Ecology and Environment ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (2): 363-369.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.02.017
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
SHI Hanzhi1,2,3( ), JIANG Qi1,2,3(
), JIANG Qi1,2,3( ), LIU Fan4, WEN Dian1,2,3, HUANG Yongdong1,2,3, DENG Tenghaobo1,2,3, WANG Xu1,2,3, XU Aiping1,2,3, LI Furong1,2,3, WU Zhichao1,2,3, LI Meixia1,2,3, PENG Jinfen1,2,3, DU Ruiying1,2,3,**(
), LIU Fan4, WEN Dian1,2,3, HUANG Yongdong1,2,3, DENG Tenghaobo1,2,3, WANG Xu1,2,3, XU Aiping1,2,3, LI Furong1,2,3, WU Zhichao1,2,3, LI Meixia1,2,3, PENG Jinfen1,2,3, DU Ruiying1,2,3,**( )
)
Received:2021-08-26
Online:2022-02-18
Published:2022-04-14
Contact:
DU Ruiying
石含之1,2,3( ), 江棋1,2,3(
), 江棋1,2,3( ), 刘帆4, 文典1,2,3, 黄永东1,2,3, 邓腾灏博1,2,3, 王旭1,2,3, 徐爱平1,2,3, 李富荣1,2,3, 吴志超1,2,3, 李梅霞1,2,3, 彭锦芬1,2,3, 杜瑞英1,2,3,**(
), 刘帆4, 文典1,2,3, 黄永东1,2,3, 邓腾灏博1,2,3, 王旭1,2,3, 徐爱平1,2,3, 李富荣1,2,3, 吴志超1,2,3, 李梅霞1,2,3, 彭锦芬1,2,3, 杜瑞英1,2,3,**( )
)
通讯作者:
杜瑞英
作者简介:石含之(1989年生)女,助理研究员,博士,主要研究方向为受污染耕地安全利用。E-mail: 692874887@qq.com第一联系人:*共同第一作者:江棋(1992年生),男,实习研究员,硕士,主要研究方向为受污染耕地安全利用。E-mail: 1262790501@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
SHI Hanzhi, JIANG Qi, LIU Fan, WEN Dian, HUANG Yongdong, DENG Tenghaobo, WANG Xu, XU Aiping, LI Furong, WU Zhichao, LI Meixia, PENG Jinfen, DU Ruiying. Effects of Returning Rice Stubble to Field on Cadmium Accumulation in Soil and Rice[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(2): 363-369.
石含之, 江棋, 刘帆, 文典, 黄永东, 邓腾灏博, 王旭, 徐爱平, 李富荣, 吴志超, 李梅霞, 彭锦芬, 杜瑞英. 水稻根茬还田对土壤及稻米中镉累积的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 363-369.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.02.017
| 土壤pH值 Soil pH | w(soil total Cd)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(SOM)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(available P)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(available K)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(alkeline-N)/ (mg∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6.06 | 0.47 | 20.5 | 13.7 | 78.5 | 115.3 |
Table 1 Basic physico-chemical properties of tested soil
| 土壤pH值 Soil pH | w(soil total Cd)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(SOM)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(available P)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(available K)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(alkeline-N)/ (mg∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6.06 | 0.47 | 20.5 | 13.7 | 78.5 | 115.3 |
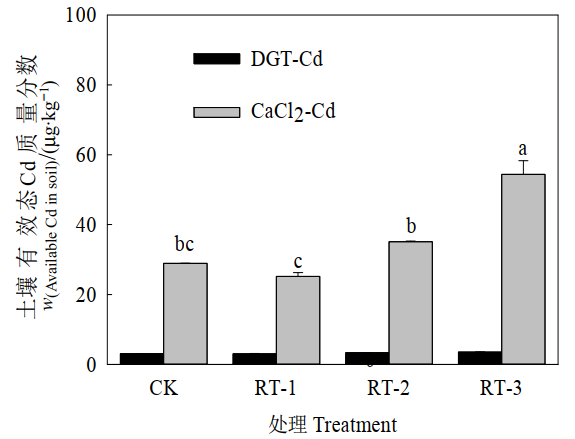
Figure 1 Effects of different treatments on available Cd in soil Different lowercase letters represent significant differences between treatments under the same determination method at P<0.05. The same below
| 处理 Treatments | pH | w(SOM)/(g∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|
| CK | 6.08±0.03ab | 19.27±0.19a |
| RT-1 | 6.16±0.06a | 21.14±0.25a |
| RT-2 | 6.12±0.07ab | 19.92±0.18a |
| RT-3 | 6.05±0.06b | 19.33±0.40a |
Table 2 Effects of different treatments on soil pH and SOM
| 处理 Treatments | pH | w(SOM)/(g∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|
| CK | 6.08±0.03ab | 19.27±0.19a |
| RT-1 | 6.16±0.06a | 21.14±0.25a |
| RT-2 | 6.12±0.07ab | 19.92±0.18a |
| RT-3 | 6.05±0.06b | 19.33±0.40a |
| 处理 Treatments | w(total Cd)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(CaCl2-Fe) /(mg∙kg-1) | w(DGT-Fe)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(CaCl2-Mn)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(DGT-Mn)/ (mg∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.46±0.02a | 5.35±0.11a | 0.22±0.00a | 16.1±0.49a | 0.21±0.03a |
| RT-1 | 0.47±0.04a | 3.75±0.46b | 0.20±0.01ab | 12.5±1.06b | 0.22±0.02a |
| RT-2 | 0.49±0.03a | 4.28±0.14b | 0.20±0.01b | 14.4±1.93ab | 0.20±0.00a |
| RT-3 | 0.52±0.04a | 4.50±0.45ab | 0.16±0.00c | 13.8±1.18ab | 0.20±0.03a |
Table 3 Effects of different treatments on the total Cd and available Fe, Mn in soil
| 处理 Treatments | w(total Cd)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(CaCl2-Fe) /(mg∙kg-1) | w(DGT-Fe)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(CaCl2-Mn)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(DGT-Mn)/ (mg∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.46±0.02a | 5.35±0.11a | 0.22±0.00a | 16.1±0.49a | 0.21±0.03a |
| RT-1 | 0.47±0.04a | 3.75±0.46b | 0.20±0.01ab | 12.5±1.06b | 0.22±0.02a |
| RT-2 | 0.49±0.03a | 4.28±0.14b | 0.20±0.01b | 14.4±1.93ab | 0.20±0.00a |
| RT-3 | 0.52±0.04a | 4.50±0.45ab | 0.16±0.00c | 13.8±1.18ab | 0.20±0.03a |
| 类型 Type | DGT-Cd | CaCl2-Cd | 稻根Cd CdRoot | 稻米Cd Cdrice | pH | 有机质SOM | DGT-Fe | DGT-Mn | CaCl2-Fe | CaCl2-Mn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DGT-Cd | 1 | |||||||||
| CaCl2-Cd | 0.904** | 1 | ||||||||
| 稻根Cd CdRoot | 0.878** | 0.862** | 1 | |||||||
| 稻米Cd CdRice | 0.848** | 0.904** | 0.738* | 1 | ||||||
| pH | -0.526 | -0.589 | -0.352 | -0.723* | 1 | |||||
| 有机质SOM | -0.491 | -0.510 | -0.162 | -0.742* | 0.759* | 1 | ||||
| DGT-Fe | -0.896** | -0.901** | -0.968** | -0.817* | 0.520 | 0.285 | 1 | |||
| DGT-Mn | -0.234 | -0.118 | -0.056 | 0.103 | -0.035 | -0.155 | 0.002 | 1 | ||
| CaCl2-Fe | 0.080 | 0.157 | -0.331 | 0.271 | -0.462 | -0.675 | 0.165 | -0.201 | 1 | |
| CaCl2-Mn | 0.041 | -0.021 | -0.349 | 0.262 | -0.199 | -0.674 | 0.283 | -0.068 | 0.740* | 1 |
Table 4 Correlation of Cd contents in rice, root and soil pH, SOM and available elements
| 类型 Type | DGT-Cd | CaCl2-Cd | 稻根Cd CdRoot | 稻米Cd Cdrice | pH | 有机质SOM | DGT-Fe | DGT-Mn | CaCl2-Fe | CaCl2-Mn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DGT-Cd | 1 | |||||||||
| CaCl2-Cd | 0.904** | 1 | ||||||||
| 稻根Cd CdRoot | 0.878** | 0.862** | 1 | |||||||
| 稻米Cd CdRice | 0.848** | 0.904** | 0.738* | 1 | ||||||
| pH | -0.526 | -0.589 | -0.352 | -0.723* | 1 | |||||
| 有机质SOM | -0.491 | -0.510 | -0.162 | -0.742* | 0.759* | 1 | ||||
| DGT-Fe | -0.896** | -0.901** | -0.968** | -0.817* | 0.520 | 0.285 | 1 | |||
| DGT-Mn | -0.234 | -0.118 | -0.056 | 0.103 | -0.035 | -0.155 | 0.002 | 1 | ||
| CaCl2-Fe | 0.080 | 0.157 | -0.331 | 0.271 | -0.462 | -0.675 | 0.165 | -0.201 | 1 | |
| CaCl2-Mn | 0.041 | -0.021 | -0.349 | 0.262 | -0.199 | -0.674 | 0.283 | -0.068 | 0.740* | 1 |
| [1] | ALMAS A R, LOMBNS P, SONG T A, et al., 2006. Speciation of Cd and Zn in contaminated soils assessed by DGT-DIFS and WHAM Model VI in relation to uptake by spinach and ryegrass[J]. Chemosphere, 6(2): 1647-1655. |
| [2] | BAI Y, GU C, TAO T, et al., 2013. Straw incorporation increases solubility and uptake of cadmium by rice plants[J]. Acta Agriculrual Scandinavica Section B-soil and Plant Science, 63: 193-199. |
| [3] |
CHOMCHOEI R, SHIOWATANA J, PONGSAKU P, 2002. Continuous- flow system for reduction of metal readsorption during sequential extraction of soil[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 472(1): 147-159.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
DING C F, ZHANG T L, WANG X X, et al., 2013. Prediction model for cadmium transfer from soil to carrot (Daucus carota L.) and its application to derive soil thresholds for food safety[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 61(43): 10273-10282.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
FERNANDEZ R, QUIROGA A, ZORATI C, et al., 2010. Carbon contents and respiration rates of aggregate size fractions under no-till and conventional tillage[J]. Soil Tillage Research, 109(2): 103-109.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
KEILUWEIT M, BOUGOURE J, NICO P, et al., 2015. Mineral protection of soil carbon counteracted by root exudates[J]. Nature Climate Change, 5: 588-595.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
LUO H L, DU P, SHI J, et al., 2021. DGT methodology is more sensitive than conventional extraction strategies in assessing amendment- induced soil cadmium availability to rice[J]. Science of The Total Environment, DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143949.
DOI |
| [8] |
LUO H L, DU P, SHI J, et al., 2021. DGT methodology is more sensitive than conventional extraction strategies in assessing amendment- induced soil cadmium availability to rice[J]. Science of the Total Environment, DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143949.
DOI |
| [9] |
MA Q, ZHAO W F, GUAN D X, et al., 2020. Comparing CaCl2, EDTA and DGT methods to predict Cd and Ni accumulation in rice grains from contaminated soils[J]. Environmental Pollution, DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114042.
DOI |
| [10] |
NOELLEMEYER E, FRANK F, ALVAREZl C, et al., 2008. Carbon contents and aggregation related to soil physical and biological properties under a land use sequence in the semiarid region of central Argentina[J]. Soil Tillage Research, 99(2): 179-190.
DOI URL |
| [11] | SORIANO D J M, SPEIR T W, GOMEZ I, et al., 2010. Evaluation of different extraction methods for the assessment of heavy metal bioavailability in various soils[J]. Water Air Soil Polluttion, 21(3): 471-483. |
| [12] |
TAHERVAND S, JALALI M, 2016. Sorption, desorption, and speciation of Cd, Ni, and Fe by four calcareous soils as affected by pH[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188(6): 1-12.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
TIAN K, XING Z, LIU G M, et al., 2018. Cadmium phytoavailability under greenhouse vegetable production system measured by diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT) and its implications for the soil threshold[J]. Environmental Pollution, 241: 412-421.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
ZHANG S Z, SHAN S Q, et al., 2006. Characterization of Pb, Cu, and Cd adsorption on particulate organic matter in soil[J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 25(9): 2366-2373.
DOI URL |
| [15] | 鲍士旦, 2000. 土壤农化分析[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社. |
| BAO S D, 2000. Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis[M]. 3rd Edition. Beijing: China Agricultural Press. | |
| [16] | 陈静, 孙琴, 姚羽, 等, 2014. DGT和传统化学法比较研究复合污染土壤中Cd的生物有效性[J]. 环境科学研究, 27(10): 1172-1179. |
| CHEN J, SUN Q, YAO Y, et al., 2014. Comparison of DGT technique with traditional methods for evaluating cadmium bioavailability in soils with combined pollution[J]. Research of Environment Scicence, 27(10): 1172-1179. | |
| [17] | 陈能场, 郑煜基, 何晓峰, 等, 2017. 《全国土壤污染状况调查公报》探析[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 36(9): 1689-1692. |
| CHEN N C, ZHENG Y J, HE X F, et al., 2017. Analysis of the report on the national survey of soil contamination[J]. Journal of Argo-Environment Science, 36(9): 1689-1692. | |
| [18] | 陈莹, 刘汉燚, 刘娜, 等, 2021. 农地土壤重金属Pb和Cd有效性测定方法的筛选与评价[J]. 环境科学, 42(7): 3494-3506. |
| CHEN Y, LIU H Y, LIU N, et al., 2021. Screening and evaluation of methods for determining available Pb and Cd in farmland soil[J]. Environmental Science, 42(7): 3494-3506. | |
| [19] | 丁园, 敖师营, 陈怡红, 等, 2021. 4种钝化剂对污染水稻土中Cu和Cd的固持机制[J]. 环境科学, 42(8): 4037-4044. |
|
DING Y, AO S Y, CHEN Y H, et al., 2021. Immobilization of mechanism of four types of amendments on Cu and Cd in polluted paddy soil[J]. Environmental Science, 42(8): 4037-4044.
DOI URL |
|
| [20] | 鄂倩, 赵玉杰, 刘潇威, 等, 2020. 不同土壤镉提取方法预测稻米富集镉性能评估[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 39(5): 1000-1009. |
| E Q, ZHAO Y J, LIU X W, et al., 2020. Screening and evaluation of soil cadmium extraction methods for predicting cadmium accumulation in rice[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 39(5): 1000-1009. | |
| [21] | 贵州省市场监督管理, 2019. 农产品产地土壤重金属镉有效态提取梯度扩散薄膜 (DGT) 法: DB52/T 1465-2019 [S]. 贵州. |
| Guizhou Provincial Market Supervision and Administration, 2019. Extrac-tion of available heavy metal cadmium in cropland soils- the diffusion gradient in thin-films (DGT) method DB52/T 1465-2019 [S]. Guizhou. | |
| [22] | 黄界颍, 武修远, 佟影影, 等, 2020. 小麦秸秆还田量对土壤Cd有效性及水稻Cd亚细胞分布的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 39(7): 1503-1511. |
| HUANG J Y, WU X Y, TONG Y Y, et al., 2020. Effects of returning wheat straw on available cadmium and subcellular distribution of cadmium in rice[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 39(7): 1503-1511. | |
| [23] | 李慧敏, 方圆, 唐翠荣, 等, 2018. 广西水稻土镉有效性、水稻镉富集系数与土壤性质关系的研究[J]. 西南农业学报, 31(12): 2678-2684. |
| LI H M, FANG Y, TANG C R, et al., 2018. Relationship among bioavailability cadmium and cadmium enrichment coefficient in rice and paddy soil properties in Guangxi[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 31(12): 2678-2684. | |
| [24] | 李志涛, 王夏晖, 赵玉杰, 等, 2017. 南方典型区域镉富集系数差异影响因素探析[J]. 环境科学与技术, 40(10): 1-7. |
|
LI Z T, WANG X H, ZHAO Y J, et al., 2017. Analysis of difference and causes in rice cadmium uptake factor in typical south region[J]. Environmental science &technology, 40(10): 1-7.
DOI URL |
|
| [25] | 鲁如坤, 2000. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社: 12-180. |
| LU R K, 2000. Soil and agricultural chemical analysis method[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: 12-180. | |
| [26] | 汤文光, 肖小平, 唐海明, 等, 2015. 长期不同耕作与秸秆还田对土壤养分库容及重金属Cd的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 26(1): 168-176. |
| TANG W G, XIAO X P, TANG H M, et al., 2015. Effects of long term tillage and straw-returning on soil nutrient pools and Cd concentration[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 26(1): 168-176. | |
| [27] | 田衍, 王尧, 房丽萍, 等, 2019. 土壤中重金属可提取态 (氯化钙法) 分析质量控制样品的研制[J]. 中国环境监测, 35(6): 110-117. |
| TIAN Y, WANG X, FANG L P, et al., 2019. Preparation and certification of quality control sample for CaCl2-Extractable heavy metals in agricultural soil[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 5(6): 110-117. | |
| [28] | 文典, 严东, 赵沛华, 等, 2018. 快速高通量全消解ICP-MS法测定《全国土壤污染状况详查》项目中14种元素[J]. 环境化学, 37(6): 1432-1435. |
| WEN D, YAN D, ZHAO P H, et at., 2018. Fast determination of 14 elements in china soil pollution survey with high throughput full digestion method by ICP-MS[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 37(6): 1432-1435. | |
| [29] | 肖亮亮, 丁园, 2019. 药渣生物炭基质联合麦饭石对土壤-黑麦草体系的调控与机制[J]. 环境科学, 40(10): 4668-4677. |
| XIAO L L, DING Y, 2019. Regulation and mechanism of a dregs biochar matrix combined with maifanite on a soil-ryegrass system[J]. Environmental Science, 40(10): 4668-4677. | |
| [30] | 杨兰, 李冰, 王昌全, 等, 2015. 长期秸秆还田对德阳地区稻田镉赋存形态的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 23(2): 725-732. |
| YANG L, LI B, WANG C Q, et al., 2015. Effects of long-term straw incorporation on cadmium speciation and bioavailability in paddy soils in Deyang Area[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 23(2): 725-732. | |
| [31] | 悦飞雪, 李继伟, 王艳芳, 等, 2018. 施用秸秆生物炭和鸡粪对镉胁迫下玉米生长及镉吸收的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 7(10): 2118-2126. |
| YUE F X, LI J W, WANG Y F, et al., 2018. Effects of soil amendments with stalk derived-biochar and chicken manure on the growth and Cd uptake of maize under Cd stresss[J]. Journal of Argo-Environment Science, 37(10): 2118-2126. | |
| [32] | 张晶, 于玲玲, 辛术贞, 等, 2013. 根茬连续还田对镉污染农田土壤中镉赋存形态和生物有效性的影响[J]. 环境科学, 34(2): 685-691. |
| ZHANG J, YU L L, XIN S Z, et al., 2013. Phytoavailability and chemical speciation of cadmium in different Cd-contaminated soils with crop root return[J]. Environmental Science, 34(2): 685-691. | |
| [33] | 张小敏, 张秀英, 钟太洋, 等, 2014. 中国农田土壤重金属富集状况及其空间分布研究[J]. 环境科学, 35(2): 692-703. |
| ZHANG X M, ZHANG X Y, ZHONG T Y, et al., 2014. Spatial distribution and accumulation of heavy metal in arable land soil of China[J]. Environmental Science, 35(2): 692-703. | |
| [34] | 赵步洪, 张洪熙, 奚岭林, 等, 2006. 杂交水稻不同器官镉浓度与累积量[J]. 中国水稻科学, 20(3): 306-312. |
| ZHAO B H, ZHANG H X, XI L L, et al., 2006. Cadmium concentration and accumulation in different organs of hybrid rice[J]. Rice Science in China, 20(3): 306-312. |
| [1] | XIAO Bo, WANG Shaojun, XIE Lingling, WANG Zhengjun, GUO Zhipeng, ZHANG Kunfeng, ZHANG Lulu, FAN Yuxiang, GUO Xiaofei, LUO Shuang, XIA Jiahui, LI Rui, LAN Mengjie, YANG Shengqiu. Effect of Ant Nesting Activity on Soil Nitrogen Component Allocation in the Xishuangbanna Tropical Forests [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1026-1036. |
| [2] | HUANG Yingmei, ZHONG Songxiong, ZHU Yiwen, WANG Xiangqin, LI Fangbai. Effects and Mechanism of Element Sulfur Inhibiting Methylmercury Accumulation in Rice Plants [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1115-1122. |
| [3] | ZHU Yongle, TANG Jiaxi, TAN Ting, LI Yu, XIANG Biao. Contaminant Characteristic of Per- and Poly-fluorinated Substances in Maize in the Surrounding of Fluorine Chemical Park [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 1001-1006. |
| [4] | ZHAO Liangxia, GAO Kun, HUANG Tingting, GAO Ye, JU Tangdan, JIANG Qiuyang, JIN Heng, XIONG Lei, TANG Zailin, GAO Canhong. The Cadmium Accumulation Characteristics of Maize Inbred Lines with High/Low Grain Cadmium Accumulation at Different Growth Stages [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 766-775. |
| [5] | YANG Yaodong, CHEN Yumei, TU Pengfei, ZENG Qingru. Phytoremediation Potential of Economic Crop Rotation Patterns for Cadmium-polluted Farmland [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 627-634. |
| [6] | XU Min, XU Chao, YU Guanghui, YIN Lichu, ZHANG Quan, ZHU Hanhua, ZHU Qihong, ZHANG Yangzhu, HUANG Daoyou. Effects of Groundwater Level and Long-term Straw Return on Soil Cadmium Availability and Cadmium Concentration in Rice [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(1): 150-157. |
| [7] | CUI Yuanyuan, ZHANG Zhengyun, LIU Peng, ZHANG Yunchun, ZHANG Qiaoying. Morphological Characteristics and Fractal Dimension of Brassia chinensis Root System under Cadmium and Polyethylene Microplastic Stress [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(1): 158-165. |
| [8] | LI Xiaohui, AI Xianbin, LI Liang, WANG Xiyang, XIN Zaijun, SUN Xiaoyan. Study on Passivation Effects of New Modified Rice Husk Biochar Materials on Cadmium Contaminated Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(9): 1901-1908. |
| [9] | LI Xiuhua, ZHAO Ling, TENG Ying, LUO Yongming, HUANG Biao, LIU Chong, LIU Benle, ZHAO Qiguo. Characteristics, Spatial Distribution and Risk Assessment of Combined Mercury and Cadmium Pollution in Farmland Soils Surrounding Mercury Mining Areas in Guizhou [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(8): 1629-1636. |
| [10] | FANG Xianbao, ZHANG Zhijun, LAI Yangqing, YE Mai, DIAO Zenghui. Remediation of Heavy Metals Cr and Cd in Soil by A Novel Sludge-derived Biochar [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(8): 1647-1656. |
| [11] | ZHAO Chaofan, ZHOU Dandan, SUN Jiancai, QIAN Kunpeng, LI Fangfang. The Effect of Soluble Components on the Adsorption of Cadmium on Biochar [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(4): 814-823. |
| [12] | WEN Dian, ZHAO Peihua, CHEN Chuguo, LI Furong, DU Ruiying, HUANG Yongdong, LI Lei, WANG Fuhua. Study on Safety Threshold of Soil Cadmium in the Vegetable Producing Areas of the Pearl River Delta [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 603-609. |
| [13] | SHANG GUAN Yuxian, YIN Hongliang, XU Yi, ZHONG Hongmei, HE Mingjiang, QIN Yusheng, GUO Song, YU Hua. Effects of Different Passivators on Cadmium Absorption in Rice and Wheat Grains [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(2): 370-379. |
| [14] | YANG Danli, LUO Ji, JIA Longyu, CHEN Yunfei. Historical Records of Pb Accumulation in Primary Succession Ecosystem of Hailuogou Glacier Retreat Area [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(12): 2393-2402. |
| [15] | QIN Qin, DUAN Haiqin, SONG Ke, SUN Lijuan, SUN Yafei, ZHOU Bin, XUE Yong. Effect of Conventional Fertilization on the Adsorption-desorption Characteristics and Chemical forms of Cadmium in Soil Water-stable Aggregates [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(12): 2403-2413. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
