2 | ||
| 15.1-20.0 | 94 | 4.7 | 10.0-24.9 | 71 | 0.0 | ||
| 20.1-25.0 | 101 | 10.4 | 25.0-49.9 | 84 | 0.0 | ||
| ≥25.1 | 113 | 32.9 | 50.0-99.9 | 70 | 0.0 | ||
| 气压 Air pressure/hPa | ≤990.0 | 120 | 28.6 | 风速 Wind speed/(m·s-1) | ≤2.0 | 116 | 17.2 |
| 990.1-1000.0 | 106 | 14.0 | 2.1-4.0 | 89 | 1.4 | ||
| 1000.1-1010.0 | 106 | 10.8 | ≥4.1 | 74 | 0.0 | ||
| ≥1010.1 | 91 | 3.1 |
Table 2 The relationship between different meteorological factor ranges and the mean concentration of O3-8 h and over-limit ratio of the concentration of O3-8 h
| 气象因子 Meteorological factors | 范围 Range | ρ(O3-8 h)/ (μg·m-3) | O3-8 h超标率 Over-limit ratio of O3-8 h/% | 气象因子 Meteorological factors | 范围 Range | ρ(O3-8 h)/ (μg·m-3) | O3-8 h超标率 Over-limit ratio of O3-8 h/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 日照时数 Sunshine duration/(h·d-1) | 0-2.9 | 65 | 0.0 | 相对湿度 Relative humidity/% | ≤60 | 86 | 0.0 |
| 3.0-5.9 | 102 | 2.4 | 61-70 | 114 | 9.8 | ||
| 6.0-8.9 | 127 | 22.4 | 71-80 | 115 | 15.6 | ||
| 9.0-11.9 | 127 | 16.9 | ≥81 | 83 | 4.5 | ||
| 气温 Temperature/℃ | ≤10.0 | 60 | 0.0 | 降水量Precipitation/mm | 0.0 | 114 | 13.2 |
| 10.1-15.0 | 84 | 0.0 | 0.1-9.9 | 88 | 6.2 | ||
| 15.1-20.0 | 94 | 4.7 | 10.0-24.9 | 71 | 0.0 | ||
| 20.1-25.0 | 101 | 10.4 | 25.0-49.9 | 84 | 0.0 | ||
| ≥25.1 | 113 | 32.9 | 50.0-99.9 | 70 | 0.0 | ||
| 气压 Air pressure/hPa | ≤990.0 | 120 | 28.6 | 风速 Wind speed/(m·s-1) | ≤2.0 | 116 | 17.2 |
| 990.1-1000.0 | 106 | 14.0 | 2.1-4.0 | 89 | 1.4 | ||
| 1000.1-1010.0 | 106 | 10.8 | ≥4.1 | 74 | 0.0 | ||
| ≥1010.1 | 91 | 3.1 |
| 超标日 Exceeded date | ρ(O3-8 h)/ (μg·m-3) | 地面天气形势 Ground weather situation | 500 hPa天气形势 500 hPa weather situation | 超标日 Exceeded day | ρ(O3-8 h)/ (μg·m-3) | 地面天气形势 Ground weather situation | 500 hPa天气形势 500 hPa weather situation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feb.4 | 113 | 弱高压脊 | 西风气流 | 7.9 | 105 | 弱高压脊 | 副高 |
| Feb.6 | 106 | 均压场 | 西风气流 | 7.17 | 101 | 弱低压槽 | 副高 |
| Feb.7 | 109 | 均压场 | 弱脊 | 7.23 | 108 | 弱低压槽 | 台风外围 |
| Feb.22 | 109 | 均压场 | 西风槽 | 7.26 | 119 | 弱低压槽 | 台风外围 |
| Feb.23 | 127 | 均压场 | 西风槽 | 7.27 | 107 | 弱低压槽 | 西北气流 |
| Mar.25 | 120 | 弱高压脊 | 西风槽 | 7.28 | 126 | 弱低压槽 | 西北气流 |
| Apr.6 | 122 | 弱高压脊 | 副高 | 7.29 | 107 | 弱低压槽 | 西风槽 |
| Apr.11 | 109 | 弱高压脊 | 偏西气流 | 8.2 | 139 | 弱低压槽 | 辐合带环流 |
| Apr.13 | 102 | 均压场 | 偏西气流 | 9.6 | 105 | 弱低压槽 | 副高 |
| Apr.21 | 132 | 均压场 | 弱脊 | 9.12 | 101 | 弱低压槽 | 副高+台风外围 |
| Apr.22 | 115 | 均压场 | 西北气流 | 9.13 | 102 | 弱低压槽 | 副高 |
| Apr.23 | 145 | 均压场 | 西北气流 | 9.18 | 115 | 弱高压脊 | 副高 |
| Apr.30 | 200 | 均压场 | 偏西气流 | 9.26 | 116 | 均压场 | 副高 |
| May.1 | 153 | 均压场 | 偏西气流 | 9.27 | 163 | 均压场 | 副高 |
| May.7 | 108 | 均压场 | 西南气流 | 9.28 | 148 | 均压场 | 反气旋环流 |
| Jun.6 | 106 | 弱低压槽 | 西北气流 | 9.29 | 130 | 均压场 | 西风槽 |
| Jun.7 | 122 | 弱低压槽 | 弱脊 | 9.30 | 107 | 均压场 | 偏西气流 |
| Jun.8 | 117 | 弱低压槽 | 副高 | 10.19 | 103 | 弱高压脊 | 偏西气流 |
Table 3 Weather situations and the mean concentrations of O3-8 h on the exceeded days of O3-8 h in Guangzhou in 2021
| 超标日 Exceeded date | ρ(O3-8 h)/ (μg·m-3) | 地面天气形势 Ground weather situation | 500 hPa天气形势 500 hPa weather situation | 超标日 Exceeded day | ρ(O3-8 h)/ (μg·m-3) | 地面天气形势 Ground weather situation | 500 hPa天气形势 500 hPa weather situation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feb.4 | 113 | 弱高压脊 | 西风气流 | 7.9 | 105 | 弱高压脊 | 副高 |
| Feb.6 | 106 | 均压场 | 西风气流 | 7.17 | 101 | 弱低压槽 | 副高 |
| Feb.7 | 109 | 均压场 | 弱脊 | 7.23 | 108 | 弱低压槽 | 台风外围 |
| Feb.22 | 109 | 均压场 | 西风槽 | 7.26 | 119 | 弱低压槽 | 台风外围 |
| Feb.23 | 127 | 均压场 | 西风槽 | 7.27 | 107 | 弱低压槽 | 西北气流 |
| Mar.25 | 120 | 弱高压脊 | 西风槽 | 7.28 | 126 | 弱低压槽 | 西北气流 |
| Apr.6 | 122 | 弱高压脊 | 副高 | 7.29 | 107 | 弱低压槽 | 西风槽 |
| Apr.11 | 109 | 弱高压脊 | 偏西气流 | 8.2 | 139 | 弱低压槽 | 辐合带环流 |
| Apr.13 | 102 | 均压场 | 偏西气流 | 9.6 | 105 | 弱低压槽 | 副高 |
| Apr.21 | 132 | 均压场 | 弱脊 | 9.12 | 101 | 弱低压槽 | 副高+台风外围 |
| Apr.22 | 115 | 均压场 | 西北气流 | 9.13 | 102 | 弱低压槽 | 副高 |
| Apr.23 | 145 | 均压场 | 西北气流 | 9.18 | 115 | 弱高压脊 | 副高 |
| Apr.30 | 200 | 均压场 | 偏西气流 | 9.26 | 116 | 均压场 | 副高 |
| May.1 | 153 | 均压场 | 偏西气流 | 9.27 | 163 | 均压场 | 副高 |
| May.7 | 108 | 均压场 | 西南气流 | 9.28 | 148 | 均压场 | 反气旋环流 |
| Jun.6 | 106 | 弱低压槽 | 西北气流 | 9.29 | 130 | 均压场 | 西风槽 |
| Jun.7 | 122 | 弱低压槽 | 弱脊 | 9.30 | 107 | 均压场 | 偏西气流 |
| Jun.8 | 117 | 弱低压槽 | 副高 | 10.19 | 103 | 弱高压脊 | 偏西气流 |
| 气象因子及O3质量浓度 Meteorological factors and concentrations of O3 | 均压场 Equalizing field | 弱高压脊 Weak high pressure ridge | 弱低压槽 Weak low pressure trough | 超标日 Exceeded days | 全年 The whole year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均气温 Mean temperature/℃ | 25.2 | 23.9 | 29.5 | 26.5 | 23.1 |
| 平均日照时数 Mean sunshine duration/(h·d-1) | 8.6 | 8.1 | 8.6 | 8.5 | 5.2 |
| 平均气压 Mean air pressure/hPa | 1004.0 | 1007.9 | 994.4 | 1001.3 | 1004.8 |
| 平均日降水量 Mean precipitation/mm | 0 | 0 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 4.2 |
| 平均相对湿度 Mean relative humidity/% | 74.2 | 72.3 | 76.3 | 74.6 | 75 |
| 平均风速 Mean wind speed/(m·s-1) | 1.6 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 2.2 |
| O3-8 h均值 Mean concentration of O3-8 h/(μg·m-3) | 191 | 173 | 173 | 181 | 103 |
| O3-8 h-90%质量浓度 Mass concentration of O3-8 h-90%/(μg·m-3) | 223 | 182 | 187 | 210 | 160 |
Table 4 Meteorological factors and the concentrations of O3 in different ground weather conditions on exceeded days of O3-8 h in Guangzhou in 2021
| 气象因子及O3质量浓度 Meteorological factors and concentrations of O3 | 均压场 Equalizing field | 弱高压脊 Weak high pressure ridge | 弱低压槽 Weak low pressure trough | 超标日 Exceeded days | 全年 The whole year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均气温 Mean temperature/℃ | 25.2 | 23.9 | 29.5 | 26.5 | 23.1 |
| 平均日照时数 Mean sunshine duration/(h·d-1) | 8.6 | 8.1 | 8.6 | 8.5 | 5.2 |
| 平均气压 Mean air pressure/hPa | 1004.0 | 1007.9 | 994.4 | 1001.3 | 1004.8 |
| 平均日降水量 Mean precipitation/mm | 0 | 0 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 4.2 |
| 平均相对湿度 Mean relative humidity/% | 74.2 | 72.3 | 76.3 | 74.6 | 75 |
| 平均风速 Mean wind speed/(m·s-1) | 1.6 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 2.2 |
| O3-8 h均值 Mean concentration of O3-8 h/(μg·m-3) | 191 | 173 | 173 | 181 | 103 |
| O3-8 h-90%质量浓度 Mass concentration of O3-8 h-90%/(μg·m-3) | 223 | 182 | 187 | 210 | 160 |
| 时间 Time | 持续天数Duration days/d | 广东省O3超标城市占比(含广州) Proportion of cities with the over-standard of O3 in Guangdong Province (including Guangzhou)/% | O3污染级别 Pollution level of O3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Feb.6-Feb.7 | 2 | 23.8 | 轻度污染 |
| Feb.22- Feb.23 | 2 | 38.1 | 轻度污染 |
| Apr.21- Apr.23 | 3 | 38.1 | 轻度污染 |
| Apr.30-May.1 | 2 | 81.0 | 中度污染 |
| Jun.6-Jun.8 | 3 | 52.4 | 轻度污染 |
| Jul.26-Jul.29 | 4 | 42.9 | 轻度污染 |
| Sep.12-Sep.13 | 2 | 33.3 | 轻度污染 |
| Sep.26-Sep.30 | 5 | 76.2 | 轻-中度污染 |
Table 5 Continuous O3 pollution processes in Guangzhou in 2021
| 时间 Time | 持续天数Duration days/d | 广东省O3超标城市占比(含广州) Proportion of cities with the over-standard of O3 in Guangdong Province (including Guangzhou)/% | O3污染级别 Pollution level of O3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Feb.6-Feb.7 | 2 | 23.8 | 轻度污染 |
| Feb.22- Feb.23 | 2 | 38.1 | 轻度污染 |
| Apr.21- Apr.23 | 3 | 38.1 | 轻度污染 |
| Apr.30-May.1 | 2 | 81.0 | 中度污染 |
| Jun.6-Jun.8 | 3 | 52.4 | 轻度污染 |
| Jul.26-Jul.29 | 4 | 42.9 | 轻度污染 |
| Sep.12-Sep.13 | 2 | 33.3 | 轻度污染 |
| Sep.26-Sep.30 | 5 | 76.2 | 轻-中度污染 |

Figure 7 The sequence diagram of the temperature at ground and 118 m of Guangzhou Tower and their temperature differences from 16:00 on April 29 to 15:00 on May 1 “Ground-118 m” is the temperature difference between the temperature at ground and 118 m of Guangzhou Tower, and negative value represents inversion
| [1] |
ANENBERG S C, HOROWITZ L W, TONG D Q, et al., 2010. An estimate of the global burden of anthropogenic ozone and fine particulate matter on premature human mortality using atmospheric modeling[J]. Environmental Health Perspectives, 118(9): 1189-1195.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | CHEN X, ZHANG L W, HUANG J J, et al., 2016. Long-term exposure to urban air pollution and lung cancer mortality: A 12-year cohort study in Northern China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 571: 885-861. |
| [3] |
FENG Z Z, HU E Z, Wang X K, et al., 2015. Ground-level O3 pollution and its impacts on food crops in China: A review[J]. Environmental Pollution, 199: 42-48.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
FU T M, ZHENG Y, PAULOT F, et al., 2015. Positive but variable sensitivity of August surface ozone to large-scale warming in the southeast United States[J]. Nature Climate Change, 5(5): 454-458.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
GHUDE S D, JENA C, CHATE D M, et al., 2014. Reductions in India's crop yield due to ozone[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 41(15): 5685-5691.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
KAVASSALIS S C, MURPHY J G, 2017. Understanding ozone-meteorology correlations: A role for dry deposition[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 44(6): 2922-2931.
DOI URL |
| [7] | LEE Y C, SHINDELL D T, FALUVEGI G, et al., 2014. Increase of ozone concentrations, its temperature sensitivity and the precursor factor in South China[J]. Tellus B, 66(1): 1-16. |
| [8] |
LELIEVELD J, EVANS J S, FNAIS M, et al., 2015. The Contribution of Outdoor Air Pollution Sources to Premature Mortality on a Global Scale[J]. Nature, 525(7569): 367-371.
DOI URL |
| [9] | POLLACK I B, RYERSON T B, TRAINER M, et al., 2015. Airborne and ground-based observations of a weekend effect in ozone, precursors, and oxidation products in the California South Coast Air Basin[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 117(D21): 405-425. |
| [10] |
SHAO M, ZHANG Y H, ZENG L M, et al., 2009. Ground-level ozone in the Pearl River Delta and the roles of VOC and NOx in its production[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 90(1): 512-518.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
YANG C X, YANG H B, GUO S, et al., 2012. Alternative ozone metrics and daily mortality in Suzhou: The China air pollution and health effects study (CAPES)[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 426: 83-89.
DOI URL |
| [12] | 陈婉莹, 陈懿昂, 褚旸晰, 等, 2022. 珠三角地区臭氧来源特征的数值模拟研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 42(3): 293-308. |
| CHEN W Y, CHEN Y A, CHU Y X, et al., 2022. Numerical simulation of ozone source characteristics in the Pearl River Delta region[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 42(3): 293-308. | |
| [13] | 陈漾, 张金谱, 黄祖照, 2017. 广州市近地面臭氧时空变化及其与气象因子的关系[J]. 中国环境监测, 33(4): 99-109. |
| CHEN Y, ZHANG J P, HUANG Z Z, 2017. Spatial-temporal variation of surface ozone in Guangzhou and its relations with meteorological factors[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 33(4): 99-109. | |
| [14] | 程念亮, 李云婷, 张大伟, 等, 2016. 2014年北京市城区臭氧超标日浓度特征及与气象条件的关系[J]. 环境科学, 37(6): 2041-2051. |
| CHENG N L, LI Y T, ZHANG D W, et al., 2016. Characteristics of ozone over standard and its relationships with meteorological conditions in Beijing City in 2014[J]. Environmental Science, 37(6): 2041-2051. | |
| [15] | 崔坤, 赵慧, 刘鹏, 等, 2021. 2019年许昌市臭氧污染情况及其与气象条件的关系[J]. 气象与环境学, 44(1): 89-95. |
| CUI K, ZHAO H, LIU P, et al., 2021. Analysis of the 2019 ozone pollution and meteorological conditions in Xuchang of Henan Province[J]. Meteorological and Environmental Sciences, 44(1): 89-95. | |
| [16] | 邓爱萍, 陆维青, 杨雪, 2017. 2013—2017年江苏省环境空气中首要污染物变化分析研究[J]. 环境科学与管理, 42(12): 19-22. |
| DENG A P, LU W Q, YANG X, 2017. Analysis on Change of Primary Pollutant in Ambient Air of Jiangsu Province during 2013 and 2017[J]. Environmental Science and Management, 42(12): 19-22. | |
| [17] | 邓慧颖, 陈立新, 余永江, 等, 2021. 武夷山市臭氧分布特征及其与气象要素关系分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(7): 1428-1435. |
| DENG H Y, CHEN L X, YU Y J, et al., 2021. Characteristics of ozone pollution distribution and its correlation analysis with meteorological factors in Wuyishan[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(7): 1428-1435. | |
| [18] | 董昊, 程龙, 王含月, 等, 2021. 安徽省臭氧污染特征及气象影响因素分析[J]. 中国环境监测, 37(1): 58-68. |
| DONG H, CHENG L, WANG H Y, et al., 2021. Analysis of ozone pollution characteristics and meteorological factors in Anhui province[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 37(1): 58-68. | |
| [19] | 符传博, 丹利, 刘丽君, 等, 2022b. 2019年秋季三亚市一次典型臭氧污染个例气象成因解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 31(1): 89-99. |
| FU C B, DAN L, LIU L J, et al., 2022b. Characteristics of a typical ozone pollution event and its meteorological reason in Sanya city in autumn 2019[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 31(1): 89-99. | |
| [20] | 符传博, 徐文帅, 丹利, 等, 2022a. 2015—2020年年海南省臭氧时空变化及其成因分析[J]. 环境科学, 43(2): 675-685. |
| FU C B, XU W S, DAN L, et al., 2022a. Temporal and spatial variations in ozone and its causes over Hainan Province from 2015 to 2020[J]. Environmental Science, 43(2): 675-685. | |
| [21] | 高素莲, 闫学军, 刘光辉, 等, 2020. 济南市夏季臭氧重污染时段VOCs污染特征及来源解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(9): 1839-1846. |
| GAO S L, YAN X J, LIU G H, et al., 2020. Characteristics and source apportionment of ambient VOCs in serious ozone pollution period of summer in Ji’nan[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29(9): 1839-1846. | |
| [22] | 国家环境保护总局, 2005. 环境空气质量自动监测技术规范: HJ/T193—2005 [S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| State Environmental Protection Administration of the People’ s Republic of China, 2005. Technical specification for automatic monitoring of ambient air quality: HJ/T193—2005 [S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. | |
| [23] | 洪莹莹, 陈辰, 保鸿燕, 等, 2021. 珠三角西南部春季臭氧来源与敏感性分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(5): 984-994. |
| HONG Y Y, CHEN C, BAO H Y, et al., 2021. Sources and sensitivity analysis of ozone in spring over the southwestern part of Pearl River Delta region[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(5): 984-994. | |
| [24] | 侯素霞, 张鉴达, 李静, 2021. 上海市大气污染物时空分布及其相关性因子分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(6): 1220-1228. |
| HOU S X, ZHANG J D, LI J, 2021. Analysis of spatiotemporal distribution and correlation factors of atmospheric pollutants in Shanghai city[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(6): 1220-1228. | |
| [25] | 黄俊, 廖碧婷, 吴兑, 等, 2018. 广州近地面臭氧浓度特征及气象影响分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 38(1): 23-31. |
| HUANG J, LIAO B T, WU D, et al., 2018. Guangzhou ground level ozone concentration characteristics and associated meteorological factors[J]. Aeta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 38(1): 23-31. | |
| [26] | 李莉, 杨闻达, 吕升, 等, 2022. 嘉兴市臭氧污染特征及其与气象条件的关系[J]. 中山大学学报 (自然科学版), 61(2): 147-153. |
| LI L, YANG W D, LÜ L, et al., 2022. Characteristics of ozone pollution and its relationship with meteorological factors in Jiaxing city[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 61(2): 147-153. | |
| [27] | 李婷苑, 陈靖扬, 翁佳烽, 等, 2022. 2015—2020年广东省臭氧污染天气型及其变化特征[J]. 中国环境科学, 42(5): 2015-2024. |
| LI T Y, CHEN J Y, WENG J F, et al., 2022. Ozone pollution synoptic patterns and their variation characteristics in Guangdong Province during 2015-2020[J]. China Environmental Science, 42(5): 2015-2024. | |
| [28] | 吕瑞鹤, 张进生, 薛艳龙, 等., 2020. 承德市臭氧污染特征及其与气象因子的相关性研究[J]. 南开大学学报 (自然科学版), 53(6): 85-91. |
| LÜ R H, ZHANG J S, XUE Y L, et al., The relevance between the pollution characteristics of O3 and meteorological factors in chengde[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Nankaiensis, 53(6): 85-91. | |
| [29] | 齐国伟, 邹爱华, 邓雪峰, 等, 2022. 乐山市臭氧生成与前体物之间的关系及其敏感性和控制分析[J]. 四川环境, 41(1): 47-57. |
| QI G W, ZOU A H, DENG X F, et al., 2022. The relationship between ozone generation and precursors, and their sensitivity and control analysis in Leshan city[J]. Sichuan Environment, 41(1): 47-57. | |
| [30] | 齐艳杰, 于世杰, 杨健, 等, 2020. 河南省臭氧污染特征与气象因子影响分析[J]. 环境科学, 41(2): 587-599. |
| QI Y J, YU S J, YANG J, et al., 2020. Analysis of Characteristic and Meteorological Influence Factors of Ozone Pollution in Henan Province[J]. Environmental Science, 41(2): 587-599. | |
| [31] | 奇奕轩, 胡君, 张鹤丰, 等, 2017. 北京市郊区夏季臭氧重污染特征及生成效率[J]. 环境科学研究, 30(5): 663-671. |
| QI Y X, HU J, ZHANG H F, et al., 2017. Pollution Characteristics and Production Efficiency of Ozone in Summertime at Rural Site in Beijing[J]. Research of Enviromental Sciences, 30(5): 663-671. | |
| [32] | 钱悦, 许彬, 夏玲君, 等, 2021. 2016—2019年江西省臭氧污染特征与气象因子影响分析[J]. 环境科学, 42(5): 2190-2201. |
| QIAN Y, XU B, XIA L J, et al., 2021. Characteristics of ozone pollution and relationships with meteorological factors in Jiangxi province[J]. Environmental Science, 42(5): 2190-2201. | |
| [33] | 沈劲, 陈多宏, 汪宇, 等, 2018. 基于情景分析的珠三角臭氧与前体物排放关系研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 27(10): 1925-1932. |
| SHEN J, CHEN D H, WANG Y, et al., 2018. Study on the relationship between ozone and precursors emission in the Pearl River Delta based on scenario analysis[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 27(10): 1925-1932. | |
| [34] | 沈劲, 黄晓波, 汪宇, 等, 2017. 广东省臭氧污染特征及其来源解析研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 37(2): 4449-4457. |
| SHEN J, HUANG X B, WANG Y, et al., 2017. Study on ozone pollution characteristics and source apportionment in Guangdong Province[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 37(12): 4449-4457. | |
| [35] | 苏筱倩, 安俊琳, 张玉欣, 等, 2019. 支持向量机回归在臭氧预报中的应用[J]. 环境科学, 40(4): 1697-1704. |
| SU X Q, AN J L, ZHANG Y X, et al., 2019. Application of support vector machine regression in ozone forecasting[J]. Environmental Science, 40(4): 1697-1704. | |
| [36] | 唐孝炎, 张远航, 邵敏, 2006. 大气环境化学[M]. 第2版. 北京: 高等教育出版社: 106-107. |
| TANG X Y, ZHANG Y H, SHAO M, 2006. Atmospheric environmental chemistry[M]. The second edition. Beijing: Higher Education Press: 106-107. | |
| [37] | 万五星, 张帅, 李洁, 等, 2021. 河北省城市空气臭氧污染及其对植物伤害的区域差异[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(11): 2185-2194. |
| WAN W X, ZHANG S, LI J, et al., 2021. Regional differences of urban ozone pollution and its damage to plants in Hebei Province[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(11): 2185-2194. | |
| [38] | 王开燕, 邓雪娇, 张剑, 等, 2015. 广州南沙区O3浓度变化及其与气象因子的关系[J]. 环境污染与防治, 34(6): 23-26. |
| WANG K Y, DENG X J, ZHANG J, et al., 2015. Analysis on the change of ozone concentration in Nansha district of Guangzhou and its relationship with meteorological factors[J]. Environmental Pollution and Control, 34(6): 23-26. | |
| [39] | 吴瑞霞, 浦一芬, 张美根, 等, 2005. 北京市夏季臭氧变化特征的观测研究[J]. 南京气象学院学报, 28(5): 690-694. |
| WU R X, PU Y F, ZHANG M G, et al., 2005. Analysis of O3 vertical variation in summer in Beijing area[J]. Journal of Nanjing Institute of Meteorology, 28(5): 690-694. | |
| [40] | 谢祖欣, 冯宏芳, 林文, 等, 2020. 气象条件对福州市夏季臭氧 (O3)浓度的影响研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(11): 2251-2261. |
| XIE Z X, FENG H F, LIN W, et al., 2020. Meteorological factors impact on summertime ozone (O3) concentration in Fuzhou[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29(11): 2251-2261. | |
| [41] | 颜敏, 黄晓波, 陈丹, 等, 2021. 深圳市臭氧污染特征及其与前体物关系分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(4): 763-770. |
| YAN M, HUANG X B, CHEN D, et al., 2021. Characteristics of ozone pollution and relationship between ozone and precursors in Shenzhen[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(4): 763-770. | |
| [42] | 易睿, 王亚林, 张殷俊, 等, 2015. 长江三角洲地区城市臭氧污染特征与影响因素分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 35(8): 2371-2377. |
| YI R, WANG Y L, ZHANG Y J, et al., 2015. Pollution characteristics and influence factors of ozone in Yangtze River Delta[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 35(8): 2370-2377. | |
| [43] | 周映彤, 王岩, 孙铭禹, 等, 2021. 近地层臭氧浓度升高对亲子代大豆叶片抗氧化系统的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(11): 2195-2203. |
| ZHOU Y T, WANG Y, SUN M Y, et al., 2021. Effect of ozone concentration increasing near the ground on antioxidant system of parent and offspring soybean leaves[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(11): 2195-2203. | |
| [44] | 邹旭东, 蔡福, 王笑影, 等, 2020. 辽宁省臭氧质量浓度变化研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(9): 1830-1838. |
| ZOU X D, CAI F, WANG X Y, et al., 2020. Study on the change of ozone concentration in Liaoning province[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29(9): 1830-1838. | |
| [45] | 中华人民共和国环境保护部, 国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 2012. 环境空气质量标准: GB 3095—2012[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’ s Republic of China, General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’ s Republic of China, 2012. Ambient ait quality standards: GB 3095—2012[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. | |
| [46] | 中华人民共和国环境保护部, 2012. 环境空气质量指数 (AQI) 技术规定 (试行): HJ 633—2012[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’ s Republic of China, 2012. Technical regulation on ambient air quality index (on trial): HJ 633—2012[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. | |
| [47] | 中华人民共和国环境保护部, 2013. 环境空气质量评价技术规范 (试行): HJ 663—2013 [S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’ s Republic of China, 2012. Technical regulation for ambient air quality assessment (on trial): HJ 663—2012 [S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. |
| [1] | DU Caiyan, YANG Peng, FENG Shuxian, MAO Yanting, TAO Qiong, CI Zhulamu, PENG Huiping, HE Jianmei, LI Weilin. Correlation between Quality and Ecological Factors of Weixi Glutinous Yam in Different Ecological Regions [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1053-1061. |
| [2] | LIU Xia, GUO Shu, WANG Lin. Study on the Value of Land Use and Ecological Services in the Region of Regional Integration: Take Shuanglai Pilot Area as An Example [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1163-1172. |
| [3] | WU Chenyu, XU Fanfan, WEI Shibo, FAN Jingjing, LIU Guanpeng, WANG Kun. Study on Response of Surface Vegetation Cover to Climate Change in Weihe River Basin [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 835-844. |
| [4] | ZHANG Junwei, XIA Shengjie, CHEN Huiru, LIU Yanhong. Influence of Landscape Pattern Evolution on Thermal Environment of Urban Agglomerations in Central Shanxi Province [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 943-955. |
| [5] | LI Jianhui, DANG Zheng, CHEN Lin. Spatial-temporal Characteristics of PM2.5 and Its Influencing Factors in the Yellow River Jiziwan Metropolitan Area [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 697-705. |
| [6] | LIU Ziwei, GE Jiwen, WANG Yuehuan, YANG Shiyu, YAO Dong, XIE Jinlin. Variation Pattern and Influential Factors of Methane Flux in the Dajiuhu Peatland [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 706-714. |
| [7] | WANG Tiezheng, QU Xinyue, LIU Chunxiang, LI Youzhi. Spatial and Temporal Changes in Water Quality in the Dongjiang Lake and Their Relationships with Land Use in the Watershed [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 722-732. |
| [8] | FENG Shuna, LÜ Jialong, HE Hailong. Effect of KI Leaching on the Hg (Ⅱ) Removal of Loess Soil and the Physicochemical Properties of the Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 776-783. |
| [9] | WANG Jiali, FENG Jingke, YANG Yuanzheng, ZU Jiaxing, CAI Wenhua, YANG Jian. Research on Spatial Relations between Impervious Surfaces and the Urban Thermal Environment in the Central Metropolitan Area of Nanning City [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 525-534. |
| [10] | QIAN Haiming, ZHANG Yunlin, LI Na, WANG Weijia, SUN Xiao, ZHANG Yibo, SHI Kun, FENG Sheng, GAO Yanghui. High Frequency Monitoring of Water Quality Dynamics for River Drinking Water Source during the Typical Rainfall Process [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 579-589. |
| [11] | YANG Yu, DENG Renjian, LONG Pei, HUANG Zhongjie, Ren Bozhi, WANG Zhenghua. Isolation and Identification of Arsenic-oxidizing Bacterium Pseudomonas sp. AO-1 and Its Oxidation Properties for As(Ⅲ) [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 619-626. |
| [12] | YANG Yaodong, CHEN Yumei, TU Pengfei, ZENG Qingru. Phytoremediation Potential of Economic Crop Rotation Patterns for Cadmium-polluted Farmland [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 627-634. |
| [13] | ZHANG Shanwen, YANG Ran, HOU Wenxing, WANG Lili, LIU Shuang, SONG Hanyang, ZHAO Wenji, LI Lingjun. Analysis of Fractional Vegetation Cover Changes and Driving Forces on Both Banks of Yongding River Before and After Ecological Water Replenishment [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(2): 264-273. |
| [14] | MA Chuang, WANG Yuyang, ZHOU Tong, WU Longhua. Enrichment Characteristics and Desorption Behavior of Cadmium and Zinc in Particulate Organic Matter of Polluted Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(9): 1892-1900. |
| [15] | WU Haoping, QIN Hongjie, HE Bin, YOU Yi, CHEN Jinfeng, ZOU Chunping, YANG Siyu, HAO Beibei. A Brief Discussion on the Development Trend of the Agricultural Non-point Source Pollution Control Model Based on Carbon Neutrality [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(9): 1919-1926. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
