生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (8): 1589-1598.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.08.005
收稿日期:2021-04-28
出版日期:2021-08-18
发布日期:2021-11-03
通讯作者:
* E-mail: longjian22@163.com作者简介:刘进(1996年生),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为环境土壤学。E-mail: milo00@126.com
基金资助:
LIU Jin1( ), LONG Jian1,*(
), LONG Jian1,*( ), LI Juan2, LI Hong1
), LI Juan2, LI Hong1
Received:2021-04-28
Online:2021-08-18
Published:2021-11-03
摘要:
为探明典型喀斯特石漠化地区优势乔木种的钙吸收能力随海拔上升的变化规律及其影响因素,从而有效指导土壤养分的合理利用和生态修复中树种的选择,以贵州花江石漠化治理示范区为研究区域,4种典型树种(香椿Toona sinensis、翅荚香槐Cladrastis platycarpa、构树Broussonetia papyrifera、栾树Koelreuteria paniculata)为研究对象,通过野外调查采集不同海拔的叶片及其土壤,进行植物-土壤总钙和理化性质的分析,对土壤和叶片钙素含量在不同海拔的差异性及其与环境因子的相关性进行研究。结果表明:(1)香椿和构树叶片及各树种土壤钙素含量随海拔变化有显著差异(P<0.05),香椿和栾树在500 m处富钙能力最强(38.99 g∙kg-1和44.72 g∙kg-1),翅荚香槐和构树分别在900 m处和1100 m处最强(41.42 g∙kg-1和51.21 g∙kg-1);(2)香椿和翅荚香槐对土壤钙素的吸收能力在900 m处最大(2.72和1.07),可作为西南石漠化地区中高海拔处植被恢复的先锋树种;栾树和构树在500 m处最大(0.79和0.82),可作为低海拔处植被恢复的先锋树种;(3)海拔差异引起的土壤钾、钠、有机质含量的变化很有可能是影响树种钙生物吸收能力的重要原因,也是树种改变对高钙环境适应策略的关键因素之一。研究结果有助于深入了解不同优势树种在西南喀斯特高钙环境中的适应特性。
中图分类号:
刘进, 龙健, 李娟, 李红. 典型喀斯特山区优势树种钙吸收能力的海拔分异特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1589-1598.
LIU Jin, LONG Jian, LI Juan, LI Hong. Differentiation Characteristics of Calcium Bioabsorption Capacity of Dominant Tree Species with Altitude in Typical Karst Mountain Area[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(8): 1589-1598.
| 海拔 Altitude/m | 土壤类型 Soil types | 主要植被类型 Main vegetation types | 植被覆盖率 Coverage/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | 黄色石灰土 Yellow calcareous soil | 构树 (Broussonetia papyrifera)、香椿 (Toona sinensis)、栾树 (Koelreuteria paniculata)、翅荚香槐 (Cladrastis platycarpa)、牡荆 (Vitex negundo L. var. cannabifolia)、飞机草 (Chromolaena odorata L.) | 60 |
| 700 | 黄色石灰土 Yellow calcareous soil | 构树 (Broussonetia papyrifera)、香椿 (Toona sinensis)、栾树 (Koelreuteria paniculata)、牡荆 (Vitex negundo L. var. cannabifolia)、八角枫 (Alangium chinense (Lour. ) Harms)、胡桃 (Juglans regia)、菩提树 (Ficus religiosa L.)、毛桐 (Mallotus barbatus) | 70 |
| 900 | 黄色石灰土 Yellow calcareous soil | 构树 (Broussonetia papyrifera)、清香木 (Pistacia weinmannifolia)、山麻杆 (Alchornea davidii)、榆树 (Ulmus pumila L.)、火棘 (Pyracantha fortuneana)、川钓樟 (Lindera pulcherrima) | 75 |
| 1100 | 黑色石灰土 Black calcareous soil | 构树 (Broussonetia papyrifera)、松树 (Pinus)、山桃 (Amygdalus davidiana)、布朗耳蕨 (Polystichum braunii (Spenn.) Fée)、石楠 (Photinia serratifolia (Desfontaines) Kalkman)、棕榈 (Trachycarpusfortunei(Hook.) H. Wendl.)、黄檗 (Phellodendron amurense Rupr.) | 85 |
表1 样区基本概况
Table 1 Basic situation in the study plot
| 海拔 Altitude/m | 土壤类型 Soil types | 主要植被类型 Main vegetation types | 植被覆盖率 Coverage/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | 黄色石灰土 Yellow calcareous soil | 构树 (Broussonetia papyrifera)、香椿 (Toona sinensis)、栾树 (Koelreuteria paniculata)、翅荚香槐 (Cladrastis platycarpa)、牡荆 (Vitex negundo L. var. cannabifolia)、飞机草 (Chromolaena odorata L.) | 60 |
| 700 | 黄色石灰土 Yellow calcareous soil | 构树 (Broussonetia papyrifera)、香椿 (Toona sinensis)、栾树 (Koelreuteria paniculata)、牡荆 (Vitex negundo L. var. cannabifolia)、八角枫 (Alangium chinense (Lour. ) Harms)、胡桃 (Juglans regia)、菩提树 (Ficus religiosa L.)、毛桐 (Mallotus barbatus) | 70 |
| 900 | 黄色石灰土 Yellow calcareous soil | 构树 (Broussonetia papyrifera)、清香木 (Pistacia weinmannifolia)、山麻杆 (Alchornea davidii)、榆树 (Ulmus pumila L.)、火棘 (Pyracantha fortuneana)、川钓樟 (Lindera pulcherrima) | 75 |
| 1100 | 黑色石灰土 Black calcareous soil | 构树 (Broussonetia papyrifera)、松树 (Pinus)、山桃 (Amygdalus davidiana)、布朗耳蕨 (Polystichum braunii (Spenn.) Fée)、石楠 (Photinia serratifolia (Desfontaines) Kalkman)、棕榈 (Trachycarpusfortunei(Hook.) H. Wendl.)、黄檗 (Phellodendron amurense Rupr.) | 85 |
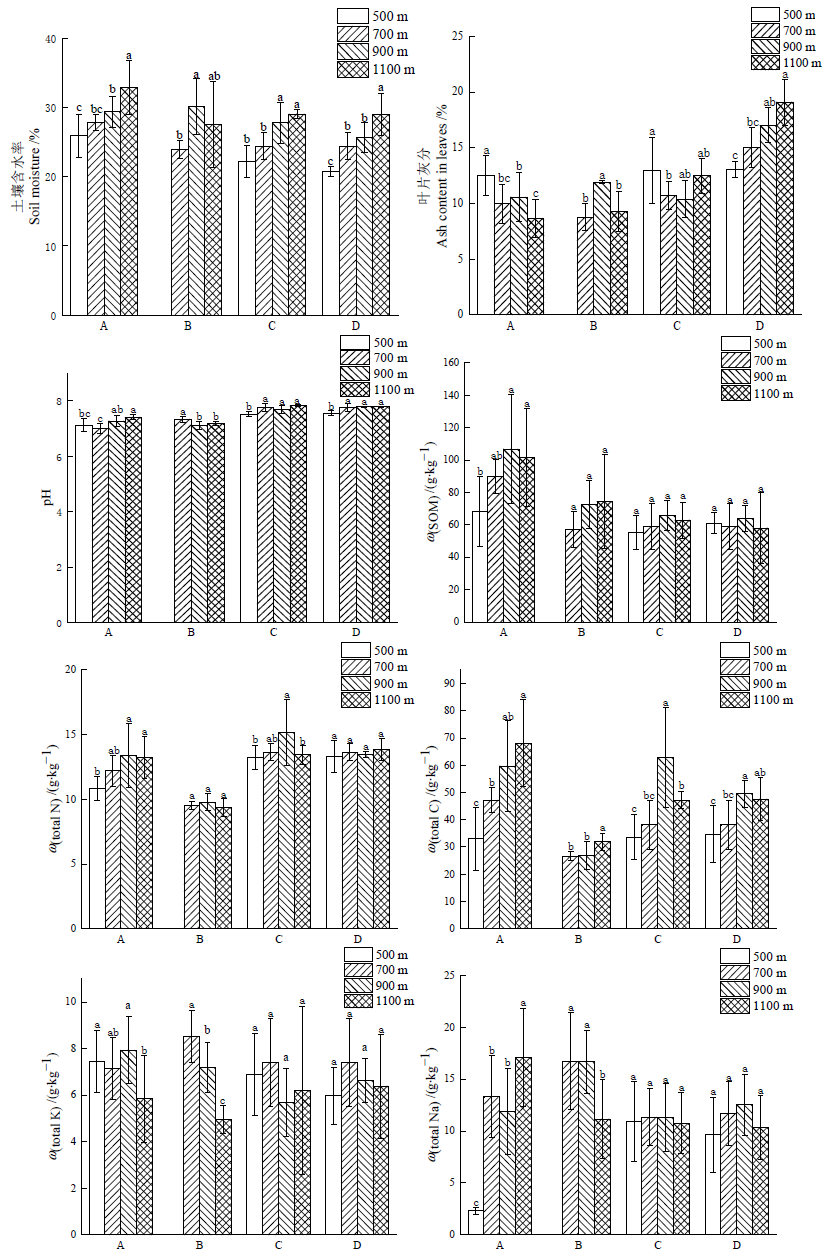
图2 4个优势树种土壤的理化指标 横坐标中的A、B、C、D分别代表香椿、翅荚香槐、栾树、构树。平均值±标准差
Fig. 2 Soil physical and chemical properties under 4 dominant species A, B, C and D in the abscissa axis represent Toona sinensis, Cladrastis platycarpa, Koelreuteria paniculata and Broussonetia papyrifera. Mean±standard deviation
| 树种 Tree species | 项目 Item | 海拔 Altitude | 土壤含水率 Soil moisture | 叶片灰分 Ash content in leaves | pH | 土壤有机质 Organic matter content | 土壤总氮 N content in soil | 土壤总碳 C content in soil | 土壤总钾 K content in soil | 土壤总钠 Na content in soil | 叶片总钙 Ca content in leaves | 土壤总钙 Ca content in soil |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 香椿 Toona sinensis | 叶片总钙 Ca content in leaves | -0.357* | -0.246 | 0.692** | -0.162 | -0.131 | -0.264 | -0.296 | 0.512** | -0.115 | ‒ | ‒ |
| 土壤总钙 Ca content in soil | -0.789** | -0.496** | 0.448** | -0.226 | -0.353* | -0.412* | -0.480** | 0.109 | -0.625** | 0.362* | ‒ | |
| 钙生物吸收系数 Ca bioabsorption coefficient | 0.294 | 0.118 | 0.345* | 0.039 | 0.092 | 0.030 | 0.043 | 0.355* | 0.354* | 0.620** | -0.473** | |
| 翅荚香槐 Cladrastis platycarpa | 叶片总钙 Ca content in leaves | 0.035 | 0.106 | 0.907** | -0.311 | -0.011 | 0.013 | -0.136 | 0.149 | 0.435* | ‒ | ‒ |
| 土壤总钙 Ca content in soil | 0.714** | 0.067 | -0.025 | -0.061 | 0.387 | -0.157 | 0.395* | -0.712** | -0.128 | -0.190 | ‒ | |
| 钙生物吸收系数 Ca bioabsorption coefficient | -0.493* | 0.172 | 0.404* | -0.287 | -0.050 | 0.364 | -0.170 | 0.627** | 0.162 | 0.604** | -0.837** | |
| 栾树 Koelreuteria paniculata | 叶片总钙 Ca content in leaves | 0.072 | -0.124 | 0.952** | -0.135 | -0.017 | 0.065 | 0.008 | -0.009 | -0.149 | ‒ | ‒ |
| 土壤总钙 Ca content in soil | 0.368* | 0.165 | -0.060 | 0.274 | 0.437* | -0.105 | 0.216 | 0.469* | 0.501* | -0.067 | ‒ | |
| 钙生物吸收系数 Ca bioabsorption coefficient | -0.249 | -0.246 | 0.656** | -0.286 | -0.306* | 0.105 | -0.151 | -0.401* | -0.464* | 0.676** | -0.752** | |
| 构树 Broussonetia papyrifera | 叶片总钙 Ca content in leaves | 0.702** | 0.552** | 0.844** | 0.464* | 0.400 | 0.238 | 0.591** | -0.310 | 0.025 | ‒ | ‒ |
| 土壤总钙 Ca content in soil | 0.445* | 0.430* | 0.450* | 0.282 | 0.579** | 0.324 | 0.707** | -0.118 | 0.101 | 0.615** | ‒ | |
| 钙生物吸收系数 Ca bioabsorption coefficient | 0.054 | -0.146 | 0.128 | 0.094 | -0.440* | -0.307 | -0.431* | -0.083 | -0.010 | 0.116 | -0.692** |
表2 植物-土壤钙素与其它因子的相关性分析
Table 2 Correlation analysis of calcium and other factors in plant and soil
| 树种 Tree species | 项目 Item | 海拔 Altitude | 土壤含水率 Soil moisture | 叶片灰分 Ash content in leaves | pH | 土壤有机质 Organic matter content | 土壤总氮 N content in soil | 土壤总碳 C content in soil | 土壤总钾 K content in soil | 土壤总钠 Na content in soil | 叶片总钙 Ca content in leaves | 土壤总钙 Ca content in soil |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 香椿 Toona sinensis | 叶片总钙 Ca content in leaves | -0.357* | -0.246 | 0.692** | -0.162 | -0.131 | -0.264 | -0.296 | 0.512** | -0.115 | ‒ | ‒ |
| 土壤总钙 Ca content in soil | -0.789** | -0.496** | 0.448** | -0.226 | -0.353* | -0.412* | -0.480** | 0.109 | -0.625** | 0.362* | ‒ | |
| 钙生物吸收系数 Ca bioabsorption coefficient | 0.294 | 0.118 | 0.345* | 0.039 | 0.092 | 0.030 | 0.043 | 0.355* | 0.354* | 0.620** | -0.473** | |
| 翅荚香槐 Cladrastis platycarpa | 叶片总钙 Ca content in leaves | 0.035 | 0.106 | 0.907** | -0.311 | -0.011 | 0.013 | -0.136 | 0.149 | 0.435* | ‒ | ‒ |
| 土壤总钙 Ca content in soil | 0.714** | 0.067 | -0.025 | -0.061 | 0.387 | -0.157 | 0.395* | -0.712** | -0.128 | -0.190 | ‒ | |
| 钙生物吸收系数 Ca bioabsorption coefficient | -0.493* | 0.172 | 0.404* | -0.287 | -0.050 | 0.364 | -0.170 | 0.627** | 0.162 | 0.604** | -0.837** | |
| 栾树 Koelreuteria paniculata | 叶片总钙 Ca content in leaves | 0.072 | -0.124 | 0.952** | -0.135 | -0.017 | 0.065 | 0.008 | -0.009 | -0.149 | ‒ | ‒ |
| 土壤总钙 Ca content in soil | 0.368* | 0.165 | -0.060 | 0.274 | 0.437* | -0.105 | 0.216 | 0.469* | 0.501* | -0.067 | ‒ | |
| 钙生物吸收系数 Ca bioabsorption coefficient | -0.249 | -0.246 | 0.656** | -0.286 | -0.306* | 0.105 | -0.151 | -0.401* | -0.464* | 0.676** | -0.752** | |
| 构树 Broussonetia papyrifera | 叶片总钙 Ca content in leaves | 0.702** | 0.552** | 0.844** | 0.464* | 0.400 | 0.238 | 0.591** | -0.310 | 0.025 | ‒ | ‒ |
| 土壤总钙 Ca content in soil | 0.445* | 0.430* | 0.450* | 0.282 | 0.579** | 0.324 | 0.707** | -0.118 | 0.101 | 0.615** | ‒ | |
| 钙生物吸收系数 Ca bioabsorption coefficient | 0.054 | -0.146 | 0.128 | 0.094 | -0.440* | -0.307 | -0.431* | -0.083 | -0.010 | 0.116 | -0.692** |
| [1] |
REN C J, ZHANG W, ZHONG Z K, et al., 2018. Differential responses of soil microbial biomass, diversity, and compositions to altitudinal gradients depend on plant and soil characteristics[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 610-611: 750-758.
DOI URL |
| [2] | KINZEL H, 1989. Calcium in the Vacuoles and Cell Walls of Plant Tissue[J]. Urban & Fischer, 182(1-2): 99-125. |
| [3] |
PHILIP J W, 2001. The pathways of calcium movement to the xylem[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 52(358): 891-899.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
ROBERT J, CHRISTINE A, JÖRG P, 2004. Calcium Loss in Central European Forest Soils[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 68(2): 588-595.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
URSULA FG, JÖRG B, MAUD EQ, et al., 1995. Is the Ca꞉Al ratio superior to pH, Ca or Al concentrations of soils in accounting for the distribution of plants in deciduous forest?[J]. Plant and Soil, 177(1): 21-31.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
WEI X H, LIU S J, MÜLLER K, et al., 2019. Urbanization-induced acid rain causes leaching loss of calcium from limestone-derived soil in South China[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 19(11): 3797-3804.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
YANG H, LIANG J H, CHEN J R, et al., 2015. Soil calcium speciation at different geomorphological positions in the Yaji karst experimental site in Guilin, China[J]. Journal of Resources and Ecology, 6(4): 224-229.
DOI URL |
| [8] | 鲍士旦, 2008. 土壤农化分析[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社. |
| BAO S D, 2000. Agrochemical Analysis of Soil[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press. | |
| [9] | 曹建华, 袁道先, 潘根兴, 2003. 岩溶生态系统中的土壤[J]. 地球科学进展, 18(1): 37-44. |
| CAO J H, YUAN D X, PAN G X, 2003. Some soil features in karst ecosystem[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 18(1): 37-44. | |
| [10] | 陈家瑞, 曹建华, 梁毅, 等, 2012. 石灰土发育过程中土壤腐殖质组成及其与土壤钙赋存形态关系[J]. 中国岩溶, 31(1): 7-11. |
| CHEN J R, CAO J H, LIANG Y, et al., 2012. Relationship of the humus components and the calcium form with the development of limestone soil[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 31(1): 7-11. | |
| [11] | 陈青松, 舒英格, 周鹏鹏, 等, 2020. 喀斯特山区不同生态恢复下石灰土钙形态特征[J]. 水土保持学报, 34(4): 48-55. |
| CHEN Q S, SHU Y G, ZHOU P P, et al., 2020. Calcium components of calcareous soil under different ecological restoration patterns in karst mountainous area[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 34(4): 48-55. | |
| [12] | 党亚爱, 2008. 黄土高原南北主要类型土壤有机碳氮库分布特征研究[D]. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学. |
| DANG Y A, 2008. Characteristics of the cool of soil organtic carbon and soil organtic nitrogen on the loess plateau from Sortn to North[D]. Xianyang: Northwest A & F University. | |
| [13] | 邸欣月, 安显金, 董慧, 等, 2015. 贵州喀斯特区域土壤有机质的分布与演化特征[J]. 地球与环境, 43(6): 697-708. |
| DI X Y, AN X J, DONG H, et al., 2015. The distribution and evolution of soil organic matter in the karst region, Guizhou province, southwestern China[J]. Earth and Environment, 43(6): 697-708. | |
| [14] | 付威波, 2015. 不同钙浓度对典型岩溶植物生长及光合生理特性的影响[D]. 南宁: 广西大学. |
| FU W B, 2015. The effect of different concentrations of calcium on growth and photosynthetic physiological characteristics of typical plants in karst[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University. | |
| [15] | 黄芬, 胡刚, 涂春燕, 等, 2015. 岩溶区不同土地利用类型土壤钙形态分布特征[J]. 南方农业学报, 46(9): 1574-1578. |
| HUANG F, HU G, TU C Y, et al., 2015. Fraction distribution of calcium in soils of different land use types in karst areas[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 46(9): 1574-1578. | |
| [16] | 黄黎英, 曹建华, 周莉, 等, 2007. 不同地质背景下土壤溶解有机碳含量的季节动态及其影响因子[J]. 生态环境, 16(4): 1282-1288. |
| HUANG L Y, CAO J H, ZHOU L, et al., 2007. Seasonal change and the influence factors of soil dissolved organic carbon at different geological background[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 16(4): 1282-1288. | |
| [17] |
姬飞腾, 李楠, 邓馨, 2009. 喀斯特地区植物钙含量特征与高钙适应方式分析[J]. 植物生态学报, 33(5): 926-935.
DOI |
| JI F T, LI N, DENG X, 2018. Calcium contents and high calcium adaptation of plants in karst areas of China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 33(5): 926-935. | |
| [18] | 李德红, 王小菁, 潘瑞炽, 1998. 钙信使与植物激素信号传递[J]. 生物学杂志, 15(4): 3-5. |
| LI D H, WANG X J, PAN R Z, 1998. Calcium messenger and plant hormone signaling[J]. Journal of Biology, 15(4): 3-5. | |
| [19] | 李菲, 李娟, 龙健, 等, 2015. 典型喀斯特山区植被类型对土壤有机碳、氮的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 34(12): 3374-3381. |
| LI F, LI J, LONG J, et al., 2015. Effect of vegetation types on soil organic carbon and nitrogen in typical karst mountainous area[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 34(12): 3374-3381. | |
| [20] | 李果, 2017. 贵州喀斯特地区不同土地利用方式下土壤理化性质与土壤肥力评价[D]. 重庆: 西南大学. |
| LI G, 2017. Soil fertility evaluation and soil physical and chemical properties of different land use patterns in Guizhou karst area[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University. | |
| [21] | 李家旭, 孙大业, 1991. 生物细胞中钙调素分布研究及其意义[J]. 细胞生物学杂志, 13(1): 1-6. |
| LI J X, SUN D Y, 1991. Distribution of calmodulin in biological cells and its significance[J]. Chinese Journal of Cell Biology, 13(1): 1-6. | |
| [22] | 李涛, 余龙江, 2006. 西南岩溶环境中典型植物适应机制的初步研究[J]. 地学前缘, 13(3): 180-184. |
| LI T, YU L J, 2006. A primary study of adaptive mechanisms of representative plants in karst areas in southwest China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 13(3): 180-184. | |
| [23] | 李小方, 2006. 岩溶环境中土壤-植物系统钙元素形态分析及其生态意义[D]. 桂林: 广西师范大学. |
| LI X F, 2006. Speciation of calcium in soil and plants’leaves in karst ecosystem and its ecological significance[D]. Guilin: Guangxi Normal University. | |
| [24] | 李新星, 刘桂民, 吴小丽, 等, 2020. 马衔山不同海拔土壤碳、氮、磷含量及生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 39(3): 758-765. |
| LI X X, LIU G M, WU X L, et al., 2018. Elevational distribution of soil organic carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus contents and their ecological stoichiometry on Maxian Mountain[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 39(3): 758-765. | |
| [25] | 理艳霞, 2008. 茂兰喀斯特森林优势树种钙循环机制[D]. 贵阳: 贵州师范大学. |
| LI Y X, 2008. Study on the mechanism of calcuim cycle of dominant tree species in Maolan karst forest[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou Normal University. | |
| [26] | 金章利, 刘高鹏, 周明涛, 等, 2019. 喀斯特山地草地群落多样性海拔特征及土壤理化性质特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(4): 661-668. |
| JIN Z L, LIU G P, ZHOU M T, et al., 2019. Elevation characteristics of grassland community diversity and effect of soil physical and chemical properties in karst mountain grassland[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28(4): 661-668. | |
| [27] | 李菁, 杨程, 靳振江, 等, 2019. 断陷盆地区不同土地利用方式土壤钙形态分布特征[J]. 中国岩溶, 38(06): 889-895. |
| LI J, YANG C, JIN Z J, et al., 2019. The characteristics of calcium fraction distribution in soil from different land use types in karst faulted basin[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 38(06): 889-895. | |
| [28] | 李忠云, 魏兴琥, 李保生, 等, 2015. 粤北岩溶丘陵区不同地貌部位土壤钙的分布特征--以英德市九龙镇为例[J]. 热带地理, 35(1): 89-95. |
| LI Z Y, WEI X H, LI B S, et al., 2015. Characteristics of calcium ions migration at different geomorphological positions in karst hilly area of northern Guangdong: a case study on Jiulong Town in Yingde City[J]. Tropical Geography, 35(1): 89-95. | |
| [29] | 廖洪凯, 龙健, 李娟, 2012. 土地利用方式对喀斯特山区土壤养分及有机碳活性组分的影响[J]. 自然资源学报, 27(12): 2081-2090. |
| LIAO H K, LONG J, LI J, 2012. Effects of different land use patterns on soil nutrients and soil active organic carbon components in karst mountain area[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 27(12): 2081-2090. | |
| [30] | 刘冠成, 黄雅曦, 王庆贵, 等, 2018. 环境因子对植物物种多样性的影响研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 34(13): 83-89. |
| LIU G C, HUANG Y X, WANG Q G, et al., 2018. Effects of environmental factors on plant species diversity: Research progress[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 34(13): 83-89. | |
| [31] | 刘丽平, 孟亚利, 杨佳蒴, 等, 2014. 不同施钾处理对棉田土壤钾素形态与土壤肥力的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 28(2): 138-142. |
| LIU L P, MENG Y L, YANG J S, et al., 2014. Effects of different k fertilizer treatments on soil k forms and soil fertility in cotton[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 28(2): 138-142. | |
| [32] | 罗绪强, 张桂玲, 杜雪莲, 等, 2014. 茂兰喀斯特森林常见钙生植物叶片元素含量及其化学计量学特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 23(7): 1121-1129. |
| LUO X Q, ZHANG G L, DU X L, et al., 2014. Characteristics of element contents and ecological stoichiometry in leaves of common calcicole species in Maolan karst forest[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 23(7): 1121-1129. | |
| [33] | 倪大伟, 王妍, 刘云根, 等, 2018. 典型岩溶小流域不同土地利用类型土壤钙分布及形态特征[J]. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学), 38(2): 83-88. |
| NI D W, WANG Y, LIU Y G, et al., 2018. Distribution and morphological characteristics of soil calcium in different land use types in typical karst small watershed[J]. Journal of Southwest Forestry University (Natural Sciences), 38(2): 83-88. | |
| [34] | 谭德水, 金继运, 黄绍文, 等, 2008. 长期施钾与秸秆还田对西北地区不同种植制度下作物产量及土壤钾素的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 14(5): 886-893. |
| TAN D S, JIN J Y, HUANG S W, et al., 2008. Effect of long-term K fertilizer application and returning wheat straw to soil on crop yield and soil K under different planting systems in northwestern China[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 14(5): 886-893. | |
| [35] | 谭玉兰, 杨丰, 陈超, 等, 2019. 喀斯特山区土地利用方式对土壤质量的影响[J]. 西南农业学报, 32(5): 1133-1138. |
| TAN Y L, YANG F, CHEN C, et al., 2019. Effects of different land use types on soil quality in karst mountainous area[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 32(5): 1133-1138. | |
| [36] | 王冬艳, 李月芬, 尚媛, 等, 2011. 吉林延边地区土壤钙元素生态地球化学[J]. 吉林大学学报 (地球科学版), 41(1): 215-221. |
| WANG D Y, LI Y F, SHANG Y, et al., 2011. Ecological geochemistry of calcium in soil of Yanbian area, Jilin[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 41(1): 215-221. | |
| [37] | 王进, 刘子琦, 张国, 等, 2019. 喀斯特石漠化治理不同恢复模式土壤养分分布特征--以贵州花江示范区为例[J]. 西南农业学报, 32(7): 1578-1585. |
| WANG J, LIU Z Q, ZHANG G, et al., 2018. Distribution characteristics of soil nutrients of different restoration models in karst rocky desertification control area: Taking Huajiang Demonstration Zone in Guizhou as example[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 32(7): 1578-1585. | |
| [38] | 王明月, 刘绍雄, 熊智, 等, 2014. 石漠化地区豆科植物根瘤菌降解碳酸钙、镁能力研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 23(10): 1581-1585. |
| WANG M Y, LIU S X, XIONG Z, et al., 2014. Leguminous plants rhizobia degradation of calcium carbonate and magnesium carbonate[J]. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 23(10): 1581-1585. | |
| [39] | 魏兴琥, 雷俐, 刘淑娟, 2017. 粤北岩溶峰林植物钙吸收、转运、返还能力及适应性分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 36(3): 368-376. |
| WEI X H, LEI L, LIU S J, et al., 2017. Analysis on the absorbing, transfer, restoration and adaptation mechanism of calcium in different peak forest plants in northern Guangdong Province, China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 36(3): 368-376. | |
| [40] | 吴安驰, 邓湘雯, 任小丽, 等, 2018. 中国典型森林生态系统乔木层群落物种多样性的空间分布格局及其影响因素[J]. 生态学报, 38(21): 7727-7738. |
| WU A C, DENG X W, REN X L, et al., 2018. Biogeographic patterns and influencing factors of the species diversity of tree layer community in typical forest ecosystems in China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(21): 7727-7738. | |
| [41] | 谢佳贵, 侯云鹏, 尹彩侠, 等, 2014. 施钾和秸秆还田对春玉米产量、养分吸收及土壤钾素平衡的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 20(5): 1110-1118. |
| XIE J G, HOU Y P, YIN C X, et al., 2014. Effect of potassium application and straw returning on spring maize yield, nutrient absorption and soil potassium balance[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 20(5): 1110-1118. | |
| [42] | 谢丽萍, 2006. 石漠化过程中土壤-植被系统营养元素的协变关系[D]. 贵阳: 中国科学院地球化学研究所. |
| XIE L P, 2006. The nutrient elements' co-variances of soil-vegetation system in the process of rocky desertification[D]. Guiyang: Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences. | |
| [43] | 杨慧, 陈家瑞, 梁建宏, 等, 2017. 桂林丫吉岩溶区土壤有机碳和pH值与钙形态分布的关系初探[J]. 地质论评, 63(4): 1117-1126. |
| YANG H, CHEN J R, LIANG J H, et al., 2017. Preliminary study on the relationship between soil organic carbon and pH value and calcium species in Yaji karst region, Guilin[J]. Geological Review, 63(4):1117-1126. | |
| [44] |
尹华军, 张子良, 刘庆, 2018. 森林根系分泌物生态学研究: 问题与展望[J]. 植物生态学报, 42(11):1055-1070.
DOI |
|
YIN H J, ZHANG Z L, LIU Q, 2018. Root exudates and their ecological consequences in forest ecosystems: Problems and perspective[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 42(11): 1055-1070.
DOI URL |
|
| [45] | 喻阳华, 王璐, 钟欣平, 等, 2018a. 贵州喀斯特山区不同海拔花椒人工林土壤质量评价[J]. 生态学报, 38(21): 7850-7858. |
| YU Y H, WANG L, ZHONG X P, et al., 2018. Evaluation of soil quality of Chinese prickly ash artificial orchard at different altitudes in Guizhou karst mountainous area[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(21): 7850-7858. | |
| [46] | 喻阳华, 秦仕忆, 钟欣平, 2018b. 喀斯特干热河谷花椒林母岩化学组成与元素含量随海拔的分异[J]. 贵州师范大学学报(自然科学版), 36(2): 9-14. |
| YU Y H, QIN S Y, ZHONG X P, 2018. The mother rock’s chemical composition and element contents of the Chinese prickly ash in the karst dry and hot valley as the altitude changes[J]. Journal of Guizhou Normal University (Natural Sciences), 36(2): 9-14. | |
| [47] | 曾玲玲, 张兴梅, 朱洪德, 等, 2009. 钾肥对大豆产量和土壤养分的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 40(6): 1381-1384. |
| ZENG L L, ZHANG X M, ZHU H D, et al., 2009. Effects of applying potassium on soybean yield and soil nutrient[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 40(6): 1381-1384. | |
| [48] | 张凯选, 范鹏鹏, 王军邦, 等, 2019. 西南喀斯特地区植被变化及其与气候因子关系研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(6): 1080-1091. |
| ZHANG K X, FAN P P, WANG J B, et al., 2019. Study on Vegetation Changes and Climate Factors in A Karst Region of Southwest China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28(6): 1080-1091. | |
| [49] | 张鹏, 胡晓农, 杨慧, 等, 2020. 云南蒙自断陷盆地石漠化区土壤钙形态特征[J]. 中国岩溶, 39(3): 368-374. |
| ZHANG P, HU X N, YANG H, et al., 2020. Characteristics of soil calcium forms of rocky desertification areas in the Mengzi fault-depression basin, Yunnan[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 39(3): 368-374. | |
| [50] |
张忠华, 胡刚, 祝介东, 等, 2011. 喀斯特森林土壤养分的空间异质性及其对树种分布的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 35(10): 1038-1049.
DOI |
| ZHANG Z H, HU G, ZHU J D, et al., 2018. Spatial heterogeneity of soil nutrients and its impact on tree species distribution in a karst forest of Southwest China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 35(10): 1038-1049. | |
| [51] | 周文杰, 吕德国, 秦嗣军, 2016. 植物与根际微生物相互作用关系研究进展[J]. 吉林农业大学学报, 38(3): 253-260. |
| ZHOU W J, LV D G, QING S J, 2016. Research Progress in Interaction between Plant and Rhizosphere Microorganism[J]. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 38(3): 253-260. | |
| [52] | 周卫, 林葆, 1996. 土壤中钙的化学行为与生物有效性研究进展[J]. 土壤肥料 (5): 19-22. |
| ZHOU W, LIN B, 1996. Research progress on chemical behavior and bioavailability of calcium in soil[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China (5): 19-22. |
| [1] | 秦浩, 李蒙爱, 高劲, 陈凯龙, 张殷波, 张峰. 芦芽山不同海拔灌丛土壤细菌群落组成和多样性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 459-468. |
| [2] | 宋志斌, 周佳诚, 谭路, 唐涛. 高原河流着生藻类群落沿海拔梯度的变化特征--以西藏黑曲、雪曲为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 274-282. |
| [3] | 黄伟佳, 刘春, 刘岳, 黄斌, 李定强, 袁再健. 南岭山地不同海拔土壤生态化学计量特征及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 80-89. |
| [4] | 曹晓云, 祝存兄, 陈国茜, 孙树娇, 赵慧芳, 朱文彬, 周秉荣. 2000—2021年柴达木盆地地表绿度变化及地形分异研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1080-1090. |
| [5] | 王小娜, 徐当会, 王谢军, 方向文. 祁连山灌丛群落结构特征随海拔梯度和经度的变化[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 231-238. |
| [6] | 蔡锡安, 黄娟, 吴彤, 刘菊秀, 蒋芬, 王森浩. 植物叶片排放甲烷的初步研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(9): 1842-1847. |
| [7] | 闫东锋, 张妍妍, 吕康婷, 周梦丽, 王婷, 赵宁. 太行山南麓不同海拔梯度天然林优势树种生态位特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1571-1580. |
| [8] | 何斌, 李青, 陈群利, 李望军, 游萍. 黔西北黄杉群落物种多样性的海拔梯度格局[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1111-1120. |
| [9] | 刘旻霞, 于瑞新, 穆若兰, 夏素娟. 兰州北山不同海拔3种典型绿化树种光合特性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(10): 1943-1951. |
| [10] | 张莎莎, 李爱琴, 王会荣, 王晶晶, 徐小牛. 不同海拔杉木人工林土壤碳氮磷生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2020, 29(1): 97-104. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
