生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 1213-1219.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.06.012
邹晨怡1,2( ), 丁洪2, 王亚萨2, 张玉树2, 余居华2, 郑祥洲2,*(
), 丁洪2, 王亚萨2, 张玉树2, 余居华2, 郑祥洲2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-11-25
出版日期:2021-06-18
发布日期:2021-09-10
通讯作者:
* 郑祥洲,E-mail: z85103@qq.com作者简介:邹晨怡(1995年生)女,硕士研究生,主要从事氮素生物地球化学循环研究。E-mail: 569662202@qq.com
基金资助:
ZOU Chenyi1,2( ), DING Hong2, WANG Yasa2, ZHANG Yushu2, YU Juhua2, ZHENG Xiangzhou2,*(
), DING Hong2, WANG Yasa2, ZHANG Yushu2, YU Juhua2, ZHENG Xiangzhou2,*( )
)
Received:2020-11-25
Online:2021-06-18
Published:2021-09-10
摘要:
秸秆还田对提高土壤肥力具有重要意义,但是秸秆还田对氮素在土壤中的转化过程的影响还不清楚。通过室内培养研究了等量施氮条件下不同秸秆还田量对尿素态氮的水解、硝化及反硝化等氮素转化过程的影响。试验设5个处理,分别为CK,不加尿素氮不加秸秆;S0,尿素氮200 mg∙kg-1+秸秆量0 g∙kg-1;S1,尿素氮200 mg∙kg-1+秸秆量4.44 g∙kg-1;S2,尿素氮200 mg∙kg-1+秸秆量8.88 g∙kg-1;S3,尿素氮200 mg∙kg-1+秸秆量13.33 g∙kg-1。结果表明,秸秆添加可促进尿素水解过程,24 h后,尿素的水解率从S0处理的71.9%增加至S3处理的98.0%。添加秸秆在前15天会减少土壤中铵态氮的含量,与S0相比,第3天时,S1、S2、S3的铵态氮含量分别减少了18.35%、27.09%、25.47%。S0处理和S1处理土壤中的硝态氮含量均随着培养时间的延长而升高,且在培养的第21天基本达到稳定;而S2和S3处理的硝态氮含量则呈先下降后上升的趋势。从培养3 d起添加秸秆的处理土壤中的硝态氮含量始终低于不添加秸秆的处理(P<0.05),且随着秸秆用量的增加土壤中的硝态氮含量显著降低(P<0.05)。添加秸秆增加了氮肥的反硝化损失,且随着秸秆用量的增加,反硝化损失率急剧增加,从S0处理的0.45%增加至S3处理的62.87%。添加秸秆处理土壤的微生物量碳(SMBC)含量和空白对照相比,均有明显的提升(P<0.05),且随着秸秆用量的增加而增加。研究表明,秸秆的添加能提高SMBC的含量,进而增加了土壤氮素的同化,但同时也增加了氮素的反硝化损失,且随秸秆添加量的增大,影响效果越明显。
中图分类号:
邹晨怡, 丁洪, 王亚萨, 张玉树, 余居华, 郑祥洲. 秸秆对尿素氮在土壤中转化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1213-1219.
ZOU Chenyi, DING Hong, WANG Yasa, ZHANG Yushu, YU Juhua, ZHENG Xiangzhou. Effect of Straw on Urea Nitrogen Transformation in Soil[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(6): 1213-1219.
| 处理 Treatment | 24 h | 48 h | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 尿素态氮含量 Urea nitrogen content/(mg∙kg-1) | 水解率 Hydrolysis rate/% | 尿素含量 Urea nitrogen content/(mg∙kg-1) | 水解率 Hydrolysis rate/% | ||
| CK | 0.94±0.24e | - | 0.89±0.19a | - | |
| S0 | 57.05±2.92b | 71.9 | 0.8±0.19a | 100.0 | |
| S1 | 21.02±8.17c | 90.0 | 0.75±0.11a | 100.1 | |
| S2 | 8.44±6.86d | 96.2 | 0.89±0.39a | 100.0 | |
| S3 | 4.95±4.05de | 98.0 | 1.05±0.18a | 99.9 | |
表1 土壤中尿素态氮含量动态变化
Table 1 Dynamic changes of urea nitrogen content in soil
| 处理 Treatment | 24 h | 48 h | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 尿素态氮含量 Urea nitrogen content/(mg∙kg-1) | 水解率 Hydrolysis rate/% | 尿素含量 Urea nitrogen content/(mg∙kg-1) | 水解率 Hydrolysis rate/% | ||
| CK | 0.94±0.24e | - | 0.89±0.19a | - | |
| S0 | 57.05±2.92b | 71.9 | 0.8±0.19a | 100.0 | |
| S1 | 21.02±8.17c | 90.0 | 0.75±0.11a | 100.1 | |
| S2 | 8.44±6.86d | 96.2 | 0.89±0.39a | 100.0 | |
| S3 | 4.95±4.05de | 98.0 | 1.05±0.18a | 99.9 | |
| 处理 Treatment | 反硝化损失总量 Total denitrification loss/ (mg∙kg-1) | 反硝化损失总量占施氮量的比例 The ratio of total denitrification loss to nitrogen application/% |
|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.28±0.11d | |
| S0 | 1.18±0.58c | 0.45c |
| S1 | 2.66±1.49c | 1.19c |
| S2 | 33.33±8.42b | 16.53b |
| S3 | 126.02±7.47a | 62.87a |
表2 尿素氮肥反硝化作用损失量
Table 2 Denitrification loss of urea nitrogen fertilizer
| 处理 Treatment | 反硝化损失总量 Total denitrification loss/ (mg∙kg-1) | 反硝化损失总量占施氮量的比例 The ratio of total denitrification loss to nitrogen application/% |
|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.28±0.11d | |
| S0 | 1.18±0.58c | 0.45c |
| S1 | 2.66±1.49c | 1.19c |
| S2 | 33.33±8.42b | 16.53b |
| S3 | 126.02±7.47a | 62.87a |
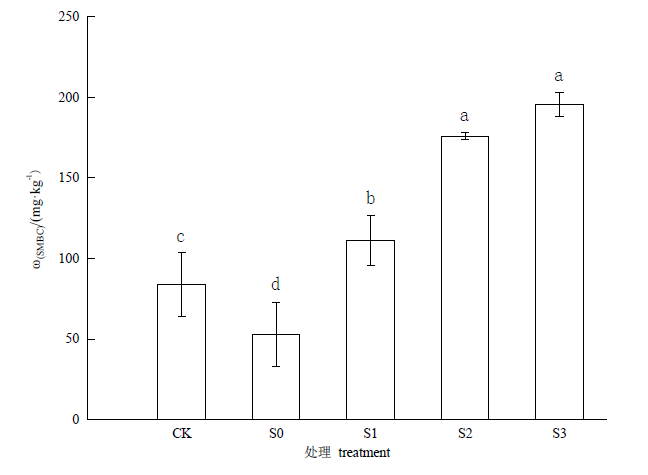
图4 不同秸秆用量对土壤中微生物量碳的影响 不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05)
Fig. 4 Influence of different straw usage on microbial biomass Carbon in soil The different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among treatments (P<0.05)
| [1] | BIRD J A, KESSEL C V, HORWATH W R, 2003. Stabilization of 13C-carbon and immobilization of 15N-nitrogen from rice straw in humic fractions[J]. Soil Science Society of America, 67(3): 806-816. |
| [2] |
BLAGODATSKAYA E, KUZYAKOV Y, 2008. Mechanisms of real and apparent priming effects and their dependence on soil microbial biomass and community structure: critical review[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 45(2): 115-131.
DOI URL |
| [3] | BRUST G E, 2019. Management Strategies for Organic Vegetable Fertility[M]// Safety and Practice for Organic Food. America: Academic Press: 193-212. |
| [4] |
BURGER M, JACKSON L E, 2003. Microbial immobilization of ammonium and nitrate in relation to ammonification and nitrification rates in organic and conventional cropping systems[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 35(1): 29-36.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
CHENG Y, CAI Z C, CHANG S X, et al., 2012. Wheat straw and its biochar have contrasting effects on inorganic N retention and N2O production in a cultivated Black Chernozem[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 48(8): 941-946.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
DONG L F, THOMTON D C O, NEDWELL D B, et al., 2000. Denitrification in sediments of the river Colne estuary, England[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 203(1): 109-122.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
HAO X, XIE Y X, XIONG Z Q, et al., 2009. Nitrogen fate and environmental consequence in paddy soil under rice wheat rotation in the Taihu lake region, China[J]. Plant and Soil, 319(1-2): 225-234.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
HYUGENS D, RUTTING T, BOECKX P, et al., 2007. Soil nitrogen conservation mechanisms in a pristine south Chilean Nothofagus forest ecosystem[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 39(10): 2448-2458.
DOI URL |
| [9] | JENKINSON D S, LADD J N, 1981. Microbial biomass in soil: Measurement and turnover[M]. Soil Biochemistry, 5: 415-458. |
| [10] |
JENKINSON D S, POWLSON D S, 1976. The effects of biocidal treatments on metabolism in soil-V. A method for measuring soil biomass[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 8(3): 209-213.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
KALVELAGE T, LAVIK G, LAM P, et al., 2013. Nitrogen cycling driven by organic matter export in the South Pacific oxygen minimum zone[J]. Nature Geoscience, 6(3): 228-234.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
LIU Y R, DONG J X, HAN L L, et al., 2016. Influence of rice straw-amendment on mercury methylation and nitrification in paddy soils[J]. Environmental Pollution, 209(15): 53-59.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
LU W, ZHANG H, MIN J, et al., 2015. Dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium in a soil under greenhouse vegetable cultivation as affected by organic amendments[J]. Journal of soil and sediments, 15(5): 1169-1177.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
MA H H, YIN Y F, GAO R, et al., 2019. Response of nitrogen transformation to glucose additions in soils at two subtropical forest types subjected to simulated nitrogen deposition[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 19(5): 2166-2175.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
MALHI S S, NYBORG M, PUURVEEN D, et al., 2012. Long-term tillage, straw management and nitrogen fertilization effects on organic matter and mineralizable carbon and nitrogen in a black chernozem soil[J]. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 43(20): 2679-2690.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
MULLER C, SHERLOCK R R, WILLIAMS P H, 1999. Field method to determine N2O emission from nitrification and denitrification[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 28(1): 51-55.
DOI URL |
| [17] | MULVANEY R, BREMNER J M, 1979. Modified diacetyl monoxime method for colorimetric determination of urea in soil extracts[J]. Communications in Soil Science &Plant Analysis, 10(8): 1163-1170. |
| [18] | NISHIO T, KOMADA M, ARAO T,et a1., 2015. Simultaneous determination of transformation rates of nitrate in soil[J]. Japan Agricuhural Research Quarterly, 35(1): 11-17. |
| [19] | NIU L A, HAO J M, ZHANG B Z, et al., 2011. Influences of long-term fertilizer and tillage management on soil fertility of the North China plain[J]. Pedosphete, 21(6): 813-820. |
| [20] |
REICHEL R, WEI J, ISLAM M S, et al., 2018. Potential of wheat straw, spruce sawdust, and lignin as high organic carbon soil amendments to improve agricultural nitrogen retention capacity: An incubation study[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00900.
DOI |
| [21] |
ROMERO C M, ENGEL R, CHEN C C, et al., 2015. Microbial immobilization of nitrogen-15 labelled ammonium and nitrate in an agricultural soil[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 79(2): 595-602.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
RYALS R, KAISER M, TORN M S, et al., 2014. Impacts of organic matter amendments on carbon and nitrogen dynamics in grassland soils[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 68: 52-61.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
SHINDO H, NISHIOT, 2005. Immobilization and remineralization of N following addition of wheat straw in to soil: Determination of gross N transformation rates by N ammonium isotope dilution technique[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 37(3): 425-432.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
WANG D, GUO L, ZHENG L, et al., 2019. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer and water management practices on nitrogen leaching from a typical open field used for vegetable planting in northern China[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 213: 913-921.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
WANG J, ZHU B, ZHANG J B, et al., 2015. Mechanisms of soil N dynamics following long-term application of organic fertilizers to subtropical rain-fed purple soil in China[J]. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, DOI: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2015.08.039.
DOI |
| [26] | XU G W, DUAN H, WANG Z Q, et al., 2010. Effect of wheat-residue application on physical and chemical characters and enzymatic activities in soil[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science, 42(3): 934-342. |
| [27] | ZHAO Y, WANG J, CAI Z C, et al., 2018. Short-term effects of nitrapyrin, rice straw and its biochar application on N transformation in soils of humid subtropical China[J]. Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica, Section B: Soil and Plant Science, 68(5): 1-9. |
| [28] | 成艳红, 黄欠如, 武琳, 等, 2017. 稻草覆盖和香根草篱对红壤坡耕地土壤酶活性和微生物群落结构的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 50(23): 4602-4612. |
| CHENG Y H, HUANG Q R, WU L, et al., 2017. Effects of straw mulching and vetiver grass hedgerows on soil enzyme activities and soil microbial community structure in red soil sloping land[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 50(23): 4602-4612. | |
| [29] | 韩新忠, 2013. 稻麦轮作条件下秸秆还田对作物、土壤微生物及碳库的影响[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学. |
| HAN X Z, 2013. Effects of straw returning on crop, soil microbial and soil organic carbon pool under rice-wheat rotation[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University. | |
| [30] | 焦晓光, 隋跃宇, 张兴义, 2008. 土壤有机质含量与土壤脲酶活性关系的研究[J]. 农业系统科学与综合研究, 24(4): 494-496. |
| JIAO X G, SUI Y Y, ZHANG X Y, 2008. Study on the relationship between soil organic matter content and soil urease Activity[J]. System Sciences and Comprehensive Studies in Agriculture, 24(4): 494-496. | |
| [31] | 金雪霞, 范晓晖, 蔡贵信, 等, 2004. 菜地土壤氮素矿化和硝化作用的特征[J]. 土壤, 36(4): 382-386. |
| JIN X X, FAN X H, CAI G X, et al., 2004. Characteristics of nitrogen mineralization and nitrification in vegetable garden soils[J]. Soils, 36(4): 382-386. | |
| [32] | 巨晓棠, 谷保静, 2014. 我国农田氮肥施用现状、问题及趋势[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 20(4): 783-795. |
| JU X T, GU B J, 2014. Status-quo, problem and trend of nitrogen fertilization in China[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 20(4): 783-795. | |
| [33] | 郎漫, 李平, 王丹丹, 等, 2015. 有机物料对黑土氮素转化的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 46(6): 1347-1351. |
| LANG M, LI P, LI D D, et al., 2015. Effect of organic materials on nitrogen transformation in black soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 46(6): 1347-1351. | |
| [34] | 李俊良, 陈新平, 李晓林, 等, 2003. 大白菜氮肥施用的产量效应,品质效应和环境效应[J]. 土壤学报, 40(2): 261-266. |
| LI J L, CHEN X P, LI X L, et al., 2003. Effect of N fertilization on yield, nitrate content and N apparent losses of chinese cabbage[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 40(2): 261-266. | |
| [35] | 刘晶晶, 汪苹, 王欢, 2008. 一株异养硝化-好氧反硝化菌的脱氮性能研究[J]. 环境科学研究, 21(3): 121-125. |
| LIU J J, WANG P, WANG X, 2008. Study on denitrification characteristics of a heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrifier[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 21(3): 121-125. | |
| [36] | 鲁如坤, 1999. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社: 150-160. |
| LU R K, 1999. Analysis methods of soil agricultural chemistry[M]. Beijing: Chinese Agricultural Science and Technology Press: 150-160. | |
| [37] | 路怡青, 朱安宁, 张佳宝, 等, 2013. 免耕和秸秆还田对潮土酶活性及微生物量碳氮的影响[J]. 土壤, 45(5): 894-898. |
| LU Y Q, ZHU A N, ZHANG J B, et al., 2013. Effects of no-tillage and straw-return on soil enzyme activities and microbial biomass[J]. Soils, 45(5): 894-898. | |
| [38] | 马力, 杨林章, 肖和艾, 等, 2011. 长期施肥和秸秆还田对红壤水稻土氮素分布和矿化特性的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 17(4): 898-905. |
| MA L, YANG L Z, XIAO H A, et al., 2011. Effects of long-term fertilization and straw returning on distribution and mineralization of nitrogen in paddy soils in subtropical China[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 17(4): 898-905. | |
| [39] | 马想, 黄晶, 赵惠丽, 等, 2018. 秸秆与氮肥不同配比对红壤微生物量碳氮的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 24(6): 1574-1580. |
| MA X, HUANG J, ZHAO H L, et al., 2018. Straw and nitrogen fertilizer ratios influence microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen in red soil[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 24(6): 1574-1580. | |
| [40] | 潘凤娥, 胡俊鹏, 索龙, 等, 2016. 添加玉米秸秆及其生物质炭对砖红壤N2O排放的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 35(2): 396-402. |
| PAN F E, HU J P, SUO L, et al., 2016. Effect of corn stalk and its biochar on N2O emissions from latosol soil[J]. Journal of agro-Environment Science, 35(2):396-402. | |
| [41] | 祁通, 刘易, 冯耀祖, 等, 2014. 氮肥施用方式对耐盐冬小麦干物质积累和氮素吸收利用的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 20(5): 1288-1293. |
| QI T, LIU Y, FENG Y Z, et al., 2014. Effects of nitrogen application patterns on the dry matter accumulation and nitrogen uptake in salt-tolerant winter wheat[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 20(5): 1288-1293. | |
| [42] | 宋贺, 徐新超, 王敬国, 等, 2012. 设施菜田土壤剖面中的反硝化特征[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 18(4): 860-868 |
| SONG H, XU X C, WANG J G, et al., 2012. Characteristics of denitrification in different soil layers in a greenhouse vegetable cropping system[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 18(4): 860-868. | |
| [43] | 王欢欢, 任天宝, 元野, 等, 2017. 生物质炭与氮肥配施对植烟土壤微生物量碳,氮和碳氮比的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 33(12): 52-57. |
| WANG H H, REN T B, YUAN Y, et al., 2017. Combined application of biomass charcoal and nitrogen fertilizer: effects on microbial biomass C, microbial biomass N and C/N in tobacco soil[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 33(12): 52-57. | |
| [44] | 张继旭, 张忠锋, 张继光, 等, 2016. 不同类型秸秆还田对烟田土壤碳氮矿化的影响[J]. 烟草科技, 49(3): 10-16. |
| ZHANG J X, ZHANG Z F, ZHANG J G, et al., 2016. Effects of different types of straw and stalk returning on carbon and nitrogen mineralization in tobacco soil[J]. Tobacco Science & Technology, 49(3): 10-16. | |
| [45] | 张亚丽, 张娟, 沈其荣, 等, 2002. 秸秆生物有机肥的施用对土壤供氮能力的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 13(12): 1575-1578. |
| ZHANG Y L, ZHANG J, SHEN Q R, et al., 2002. Effect of combined application of bioorganic manure and inorganic nitrogen fertilizer on soil nitrogen supplying characteristics[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 13(12): 1575-1578. | |
| [46] | 赵亚丽, 郭海斌, 薛志伟, 等, 2015. 耕作方式与秸秆还田对土壤微生物数量、酶活性及作物产量的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 26(6): 1785-1792. |
| ZHAO Y L, GUO H B, XUE Z W, et al., 2015. Effects of tillage and straw returning on microorganism quantity, enzyme activities in soils and grain yield[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 26(6): 1785-1792. | |
| [47] | 郑祥洲, 丁洪, 雷俊杰, 等, 2013. 吡虫啉和毒死蜱对尿素氮在土壤中转化的影响[J]. 农药学学报, 15(6): 648-654. |
| ZHENG X Z, DING H, LEI J J, et al., 2013. Effects of imidacloprid and chlorpyrifos on transformation of urea nitrogen in soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Pesticide Science, 15(6): 648-654. | |
| [48] | 周巍, 2008. 施用有机物料对吉林黑土中尿素氮转化因子的影响[D]. 长春: 吉林农业大学. |
| ZHOU W, 2008. The influence of organic material on urea nitrogen transformation factors in the loam Jilin province[D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University. |
| [1] | 王云, 郑西来, 曹敏, 李磊, 宋晓冉, 林晓宇, 郭凯. 滨海含水层咸-淡水过渡带反硝化性能与控制因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 980-988. |
| [2] | 徐敏, 许超, 余光辉, 尹力初, 张泉, 朱捍华, 朱奇宏, 张杨珠, 黄道友. 地下水位和长期秸秆还田对土壤镉有效性及稻米镉含量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 150-157. |
| [3] | 郝小雨, 王晓军, 高洪生, 毛明艳, 孙磊, 马星竹, 周宝库, 迟凤琴, 李伟群. 松嫩平原不同秸秆还田方式下农田温室气体排放及碳足迹估算[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 318-325. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
