生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 1202-1212.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.06.011
郑智恒1,2( ), 熊康宁1,2,*(
), 熊康宁1,2,*( ), 容丽1,3, 池永宽1,2
), 容丽1,3, 池永宽1,2
收稿日期:2021-01-18
出版日期:2021-06-18
发布日期:2021-09-10
通讯作者:
* 熊康宁,教授,博士研究生导师,主要研究方向为喀斯特地貌与洞穴、石漠化生态治理。E-mail: xiongkn@163.com作者简介:郑智恒(1992年生),硕士研究生,主要研究方向为石漠化生态治理。E-mail: z1h2e3n4g5199261@163.com
基金资助:
ZHENG Zhiheng1,2( ), XIONG Kangning1,2,*(
), XIONG Kangning1,2,*( ), RONG Li1,3, CHI Yongkuan1,2
), RONG Li1,3, CHI Yongkuan1,2
Received:2021-01-18
Online:2021-06-18
Published:2021-09-10
摘要:
生物结皮是喀斯特生态系统中重要的地表覆盖植被,在石漠化土地恢复和生态治理工程中扮演着关键角色。通过土壤农化学分析方法研究不同石漠化等级下各类型生物结皮对其下层土壤理化性质的影响,对于探索喀斯特生态脆弱区土壤的形成发育及土壤环境的稳定至关重要。研究结果表明:在结皮层中全氮、速效氮、全磷、速效磷、速效钾、土壤有机碳、土壤田间持水量、土壤孔隙度均表现为苔藓结皮>混生结皮>地衣结皮>藻类结皮(P<0.05),土壤容重则表现为藻类结皮>地衣结皮≥混生结皮≥苔藓结皮(P>0.05)。生物结皮下0—5 cm和5—10 cm土层理化性质的变化规律与结皮层相似。整体上看,生物结皮在潜在-轻度和中度-强度这两种典型石漠化区域内,对下层土壤理化性质改善有较好的影响,土壤恢复指数体现为苔藓结皮>混生结皮>地衣结皮>藻类结皮,不同类型的生物结皮对下层土壤理化性质的影响随着土层的加深而减小。在撒拉溪研究区中,对比空白组,苔藓结皮、混生结皮和藻类结皮的土壤养分恢复指数分别为25.1%、18.6%、10.4%和6.3%;而在花江研究区中,苔藓结皮、混生结皮和藻类结皮的土壤养分恢复指数分别为25.8%、18.9%、7.6%和5.7%。除pH值外,不同类型的生物结皮各土层间土壤理化性质均呈显著相关。生物结皮能有效改善土壤的理化性质,增加土壤养分含量,提升土地承载力与抗侵蚀能力,加速石漠化地区土壤养分的积累及恢复,平衡土壤环境稳定,为植被的生长发育提供良好的先决条件。因此研究并掌握喀斯特石漠化地区生物结皮对土壤理化性改良机理及其与土壤环境的交互机制进而对研究喀斯特生态系统的生物多样性建设,物质能量循环及石漠化生态治理措施等意义重大。
中图分类号:
郑智恒, 熊康宁, 容丽, 池永宽. 两种等级喀斯特石漠化地区生物结皮对土壤养分恢复的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1202-1212.
ZHENG Zhiheng, XIONG Kangning, RONG Li, CHI Yongkuan. Effects of Biological Crusts on Soil Properties in Karst Rocky Desertification Areas of Different Levels[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(6): 1202-1212.
| 研究区 Research area | 位置 Location | 中心点坐标 Center point coordinates | 地貌类型 Land form type | 植被群落构成 Vegetation community composition | 土壤类型 Soil type | 石漠化等级 Rocky desertification grade | 样品数及编号 Sample number and serial number | 样地结皮 盖度 Crust coverage | 研究区植被盖度 Research area vegetation coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 毕节撒拉溪(Ⅰ) Bijie salaxi(Ⅰ) | 毕节市撒拉溪镇 Salaxi Town, Bijie City | 27°15'40″N, 105°04'50″E | 喀斯特 高原山地 Karst plateau mountains | 木、草、刺、藤、灌丛 Wood, grass, thorn, vine, shrub | 黄壤土、 紫砂土 Yellow loam, purple sand | 潜在-轻度 Potential-mild | SK(1-18) | 0% | 81% |
| TX(1-18) | 85% | ||||||||
| HH(1-18) | 82% | ||||||||
| DY(1-18) | 81% | ||||||||
| ZL(1-18) | 89% | ||||||||
| 关岭- 贞丰花江(Ⅱ) Guan- zhenfenghuajiang | 安顺市花江镇 Huajiang Town, Anshun City, | 25°40'40″N, 106°38'50″E | 喀斯特 高原峡谷 Karst plateau canyon | 木、草、刺、藤、灌丛 Wood, grass, thorn, vine, shrub | 黄壤土、 黄色石灰土 Yellow loam, yellow lime soil | 中度-强度 Moderate- intensity | SK(19-36) | 0% | 75% |
| TX(19-36) | 83% | ||||||||
| HH(19-36) | 80% | ||||||||
| DY(19-36) | 85% | ||||||||
| ZL(19-36) | 87% |
表1 试验区基础信息及样地设置
Table 1 Basic information and plot settings of the experimental area
| 研究区 Research area | 位置 Location | 中心点坐标 Center point coordinates | 地貌类型 Land form type | 植被群落构成 Vegetation community composition | 土壤类型 Soil type | 石漠化等级 Rocky desertification grade | 样品数及编号 Sample number and serial number | 样地结皮 盖度 Crust coverage | 研究区植被盖度 Research area vegetation coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 毕节撒拉溪(Ⅰ) Bijie salaxi(Ⅰ) | 毕节市撒拉溪镇 Salaxi Town, Bijie City | 27°15'40″N, 105°04'50″E | 喀斯特 高原山地 Karst plateau mountains | 木、草、刺、藤、灌丛 Wood, grass, thorn, vine, shrub | 黄壤土、 紫砂土 Yellow loam, purple sand | 潜在-轻度 Potential-mild | SK(1-18) | 0% | 81% |
| TX(1-18) | 85% | ||||||||
| HH(1-18) | 82% | ||||||||
| DY(1-18) | 81% | ||||||||
| ZL(1-18) | 89% | ||||||||
| 关岭- 贞丰花江(Ⅱ) Guan- zhenfenghuajiang | 安顺市花江镇 Huajiang Town, Anshun City, | 25°40'40″N, 106°38'50″E | 喀斯特 高原峡谷 Karst plateau canyon | 木、草、刺、藤、灌丛 Wood, grass, thorn, vine, shrub | 黄壤土、 黄色石灰土 Yellow loam, yellow lime soil | 中度-强度 Moderate- intensity | SK(19-36) | 0% | 75% |
| TX(19-36) | 83% | ||||||||
| HH(19-36) | 80% | ||||||||
| DY(19-36) | 85% | ||||||||
| ZL(19-36) | 87% |
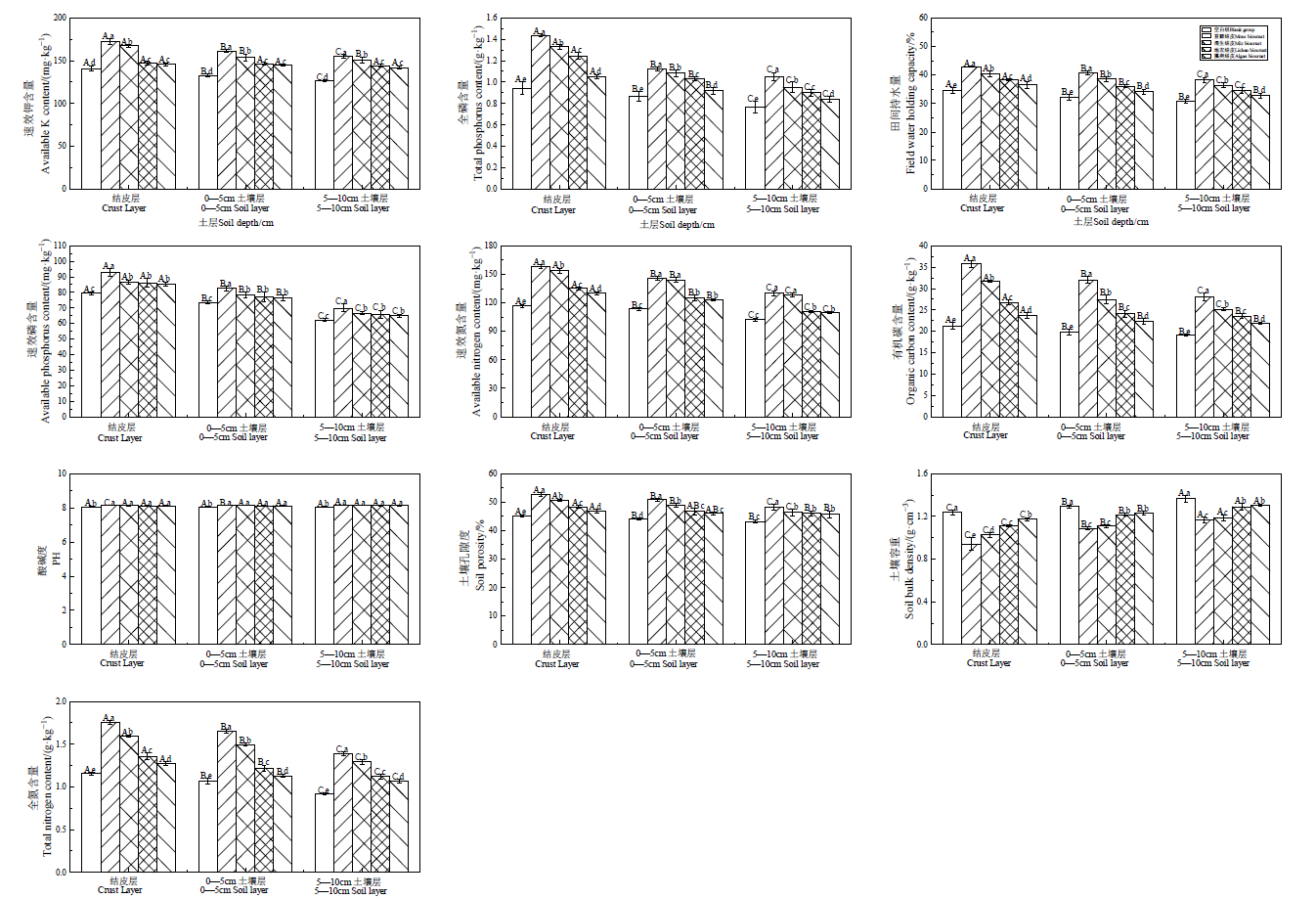
图1 撒拉溪研究区不同类型结皮及下层土壤物理和化学性质 不同小写字母表示同一土壤层次在不同类型生物结皮间差异显著,P<0.05;不同大写字母表示同一类型生物结皮在不同土层间差异显著,P<0.05。下同
Fig. 1 Physical and chemical properties of different types of crusts and their underlying soils in the Salaxi research area Different lowercase letters indicate that the same soil layer has significant differences between different types of biological crusts, P<0.05; different capital letters indicate that the same type of biological crusts are insignificant difference between different soil layers, P<0.05. The same below
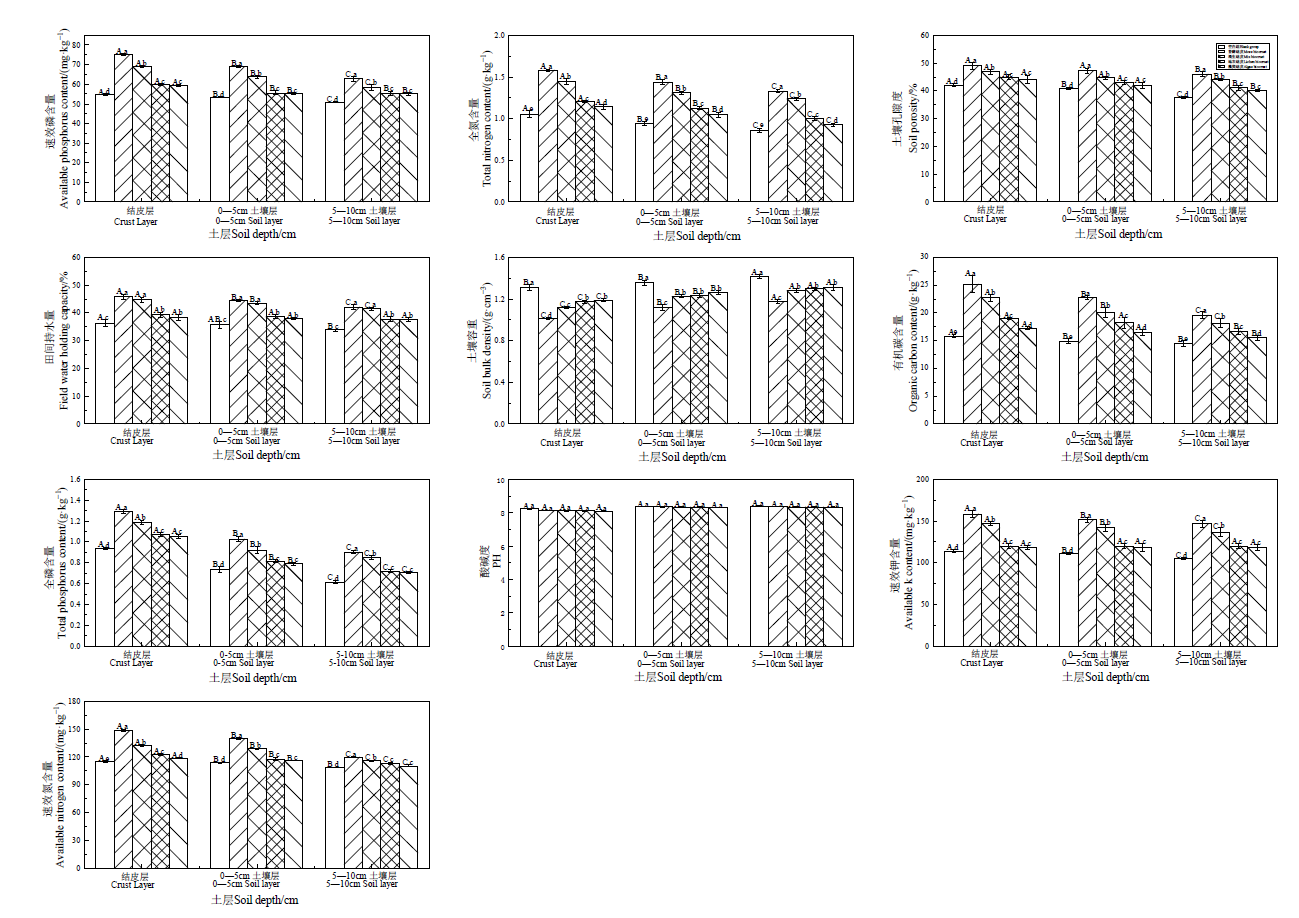
图2 花江研究区不同类型结皮及其下层土壤物理和化学性质
Fig. 2 Different types of crusts and the physical and chemical properties of the underlying soil in the Huajiang research area
| Factor | pH | TN | AN | TP | AP | AK | SOC | SBD | FC | SP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 0.875 | 0.903 | 0.882 | 0.916 | 0.951 | 0.887 | -0.907 | 0.902 | 0.932 | |
| TN | 0.985** | 0.992** | 0.922* | 0.977** | 0.993** | -0.996** | 0.989** | 0.983** | ||
| AN | 0.976** | 0.882* | 0.983** | 0.967** | -0.994** | 0.969** | 0.965** | |||
| TP | 0.919* | 0.966** | 0.993** | -0.992** | 0.997** | 0.983** | ||||
| AP | 0.944* | 0.952* | -0.920 * | 0.945* | 0.971** | |||||
| AK | 0.973** | -0.987** | 0.973** | 0.987** | ||||||
| SOC | -0.989** | 0.997** | 0.993** | |||||||
| SBD | -0.990** | -0.986** | ||||||||
| FC | 0.993** | |||||||||
| SP |
表2 撒拉溪研究区生物结皮土壤理化性质相关系数
Table 2 Correlation coefficients of physical and chemical properties of biological crust soil in the Salarxi research area
| Factor | pH | TN | AN | TP | AP | AK | SOC | SBD | FC | SP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 0.875 | 0.903 | 0.882 | 0.916 | 0.951 | 0.887 | -0.907 | 0.902 | 0.932 | |
| TN | 0.985** | 0.992** | 0.922* | 0.977** | 0.993** | -0.996** | 0.989** | 0.983** | ||
| AN | 0.976** | 0.882* | 0.983** | 0.967** | -0.994** | 0.969** | 0.965** | |||
| TP | 0.919* | 0.966** | 0.993** | -0.992** | 0.997** | 0.983** | ||||
| AP | 0.944* | 0.952* | -0.920 * | 0.945* | 0.971** | |||||
| AK | 0.973** | -0.987** | 0.973** | 0.987** | ||||||
| SOC | -0.989** | 0.997** | 0.993** | |||||||
| SBD | -0.990** | -0.986** | ||||||||
| FC | 0.993** | |||||||||
| SP |
| Factor | pH | TN | AN | TP | AP | AK | SOC | SBD | FC | SP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 0.819 | 0.921 | 0.877 | 0.852 | 0.907 | 0.975 | -0.901 | 0.943 | 0.879 | |
| TN | 0.976** | 0.990** | 0.991** | 0.992** | 0.995** | -0.951* | 0.987** | 0.978** | ||
| AN | 0.974** | 0.990** | 0.980** | 0.972** | -0.924* | 0.939* | 0.959** | |||
| TP | 0.995** | 0.986** | 0.991** | -0.982** | 0.982** | 0.997** | ||||
| AP | 0.995** | 0.985** | -0.959* | 0.975** | 0.986** | |||||
| AK | 0.978** | -0.937* | 0.985** | 0.974** | ||||||
| SOC | -0.967** | 0.976** | 0.983** | |||||||
| SBD | -0.952* | -0.992** | ||||||||
| FC | 0.976** | |||||||||
| SP |
表3 花江研究区生物结皮土壤理化性质相关系数
Table 3 Correlation coefficients of physical and chemical properties of biological crust soils in the Huajiang research area
| Factor | pH | TN | AN | TP | AP | AK | SOC | SBD | FC | SP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 0.819 | 0.921 | 0.877 | 0.852 | 0.907 | 0.975 | -0.901 | 0.943 | 0.879 | |
| TN | 0.976** | 0.990** | 0.991** | 0.992** | 0.995** | -0.951* | 0.987** | 0.978** | ||
| AN | 0.974** | 0.990** | 0.980** | 0.972** | -0.924* | 0.939* | 0.959** | |||
| TP | 0.995** | 0.986** | 0.991** | -0.982** | 0.982** | 0.997** | ||||
| AP | 0.995** | 0.985** | -0.959* | 0.975** | 0.986** | |||||
| AK | 0.978** | -0.937* | 0.985** | 0.974** | ||||||
| SOC | -0.967** | 0.976** | 0.983** | |||||||
| SBD | -0.952* | -0.992** | ||||||||
| FC | 0.976** | |||||||||
| SP |
| [1] |
THOMAS A D, DOUGILL A J, 2006. Distribution and characteristics of cyanobacterial soil crusts in the Molopo Basin, South Africa[J]. Journal of Arid Environments. 64(2): 270-283.
DOI URL |
| [2] | ANTONINKA A, FAIST A, Rodriguez-Caballero E, et al., 2020. Biological soil crusts in ecological restoration: emerging research and perspectives[J]. Restoration Ecology, 42(29): 213-225. |
| [3] | BAO T L, GAO L Q, WANG S S, et al., 2005. Moderate disturbance increases the PLFA diversity and biomass of the microbial community in biocrusts in the Loess Plateau region of China[J]. Environ Microbiol, 7(1): 1-12. |
| [4] | DAI Q H, PENG X D, WANG P J, et al., 2018. Surface erosion and underground leakage of yellow soil on slopes in karst regions of southwest China[J]. Land Degradation and Development, 29(7): 115-119. |
| [5] | STEGGLES E K, FACELLI J M, AINSLEY P J, et al., 2019. Biological soil crust and vascular plant interactions in Western Myall (Acacia papyrocarpa) open woodland in South Australia[J]. Journal of Vegetation Science, 30(8): 4-5. |
| [6] | GAO L Q, ZHAO Y G, XU M X, et al., 2018. The effects of biological soil crust succession on soil ecological stoichiometry characteristics[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(2): 678-688. |
| [7] |
HU R, WANG X P, PAN Y X, et al., 2015. Seasonal variation of net N mineralization under different biological soil crusts in Tengger Desert, North China[J]. CATENA, 127(31): 9-16.
DOI URL |
| [8] | KAKEH J, GORJI M, MOHAMMADI M H, et al., 2020. MHBiological soil crusts determine soil properties and salt dynamics under arid climatic condition in Qara Qir, Iran[J]. Science of the total environment, 732(25): 139-168. |
| [9] | LI L, XIONG K N, 2020. Study on peak cluster-depression rocky desertification landscape evolution and human activity-influence in South of China[J]. European journal of remote sensing, 47(2): 120-130. |
| [10] |
MIRALLES I, DOMINGO F, GARCIA-CAMPSS E, et al., 2012. Elena Biological and microbial activity in biological soil crusts from the Tabernas desert, a sub-arid zone in SE Spain[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 55(55): 113-121.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
SONG G, LI X R, HU R, 2017. Biological soil crusts determine the germination and growth of two exotic plants[J]. Ecology and Evolution, 7(22): 9441-9450.
DOI URL |
| [12] | WANG S J, HUANG X F, ZHOU Y C, 2018. Soil organic carbon change relating to the prevention and control of rocky desertification in Guizhou Province, SW China[J]. International Journal of Global Warming, 135(15): 3-5. |
| [13] | YING B, XIAO S Z, XIONG K N, et al., 2014. Comparative studies of the distribution characteristics of rocky desertification and land use/land cover classes in typical areas of Guizhou province, China[J]. Environmental earth sciences, 71(2): 4631-645. |
| [14] | ZHANG Y R, KE T, YE C R, et al., 2019. The facilitative effects of shrub on induced biological soil crust development and soil properties[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 137(3): 16-19. |
| [15] | ZHANG Y, XIONG K N, QIN Y, et al., 2020. Stoichiometric characteristics of ecological-economic forests in karst rocky desertification areas of southern China[J]. Austrian Journal of Forest Science, 137(2): 109-131. |
| [16] |
ZHANG Y, XIONG K N, YU Y H, et al., 2020. Stoichiometric characteristics and driving mechanisms of plants in karst areas of rocky desertification of southern china[J]. Applied ecology and environmental research, 18(1): 1961-1979.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
ZHAO C L, YANG Y S, WANG S F, et al., 2015. Wind erosion prevention characteristics and key influencing factors of bryophytic soil crusts[J]. Plant and Soil, 397(10): 163-174.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
ZHOU Y Y, LI X R, GAO Y H, et al., 2020. Carbon fluxes response of an artificial sand-binding vegetation system to rainfall variation during the growing season in the Tengger Desert[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, DOI: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110556.
DOI |
| [19] | 程才, 李晓娜, 李玉杰, 等, 2019. 苔藓结皮在我国喀斯特石漠化治理中的应用潜力[J]. 应用生态学报, 30(7): 2501-2510. |
| CHENG C, LI X N, LI Y J, et al., 2019. Application potential of bryophyte soil crust on the control of karst rocky desertification[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 30(7): 2501-2510. | |
| [20] | 从春蕾, 刘天雷, 孔祥远, 等, 2017. 贵州普定喀斯特受损生态系统石生藓类植物区系及物种多样性研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 36(2):179-186. |
| CONG C L, LIU T L, KONG X Y, et al., 2017. Flora and species diversity of epilithic mosses on rock desertification in the Puding karst area[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 36(2): 179-186. | |
| [21] | 都军, 李宜轩, 杨晓霞, 等, 2018. 腾格里沙漠东南缘生物土壤结皮对土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 38(1): 111-116. |
| DU J, LI Y X, YANG X X, et al., 2018. Effects of Biological Soil Crusts Types on Soil Physicochemical Properties in the Southeast Fringe of the Tengger Desert[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 38(1): 111-116. | |
| [22] | 符裕红, 喻理飞, 黄宗胜, 等, 2020. 岩溶区根系地下生境优势植物及其养分利用特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(12): 2337-2345. |
| FU Y H, YU L F, HUANG Z S, et al., 2020. Nutrient Utilization Characteristics of Dominant Plants of Root Underground Habitat in Karst Areas[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29(12): 2337-2345. | |
| [23] | 高丽倩, 赵允格, 许明祥, 等, 2018. 生物土壤结皮演替对土壤生态化学计量特征的影响[J]. 生态学报, 38(2): 678-688. |
| GAO L Q, ZHAO Y G, XU M X, et al., 2018. Influence of Biological Soil Crust Succession on Soil Ecological Stoichiometry[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(2): 678-688. | |
| [24] | 葛秋诗, 张萍, 倪茂飞, 等, 2021. 典型喀斯特高原水库浮游植物与环境因子的关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(1): 156-164. |
| GE Q S, ZHANG P, NI M F, et al., 2021. Relationships between Phytoplankton and Environmental Factors in A Typical Karst Plateau Reservoir[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(1): 156-164. | |
| [25] | 韩炳宏, 牛得草, 贺磊, 等, 2017. 生物土壤结皮发育及其影响因素研究进展[J]. 草业科学, 34(9): 1793-1801. |
| HAN B H, NIU D C, HE L, et al., 2017. A review on the development and effect of biological soil crusts[J]. Pratacultural Science, 34(9): 1793-1801. | |
| [26] | 吉雪花, 张元明, 周小兵, 等, 2014. 不同尺度苔藓结皮土壤性状的空间分布特征[J]. 生态学报, 34(14): 4006-4016. |
| JI X H, ZHANG Y M, ZHOU X B, et al., 2014. Spatial distribution of soil properties covered by moss crusts on different scales[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34(14): 4006-4016. | |
| [27] | 李冰, 张朝晖, 2009. 喀斯特石漠结皮层藓类物种多样性及在石漠化治理中的作用研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 28(1): 55-60. |
| LI B, ZHANG Z H, 2009. Species diversity of mosses crust and the effect in karst rocky desertification control[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 28(1): 55-60. | |
| [28] | 李军峰, 贾少华, 王智慧, 等, 2015. 喀斯特石漠化过程中苔藓植物多样性及分布与环境关系[J]. 生态科学, 34(1): 68-73. |
| LI J F, JIA S H, WANG Z H, et al., 2015. The diversity of bryophytes and their distribution associated with environmental factors during the process of karst rocky desertification[J]. Ecological Science, 34(1): 68-73. | |
| [29] | 李茜倩, 张元明, 2018. 荒漠藓类结皮斑块中土壤理化性质、酶活性及微生物生物量分布的边缘效应[J]. 生态学杂志, 37(7): 2114-2121. |
| LI X Q, ZHANG Y M, 2018. The horizontal distribution of soil physicochemical properties, soil enzyme activities, and microbial biomass in moss crust patch in a temperate desert[J]. Chinese Journa of Ecology, 37(7): 2114-2121. | |
| [30] | 李新荣, 谭会娟, 回嵘, 等, 2018. 中国荒漠与沙地生物土壤结皮研究[J]. 科学通报, 63(23): 2320-2334. |
| LI X R, TAN H J, HUI R, et al., 2018. Researches in biological soil crust of China: A review[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 63(23): 2320-2334. | |
| [31] | 刘润, 申家琛, 张朝晖, 2018. 4种苔藓植物在喀斯特石漠化地区的生态修复意义[J]. 水土保持学报, 32(6): 220-230. |
| LIU R, SHENG J C, ZHANG Z H, 2018. Study on the Significance of Ecological Restoration of Four Bryophytes in Karst Rocky Desertification Area[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 32(6): 220-230. | |
| [32] | 秦福雯, 康濒月, 姜风岩, 等, 2019. 生物土壤结皮演替对高寒草原植被结构和土壤养分的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(6): 1100-1107. |
| QIN F W, KANG B Y, JIANG F Y, et al., 2019. Effects of Biological Soil Crust Succession on Vegetation Structure and Soil Nutrients in Alpine Steppe[J]. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 28(6): 1100-1107. | |
| [33] | 申家琛, 张朝晖, 王慧慧, 等, 2017. 贵阳喀斯特公园南石林秋季藓类植物的持水特性[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 33(10): 907-912. |
| SHEN J C, ZHANG Z H, WANG H H, et al., 2017. Water Retention Capacity of Autumn Mosses in South Stone Forest of Guiyang Karst Park[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 33(10): 907-912. | |
| [34] | 苏延桂, 李新荣, 赵昕, 等, 2011. 不同类型生物土壤结皮固氮活性及对环境因子的响应研究[J]. 地球科学进展, 26(3): 332-338. |
| SU Y G, LI X R, ZHAO X, et al., 2011. The Nitrogenase Activity of Biological Soil Crusts and Their Responses to Environmental Factors[J]. Advances in earth science, 26(3): 332-338. | |
| [35] | 熊康宁, 李晋, 龙明忠, 2012. 典型喀斯特石漠化治理区水土流失特征与关键问题[J]. 地理学报, 67(7): 878-888. |
| XIONG K N, LI J, LONG M Z, 2012. Features of Soil and Water Loss and Key Issues in Demonstration Areas for Combating Karst Rocky Desertification[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 67(7): 878-888. | |
| [36] | 杨睿, 李娟, 龙健, 廖洪凯, 等, 2021. 贵州喀斯特山区不同种植年限花椒根际土壤细菌群落结构特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(1): 81-91. |
| YANG R, LONG J, LIAO H K, et al., 2021. Structural Characteristics of Bacterial Community in Rhizosphere Soil of Zanthoxylum bungeamun in Different Planting Years in Karst Areas of Guizhou[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 37(1): 81-91. | |
| [37] | 杨巧云, 赵允格, 包天莉, 等, 2019. 黄土丘陵区不同类型生物结皮下的土壤生态化学计量特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 30(8): 2699-2706. |
| YANG Q Y, ZHAO Y G, BAO T L, et al., 2019. Soil ecological stoichiometry characteristics under different types of biological soil crusts in the hilly Loess Plateau region, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 30(8): 2699-2706. | |
| [38] | 张健, 徐明, 邹晓, 等, 2019. 不同土壤和植被生境下生物结皮对土壤性质的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 33(5): 323-328. |
| ZHANG J, XU M, ZOU X, et al., 2019. Effects of Biological Crusts on Soil Properties Under Different Soil and Vegetation Habitats[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 33(5): 323-328. | |
| [39] | 张元明, 2005. 荒漠地表生物土壤结皮的微结构及其早期发育特征[J]. 科学通报, 15(1): 42-47. |
| ZHANG Y M, 2005. Microstructure and early development characteristics of soil crusts in desert surface organisms[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 15(1): 42-47. | |
| [40] | 张元明, 曹同, 潘伯荣, 2002. 干旱与半干旱地区苔藓植物生态学研究综述[J]. 生态学报, 22(7): 1129-1134. |
| ZHANG Y M, CAO T, PAN B R, 2002. A Review on the Studies of Bryophyte Ecology in Arid and Semi-arid Areas[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 22(7): 1129-1134. | |
| [41] | 郑云普, 赵建成, 张丙昌, 等, 2009. 荒漠生物结皮中藻类和苔藓植物研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 44(3): 371-378. |
| ZHENG Y P, ZHAO J C, ZHANG B C, et al., 2009. Advances on Ecological Studies of Algae and Mosses in Biological Soil Crust[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany. 44(3): 371-378. | |
| [42] | 郑智恒, 熊康宁, 容丽, 等, 2020. 生物土壤结皮在喀斯特生态治理中的应用潜力[J]. 西北植物学报, 40(6): 1075-1086. |
| ZHENG Z H, XIONG K N, RONG L, et al., 2020. Application potential of biological soil crust in karst ecological management[J]. Northwest Botany, 40(6): 1075-1086. | |
| [43] | 朱远达, 蔡强国, 胡霞, 等, 2004. 土壤理化性质对结皮形成的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 41(1): 13-19. |
| ZHU Y D, CAI Q G, HU X, et al., 2004. Effects of soil Physical and Chemical Properties on Soil Crusting[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 41(1): 13-19. |
| [1] | 杜丹丹, 高瑞忠, 房丽晶, 谢龙梅. 旱区盐湖盆地土壤重金属空间变异及对土壤理化因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1123-1132. |
| [2] | 张贝儿, 吴建强, 王敏, 熊丽君, 谭娟, 沈城, 黄波涛, 黄沈发. 耕地生态保育工程的土壤健康度评价方法初探[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 388-396. |
| [3] | 王礼霄, 刘晋仙, 柴宝峰. 华北亚高山土壤细菌群落及氮循环对退耕还草的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1537-1546. |
| [4] | 王磊, 温远光, 周晓果, 朱宏光, 孙冬婧. 尾巨桉与红锥混交对林下植被和土壤性质的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1340-1349. |
| [5] | 杨冲, 王春燕, 王文颖, 毛旭峰, 周华坤, 陈哲, 索南吉, 靳磊, 马华清. 青藏高原黄河源区高寒草地土壤营养特征变化及质量评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 896-908. |
| [6] | 赵隽宇, 黄小芮, 石媛媛, 宋贤冲, 覃祚玉, 唐健. 南亚热带多代连栽桉树人工林根际土壤FTIR特征分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 688-694. |
| [7] | 夏开, 邓鹏飞, 马锐豪, 王斐, 温正宇, 徐小牛. 马尾松次生林转换为湿地松和杉木林对土壤细菌群落结构和多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 460-469. |
| [8] | 谢邵文, 郭晓淞, 杨芬, 黄强, 陈曼佳, 魏兴琥, 刘承帅. 广州市城市公园土壤重金属累积特征、形态分布及其生态风险[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2206-2215. |
| [9] | 刘佩伶, 刘效东, 冯英杰, 苏宇乔, 甘先华, 张卫强. 新丰江水库库区水源涵养林土壤饱和导水率特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 1993-2001. |
| [10] | 辛未冬, 杜一丹, 刘华煜, 杨轶萌, 赵浩志, 杨丹. 地表节肢动物多样性对煤矸石山不同植被恢复方式的响应及生物指示作用[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 2079-2088. |
| [11] | 陈双双, 朱宁华, 周光益, 袁星明, 尚海, 王迤翾. 不同等级石漠化环境下人工乔木林的植被与土壤物理特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 52-61. |
| [12] | 王瑞, 宋祥云, 柳新伟. 黄河三角洲不同植被类型土壤酶活性的季节变化[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 62-69. |
| [13] | 林丽, 代磊, 林泽北, 吴际通, 颜伟, 王志杰. 黔中城市森林群落植物多样性及其与土壤理化性质的关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(11): 2130-2141. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
