生态环境学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (3): 514-524.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.03.009
收稿日期:2022-11-22
出版日期:2023-03-18
发布日期:2023-06-02
作者简介:吴雅睿(1984年生),女,副教授,博士,主要从事环境监测与治理研究。E-mail: wuyarui@xust.edu.cn
基金资助:
WU Yarui1( ), WANG Meijing1, WANG Tao1,2, YANG Meihuan1
), WANG Meijing1, WANG Tao1,2, YANG Meihuan1
Received:2022-11-22
Online:2023-03-18
Published:2023-06-02
摘要:
二氧化氮(NO2)是重要的大气污染物之一,其浓度水平主要受人类活动影响。2020年初新冠疫情发生,人民生产生活受到限制,进而对NO2的排放产生了重要影响。陕西省作为丝绸之路向西推进的前沿、“一带一路”战略中的黄金要地,开展新冠疫情背景下NO2时空变化特征及其所反映的社会经济活动变化,对于科学认识陕西省人类活动与污染物之间的相互关系具有重要意义。以陕西省为例,在2020年1月21日-2022年1月22日期间选取同比期、环比期、疫情期I、疫情期II共4个重要时段,基于目前技术性能最先进、空间分辨率最高的TropOMI数据,利用标准化社会经济活动指数(SSEI)、NO2减排效应估算等方法,开展了陕西省新冠疫情对NO2时空分布特征和社会经济活动影响研究。结果表明,(1)地面监测NO2浓度与TropOMI反演的NO2柱浓度呈现较好的正相关关系,利用TropOMI反演的对流层NO2柱浓度数据具有较高可靠性。(2)疫情期I陕西省对流层NO2柱浓度较同比期和环比期分别下降39.15%和55.99%,较疫情期II下降59.29%。新冠疫情导致陕西省对流层NO2柱浓度高的地区下降明显,而低的地区受影响相对较小。对流层NO2柱浓度在空间上总体表现为关中地区和陕北北部及城市周边高于其他地区的分布特征。(3)陕西省社会经济活动受疫情管控影响较大。2020、2021、2022年春节前5周至春节后7周共13周的SSEI总体变化趋势保持一致。2020年疫情期I陕西省SSEI明显低于2021年同时段无疫情时期和2022年疫情期II。研究结论认为NO2变化与人类活动关系密切,利用TropOMI遥感反演的NO2浓度数据可用于开展大范围、多尺度的社会经济活动评价。
中图分类号:
吴雅睿, 王美景, 王涛, 杨梅焕. 新冠疫情下NO2时空变化特征——以陕西省为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 514-524.
WU Yarui, WANG Meijing, WANG Tao, YANG Meihuan. Effect of COVID-19 on Temporal and Spatial Distribution of NO2 Concentration and Socio-Economic Life: A Case Study of Shaanxi Province[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 514-524.
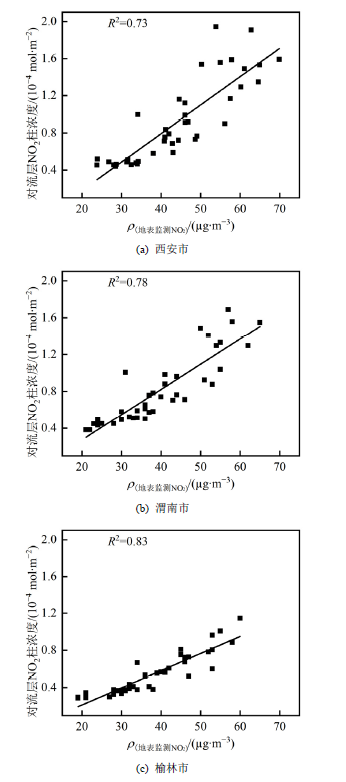
图2 西安市(a)、渭南市(b)、榆林市(c)遥感反演对流层NO2柱浓度与地面监测浓度相关性
Figure 2 Linear fitting of NO2 retrieved from remote sensing and ground monitoring value in Xi'an (a), Weinan (b) and Yulin (c) city, respectively
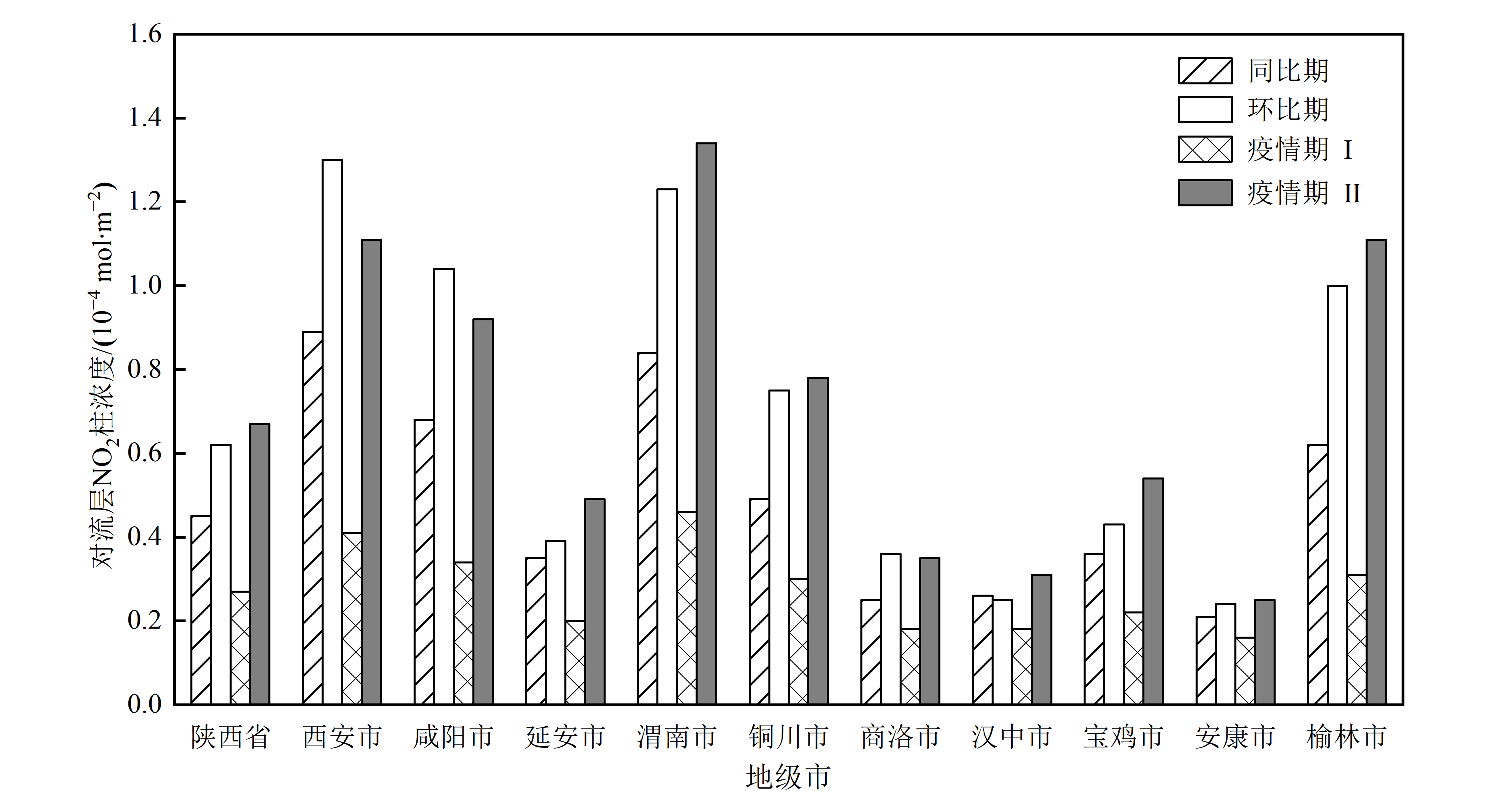
图3 陕西省各地市疫情期I、同比期、环比期、疫情期II对流层NO2柱浓度柱状图
Figure 3 Histogram of concentrations in epidemic phase I, year-on-year period, the sequential period and the epidemic phase II in Shaanxi Province

图4 陕西省各地市疫情期 I较同比期、环比期、疫情期 II对流层NO2柱浓度下降率柱状图
Figure 4 Histogram of the decrease rate of epidemic phase I compared with the year-on-year period, the sequential period and the epidemic phase II in Shaanxi Province
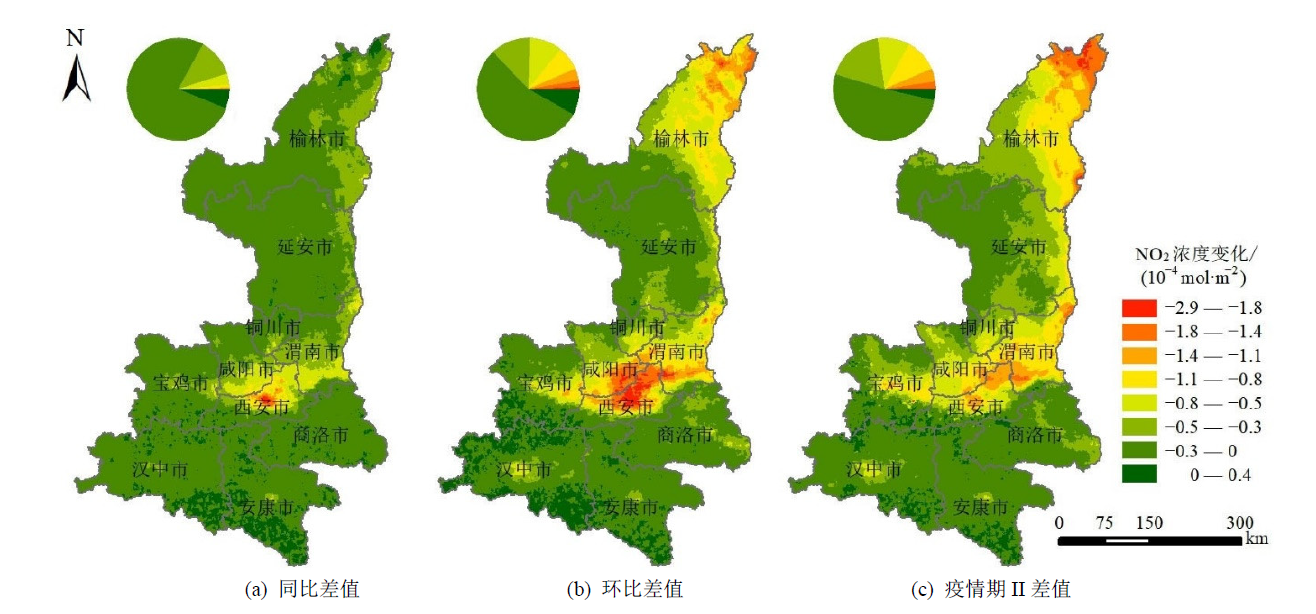
图6 陕西省疫情期I较同比期、环比期、疫情期II对流层NO2柱浓度变化空间分布
Figure 6 Spatial distribution of tropospheric NO2 column concentration during epidemic period I compared with the year-on-year period, the sequential period and the epidemic period II in Shaanxi province
| 阶段 | 估算柱浓度/ (10-4 mol∙m-2) | 实际柱浓度/ (10-4 mol∙m-2) | 减排估算 柱浓度/ (10-4 mol∙m-2) | 减排量占实际柱浓度比重/ % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 疫情期I | 0.32 | 0.27 | 0.05 | 18.44 |
| 疫情期II | 0.69 | 0.67 | 0.02 | 2.41 |
表1 陕西省对流层NO2柱浓度估计值与实际值对比
Table 1 Comparison between the estimated and actual tropospheric NO2 column concentration in Shaanxi Province
| 阶段 | 估算柱浓度/ (10-4 mol∙m-2) | 实际柱浓度/ (10-4 mol∙m-2) | 减排估算 柱浓度/ (10-4 mol∙m-2) | 减排量占实际柱浓度比重/ % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 疫情期I | 0.32 | 0.27 | 0.05 | 18.44 |
| 疫情期II | 0.69 | 0.67 | 0.02 | 2.41 |
| [1] |
BURROWS J P, WEBER M, BUCHWITZ M, et al., 1999. The global ozone monitoring experiment (GOME): Mission concept and first scientific results[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 56(2): 151-175.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
CHU B, ZHANG S, LIU J, et al., 2021. Significant concurrent decrease in PM2.5 and NO2 concentrations in China during COVID-19 epidemic[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 99(1): 346-353.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
JUDD L M, AL-SAADI J A, SZYKMAN J J, et al., 2020. Evaluating Sentinel-5P TROPOMI tropospheric NO2 column densities with airborne and Pandora spectrometers near New York City and Long Island Sound[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 13(11): 6113-6140.
DOI URL |
| [4] | KROTKOV N A, MCLINDEN C A, LI C, et al., 2016. Aura OMI observations of regional SO2 and NO2 pollution changes from 2005 to 2015[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 16(7): 4605-4629. |
| [5] | SHOWSTACK R, 2014. Sentinel Satellites Initiate New Era in Earth Observation[J]. Transactions American Geophysical Union, 95(26): 239-240. |
| [6] | STEINFELD J I, 1998. Atmospheric chemistry and physics: from air pollution to climate change[J]. Environment: Science and Policy for Sustainable Development, 40(7): 26-26. |
| [7] |
STOLARSKI R S, BLOOMFIELD P, MCPETERS R D, et al., 1991. Total ozone trends deduced from Nimbus 7 TOMS data[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 18(6): 1015-1018.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
ZHANG R, ZHANG Y, LIN H, et al., 2020. NOx emission reduction and recovery during COVID-19 in East China[J]. Atmosphere, 11(4): 433-448.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
ZHENG B. Zhang Q, Geng G et al., 2021. Changes in China's anthropogenic emissions and air quality during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020[J]. Earth System Science Data, 13(6): 2895-2907.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
ZHENG Z H, YANG Z W, WU Z F, et al., 2019. Spatial variation of NO2 and its impact factors in China: An application of sentinel-5P products[J]. Remote Sensing, 11(16): 1939-1962.
DOI URL |
| [11] | 蔡晓斌, 任永鹏, 张媛, 等, 2020. 利用卫星遥感NO2监测结果分析COVID-19疫情对我国社会经济活动的短期影响[J]. 华中师范大学学报(自然科学版), 54(6): 1045-1050. |
| CAI X B, REN Y P, ZHANG Y, et al., 2020. The short-term impact estimate of COVID-19 epidemic on social-economic activity of China by using remotely sensed NO2 observations[J]. Journal of Central Normal University, 54(6): 1045-1050. | |
| [12] | 陈罕立, 王金南, 2005. 关于我国NOx排放总量控制的探讨[J]. 环境科学研究, 18(5): 107-110. |
| CHEN H L, WANG J N, 2005. Exploring the total emission control of nitrogen oxides in China[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 18(5): 107-110. | |
| [13] | 江文华, 马建中, 颜鹏, 等, 2006. 利用GOME卫星资料分析北京大气NO2污染变化[J]. 应用气象学报, 17(1): 67-72. |
| JIANG W H, MA J Z, YAN P, et al., 2006. Characterization of NO2 pollution changes in beijjing Using GOME satellite data[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 17(1): 67-72. | |
| [14] | 李令军, 王英, 2011. 基于卫星遥感与地面监测分析北京大气NO2污染特征[J]. 环境科学学报, 31(12): 2762-2768. |
| LI L J, WANG Y, 2011. The characterization of NO2 pollution in Beijing based on satellite and conventional observation data[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 31(12): 2762-2768. | |
| [15] |
李龙, 施润和, 陈圆圆, 等, 2013. 基于OMI数据的中国NO2时空分布与人类影响分析[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 15(5): 688-694.
DOI |
| LI L, SHI R H, CHEN Y Y, et al., 2013. Spatio-temporal characteristics of NO2 in China and the anthropogenic influences analysis based on OMI data[J]. Journal of Geo-information Sciences, 15(5): 688-694. | |
| [16] | 李鹏, 肖致美, 陈魁, 等, 2016. 基于OMI数据天津市NO2浓度分布特征及其适用性[J]. 环境科学与技术, 39(1): 183-186, 204. |
| LI P, XIAO Z M, CHEN K, et al., 2016. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of tropospheric NO2 and its adaptability in Tianjin using OMI satellite remote sensing data[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 39(1): 183-186, 204. | |
| [17] | 李旭文, 张悦, 姜晟, 等, 2019. “哨兵-5P” 卫星TROPOMI传感器在江苏省域大气污染监测中的初步应用[J]. 环境监控与预警, 11(2): 10-16. |
| LI X W, ZHANG Y, JIANG S, et al., 2019. Preliminary Application of Atmospheric Pollution Monitoring in Jiangsu Province with TROPOMI Sensor Onboard Sentinel - 5P Satellite[J]. Environment Monitoring and Forewarning, 11(2): 10-16. | |
| [18] | 刘文清, 陈臻懿, 刘建国, 2016. 我国大气环境立体监测技术及应用[J]. 科学通报, 61(30): 3196-3207. |
| LIU W Q, CHEN Z Y, LIU J G, 2016. Stereoscopic monitoring technology and applications for the atmospheric environment in China[J]. Science China Press, 61(30): 3196-3207. | |
| [19] | 刘跃斌, 张远, 张逸冰, 等, 2021. 邯郸市新冠疫情前后空气质量指数(AQI)对比与疫情防控期间大气污染特征分析[J]. 环境化学, 40(12): 3743-3754. |
| LIU Y B, ZHANG Y, ZHANG Y B, et al., 2021. Comparison of air quality index (AQI) before and after COVID-19 in Handan City and analysis of air pollution characteristics during COVID-19 prevention and control[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 40(12): 3743-3754. | |
| [20] | 秦臻, 张明, 张月莹, 等, 2021. COVID-19疫情对河南省空气质量及社会经济活动短期影响[J]. 中国环境监测, 37(6): 221-228. |
| QIN Z, ZHANG M, ZHANG Y Y, et al., 2021. Short term impact of COVID-19 on Air quality and social economic activities in Henan province[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 37(6): 221-228. | |
| [21] | 陕西省统计局, 国家统计局陕西调查总队, 2020. 陕西统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社:52- 53. |
| Shaanxi Bureau of Statistics, Shaanxi Survey Team of National Bureau of Statistics, 2019. Shaanxi statistical yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press:52- 53. | |
| [22] | 陕西省统计局, 国家统计局陕西调查总队, 2021. 陕西统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社:52- 53. |
| Shaanxi Bureau of Statistics, Shaanxi Survey Team of National Bureau of Statistics, 2020. Shaanxi statistical yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press:52- 53. | |
| [23] | 陕西省统计局, 国家统计局陕西调查总队, 2022. 陕西统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社:52- 53. |
| Shaanxi Bureau of Statistics, Shaanxi Survey Team of National Bureau of Statistics, 2021. Shaanxi statistical yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press:52- 53. | |
| [24] | 陶金花, 王子峰, 韩冬, 等, 2009. 华北地区秸秆禁烧前后的NO2卫星遥感监测分析[J]. 中国环境科学, 29(10): 1016-1020. |
| TAO J H, WANG Z F, HAN D, et al., 2009. Analysis of crop residue burning and tropospheric NO2 vertical column density retrieved from satellite remote sensing in North China.[J]. China Environmental Science, 29(10): 1016-1020. | |
| [25] | 陶金花, 范萌, 顾坚斌, 等, 2020. 新冠病毒疫情期间复工复产卫星遥感监测[J]. 遥感学报, 24(7): 824-836. |
| TAO J H, FAN M, GU J B, et al., 2020. Satellite observations of the return-to- work over China during the period of COVID-19[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 24(7): 824-836. | |
| [26] | 王厚俊, 陈志芳, 吴莹, 等, 2022. 基于TROPOMI的扬州市对流层甲醛和二氧化氮时空分布特征分析[J]. 环境监控与预警, 14(3): 70-75, 94. |
| WANG H J, CHEN Z F, WU Y, et al., 2022. Analysis of temporal and spatial variation characteristics of formaldehyde and nitrogen dioxide in troposphere in Yangzhou city based on TROPOMI[J]. Environment Monitoring and Forewarning, 14(3): 70-75, 94. | |
| [27] | 姚凌, 吕宁, 师华定, 2012. 利用SCIAMACHY遥感资料研究我国NO2柱浓度及其时空分布[J]. 环境科学研究, 25(4): 419-424. |
| YAO L, LÜ N, SHI H D, 2012. Study on spatial-temporal variations in total NO2 column amounts over China using SCIAMACHY data[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 25(4): 419-424. | |
| [28] | 乐旭, 雷亚栋, 周浩, 等, 2020. 新冠肺炎疫情期间中国人为碳排放和大气污染物的变化[J]. 大气科学学报, 43(2): 265-274. |
| YUE X, LI Y D, ZHOU H, et al., 2020. Changes of anthropogenic carbon emissions and air pollutants during the COVID-19 epidemic in China[J]. Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 43(2): 265-274. | |
| [29] | 张晗, 余超, 苏林, 等, 2017. MODIS和OMI数据评估阅兵期间北京市大气减排成效[J]. 遥感学报, 21(4): 622-632. |
| ZHAN H, YU C, SU L, et al., 2017. Emission control effects observed from space during the military parade 2015 in Beijing[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 21(4): 622-632. | |
| [30] | 张连华, 周春艳, 厉青, 等, 2019. 2016-2018年汾渭平原对流层NO2柱浓度时空变化遥感监测[J]. 环境生态学, 1(4): 67-73. |
| ZHANG L H, ZHOU C Y, LI Q, et al., 2019. Remote sensing monitoring of spatiotemporal changes of tropospheric NO2 column concentration of Fen-Wei Plain in the year of 2016-2018[J]. Environmental Ecology, 1(4): 67-73. | |
| [31] |
张岳军, 朱凌云, 郭伟, 等, 2020. 汾渭平原大气SO2和NO2时空变化特征分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(6): 1147-1156.
DOI |
| ZHANG Y J, ZHU L Y, GUO W, et al., 2020. Analysis of temporal and spatial variation characteristics of atmospheric SO2 and NO2 in Fenwei Plain[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29(6): 1147-1156. | |
| [32] | 赵金环, 蔡坤, 李莘莘, 等, 2021. 新冠疫情对我国NO2排放影响的时空分析[J]. 中国环境科学, 41(1): 56-62. |
| ZHAO J H, CAI K, LI S S, et al., 2021. Spatiotemporal analysis on the impact of COVID-19 pandemic on NO2 emission in China[J]. China Environmental Science, 41(1): 56-62. | |
| [33] | 郑晓霞, 李令军, 赵文吉, 等, 2014. 京津冀地区大气NO2污染特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 23(12):1938-1945. |
| ZHENG X X, LI L J, ZHAO W J, et al., 2014. Spatial and temporal characteristics of atmospheric NO2 in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 23(12): 1938-1945. | |
| [34] | 郑子豪, 吴志峰, 陈颖彪, 等, 2021. 基于Sentinel-5P的粤港澳大湾区NO2污染物时空变化分析[J]. 中国环境科学, 41(1): 63-72. |
| ZHENG Z H, WU Z F, CHEN Y B, et al., 2021. Analysis of temporal and spatial variation characteristics of NO2 pollutants in Guangdong Hong Kong Macao Greater Bay Area based on Sentinel -5P satellite data[J]. China Environmental Science, 41(1): 63-72. | |
| [35] | 周春艳, 厉青, 王中挺, 等, 2016. 2005年-2014年京津冀对流层NO2 柱浓度时空变化及影响因素[J]. 遥感学报, 20(3): 468-480. |
| ZHOU C Y, LI Q, WANG Z T, et al., 2016. Spatio-temporal trend and changing factors of tropospheric NO2 column density in Bijing Tianjin-Hebei region[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 20(3): 468-480. | |
| [36] | 周黎, 胡海涛, 王晓峰, 2022. 利用哨兵5P卫星数据初探攀枝花市域大气遥感监测[J]. 环保科技, 28(2): 40-44. |
| ZHOU L, HU H T, WANG X F, 2022. A preliminary study on the atmospheric remote sensing monitoring in Panzhihua City using Sentinel 5 P satellite data[J]. Environmental Technology, 28(2): 40-44. |
| [1] | 雷社平, 樊艳翔, 解建仓. 黄土高原城市工业污水排放脱钩分析及驱动效应分解--以陕西省为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 351-360. |
| [2] | 孙正, 曹亚非, 王德彩, 刘峰, 宋效东, 张甘霖, 吴华勇. 近30年京津冀电镀场地时空演变特征及趋势预测[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 183-194. |
| [3] | 贺斌, 胡茂川. 广东省各区县农业面源污染负荷估算及特征分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 771-776. |
| [4] | 王金杰, 赵安周, 胡小枫. 京津冀植被净初级生产力时空分布及自然驱动因子分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1158-1167. |
| [5] | 王薇, 程歆玥, 胡春, 夏斯涵, 王甜. 城市街道峡谷PM2.5时空分布特征与空气质量评价——以合肥市长淮街道为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(11): 2157-2164. |
| [6] | 郑诗禹, 张绿水, 郭晓敏, 黄子峻, 肖以华. 不同森林郁闭度环境内空气负氧离子的时空变化及环境影响要素研究——以广州帽峰山为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(11): 2204-2212. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
