生态环境学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (6): 888-901.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2025.06.006
收稿日期:2024-11-22
出版日期:2025-06-18
发布日期:2025-06-11
通讯作者:
* 罗明良, E-mail: 作者简介:王天雯(2001年生),女,硕士研究生,主要从事GIS生态系统服务应用研究。E-mail: wtw8882023@163.com
基金资助:
WANG Tianwen1,2( ), LUO Mingliang1,2,*(
), LUO Mingliang1,2,*( ), BAI Leichao1,2
), BAI Leichao1,2
Received:2024-11-22
Online:2025-06-18
Published:2025-06-11
摘要:
嘉陵江流域作为长江上游重要生态屏障,其生态系统服务的有效管理对保障生态安全与推动可持续发展具有重要意义。基于InVEST模型,评估了2000-2020年间土壤保持、生境质量、碳储量和产水服务等4项生态系统服务的时空变化特征;结合地理探测器分析了自然因子和人类活动对其的驱动作用;以地形梯度进行分区,通过皮尔逊相关性和空间自相关方法,揭示了全域和分区情形下不同服务间的权衡与协同关系。结果表明,1)20年间,嘉陵江流域的生态系统服务呈现“整体上升、局部平稳”特征。土壤保持和产水服务显著增长,土壤保持高值区集中于地势陡峭、植被良好的东南和西北地区;而产水服务呈“南高北低”格局,高值区位于降水充沛的南部;生境质量略有下降,碳储量相对稳定,空间分布与土壤保持服务类似。2)生态系统服务在自然因子和人类活动的共同驱动下发生变化,受土地利用、植被覆盖、坡度、降水和高程等因素及其交互作用的显著影响。3)流域生态系统服务的权衡与协同关系在时间、空间及地形梯度分区上差异显著,不同梯度内部服务关系各具特征,其中低梯度区作用较弱,中梯度区协同性增强,高梯度区以权衡为主。该研究揭示了嘉陵江流域生态系统服务的时空动态特征及其权衡协同关系,为流域优化生态功能布局、提升生态服务水平提供了科学支持。
中图分类号:
王天雯, 罗明良, 白雷超. 嘉陵江流域生态系统服务动态变化及权衡协同分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(6): 888-901.
WANG Tianwen, LUO Mingliang, BAI Leichao. Dynamic Changes and Trade-off-Synergy Analysis of Ecosystem Services in the Jialing River Basin[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2025, 34(6): 888-901.
| 编号 | 因素类别 | 影响因素 | 选取理由 |
|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 地形地貌 | 高程 | 高程与坡度共同影响区域气候、水文过程及植被分布,调节地表径流与土壤侵蚀强度,决定了生态系统服务的空间分布格局 |
| X2 | 坡度 | ||
| X3 | 植被 | 归一化植被指数(NDVI) | 反映了植被覆盖率 |
| X4 | 气候 | 年平均气温 | 气温和降水作为气候变化的关键指标,通过调节水热条件、影响植被生长环境及区域水文过程,对生态系统服务的供给和空间分布产生重要影响 |
| X5 | 年平均降水量 | ||
| X6 | 人为因素 | 土地利用情况 | 土地利用类型直接决定生态系统服务的功能分布;GDP和人口密度共同反映了经济发展水平和人类活动强度,城镇扩张、资源开发及高密度人类活动可能导致土地资源过度利用,显著影响生态系统服务的供给与调节能力 |
| X7 | 国内生产总值(GDP) | ||
| X8 | 人口密度 |
表1 地理探测因子的选取
Table 1 Selection of geographic detection factors
| 编号 | 因素类别 | 影响因素 | 选取理由 |
|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 地形地貌 | 高程 | 高程与坡度共同影响区域气候、水文过程及植被分布,调节地表径流与土壤侵蚀强度,决定了生态系统服务的空间分布格局 |
| X2 | 坡度 | ||
| X3 | 植被 | 归一化植被指数(NDVI) | 反映了植被覆盖率 |
| X4 | 气候 | 年平均气温 | 气温和降水作为气候变化的关键指标,通过调节水热条件、影响植被生长环境及区域水文过程,对生态系统服务的供给和空间分布产生重要影响 |
| X5 | 年平均降水量 | ||
| X6 | 人为因素 | 土地利用情况 | 土地利用类型直接决定生态系统服务的功能分布;GDP和人口密度共同反映了经济发展水平和人类活动强度,城镇扩张、资源开发及高密度人类活动可能导致土地资源过度利用,显著影响生态系统服务的供给与调节能力 |
| X7 | 国内生产总值(GDP) | ||
| X8 | 人口密度 |

图2 2000-2020年嘉陵江流域生态系统服务时空分布格局
Figure 2 The spatial and temporal distribution pattern of ecosystem services in the Jialing River Basin from 2000 to 2020
| 年份 | 土壤保持量/ (t∙hm−2) | 产水量/ (m3∙hm−2) | 生境质量 指数 | 碳储存量(以C计)/ (Mg∙hm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 2486.3 | 2596.8 | 0.56 | 272 |
| 2010 | 2944.5 | 3879.6 | 0.54 | 278 |
| 2020 | 3125.6 | 5736.5 | 0.52 | 281 |
表2 2000-2020年嘉陵江流域生态系统服务量
Table 2 The ecosystem service values in the Jialing River Basin from 2000 to 2020
| 年份 | 土壤保持量/ (t∙hm−2) | 产水量/ (m3∙hm−2) | 生境质量 指数 | 碳储存量(以C计)/ (Mg∙hm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 2486.3 | 2596.8 | 0.56 | 272 |
| 2010 | 2944.5 | 3879.6 | 0.54 | 278 |
| 2020 | 3125.6 | 5736.5 | 0.52 | 281 |
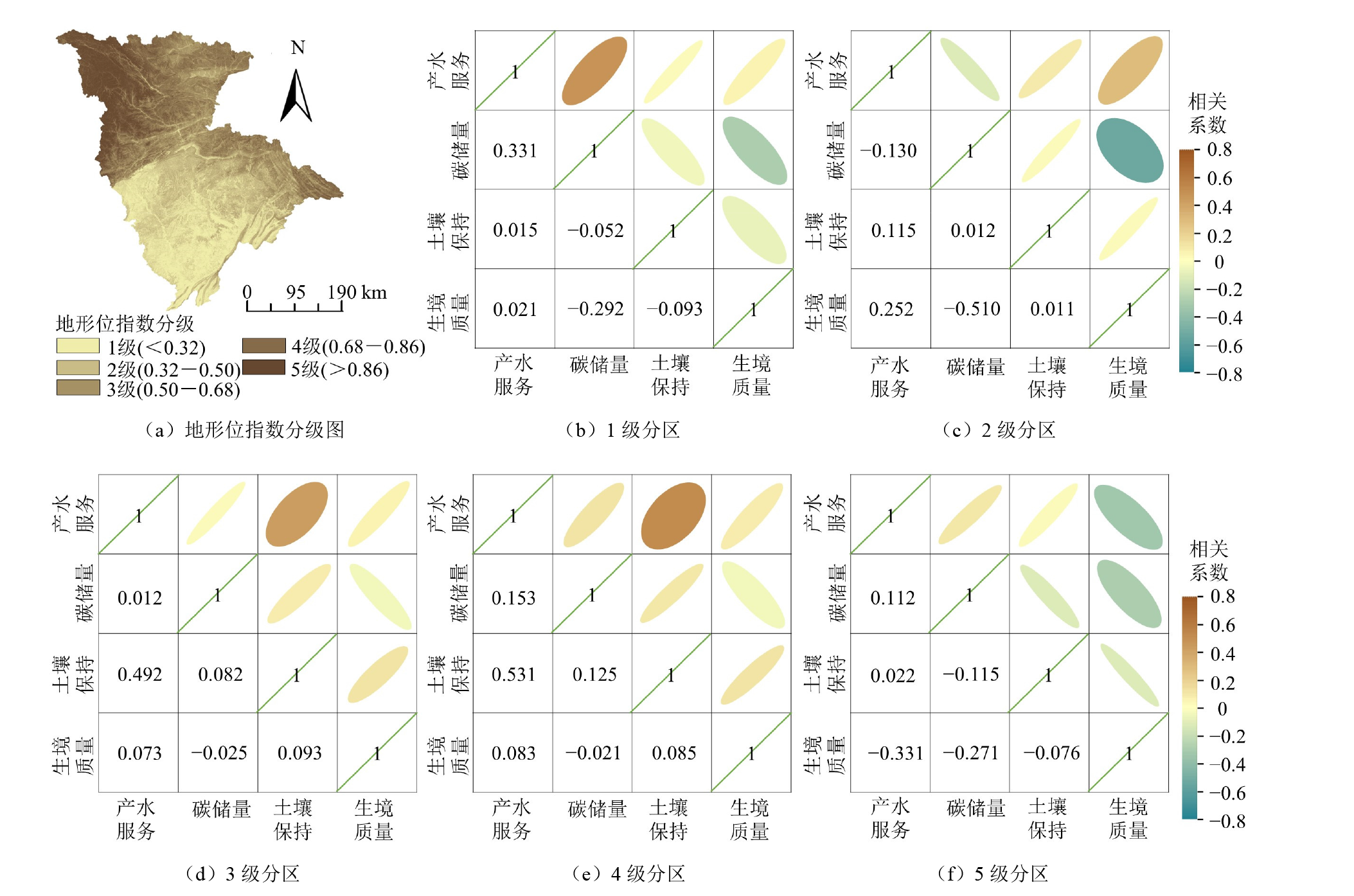
图7 嘉陵江流域各地形梯度分区生态系统服务权衡协同相关系数
Figure 7 Trade-offs and synergies correlation coefficients of ecosystem services in different topographic gradient zones of the Jialing River Basin
| [1] | BAGSTAD K J, SEMMENS D J, WAAGE S, et al., 2013. A comparative assessment of decision-support tools for ecosystem services quantification and valuation[J]. Ecosystem Services, 5: 27-39. |
| [2] | BOYD J, BANZHAF S, 2007. What are ecosystem services? The need for standardized environmental accounting units[J]. Ecological Economics, 63(2-3): 616-626. |
| [3] |
CARPENTER S R, MOONEY H A, AGARD J, et al., 2009. Science for managing ecosystem services: Beyond the millennium ecosystem assessment[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106(5): 1305-1312.
DOI PMID |
| [4] | CHEN X, SIVAPALAN M, 2020. Hydrological basis of the Budyko curve: Data-guided exploration of the mediating role of soil moisture[J]. Water Resources Research, 56(10): WR028221. |
| [5] | COSTANZA R, DARGE R, GROOT R, et al., 1998. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital[J]. Ecological Economics, 25(1): 3-15. |
| [6] | CUMMING G S, BUERKERT A, HOFFMANN E M, et al., 2014. Implications of agricultural transitions and urbanization for ecosystem services[J]. Nature, 515: 50-57. |
| [7] | HASSAN R M, SCHOLES R, ASH N, 2005. Ecosystems and human well-being: Biodiversity synthesis[M]. Washington DC: Island Press. |
| [8] | PENG J, XIA P, LIU Y X, et al., 2023. Ecosystem services research: From golden era to next crossing[J]. Transactions in Earth, Environment, and Sustainability, 1(1): 9-19. |
| [9] |
陈心盟, 王晓峰, 冯晓明, 等, 2021. 青藏高原生态系统服务权衡与协同关系[J]. 地理研究, 40(1): 18-34.
DOI |
| CHEN X M, WANG X F, FENG X M, et al., 2021. Ecosystem service trade-off and synergy on Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Geographical Research, 40(1): 18-34. | |
| [10] |
戴尔阜, 王晓莉, 朱建佳, 等, 2016. 生态系统服务权衡: 方法、模型与研究框架[J]. 地理研究, 35(6): 1005-1016.
DOI |
| DAI E F, WANG X L, ZHU J J, et al., 2016. Methods, tools and research framework of ecosystem service trade-offs[J]. Geographical Research, 35(6): 1005-1016. | |
| [11] |
戴尔阜, 王亚慧, 2020. 横断山区产水服务空间异质性及归因分析[J]. 地理学报, 75(3): 607-619.
DOI |
|
DAI E F, WANG Y H, 2020. Spatial heterogeneity and driving mechanisms of water yield service in the Hengduan Mountain region[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 75(3): 607-619.
DOI |
|
| [12] | 董鑫, 李艳忠, 董亭忆, 等, 2024. 基于GEE的嘉陵江流域生态环境质量演变及驱动因子分析[J/OL]. 广西科学, 1-12 [2025-3-24]. https://doi.org/10.13656/j.cnki.gxkx.20240912.001. |
| DONG X, LI Y Z, DONG T Y, et al., 2024. Analysis of Long-term Dynamic Evolution Characteristics and Driving Mechanism of Ecological Environment Quality in the Jialing River Basin Based on GEE[J/OL]. Guangxi Sciences, 1-12 [2025-3-24]. https://doi.org/10.13656/j.cnki.gxkx.20240912.001. | |
| [13] | 傅伯杰, 2010. 我国生态系统研究的发展趋势与优先领域[J]. 地理研究, 29(3): 383-396. |
| FU B J, 2010. Trends and priority areas in ecosystem research of China[J]. Geographical Research, 29(3): 383-396. | |
| [14] |
傅伯杰, 于丹丹, 2016. 生态系统服务权衡与集成方法[J]. 资源科学, 38(1): 1-9.
DOI |
|
FU B J, YU D D, 2016. Trade-off analyses and synthetic integrated method of multiple ecosystem services[J]. Resources Science, 38(1): 1-9.
DOI |
|
| [15] | 傅伯杰, 张军泽, 2024. 全球及中国可持续发展目标进展与挑战[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 39(5): 804-808. |
| FU B J, ZHANG J Z, 2024. Progress and challenges of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in the World and in China[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 39(5): 804-808. | |
| [16] |
高雅玉, 宋玉, 赵廷红, 等, 2024. 马莲河下游产水量时空演变特征[J]. 干旱区研究, 41(5): 776-787.
DOI |
|
GAO Y Y, SONG Y, ZHAO T H, et al., 2024. Spatiotemporal evolution of water yield in the lower Malian River Basin[J]. Arid Zone Research, 41(5): 776-787.
DOI |
|
| [17] | 郭丹, 蒋进元, 李莹杰, 等, 2022. 嘉陵江流域主要生态环境问题识别及建议[J]. 环境保护, 50(17): 33-36. |
| GUO D, JIANG J Y, LI Y J, et al., 2022. Main problems and countermeasures of ecological environment in Jialing River Basin[J]. Environmental Protection, 50(17): 33-36. | |
| [18] | 郭宗亮, 刘亚楠, 张璐, 等, 2022. 生态系统服务研究进展与展望[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 12(3): 928-936. |
| GUO Z L, LIU Y N, ZHANG L, et al., 2022. Research progress and prospect of ecosystem services[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 12(3): 928-936. | |
| [19] |
韩会庆, 张娇艳, 马庚, 等, 2018. 气候变化对生态系统服务影响的研究进展[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 42(2): 184-190.
DOI |
| HAN H Q, ZHANG J Y, MA G, et al., 2018. Advances on impact of climate change on ecosystem services[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 42(2): 184-190. | |
| [20] | 韩磊, 高毅丰, 常钰卿, 等, 2024. 黄土高原城镇化与生态系统服务脱钩关系[J]. 生态学报, 44(20): 9108-9121. |
| HAN L, GAO Y F, CHANG Y Q, et al., 2024. Decoupling relationship between urbanization and ecosystem services on the Loess Plateau[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 44(20): 9108-9121. | |
| [21] | 胡孟珂, 于欢, 孔博, 等, 2022. 2001-2020年嘉陵江流域植被覆盖度时空变化特征[J]. 人民长江, 53(1): 82-89, 96. |
| HU M K, YU H, KONG B, et al., 2022. Spatial-temporal variations of fractional vegetation coverage in Jialing River Basin from 2001 to 2020[J]. Yangtze River, 53(1): 82-89, 96. | |
| [22] | 虎帅, 张学儒, 官冬杰, 2018. 基于InVEST模型重庆市建设用地扩张的碳储量变化分析[J]. 水土保持研究, 25(3): 323-331. |
| HU S, ZHANG X R, GUAN D J, 2018. Analysis on carbon storage change of construction land expansion in Chongqing based on InVEST Model[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 25(3): 323-331. | |
| [23] | 李双成, 张才玉, 刘金龙, 等, 2013. 生态系统服务权衡与协同研究进展及地理学研究议题[J]. 地理研究, 32(8): 1379-1390. |
| LI S C, ZHANG C Y, LIU J L, et al., 2013. The tradeoffs and synergies of ecosystem services: Research progress, development trend, and themes of geography[J]. Geographical Research, 32(8): 1379-1390. | |
| [24] | 李婷, 吕一河, 2018. 生态系统服务建模技术研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 38(15): 5287-5296. |
| LI T, LÜ Y H, 2018. A review on the progress of modeling techniques in ecosystem services[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(15): 5287-5296. | |
| [25] |
廖洪圣, 卫伟, 石宇, 2024. 黄土丘陵区典型流域土壤侵蚀时空演变特征及其驱动机制: 以祖厉河为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 33(6): 908-918.
DOI |
| LIAO H S, WEI W, SHI Y, 2024. Characteristics of spatial and temporal evolution of soil erosion in typical watersheds in Loess Hilly Areas and its driving mechanisms: A case study of Zuli River[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 33(6): 908-918. | |
| [26] |
刘如龙, 赵媛媛, 陈国清, 等, 2024. 内蒙古黄河流域1990-2020年生境质量评估[J]. 干旱区研究, 41(4): 674-683.
DOI |
|
LIU R L, ZHAO Y Y, CHEN G Q, et al., 2024. Assessment of habitat quality in the Yellow River Basin in Inner Mongolia from 1990 to 2020[J]. Arid Zone Research, 41(4): 674-683.
DOI |
|
| [27] | 刘月, 赵文武, 贾立志, 等, 2019. 土壤保持服务: 概念、评估与展望[J]. 生态学报, 39(2): 432-440. |
| LIU Y, ZHAO W W, JIA L Z, et al., 2019. Soil conservation service: Concept, assessment, and outlook[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(2): 432-440. | |
| [28] | 潘竟虎, 李真, 2017. 干旱内陆河流域生态系统服务空间权衡与协同作用分析[J]. 农业工程学报, 33(17): 280-289. |
| PAN J H, LI Z, 2017. Analysis on trade-offs and synergies of ecosystems services in arid inland river basin[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 33(17): 280-289. | |
| [29] | 庞彩艳, 文琦, 丁金梅, 等, 2024. 黄河上游流域生态系统服务变化及权衡与协同关系研究[J]. 生态学报, 44(12): 5003-5013. |
| PANG C Y, WEN Q, DING J M, et al., 2024. Ecosystem services and their trade-offs and synergies in the upper reaches of the Yellow River basin[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 44(12): 5003-5013. | |
| [30] | 石秀秀, 2021. 习近平总书记关于长江经济带绿色发展重要论述研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学: 1-182. |
| SHI X X, 2021. Research on the general Secretary Xi Jinping’s important discourse on green development of the Yangtze River economic belt[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences: 1-182. | |
| [31] | 孙彦, 蔺星娜, 李生, 等, 2024. 贵州省生态系统服务权衡时空动态与驱动因子评估[J]. 环境科学学报, 44(9): 401-413. |
| SUN Y, LIN X N, LI S, et al., 2024. Spatiotemporal dynamics and driving factor assessment of ecosystem service trade-offs in Guizhou Province[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 44(9): 401-413. | |
| [32] | 谭晶华, 张运春, 张桥英, 等, 2024. 嘉陵江生态环境研究回顾与展望——基于文献计量的可视化分析[J]. 西华师范大学学报(自然科学版), 45(1): 9-16. |
| TAN J H, ZHANG Y C, ZHANG Q Y, et al., 2024. Review and prospect of ecological environment research on the Jialing River: visualized analysis based on bibliometric[J]. Journal of China West Normal University (Natural Sciences), 45(1): 9-16. | |
| [33] |
王劲峰, 徐成东, 2017. 地理探测器: 原理与展望[J]. 地理学报, 72(1): 116-134.
DOI |
|
WANG J F, XU C D, 2017. Geodetector: Principle and prospective[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 72(1): 116-134.
DOI |
|
| [34] | 王启名, 杨昆, 李立晓, 等, 2023. 滇池流域水文生态系统服务权衡与协同时空异质性及其归因分析[J]. 生态学报, 43(12): 4876-4891. |
| WANG Q M, YANG K, LI L X, et al., 2023. Spatio-temporal heterogeneity and attribution analysis of hydrological ecosystem services trade-offs and synergies in Dianchi Lake Basin[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 43(12): 4876-4891. | |
| [35] | 王万忠, 焦菊英, 1996. 中国的土壤侵蚀因子定量评价研究[J]. 水土保持通报 (5): 1-20. |
| WANG W Z, JIAO J Y, 1996. Quantitative evaluation on factors influencing soil erosion in China[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation (5): 1-20. | |
| [36] | 王奕淇, 孙学莹, 2025. 黄河流域生态系统服务权衡协同关系及其时空异质性[J]. 环境科学, 46(2): 972-989. |
| WANG Y Q, SUN X Y, 2025. Trade-off and synergy of ecosystem services in the Yellow River Basin and their spatiotemporal heterogeneity[J]. Environmental Science, 46(2): 972-989. | |
| [37] |
文志, 郑华, 欧阳志云, 等, 2020. 生物多样性与生态系统服务关系研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 31(1): 340-348.
DOI |
|
WEN Z, ZHENG H, OUYANG Z Y, et al., 2020. Research progress on the relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem services[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 31(1): 340-348.
DOI |
|
| [38] | 杨强强, 徐光来, 李爱娟, 等, 2021. 青弋江流域生态系统服务评估与权衡研究[J]. 生态学报, 41(23): 9315-9327. |
| YANG Q Q, XU G L, LI A J, et al., 2021. Evaluation and trade-off of ecosystem services in the Qingyijiang River Basin[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(23): 9315-9327. | |
| [39] | 袁乐, 阿不都克依木·阿布力孜, 于苏云江·吗米提敏, 等, 2024. 基于生态系统服务簇的生态功能区权衡与协同关系演变: 以吐哈地区为例[J/OL]. 环境科学, 1-21 [2025-3-24]. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.202404272. |
| YUAN L, ABULIZI A, MAMITIMIN Y, et al., 2024. Evolution of trade-offs and synergies in eco-functional zones based on ecosystem service bundles: A case study of the Turpan-Hami region[J/OL]. Environmental Science, 1-21 [2025-3-24]. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.202404272. | |
| [40] | 张继平, 刘春兰, 王辉, 等, 2025. 基于生态系统服务及其权衡关系时空演变特征的生态功能分区研究: 以潮白河流域为例[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 41(1): 61-71. |
| ZHANG J P, LIU C L, WANG H, et al., 2025. Ecological function zoning based on the spatial-temporal change pattern of ecosystem services and their trade-offs: A Case study of the Chaobai River basin[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 41(1): 61-71. | |
| [41] | 张竞哲, 莫淑红, 蒋凯鑫, 等, 2023. 基于模型适用性分析的嘉陵江流域降雨侵蚀力时空演变特征[J/OL]. 西安理工大学学报, 1-9 [2025-3-24]. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/61.1294.N.20231016.1914.004. |
| ZHANG J Z, MO S H, JIANG K X, et al., 2023. Spatial and temporal evolutionary characteristics of rainfall erosivity in Jialing River Basin using applicability analysis of model[J/OL]. Journal of Xi’an University of Technology, 1-9 [2025-3-24]. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/61.1294.N.20231016.1914.004. | |
| [42] |
张维琛, 王惺琪, 王博杰, 2024. 塔布河流域生态系统服务时空格局及影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 33(7): 1142-1152.
DOI |
| ZHANG W C, WANG X Q, WANG B J, 2024. Spatiotemporal Pattern and Influencing Factors of the Ecosystem Services in the Tabu River Basin[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 33(7): 1142-1152. | |
| [43] |
张小瑜, 周自翔, 唐志雄, 等, 2024. 无定河流域生境质量时空变化及预测[J]. 中国沙漠, 44(3): 75-84.
DOI |
|
ZHANG X Y, ZHOU Z X, TANG Z X, et al., 2024. Spatio-temporal variation and prediction of habitat quality in Wuding River Basin[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 44(3): 75-84.
DOI |
|
| [44] | 赵宾华, 马方铭, 李占斌, 等, 2023. 嘉陵江流域潜在蒸散发时空演变特征及其影响因素[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 34(5): 43-51. |
| ZHAO B H, MA F M, LI Z B, et al., 2023. Temporal and spatial evolution characteristics of potential evapotranspiration and its influencing factors in Jialing River Basin[J]. Journal of Water Resources & Water Engineering, 34(5): 43-51. | |
| [45] |
赵文武, 刘月, 冯强, 等, 2018. 人地系统耦合框架下的生态系统服务[J]. 地理科学进展, 37(1): 139-151.
DOI |
|
ZHAO W W, LIU Y, FENG Q, et al., 2018. Ecosystem services for coupled human and environment systems[J]. Progress in Geography, 37(1): 139-151.
DOI |
|
| [46] | 朱月华, 2023. 社会生态视角下嘉陵江流域生态系统服务时空变化及其权衡/协同关系[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学: 1-80. |
| ZHU Y H, 2023. Spatiotemporal changes of ecosystem services and their tradeoffs/synergies in the Jialingjiang Watershed, China from the perspective of social-ecological system[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University: 1-80. |
| [1] | 黄霄宇, 李欢欢, 王新宇, 王进欣. 中国黄泛区生态系统服务供需匹配特征及冲突识别[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(6): 863-875. |
| [2] | 周瑞娇, 张虹, 钱敏. 近30年三峡库区生态系统服务流时空演变与影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(6): 876-887. |
| [3] | 杨昊彧, 黄康江, 陈晓东, 赵劼, 熊军, 田康. 贵州省生态空间效率演变及景观格局的影响归因[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(6): 902-913. |
| [4] | 吴雨桐, 於冉, 余祺琪, 王成, 张紫涵. 皖江流域生境质量评价及多情景优化研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(6): 961-973. |
| [5] | 赵志轩, 魏芳菲, 吴皓天, 王怡宁, 王澎喆. 澜沧江-湄公河流域生态系统服务价值对土地利用变化的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(5): 688-698. |
| [6] | 张洪波, 尹班, 李春勇, 崔松云, 和艳, 李小红, 邓丽仙. 近40年红河流域(中国部分)水源涵养功能动态演变特征及驱动因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(4): 556-569. |
| [7] | 李曼, 吴东丽, 何昊, 余慧婕, 赵琳, 刘聪, 胡正华, 李琪. 1990-2020年黄河流域碳储量时空演变及驱动因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(3): 333-344. |
| [8] | 郭昭, 师芸, 刘铁铭, 张雨欣, 闫永智. 2001-2020年秦岭北麓NPP时空格局及驱动因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(3): 401-410. |
| [9] | 张任菲, 肖萌, 刘志成. 京津冀地区景观破碎化的时空异质性及驱动因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(3): 461-473. |
| [10] | 张继, 杨世琦, 赵磊, 冯介玲, 陈艳英. 基于InVEST模型的重庆市“一带三屏”生境质量时空演变特征分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(2): 167-180. |
| [11] | 陶德凯, 张子建. 江苏省国土空间绿色发展水平与生态系统服务耦合协同关系研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(2): 181-196. |
| [12] | 马月伟, 陈玉美, 张盛蓝, 桂雅丽, 陈艳梅. 夹金山脉大熊猫栖息地生境质量与人类活动强度耦合协调研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(2): 197-208. |
| [13] | 赵乐鋆, 王诗瑶, 赵子渝, 洪星, 李夫星, 吴佳仪, 华婧妤. 2008-2022年华北平原七省市AOD时空变化特征及主要影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(2): 256-267. |
| [14] | 赵忠宝, 李婧, 刘小丹, 柏祥, 刘昊野, 徐晓娜, 耿世刚, 鲁少波. 河北省森林生态产品价值评估及其空间分布驱动因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(2): 321-332. |
| [15] | 叶俊宏, 刘珍环, 刘子瑜. 珠江三角洲城市群国土空间生态修复分区情景模拟[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(1): 4-12. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
