生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (1): 62-69.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.01.008
收稿日期:2021-02-16
出版日期:2022-01-18
发布日期:2022-03-10
通讯作者:
*柳新伟(1976年生),男,副教授,博士,硕士研究生导师,主要从事农业生态学研究。E-mail: sdxw@163.com作者简介:王瑞(1995年生),男,硕士研究生,主要从事土壤研究。E-mail: 390875731@qq.com
基金资助:
WANG Rui( ), SONG Xiangyun, LIU Xinwei*(
), SONG Xiangyun, LIU Xinwei*( )
)
Received:2021-02-16
Online:2022-01-18
Published:2022-03-10
摘要:
黄河三角洲自然保护区的酶活性季节特征一定程度影响了该地植被分布类型,为研究黄河三角洲自然保护区不同植被土壤酶活性的季节特征,分别选取碱蓬(Suaeda salsa)、柽柳(Tamarix chinensis)、芦苇(Phragmites communis)、刺槐(Black Locust)和高粱(Sorghum)5种典型植被作为研究对象,分别在4个季节采集不同深度土壤,测定土壤脲酶、过氧化氢酶、碱性磷酸酶、脱氢酶、蔗糖酶活性。结果表明,土壤脱氢酶活性规律表现为碱蓬>柽柳>刺槐>高粱>芦苇,其他酶活性总体变化规律表现为刺槐>柽柳>高粱>芦苇>碱蓬;在同一季节中,不同植被间酶活性存在显著性差异,柽柳和刺槐林土壤脲酶、碱性磷酸酶和蔗糖酶活性普遍高于其他群落,碱蓬最低;土壤酶活性与土壤基础理化指标有着密切关系,土壤过氧化氢酶活性、脲酶活性和蔗糖酶活性之间存在极显著性正相关(P<0.01),过氧化氢酶,脲酶和蔗糖酶与有机质、碱解氮呈显著性正相关(P<0.01),脱氢酶与速效磷呈显著性正相关与pH之间呈负相关(P<0.01);在0—40 cm土层中,碱性磷酸酶活性随着土层深度增加而增加,而过氧化氢酶,脱氢酶,脲酶和蔗糖酶随着土层深度增加而减少;进一步分析不同土壤酶活性之间的关系,过氧化氢酶、脲酶和蔗糖酶之间存在极显著性正相关(P<0.01)。该研究结果可为黄河三角洲不同植被的管理提供数据支撑。
中图分类号:
王瑞, 宋祥云, 柳新伟. 黄河三角洲不同植被类型土壤酶活性的季节变化[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 62-69.
WANG Rui, SONG Xiangyun, LIU Xinwei. Seasonal Characteristics of Soil Enzymes in Different Vegetations in the Yellow River Delta[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(1): 62-69.
| 植被类型 Vegetation type | 经度 Longitude | 纬度 Latitude |
|---|---|---|
| 碱蓬 Suaeda salsa | 119°9′17″E | 37°46′7″N |
| 柽柳 Tamarix chinensis | 119°8′19″E | 37°44′40″N |
| 芦苇 Phragmites communis | 119°3′7″E | 37°45′46″N |
| 刺槐 Black Locust | 119°0′44″E | 37°47′58″N |
| 高粱 Sorghum | 119°0′46″E | 37°47′56″N |
表1 不同植被下土壤地理坐标
Table1 Soil geographic coordinates under different vegetation
| 植被类型 Vegetation type | 经度 Longitude | 纬度 Latitude |
|---|---|---|
| 碱蓬 Suaeda salsa | 119°9′17″E | 37°46′7″N |
| 柽柳 Tamarix chinensis | 119°8′19″E | 37°44′40″N |
| 芦苇 Phragmites communis | 119°3′7″E | 37°45′46″N |
| 刺槐 Black Locust | 119°0′44″E | 37°47′58″N |
| 高粱 Sorghum | 119°0′46″E | 37°47′56″N |
| 季节 Season | 植被类型 Vegetation types | w(有机质 Organic matter)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(碱解氮 Available nitrogen)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(有效磷 Available phosphorus)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(速效钾 Available potassium)/ (mg∙kg-1) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 春季 Spring | 碱蓬 Suaeda salsa | 8.03±0.14Ac | 10.5±3Bd | 3.25±1.04Bb | 209.32±5.72Aa | 8.76±0.03Ac |
| 柽柳Tamarix chinensis | 18.03±0.57Da | 99.17±14Bb | 3.75±0.30BCb | 163.04±9.91Ab | 8.85±0.03Bb | |
| 芦苇 Phragmites communis | 8.82±0.15Bc | 22.17±4Ad | 3.45±0.30BCb | 73.79±4.96Ac | 8.99±0.03Aa | |
| 刺槐 Black Locust | 18.69±0.97Aa | 249.66±9Aa | 6.24±0.86Aa | 151.47±2.86Ab | 8.45±0.03Ad | |
| 高粱 Sorghum | 15.88±0.71Cb | 73.5±14Bc | 4.35±1.07Bb | 96.93±7.57Ac | 8.08±0.05De | |
| 夏季 Summer | 碱蓬 Suaeda salsa | 7.99±0.38Ac | 7.93±2Bd | 3.46±0.79Bab | 209.32±5.72Aa | 8.34±0.03Bd |
| 柽柳 Tamarix chinensis | 21.49±0.95Ca | 74.67±8Cb | 5.05±0.45Ba | 163.04±9.91Ab | 8.89±0.06Bb | |
| 芦苇 Phragmites communis | 4.12±0.48Dd | 4.2±1Cd | 4.65±0.89Bab | 73.78±4.96Ad | 8.99±0.02Aa | |
| 刺槐 Black Locust | 10.15±0.56Bb | 196±12Ba | 3.26±0.75Bb | 151.47±2.86Ab | 8.33±0.06Ad | |
| 高粱 Sorghum | 11.25±0.82Db | 22.83±2Cc | 5.05±1.20Ba | 96.92±7.57Ac | 8.64±0.07Bc | |
| 秋季 Autumn | 碱蓬 Suaeda salsa | 9.21±0.39Ad | 15.17±5cBd | 5.74±1.34Aa | 161.39±2.86Ca | 8.33±0.03Be |
| 柽柳 Tamarix chinensis | 28.88±0.05Aa | 107.33±12Bb | 2.56±0.30Cb | 129.98±7.57Bb | 9.15±0.04Aa | |
| 芦苇 Phragmites communis | 17.84±0.72Ac | 12.83±2Bd | 2.96±0.45Cb | 50.64±2.86Bd | 8.70±0.03Bc | |
| 刺槐 Black Locust | 17.51±0.68Ac | 226.33±14Aa | 3.55±1.20Bb | 129.98±11.45Bb | 8.47±0.04Ad | |
| 高粱 Sorghum | 19.90±0.52Ab | 31.5±9Cc | 2.16±0.17Cb | 72.13±7.57Bc | 8.91±0.07Ab | |
| 冬季 Winter | 碱蓬 Suaeda salsa | 8.68±1.18Ac | 35±3Ad | 6.34±0.45Ac | 179.57±10.32Ba | 8.76±0.07Aa |
| 柽柳 Tamarix chinensis | 24.30±0.72Ba | 134.17±4Ab | 8.73±1.69Ab | 125.03±2.86Bc | 8.36±0.02Cb | |
| 芦苇 Phragmites communis | 5.64±0.38Cd | 16.33±5ABe | 6.64±0.91Ac | 57.26±10.32Be | 8.32±0.04Cb | |
| 刺槐 Black Locust | 17.95±0.09Ab | 233.33±14Aa | 7.23±0.69Abc | 144.86±7.57Ab | 8.34±0.05Ab | |
| 高粱 Sorghum | 17.81±0.68Bb | 106.17±5Ac | 16.68±1.24Aa | 96.93±5.72Ad | 8.41±0.04Cb |
表2 土壤基础理化性质
Table 2 Basic physical and chemical properties of soil table
| 季节 Season | 植被类型 Vegetation types | w(有机质 Organic matter)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(碱解氮 Available nitrogen)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(有效磷 Available phosphorus)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(速效钾 Available potassium)/ (mg∙kg-1) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 春季 Spring | 碱蓬 Suaeda salsa | 8.03±0.14Ac | 10.5±3Bd | 3.25±1.04Bb | 209.32±5.72Aa | 8.76±0.03Ac |
| 柽柳Tamarix chinensis | 18.03±0.57Da | 99.17±14Bb | 3.75±0.30BCb | 163.04±9.91Ab | 8.85±0.03Bb | |
| 芦苇 Phragmites communis | 8.82±0.15Bc | 22.17±4Ad | 3.45±0.30BCb | 73.79±4.96Ac | 8.99±0.03Aa | |
| 刺槐 Black Locust | 18.69±0.97Aa | 249.66±9Aa | 6.24±0.86Aa | 151.47±2.86Ab | 8.45±0.03Ad | |
| 高粱 Sorghum | 15.88±0.71Cb | 73.5±14Bc | 4.35±1.07Bb | 96.93±7.57Ac | 8.08±0.05De | |
| 夏季 Summer | 碱蓬 Suaeda salsa | 7.99±0.38Ac | 7.93±2Bd | 3.46±0.79Bab | 209.32±5.72Aa | 8.34±0.03Bd |
| 柽柳 Tamarix chinensis | 21.49±0.95Ca | 74.67±8Cb | 5.05±0.45Ba | 163.04±9.91Ab | 8.89±0.06Bb | |
| 芦苇 Phragmites communis | 4.12±0.48Dd | 4.2±1Cd | 4.65±0.89Bab | 73.78±4.96Ad | 8.99±0.02Aa | |
| 刺槐 Black Locust | 10.15±0.56Bb | 196±12Ba | 3.26±0.75Bb | 151.47±2.86Ab | 8.33±0.06Ad | |
| 高粱 Sorghum | 11.25±0.82Db | 22.83±2Cc | 5.05±1.20Ba | 96.92±7.57Ac | 8.64±0.07Bc | |
| 秋季 Autumn | 碱蓬 Suaeda salsa | 9.21±0.39Ad | 15.17±5cBd | 5.74±1.34Aa | 161.39±2.86Ca | 8.33±0.03Be |
| 柽柳 Tamarix chinensis | 28.88±0.05Aa | 107.33±12Bb | 2.56±0.30Cb | 129.98±7.57Bb | 9.15±0.04Aa | |
| 芦苇 Phragmites communis | 17.84±0.72Ac | 12.83±2Bd | 2.96±0.45Cb | 50.64±2.86Bd | 8.70±0.03Bc | |
| 刺槐 Black Locust | 17.51±0.68Ac | 226.33±14Aa | 3.55±1.20Bb | 129.98±11.45Bb | 8.47±0.04Ad | |
| 高粱 Sorghum | 19.90±0.52Ab | 31.5±9Cc | 2.16±0.17Cb | 72.13±7.57Bc | 8.91±0.07Ab | |
| 冬季 Winter | 碱蓬 Suaeda salsa | 8.68±1.18Ac | 35±3Ad | 6.34±0.45Ac | 179.57±10.32Ba | 8.76±0.07Aa |
| 柽柳 Tamarix chinensis | 24.30±0.72Ba | 134.17±4Ab | 8.73±1.69Ab | 125.03±2.86Bc | 8.36±0.02Cb | |
| 芦苇 Phragmites communis | 5.64±0.38Cd | 16.33±5ABe | 6.64±0.91Ac | 57.26±10.32Be | 8.32±0.04Cb | |
| 刺槐 Black Locust | 17.95±0.09Ab | 233.33±14Aa | 7.23±0.69Abc | 144.86±7.57Ab | 8.34±0.05Ab | |
| 高粱 Sorghum | 17.81±0.68Bb | 106.17±5Ac | 16.68±1.24Aa | 96.93±5.72Ad | 8.41±0.04Cb |
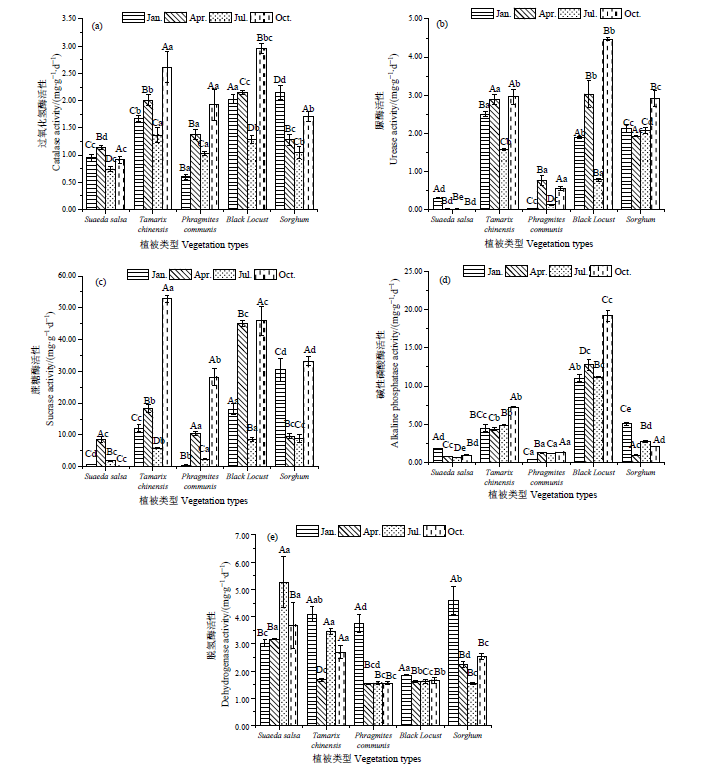
图1 不同植被土壤酶活性季节动态 大写字母表示相同群落不同季节差异性显著(P<0.05);小写字母表示相同季节不同群落差异性显著(P<0.05)
Figure 1 Seasonal dynamics of soil enzyme activity in different vegetation Capital letters indicate that the same community has significant difference in different seasons (P<0.05); Lowercase letters indicate significant difference among different communities in the same season (P<0.05)
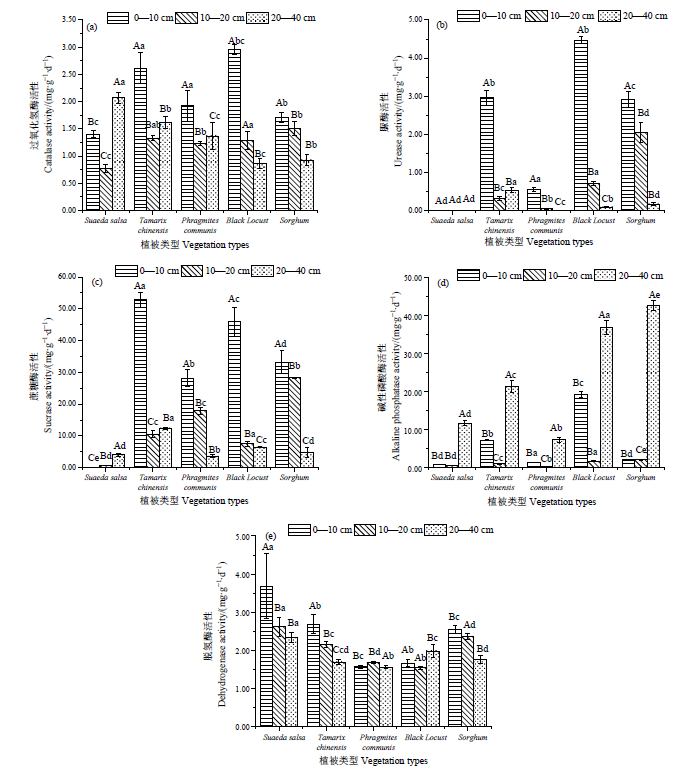
图2 不同植被不同深度土壤酶活性 大写字母表示相同群落不同深度差异性显著(P<0.05);小写字母表示相同深度不同群落差异性显著(P<0.05)
Figure 2 Soil enzyme activity at different depths in different vegetation Capital letters indicate that the same community has significant difference in different seasons (P<0.05); Lowercase letters indicate significant difference among different communities in the same season (P<0.05)
| 酶活性 Enzyme activity | 过氧化 氢酶 Catalase | 脲酶 Urease | 蔗糖酶 Sucrase | 碱性磷酸酶 Alkaline phosphatase | 脱氢酶 Dehydrogenase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 过氧化氢酶 Catalase | 1 | ||||
| 脲酶 Urease | 0.833** | 1 | |||
| 蔗糖酶 Sucrase | 0.912** | 0.781** | 1 | ||
| 碱性磷酸酶 Alkaline phosphatase | 0.730** | 0.683** | 0.626** | 1 | |
| 脱氢酶 Dehydrogenase | -0.326 | -0.291 | -0.284 | -0.358 | 1 |
表3 土壤酶之间的相关性
Table 3 Correlation of soil enzymes
| 酶活性 Enzyme activity | 过氧化 氢酶 Catalase | 脲酶 Urease | 蔗糖酶 Sucrase | 碱性磷酸酶 Alkaline phosphatase | 脱氢酶 Dehydrogenase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 过氧化氢酶 Catalase | 1 | ||||
| 脲酶 Urease | 0.833** | 1 | |||
| 蔗糖酶 Sucrase | 0.912** | 0.781** | 1 | ||
| 碱性磷酸酶 Alkaline phosphatase | 0.730** | 0.683** | 0.626** | 1 | |
| 脱氢酶 Dehydrogenase | -0.326 | -0.291 | -0.284 | -0.358 | 1 |
| 因子 Parameters | 有机质 Organic matter | 碱解氮 Available nitrogen | 速效磷 Available phosphorus | 速效钾 Available potassium | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 过氧化氢酶 Catalase | 0.760** | 0.670** | -0.079 | -0.084 | 0.155 |
| 脱氢酶 Dehydrogenase | -0.024 | -0.303 | 0.458* | 0.335 | -0.455* |
| 脲酶 Urease | 0.753** | 0.659** | 0.055 | -0.088 | -0.008 |
| 碱性磷酸酶 Alkaline phosphatase | 0.408 | 0.923** | 0.039 | 0.173 | -0.051 |
| 蔗糖酶 Sucrase | 0.712** | 0.548** | -0.013 | -0.162 | 0.232 |
表4 土壤酶与理化性质之间的相关性
Table 4 Correlation between soil enzymes and physical and chemical properties
| 因子 Parameters | 有机质 Organic matter | 碱解氮 Available nitrogen | 速效磷 Available phosphorus | 速效钾 Available potassium | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 过氧化氢酶 Catalase | 0.760** | 0.670** | -0.079 | -0.084 | 0.155 |
| 脱氢酶 Dehydrogenase | -0.024 | -0.303 | 0.458* | 0.335 | -0.455* |
| 脲酶 Urease | 0.753** | 0.659** | 0.055 | -0.088 | -0.008 |
| 碱性磷酸酶 Alkaline phosphatase | 0.408 | 0.923** | 0.039 | 0.173 | -0.051 |
| 蔗糖酶 Sucrase | 0.712** | 0.548** | -0.013 | -0.162 | 0.232 |
| [1] | CAO D, SHI F C, KOIKE T, et al., 2014. Halophyte plant communities affecting enzyme activity and microbes in saline soils of the Yellow River Delta in China[J]. CLEAN-Soil Air Water, 8: 1433-1440. |
| [2] |
JING C L, XU Z C, ZOU P, et al., 2019. Coastal halophytes alter properties and microbial community structure of the saline soils in the Yellow River Delta, China[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 134: 1-7.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
TIAN L, SHI W, 2014. Short-term effects of plant litter on the dynamics, amount, and stoichiometry of soil enzyme activity in agroecosystems[J]. European Journal of Soil Biology, 65: 23-29.
DOI URL |
| [4] | XU X F, SONG C C, SONG X, et al., 2004. Carbon mineralization and the related enzyme activity of soil in wetland[J]. Ecology and Environment, 13(1): 40-42. |
| [5] |
ZHENG L D, ZHANG M X, XIAO R, et al., 2017. Impact of salinity and Pb on enzyme activities of a saline soil from the Yellow River delta: A microcosm study[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C, 97: 77-87.
DOI URL |
| [6] | 鲍士旦, 2000. 土壤农化分析[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社: 25-114. |
| BAO S D, 2000. Soil agrochemical analysis[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press: 25-114. | |
| [7] | 陈为峰, 周维芝, 史衍玺, 2003. 黄河三角洲湿地面临的问题及其保护[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 22(4): 499-502. |
| CHEN W F, ZHOU W Z, SHI Y X, 2003. Crisis of wetlands in the Yellow River Delta and its protection[J]. Journal of Agro- Environment Science, 22(4): 499-502. | |
| [8] | 陈为峰, 史衍玺, 2010. 黄河三角洲新生湿地不同植被类型土壤的微生物分布特征[J]. 草地学报, 18(6): 859-864. |
| CHEN W F, SHI Y X, 2010. Distribution characteristics of microbes in new-born wetlands of the Yellow River Delta[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 18(6): 859-864. | |
| [9] | 关松荫, 1986. 土壤酶及其研究法[M]. 北京: 农业出版社: 274-320. |
| GUAN S Y, 1986, Soil enzymes and their research methods[M]. Beijing: Agricultural Press: 274-320. | |
| [10] | 李传荣, 许景伟, 宋海燕, 等, 2006. 黄河三角洲滩地不同造林模式的土壤酶活性[J]. 植物生态学报, 30(5): 802-809. |
|
LI C R, XU J W, SONG H Y, et al., 2006. Soil enzyme activities in different plantations in lowlands of The Yellow River Delta, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 30(5): 802-809.
DOI URL |
|
| [11] | 李晓红, 2019. 鄱阳湖湿地不同植物群落土壤养分和土壤酶活性垂直分布特征[J]. 水土保持研究, 26(1): 69-75. |
| LI X H, 2019. Profile distribution characteristics of soil nutrients and enzymes in the Wetland of Poyang Lake[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 26(1): 69-75. | |
| [12] | 刘超, 赵光影, 宋艳宇, 等, 2019. 气候变化背景下湿地土壤酶活性研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 35(33): 91-97. |
| LIU C, ZHAO G Y, SONG Y Y, et al., 2019. Soil enzyme activity in wetland under the background of climate change: research progress[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 35(33): 91-97. | |
| [13] | 刘善江, 夏雪, 陈桂梅, 2011. 土壤酶的研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 27(21): 1-7. |
| LIU S J, XIA X, CHEN G M, 2011. Study progress on functions and affecting factors of soil enzymes[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 27(21): 1-7. | |
| [14] | 刘艳, 马风云, 宋玉民, 等, 2008. 黄河三角洲冲积平原湿地土壤酶活性与养分相关性研究[J]. 水土保持研究, 15(1): 60-61. |
| LIU Y, MA F Y, SONG Y M, et al., 2008. Correlative research on the activity of enzyme and soil nutrient of different wetlands in Yellow River Delta[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 15(1): 60-61. | |
| [15] | 刘杨, 王小沁, 沈丹杰, 等, 2019. 水分梯度下川西高寒湿地土壤酶活性变化特征[J]. 四川农业大学学报, 37(4): 517-524. |
| LIU Y, WANG X Q, SHEN D J, et al., 2019. Soil enzymatic activities dynamics along a moisture gradient in alpine wetland in western Sichuan province[J]. Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University, 37(4): 517-524. | |
| [16] | 罗慧, 冯程程, 岳中辉, 等, 2020. 植被修复对重度盐碱地土壤酶活性和酶反应热力学特征的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 31(12): 4243-4250. |
| LUO H, FENG C C, YUE Z H, et al., 2020. Effects of phytoremediation on soil enzyme activity and thermodynamic characteristics of enzymatic reaction in severe saline-alkali land[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 31(12): 4243-4250. | |
| [17] | 马宁, 齐继薇, 刘长发, 等, 2018. 辽河口潮滩湿地不同植被土壤4种碳代谢酶活性及其与有机碳含量、pH值关系[J]. 中国农学通报, 34(1): 90-97. |
| MA N, QI J W, LIU C F, et al., 2018. Relationship between 4 carbon metabolism enzymes and organic carbon, pH value under different vegetation in Liaohe estuary tidal flat wetland[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 34(1): 90-97. | |
| [18] | 马云波, 牛聪傑, 许中旗, 2016. 人工与自然植被恢复下尾矿土壤微生物及酶活性的时空变化[J]. 林业科学, 52(6): 93-100. |
| MA Y B, NIU C J, XU Z Q, 2016. Temporal and spatial variation of soil microbes and enzyme activities in iron tailings under natural restoration and plantation[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 52(6): 93-100. | |
| [19] | 毛志刚, 谷孝鸿, 刘金娥, 等, 2010. 盐城海滨湿地盐沼植被及农作物下土壤酶活性特征[J]. 生态学报, 30(18): 5043-5049. |
| MAO Z G, GU X H, LIU J E, et al., 2010. Distribution of the soil enzyme activities in different vegetation zones and farms in Yancheng coastal wetland[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30(18): 5043-5049. | |
| [20] | 牛世全, 李君锋, 杨婷婷, 等, 2010. 甘南玛曲沼泽湿地土壤微生物量、理化因子与土壤酶活的关系[J]. 冰川冻土, 32(5): 1022-1029. |
| NIU S Q, LI J F, YANG T T, et al., 2010. The relationships of soil microbial biomass, physicochemical factors and soil enzyme activities in Maqu Swamp Wetland of Gannan prefecture[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 32(5): 1022-1029. | |
| [21] | 庞威, 方晰, 2018. 湘中丘陵区森林土壤酶活性的季节变化研究[J]. 南方农机, 49(2): 178-181. |
| PANG W, FANG X, 2018. Seasonal variation of forest soil enzyme activity in hilly region of central Hunan[J]. China Southern Agricultural Machinery, 49(2): 178-181. | |
| [22] | 荣国华, 2018. 秸秆还田对土壤酶活性、微生物量及群落功能多样性的影响[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学: 44-45. |
| RONG G H, 2018. Effects of straw incorporation on soil enzyme activities, microbial biom ass and functional diversity of com munities[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University: 44-45. | |
| [23] | 孙英杰, 徐广平, 沈育伊, 等, 2018. 桂林会仙喀斯特湿地芦苇群落区土壤酶活性[J]. 湿地科学, 16(2): 196-203. |
| SUN Y J, XU G P, SHEN Y Y, et al., 2018. Soil enzyme activities of phragmites australis community area in Huixian karst wetland, Guilin[J]. Wetland Science, 16(2): 196-203. | |
| [24] | 田平雅, 沈聪, 赵辉, 等, 2020. 银北盐碱区植物根际土壤酶活性及微生物群落特征研究[J]. 土壤学报, 57(1): 217-226. |
| TIAN P Y, SHEN C, ZHAO H, et al., 2020. Enzyme activities and microbial communities in rhizospheres of plants in salinized soil in North Yinchuan, China[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 57(1): 217-226. | |
| [25] | 田应兵, 宋光煜, 艾天成, 2002. 湿地土壤及其生态功能[J]. 生态学杂志, 21(6): 36-39. |
| TIAN Y B, SONG G Y, AI T C, 2002, Wetland soil and its ecological functions[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 21(6): 36-39. | |
| [26] | 咸义, 2017. 竺山湾湖泊缓冲带退化湿地生态系统调控研究[D]. 南京: 南京师范大学: 53-54. |
| XIAN Y, 2017. Regulation of degraded wetland ecosystem in lake buffer zone of Zhushan Bay[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Normal University: 53-54. | |
| [27] | 张勇, 杜华栋, 张振国, 等, 2014. 黄土丘陵区自然植被恢复下土壤微生物学质量演变特征[J]. 水土保持研究, 21(1): 7-17. |
| ZHANG Y, DU H D, ZHANG Z G, et al., 2014. Evolution characteristics of soil biological property in Loess Hilly Region under natural vegetation restoration[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 21(1): 7-17. | |
| [28] | 赵兰坡, 姜岩, 1986. 土壤磷酸酶活性测定方法的探讨[J]. 土壤通报 (3): 138-141. |
| ZHAO L P, JIANG Y, 1986. Discussion on the determination method of soil phosphatase activity[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science (3): 138-141. | |
| [29] | 郑佳玉, 2018. 辽河口湿地土壤酶活性及其盐分的影响[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳大学: 46-47. |
| ZHENG J Y, 2018. Soil Enzyme and Salinity Impacts in Wetland of the Liaohe Estuary[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang University: 46-47. | |
| [30] | 周晓明, 2018. 黄河三角洲湿地土壤微生物多样性及土壤酶活性的研究[D]. 曲阜: 曲阜师范大学: 28-29. |
| ZHOU X M, 2018. Study on soil microbial diversity and soil enzyme activity in Yellow River Delta wetland[D]. Qufu: Qufu Normal University: 28-29. |
| [1] | 王雪梅, 杨雪峰, 赵枫, 安柏耸, 黄晓宇. 基于机器学习算法的干旱区绿洲地上生物量估算[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1007-1015. |
| [2] | 杜丹丹, 高瑞忠, 房丽晶, 谢龙梅. 旱区盐湖盆地土壤重金属空间变异及对土壤理化因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1123-1132. |
| [3] | 巫晨煜, 许帆帆, 魏士博, 樊晶晶, 刘观鹏, 王坤. 渭河流域地表植被覆盖对气候变化的响应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 835-844. |
| [4] | 李晖, 李必龙, 葛黎黎, 韩琛惠, 杨倩, 张岳军. 2000-2021年汾河流域植被时空演变特征及地形效应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 439-449. |
| [5] | 张怀成, 韩红, 王在峰, 韩立钊, 刘克, 张桂芹, 范晶, 魏小锋. 济南市城市扬尘的微观形貌和化学组分特征分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 545-555. |
| [6] | 郝金虎, 韦玮, 李胜男, 马牧源, 李肖夏, 杨洪国, 姜琦宇, 柴沛东. 基于GEE平台的京津冀长时序水体时空格局及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 556-566. |
| [7] | 张鐥文, 杨冉, 侯文星, 王丽丽, 刘爽, 宋汉扬, 赵文吉, 李令军. 生态补水前后永定河两岸植被覆盖度变化及驱动力分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 264-273. |
| [8] | 盛美君, 李胜君, 杨昕玥, 王蕊, 李洁, 李刚, 修伟明. 华北潮土农田土壤酶活性对土地利用强度的响应特征探讨[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 299-308. |
| [9] | 李少宁, 李婷婷, 陶雪莹, 赵娜, 徐晓天, 鲁绍伟. 4种落叶树种释放有益挥发性有机物的比较研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 123-128. |
| [10] | 张立进, 杜虎, 曾馥平, 黄国勤, 宋敏, 宋同清. 喀斯特峰丛洼地植被恢复过程中生产力与多样性关系探讨[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 26-35. |
| [11] | 王洁, 单燕, 马兰, 宋延静, 王向誉. 秸秆/生物质炭协同还田措施对黄河三角洲盐碱土壤的改良效果研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 90-98. |
| [12] | 吴胜义, 王飞, 徐干君, 马浩, 党禹杰, 吴菲. 川西北高山峡谷区森林碳储量及空间分布研究--以四川洛须自然保护区为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1735-1744. |
| [13] | 秦艳培, 徐少君, 田耀武. 黄河流域河南段植被和土壤及其碳密度空间分异研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1745-1753. |
| [14] | 陈小南, 李琼雯, 余建平, 余顺海, 李双, 曹铭昌. 钱江源国家公园白颈长尾雉生境适宜性评价研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1832-1839. |
| [15] | 阮惠华, 许剑辉, 张菲菲. 2001—2020年粤港澳大湾区植被和地表温度时空变化研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1510-1520. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
