生态环境学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (5): 679-688.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.05.002
收稿日期:2024-02-18
出版日期:2024-05-18
发布日期:2024-06-27
通讯作者:
* 石艳军。E-mail: 251670231@qq.com作者简介:何沐全(1991年生),男,工程师,硕士研究生,主要从事生态与农业遥感研究。E-mail: wxzhmq@outlook.com
基金资助:
HE Muquan( ), SHI Yanjun*(
), SHI Yanjun*( ), WANG Chenxi, LUO Zuhong, ZHANG Shaotong
), WANG Chenxi, LUO Zuhong, ZHANG Shaotong
Received:2024-02-18
Online:2024-05-18
Published:2024-06-27
摘要:
植被生态质量体现了植被的生产功能、多样性和服务功能,其变化受气象条件和人类活动的共同影响,科学地评估植被变化的气象条件贡献率对区域生态修复和应对气候变化具有重要的意义。以广东省为例,基于中国气象局发布的NDVI、FVC、NPP和气象条件贡献率等数据,运用统计分析与空间分析方法,探讨了广东省植被生态质量的时空分布特征,并定量评估了气象条件对广东植被变化的贡献。结果表明:1)2001-2022年,广东省的NDVI、FVC和NPP均呈波动上升变化,三者的年平均变化范围分别为0.494-0.627、0.594-0.706和C 831-1.15×103 g∙m−2,多年平均值分别为0.565、0.653和C 976 g∙m−2,峰值分别出现于2016年(NPP)、2021年(NDVI)、2022年(FVC),谷值出现于2005年(NDVI、FVC)和2003年(NPP);2)空间上,广东省植被生态质量存在明显的区域差异,表现为粤北>粤东北>粤西>粤东>珠三角,其中阳江、肇庆、云浮、清远、韶关等城市植被生态质量较好,东莞、佛山较差;3)近20多年来气象条件对广东省植被生态质量变化的影响以正贡献为主,气象条件贡献率整体以−1.60×10−2/a的变化率呈波动下降趋势,气象条件对广东植被变化的影响总体变小;4)气象条件对粤北植被的影响以正向驱动为主,对粤东、粤西以负向驱动为主且对粤东的影响程度大于粤西,其中2007、2017-2018、2020-2022年气象条件对广东植被生态质量变化影响以负贡献为主,2022年呈高度负贡献。气象因素对广东植被生态质量变化的影响较大且存在明显的区域差异,在气象条件相对稳定的情况下,植被长势明显变好。
中图分类号:
何沐全, 石艳军, 王晨茜, 罗祖红, 张少通. 广东省植被生态质量演变与气象条件贡献分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(5): 679-688.
HE Muquan, SHI Yanjun, WANG Chenxi, LUO Zuhong, ZHANG Shaotong. Spatiotemporal Distribution Characteristics of Vegetation Ecology and Its Meteorological Contribution in Guangdong Province[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(5): 679-688.
| 分级指标 | 评价等级 | 释义 |
|---|---|---|
| 高度正贡献 | 气象条件极有利于植被生态质量提升 | |
| 0.1< | 中度正贡献 | 气象条件有利于植被生态质量提升 |
| −0.1≤ | 微贡献 | 气象条件对植被生态质量影响不显著 |
| −1< | 中度负贡献 | 气象条件不利于植被生态质量提升 |
| 高度负贡献 | 气象条件极不利于植被生态质量提升 |
表1 气象条件贡献率评价等级
Table 1 Evaluation level of contribution rate of meteorological conditions
| 分级指标 | 评价等级 | 释义 |
|---|---|---|
| 高度正贡献 | 气象条件极有利于植被生态质量提升 | |
| 0.1< | 中度正贡献 | 气象条件有利于植被生态质量提升 |
| −0.1≤ | 微贡献 | 气象条件对植被生态质量影响不显著 |
| −1< | 中度负贡献 | 气象条件不利于植被生态质量提升 |
| 高度负贡献 | 气象条件极不利于植被生态质量提升 |

图7 2001-2022年广东省植被生态质量变化气象条件贡献率分级空间分布
Figure 7 Spatial distribution of meteorological condition contribution rate classification for changes in vegetation ecological quality in Guangdong Province from 2001 to 2022
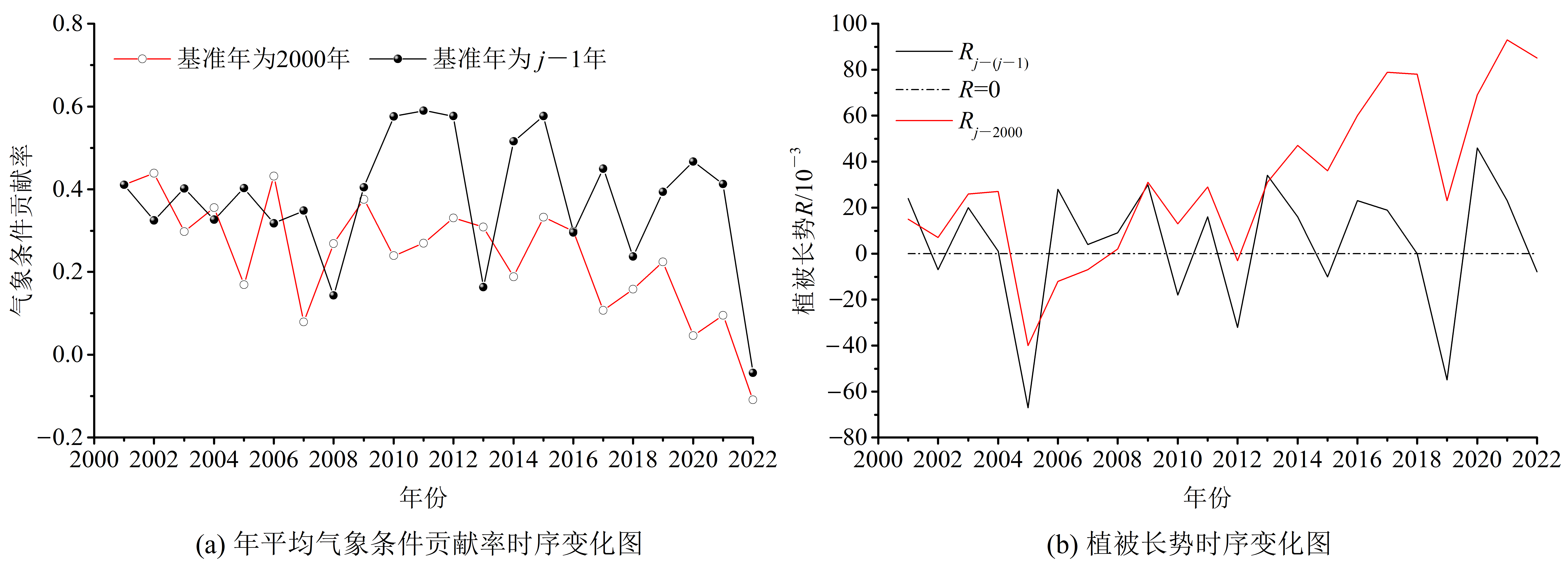
图8 2001-2022年广东省植被生态质量变化气象条件贡献率和植被长势时序图
Figure 8 The time series of meteorological condition contribution rate and vegetation growth in Guangdong Province from 2001 to 2022
| [1] | ANNALA L, HONKAVAARA E, TUOMINEN S, et al., 2020. Chlorophyll concentration retrieval by training convolutional neural network for stochastic model of leaf optical properties (SLOP) inversion[J]. Remote Sensing, 12(283): 1-22. |
| [2] | CHENG D D, QI G Z, SONG J X, et al., 2021. Quantitative assessment of the contributions of climate change and human activities to vegetation variation in the Qinling Mountains[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 9: 782287. |
| [3] | HE Y, QIU H J, SONG J X, et al., 2019. Quantitative contribution of climate change and human activities to runoff changes in the Bahe River watershed of the Qinling Mountains, China[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 51(1-3): 101729. |
| [4] | JIAPAER G, CHEN X, BAO A M, 2011. A comparison of methods for estimating fractional vegetation cover in arid regions[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 151(12): 1698-1710. |
| [5] | KALAITZIDIS C, HEINZEL V, ZIANIS D, 2010. A review of multispectral vegetation indices for biomass estimation[C]// Chania. Proceedings of the 29th symposium of the European association of remote sensing laboratories. Greece: IOS Press Ebook: 201-208. |
| [6] | LIU Y, LIU H H, CHEN Y, et al., 2022. Quantifying the contributions of climate change and human activities to vegetation dynamic in China based on multiple indices[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 838(Part 4): 156553. |
| [7] | RAMMIG A, MAHECHA M D, 2015. Ecosystem responses to climate extremes[J]. Nature, 527(7578): 315-316. |
| [8] | ROUSE J W, HAAS R H, SCHELL J A, et al., 1974. Monitoring vegetation systems in the great plains with Erts[J]. NASA Special Publication, 351(1): 309. |
| [9] | SELLERS P J, 1985. Canopy reflectance, photosynthesis and transpiration[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 6(8): 1335-1372. |
| [10] | WANG S, ZHANG B, XIE G D, et al., 2020. Vegetation cover changes and sand-fixing service responses in the Beijing-Tianjin sandstorm source control project area[J]. Environmental Development, 34: 100455. |
| [11] | 曹云, 孙应龙, 陈紫璇, 等, 2022. 2000-2020年黄河流域植被生态质量变化及其对极端气候的响应[J]. 生态学报, 42(11): 4524-4535. |
| CAO Y, SUN Y L, CHEN Z X, et al., 2022. Dynamic changes of vegetation ecological quality in the Yellow River Basin and its response to extreme climate during 2000-2020[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42(11): 4524-4535. | |
| [12] |
常屹冉, 张弛, 魏嘉诚, 等, 2023. 气候变化和人类活动对内蒙古植被净初级生产力的影响[J]. 草地学报, 31(11): 3444-3452.
DOI |
| CHANG Y R, ZHANG C, WEI J C, et al., 2023. Impacts of climate change and human activities on the net primary productivity of vegetation in Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 31(11): 3444-3452. | |
| [13] |
陈文裕, 夏丽华, 徐国良, 等, 2022. 2000-2020年珠江流域NDVI动态变化及影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 31(7): 1306-1316.
DOI |
| CHEN W Y, XIA L H, XU G L, et al., 2022. Dynamic variation of NDVI and its influencing factors in the Pearl River Basin from 2000 to 2020[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 31(7): 1306-1316. | |
| [14] | 陈晓杰, 张长城, 张金亭, 等, 2022. 基于CASA模型的植被净初级生产力时空演变格局及其影响因素——以湖北省为例[J]. 水土保持研究, 29(3): 253-261. |
| CHEN X J, ZHANG C C, ZHANG J T, et al., 2022. Analysis of the spatiotemporal evolution patterns of vegetation net primary productivity and its influencing factors based on CASA model[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 29(3): 253-261. | |
| [15] | 崔浩楠, 罗海江, 张学珍, 2021. 1982-2019年长江经济带植被覆盖变化的时空特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 40(8): 2517-2529. |
| CUI H N, LUO H J, ZHANG X Z, 2021. Temporal and spatial characteristics of green vegetation cover changes in the Yangtze River Economic Belt from 1982-2019[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 40(8): 2517-2529. | |
| [16] |
邓玉娇, 王捷纯, 徐杰, 等, 2021. 广东省NDVI时空变化特征及其对气候因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(1): 37-43.
DOI |
| DENG Y J, WANG J C, XU J, et al., 2021. Spatiotemporal variation of NDVI and its response to climatic factors in Guangdong Province[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(1): 37-43. | |
| [17] |
邓玉娇, 王捷纯, 徐杰, 等, 2022. 广东省植被固碳量时空变化及气象贡献率研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 31(1): 1-8.
DOI |
| DENG Y J, WANG J C, XU J, et al., 2022. Spatiotemporal variation of vegetation carbon sequestration and its meteorological contribution in Guangdong Province[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 31(1): 1-8. | |
| [18] | 方贺, 严佩文, 石见, 等, 2022. 阿克苏地区植被生态质量时空变化及其驱动机制[J]. 干旱区研究, 39(6): 1907-1916. |
| FANG H, YAN P W, SHI J, et al., 2022. Temporal and spatial variation of vegetation ecological quality and its driving mechanism in Aksu prefecture[J]. Arid Zone Research, 39(6): 1907-1916. | |
| [19] | 方贺, 张育慧, 何月, 等, 2023. 浙江省植被生态质量时空变化及其驱动因素分析[J]. 自然资源遥感, 35(2): 245-254. |
| FANG H, ZHANG Y H, HE Y, et al., 2023. Spatio-temporal variations of vegetation ecological quality in Zhejiang Province and their driving factors[J]. Remote Sensing for Natural Resources, 35(2): 245-254. | |
| [20] | 冯娴慧, 曾芝琳, 张德顺, 2022. 基于MODIS NDVI数据的粤港澳大湾区植被覆盖时空演变[J]. 中国城市林业, 20(1): 1-6. |
| FENG X H, ZENG Z L, ZHANG D S, 2022. Temporal-spatial evolution of vegetation coverage in Guangdong-HongKong-Macao greater bay area based on MODIS NDVI data[J]. Journal of Chinese Urban Forestry, 20(1): 1-6. | |
| [21] | 耿庆玲, 陈晓青, 赫晓慧, 等, 2022. 中国不同植被类型归一化植被指数对气候变化和人类活动的响应[J]. 生态学报, 42(9): 3557-3568. |
| GENG Q L, CHEN X Q, HE X H, et al., 2022. Vegetation dynamics and its response to climate change and human activities based on different vegetation types in China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42(9): 3557-3568. | |
| [22] | 韩静, 张国峰, 李伟光, 等, 2022. 近20年海南岛植被生态质量变化特征分析[J]. 生态科学, 41(1): 20-30. |
| HAN J, ZHANG G F, LI W G, et al., 2022. Analysis on the change characteristics of vegetation ecological quality in Hainan Island in recent 20 years[J]. Ecological Science, 41(1): 20-30. | |
| [23] |
何全军, 2019. 基于MODIS数据的珠三角地区NDVI时空变化特征及对气象因素的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(9): 1722-1730.
DOI |
| HE Q J, 2019. Spatio-temporal variation of NDVI and its response to meteorological factors in Pearl River Delta based on MODIS data[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28(9): 1722-1730. | |
| [24] | 侯鑫, 2022. 森林绿度异常的时空动态变化及其驱动因素分析[D]. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学: 1-50. |
| HOU X, 2022. Temporal and spatial dynamics of forest greenness anomaly and its driving factors[D]. Xianyang: Northwest A&F University: 1-50. | |
| [25] | 侯鑫, 赵杰, 赵洪飞, 等, 2022. 2003-2018年干旱对中国森林绿度异常的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 42(1): 336-344. |
| HOU X, ZHAO J, ZHAO H F, et al., 2022. Drought effects on forest greenness anomalies in China from 2003 to 2018[J]. China Environmental Science, 42(1): 336-344. | |
| [26] | 金凯, 2019. 中国植被覆盖时空变化及其与气候和人类活动的关系[D]. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学: 1-147. |
| JIN K, 2019. Spatio-temporal variations of vegetation cover and its relationships between climate change and human activities over China[D]. Xianyang: Northwest A & F University: 1-147. | |
| [27] |
金凯, 王飞, 韩剑桥, 等, 2020. 1982-2015年中国气候变化和人类活动对植被NDVI变化的影响[J]. 地理学报, 75(5): 961-974.
DOI |
|
JIN K, WANG F, HAN J Q, et al., 2020. Contribution of climatic change and human activities to vegetation NDVI change over China during 1982-2015[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 75(5): 961-974.
DOI |
|
| [28] | 赖金林, 齐实, 廖瑞恩, 等, 2023. 2000-2019年西南高山峡谷区植被变化对气候变化和人类活动的响应[J]. 农业工程学报, 39(14): 155-163. |
| LAI J L, QI S, LIAO R E, et al., 2023. Vegetation change responses to climate change and human activities in southwest alpine canyon areas of China from 2000 to 2019[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 39(14): 155-163. | |
| [29] | 李超, 李雪梅, 2021. 2000-2018年中国植被生态质量时空变化特征[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 30(9): 2154-2165. |
| LI C, LI X M, 2021. Characteristics of spatio-temporal variation of ecological quality for vegetation in China from 2000-2018[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 30(9): 2154-2165. | |
| [30] | 李长爱, 郭春凤, 刘玲, 等, 2023. 8种园林灌木光合特性及固碳释氧能力分析[J]. 西北农业学报, 32(9): 1411-1421. |
| LI C A, GUO C F, LIU L, et al., 2023. Photosynthetic characteristics and capacities of carbon sequestration and oxygen release in eight ornamental shrubs[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 32(9): 1411-1421. | |
| [31] |
林纾, 李红英, 黄鹏程, 等, 2022. 2022年夏季我国高温干旱特征及其环流形势分析[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5): 748-763.
DOI |
| LIN S, LI H Y, HUANG P C, et al., 2022. Characteristics of high temperature, drought and circulation situation in summer 2022 in China[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 40(5): 748-763. | |
| [32] | 刘华, 2021. 亚热带植被覆盖度和净初级生产力时空演变及气候驱动[D]. 杭州: 浙江农林大学: 1-49. |
| LIU H, 2021. Spatiotemporal evolution of fractional vegetation cover and net primary productivity in the Subtropical Region and climate[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang A & F University: 1-49. | |
| [33] | 刘可, 杜灵通, 侯静, 等, 2018. 近30年中国陆地生态系统NDVI时空变化特征[J]. 生态学报, 38(6): 1885-1896. |
| LIU K, DU L T, HOU J, et al., 2018. Spatiotemporal variations of NDVI in terrestrial ecosystems in China from 1982-2012[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(6): 1885-1896. | |
| [34] | 路利杰, 王立辉, 李扬, 等, 2023. 丹江口库区2001-2020年植被生态系统质量遥感监测与时空演变分析[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 32(6): 1291-1304. |
| LU L J, WANG L H, LI Y, et al., 2023. Remote sensing monitoring and spatial temporal pattern evolution analysis of the vegetation ecosystem quality in the Danjiangkou Reservoir Area from 2001 to 2020[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 32(6): 1291-1304. | |
| [35] | 毛智慧, 黎丽莉, 程露, 等, 2023. 广东省植被叶面积指数时空变化特征及其影响因素[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 45(4): 907-919. |
| MAO Z H, LI L L, CHENG L, et al., 2023. Spatio-temporal variation of vegetation leaf area index and its influencing factors in Guangdong Province, China[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 45(4): 907-919. | |
| [36] | 朴世龙, 张新平, 陈安平, 等, 2019. 极端气候事件对陆地生态系统碳循环的影响[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 49(9): 1321-1334. |
| PIAO S L, ZHANG X P, CHEN A P, et al., 2019. The impacts of climate extremes on the terrestrial carbon cycle: A review[J]. Science China: Terrae, 49(9): 1321-1334. | |
| [37] | SHOBAIRI S O, 荣媛, 李明阳, 等, 2017. 广东省植被覆盖度时空变化及驱动因素分析[J]. 西南林业大学学报, 37(1): 144-148, 169. |
| SHOBAIRI S O, RONG Y, LI M Y, et al., 2017. Analysis of spatial-temporal dynamics and driving factors of vegetation fractional coverage in Guangdong Province[J]. Journal of Southwest Forestry University, 34(1): 144-148, 169. | |
| [38] | 王思, 张路路, 林伟彪, 等, 2022. 基于MODIS归一化植被指数的广东省植被覆盖与土地利用变化研究[J]. 生态学报, 42(6): 2149-2163. |
| WANG S, ZHANG L L, LING W B, et al., 2022. Study on vegetation coverage and land-use change of Guangdong Province based on MODIS-NDVI[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42(6): 2149-2163. | |
| [39] |
王田野, 王平, 吴泽宁, 等, 2023. 干旱胁迫下植被生态韧性研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 38(8): 790-801.
DOI |
|
WANG T Y, WANG P, WU Z N, et al., 2023. Progress in the study of ecological resilience of vegetation under drought stress[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 38(8): 790-801.
DOI |
|
| [40] |
王雪梅, 杨雪峰, 赵枫, 等, 2023. 基于机器学习算法的干旱区绿洲地上生物量估算[J]. 生态环境学报, 32(6): 1007-1015.
DOI |
| WANG X M, YANG X F, ZHAO F, et al., 2023. Estimation of aboveground biomass in the arid oasis based on the machine learning algorithm[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 32(6): 1007-1015. | |
| [41] | 徐勇, 黄海艳, 戴强玉, 等, 2023a. 西南地区陆地植被生态系统NPP时空演变及驱动力分析[J]. 环境科学, 44(5): 2704-2714. |
| XU Y, HUANG H Y, DAI Q Y, et al., 2023a. Spatial-temporal variation in net primary productivity in terrestrial vegetation ecosystems and its driving forces in Southwest China[J]. Environmental Science, 44(5): 2704-2714. | |
| [42] | 徐勇, 卢云贵, 戴强玉, 等, 2023b. 气候变化和土地利用变化对长江中下游地区植被NPP变化相对贡献分析[J]. 中国环境科学, 43(9): 4988-5000. |
| XU Y, LU Y G, DAI Q Y, et al., 2023b. Assessment of the relative contribution of climate change and land use change on net primary productivity variation in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River Basin[J]. China Environmental Science, 43(9): 4988-5000. | |
| [43] | 许幼霞, 周旭, 赵翠薇, 等, 2017. 1990-2015年间贵州省植被生态环境质量变化特征[J]. 地球与环境, 45(4): 434-440. |
| XU Y X, ZHOU X, ZHAO C W, et al., 2017. Analysis of vegetation eco-environment quality change features in Guizhou Province from 1990 to 2015[J]. Earth and Environment, 45(4): 434-440. | |
| [44] |
杨鑫, 曹文侠, 鱼小军, 等, 2021. 基于近20年MODIS NDVI日数据的青海省草地资源动态监测及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 草业学报, 30(9): 1-14.
DOI |
|
YANG X, CAO W X, YU X J, et al., 2021. Dynamic monitoring of grassland resources and their responses to environmental factors in Qinghai Province based on analyses of daily MODIS NDVI data from the past 20 years[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 30(9): 1-14.
DOI |
|
| [45] | 杨远航, 尹家波, 郭生练, 等, 2023. 中国陆域干旱演变预估及其生态水文效应[J]. 科学通报, 68(7): 817-829. |
| YANG Y H, YIN J B, GUO S L, et al., 2023. Projection of terrestrial drought evolution and its eco-hydrological effects in China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 68(7): 817-829. | |
| [46] | 殷崎栋, 柳彩霞, 田野, 2021. 基于MODIS NDVI数据的陕西省植被绿度时空变化及人类活动影响[J]. 生态学报, 41(4): 1571-1582. |
| YIN Q D, LIU C X, TIAN Y, 2021. Spatio-temporal greenness and anthropogenic analysis in Shaanxi based on MODIS NDVI from 2001 to 2018[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(4): 1571-1582. | |
| [47] | 于忠亮, 付世萃, 王梓默, 等, 2022. 吉林省辽河流域不同植被类型土壤水源涵养能力分析[J]. 中国水土保持, 7: 51-55. |
| YU Z L, FU S C, WANG Z M, et al., 2022. Water conservation capacity of different vegetation types in Liaohe River Basin of Jilin Province[J]. Soil and Water Conservation in China, 7: 51-55. | |
| [48] | 岳祝, 2019. 中国大陆沿海地区极端气温和降水时空趋势及其对植被生长的影响[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学: 1-82. |
| YUE Z, 2019. Temporal and Spatial Trends of extreme temperature and precipitation in coastal areas of mainland China and their effects on vegetation[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University: 1-82. | |
| [49] |
张晶, 郝芳华, 吴兆飞, 等, 2023. 植被物候对极端气候响应及机制[J]. 地理学报, 78(9): 2241-2255.
DOI |
|
ZHANG J, HAO F H, WU Z F, et al., 2023. Response of vegetation phenology to extreme climate and its mechanism[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 78(9): 2241-2255.
DOI |
|
| [50] | 张琳, 宋创业, 袁伟影, 等, 2023. 基于地面调查的植被生态质量综合评估指标体系构建[J]. 生态学报, 43(1): 128-139. |
| ZHANG L, SONG C Y, YUAN W Y, et al., 2023. Construction of comprehensive evaluation index system of vegetation ecological quality based on field survey[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 43(1): 128-139. | |
| [51] | 张猛, 曾永年, 2018. 融合高时空分辨率数据估算植被净初级生产力[J]. 遥感学报, 22(1): 143-152. |
| ZHANG M, ZENG Y N, 2018. Net primary production estimation by using fusion remote sensing data with high spatial and temporal resolution[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 22(1): 143-152. | |
| [52] | 张强, 姚玉璧, 李耀辉, 等, 2020. 中国干旱事件成因和变化规律的研究进展与展望[J]. 气象学报, 78(3): 500-521. |
| ZHANG Q, YAO Y B, LI Y H, et al., 2020. Progress and prospect on the study of causes and variation regularity of droughts in China[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 78(3): 500-521. | |
| [53] | 张世喆, 朱秀芳, 刘婷婷, 等, 2022. 气候变化下中国不同植被区总初级生产力对干旱的响应[J]. 生态学报, 42(8): 3429-3440. |
| ZHANG S Z, ZHU X F, LIU T T, et al., 2022. Response of gross primary production to drought under climate change in different vegetation regions of China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42(8): 3429-3440. | |
| [54] | 赵燕红, 侯鹏, 蒋金豹, 等, 2021. 植被生态遥感参数定量反演研究方法进展[J]. 遥感学报, 25(11): 2173-2197. |
| ZHAO Y H, HOU P, JIANG J B, et al., 2021. Progress in quantitative inversion of vegetation ecological remote sensing parameters[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin, 25(11): 2173-2197. | |
| [55] | 周波涛, 钱进, 2021. IPCC AR6报告解读: 极端天气气候事件变化[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 17(6): 713-718. |
| ZHOU B T, QIAN J, 2021. Changes of weather and climate extremes in the IPCC AR6[J]. Climate Change Research, 17(6): 713-718. | |
| [56] | 周广胜, 周莉, 周怀林, 等, 2023. 植被生态质量的气候变化影响评价方法: GB/T 42961—2023[S]. 北京: 国家市场监督管理总局, 国家标准化管理委员会: 1-10. |
| ZHOU G S, ZHOU L, ZHOU H L, et al., 2023. Assessment method for climate change impact on vegetation ecological quality: GB/T 42961—2023[S]. Beijing: State Administration for Market Regulation, Standardization Administration: 1-10. | |
| [57] |
周贵尧, 周灵燕, 邵钧炯, 等, 2020. 极端干旱对陆地生态系统的影响:进展与展望[J]. 植物生态学报, 44(5): 515-525.
DOI |
| ZHOU G Y, ZHOU L Y, SHAO J J, et al., 2020. Effects of extreme drought on terrestrial ecosystems: Review and prospects[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 44(5): 515-525. |
| [1] | 张杨, 徐永明, 卢响军, 莫亚萍, 吉蒙, 祝善友. 基于OCO-2遥感数据的新疆维吾尔自治区大气XCO2空间化研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(2): 231-241. |
| [2] | 李佳婧, 梁咏亮, 李静尧, 李小伟, 杨君珑. 基于叶片功能性状的贺兰山西坡植物生态策略分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(1): 45-53. |
| [3] | 袁茜, 傅开道, 陶雨晨, 张年, 杨丽莎. 澜沧江(云南段)水-气界面氧化亚氮释放通量时空分布特征及其影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(1): 54-61. |
| [4] | 宁健, 程晓波, 苏超丽, 汤泽平, 余泽峰. 广东省伴生放射性矿周围土壤放射性水平分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(9): 1692-1699. |
| [5] | 倪广艳. 外来植物入侵对生态系统碳循环影响的研究概述[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1325-1332. |
| [6] | 王雪梅, 杨雪峰, 赵枫, 安柏耸, 黄晓宇. 基于机器学习算法的干旱区绿洲地上生物量估算[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1007-1015. |
| [7] | 巫晨煜, 许帆帆, 魏士博, 樊晶晶, 刘观鹏, 王坤. 渭河流域地表植被覆盖对气候变化的响应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 835-844. |
| [8] | 李晖, 李必龙, 葛黎黎, 韩琛惠, 杨倩, 张岳军. 2000-2021年汾河流域植被时空演变特征及地形效应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 439-449. |
| [9] | 吴雅睿, 王美景, 王涛, 杨梅焕. 新冠疫情下NO2时空变化特征——以陕西省为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 514-524. |
| [10] | 张鐥文, 杨冉, 侯文星, 王丽丽, 刘爽, 宋汉扬, 赵文吉, 李令军. 生态补水前后永定河两岸植被覆盖度变化及驱动力分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 264-273. |
| [11] | 李姝亭, 胡冠九, 罗小三. 大气环境中全(多)氟烷基化合物(PFASs)的来源、分布及健康风险研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(12): 2103-2114. |
| [12] | 鲁言波, 陈湛峰, 李彤. 基于改进TOPSIS模型的广东省主要湖库水质特征分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(12): 2194-2206. |
| [13] | 刘明宇, 郑旭, 强丽媛, 李鲁华, 张若宇, 王家平. 1994-2020年中国农用薄膜使用量变化与农膜微塑料污染现状分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(11): 2050-2061. |
| [14] | 樊艳翔, 雷社平, 解建仓. 广东省河流水体富营养化综合评价及分异特征——基于博弈论组合赋权法与VIKOR模型[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(10): 1811-1821. |
| [15] | 孙正, 曹亚非, 王德彩, 刘峰, 宋效东, 张甘霖, 吴华勇. 近30年京津冀电镀场地时空演变特征及趋势预测[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 183-194. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
