Ecology and Environment ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (9): 1888-1895.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.09.013
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Furong1,2( ), WANG Xu1,2,*(
), WANG Xu1,2,*( ), LI Qingrong3, WU Zhichao1,2, FENG Qi4, WEN Dian1,2, XU Aiping1,2, ZHAO Peihua1,2
), LI Qingrong3, WU Zhichao1,2, FENG Qi4, WEN Dian1,2, XU Aiping1,2, ZHAO Peihua1,2
Received:2021-07-09
Online:2021-09-18
Published:2021-12-08
Contact:
WANG Xu
李富荣1,2( ), 王旭1,2,*(
), 王旭1,2,*( ), 李庆荣3, 吴志超1,2, 冯起4, 文典1,2, 徐爱平1,2, 赵沛华1,2
), 李庆荣3, 吴志超1,2, 冯起4, 文典1,2, 徐爱平1,2, 赵沛华1,2
通讯作者:
王旭
作者简介:李富荣(1984年生),女,副研究员,博士,主要从事农产品产地环境安全控制方面的研究。E-mail: lifr0314@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
LI Furong, WANG Xu, LI Qingrong, WU Zhichao, FENG Qi, WEN Dian, XU Aiping, ZHAO Peihua. Passivation Effect of Silkworm Excrement Composited Boron Conditioner on Cd and Pb in Acid Vegetable Soil[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(9): 1888-1895.
李富荣, 王旭, 李庆荣, 吴志超, 冯起, 文典, 徐爱平, 赵沛华. 蚕沙复合硼调理剂对酸性菜地土壤镉铅的钝化效应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(9): 1888-1895.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.09.013
| 试验材料 Materials | 土壤 Soil | 蚕沙 Silkworm excrement |
|---|---|---|
| pH值 pH value | 5.62 | 7.67 |
| w(有机质Organic matter)/% | 10.23 | 39.99 |
| w(全氮 Total nitrogen)/% | 0.048 | 1.97 |
| w(碱解氮 Alkali-hydro N)/(mg∙kg-1) | 21.03 | 2.9×103 |
| w(有效磷 Available P)/(mg∙kg-1) | 144.4 | 5.8×103 |
| w(速效钾 Available K)/(mg∙kg-1) | 240.2 | 1.4×104 |
| w(全镉 Total Cd)/(mg∙kg-1) | 0.053 | 1.01 |
| w(全铅 Total Pb)/(mg∙kg-1) | 143.05 | 36.32 |
| w(有效态镉 Available Cd)/(mg∙kg-1) | 0.007 | 0.0012 |
| w(有效态铅 Available Pb)/(mg∙kg-1) | 0.28 | 0.0036 |
Table 1 Basic physical and chemical properties of soil and silkworm excrement used in the experiment
| 试验材料 Materials | 土壤 Soil | 蚕沙 Silkworm excrement |
|---|---|---|
| pH值 pH value | 5.62 | 7.67 |
| w(有机质Organic matter)/% | 10.23 | 39.99 |
| w(全氮 Total nitrogen)/% | 0.048 | 1.97 |
| w(碱解氮 Alkali-hydro N)/(mg∙kg-1) | 21.03 | 2.9×103 |
| w(有效磷 Available P)/(mg∙kg-1) | 144.4 | 5.8×103 |
| w(速效钾 Available K)/(mg∙kg-1) | 240.2 | 1.4×104 |
| w(全镉 Total Cd)/(mg∙kg-1) | 0.053 | 1.01 |
| w(全铅 Total Pb)/(mg∙kg-1) | 143.05 | 36.32 |
| w(有效态镉 Available Cd)/(mg∙kg-1) | 0.007 | 0.0012 |
| w(有效态铅 Available Pb)/(mg∙kg-1) | 0.28 | 0.0036 |
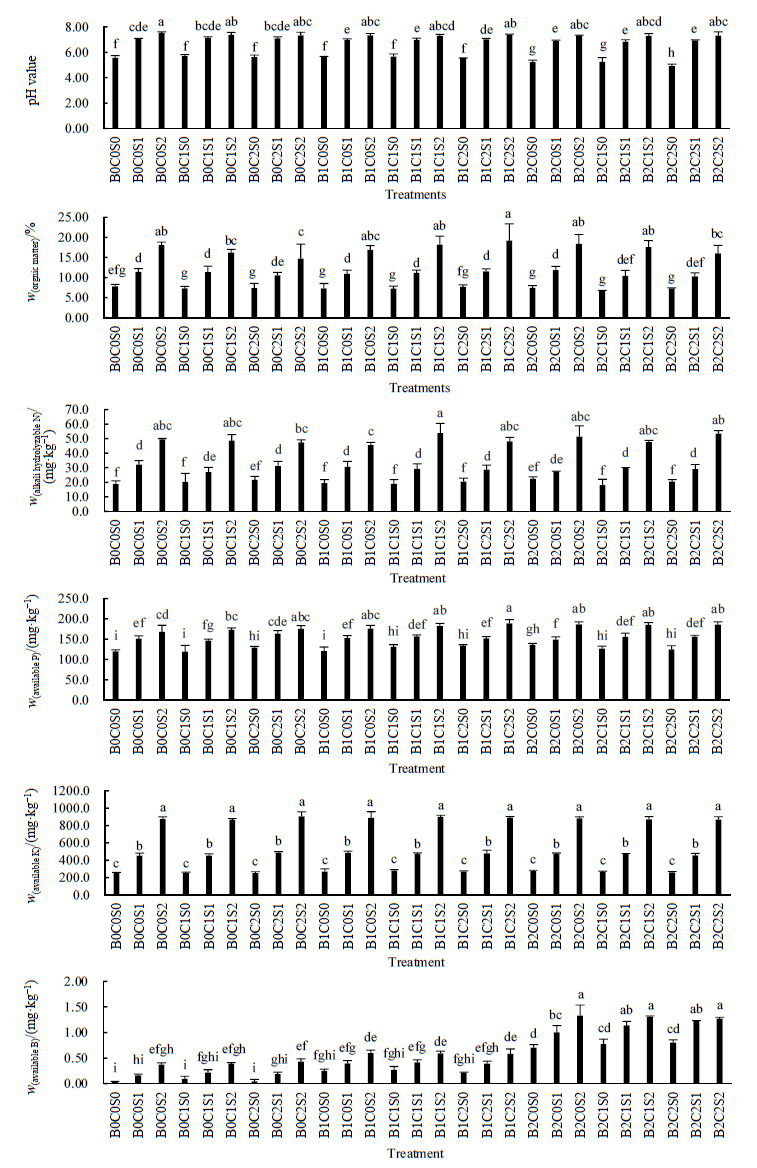
Fig. 1 Effect of different treatments on the basic physical and chemical properties of soil In the different treatments, the capital letters B, C and S indicated boron, cadmium and silkworm excrement addition respectively. For example, B0C0S0 was the control which meant the addition of boron, cadmium and silkworm sand were 0; B2C2S2 was the treatment of the addition amounts with B2 (2.0 mg∙kg-1), C2 (2.8 mg∙kg-1) and S2 (60 g∙kg-1), respectively. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different soil depth in the same succession stage at the level of 0.05, n=3, the same as below
| 处理 Treatment | pH值 pH value | 有机质 Organic Matter | 碱解氮 Alkali-hydro N | 有效磷 Available P | 速效钾 Available K | 有效态硼 Available B | 有效态镉 Available Cd | 有效态铅 Available Pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | 1.08** | 5.09 | 4.09 | 652.02** | 175.46 | 6.53 | 0.03** | 0.32** |
| S | 54.92** | 1350.55** | 12229.96** | 38301.69** | 5354983.33** | 1.62** | 6.83** | 2.75** |
| Cd | 0.03 | 5.21 | 9.57 | 428.52** | 3474.38 | 0.13 | 4.26** | 0.02 |
| B*S | 0.66** | 9.85 | 30.96 | 468.66 | 494.03 | 0.12 | 0.06** | 0.62** |
| B*Cd | 0.02 | 19.9 | 58.45 | 509.06 | 4401.79 | 0.25 | 0.04** | 0.02 |
| S* Cd | 0.17 | 3.8 | 22.04 | 30.97 | 1060.23 | 0.13 | 7.07** | 0.04 |
| B*S*Cd | 0.17 | 13.08 | 181.3 | 646.82 | 1712.27 | 0.2 | 0.07** | 0.03 |
Table 2 Multivariate analysis of variance for different treatments
| 处理 Treatment | pH值 pH value | 有机质 Organic Matter | 碱解氮 Alkali-hydro N | 有效磷 Available P | 速效钾 Available K | 有效态硼 Available B | 有效态镉 Available Cd | 有效态铅 Available Pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | 1.08** | 5.09 | 4.09 | 652.02** | 175.46 | 6.53 | 0.03** | 0.32** |
| S | 54.92** | 1350.55** | 12229.96** | 38301.69** | 5354983.33** | 1.62** | 6.83** | 2.75** |
| Cd | 0.03 | 5.21 | 9.57 | 428.52** | 3474.38 | 0.13 | 4.26** | 0.02 |
| B*S | 0.66** | 9.85 | 30.96 | 468.66 | 494.03 | 0.12 | 0.06** | 0.62** |
| B*Cd | 0.02 | 19.9 | 58.45 | 509.06 | 4401.79 | 0.25 | 0.04** | 0.02 |
| S* Cd | 0.17 | 3.8 | 22.04 | 30.97 | 1060.23 | 0.13 | 7.07** | 0.04 |
| B*S*Cd | 0.17 | 13.08 | 181.3 | 646.82 | 1712.27 | 0.2 | 0.07** | 0.03 |
| [1] |
CAI L M, XU Z C, REN M Z, et al., 2012. Source identification of eight hazardous heavy metals in agricultural soils of Huizhou, Guangdong Province, China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 78: 2-8.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
CHEN D M, CHEN D Q, XUE R R, et al., 2019. Effects of boron, silicon and their interactions on cadmium accumulation and toxicity in rice plants[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 367: 447-455.
DOI URL |
| [3] | ERIKSSON J E, 1989. The influence of pH, soil type and time on adsorption and uptake by plants of Cd added to the soil[J]. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 48: 317-335. |
| [4] |
IVÁN F, CARLOS G, CALA V, et al., 2017. The use of spent mushroom compost to enhance the ability of Atriplex halimus to phytoremediate contaminated mine soils[J]. Environmental Technology, 38(9): 1075-1084.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
LI F R, WEN D, WANG F H, et al., 2019. Derivation of soil Pb/Cd/As thresholds for safety of vegetable planting: A case study for pakchoi in Guangdong Province, China[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 18(1): 179-189.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
LI F R, WANG X, WANG F H, et al., 2021. A risk-based approach for the safety analysis of eight trace elements in Chinese flowering cabbage (Brassica parachinensis L.) in China[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, DOI: 10.1002/jsfa.11209.
DOI |
| [7] |
MPATANI F M, HAN R P, ARYEE A A, et al., 2021. Adsorption performance of modified agricultural waste materials for removal of emerging micro-contaminant bisphenol A: A comprehensive review[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 780: 146629-146629.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
QIAN Z Z, TANG L Z, ZHUANG S Y, et al., 2020. Effects of biochar amendments on soil water retention characteristics of red soil at south China[J]. Biochar, 2(4): 479-488.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
QIN G W, NIU Z D, YU J D, et al., 2021. Soil heavy metal pollution and food safety in China: Effect, sources and removing technology[J]. Chemosphere, DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129205.
DOI |
| [10] |
QIN S Y, LIU H G, E, RENGEL Z, et al., 2020. Boron inhibits cadmium uptake in wheat (Triticum aestivum) by regulating gene expression[J]. Plant Science, DOI: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2020.110522.
DOI |
| [11] |
RIAZ M, YAN L, WU X W, et al., 2018. Boron increases root elongation by reducing aluminum induced disorganized distribution of HG epitopes and alterations in subcellular cell wall structure of trifoliate orange roots[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 165: 202-210.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
SETIA R, DHALIWAL S S, SINGH R, et al., 2020. Phytoavailability and human risk assessment of heavy metals in soils and food crops around Sutlej river, India[J]. Chemosphere, DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020. 128321.
DOI |
| [13] |
WANG R G, GUO J K, XU Y M, et al., 2016. Evaluation of silkworm excrement and mushroom dreg for the remediation of multiple heavy metal/metalloid contaminated soil using pakchoi[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 124: 239-247.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
WANG R G, GUO J K, XU Y M, et al., 2016. Evaluation of silkworm excrement and mushroom dreg for the remediation of multiple heavy metal/metalloid contaminated soil using pakchoi[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 124: 239-247.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
WU J H, SONG Q M, ZHOU J Y, et al., 2021. Cadmium threshold for acidic and multi-metal contaminated soil according to Oryza sativa L. Cadmium accumulation: Influential factors and prediction model[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, DOI: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020. 111420.
DOI |
| [16] |
WU X W, SONG H X, GUAN C Y, et al., 2020a. Boron mitigates cadmium toxicity to rapeseed (Brassica napus) shoots by relieving oxidative stress and enhancing cadmium chelation onto cell walls[J]. Science of the Total Environment, DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114546.
DOI |
| [17] |
WU Z C, WANG F H, LIU S, et al., 2016. Comparative responses to silicon and selenium in relation to cadmium uptake, compartmentation in roots, and xylem transport in flowering Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris L.) under cadmium stress[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 131: 173-180.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
WU X W, SONG H X, GUAN C Y, et al., 2020b. Boron alleviates cadmium toxicity in Brassica napus by promoting the chelation of cadmium onto the root cell wall components[J]. Science of the Total Environment, DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138833.
DOI |
| [19] |
XIAO W D, YE X Z, ZHANG Q, et al., 2018. Evaluation of cadmium transfer from soil to leafy vegetables: Influencing factors, transfer models, and indication of soil threshold contents[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 164: 355-362.
DOI URL |
| [20] | 蔡轩, 龙新宪, 种云霄, 等, 2015. 无机-有机混合改良剂对酸性重金属复合污染土壤的修复效应[J]. 环境科学学报, 35(12): 3991-4002. |
| CAI X, LONG X X, CHONG Y X, et al., 2015. Inorganic-organic amendments for immobilization of metal contaminants in an acidic soil[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 35(12): 3991-4002. | |
| [21] | 杜应琼, 廖新荣, 黄志尧, 等, 2000. pH和质地对土壤供硼影响的研究[J]. 土壤与环境, 9(2): 125-128. |
| DU YQ, LIAO X R, HUANG Z Y, et al., 2000. Effects of soil pH and texture on soil B supply[J]. Soil and Environmental Sciences, 9(2): 125-128. | |
| [22] | 杜应琼, 疏仁宗, 王富华, 等, 2015. 镉污染土壤上偏施氮磷钾肥对蕹菜产量及镉积累的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 24(3): 511-516. |
| DU Y Q, SU R Z, WANG F H, et al., 2015. Effects of partial NPK fertilizer application on the yield and Cd accumulation of water spinach in Cd contaminated soil[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 24(3): 511-516. | |
| [23] | 黄永东, 杜应琼, 陈永坚, 等, 2018. 农业废弃物生物炭理化性质的差异及对菜心产量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 27(2): 356-363. |
| HUANG Y D, DU Y Q, CHEN Y J, et al., 2018. Physicochemical properties of biochars originated from different agricultural wastes and their impact on the yield of Brassica campestris L.[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 27(2): 356-363. | |
| [24] | 黄赛花, 刘通, 黄友良, 等, 2021. 蚯蚓粪复配硼钼调理剂对土壤改良和茄子生长的影响作用[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(3): 523-531. |
| HUANG S H, LIU T, HUANG Y L, et al., 2021. Effects of molybdenumand boron-enriched earthworm cast As a soil conditioner on soil improvement and eggplant growth[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(3): 523-531. | |
| [25] | 黎秋君, 黎大荣, 王英辉, 等, 2013. 3种有机物料对土壤理化性质和重金属有效态的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 27(6): 182-185. |
| LI QJ, LI D R, WANG Y H, et al., 2013. Effects of three kinds of organic materials on physicochemical properties and available heavy metals in soil[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 27(6): 182-185. | |
| [26] | 李苹, 付弘婷, 张发宝, 等, 2015. 蚕沙有机肥对作物产量、品质及土壤性质的影响[J]. 南方农业学报, 46(7): 1195-1199. |
| LI P, FU H T, ZHANG F B, et al., 2015. Effects of silkworm excrement-derived organic fertilizer on yield and quality of crops and soil property[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 46(7): 1195-1199. | |
| [27] | 刘登彪, 蒋成爱, 张嘉慧, 等, 2014. 不同硼浓度对三种超富集植物吸收硼及重金属的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 33(6): 1106-1111. |
| LIU D B, JIANG C A, ZHANG J H, et al., 2014. Effects of Boron concentrations on uptake of boron and heavy metals by three hyperaccumulators[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 33(6): 1106-1111. | |
| [28] | 刘顺翱, 胡钧铭, 吴昊, 等, 2021. 蚕沙与海泡石联合施用对水稻根际土壤Cd生物有效性及籽粒Cd富集的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 40(8): 1686-1695. |
| LIU S X, HU J M, WU H, et al., 2021. Effects of the combined application of silkworm excrement and sepiolite on Cd bioavailability in rhizosphere soil and Cd accumulation in grains of rice[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 40(8): 1686-1695. | |
| [29] | 刘宇庆, 刘燕, 范红梅, 2009. 硼对植物细胞的影响及与其它元素关系的研究进展[J]. 中国土壤与肥料 (5): 1-4, 9. |
| LIU YQ, LIU Y, FAN H M, 2009. Review of boron and plant cells and its relationship with other elements[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China (5): 1-4, 9. | |
| [30] | 罗开萍, 黄艳玲, 秦豪, 等, 2020. 蚕沙钝化材料对矿区周边农田土壤镉锌污染的钝化效果研究[J]. 轻工科技, 36(11): 62-63, 90. |
| LUO K P, HUANG Y L, QIN H, et al., 2020. Study on the passivation effect of silkworm excrement passivation material on cadmium and zinc pollution of farmland soil around mining area[J]. Guangxi Journal of Light Industry, 36(11): 62-63, 90. | |
| [31] | 王运华, 徐芳森, 鲁剑巍, 2015. 中国农业中的硼[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社. |
| WANG Y H, XU F S, LU J W, 2015. Boron in Chinese agriculture[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Publishing House. | |
| [32] | 魏益华, 邱素艳, 张金艳, 等, 2019. 农业废弃物中重金属含量特征及农用风险评估[J]. 农业工程学报, 35(14): 212-220. |
| WEI Y H, QIU S Y, ZHANG J Y, et al., 2019. Characteristic of heavy metal contents in agricultural wastes and agricultural risk assessment[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 35(14): 212-220. | |
| [33] | 肖艳辉, 何金明, 潘春香, 等, 2015. 茴香对镉胁迫下钼硼锌协同处理的响应及精油组分的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 24(9): 1570-1575. |
| XIAO Y H, HE J M, PAN C X, et al., 2015. Effects of Molybdenum, Boron and Zinc Coordination Treatment on Response and Essential Oil Components of Fennel Plant under Cadmium Stress[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 24(9): 1570-1575. | |
| [34] | 肖艳辉, 李应文, 邹碧, 等, 2021. 钝化剂抑制南方污染农田籽粒苋吸收重金属的效应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(4): 825-833. |
| XIAO Y H, LI Y W, ZHOU B, et al., 2021. Reduction of heavy metal uptake by amaranth by 3 soil amendments in contaminated farmland of South China[J]. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 30(4): 825-833. | |
| [35] | 徐蒙蒙, 涂春艳, 黄河, 等, 2018. 淹水条件下蚕沙复配材料对酸性水稻土中镉铅钝化的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 12(4): 1182-1189. |
| XU M M, TU C Y, HUANG H, et al., 2018. Effect of silkworm excrement composites on passivation of cadmium and lead in acid paddy soil under flooded condition[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 12(4): 1182-1189. | |
| [36] | 严静娜, 覃霞, 梁定国, 等, 2015. 同热解温度蚕沙生物质炭对土壤镉、铅钝化效果研究[J]. 西南农业学报, 28(4): 1752-1756. |
| YAN J N, QIN X, LIANG D G, et al., 2015. Immobilization of cadmium and lead in contaminated soils by using biochars prepared with silkworm at different temperatures[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 28(4): 1752-1756. | |
| [37] | 张贺, 杨静, 周吉祥, 等, 2021. 连续施用土壤改良剂对砂质潮土团聚体及作物产量的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 27(5): 791-801. |
| ZHANG H, YANG J, ZHOU J X, et al., 2021. Effects of organic and inorganic amendments on aggregation and crop yields in sandy fluvo-aquic soil[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 27(5): 791-801. |
| [1] | DU Dandan, GAO Ruizhong, FANG Lijing, XIE Longmei. Spatial Variation of Soil Heavy Metals and Their Responses to Physicochemical Factors of Salt Lake Basin in Arid Area [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1123-1132. |
| [2] | LI Chuanfu, ZHU Taochuan, MING Yufei, YANG Yuxuan, GAO Shu, DONG Zhi, LI Yongqiang, JIAO Shuying. Effect of Organic Fertilizer and Desulphurized Gypsum on Soil Aggregates and Organic Carbon and Its Fractions Contents in the Saline-alkali Soil of the Yellow River Delta [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 878-888. |
| [3] | FENG Shuna, LÜ Jialong, HE Hailong. Effect of KI Leaching on the Hg (Ⅱ) Removal of Loess Soil and the Physicochemical Properties of the Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 776-783. |
| [4] | CHEN Minyi, ZHU Hanghai, SHE Weiduo, YIN Guangcai, HUANG Zuzhao, YANG Qiaoling. Health Risk Assessment and Source Apportionment of Soil Heavy Metals at A Legacy Shipyard Site in Pearl River Delta [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 794-804. |
| [5] | XIAO Jieyun, ZHOU Wei, SHI Peiqi. Hyperspectral Inversion of Soil Heavy Metals [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(1): 175-182. |
| [6] | HAUNG Hong, ZHENG Xinyun, LI Yingdong, ZHAO Xu, YU Jinchen, WANG Zhenhua. A study on Enrichment of Heavy Metals in Sebastiscus marmoratus at Different Ages in Dachen Islands Sea Area [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(9): 1885-1891. |
| [7] | MA Chuang, WANG Yuyang, ZHOU Tong, WU Longhua. Enrichment Characteristics and Desorption Behavior of Cadmium and Zinc in Particulate Organic Matter of Polluted Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(9): 1892-1900. |
| [8] | TAO Ling, HUANG Lei, ZHOU Yilei, LI Zhongxing, REN Jun. Influences of Biochar Prepared by Co-pyrolysis with Sludge and Attapulgite on Bioavailability and Environmental Risk of Heavy Metals in Mining Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(8): 1637-1646. |
| [9] | LI Ying, ZHANG Zhou, YANG Gaoming, ZU Yanqun, LI Bo, CHEN Jianjun. The Relationship between the Radial Oxygen Loss and the Iron Plaque on Root Surfaces to Wetland Plants Absorb Heavy Metals [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(8): 1657-1666. |
| [10] | LUO Songying, LI Qiuxia, QIU Jinkun, DENG Suyan, LI Yifeng, CHEN Bishan. Speciation Characteristics, Migration and Transformation of Heavy Metals in Mangrove Soil-plant System in Nansan Island [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(7): 1409-1416. |
| [11] | DONG Leheng, WANG Xugang, CHEN Manjia, WANG Zihao, SUN Lirong, SHI Zhaoyong, Wu Qiqi. Interaction of Iron Redox and Cu Activities in Calcareous Paddy Soil under Light and Dark Condition [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(7): 1448-1455. |
| [12] | PENG Hongli, TAN Haixia, WANG Ying, WEI Jianmei, FENG Yang. The Discrepancy of Heavy Metals Morphological Distribution in Soil and Its Associated Ecological Risk Evaluation under Different Planting Patterns [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(6): 1235-1243. |
| [13] | HUANG Min, ZHAO Xiaofeng, LIANG Rongxiang, WANG Pengzhong, DAI Anran, HE Xiaoman. Comparison of Three Chelating Agents to Remove the Cd and Cu in Contaminated Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(6): 1244-1252. |
| [14] | ZHU Li'an, ZHANG Huihua, CHENG Jiong, LI Ting, LIN ZI, LI Junjie. Potential Ecological Risk Pattern Analysis of Heavy Metals in Soil of Forestry Land in The Pearl River Delta [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(6): 1253-1262. |
| [15] | SHI Jianfei, JIN Zhengzhong, ZHOU Zhibin, WANG Xin. Evaluation of Heavy Metal Pollution in the Soil Around A Typical Tailing Reservoir in Irtysh River Basin [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(5): 1015-1023. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
