Ecology and Environment ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (6): 1225-1234.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.06.019
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
GAO Peng1( ), GAO Pin1, SUN Weimin2, KONG Tianle1,2, HUANG Duanyi2, LIU Huaqing2, SUN Xiaoxun2,*
), GAO Pin1, SUN Weimin2, KONG Tianle1,2, HUANG Duanyi2, LIU Huaqing2, SUN Xiaoxun2,*
Received:2022-01-26
Online:2022-06-18
Published:2022-07-29
Contact:
SUN Xiaoxun
高鹏1( ), 高品1, 孙蔚旻2, 孔天乐1,2, 黄端仪2, 刘华清2, 孙晓旭2,*
), 高品1, 孙蔚旻2, 孔天乐1,2, 黄端仪2, 刘华清2, 孙晓旭2,*
通讯作者:
孙晓旭
作者简介:高鹏(1998年生),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为土壤微生物。E-mail: gaopeng9839@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
GAO Peng, GAO Pin, SUN Weimin, KONG Tianle, HUANG Duanyi, LIU Huaqing, SUN Xiaoxun. Response of the Endosphere and Rhizosphere Microbial Community in Petris vittata L. to Arsenic Stress[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(6): 1225-1234.
高鹏, 高品, 孙蔚旻, 孔天乐, 黄端仪, 刘华清, 孙晓旭. 蜈蚣草根际及内生微生物群落对砷污染胁迫的响应机制研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1225-1234.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.06.019
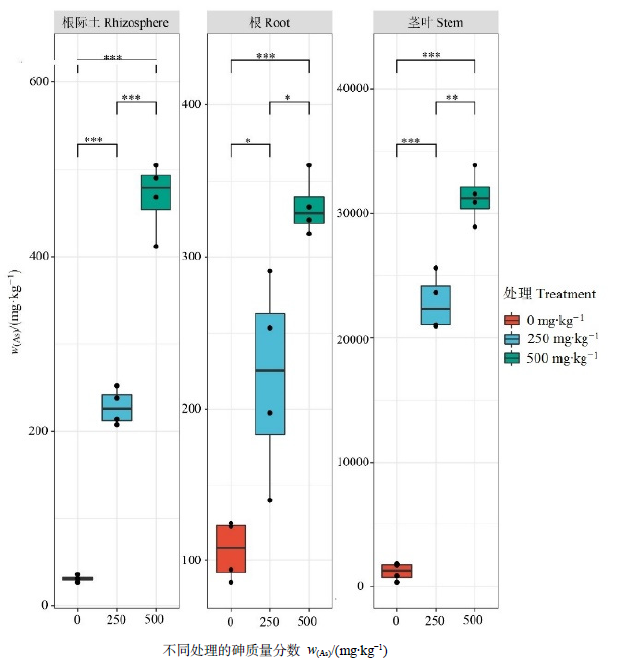
Figure 1 As concentration in rhizosphere, roots and stems of Pteris vittata L. contaminated with different concentration of As * in the figure indicates significant differences between different treatment of arsenic concentrations (* P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001)
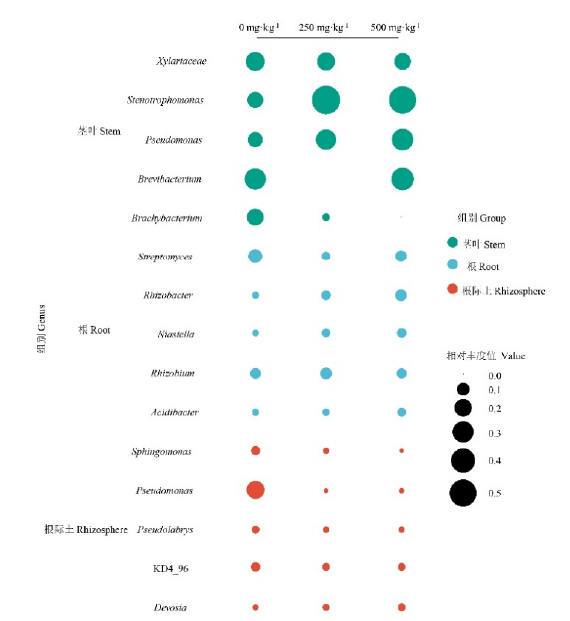
Figure 5 Relative abundances of the top 5 most-abundant genera within the microbial communities in rhizosphere, roots and stems of Pteris vittata L. respectively
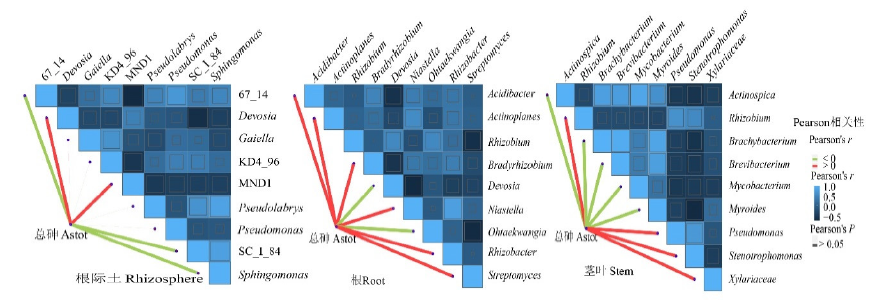
Figure 7 The correlation between microorganisms of the top 9 most-abundant genera and arsenic in the rhizosphere, roots, and stems of Pteris vittata L.
| [1] | AHMAD A, HEIJNEN L, DE WAAL L, et al., 2020. Mobility and redox transformation of arsenic during treatment of artificially recharged groundwater for drinking water production[J]. Water Research, 178: 115826. |
| [2] | BOLYEN E, RIDEOUT J R, DILLON M R, et al., 2019. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 37(8): 852-857. |
| [3] | BROECKLING C D, BROZ A K, BERGELSON J, et al., 2008. Root exudates regulate soil fungal community composition and diversity[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 74(3): 738-744. |
| [4] | CANTAMESSA S, MASSA N, GAMALERO E, et al., 2020. Phytoremediation of a highly arsenic polluted site, using Pteris vittata L. and Arbuscular Mycorrhizal fungi[J]. Plants, 9(9): 1211. |
| [5] | CAPORASO J G, LAUBER C, WALTERS W A, 2010. Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 108(Suppl 1): 4516-4522. |
| [6] | CHEN T B, WEI C Y, HUANG Z C, et al., 2002. Arsenic hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata L. and its arsenic accumulation[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 47(11): 902-905. |
| [7] | CHHETRI G, KIM I, KANG M, et al., 2022. Devosia rhizoryzae sp. nov., and Devosia oryziradicis sp. nov., novel plant growth promoting members of the genus Devosia, isolated from the rhizosphere of rice plants[J]. Journal of Microbiology, 60: 1-10. |
| [8] | DAS S, CHOU M L, JEAN J S, et al., 2016. Water management impacts on arsenic behavior and rhizosphere bacterial communities and activities in a rice agro-ecosystem[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 542(Part A): 642-652. |
| [9] | DEEPIKA K, RAGHURAM M, KARIALI E, et al., 2016. Biological responses of symbiotic Rhizobium radiobacter strain VBCK1062 to the arsenic contaminated rhizosphere soils of mung bean[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 134( Part 1): 1-10. |
| [10] | DIXIT S, HERING J G, 2003. Comparison of arsenic (V) and arsenic (Ⅲ) sorption onto iron oxide minerals: implications for arsenic mobility[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 37(18): 4182-4189. |
| [11] | DREWNIAK L, CIEZKOWSKA M, RADLINSKA M, et al., 2015. Construction of the recombinant broad-host-range plasmids providing their bacterial hosts arsenic resistance and arsenite oxidation ability[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 196-197: 42-51. |
| [12] | GAO M, XIONG C, GAO C, et al., 2021. Disease-induced changes in plant microbiome assembly and functional adaptation[J]. Microbiome, 9(1): 1-18. |
| [13] | GHNAYA T, MNASSRI M, GHABRICHE R, et al., 2015. Nodulation by Sinorhizobium meliloti originated from a mining soil alleviates Cd toxicity and increases Cd-phytoextraction in Medicago sativa L.[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 6: 863. |
| [14] | HAN Y H, FU J W, CHEN Y, et al., 2016. Arsenic uptake, arsenite efflux and plant growth in hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata: Role of arsenic-resistant bacteria[J]. Chemosphere, 144: 1937-1942. |
| [15] | HAN Y H, FU J W, XIANG P, et al., 2017a. Arsenic and phosphate rock impacted the abundance and diversity of bacterial arsenic oxidase and reductase genes in rhizosphere of As-hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 321: 146-153. |
| [16] | HAN Y H, LIU X, RATHINASABAPATHI B, et al., 2017b. Mechanisms of efficient As solubilization in soils and As accumulation by As-hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata[J]. Environmental Pollution, 227: 569-577. |
| [17] | JIA M, SANGWAN N, TZENG A, et al., 2021. Interplay Between Class II HLA Genotypes and the Microbiome and Immune Phenotypes in Individuals With PTEN Hamartoma Tumor Syndrome[J]. JCO Precision Oncology, 5: 357-369. |
| [18] | MA L Q, KOMAR K M, TU C, et al., 2001. A fern that hyperaccumulates arsenic[J]. Nature, 409(6820): 579-579. |
| [19] | MAHIEU S, FRéROT H, VIDAL C, et al., 2011. Anthyllis vulneraria/ Mesorhizobium metallidurans, an efficient symbiotic nitrogen fixing association able to grow in mine tailings highly contaminated by Zn, Pb and Cd[J]. Plant and Soil, 342(1-2): 405-417. |
| [20] | NAIDU P, SMITH S, 2012. A review of 11 years of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia blood isolates at a tertiary care institute in Canada[J]. Canadian Journal of Infectious Diseases and Medical Microbiology, 23(4): 165-169. |
| [21] | NIHORIMBERE V, ONGENA M, SMARGIASSI M, et al., 2011. Beneficial effect of the rhizosphere microbial community for plant growth and health[J]. Biotechnologie, Agronomie, Société et Environnement, 15(2): 327-337. |
| [22] | SCHROEDER P J, JENKINS D G, 2018. How robust are popular beta diversity indices to sampling error?[J]. Ecosphere, 9(2): e02100. |
| [23] | SUN W M, SUN X X, LI B Q, et al., 2019. Bacterial response to antimony and arsenic contamination in rice paddies during different flooding conditions[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 675: 273-285. |
| [24] | SUN X X, KONG T L, XU R, et al., 2020. Comparative characterization of microbial communities that inhabit arsenic-rich and antimony-rich contaminated sites: Responses to two different contamination conditions[J]. Environmental Pollution, 260: 114052. |
| [25] | SUN X X, SONG B R, XU R, et al., 2021. Root-associated (rhizosphere and endosphere) microbiomes of the Miscanthus sinensis and their response to the heavy metal contamination[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 104(6): 387-398. |
| [26] | TAKARINA N D, PIN T G, 2017. Bioconcentration factor (BCF) and translocation factor (TF) of heavy metals in mangrove trees of Blanakan fish farm[J]. Makara Journal of Science, 21(2): 4. |
| [27] | TANG J W, LIAO Y P, YANG Z H, et al., 2016. Characterization of arsenic serious-contaminated soils from Shimen realgar mine area, the Asian largest realgar deposit in China[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 16(5): 1519-1528. |
| [28] | TURPEINEN R, PANTSAR-KALLIO M, HÄGGBLOM M, et al., 1999. Influence of microbes on the mobilization, toxicity and biomethylation of arsenic in soil[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 236(1-3): 173-180. |
| [29] | XIONG J B, WU L Y, TU S X, et al., 2010. Microbial communities and functional genes associated with soil arsenic contamination and the rhizosphere of the arsenic-hyperaccumulating plant Pteris vittata L.[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 76(21): 7277-7284. |
| [30] | YANG C, HO Y N, INOUE C, et al., 2020. Long-term effectiveness of microbe-assisted arsenic phytoremediation by Pteris vittata in field trials[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 740: 140137. |
| [31] | 陈同斌, 李海翔, 雷梅, 等, 2010. 植物修复过程中蜈蚣草对土壤养分的吸收动态: 5年田间定位试验[J]. 环境科学学报, 30(2): 402-408. |
| CHEN T B, LI H Y, LEI M, et al., 2010. The absorption dynamics of soil nutrients by centipede grass during phytoremediation: A 5-year field trial[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 30(2): 402-408. | |
| [32] | 陈焱山, 贾梦茹, 曹越, 等, 2018. 蜈蚣草砷富集的分子机制研究进展[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 37(7): 1402-1408. |
| CHEN Y S, JIA M R, CAO Y, et al., 2018. Research progress on the molecular mechanism of arsenic enrichment in centipede grass[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 37(7): 1402-1408. | |
| [33] | 仇荣亮, 仇浩, 雷梅, 等, 2009. 矿山及周边地区多金属污染土壤修复研究进展[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 28(6): 1085-1091. |
| CHOU R L, CHOU H, LEI M, et al., 2008. Research progress on polymetallic contaminated soil remediation in mines and surrounding areas[J]. Journal of Agro-Environmental Science, 28(6): 1085-1091. | |
| [34] | 戴志楠, 温尔刚, 陈翰博, 等, 2021. 施用原始及铁改性生物质炭对土壤吸附砷(Ⅴ)的影响[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 38(2): 346-354. |
| DAI Z N, WEN E G, CHEN H B, et al., 2021. Effects of application of original and iron-modified biomass charcoal on the adsorption of arsenic(Ⅴ) in soil[J]. Journal of Zhejiang A & F University, 38(2): 346-354. | |
| [35] | 谷倩, 张琢, 张丽, 等, 2021. 砷污染场地土壤的稳定化技术工程应用研究[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 11(4): 734-739. |
| GU Q, ZHANG Z, ZHANG L, et al., 2021. Research on engineering application of stabilization technology for arsenic contaminated site soil[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 11(4): 734-739. | |
| [36] | 韩永和, 贾梦茹, 傅景威, 等, 2017. 不同浓度砷酸盐胁迫对蜈蚣草根际微生物群落功能多样性特征的影响[J]. 南京大学学报 (自然科学版), 53(2): 275-285. |
| HAN Y H, JIA M R, FU J W, et al., 2017. Effects of arsenic acid stress at different concentrations on functional diversity characteristics of the rhizosphere microbial community of Centipede grass[J]. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Sciences), 3(2): 275-285. | |
| [37] | 焦常锋, 常会庆, 王启震, 等, 2020. 碳酸钙和壳聚糖联用对高pH值石灰性土壤砷污染的钝化[J]. 农业工程学报, 36(11): 234-240. |
| JIAO C F, CHANG H Q, WANG Q Z, et al., 2020. Combined use of calcium carbonate and chitosan to passivate arsenic pollution in high pH calcareous soil[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 36(11): 234-240. | |
| [38] | 孟伟, 何邵麟, 吴攀, 等, 2021. 贵州中部土壤砷累积特征及异常富集成因研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 21(2): 841-848. |
| MENG W, HE S L, WU P, et al., 2021. Study on the accumulation characteristics and abnormal enrichment causes of arsenic in the soils of central Guizhou[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 21(2): 841-848. | |
| [39] | 莫昌琍, 吴丰昌, 符志友, 等, 2013. 湖南锡矿山锑矿区农用土壤锑、砷及汞的污染状况初探[J]. 矿物学报, 33(3): 344-350. |
| MO C L, WU F C, FU Z Y, et al., 2013. A preliminary study on the pollution status of antimony, arsenic and mercury in agricultural soil in the antimony mining area of Hunan Tin Mine[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 33(3): 344-350. | |
| [40] | 生态环境部南京环境科学研究所, 2007. 土壤环境质量标准: GB15618–2008[S]. 北京: 中国环境出版社. |
| Nanjing Institute of Environmental Sciences, MEE, 2007. Environmental quality standards soils: GB15618-2008[S]. Beijing: China Environment Publishing Group. | |
| [41] |
汪京超, 李楠楠, 谢德体, 等, 2015. 砷在植物体内的吸收和代谢机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 50(4): 516-526.
DOI |
| WANG J C, LI N N, XIE D T, et al., 2015. Research Progress on Arsenic Absorption and Metabolism in Plants[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 50(4): 516-526. | |
| [42] | 熊金波, 2010. 微生物群落结构在砷污染土壤蜈蚣草根际和不同深度土壤中的变化[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学. |
| XIONG J B, 2010. Changes of microbial community structure in the rhizosphere of centipede grass in arsenic-contaminated soil and soils at different depths[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University. | |
| [43] | 许飞飞, 2017. 不同生态型蜈蚣草砷吸收差异特征及其机理[D]. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学. |
| XU F F, 2017. Characteristics and mechanism of arsenic absorption differences in different ecotypes of centipede grass[D]. Xianyang: Northwest A & F University. | |
| [44] | 叶文玲, 樊霆, 鲁洪娟, 等, 2014. 蜈蚣草的植物修复作用对土壤中砷总量及形态分布的影响研究[J]. 土壤通报, 45(4): 1003-1007. |
| YE W L, FAN T, LU H J, et al., 2014. Study on the effect of phytoremediation of centipede grass on the total arsenic content and speciation distribution in soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 45(4): 1003-1007. | |
| [45] | 张田, 闫慧莉, 何振艳, 2020. 蜈蚣草中砷超富集的分子机制研究进展[J]. 生物工程学报, 36(3): 397-406. |
| ZHANG T, YAN H L, HE Z Y, 2020. Research progress on the molecular mechanism of arsenic hyperaccumulation in centipede grass[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 36(3): 397-406. | |
| [46] | 赵根成, 廖晓勇, 阎秀兰, 等, 2010. 微生物强化蜈蚣草累积土壤砷能力的研究[J]. 环境科学, 31(2): 431-436. |
| ZHAO G C, LIAO X Y, YAN X L, et al., 2010. Study on microbial enhancing the ability of centipede grass to accumulate arsenic in soil[J]. Environmental Science, 31(2): 431-436. |
| [1] | WANG Yun, ZHENG Xilai, CAO Min, LI Lei, SONG Xiaoran, LIN Xiaolei, GUO Kai. Study on Denitrification Performance and Control Factors in Brackish-Freshwater Transition Zone of Coastal Aquifer [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 980-988. |
| [2] | YANG Nie, SUN Xiaoxun, KONG Tianle, SUN Weimin, CHEN Quanyuan, GAO Pin. Response of Microbial Communities to Changes in Antimony Pollution Concentrations in Fluvial Sediment [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 609-618. |
| [3] | YANG Yu, DENG Renjian, LONG Pei, HUANG Zhongjie, Ren Bozhi, WANG Zhenghua. Isolation and Identification of Arsenic-oxidizing Bacterium Pseudomonas sp. AO-1 and Its Oxidation Properties for As(Ⅲ) [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 619-626. |
| [4] | YIN Haojun, LONG Mingliang, LIU Wei, NI Chunlin, LI Fangbai, WU Yundang. Dissolved Oxygen Concentration Regulates Arsenic Reduction in Aeromonas hydrophila: Effects and Mechanisms [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(2): 381-387. |
| [5] | HUA Li, CHENG Taozhi, LIANG Zhiyong. Remediation Effect of Petroleum-Contaminated Soil by Immobilized Mixed Bacteria in Northern Shaanxi Province of China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(8): 1610-1615. |
| [6] | ZHU Yihao, LI Qingmei, LIU Xiaoli, LI Na, SONG Fengling, CHEN Weifeng. Characteristics of Soil Microbial Community in Newly Cultivated Land under Different Land Consolidation Types [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(5): 909-917. |
| [7] | XU Meihua, GU Minghua, WANG Chengzhen, LEI Jing, WEI Yanyan, SHEN Fangke. Effect of Manganese on Arsenic Speciation in Soil and Arsenic Migration to Rice [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(4): 802-813. |
| [8] | MEI Chuang, CAI Kunzheng, LI Zishan, XU Meili, HUANG Fei. Effects of Rice-straw Biochar on the Transformation of Cadmium Fractions and Microbial Community in Paddy Soils [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(2): 380-390. |
| [9] | LIU Chang, LUO Yanli, LIU Chentong, ZHENG Yuhong, CHAO Bo, DONG Lele. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Arsenic in Groundwater and Cropland Soil in the Lower Reaches of Kuitun River [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(10): 2070-2078. |
| [10] | LIU Bingru. Response of Thermal Adaptability of Soil Microbial Respiration and Microbial Community and Diversity to Global Climate Change: A Review [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(1): 181-186. |
| [11] | CONG Chao, YANG Ningke, WANG Haijuan, WANG Hongbin. Enhancing Arsenic and Cadmium Accumulation in Pteris vittata and Solanum nigrum by Combined Application of Indoleacetic Acid and Kinetin: A Field Experiment [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(6): 1299-1309. |
| [12] | ZHANG Jinlong, HUANG Ying, WU Lifang, GONG Yunhui, LIU Yungen, WANG Yan, YANG Silin. As Subcellular Distribution and Physiological Response of Typha angustifolia L. to As Exposure [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(5): 1042-1050. |
| [13] | GE Yinglan, SUN Ting. Soil Microbial Community Structure and Diversity of Potato in Rhizosphere and Non-rhizosphere Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2020, 29(1): 141-148. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
