Ecology and Environment ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (9): 1903-1915.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.09.015
Special Issue: 生物多样性专题汇编
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
XING Shuwen( ), XU Jiamin, HUANG Bin, GAO Jingting, HAN Li
), XU Jiamin, HUANG Bin, GAO Jingting, HAN Li
Received:2021-04-11
Online:2021-09-18
Published:2021-12-08
作者简介:邢树文(1963年生),男,副教授,研究方向为土壤动物生态学。E-mail: xsw501@126.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
XING Shuwen, XU Jiamin, HUANG Bin, GAO Jingting, HAN Li. Effect of Heavy Metal Pollution on the Community Structure and Diversity of Soil Animals in Tea Garden Located in A Tungsten Mining Area[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(9): 1903-1915.
邢树文, 许佳敏, 黄彬, 高锦婷, 韩丽. 钨尾矿重金属污染对茶园土壤动物群落结构及多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(9): 1903-1915.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.09.015
| 样地 Sample | 采样点 Sampling site | 茶园土壤重金属元素质量分数w/(mg∙kg-1)及单项污染指数Pi Soil heavy metal content w/(mg∙kg-1) of tea garden and single term pollution index (Pi) | 综合污染指数 Comprehensive pollution index | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wZn | PZn | wCu | PCu | wNi | PNi | wPb | PPb | wCd | PCd | wAs | PAs | |||
| 茶园Ⅰ TⅠ | 1 | 166.2 | 0.83 | 148.2 | 2.96 | 54.3 | 1.36 | 195.5 | 0.78 | 5.48 | 18.27 | 1134 | 28.35 | 20.98 |
| 2 | 147 | 0.74 | 141.4 | 2.83 | 53.4 | 1.34 | 223.6 | 0.89 | 6.05 | 20.17 | 1101 | 27.53 | 20.46 | |
| 3 | 182 | 0.91 | 150.4 | 3.01 | 56.6 | 1.42 | 215.6 | 0.86 | 6.42 | 21.40 | 1232.5 | 30.81 | 22.83 | |
| 4 | 159 | 0.80 | 168.6 | 3.37 | 48.3 | 1.21 | 212.2 | 0.85 | 5.26 | 17.53 | 1108 | 27.70 | 20.5 | |
| 5 | 132 | 0.66 | 132.3 | 2.65 | 53.2 | 1.33 | 208.3 | 0.83 | 5.54 | 18.47 | 1319.5 | 32.99 | 24.27 | |
| 6 | 167 | 0.84 | 180.5 | 3.61 | 51.8 | 1.30 | 198.5 | 0.79 | 6.82 | 22.73 | 1251.5 | 31.29 | 23.25 | |
| 茶园Ⅱ TⅡ | 1 | 136.2 | 0.68 | 88.2 | 1.76 | 44.3 | 1.11 | 105.5 | 0.42 | 3.48 | 11.60 | 134 | 3.35 | 8.5 |
| 2 | 147 | 0.74 | 41.4 | 0.83 | 53.4 | 1.34 | 113.6 | 0.45 | 4.05 | 13.50 | 101 | 2.53 | 9.82 | |
| 3 | 132 | 0.66 | 50.4 | 1.01 | 50.6 | 1.27 | 95.6 | 0.38 | 3.84 | 12.80 | 72.5 | 1.81 | 9.29 | |
| 4 | 119 | 0.60 | 48.6 | 0.97 | 48.3 | 1.21 | 132.2 | 0.53 | 2.76 | 9.20 | 108 | 2.70 | 6.75 | |
| 5 | 126 | 0.63 | 72.3 | 1.45 | 53.2 | 1.33 | 98.3 | 0.39 | 3.54 | 11.80 | 79.5 | 1.99 | 8.6 | |
| 6 | 127 | 0.64 | 80.5 | 1.61 | 47.8 | 1.20 | 128.5 | 0.51 | 2.02 | 6.73 | 91.5 | 2.29 | 5.00 | |
| 对照CK | 1 | 112 | 0.56 | 45 | 0.9 | 34.6 | 0.87 | 103.4 | 0.41 | 0.35 | 1.17 | 25.6 | 0.64 | 1.03 |
| 茶园 CT | 2 | 109 | 0.55 | 50 | 1 | 32.2 | 0.81 | 84.5 | 0.34 | 0.26 | 0.87 | 25.5 | 0.63 | 0.92 |
| 3 | 99 | 0.50 | 48 | 0.96 | 31.5 | 0.79 | 92.5 | 0.37 | 0.32 | 1.07 | 29.2 | 0.73 | 0.97 | |
| 4 | 102 | 0.51 | 55 | 1.1 | 34.2 | 0.86 | 99.3 | 0.40 | 0.23 | 0.77 | 23.4 | 0.59 | 0.98 | |
| 5 | 114 | 0.57 | 42 | 0.84 | 30.7 | 0.77 | 88.7 | 0.35 | 0.27 | 0.9 | 27.2 | 0.68 | 0.86 | |
| 6 | 106 | 0.53 | 53 | 1.06 | 30.8 | 0.77 | 85.7 | 0.34 | 0.25 | 0.83 | 25.1 | 0.63 | 0.95 | |
Table 1 Soil heavy metal content and pollution index in different tea garden
| 样地 Sample | 采样点 Sampling site | 茶园土壤重金属元素质量分数w/(mg∙kg-1)及单项污染指数Pi Soil heavy metal content w/(mg∙kg-1) of tea garden and single term pollution index (Pi) | 综合污染指数 Comprehensive pollution index | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wZn | PZn | wCu | PCu | wNi | PNi | wPb | PPb | wCd | PCd | wAs | PAs | |||
| 茶园Ⅰ TⅠ | 1 | 166.2 | 0.83 | 148.2 | 2.96 | 54.3 | 1.36 | 195.5 | 0.78 | 5.48 | 18.27 | 1134 | 28.35 | 20.98 |
| 2 | 147 | 0.74 | 141.4 | 2.83 | 53.4 | 1.34 | 223.6 | 0.89 | 6.05 | 20.17 | 1101 | 27.53 | 20.46 | |
| 3 | 182 | 0.91 | 150.4 | 3.01 | 56.6 | 1.42 | 215.6 | 0.86 | 6.42 | 21.40 | 1232.5 | 30.81 | 22.83 | |
| 4 | 159 | 0.80 | 168.6 | 3.37 | 48.3 | 1.21 | 212.2 | 0.85 | 5.26 | 17.53 | 1108 | 27.70 | 20.5 | |
| 5 | 132 | 0.66 | 132.3 | 2.65 | 53.2 | 1.33 | 208.3 | 0.83 | 5.54 | 18.47 | 1319.5 | 32.99 | 24.27 | |
| 6 | 167 | 0.84 | 180.5 | 3.61 | 51.8 | 1.30 | 198.5 | 0.79 | 6.82 | 22.73 | 1251.5 | 31.29 | 23.25 | |
| 茶园Ⅱ TⅡ | 1 | 136.2 | 0.68 | 88.2 | 1.76 | 44.3 | 1.11 | 105.5 | 0.42 | 3.48 | 11.60 | 134 | 3.35 | 8.5 |
| 2 | 147 | 0.74 | 41.4 | 0.83 | 53.4 | 1.34 | 113.6 | 0.45 | 4.05 | 13.50 | 101 | 2.53 | 9.82 | |
| 3 | 132 | 0.66 | 50.4 | 1.01 | 50.6 | 1.27 | 95.6 | 0.38 | 3.84 | 12.80 | 72.5 | 1.81 | 9.29 | |
| 4 | 119 | 0.60 | 48.6 | 0.97 | 48.3 | 1.21 | 132.2 | 0.53 | 2.76 | 9.20 | 108 | 2.70 | 6.75 | |
| 5 | 126 | 0.63 | 72.3 | 1.45 | 53.2 | 1.33 | 98.3 | 0.39 | 3.54 | 11.80 | 79.5 | 1.99 | 8.6 | |
| 6 | 127 | 0.64 | 80.5 | 1.61 | 47.8 | 1.20 | 128.5 | 0.51 | 2.02 | 6.73 | 91.5 | 2.29 | 5.00 | |
| 对照CK | 1 | 112 | 0.56 | 45 | 0.9 | 34.6 | 0.87 | 103.4 | 0.41 | 0.35 | 1.17 | 25.6 | 0.64 | 1.03 |
| 茶园 CT | 2 | 109 | 0.55 | 50 | 1 | 32.2 | 0.81 | 84.5 | 0.34 | 0.26 | 0.87 | 25.5 | 0.63 | 0.92 |
| 3 | 99 | 0.50 | 48 | 0.96 | 31.5 | 0.79 | 92.5 | 0.37 | 0.32 | 1.07 | 29.2 | 0.73 | 0.97 | |
| 4 | 102 | 0.51 | 55 | 1.1 | 34.2 | 0.86 | 99.3 | 0.40 | 0.23 | 0.77 | 23.4 | 0.59 | 0.98 | |
| 5 | 114 | 0.57 | 42 | 0.84 | 30.7 | 0.77 | 88.7 | 0.35 | 0.27 | 0.9 | 27.2 | 0.68 | 0.86 | |
| 6 | 106 | 0.53 | 53 | 1.06 | 30.8 | 0.77 | 85.7 | 0.34 | 0.25 | 0.83 | 25.1 | 0.63 | 0.95 | |
| 等级 Rank | 土壤单因子评价分级标准 Soil single factor evaluation and grading standards | 土壤综合污染指数分级标准 Comprehensive soil pollution index grading standard | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 单项污染指数 Single pollution index | 污染评价 Pollution assessment | 综合污染指数 Comprehensive pollution index | 污染评价 Pollution assessment | ||
| Ⅰ | Pi≤0.7 | 无污染 Pollution-free | P≤0.7 | 清洁 Clean | |
| Ⅱ | 0.7<Pi≤1.0 | 轻微污染 Minor pollution | 0.7<P≤1.0 | 尚清洁 Still clean | |
| Ⅲ | 1.0<Pi≤2.0 | 轻度污染 Mild contamination | 1.0<P≤2.0 | 轻度污染 Mild contamination | |
| Ⅳ | 2.0<Pi≤3.0 | 中度污染 Intermediate pollution | 2.0<P≤3.0 | 中度污染 Intermediate pollution | |
| Ⅴ | Pi3.0 | 重度污染 Heavy pollution | P>3.0 | 重度污染 Heavy pollution | |
Table 2 Evaluation grading standard of soil heavy metal pollution index
| 等级 Rank | 土壤单因子评价分级标准 Soil single factor evaluation and grading standards | 土壤综合污染指数分级标准 Comprehensive soil pollution index grading standard | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 单项污染指数 Single pollution index | 污染评价 Pollution assessment | 综合污染指数 Comprehensive pollution index | 污染评价 Pollution assessment | ||
| Ⅰ | Pi≤0.7 | 无污染 Pollution-free | P≤0.7 | 清洁 Clean | |
| Ⅱ | 0.7<Pi≤1.0 | 轻微污染 Minor pollution | 0.7<P≤1.0 | 尚清洁 Still clean | |
| Ⅲ | 1.0<Pi≤2.0 | 轻度污染 Mild contamination | 1.0<P≤2.0 | 轻度污染 Mild contamination | |
| Ⅳ | 2.0<Pi≤3.0 | 中度污染 Intermediate pollution | 2.0<P≤3.0 | 中度污染 Intermediate pollution | |
| Ⅴ | Pi3.0 | 重度污染 Heavy pollution | P>3.0 | 重度污染 Heavy pollution | |
| 土壤理化因子 Soil physicochemical factor | 茶园Ⅰ Tea gardenⅠ | 茶园Ⅱ Tea gardenⅡ | 对照组茶园 Control Tea garden |
|---|---|---|---|
| w(SOC)/(g∙kg-1) | 9.172±0.725b | 10.506±0.613b | 25.319±1.846a |
| w(TN)/(g·kg-1) | 0.334±0.029b | 0.305±0.041b | 0.872±0.145a |
| 土壤含水量 Soil moisture content/% | 0.779±0.134b | 0.779±0.134b | 1.068±0.145a |
| pH | 4.726±0.337b | 4.726±0.337b | 6.166±0.413a |
| w(TP)/(g∙kg-1) | 0.686±0.033a | 0.685±0.077a | 0.648±0.421a |
| w(Olsen-P)/(g·kg-1) | 0.015±0.001c | 0.031±0.002b | 0.034±0.002a |
| w(TK)/(g·kg-1) | 34.971±0.841c | 37.637±1.115a | 36.321±0.557b |
Table 3 Soil physicochemical properties of different tea gardens
| 土壤理化因子 Soil physicochemical factor | 茶园Ⅰ Tea gardenⅠ | 茶园Ⅱ Tea gardenⅡ | 对照组茶园 Control Tea garden |
|---|---|---|---|
| w(SOC)/(g∙kg-1) | 9.172±0.725b | 10.506±0.613b | 25.319±1.846a |
| w(TN)/(g·kg-1) | 0.334±0.029b | 0.305±0.041b | 0.872±0.145a |
| 土壤含水量 Soil moisture content/% | 0.779±0.134b | 0.779±0.134b | 1.068±0.145a |
| pH | 4.726±0.337b | 4.726±0.337b | 6.166±0.413a |
| w(TP)/(g∙kg-1) | 0.686±0.033a | 0.685±0.077a | 0.648±0.421a |
| w(Olsen-P)/(g·kg-1) | 0.015±0.001c | 0.031±0.002b | 0.034±0.002a |
| w(TK)/(g·kg-1) | 34.971±0.841c | 37.637±1.115a | 36.321±0.557b |
| 动物类群 Animals groups | 茶园Ⅰ丰度 Tea garden Ⅰ abundance | 茶园Ⅱ丰度 Tea garden Ⅱ abundance | 对照茶园丰度 Control tea garden abundance | F2,24 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 蜘蛛目 Araneae | 25.56±5.94b | 37.44±6.98a | 42.78±9.90a | 0.29 |
| 双尾目 Diplura | 1.44±1.01a | 0.92±0.01b | 0.672±0.22b | 8.15** |
| 蜚蠊目 Blattoptera | 2.44±1.13a | 3.33±0.73a | 4.11±2.76a | 5.02** |
| 等足目 Isopoda | 0.00±0.00b | 0.00±0.00b | 2.33±1.04a | 14.30*** |
| 华蚖目 Sinentomata | 0.00±0.00a | 0.11±0.33a | 0.00±0.00a | 5.22** |
| 弹尾目 Collembola | 1.11±0.00b | 2.56±0.67b | 14.22±6.00a | 15.91*** |
| 蜱螨目 Acarina | 1.00±0.03c | 1.44±0.89b | 11.78±5.28a | 16.32*** |
| 等翅目 Isoptera | 1.33±1.12a | 1.22±0.20a | 0.00±0.00b | 10.17*** |
| 膜翅目 Hymenoptera | 2.67±1.00b | 3.67±0.99b | 8.00±2.75a | 4.73** |
| 半翅目 Hemiptera | 3.67±1.45a | 7.33±3.81a | 6.33±2.92a | 2.38** |
| 直翅目 Orthoptera | 7.33±2.50a | 9.00±2.11a | 2.78±0.83b | 4.88** |
| 鞘翅目 Coleoptera | 1.89±0.93b | 1.78±0.83b | 6.78±1.47a | 13.52*** |
| 鳞翅目 Lepidoptera | 2.67±1.50a | 3.67±1.50a | 0.44±0.53b | 8.13** |
| 缺翅目 Zoraptera | 0.00±0.00a | 0.00±0.00a | 0.44±1.33a | 5.22** |
| 同翅目 Homoptera | 1.22±0.97a | 0.89±1.05a | 0.67±1.32a | 0.10 |
| 脉翅目 Neuroptera | 0.00±0.00a | 0.00±0.00a | 0.11±0.33a | 5.22** |
| 革翅目 Dermaptera | 0.00±0.00b | 0.48±0.00b | 2.67±2.40a | 21.17*** |
| 正蚓目 Lumbricida | 0.00±0.00a | 0.80±0.00a | 2.33±4.36a | 10.740*** |
| 石蜈蚣目 Lithomorpha | 0.00±0.00b | 0.00±0.00b | 5.78±1.15a | 18.23*** |
| 蜈蚣目 Scolopendromorpha | 0.00±0.00b | 0.00±0.00b | 1.22±1.79a | 18.45*** |
| 马陆目 Polydesmida | 0.00±0.00b | 0.00±0.00b | 1.22±0.83a | 27.45*** |
| 地蜈蚣目 Geophilomopha | 0.00±0.00a | 0.36±0.00a | 2.00±3.46a | 4.80** |
| 柄眼目 Stylomnatophora | 0.00±0.00a | 0.88±0.00a | 1.00±2.00a | 8.00** |
Table 4 Composition and quantity of the surface of large soil fauna in different tea gardens
| 动物类群 Animals groups | 茶园Ⅰ丰度 Tea garden Ⅰ abundance | 茶园Ⅱ丰度 Tea garden Ⅱ abundance | 对照茶园丰度 Control tea garden abundance | F2,24 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 蜘蛛目 Araneae | 25.56±5.94b | 37.44±6.98a | 42.78±9.90a | 0.29 |
| 双尾目 Diplura | 1.44±1.01a | 0.92±0.01b | 0.672±0.22b | 8.15** |
| 蜚蠊目 Blattoptera | 2.44±1.13a | 3.33±0.73a | 4.11±2.76a | 5.02** |
| 等足目 Isopoda | 0.00±0.00b | 0.00±0.00b | 2.33±1.04a | 14.30*** |
| 华蚖目 Sinentomata | 0.00±0.00a | 0.11±0.33a | 0.00±0.00a | 5.22** |
| 弹尾目 Collembola | 1.11±0.00b | 2.56±0.67b | 14.22±6.00a | 15.91*** |
| 蜱螨目 Acarina | 1.00±0.03c | 1.44±0.89b | 11.78±5.28a | 16.32*** |
| 等翅目 Isoptera | 1.33±1.12a | 1.22±0.20a | 0.00±0.00b | 10.17*** |
| 膜翅目 Hymenoptera | 2.67±1.00b | 3.67±0.99b | 8.00±2.75a | 4.73** |
| 半翅目 Hemiptera | 3.67±1.45a | 7.33±3.81a | 6.33±2.92a | 2.38** |
| 直翅目 Orthoptera | 7.33±2.50a | 9.00±2.11a | 2.78±0.83b | 4.88** |
| 鞘翅目 Coleoptera | 1.89±0.93b | 1.78±0.83b | 6.78±1.47a | 13.52*** |
| 鳞翅目 Lepidoptera | 2.67±1.50a | 3.67±1.50a | 0.44±0.53b | 8.13** |
| 缺翅目 Zoraptera | 0.00±0.00a | 0.00±0.00a | 0.44±1.33a | 5.22** |
| 同翅目 Homoptera | 1.22±0.97a | 0.89±1.05a | 0.67±1.32a | 0.10 |
| 脉翅目 Neuroptera | 0.00±0.00a | 0.00±0.00a | 0.11±0.33a | 5.22** |
| 革翅目 Dermaptera | 0.00±0.00b | 0.48±0.00b | 2.67±2.40a | 21.17*** |
| 正蚓目 Lumbricida | 0.00±0.00a | 0.80±0.00a | 2.33±4.36a | 10.740*** |
| 石蜈蚣目 Lithomorpha | 0.00±0.00b | 0.00±0.00b | 5.78±1.15a | 18.23*** |
| 蜈蚣目 Scolopendromorpha | 0.00±0.00b | 0.00±0.00b | 1.22±1.79a | 18.45*** |
| 马陆目 Polydesmida | 0.00±0.00b | 0.00±0.00b | 1.22±0.83a | 27.45*** |
| 地蜈蚣目 Geophilomopha | 0.00±0.00a | 0.36±0.00a | 2.00±3.46a | 4.80** |
| 柄眼目 Stylomnatophora | 0.00±0.00a | 0.88±0.00a | 1.00±2.00a | 8.00** |

Fig. 2 NMDS plots indicating 2-dimensional distances of large surface soil animals in tea gardenⅠ, tea gardenⅡ and control tea garden TⅠ: Tea gardenⅠ; TⅡ: Tea gardenⅡ; CT: Control Tea garden
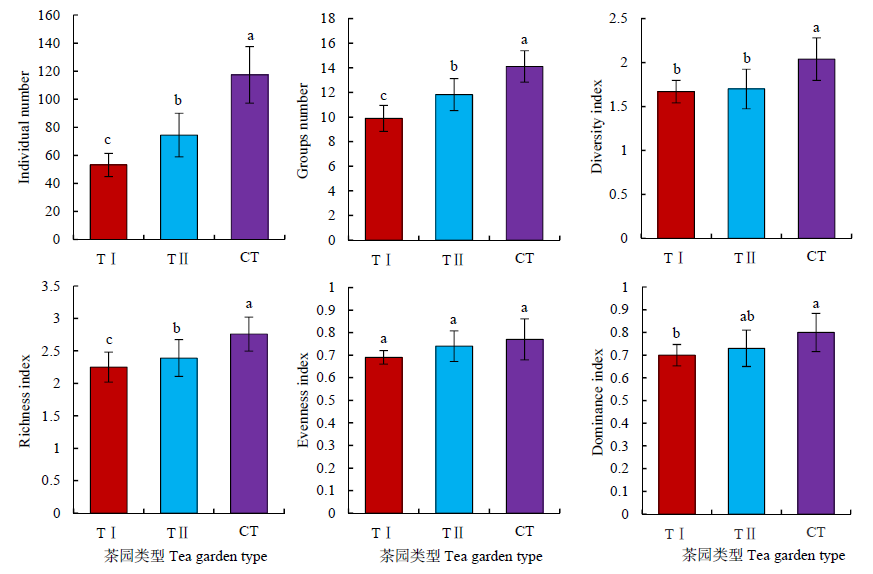
Fig. 3 Characteristic index of soil animal community in different tea gardens TⅠ: Tea gardenⅠ; TⅡ: Tea gardenⅡ; CT: Contrast tea garden; Different small letters indicate significant difference at P<0.05
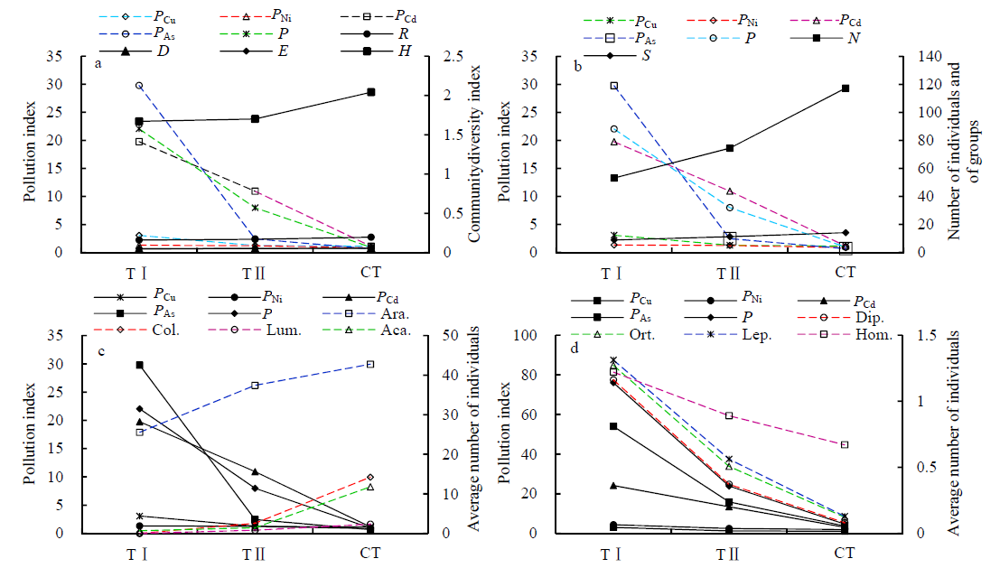
Fig. 4 Change of heavy metal pollution index, individual number, groups, indicating animal groups and the ecological index of surface soil animals community in tea garden (a) Change of heavy metal pollution index and the Ecological index; (b) Change of heavy metal pollution index, Individual number and groups; (c) Change of heavy metal pollution index and Indicating animal (Araneae, Collembola, Acarina and Lumbricida) groups numbers of surface soil animals community in 3 Tea garden; (d) Change of heavy metal pollution index and Indicating animal (Diplura, Orthoptera, Lepidoptera and Homoptera) groups numbers of surface soil animals community in 3 Tea garden. TⅠ: Tea gardenⅠ; TⅡ: Tea gardenⅡ; CT: Control Tea garden. PCu: Cu pollution index; PNi: Ni pollution index; PCd: Cd pollution index; PAs: As pollution index; P: Comprehensive pollution index. Ara.: Araneae; Col.: Collembola; Aca: Acarina; Lum.: Lumbricida

Fig. 5 RDA two-dimensional sorting diagram of soil fauna community and environmental factors in 3 tea gardens Ara.: Araneae; Dip.: Diplura; Blat.: Blattoptera; Isopo.: Isopoda; Sin.: Sinentomata; Coll.: Collembola; Isopt.: Isoptera; Hym.: Hymenoptera; Hem.: Hemiptera; Ort.: Orthoptera; Cole.: Coleoptera; Lep.: Lepidoptera; Zor.: Zoraptera; Hom.: Homoptera; Neu.: Neuroptera; Der.: Dermaptera; Lit.: Lithomorpha; Sco.: Scolopendromorpha; Pol.: Polydesmida; Geo.: Geophilomopha; Sty.: Stylomnatophora; Lum.: Lumbricida. TN: Total nitrogen; TK: Total potassium; TP: Total phosphorus; SWC: Soil water content; pH: pH value; SOM: Soil organic matter
| 变量 Variable | I | F | P | 贡献率 Contribution rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤有机质 Soil organic matter | 0.289 | 6.511 | 0.001 | 51.423 |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | 0.051 | 1.262 | 0.263 | 9.075 |
| 土壤含水量 Soil moisture | 0.025 | 0.597 | 0.769 | 4.448 |
| pH值 Soil pH value | 0.025 | 0.570 | 0.791 | 4.448 |
| 全磷 Total phosphorus | 0.063 | 1.464 | 0.196 | 11.210 |
| 速效磷 Available phosphorus | 0.054 | 1.299 | 0.226 | 9.609 |
| 全钾 Total kalium | 0.054 | 1.265 | 0.242 | 9.609 |
Table 5 Contribution rate of soil physicochemical properties to soil animal community of different tea gardens
| 变量 Variable | I | F | P | 贡献率 Contribution rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤有机质 Soil organic matter | 0.289 | 6.511 | 0.001 | 51.423 |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | 0.051 | 1.262 | 0.263 | 9.075 |
| 土壤含水量 Soil moisture | 0.025 | 0.597 | 0.769 | 4.448 |
| pH值 Soil pH value | 0.025 | 0.570 | 0.791 | 4.448 |
| 全磷 Total phosphorus | 0.063 | 1.464 | 0.196 | 11.210 |
| 速效磷 Available phosphorus | 0.054 | 1.299 | 0.226 | 9.609 |
| 全钾 Total kalium | 0.054 | 1.265 | 0.242 | 9.609 |
| 变量 Variable | I | F | P | 贡献率 Contribution rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn | 0.042 | 0.992 | 0.412 | 7.241 |
| Cu | 0.045 | 1.056 | 0.395 | 7.759 |
| Mn | 0.036 | 0.843 | 0.549 | 6.207 |
| Ni | 0.270 | 5.924 | 0.001 | 46.552 |
| Pb | 0.047 | 1.092 | 0.346 | 8.103 |
| Cd | 0.082 | 1.911 | 0.055 | 14.138 |
| As | 0.057 | 1.357 | 0.202 | 9.828 |
Table 6 Contribution rate of soil heavy metal to soil animal community of tea garden
| 变量 Variable | I | F | P | 贡献率 Contribution rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn | 0.042 | 0.992 | 0.412 | 7.241 |
| Cu | 0.045 | 1.056 | 0.395 | 7.759 |
| Mn | 0.036 | 0.843 | 0.549 | 6.207 |
| Ni | 0.270 | 5.924 | 0.001 | 46.552 |
| Pb | 0.047 | 1.092 | 0.346 | 8.103 |
| Cd | 0.082 | 1.911 | 0.055 | 14.138 |
| As | 0.057 | 1.357 | 0.202 | 9.828 |
| [1] |
BARTON P S, MANNING A D, GIB B H, et al., 2009. Conserving ground dwelling beetles in an endangered woodland community: Multi-scale habitat effects on assemblage diversity[J]. Biological Conservation, 142(8): 1701-1709.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
CARAVACA F, LOZANO Z, RODRIGUEZ-CABALLERO, et al., 2017. Spatial shifts in soil microbial activity and degradation of pasture cover caused by prolonged exposure to cement dust[J]. Land Degradation & Development, DOI: 10.1002/ldr.2564.
DOI |
| [3] | CLARKE K R, 1993. Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes incommunity structure[J]. Australian Journal of Ecology, 18(1): 117-143. |
| [4] | COLWELL R K, 2013. Estimates: Statistical estimation of species richness and shared species from samples[M]. version 9. User's Guide and Application. http://purl.Oclc.Org/estimates. |
| [5] |
CARRASCOSA M, SÁNCHEZ-MORENO S, ALONSO-PRADOS J L, 2015. Effects of organic and conventional pesticides on plant biomass, nematode diversity and the structure of the soil food web[J]. Nematology, 17(1): 11-26.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
DELGADO-BAQUERIZO M, MAESTRE F T, REICH P B, et al., 2016. Microbial diversity drives multifunctionality in terrestrial ecosystems[J]. Nature Communications, DOI: 10.1038/ncomms10541.
DOI |
| [7] |
EISENHAUER N, BONN A, GUERRA C A, 2019. Recognizing the quiet extinction of invertebrates[J]. Nature Communications, DOI: 10.1038/ s41467-018-07916-1.
DOI |
| [8] |
FILSER J, WITTMAN R, LANG A, 2000. Response types in Collembola towards copper in the environment[J]. Environmental Pollut, 107(1): 71-78.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
FOUNTAIN M T, HOPKIN S P, 2004. Biodiversity of Collembola in urban soils and the use of Folsomia candida to assess soil ‘quality'[J]. Ecotoxicology, 13: 555-572.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
JIAO S, CHEN W M, WANG E T, et al., 2016. Microbial succession in response to pollutants in batch-enrichment culture[J]. Scientific Reports, 6(1):21791.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
JUNG M P, KIM S T, KIM H, et al., 2008. Species diversity and community structure of ground dwelling spiders in unpolluted and moderately heavy metal polluted habitats[J]. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 195: 15-22.
DOI URL |
| [12] | LI T, LI C Y, YU D N, et al., 2010. Effects of heavy metals from road traffic on the community structure and spatial distribution of cropland soil animals[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30(18): 5001-5011. |
| [13] |
LI Y F, CAO Z P, HU C, et al., 2014. Response of nematodes to agricultural input levels in various reclaimed and unreclaimed habitats[J]. European Journal of Soil Biology, 60: 120-129.
DOI URL |
| [14] | MARIA C, HERNANDEZ, SORIANO D R, 2013. Soil Processes and Current Trends in Quality Assessment[M]. London: IntechOpen Limited. |
| [15] | MCCUNE B, GRACE J B, 2002. Analysis of Ecological Communities[M]. Oregon: MJM Software Design. |
| [16] | NIU X Q, REN T, TIAN X G, et al., 2013. The Community Organization and Concentration of Soil Animals in Heavy Metal Polluted Areas: A Case of the Farmland Around Linfen Iron-works in Shanxi Province[J]. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 32(6): 889-897. |
| [17] |
PARK B Y, LEE J K, RO H M, et al., 2011. Effects of heavy metal contamination from an abandoned mine on nematode community structure as an Indicator of soil ecosystem health[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 51(6): 17-24.
DOI URL |
| [18] | SKORUPSKI M, BUTKIEWICZ G, WIERZBICKA A, 2009. The first reaction of soil mite fauna (Acari, Mesostigmata) caused by conversion of Norways pruce stand in the Szklarska Pore, ba Forest District[J]. Journal of Forest Science, 55(5): 234-243. |
| [19] |
SANTORUFO L, VAN G C, ROCCO A, 2012. Soil invertebrates as bioindicators of urban soil quality[J]. Environmental Pollution, 161: 57-63.
DOI URL |
| [20] | STEINER W A, 1995. Influence of air pollution on moss dwelling animals: III: Terrestrial fauna, with emphasis on Oribatida and Collembola[J]. Acarologia, 36(2): 149-173. |
| [21] |
SACKETT T E, CLASSENN A T, SANDERS N J, 2010. Linking soil food web structure to above and belowground ecosystem processes: A meta-analysis[J]. Oikos, 119: 1984-1992.
DOI URL |
| [22] | ZHOU Q X, WANG Y, 2012. Methodological systems of building agricultural soil quality criteria in China[J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 12(S1): 38-44. |
| [23] |
ZHU D, KE X, WU L H, et al., 2016. Ecotoxicity of cadmium in a soil collembolan-predatory mite food chain: Can we use the N-15 labeled litter addition method to assess soil functional change?[J]. Environ Pollut, 219: 37-46.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
WANG S J, WANG H, LI J H, et al., 2017. Ants can exert a diverse effect on soil carbon and nitrogen pools in a Xishuangbanna tropical forest[J]. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 113: 45-52.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
XIAO R, WANG S, LI R H, et al., 2017. Soil heavy metal contamination and health risks associated with artisanal gold mining in Tongguan, Shaanxi, China[J]Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 141: 17-24.
DOI URL |
| [26] | 鲍士旦, 2002. 土壤农化分析[M]. 3 版. 北京: 中国农业出版社: 22-162. |
| BAO S D, 2000. Soil Agrochemical Analysis[M]. Third Edition. Beijing: China Agriculture Press: 22-162. | |
| [27] | 陈怀满, 2005. 环境土壤学[M]. 北京: 中国环境出版社: 522-523. |
| CHEN Y M, 2005. Environmental Soil science[M]. Beijing: China Environment Press: 522-523. | |
| [28] | 崔鲁楠, 2016. 淮南矿区不同塌陷类型土壤典型特性研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽大学: 16-38. |
| CUI L N, 2016. Study on soil typical characteristics of different types of subsidence in Huainan Mining Area[D]. Hefei: Anhui University: 16-38. | |
| [29] | 杜晓芳, 李英滨, 刘芳, 等, 2018. 土壤微食物网结构与生态功能[J]. 应用生态学, 29(2): 403-411. |
| DU X F, LI Y B, LIU F, et al., 2018. Structure and ecological functions of soil micro-food web[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 29(2): 403-411. | |
| [30] | 段桂兰, 崔慧灵, 杨雨萍, 等, 2020. 重金属污染土壤中生物间相互作用及其协同修复应用[J]. 生物工程学报, 36(3): 455-470. |
| DUAN G L, CUI H L, YANG Y P, et al., 2020. Interactions among soil biota and their applications in synergistic bioremediation of heavy-metal contaminated soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 36(3): 455-470. | |
| [31] | 李荣华, 沈锋, 李晓龙, 等, 2015. 陕西某铅锌冶炼厂区及周边农田重金属污染土壤的稳定化修复理论与实践[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 34(7): 1269-1276. |
| LI R H, SHEN F, LI X L, et al., 2015. Theoretical Research and Immobilization Practice of Heavy Metal Polluted Soil in a Closed Lead-Zinc Smelter and Surrounding Farmland in Tongguan, Shaanxi[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 34(7): 1269-1276. | |
| [32] | 李孝刚, 丁昌峰, 王兴祥, 2014. 重金属污染对红壤旱地小节肢类土壤动物群落结构的影响[J]. 生态学报, 34(21): 6198-6204. |
| LI X G, DING C F, WANG X X, 2014. Effects of heavy metal pollution on soil microarthropods in upland red soil[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34(21): 6198-6204. | |
| [33] | 李钰飞, 李吉进, 许俊香, 等, 2020. 铜、锌污染梯度对自然林地和农田土壤线虫群落的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 57(6): 1492-1503. |
| LI Y F, LI J J, XU J X, et al., 2020. Effects of copper and zinc contamination on soil nematode communities from natural woodland and farmland[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 57(6): 1492-1503. | |
| [34] | 李大乐, 陈建文, 张红, 等, 2021. Pb和Cd对森林土壤细菌功能多样性及群落结构的影响[J]. 生态学报, 41(21): 1-12. |
|
LI D L, CHEN J W, ZHANG H, et al., 2021. Effects of Pb and Cd on forest soil bacterial functional diversity and community structure[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(21): 1-12.
DOI URL |
|
| [35] | 刘贝贝, 陈冬, 康秋玉, 等, 2013. 土壤生物对农药场地土壤环境的生物指示作用[J]. 土壤通报, 44(5): 1210-1217. |
| LIU B B, CHEN D, KANG Q Y, et al., 2013. The biological indication of soil organisms to soil environment of insecticide factory[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 44(5): 1210-1217. | |
| [36] | 刘继亮, 赵文智, 李锋瑞, 2015. 黑河中游荒漠地面节肢动物分布特征[J]. 干旱区研究, 32(6): 1192-1200. |
| LIU J L, ZHAO W Z, LI F R, 2015. Distribution of ground arthropod community in arid desertin the middle reaches of Heihe River[J]. Arid Zone Research, 32(6): 1192-1200. | |
| [37] | 刘文华, 李媛媛, 赵秋香, 等, 2014. 珠三角农用地土壤重金属污染治理修复研究实践与展望[J]. 环境科技, 27(6): 32-37. |
| LIU W H, LI Y Y, ZHAO Q X, et al., 2014. Study the Application of the Stable Passivation Technology to Rehabilitate the Pearl River Delta Soil Heavy Metal Pollution[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 27(6): 32-37. | |
| [38] | 刘晋仙, 2019. 铜尾矿废水中微生物多样性格局及其适应机制[D]. 太原: 山西大学: 1-135. |
| LIU J X, 2019. Diversity Patterns and Adaptation Mechanisms of MicrobialCommunities in Copper Tailings Drainag[D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi University: 1-135. | |
| [39] | 鲁如坤, 1999. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社: 1-188. |
| LU R K, 1999. Methods for chemical analysis of soil agriculture[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: 1-188. | |
| [40] | 牛晓倩, 任婷, 田小刚, 等, 2013. 重金属污染区农田土壤动物群落结构及富集研究--以山西省临汾钢铁厂周围农田为例[J]. 四川动物, 32(6): 889-897. |
| NIU X Q, REN T, TIAN X G, et al., 2013. The Community Organization and Concentration of Soil Animals in Heavy Metal Polluted Areas: A Case of the Farmland Around Linfen Iron-works in Shanxi Province[J]. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 32(6): 889-897. | |
| [41] | 聂立凯, 于政达, 孔范龙, 等, 2019. 土壤动物对土壤碳循环的影响研究进展[J]. 生态学杂志, 38(3): 882-890. |
| NIE L K, YU Z D, KONG F L, et al., 2019. Advance in study on effects of soil fauna on soil carbon cycling[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 38(3): 882-890. | |
| [42] | 秦旭芝, 罗志祥, 季文兵, 等, 2021. 桂西北地质高背景区有色金属冶炼对周边土壤重金属污染与生态风险评价[EB/OL]. 生态学杂志: 1-17 [2021-07-01]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1148.Q.20210701.0957.001.html. |
| QIN X Z, LUO Z X, JI W B, et al., 2021. Pollution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surrounding soil by nonferrous metal smelting with high geological background in Northwest Guangxi[EB/OL]. Chinese Journal of Ecology: 1-17 [2021-07-01]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1148.Q.20210701.0957.001.html. | |
| [43] | 任若凡, 赵腾飞, 王晴晴, 等, 2015. 重金属污染对土壤动物群落结构的影响[J]. 河南农业科学, 44(10): 90-94. |
| REN R F, ZHAO T F, WANG Q Q, et al., 2015. Effect of heavy metal pollution on soil animal community structure[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 44(10): 90-94. | |
| [44] | 邵佳, 赵远来, 冯琰玉, 等, 2021. 生物质炭对长期铅镉复合污染土壤微生物群落丰度及活性的影响[EB/OL]. 农业环境科学学报: 1-16 [2021-07-05]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/12.1347.S.20210702.1751.004.html. |
| SHAO J, ZHAO Y L, FENG Y Y, et al., 2021. Effects of biochar on microbial community abundance and activity in long-term Pb and Cd contaminated soils[EB/OL]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science: 1-16 [2021-07-05]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/12.1347.S.20210702.1751.004.html. | |
| [45] | 苏越, 邬天媛, 张雪萍, 2011. 我国土壤动物环境指示功能研究进展[J]. 国土与自然资源研究, 198(6): 64-67. |
| SU Y, WU T Y, ZHANG X P, 2011. Research Advances in the Indicative Function Soil Fauna to Environment in China[J]. Territory and Natural Resources Study, 198(6): 64-67. | |
| [46] | 孙贤斌, 李玉成, 2014. 淮南煤矿废弃地重金属污染对土壤动物群落的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 33(2): 408-414. |
| SUN X B, LI Y C, 2014. Impact of heavy metal pollution on soil animal communities in abandoned coal mine area in Huainan City, Anhui Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 33(2): 408-414. | |
| [47] | 孙艳芳, 王国利, 刘长仲, 2014. 重金属污染对农田土壤无脊椎动物群落结构的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 45(1): 210-215. |
| SUN Y F, WANG G L, LIU C Z, 2014. Effects of Heavy Metal Pollution on Soil Faunal Community Structure[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 45(1): 210-215. | |
| [48] | 宁应之, 徐富荣, 王婷婷, 2020. 庆阳市庆城县退耕还林区土壤纤毛虫群落特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(3): 506-515. |
| NING Y Z, XU F R, WANG T T, 2020. Community characteristics of soil ciliates in forestlands converted from cultivated lands in Qingcheng county, Qingyang city[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29(3): 506-515. | |
| [49] | 王昱, 李宝龙, 冯起, 等, 2021. 黑河重金属空间分布及与大型底栖动物的关系[J]. 中国环境科学, 41(3): 1354-1365. |
| WANG Y, LI B L, FENG Q, et al., 2021. Space distribution of heavy metals and its relationship with macrozoobenthos in the Heihe River, Northwest China[J]. China Environmental Science, 41(3): 1354-1365. | |
| [50] |
王邵军, 阮宏华, 2008. 土壤生物对地上生物的反馈作用及其机制[J]. 生物多样性, 16(4): 407-416.
DOI |
|
WANG S J, RUAN H H, 2008. Feedback mechanisms of soil biota to aboveground biology in terrestrial ecosystems[J]. Biodiversity Science, 16(4): 407-416.
DOI URL |
|
| [51] | 魏志文, 2019. 赣南稀土尾矿修复区细菌多样性研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学: 1-74. |
| WEI Z W, 2019. Study on the bacterial diversity in the restoration area of rare earth mine tailings of Gannan[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University: 1-74. | |
| [52] | 邢树文, 许佳敏, 高锦婷, 等, 2018. 不同林龄桉树林地表节肢动物对钨尾矿重金属污染的响应[J]. 韩山师范学院学报, 39(6): 12-23. |
| XING S W, XU J M, GAO J T, et al., 2018. Response of Ground Surface Arthropods in Eucalyptus Forests of Different Ages to Heavy Metal Pollution of Tungsten Tailings[J]. Journal of Hanshan Teachers College, 39(6): 12-23. | |
| [53] | 邢树文, 王桔红, 梁秀霞, 等, 2019. 钨尾矿生态恢复中桉树林地表节肢动物群落特征及影响因子研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(4): 840-849. |
| XING S W, WANG J H, LIANG X X, et al. 2019. Study on community characteristics and influencing factors of surface arthropod in Eucalyptus forest during the process of ecological recovery of tungsten tailings[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28(4): 840-849. | |
| [54] | 许洪扬, 付冰清, 康慧, 等, 2021. 铅锌矿渣污染土壤的重金属含量及真菌群落特征分析[J]. 湖南农业大学学报 (自然科学版), 47(2): 203-211. |
| XU H Y, FU B Q, KANG H, et al., 2021. Analysis of heavy metals contents and the characteristics of fungal communities in Pb-Zn tailings contaminated soils[J]. Journal of Hunan Agricultural University (Natural Sciences), 47(2): 203-211. | |
| [55] | 尹文英, 胡圣豪, 沈韫芬, 1998. 中国土壤动物检索图鉴[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 131-387. |
| YIN W Y, HU S H, SHEN Y F, 1998. Chinese soil animal retrieval illustrated handbook[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 131-387. | |
| [56] | 尹文英, 1992. 中国亚热带土壤动物[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 221-552. |
| YIN W Y, 1992. Subtropical soil fauna in China[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 221-552. | |
| [57] | 中国环境监测总站, 1990. 中国土壤元素背景值[M]. 北京: 中国环境出版社: 330-369. |
| China Environmental Monitoring Station, 1990. China Soil ellement background values[M]. Beijing: China Environment Press: 330-369. | |
| [58] | 张怡悦, 2021. 金/铁矿区土壤-植物铅锌同位素特征及微生物演化机制[D]. 北京: 北京科技大学: 37-127. |
| ZHANG Y Y, 2021. Pb-Zn isotopic characteristics and microbial evolution mechanisms of soil-plant system in gold/iron mining area[D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing: 37-127. | |
| [59] | 郑乐怡, 归鸿, 1999. 昆虫分类学(上、下)[M]. 南京: 南京师范大学出版社: 27-975. |
| ZHENG L Y, GUI H, 1999. Insect Classification, Vol. 1 & Vol. 2[M]. Nanjing: Nanjing Normal University Press: 27-975. | |
| [60] | 朱永恒, 李克中, 余健, 等, 2013. 铜尾矿复垦地土壤动物群落的恢复[J]. 动物学杂志, 48(3): 417-427. |
| ZHU Y H, LI K Z, YU J, et al., 2013. Rehabilitation of Soil Fauna in Reclaimed Abandoned Land of Copper-mine-tailings[J]. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 48(3): 417-427. |
| [1] | HOU Hui, YAN Peixuan, XIE Qinmi, ZHAO Hongliang, PANG Danbo, CHEN Lin, LI Xuebin, HU Yang, LIANG Yongliang, NI Xilu. Characterization of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungal Community Diversity in the Rhizosphere Soils of Prunus mongolica Scrub of Helan Mountain [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 857-865. |
| [2] | JIANG Yongwei, DING Zhenjun, YUAN Junbin, ZHANG Zheng, LI Yang, WEN Qingchun, WANG Yeyao, JIN Xiaowei. Study on Benthic Macroinvertebrates Community Structure and Water Quality Evaluation in Main Rivers of Liaoning Province [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 969-979. |
| [3] | WANG Yun, ZHENG Xilai, CAO Min, LI Lei, SONG Xiaoran, LIN Xiaolei, GUO Kai. Study on Denitrification Performance and Control Factors in Brackish-Freshwater Transition Zone of Coastal Aquifer [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 980-988. |
| [4] | KOU Zhu, QING Chun, YUAN Changguo, LI Ping. Diversity and Distribution of Sulfur Oxidizing Bacteria in Hot Springs of Northeast Tibet, China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 989-1000. |
| [5] | HU Fang, LIU Jutao, WEN Chunyun, HAN Liu, WEN Hui. Phytoplankton Community Structure and Evaluation of Aquatic Ecological Conditions in Fu River Basin [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 744-755. |
| [6] | YU Fei, ZENG Hailong, FANG Huaiyang, FU Lingfang, LIN Shu, DONG Jiahao. Spatio-temporal Variation Characteristics of Phytoplankton Functional Groups and Water Quality Evaluation in the Typical Tidal River Network [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 756-765. |
| [7] | WANG Lixiao, LIU Jinxian, CHAI Baofeng. Response of Soil Bacterial Community and Nitrogen Cycle during the Natural Recovery of Abandoned Farmland in Subalpine of the North China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(8): 1537-1546. |
| [8] | QIAN Lianwen, YU Tiantian, LIANG Xujun, WANG Yixiang, CHEN Yongshan. Stability of Biochar after Application for 5 Years in the Amendment of Acidified Tea Garden Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(7): 1442-1447. |
| [9] | GONG Lingxuan, WANG Lili, ZHAO Jianning, LIU Hongmei, YANG Dianlin, ZHANG Guilong. Effects of Different Cover Crop Patterns on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Organic Carbon Mineralization in Tea Gardens [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(6): 1141-1150. |
| [10] | WANG Yingcheng, YAO Shiting, JIN Xin, YU Wenzhen, LU Guangxin, WANG Junbang. Comparative Study on Soil Bacterial Diversity of Degraded Alpine Meadow in the Sanjiangyuan Region [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(4): 695-703. |
| [11] | LIU Hongmei, HAI Xiang, AN Kerui, ZHANG Haifang, WANH Hui, ZHANG Yanjun, WANG Lili, ZHANG Guilong, YANG Dianlin. Effects of Different Fertilization Regimes on Community Structure Diversity of CO2-assimilating Bacteria in Maize Field of Fluvo-aquic Soil in North China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(4): 715-722. |
| [12] | XIA Kai, DENG Pengfei, MA Ruihao, WANG Fei, WEN Zhengyu, XU Xiaoniu. Changes of Soil Bacterial Community Structure and Diversity from Conversion of Masson Pine Secondary Forest to Slash Pine and Chinese Fir Plantations [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 460-469. |
| [13] | SONG Xiuli, HUANG Ruilong, KE Caijie, HUANG Wei, ZHANG Wu, TAO Bo. Effects of Different Cropping Systems on Bacterial Community Structure and Diversity in Continuous Cropping Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 487-496. |
| [14] | BAI Haifeng, WANG Yirui, SONG Jinxi, KONG Feihe, ZHANG Xuexian, LI Qi. Characteristics of Plankton Community Structure and Its Relation to Environmental Factors in Weihe River, China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(1): 117-130. |
| [15] | HE Rui, JIANG Ran, YANG Fang, ZHANG Xinfeng, LIN Jianluan, ZHU Xiaoping, PENG Songyao. Characteristics of Meso-zooplankton Community and Its Relationship with Environmental Factors in Sea Water near Maoming [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(1): 142-150. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
