Ecology and Environment ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (7): 1313-1324.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.07.014
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Zhenguo( ), HAO Xingyu, HE Tianlian, JING Rui, RONG Cheng, GU Chengzhen, ZHENG Xinyu*(
), HAO Xingyu, HE Tianlian, JING Rui, RONG Cheng, GU Chengzhen, ZHENG Xinyu*( )
)
Received:2023-04-06
Online:2023-07-18
Published:2023-09-27
Contact:
ZHENG Xinyu
李振国( ), 郝星雨, 贺甜莲, 景蕊, 荣成, 顾承真, 郑新宇*(
), 郝星雨, 贺甜莲, 景蕊, 荣成, 顾承真, 郑新宇*( )
)
通讯作者:
郑新宇
作者简介:李振国(1998年生),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为植物生态学。E-mail: 2446273211@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
LI Zhenguo, HAO Xingyu, HE Tianlian, JING Rui, RONG Cheng, GU Chengzhen, ZHENG Xinyu. Study on the Alleviating Effect of Bamboo Vinegar on Cadmium Toxicity of Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt.[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(7): 1313-1324.
李振国, 郝星雨, 贺甜莲, 景蕊, 荣成, 顾承真, 郑新宇. 竹醋液对紫苏镉毒的缓解效应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1313-1324.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.07.014
| 类别 | 序号 | 有机物名称 | 相对含量/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 酚类 | 1 | 苯酚 | 12.355 |
| 2 | 愈创木酚 | 7.817 | |
| 3 | 对甲酚 | 5.758 | |
| 4 | 4-乙基苯酚 | 4.880 | |
| 5 | 2-甲基苯酚 | 4.049 | |
| 6 | 2, 4-二甲基苯酚 | 1.609 | |
| 7 | 麦芽酚 | 1.066 | |
| 8 | 2, 6-二甲氧基苯酚 | 3.361 | |
| 9 | 4-乙基-2-甲氧基苯酚 | 1.660 | |
| 小计 | 42.554 | ||
| 酯类 | 10 | 乙酸甲酯 | 9.553 |
| 11 | 4-羟基丁酸乙酰酯 | 2.008 | |
| 12 | 丙酸甲酯 | 0.733 | |
| 小计 | 12.293 | ||
| 酸类 | 13 | 丙酸 | 6.659 |
| 14 | 丁酸 | 2.526 | |
| 15 | 乙酸 | 0.898 | |
| 小计 | 10.083 | ||
| 酮类 | 16 | 2-环戊烯酮 | 1.934 |
| 17 | 甲基环戊烯醇酮 | 1.492 | |
| 18 | 甲基环戊烯醇酮 | 1.388 | |
| 19 | 2, 3-二甲基-2-环戊烯酮 | 1.188 | |
| 20 | 3-甲基-2-环戊烯-1-酮 | 1.115 | |
| 21 | 1-羟基-2-丁酮 | 1.078 | |
| 22 | 环戊酮 | 0.699 | |
| 23 | 2, 5-二氢-3, 5-二甲基呋喃酮 | 0.682 | |
| 小计 | 9.576 | ||
| 醛类 | 24 | 3-糠醛 | 6.791 |
| 25 | 5-甲基呋喃醛 | 0.822 | |
| 小计 | 7.613 | ||
| 醇类 | 26 | 丝氨醇 | 0.830 |
| 27 | 1, 3-二氧杂烷-2-甲醇 | 0.709 | |
| 小计 | 1.539 | ||
| 其它 | 28 | 2-呋喃甲酰乙腈 | 3.340 |
| 29 | 丁酸酐 | 2.953 | |
| 30 | 3-羟基-4-甲氧基甲苯 | 2.822 | |
| 31 | 丙酸酐 | 2.129 | |
| 32 | 2-乙酰基呋喃 | 2.104 | |
| 33 | 异丁酸酐 | 2.061 | |
| 34 | 吡啶 | 0.934 | |
| 小计 | 16.342 |
Table 1 Composition and relative content of organic matter in bamboo vinegar
| 类别 | 序号 | 有机物名称 | 相对含量/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 酚类 | 1 | 苯酚 | 12.355 |
| 2 | 愈创木酚 | 7.817 | |
| 3 | 对甲酚 | 5.758 | |
| 4 | 4-乙基苯酚 | 4.880 | |
| 5 | 2-甲基苯酚 | 4.049 | |
| 6 | 2, 4-二甲基苯酚 | 1.609 | |
| 7 | 麦芽酚 | 1.066 | |
| 8 | 2, 6-二甲氧基苯酚 | 3.361 | |
| 9 | 4-乙基-2-甲氧基苯酚 | 1.660 | |
| 小计 | 42.554 | ||
| 酯类 | 10 | 乙酸甲酯 | 9.553 |
| 11 | 4-羟基丁酸乙酰酯 | 2.008 | |
| 12 | 丙酸甲酯 | 0.733 | |
| 小计 | 12.293 | ||
| 酸类 | 13 | 丙酸 | 6.659 |
| 14 | 丁酸 | 2.526 | |
| 15 | 乙酸 | 0.898 | |
| 小计 | 10.083 | ||
| 酮类 | 16 | 2-环戊烯酮 | 1.934 |
| 17 | 甲基环戊烯醇酮 | 1.492 | |
| 18 | 甲基环戊烯醇酮 | 1.388 | |
| 19 | 2, 3-二甲基-2-环戊烯酮 | 1.188 | |
| 20 | 3-甲基-2-环戊烯-1-酮 | 1.115 | |
| 21 | 1-羟基-2-丁酮 | 1.078 | |
| 22 | 环戊酮 | 0.699 | |
| 23 | 2, 5-二氢-3, 5-二甲基呋喃酮 | 0.682 | |
| 小计 | 9.576 | ||
| 醛类 | 24 | 3-糠醛 | 6.791 |
| 25 | 5-甲基呋喃醛 | 0.822 | |
| 小计 | 7.613 | ||
| 醇类 | 26 | 丝氨醇 | 0.830 |
| 27 | 1, 3-二氧杂烷-2-甲醇 | 0.709 | |
| 小计 | 1.539 | ||
| 其它 | 28 | 2-呋喃甲酰乙腈 | 3.340 |
| 29 | 丁酸酐 | 2.953 | |
| 30 | 3-羟基-4-甲氧基甲苯 | 2.822 | |
| 31 | 丙酸酐 | 2.129 | |
| 32 | 2-乙酰基呋喃 | 2.104 | |
| 33 | 异丁酸酐 | 2.061 | |
| 34 | 吡啶 | 0.934 | |
| 小计 | 16.342 |
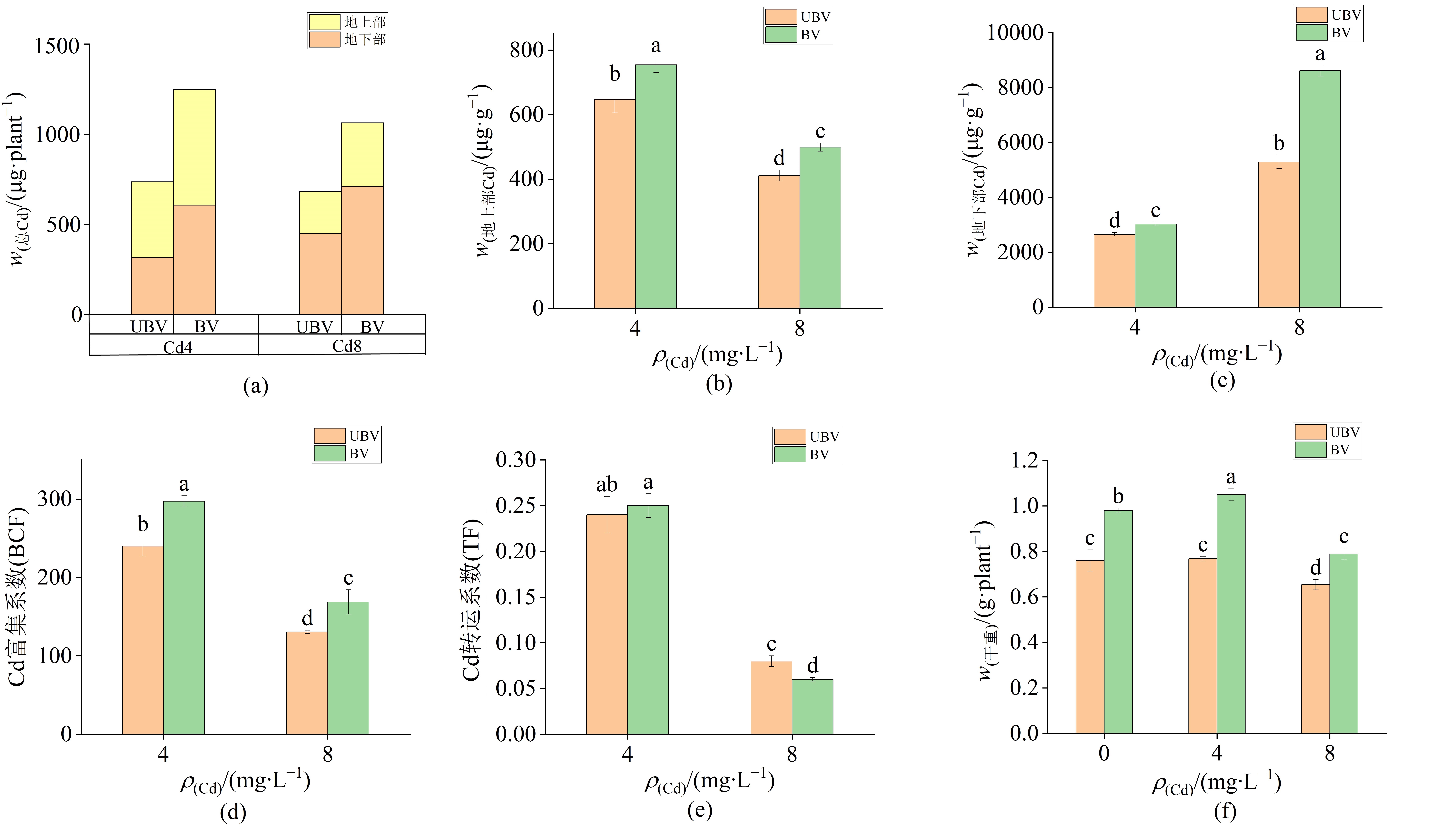
Figure 1 Effects of BV spray on total Cd enrichment (a), Cd content (b-aboveground part, c-underground part), BCF(d), TF(e) and dry weight (f) of Perilla frutescens per plant at 0, 4 mg·L-1 and 8 mg·L-1 Cd concentrations
| 处理 | w(没食子酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(原儿茶酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(绿原酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(对羟基苯甲酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(咖啡酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(丁香酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(香兰素)/(μg·g-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBVCd0 | 0.382±0.003e | 5.677±0.072e | 2.986±0.153d | 2.886±0.153d | 3.161±0.216e | 3.182±0.149e | 28.165±1.530e | ||||
| UBVCd4 | 1.139±0.090d | 6.481±0.276d | 4.346±0.056bc | 4.246±0.056bc | 6.955±0.089d | 5.903±0.272c | 42.562±1.351d | ||||
| UBVCd8 | 1.335±0.074c | 15.312±0.449a | 4.223±0.244c | 4.123±0.244c | 21.807±1.066c | 8.889±0.060a | 64.548±0.233b | ||||
| BVCd0 | 1.162±0.062d | 7.335±0.287c | 4.552±0.228b | 4.452±0.228b | 8.252±0.430d | 4.388±0.247d | 49.928±1.542c | ||||
| BVCd4 | 2.032±0.061b | 12.934±0.471b | 6.864±0.222a | 6.764±0.222a | 30.141±0.427b | 9.324±0.713a | 102.311±2.176a | ||||
| BVCd8 | 2.287±0.053a | 14.983±0.384a | 4.316±0.109bc | 4.216±0.109bc | 36.999±2.756a | 6.642±0.365b | 106.422±5.729a | ||||
| 处理 | w(对香豆酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(异绿原酸A)/(μg·g-1) | w(香豆素)/(μg·g-1) | w(苯甲酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(迷迭香酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(肉桂酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(可溶性酚酸总量)/(μg·g-1) | ||||
| UBVCd0 | 3.981±0.023d | 263.144±10.848e | 6.509±0.186e | 189.759±10.632e | 116.656±9.937d | 0.715±0.076cd | 627.204±11.565d | ||||
| UBVCd4 | 4.869±0.112c | 313.408±2.736d | 5.986±0.226e | 187.760±3.292e | 69.065±5.968e | 0.934±0.125b | 653.656±3.716d | ||||
| UBVCd8 | 5.546±0.056b | 383.415±13.20c | 11.709±0.160c | 373.038±34.147c | 131.269±5.271cd | 1.158±0.059a | 1026.372±37.713b | ||||
| BVCd0 | 4.570±0.034c | 305.021±6.124d | 9.601±0.409d | 276.238±33.507d | 188.393±13.377b | 0.692±0.077d | 864.585±55.811c | ||||
| BVCd4 | 7.590±0.093a | 507.493±2.122a | 35.527±1.393a | 510.685±32.380b | 311.672±20.646a | 0.651±0.036d | 1543.987±22.459a | ||||
| BVCd8 | 8.085±0.673a | 456.245±3.651b | 27.788±0.852b | 721.729±56.173a | 146.704±15.716c | 0.899±0.183bc | 1537.315±58.656a | ||||
Table 2 Effects of BV spray on soluble phenolic acid content in Perilla frutescens leaves treated with 0, 4 mg·L-1 and 8 mg·L-1 Cd
| 处理 | w(没食子酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(原儿茶酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(绿原酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(对羟基苯甲酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(咖啡酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(丁香酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(香兰素)/(μg·g-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBVCd0 | 0.382±0.003e | 5.677±0.072e | 2.986±0.153d | 2.886±0.153d | 3.161±0.216e | 3.182±0.149e | 28.165±1.530e | ||||
| UBVCd4 | 1.139±0.090d | 6.481±0.276d | 4.346±0.056bc | 4.246±0.056bc | 6.955±0.089d | 5.903±0.272c | 42.562±1.351d | ||||
| UBVCd8 | 1.335±0.074c | 15.312±0.449a | 4.223±0.244c | 4.123±0.244c | 21.807±1.066c | 8.889±0.060a | 64.548±0.233b | ||||
| BVCd0 | 1.162±0.062d | 7.335±0.287c | 4.552±0.228b | 4.452±0.228b | 8.252±0.430d | 4.388±0.247d | 49.928±1.542c | ||||
| BVCd4 | 2.032±0.061b | 12.934±0.471b | 6.864±0.222a | 6.764±0.222a | 30.141±0.427b | 9.324±0.713a | 102.311±2.176a | ||||
| BVCd8 | 2.287±0.053a | 14.983±0.384a | 4.316±0.109bc | 4.216±0.109bc | 36.999±2.756a | 6.642±0.365b | 106.422±5.729a | ||||
| 处理 | w(对香豆酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(异绿原酸A)/(μg·g-1) | w(香豆素)/(μg·g-1) | w(苯甲酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(迷迭香酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(肉桂酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(可溶性酚酸总量)/(μg·g-1) | ||||
| UBVCd0 | 3.981±0.023d | 263.144±10.848e | 6.509±0.186e | 189.759±10.632e | 116.656±9.937d | 0.715±0.076cd | 627.204±11.565d | ||||
| UBVCd4 | 4.869±0.112c | 313.408±2.736d | 5.986±0.226e | 187.760±3.292e | 69.065±5.968e | 0.934±0.125b | 653.656±3.716d | ||||
| UBVCd8 | 5.546±0.056b | 383.415±13.20c | 11.709±0.160c | 373.038±34.147c | 131.269±5.271cd | 1.158±0.059a | 1026.372±37.713b | ||||
| BVCd0 | 4.570±0.034c | 305.021±6.124d | 9.601±0.409d | 276.238±33.507d | 188.393±13.377b | 0.692±0.077d | 864.585±55.811c | ||||
| BVCd4 | 7.590±0.093a | 507.493±2.122a | 35.527±1.393a | 510.685±32.380b | 311.672±20.646a | 0.651±0.036d | 1543.987±22.459a | ||||
| BVCd8 | 8.085±0.673a | 456.245±3.651b | 27.788±0.852b | 721.729±56.173a | 146.704±15.716c | 0.899±0.183bc | 1537.315±58.656a | ||||
| 处理 | w(原儿茶酸)/ (μg·g-1) | w(绿原酸)/ (μg·g-1) | w(对羟基苯甲酸)/ (μg·g-1) | w(咖啡酸)/ (μg·g-1) | w(丁香酸)/ (μg·g-1) | w(异绿原酸A)/ (μg·g-1) | w(香豆素)/ (μg·g-1) | w(苯甲酸)/ (μg·g-1) | w(可溶性酚酸总量)/ (μg·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBVCd0 | 1.298±0.106d | 8.838±0.382bc | 2.638±0.890d | 8.397±0.090c | 1.832±0.043c | 3.070±0.132cd | 1.550±0.044c | 35.280±2.434de | 62.905±2.326de |
| UBVCd4 | 1.617±0.063c | 7.201±0.541c | 3.635±0.196c | 8.222±0.397c | 2.801±0.197b | 3.616±0.189c | 1.375±0.187c | 48.347±3.909cd | 76.814±5.244d |
| UBVCd8 | 2.170±0.082b | 8.804±0.383c | 3.813±0.467c | 7.701±0.044cd | 4.004±0.079a | 10.122±0.94a | 1.915±0.226b | 87.692±2.777b | 126.221±3.034b |
| BVCd0 | 1.124±0.012d | 8.708±0.044c | 3.167±0.147cd | 6.943±0.281d | 1.497±0.052d | 2.747±0.077d | 0.999±0.018d | 32.941±1.231e | 58.127±1.392e |
| BVCd4 | 2.481±0.156a | 11.000±0.564b | 4.989±0.169b | 15.078±0.098b | 2.587±0.150b | 4.866±0.191b | 2.294±0.160a | 57.956±11.319c | 101.250±11.836c |
| BVCd8 | 2.588±0.145a | 16.310±2.822a | 8.356±0.552a | 19.640±1.081a | 2.741±0.289b | 10.120±0.531a | 1.528±0.132c | 161.020±15.377a | 222.304±18.065a |
Table 3 Effects of BV spray on soluble phenolic acid content in Perilla frutescens root treated with 0, 4 mg·L-1and 8 mg·L-1
| 处理 | w(原儿茶酸)/ (μg·g-1) | w(绿原酸)/ (μg·g-1) | w(对羟基苯甲酸)/ (μg·g-1) | w(咖啡酸)/ (μg·g-1) | w(丁香酸)/ (μg·g-1) | w(异绿原酸A)/ (μg·g-1) | w(香豆素)/ (μg·g-1) | w(苯甲酸)/ (μg·g-1) | w(可溶性酚酸总量)/ (μg·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBVCd0 | 1.298±0.106d | 8.838±0.382bc | 2.638±0.890d | 8.397±0.090c | 1.832±0.043c | 3.070±0.132cd | 1.550±0.044c | 35.280±2.434de | 62.905±2.326de |
| UBVCd4 | 1.617±0.063c | 7.201±0.541c | 3.635±0.196c | 8.222±0.397c | 2.801±0.197b | 3.616±0.189c | 1.375±0.187c | 48.347±3.909cd | 76.814±5.244d |
| UBVCd8 | 2.170±0.082b | 8.804±0.383c | 3.813±0.467c | 7.701±0.044cd | 4.004±0.079a | 10.122±0.94a | 1.915±0.226b | 87.692±2.777b | 126.221±3.034b |
| BVCd0 | 1.124±0.012d | 8.708±0.044c | 3.167±0.147cd | 6.943±0.281d | 1.497±0.052d | 2.747±0.077d | 0.999±0.018d | 32.941±1.231e | 58.127±1.392e |
| BVCd4 | 2.481±0.156a | 11.000±0.564b | 4.989±0.169b | 15.078±0.098b | 2.587±0.150b | 4.866±0.191b | 2.294±0.160a | 57.956±11.319c | 101.250±11.836c |
| BVCd8 | 2.588±0.145a | 16.310±2.822a | 8.356±0.552a | 19.640±1.081a | 2.741±0.289b | 10.120±0.531a | 1.528±0.132c | 161.020±15.377a | 222.304±18.065a |
| 处理 | w(没食子酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(原儿茶酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(绿原酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(对羟基苯甲酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(咖啡酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(丁香酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(香兰素)/(μg·g-1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBVCd0 | 9.003±0.120e | 6.553±0.594c | 40.243±3.678d | 17.673±1.119c | 70.49±5.606d | 4.553±1.070c | 1.617±0.369c | ||||||
| UBVCd4 | 14.889±1.406c | 6.650±1.139c | 58.672±5.292c | 25.354±2.544ab | 108.304±9.917c | 9.740±0.418b | 1.841±0.580bc | ||||||
| UBVCd8 | 25.129±1.036a | 21.782±0.384a | 79.683±2.735b | 23.987±2.876ab | 232.859±9.919a | 14.326±1.363a | 3.244±0.178a | ||||||
| BVCd0 | 12.037±1.65ed | 7.995±1.194c | 72.711±12.36bc | 26.130±3.010ab | 97.994±7.402c | 15.198±1.881a | 2.765±0.440ab | ||||||
| BVCd4 | 15.279±1.103c | 15.064±2.179b | 71.719±11.071bc | 27.222±3.409a | 184.715±9.089b | 10.817±1.712b | 3.449±0.908a | ||||||
| BVCd8 | 19.362±1.782b | 19.96±1.748a | 96.241±12.735a | 20.473±5.517bc | 238.688±13.239a | 9.218±1.851b | 2.989±0.490a | ||||||
| 处理 | w(对香豆酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(阿魏酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(异绿原酸A)/(μg·g-1) | w(苯甲酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(肉桂酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(结合态酚酸总量)/(μg·g-1) | |||||||
| UBVCd0 | 102.688±8.512b | 29.736±2.366c | 8.534±1.105c | 12.415±1.064e | 0.462±0.029a | 303.967±18.260d | |||||||
| UBVCd4 | 128.925±5.770a | 38.532±4.058ab | 12.953±1.367ab | 20.458±6.179d | 0.430±0.012a | 426.749±27.125c | |||||||
| UBVCd8 | 128.984±5.305a | 40.642±3.690a | 12.131±1.838bc | 47.992±2.369a | 0.472±0.009a | 631.232±6.895a | |||||||
| BVCd0 | 100.916±6.369b | 34.231±4.161abc | 16.349±1.889a | 23.801±2.414d | 0.448±0.059a | 410.574±21.036c | |||||||
| BVCd4 | 136.678±7.821a | 33.420±4.389bc | 15.354±3.112ab | 33.071±5.194c | 0.497±0.072a | 547.285±29.026b | |||||||
| BVCd8 | 136.867±5.834a | 35.282±3.925abc | 11.858±2.500bc | 41.406±1.942b | 0.501±0.023a | 632.852±11.174a | |||||||
Table 4 Effects of BV spray on the content of bound phenolic acid in Perilla frutescens leaves treated with 0, 4 mg·L-1 and 8 mg·L-1 Cd
| 处理 | w(没食子酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(原儿茶酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(绿原酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(对羟基苯甲酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(咖啡酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(丁香酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(香兰素)/(μg·g-1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBVCd0 | 9.003±0.120e | 6.553±0.594c | 40.243±3.678d | 17.673±1.119c | 70.49±5.606d | 4.553±1.070c | 1.617±0.369c | ||||||
| UBVCd4 | 14.889±1.406c | 6.650±1.139c | 58.672±5.292c | 25.354±2.544ab | 108.304±9.917c | 9.740±0.418b | 1.841±0.580bc | ||||||
| UBVCd8 | 25.129±1.036a | 21.782±0.384a | 79.683±2.735b | 23.987±2.876ab | 232.859±9.919a | 14.326±1.363a | 3.244±0.178a | ||||||
| BVCd0 | 12.037±1.65ed | 7.995±1.194c | 72.711±12.36bc | 26.130±3.010ab | 97.994±7.402c | 15.198±1.881a | 2.765±0.440ab | ||||||
| BVCd4 | 15.279±1.103c | 15.064±2.179b | 71.719±11.071bc | 27.222±3.409a | 184.715±9.089b | 10.817±1.712b | 3.449±0.908a | ||||||
| BVCd8 | 19.362±1.782b | 19.96±1.748a | 96.241±12.735a | 20.473±5.517bc | 238.688±13.239a | 9.218±1.851b | 2.989±0.490a | ||||||
| 处理 | w(对香豆酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(阿魏酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(异绿原酸A)/(μg·g-1) | w(苯甲酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(肉桂酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(结合态酚酸总量)/(μg·g-1) | |||||||
| UBVCd0 | 102.688±8.512b | 29.736±2.366c | 8.534±1.105c | 12.415±1.064e | 0.462±0.029a | 303.967±18.260d | |||||||
| UBVCd4 | 128.925±5.770a | 38.532±4.058ab | 12.953±1.367ab | 20.458±6.179d | 0.430±0.012a | 426.749±27.125c | |||||||
| UBVCd8 | 128.984±5.305a | 40.642±3.690a | 12.131±1.838bc | 47.992±2.369a | 0.472±0.009a | 631.232±6.895a | |||||||
| BVCd0 | 100.916±6.369b | 34.231±4.161abc | 16.349±1.889a | 23.801±2.414d | 0.448±0.059a | 410.574±21.036c | |||||||
| BVCd4 | 136.678±7.821a | 33.420±4.389bc | 15.354±3.112ab | 33.071±5.194c | 0.497±0.072a | 547.285±29.026b | |||||||
| BVCd8 | 136.867±5.834a | 35.282±3.925abc | 11.858±2.500bc | 41.406±1.942b | 0.501±0.023a | 632.852±11.174a | |||||||
| 处理 | w(没食子酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(原儿茶酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(绿原酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(对羟基苯甲酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(咖啡酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(丁香酸)/(μg·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBVCd0 | 17.250±0.929c | 5.803±0.225cd | 81.084±2.491d | 20.161±1.743b | 99.211±5.046d | 43.651±1.774b |
| UBVCd4 | 21.336±0.301b | 6.244±1.386c | 85.943±4.110d | 22.302±2.821b | 87.819±1.000e | 54.415±1.888a |
| UBVCd8 | 24.277±0.708a | 7.858±1.615c | 112.827±5.593b | 23.935±0.397b | 114.76±6.562c | 45.310±2.816b |
| BVCd0 | 10.884±1.263d | 3.642±0.119d | 49.619±4.044e | 15.324±1.765c | 31.780±1.050f | 6.837±0.482c |
| BVCd4 | 20.553±1.631b | 11.849±1.683b | 100.625±3.652c | 28.541±0.621a | 130.723±5.51b | 41.544±6.112b |
| BVCd8 | 21.328±0.314b | 14.855±1.433a | 125.270±5.268a | 28.738±4.003a | 175.552±3.89a | 11.794±0.619c |
| 处理 | w(香兰素)/(μg·g-1) | w(阿魏酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(对香豆酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(香豆素)/(μg·g-1) | w(苯甲酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(结合态酚酸总量)/(μg·g-1) |
| UBVCd0 | 0.884±0.256c | 12.773±0.892c | 18.703±2.131a | 1.055±0.010bc | 13.013±1.362a | 313.589±6.187c |
| UBVCd4 | 1.414±0.244b | 7.511±0.571d | 11.826±2.452bc | 1.067±0.106bc | 6.640±0.559c | 306.518±11.417c |
| UBVCd8 | 1.641±0.090b | 13.555±0.968c | 11.426±2.988c | 1.005±0.033c | 6.358±0.082c | 362.953±10.921b |
| BVCd0 | 0.631±0.138c | 4.233±0.161e | 10.041±0.749c | 0.549±0.002d | 10.951±0.161b | 144.491±1.959d |
| BVCd4 | 1.479±0.154b | 16.831±0.966b | 12.252±2.288bc | 1.130±0.025b | 6.989±0.720c | 372.517±7.308b |
| BVCd8 | 2.257±0.193a | 19.824±1.303a | 15.445±1.206ab | 1.739±0.084a | 6.119±0.720c | 422.922±3.679a |
Table 5 Effects of BV spray on the content of binding phenolic acid in Perilla frutescens root treated with 0, 4 mg·L-1 and 8 mg·L-1 Cd
| 处理 | w(没食子酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(原儿茶酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(绿原酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(对羟基苯甲酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(咖啡酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(丁香酸)/(μg·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBVCd0 | 17.250±0.929c | 5.803±0.225cd | 81.084±2.491d | 20.161±1.743b | 99.211±5.046d | 43.651±1.774b |
| UBVCd4 | 21.336±0.301b | 6.244±1.386c | 85.943±4.110d | 22.302±2.821b | 87.819±1.000e | 54.415±1.888a |
| UBVCd8 | 24.277±0.708a | 7.858±1.615c | 112.827±5.593b | 23.935±0.397b | 114.76±6.562c | 45.310±2.816b |
| BVCd0 | 10.884±1.263d | 3.642±0.119d | 49.619±4.044e | 15.324±1.765c | 31.780±1.050f | 6.837±0.482c |
| BVCd4 | 20.553±1.631b | 11.849±1.683b | 100.625±3.652c | 28.541±0.621a | 130.723±5.51b | 41.544±6.112b |
| BVCd8 | 21.328±0.314b | 14.855±1.433a | 125.270±5.268a | 28.738±4.003a | 175.552±3.89a | 11.794±0.619c |
| 处理 | w(香兰素)/(μg·g-1) | w(阿魏酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(对香豆酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(香豆素)/(μg·g-1) | w(苯甲酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(结合态酚酸总量)/(μg·g-1) |
| UBVCd0 | 0.884±0.256c | 12.773±0.892c | 18.703±2.131a | 1.055±0.010bc | 13.013±1.362a | 313.589±6.187c |
| UBVCd4 | 1.414±0.244b | 7.511±0.571d | 11.826±2.452bc | 1.067±0.106bc | 6.640±0.559c | 306.518±11.417c |
| UBVCd8 | 1.641±0.090b | 13.555±0.968c | 11.426±2.988c | 1.005±0.033c | 6.358±0.082c | 362.953±10.921b |
| BVCd0 | 0.631±0.138c | 4.233±0.161e | 10.041±0.749c | 0.549±0.002d | 10.951±0.161b | 144.491±1.959d |
| BVCd4 | 1.479±0.154b | 16.831±0.966b | 12.252±2.288bc | 1.130±0.025b | 6.989±0.720c | 372.517±7.308b |
| BVCd8 | 2.257±0.193a | 19.824±1.303a | 15.445±1.206ab | 1.739±0.084a | 6.119±0.720c | 422.922±3.679a |

Figure 4 Effects of BV spray on PDD activity (a), CAT activity (b), SOD activity (c), APX activity (d) and MDA content (e) in Perilla frutescens leaves treated with 0, 4 mg·L-1 and 8 mg·L-1 Cd concentrations

Figure 5 Effects of BV spray on PDD activity (a), CAT activity (b), SOD activity (c), APX activity (d) and MDA content (e) in Perilla frutescens root treated with 0, 4 mg·L-1 and 8 mg·L-1 Cd concentrations
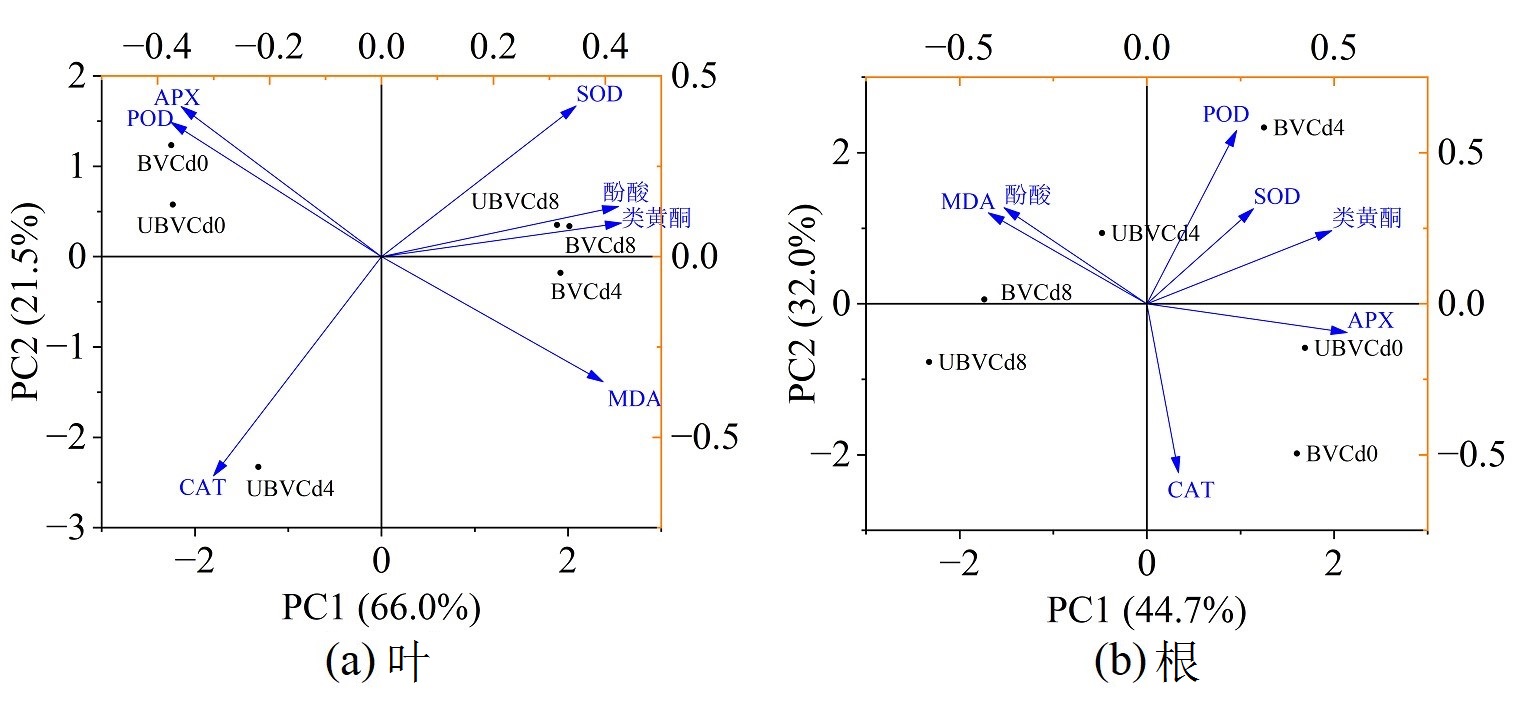
Figure 6 Principal component analysis (PCA) scores of enzymatic and non-enzymatic systems of Perilla frutescens at 0, 4 mg·L-1 and 8 mg·L-1 Cd concentrations treated with BV

Figure 7 Pearson correlation coefficient was used to determine the relationship between heavy metals and phenolic acids and flavonoids contents in Perilla frutescens roots and leaves
| [1] |
BHAT S A, BASHIR O, UL HAQ S A, et al., 2022. Phytoremediation of heavy metals in soil and water: An eco-friendly, sustainable and multidisciplinary approach[J]. Chemosphere, 303(Part 1): 134788.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
CHEN S, LIN R Y, LU H L, et al., 2020. Effects of phenolic acids on free radical scavenging and heavy metal bioavailability in kandelia obovata under cadmium and zinc stress[J]. Chemosphere, 249: 126341.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
CHOUDHURY F K, RIVERO R M, BLUMWALD E, et al., 2017. Reactive oxygen species, abiotic stress and stress combination[J]. The Plant Journal, 90(5): 856-867.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
DAS P, SAMANTARAY S, ROUT G R, 1997. Studies on cadmium toxicity in plants: A review[J]. Environmental Pollution, 98(1): 29-36.
DOI PMID |
| [5] |
DE ASCENSAO A R, DUBERY I A, 2003. Soluble and wall-bound phenolics and phenolic polymers in Musa acuminata roots exposed to elicitors from Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense[J]. Phytochemistry, 63(6): 679-686.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
DOU H J, NIU G H, GU M M, et al., 2018. Responses of sweet basil to different daily light integrals in photosynthesis, morphology, yield, and nutritional quality[J]. HortScience, 53(4): 496-503.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
FERRER J L, AUSTIN M B, STEWART C J R., et al., 2008. Structure and function of enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of phenylpropanoids[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 46(3): 356-370.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
GE J, TIAN S K, YU H Y, et al., 2021. Exogenous application of Mn significantly increased Cd accumulation in the Cd/Zn hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii[J]. Environmental Pollution, 278: 116837.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
HAGNER M, RÄTY M, NIKAMA J, et al., 2021. Slow pyrolysis liquid in reducing NH3 emissions from cattle slurry-Impacts on plant growth and soil organisms[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 784: 147139.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
HAN R, DAI H P, SKUZA L, et al., 2021. Comparative study on different organic acids for promoting Solanum nigrum L. hyperaccumulation of Cd and Pb from the contaminated soil[J]. Chemosphere, 278: 130446.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
IRTELLI B, NAVARI-IZZO F, 2006. Influence of sodium nitrilotriacetate (NTA) and citric acid on phenolic and organic acids in Brassica juncea grown in excess of cadmium[J]. Chemosphere, 65(8): 1348-1354.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
KANG Y C, LIU J X, YANG L, et al., 2022. Foliar application of flavonoids (rutin) regulates phytoremediation efficiency of Amaranthus hypochondriacus L. by altering the permeability of cell membranes and immobilizing excess Cd in the cell wall[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 425: 127875.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
KOVÁCIK J, KLEJDUS B, 2008. Dynamics of phenolic acids and lignin accumulation in metal-treated Matricaria chamomilla roots[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 27(3): 605-615.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
KÜPPER H, MIJOVILOVICH A, MEYER-KLAUCKE W, et al., 2004. Tissue- and age-dependent differences in the complexation of cadmium and zinc in the cadmium/zinc hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens (Ganges ecotype) revealed by x-ray absorption spectroscopy[J]. Plant Physiology, 134(2): 748-757.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
LASHARI M S, LIU Y M, LI L Q, et al., 2013. Effects of amendment of biochar-manure compost in conjunction with pyroligneous solution on soil quality and wheat yield of a salt-stressed cropland from Central China Great Plain[J]. Field Crops Research, 144: 113-118.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
LIU X Y, MAO Y, ZHANG X, et al., 2019. Effects of PASP/NTA and TS on the phytoremediation of pyrene-nickel contaminated soil by Bidens pilosa L[J]. Chemosphere, 237: 124502.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
LÜ Q X, XIAO Q T, GUO Y R, et al., 2022. Pollution monitoring, risk assessment and target remediation of heavy metals in rice from a five-year investigation in western Fujian region, China[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 424(2): 127551.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
MARTINEZ V, MESTRE T C, RUBIO F, et al., 2016. Accumulation of flavonols over hydroxycinnamic acids favors oxidative damage protection under abiotic stress[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 7: 838.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
NIGGEWEG R, MICHAEL A J, MARTIN C, 2004. Engineering plants with increased levels of the antioxidant chlorogenic acid[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 22(6): 746-754.
DOI PMID |
| [20] | PAN B G, MO H Q, WANG W, et al., 2021. Regulating effects of silicon on Cd-accumulation and stress-resistant responding in rice seedling[J]. The Journal of Applied Ecology, 32(3): 1096-1104. |
| [21] |
RAI P K, LEE S S, ZHANG M, et al., 2019. Heavy metals in food crops: Health risks, fate, mechanisms, and management[J]. Environment International, 125: 365-385.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
RAZAL R A, ELLIS S, SINGH S, et al., 1996. Nitrogen recycling in phenylpropanoid metabolism[J]. Phytochemistry, 41(1): 31-35.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
SAIDI I, GUESMI F, KHARBECH O, et al., 2021. Gallic acid improves the antioxidant ability against cadmium toxicity: Impact on leaf lipid composition of sunflower (Helianthus annuus) seedlings[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 210: 111906.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
SGHERRI C, COSI E, NAVARI-IZZO F, 2003. Phenols and antioxidative status of Raphanus sativus grown in copper excess[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 118(1): 21-28.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
SHARMA A, SHAHZAD B, REHMAN A, et al., 2019. Response of phenylpropanoid pathway and the role of polyphenols in plants under abiotic stress[J]. Molecules, 24(13): 2452.
DOI URL |
| [26] | SIVARAM A K, LOGESHWARAN P, ABINANDAN S, et al., 2022. Cyto-genotoxicity evaluation of pyroligneous acid using Allium cepa assay[J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Health. Part A, Toxic/hazardous Substances & Environmental Engineering vol, 57(10): 852-857. |
| [27] |
SUN H J, FENG Y F, XUE L H, et al., 2020. Responses of ammonia volatilization from rice paddy soil to application of wood vinegar alone or combined with biochar[J]. Chemosphere, 242: 125247.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
TIAN S K, LU L L, LABAVITCH J, et al., 2011. Cellular sequestration of cadmium in the hyperaccumulator plant species Sedum alfredii[J]. Plant Physiology, 157(4): 1914-1925.
DOI URL |
| [29] | VASCONCELOS M T, AZENHA M, DE FREITAS V, 1999. Role of polyphenols in copper complexation in red wines[J]. Ournal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 47(7): 2791-2796. |
| [30] |
WANG X S, FU H L, GONG F Y, et al., 2020. Lignin side chain region participates in Cd detoxification related to the cultivar-dependent Cd accumulation in Brassica chinensis L[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 392: 122264.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
WIN KT, TOYOTA, MOTOBAYASHI T, et al., 2009. Suppression of ammonia volatilization from a paddy soil fertilized with anaerobically digested cattle slurry by wood vinegar application and floodwater management (vol 55, pg 190, 2009)[J]. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 55(1): 190-202.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
XIAO Q T, WANG Y J, LÜ Q X, et al., 2020. Responses of glutathione and phytochelatins biosysthesis in a cadmium accumulator of Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt. under cadmium contaminated conditions[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 201: 110805.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
YU H, QIU J F, MA L J, et al., 2017. Phytochemical and phytopharmacological review of Perilla frutescens L. (Labiatae), a traditional edible-medicinal herb in China[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 108(Part B): 375-391.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
YUAN X H, XUE N D, HAN Z G, 2021. A meta-analysis of heavy metals pollution in farmland and urban soils in China over the past 20 years[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences (China), 101: 217-226.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
ZHANG X F, XIA H P, LI Z A, et al., 2011. Identification of a new potential Cd-hyperaccumulator Solanum photeinocarpum by soil seed bank-metal concentration gradient method[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 189(1-2): 414-419.
DOI PMID |
| [36] |
ZHU K M, GU S C, LIU J H, et al., 2021. Wood vinegar as a complex growth regulator promotes the growth, yield, and quality of rapeseed[J]. Agronomy, 11(3): 510.
DOI URL |
| [37] | 李忠光, 龚明, 2008. 愈创木酚法测定植物过氧化物酶活性的改进[J]. 植物生理学通讯, 44(2): 323-324. |
| LI Z G, GONG M, 2008. Improvement of guaiacol method for determination of plant peroxidase activity[J]. Plant Physiology Communications, 44(2): 323-324. | |
| [38] | 林琳, 旦增卓嘎, 吴玲玲, 2022. 铅、镉单一及复合胁迫对生菜幼苗抗氧化酶及亚细胞结构的毒性效应[J]. 生态毒理学报, 17(2): 337-348. |
| LIN L, DAN Z Z G, WU L L, 2022. Toxic effects of lead and cadmium on antioxidant enzymes and subcellular structure of lettuce seedlings[J]. Journal of Ecotoxicology, 17(2): 337-348. | |
| [39] |
谭新中, 彭喜旭, 胡耀军, 等, 2010. 镍处理下水稻酚酸和酚多聚物含量的变化与白叶枯病诱导抗性的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 24(4): 438-442.
DOI |
| TAN X Z, PENG X X, HU Y J, et al., 2010. Relationship between changes of phenolic acid and phenolic polymer contents in rice and induced resistance to bacterial blight under nickel treatment[J]. China Rice Science, 24(4): 438-442. | |
| [40] | 汪敦飞, 郑新宇, 肖清铁, 等, 2019. 铜绿假单胞菌对镉胁迫苗期水稻根系活力及叶片生理特性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 30(8): 2767-2774. |
| WANG D F, ZHENG X Y, XIAO Q T, et al., 2019. Effects of Pseudomonas aeruginosa on root activity and leaf physiological characteristics of rice under cadmium stress at seedling stage[J]. Journal of Applied Ecology, 30(8): 2767-2774. | |
| [41] | 吴苗苗, 2022. 木醋液/黑麦草联合对土壤重金属Cd的修复效果研究[D]. 郑州: 河南农业大学. |
| WU M M, 2022. Study on the remediation effect of wood vinegar/ryegrass combination on heavy metal Cd in soil[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University. | |
| [42] | 肖清铁, 郑新宇, 韩永明, 等, 2018. 不同栽培措施对紫苏镉富集能力的影响[J]. 福建农业学报, 33(7): 724-731. |
| XIAO Q T, ZHENG X Y, HAN Y M, et al., 2018. Effects of different cultivation measures on cadmium enrichment ability of Perilla frutescens[J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture, 33(7): 724-731. | |
| [43] | 谢惠玲, 陈爱萍, 张凤英, 等, 2011. 紫苏对不同浓度镉胁迫的生理响应[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 19(3): 672-675. |
| XIE H L, CHEN A P, ZHANG F Y, et al., 2011. Physiological response of Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt. to cadimium[J]. Journal of China Ecological Agriculture, 19(3): 672-675. | |
| [44] | 杨春燕, 2020. 不同品种龙葵对重金属镉的富集能力与耐性机理研究[D]. 西安: 陕西科技大学. |
| YANG C Y, 2020. Study on the enrichment ability and tolerance mechanism of different varieties of Solanum nigrum to heavy metal cadmium[D]. Xian: Shaanxi University of Science and Technology. | |
| [45] | 张宏, 李文珠, 张文标, 等, 2014. 两种精制竹醋液组分及含量的分析比较[J]. 竹子研究汇刊, 33(3): 32-37. |
| ZHANG H, LI W Z, ZHANG W B, et al., 2014. Analysis and comparison of components and contents of two refined bamboo vinegars[J]. Journal of Bamboo Rresearch, 33(3): 32-37. | |
| [46] | 张洪, 黄建韶, 赵东海, 2006. 紫苏营养成分的研究[J]. 湖南文理学院学报(自然科学版), 18(1): 49-52. |
| ZHANG H, HUANG J S, ZHAO D H, 2006. Study on nutritional components of Perilla frutescens[J]. Journal of Hunan University of Arts and Science (Natural Science Edition), 18(1): 49-52. | |
| [47] | 郑梅琴, 魏燕霞, 林瑞余, 2018. 不同紫苏挥发油化学成分分析[J]. 湖北农业科学, 57(24): 143-146. |
| ZHENG M Q, WEI Y X, LIN R Y, 2018. Analysis of chemical constituents of volatile oil from different Perilla frutescens[J]. Hubei Agricultural Science, 57(24): 143-146. | |
| [48] | 郑新宇, 叶仁杰, 何印波, 等, 2013. 固相萃取-高效液相色谱测定化感水稻根系分泌的酚酸类化合物[J]. 云南大学学报(自然科学版), 35(2): 219-224. |
| ZHENG X Y, YE R J, HE Y B, et al., 2013. Determination of phenolic acids secreted by allelopathic rice roots by solid phase extraction-high performance liquid chromatography[J]. Journal of Yunnan University (Natural Science Edition), 35(2): 219-224. |
| [1] | WANG Lihua, WANG Lei, XU Duanping, XUE Yang. Adsorption Characteristics of Copper and Cadmium on Coal Colloid [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(7): 1293-1300. |
| [2] | LI Zhimei, AN Ya, LI Mei, WANG Shiping, QIN Haoli. Study on Passivation Behavior for Cadmium with Sulfhydryl/iron-based Functionalized Montmorillonite in Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(7): 1301-1312. |
| [3] | ZHAO Liangxia, GAO Kun, HUANG Tingting, GAO Ye, JU Tangdan, JIANG Qiuyang, JIN Heng, XIONG Lei, TANG Zailin, GAO Canhong. The Cadmium Accumulation Characteristics of Maize Inbred Lines with High/Low Grain Cadmium Accumulation at Different Growth Stages [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 766-775. |
| [4] | YANG Yaodong, CHEN Yumei, TU Pengfei, ZENG Qingru. Phytoremediation Potential of Economic Crop Rotation Patterns for Cadmium-polluted Farmland [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 627-634. |
| [5] | LIU Kanghan, ZHENG Liugen, ZHANG Liqun, DING Dan, SHAN Shifeng. Effect of Complex Plant Derived Activator on the Remediation of As Contaminated Soil by Pteris vittata [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 635-642. |
| [6] | XU Min, XU Chao, YU Guanghui, YIN Lichu, ZHANG Quan, ZHU Hanhua, ZHU Qihong, ZHANG Yangzhu, HUANG Daoyou. Effects of Groundwater Level and Long-term Straw Return on Soil Cadmium Availability and Cadmium Concentration in Rice [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(1): 150-157. |
| [7] | CUI Yuanyuan, ZHANG Zhengyun, LIU Peng, ZHANG Yunchun, ZHANG Qiaoying. Morphological Characteristics and Fractal Dimension of Brassia chinensis Root System under Cadmium and Polyethylene Microplastic Stress [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(1): 158-165. |
| [8] | LI Xiaohui, AI Xianbin, LI Liang, WANG Xiyang, XIN Zaijun, SUN Xiaoyan. Study on Passivation Effects of New Modified Rice Husk Biochar Materials on Cadmium Contaminated Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(9): 1901-1908. |
| [9] | LI Xiuhua, ZHAO Ling, TENG Ying, LUO Yongming, HUANG Biao, LIU Chong, LIU Benle, ZHAO Qiguo. Characteristics, Spatial Distribution and Risk Assessment of Combined Mercury and Cadmium Pollution in Farmland Soils Surrounding Mercury Mining Areas in Guizhou [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(8): 1629-1636. |
| [10] | FANG Xianbao, ZHANG Zhijun, LAI Yangqing, YE Mai, DIAO Zenghui. Remediation of Heavy Metals Cr and Cd in Soil by A Novel Sludge-derived Biochar [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(8): 1647-1656. |
| [11] | ZHAO Chaofan, ZHOU Dandan, SUN Jiancai, QIAN Kunpeng, LI Fangfang. The Effect of Soluble Components on the Adsorption of Cadmium on Biochar [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(4): 814-823. |
| [12] | WEN Dian, ZHAO Peihua, CHEN Chuguo, LI Furong, DU Ruiying, HUANG Yongdong, LI Lei, WANG Fuhua. Study on Safety Threshold of Soil Cadmium in the Vegetable Producing Areas of the Pearl River Delta [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 603-609. |
| [13] | SHI Hanzhi, JIANG Qi, LIU Fan, WEN Dian, HUANG Yongdong, DENG Tenghaobo, WANG Xu, XU Aiping, LI Furong, WU Zhichao, LI Meixia, PENG Jinfen, DU Ruiying. Effects of Returning Rice Stubble to Field on Cadmium Accumulation in Soil and Rice [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(2): 363-369. |
| [14] | SHANG GUAN Yuxian, YIN Hongliang, XU Yi, ZHONG Hongmei, HE Mingjiang, QIN Yusheng, GUO Song, YU Hua. Effects of Different Passivators on Cadmium Absorption in Rice and Wheat Grains [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(2): 370-379. |
| [15] | QIN Qin, DUAN Haiqin, SONG Ke, SUN Lijuan, SUN Yafei, ZHOU Bin, XUE Yong. Effect of Conventional Fertilization on the Adsorption-desorption Characteristics and Chemical forms of Cadmium in Soil Water-stable Aggregates [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(12): 2403-2413. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
