Ecology and Environment ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (3): 579-589.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.03.015
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
QIAN Haiming1,2( ), ZHANG Yunlin2, LI Na2, WANG Weijia2, SUN Xiao2, ZHANG Yibo2,3, SHI Kun2,3, FENG Sheng1,*(
), ZHANG Yunlin2, LI Na2, WANG Weijia2, SUN Xiao2, ZHANG Yibo2,3, SHI Kun2,3, FENG Sheng1,*( ), GAO Yanghui4
), GAO Yanghui4
Received:2022-11-18
Online:2023-03-18
Published:2023-06-02
Contact:
FENG Sheng
钱海铭1,2( ), 张运林2, 李娜2, 王玮佳2, 孙晓2, 张毅博2,3, 施坤2,3, 冯胜1,*(
), 张运林2, 李娜2, 王玮佳2, 孙晓2, 张毅博2,3, 施坤2,3, 冯胜1,*( ), 高阳辉4
), 高阳辉4
通讯作者:
冯胜
作者简介:钱海铭(1998年生),硕士研究生,主要从事水环境研究。E-mail: hmqian1998@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
QIAN Haiming, ZHANG Yunlin, LI Na, WANG Weijia, SUN Xiao, ZHANG Yibo, SHI Kun, FENG Sheng, GAO Yanghui. High Frequency Monitoring of Water Quality Dynamics for River Drinking Water Source during the Typical Rainfall Process[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 579-589.
钱海铭, 张运林, 李娜, 王玮佳, 孙晓, 张毅博, 施坤, 冯胜, 高阳辉. 典型降雨过程中河流饮用水源地水质高频监测研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 579-589.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.03.015

Figure 1 Land use type of Ganzhou municipal district in 2020 and the monitoring point of Ground-based hyperspectral proximal sensing and Meteorological Station
| 土地利用类型 | 占比/% | 土地利用类型 | 占比/% | 土地利用类型 | 占比/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 雨养农田 | 23.7 | 落叶阔叶林 | 1.3 | 湿地 | 0.04 |
| 灌溉农田 | 13.3 | 常绿针叶林 | 30.76 | 不透水面 | 7.5 |
| 常绿阔叶林 | 20.7 | 常绿灌木林 | 1.1 | 水体 | 1.6 |
Table 1 Proportion of land use types in Ganzhou municipal districts
| 土地利用类型 | 占比/% | 土地利用类型 | 占比/% | 土地利用类型 | 占比/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 雨养农田 | 23.7 | 落叶阔叶林 | 1.3 | 湿地 | 0.04 |
| 灌溉农田 | 13.3 | 常绿针叶林 | 30.76 | 不透水面 | 7.5 |
| 常绿阔叶林 | 20.7 | 常绿灌木林 | 1.1 | 水体 | 1.6 |

Figure 3 Comparison between of measured and monitored TSM (a), TN (b), NH4+-N (c), TP (d) mass concentrations from ground-based hyperspectral proximal sensing
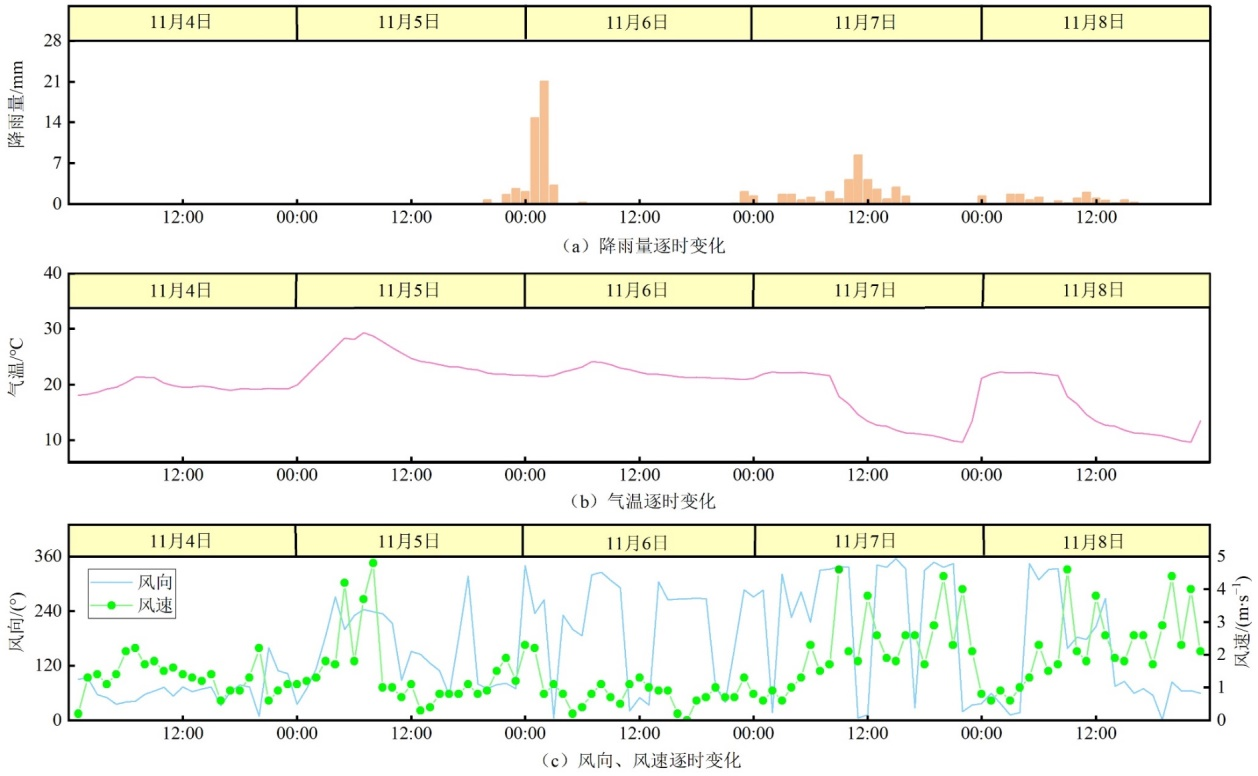
Figure 4 Hourly variations of rainfall (a), air temperature (b), wind direction (c) and wind speed (c) of meteorological station from November 4 to 8, 2021
| [1] |
BARCO J, WONG K M, STENSTROM M K, 2008. Automatic calibration of the U.S. EPA SWMM Model for a large urban catchment[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 134(4): 466-474.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BREZONIK P L, STADELMANN T H, 2002. Analysis and predictive models of stormwater runoff volumes, loads, and pollutant concentrations from watersheds in the Twin Cities metropolitan area, Minnesota, USA[J]. Water Research, 36(7): 1743-1757.
PMID |
| [3] |
EBODÉ V B, BRAUN J J, NNOMO B N, et al., 2022. Impact of rainfall variability and land use change on river discharge in South Cameroon[J]. Water, 14(6): 941.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
KAWASAKI A, TAKAMATSU M, HE J, et al., 2010. An integrated approach to evaluate potential impact of precipitation and land-use change on streamflow in Srepok River Basin[J]. Theory and Applications of GIS, 18(2): 117-128.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
KAWASAKI A, TAKAMATSU M, HE J, et al., 2019. An integrated approach to evaluate potential impact of precipitation and land-use change on streamflow in Srepok River Basin[J]. Theory and Applications of GIS, 18(2): 117-128.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
LI C H, ZHENG X K, ZHAO F, et al., 2017. Effects of urban non-point source pollution from Baoding City on Baiyangdian Lake, China[J]. Water, 9(4): 249.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
LI J, TAO T, PANG Z H, et al., 2015. Identification of different moisture sources through isotopic monitoring during a storm event[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 16(4): 1918-1927.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
LI L Q, YIN C Q, HE Q C, et al., 2007. First flush of storm runoff pollution from an urban catchment in China[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 19(3): 295-299.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
MANNINGS S, SMITH S, BELL J N B, 1996. Effect of acid deposition on soil acidification and metal mobilisation[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 11(1-2): 139-143.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
MARCÉ R, GEORGE G, BUSCARINU P, et al., 2016. Automatic high frequency monitoring for improved lake and reservoir management[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 50(20): 10780-10794.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
RUMELHART D, HINTONG G, WILLIAMS R, 1986. Learning internal representation by Back-Propagation errors[J]. Nature, 323: 533-536.
DOI |
| [12] |
SEIFERT-DÄHNN I, FURUSETH I S, VONDOLIA G K, et al., 2021. Costs and benefits of automated high-frequency environmental monitoring - The case of lake water management[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 285: 112108.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
SIMPSON I M, WINSTON R J, BROOKER M R, 2022. Effects of land use, climate, and imperviousness on urban stormwater quality: A meta-analysis[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 809: 152206.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
TSIHRINTZIS V A, HAMID R, 1998. Runoff quality prediction from small urban catchments using SWMM[J]. Hydrological Processes, 12(2): 311-329.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
XU H, PAERL H W, ZHU G W, et al., 2017. Long-term nutrient trends and harmful cyanobacterial bloom potential in hypertrophic Lake Taihu, China[J]. Hydrobiologia, 787(1): 229-242.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
ZHANG Y L, SHI K, ZHOU Y Q, et al., 2016. Monitoring the river plume induced by heavy rainfall events in large, shallow, Lake Taihu using MODIS 250m imagery[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 173: 109-121.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
ZHU Q D, SUN J H, HUA G F, et al., 2015. Runoff characteristics and non-point source pollution analysis in the Taihu Lake Basin: a case study of the town of Xueyan, China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22(19): 15029-15036.
DOI URL |
| [18] | 包鑫, 江燕, 胡羽聪, 等, 2021. 潮河流域降雨径流事件污染物输出特征[J]. 环境科学, 42(7): 3316-3327. |
|
BAO X, JIANG Y, HU Y C, et al., 2021. Characteristics of pollutant dynamics under rainfall-rainoff events in the Chaohe River watershed[J]. Environmental Science, 42(7): 3316-3327.
DOI URL |
|
| [19] | 段洪涛, 万能胜, 邱银国, 等, 2020. 富营养化湖库天空地——体化监控平台系统设计与实践[J]. 湖泊科学, 32(5): 1396-1405. |
|
DUAN H T, WAN N S, QIU Y G, et al., 2020. Discussions and practices on the framework of monitoring system in eutrophic lakes and reservoirs[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 32(5): 1396-1405.
DOI URL |
|
| [20] | 郭强, 叶许春, 刘佳, 等, 2020. 土地利用变化对流域水文过程时空分异的影响——以赣江流域为例[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 29(12): 2747-2759. |
| GUO Q, YE X C, LIU J, et al., 2020. Impact of land use change on spatio-temporal differentiation of watershed hydrological processes: a case study of Ganjiang River Basin[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 29(12): 2747-2759. | |
| [21] |
何岩, 沈叔云, 黄民生, 等, 2012. 城市黑臭河道底泥内源氮硝化-反硝化作用研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 21(6): 1166-1170.
DOI |
| HE Y, SHEN S Y, HUANG M S, et al., 2012. Research of nitrification-denitrification regarding endogenous nitrogen from urban malodorous riversediments: A review[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 21(6): 1166-1170. | |
| [22] | 黄金良, 黄亚玲, 李青生, 等, 2012. 流域水质时空分布特征及其影响因素初析[J]. 环境科学, 33(4): 1098-1107. |
| HUANG J L, HUANG Y L, LI Q S, et al., 2012. Preliminary analysis of spatiotemporal variation of water quality and its influencing factors in the Jiulong River watershed[J]. Environmental Science, 33(4): 1098-1107. | |
| [23] | 李慧赟, 王裕成, 单亮, 等, 2022. 暴雨径流对新安江入库总磷负荷量的影响[J]. 环境科学研究, 35(4): 887-895. |
| LI H Y, WANG Y C, SHAN L, et al., 2022. Effect of rainstorm runoff on total phosphorus load in Xin'anjiang[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 35(4): 887-895. | |
| [24] | 李云良, 张奇, 姚静, 等, 2013. 鄱阳湖湖泊流域系统水文水动力联合模拟[J]. 湖泊科学, 25(2): 227-235. |
|
LI Y L, ZHANG Q, YAO J, et al., 2013. Integrated simulation of hydrological and hydrodynamic processes for Lake Poyang-catchment system[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 25(2): 227-235.
DOI URL |
|
| [25] | 刘京, 周密, 陈鑫, 等, 2014. 国家地表水水质自动监测网建设与运行管理的探索与思考[J]. 环境监控与预警, 6(1): 10-13. |
| LIU J, ZHOU M, CHEN X, et al., 2014. Study on the construction and management of the quality automatic monitoring network of state surface water[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Forewarning, 6(1): 10-13. | |
| [26] | 马晓宇, 朱元励, 梅琨, 等, 2012. SWMM模型应用于城市住宅区非点源污染负荷模拟计算[J]. 环境科学研究, 25(1): 95-102. |
| MA X Y, ZHU Y L, MEI K, et al., 2012. Application of SWMM in the simulation of non-point source pollution load in urban residential area[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 25(1): 95-102. | |
| [27] | 孟祥巍, 许学工, 2014. 平原城市河流面源污染研究范围及方法的选择与效果比较[J]. 生态环境学报, 2014, 23(01): 145-150. |
| MENG X W, XU X G, 2014. The Studied area selection and result comparison of river non-point source pollution in plain urban area[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 23(1): 145-150. | |
| [28] | 宋嘉, 李怀恩, 李家科, 等, 2021. 鹦鹉沟小流域天然降雨条件下水土及养分流失特征[J]. 水土保持研究, 28(5): 7-12, 21. |
| SONG J, LI H E, LI J K, et al., 2021. Characteristics of soil and nutrient losses under rainfall in Yingwugou small watershed[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 28(5): 7-12, 21. | |
| [29] | 王书敏, 郭树刚, 何强, 等, 2015. 城市流域降雨径流水质特性及初期冲刷现象[J]. 环境科学研究, 28(4): 532-539. |
| WANG S M, GUO S G, HE Q, et al., 2015. Water quality characteristics of stormwater runoff and the first flush effect in urban regions[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 28(4): 532-539. | |
| [30] | 辛苑, 李萍, 吴晋峰, 等, 2021. 强降雨对北运河流域沙河水库水质的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 41(1): 199-208. |
| XIN Y, LI P, WU J F, et al., 2021. Impacts of heavy rainfall on the water quality of shahe reservoir in the north canal basin[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 41(1): 199-208. | |
| [31] | 严莉, 黄炳彬, 何春利, 等, 2022. 沙河水库周边典型排口降雨溢流污染特征研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 42(3): 28-39. |
| YAN L, HUANG B B, HE C L, et al., 2022. Research on the pollution of the combined sewer overflow in Shahe Reservoir watershed[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 42(3): 28-39. | |
| [32] | 张运林, 孙晓, 李娜, 等, 2020. 复杂场景下水体叶绿素和藻蓝素陆基遥感机器学习算法: 中国, CN 112070234 A[P]. 2020-12-11. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?FileName=CN112070234A&DbName=SCPD2020. |
| ZHANG Y L, SUN X, LI N, et al, 2020. Land-based remote sensing machine learning algorithm for chlorophyll and phycocyanin in complex scene. Chinese: CN 112070234 A[P]. 2020-12-11. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?FileName=CN112070234A&DbName=SCPD2020. | |
| [33] | 张运林, 孙晓, 李娜, 等, 2021. 水体营养盐和化学需氧量的陆基遥感监测方法: 中国, CN 112816421 A[P]. 2021-05-18. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?FileName=CN112816421A&DbName=SCPD2021. |
| ZHANG Y L, SUN X, LI N, et al, 2021. Land-based remote sensing monitoring of nutrients and Chemical oxygen demand in water.Chinese: CN 112816421 A[P]. 2021-05-18. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?FileName=CN112816421A&DbName=SCPD2021. | |
| [34] | 张彦, 邹磊, 梁志杰, 等, 2022. 暴雨前后河南北部河流水质分异特征及其污染源解析[J]. 环境科学, 43(5): 2537-2547. |
|
ZHANG Y, ZOU L, LIANG Z J, et al., 2022. Differential characteristics and source identification of water quality of the rivers in northern Henan before and after rainstorm[J]. Environmental Science, 43(5): 2537-2547.
DOI URL |
|
| [35] |
张郁婷, 陈永华, 汤春芳, 等, 2017. 东江上游高风险支流不同功能区初期雨水径流污染特征分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 26(11): 1942-1949.
DOI |
| ZHANG Y T, CHEN Y H, TANG C F, et al., 2017. Analysis on pollution characteristics of initial rainwater runoff from different functional areas of high risk tributary in Dongjiang upriver[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 26(11): 1942-1949. | |
| [36] | 郑清, 黎云祥, 朱广伟, 等, 2022. 夏季强降雨期间千岛湖有机碳的时空分布特征及影响因素[J]. 环境科学研究, 35(4): 896-907. |
| ZHENG Q, LI Y X, ZHU G W, et al., 2022. Spatio-temporal distribution and driving factors of organic carbon in Qiandaohu Reservoir during summer storm[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 35(4): 896-907. |
| [1] | DONG Zhijin, ZHANG Chengchun, ZHAN Xiuli, ZHANG Weifu. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Soil Nutrients of Biological Soil Crusts and Their Underlying Soil of Sandy Land in the East of Yellow River in Ningxia [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 910-919. |
| [2] | PAN Yuling, QU Xiangning, LI Qing, WANG Lei, WANG Xiaoping, TAN Peng, CUI Geng, AN Yu, TONG Shouzheng. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Soil Physicochemical Factors and Their Response to Microtopography in a Typical Beach Wetland of the Yellow River in Ningxia [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 668-677. |
| [3] | DAI Demin, JIANG Xusheng, LIU Jie, WANG Luyang, CHEN Shiqi, HAN Qingkun. Study on Suitability of Pb/Zn Mine Tailings Using Three Different Organic Amendments [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 784-793. |
| [4] | ZHANG Beier, WU Jianqiang, WANG Min, XIONG Lijun, TAN Juan, SHEN Cheng, HUANG Botao, HUANG Shenfa. Evaluation of Soil Health in Different Arable Land Ecological Conservation Projects [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(2): 388-396. |
| [5] | TONG Yindong, HUANG Lanlan, YANG Ning, ZHANG Yiyan, LI Zipeng, SHAO Bo. Distribution Characteristics and Potential Environmental Risk Analysis of Microcystins in Global Water Bodies [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(1): 129-138. |
| [6] | HUANG Weijia, LIU Chun, LIU Yue, HUANG Bin, LI Dingqiang, YUAN Zaijian. Soil Ecological Stoichiometry and Its Influencing Factors at Different Elevations in Nanling Mountains [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(1): 80-89. |
| [7] | WANG Jie, SHAN Yan, MA Lan, SONG Yanjing, WANG Xiangyu. Effects of Straw and Biochar Synergistic Returning on the Improvement of Salt-affected Soil in the Yellow River Delta [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(1): 90-98. |
| [8] | WU Haoping, QIN Hongjie, HE Bin, YOU Yi, CHEN Jinfeng, ZOU Chunping, YANG Siyu, HAO Beibei. A Brief Discussion on the Development Trend of the Agricultural Non-point Source Pollution Control Model Based on Carbon Neutrality [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(9): 1919-1926. |
| [9] | LIU Zhanhang, ZHANG Shuyan, HOU Yuping, ZHU Shuyu, WANG Lidong, SHI Xinyue, LI Peiguang, HAN Guangxuan, XIE Baohua. Effects of Spartina alterniflora Invasion on Soil Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Their Ecostoichiometric Characteristics in the Yellow River Estuary Wetlands [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(7): 1360-1369. |
| [10] | XIA Enlong, NONG Junqing, WEI Songpo, LIU Xizhen, LIU Guanglu. Changes in Soil Nutrient Characteristics in Moso Bamboo Forest Expanding into Broadleaved Forest [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(6): 1110-1117. |
| [11] | DENG Xiao, WU Chunyuan, YANG Guisheng, LI Yi, LI Qinfen. Improvement Effect of Coconut-shell Biochar on Coastal Soil in Hainan [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(4): 723-731. |
| [12] | LONG Jing, HUANG Yao, LIU Zhanfeng, JIAN Shuguang, WEI Liping, WANG Jun. Leaf Traits and Nutrient Resorption of Two Woody Species on A Tropical Coral Island [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(2): 248-256. |
| [13] | HUANG Qiaoyi, YU Junhong, HUANG Jianfeng, HUANG Xu, LI Ping, FU Hongting, TANG Shuanhu, LIU Yifeng, XU Peizhi. Nutrient Resources of Main Crop Straw and Its Potential of Substituting for Chemical Fertilizer in Guangdong Province [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(2): 297-306. |
| [14] | YU Fei, YE Caihong, XU Tiaozi, ZHANG Zhongrui, ZHU Hangyong, ZHANG Geng, HUA Lei, DENG Jianfeng, DING Xiaogang. Evaluation of Heavy Metal Pollution in Woodland Soil of Granite Area in Shaoguan City [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(2): 354-362. |
| [15] | SHENG Jifeng, LI Yao, YU MeiJia, HAN Yanying, YE Yanhui. Effects of Nitrogen and Phosphorus An Addition on Soil Nutrients and Activity of Related Enzymes in Alpine Grassland [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(12): 2302-2309. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
