生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (5): 1076-1083.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.05.021
汪碧玲1( ), 陈碧珊2,*(
), 陈碧珊2,*( ), 刘发耀2, 苏薇薇2, 柯柳聪2, 黄欣欣2
), 刘发耀2, 苏薇薇2, 柯柳聪2, 黄欣欣2
收稿日期:2020-08-09
出版日期:2021-05-18
发布日期:2021-08-06
通讯作者:
* 共同第一作者和通信作者:陈碧珊(1982年生),女,副教授,博士,从事自然地理、土壤环境等研究。E-mail:chenbishan2008@126.com作者简介:汪碧玲(1996年生),女,硕士研究生,从事自然地理研究。E-mail:15218315148@163.com
基金资助:
WANG Biling1( ), CHEN Bishan2,*(
), CHEN Bishan2,*( ), LIU Fayao2, SU Weiwei2, KE Liucong2, HUANG Xinxin2
), LIU Fayao2, SU Weiwei2, KE Liucong2, HUANG Xinxin2
Received:2020-08-09
Online:2021-05-18
Published:2021-08-06
摘要:
通过测定雷州半岛土壤及水果作物As、Cd、Cr、Cu、Hg、Ni、Pb和Zn等8种重金属元素的含量,分析雷州半岛水果作物表层土壤重金属元素潜在生态风险,并探讨土壤-水果作物系统中重金属元素的富集特征。结果表明,(1)雷州半岛水果作物表层土壤重金属元素含量的平均值除Pb元素之外,其他均超过广东省土壤环境背景值,As、Cd、Cr、Cu、Hg、Ni、Pb和Zn元素分别为广东省土壤环境背景值的1.72、3.26、1.97、5.30、2.77、7.83、0.94和3.61倍,表明雷州半岛表层土壤重金属元素呈现一定程度的富集现象;从变异系数看,Ni元素的变异系数为115%,属于强变异性;其余7种元素的变异系数在10%—100%之间,具中等变异性,表明雷州半岛水果作物表层土壤重金属元素含量受人为活动影响较大。(2)雷州半岛水果作物表层土壤潜在生态风险平均值为267.16,总体上属于中等—强污染风险;其中,徐闻县、雷州市、麻章区为强污染风险,廉江市、霞山区、坡头区和吴川市为中等污染风险。(3)研究区水果重金属元素含量除了草莓外,其他水果的重金属含量均未超过国家食品污染物限量标准,总体上处于安全状态;但不同水果对同一种重金属元素的吸附能力存在差异,以草莓和番石榴对重金属元素的吸附能力最强,与农药化肥的施用有一定的关系。(4)研究区水果作物与土壤的重金属含量总体上为较弱正相关,富集系数平均值均<1,表明重金属元素在土壤-水果作物系统中迁移、转化和富集能力较低。
中图分类号:
汪碧玲, 陈碧珊, 刘发耀, 苏薇薇, 柯柳聪, 黄欣欣. 雷州半岛土壤-水果作物系统重金属元素潜在生态风险评价及富集特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(5): 1076-1083.
WANG Biling, CHEN Bishan, LIU Fayao, SU Weiwei, KE Liucong, HUANG Xinxin. Potential Risk Assessment and Enrichment Characteristics of Heavy Metals in Soil Fruit Crop System of Leizhou Peninsula[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(5): 1076-1083.
| Element | As | Cr | Cd | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | 20.90 | 373.00 | 0.262 | 122.00 | 0.23 | 328 | 63.90 | 214.00 |
| Minimum | 4.48 | 6.42 | 0.005 | 3.00 | 0.022 | 0.80 | 8.30 | 9.00 |
| Average value | 9.30 | 117.93 | 0.067 | 42.40 | 0.083 | 86.00 | 22.00 | 75.85 |
| Standard deviation | 3.90 | 106.34 | 0.05 | 37.00 | 0.04 | 98.70 | 12.00 | 47.76 |
| Background values | 5.400 | 36.14 | 0.034 | 8.000 | 0.030 | 10.98 | 23.40 | 21.00 |
| Standard value | 40.00 | 200 | 0.300 | 100 | 2.40 | 100 | 120 | 250 |
| Pollution index | 1.72 | 3.26 | 1.97 | 5.30 | 2.77 | 7.83 | 0.94 | 3.61 |
| Coefficient of Variation | 0.42 | 0.90 | 0.75 | 0.87 | 0.48 | 1.15 | 0.55 | 0.63 |
| Over-standard rate/% | 0 | 25.50 | 0 | 9.09 | 0 | 36.36 | 0 | 0 |
表1 雷州半岛表层土壤重金属元素的含量特征
Table 1 Content characteristics of heavy metal elements in the surface soil of Leizhou Peninsula
| Element | As | Cr | Cd | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | 20.90 | 373.00 | 0.262 | 122.00 | 0.23 | 328 | 63.90 | 214.00 |
| Minimum | 4.48 | 6.42 | 0.005 | 3.00 | 0.022 | 0.80 | 8.30 | 9.00 |
| Average value | 9.30 | 117.93 | 0.067 | 42.40 | 0.083 | 86.00 | 22.00 | 75.85 |
| Standard deviation | 3.90 | 106.34 | 0.05 | 37.00 | 0.04 | 98.70 | 12.00 | 47.76 |
| Background values | 5.400 | 36.14 | 0.034 | 8.000 | 0.030 | 10.98 | 23.40 | 21.00 |
| Standard value | 40.00 | 200 | 0.300 | 100 | 2.40 | 100 | 120 | 250 |
| Pollution index | 1.72 | 3.26 | 1.97 | 5.30 | 2.77 | 7.83 | 0.94 | 3.61 |
| Coefficient of Variation | 0.42 | 0.90 | 0.75 | 0.87 | 0.48 | 1.15 | 0.55 | 0.63 |
| Over-standard rate/% | 0 | 25.50 | 0 | 9.09 | 0 | 36.36 | 0 | 0 |
| Element | Cd | Pb | As | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guava | 0.019 | 0.839 | 0.258 | 2.165 | 4.02 | 0.002 | 1.40 | 11.4 |
| Red orange | 0.009 | 0.624 | 0.162 | 2.88 | 3.15 | 0.003 | 1.46 | 11.1 |
| Strawberry | 0.272 | 1.021 | 0.274 | 0.595 | 8.25 | 0.005 | 1.17 | 30.2 |
| Pineapple | 0.035 | 0.784 | 0.258 | 0.40 | 8.54 | 0.044 | 3.05 | 11.8 |
| Banana | 0.002 | 0.092 | 0.042 | 0.26 | 4.15 | 0.005 | 0.63 | 11.5 |
| Mango | 0.013 | 0.195 | 0.045 | 0.31 | 6.29 | 0.006 | 1.10 | 8.2 |
| National Food Contaminants Limit Standard | 0.05 | 1 | No standard | No standard | No standard | No standard | No standard | No standard |
表2 雷州半岛不同水果种类可食用部分重金属元素含量
Table 2 Results of heavy metal elements in edible parts of different fruit types in Leizhou Peninsula μg∙g-1
| Element | Cd | Pb | As | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guava | 0.019 | 0.839 | 0.258 | 2.165 | 4.02 | 0.002 | 1.40 | 11.4 |
| Red orange | 0.009 | 0.624 | 0.162 | 2.88 | 3.15 | 0.003 | 1.46 | 11.1 |
| Strawberry | 0.272 | 1.021 | 0.274 | 0.595 | 8.25 | 0.005 | 1.17 | 30.2 |
| Pineapple | 0.035 | 0.784 | 0.258 | 0.40 | 8.54 | 0.044 | 3.05 | 11.8 |
| Banana | 0.002 | 0.092 | 0.042 | 0.26 | 4.15 | 0.005 | 0.63 | 11.5 |
| Mango | 0.013 | 0.195 | 0.045 | 0.31 | 6.29 | 0.006 | 1.10 | 8.2 |
| National Food Contaminants Limit Standard | 0.05 | 1 | No standard | No standard | No standard | No standard | No standard | No standard |
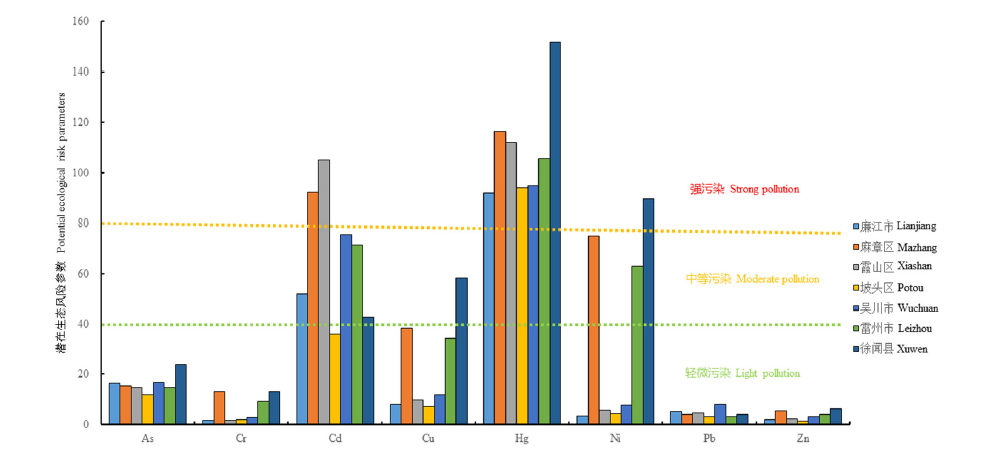
图3 雷州半岛各市(县、区)土壤重金属潜在生态风险参数
Fig. 3 Potential ecological risk parameters of heavy metals in soils of cities (counties and districts) in Leizhou Peninsula
| Correlation coefficient | As | Cr | Cd | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | 0.112 | -0.357 | -0.019 | 0.561* | 0.164 | 0.272 | 0.477 | -0.312 |
| P | 0.702 | 0.210 | 0.950 | 0.037 | 0.576 | 0.346 | 0.085 | 0.278 |
表3 土壤-水果作物重金属元素相关系数分析结果
Table 3 Analysis results of correlation coefficients of heavy metal elements in soil-fruit crops
| Correlation coefficient | As | Cr | Cd | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | 0.112 | -0.357 | -0.019 | 0.561* | 0.164 | 0.272 | 0.477 | -0.312 |
| P | 0.702 | 0.210 | 0.950 | 0.037 | 0.576 | 0.346 | 0.085 | 0.278 |
| Fruit name | Cd | Cu | Zn | Hg | Cr | Ni | Pb | As |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guava | 0.057 | 0.027 | 0.057 | 0.161 | 0.235 | 0.026 | 0.297 | 0.022 |
| Red orange | 0.051 | 0.138 | 0.141 | 0.042 | 0.282 | 0.290 | 0.105 | 0.024 |
| Strawberry | 4.583 | 0.681 | 0.649 | 0.074 | 0.021 | 0.096 | 0.043 | 0.037 |
| Pineapple | 1.495 | 0.097 | 0.133 | 0.423 | 0.002 | 0.021 | 0.029 | 0.016 |
| Banana | 0.093 | 0.209 | 0.220 | 0.076 | 0.003 | 0.014 | 0.005 | 0.005 |
| Mango | 0.106 | 0.098 | 0.105 | 0.067 | 0.002 | 0.008 | 0.016 | 0.007 |
| Average value | 0.922 | 0.203 | 0.212 | 0.129 | 0.098 | 0.086 | 0.079 | 0.018 |
表4 雷州半岛中土壤-水果作物系统重金属元素富集系数
Table 4 Migration coefficient of heavy metal elements in soil-fruit crop system in Leizhou Peninsula
| Fruit name | Cd | Cu | Zn | Hg | Cr | Ni | Pb | As |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guava | 0.057 | 0.027 | 0.057 | 0.161 | 0.235 | 0.026 | 0.297 | 0.022 |
| Red orange | 0.051 | 0.138 | 0.141 | 0.042 | 0.282 | 0.290 | 0.105 | 0.024 |
| Strawberry | 4.583 | 0.681 | 0.649 | 0.074 | 0.021 | 0.096 | 0.043 | 0.037 |
| Pineapple | 1.495 | 0.097 | 0.133 | 0.423 | 0.002 | 0.021 | 0.029 | 0.016 |
| Banana | 0.093 | 0.209 | 0.220 | 0.076 | 0.003 | 0.014 | 0.005 | 0.005 |
| Mango | 0.106 | 0.098 | 0.105 | 0.067 | 0.002 | 0.008 | 0.016 | 0.007 |
| Average value | 0.922 | 0.203 | 0.212 | 0.129 | 0.098 | 0.086 | 0.079 | 0.018 |
| [1] |
HU B F, JIA X L, HU J, et al., 2017. Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution and Health Risks in the Soil-Plant-Human System in the Yangtze River Delta, China[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14(9): 1042.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
TENG Y G, WU J, LU S J, et al., 2014. Soil and soil environmental quality monitoring in China: A review[J]. Environment International, 69(8): 177-199.
DOI URL |
| [3] | 陈明, 蔡青云, 徐慧, 等, 2015. 水体沉积物重金属污染风险评价研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 24(6): 1069-1074. |
| CHEN M, CAI Q y, XU H, et al., 2015. Research progress of risk assessment of heavy metals pollution in water body sediments[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 24(6): 1069-1074. | |
| [4] | 陈燕, 谢正生, 郑小林, 等, 2009. 杨桃对土壤重金属元素的吸收与富集迁移[J]. 云南植物研究, 31(4): 369-373. |
| CHEN Y, XIE Z S, ZHENG X L, et al., 2009. Absorption, enrichment and migration of heavy metal elements in soil by carambola[J]. Yunnan Plant Research, 31(4): 369-373. | |
| [5] | 串丽敏, 赵同科, 郑怀国, 等, 2014. 土壤重金属污染修复技术研究进展[J]. 环境科学与技术, 37(120): 213-222. |
| CHUAN L M, ZHAO T K, ZHENG H G, et al., 2014. Research progress of soil heavy metal pollution remediation technology[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 37(120): 213-222. | |
| [6] | 窦韦强, 2020. 不同耕作制度下农用地土壤镉的生态安全阈值研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院:3-4. |
| DOU W Q, 2020. Ecological security threshold of soil cadmium under different tillage systems[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences:3-4. | |
| [7] | 董峰光, 王桂强, 宫春波, 等, 2018. 2013—2016年烟台市市售水果重金属污染状况及暴露风险评估[J]. 职业与健康, 34(9): 1183-1186. |
| DONG F G, WANG G Q, GONG C B, et al., 2018. Heavy metal pollution status and exposure risk assessment of fruits sold in Yantai city from 2013 to 2016 [J]. Occupation and Health, 34(9): 1183-1186. | |
| [8] | 郝变青, 马利平, 秦曙, 等, 2015. 苹果、梨、桃和枣4种水果5种重金属含量检测与分析[J]. 山西农业科学, 43(3): 329-332, 336. |
| HAO C Q, MA L P, QIN S, et al., 2015. Detection and analysis of five heavy metals in apple, pear, peach and jujube[J]. Shanxi Agricultural Sciences, 43(3): 329-332, 336. | |
| [9] | 何东, 邱波, 彭尽晖, 等, 2013. 湖南下水湾铅锌尾矿库优势植物重金属含量及富集特征[J]. 环境科学, 34(9): 3595-3600. |
| HE D, QIU B, PENG J H, et al., 2013. Heavy metal content and enrichment characteristics of dominant plants in the Xiashuiwan lead-zinc tailings pond in Hunan[J]. Environmental Science, 34(9): 3595-3600. | |
| [10] | 金枚, 2013. 大厂矿区农产品安全性分析[D]. 南宁: 广西师范学院:19-23. |
| JIN M, 2013. Safety analysis of agricultural products in Dachang mining area[D]. Nanning: Guangxi Normal University:19-23. | |
| [11] | 李嘉蕊, 2019. 基于土壤-作物-人体系统的耕地重金属污染评价和健康风险评估[D]. 浙江: 浙江大学:6-10. |
| LI J R, 2019. Heavy metal pollution assessment and health risk assessment of cultivated land based on soil crop human system[D]. Zhejiang: Zhejiang University:6-10. | |
| [12] | 刘品祯, 2018. 都匀废弃铅锌矿区土壤-作物重金属污染调查及健康风险分析[D]. 贵阳: 贵州师范大学:8-14. |
| LIU P Z, 2018. Investigation of soil-crop heavy metal pollution and health risk analysis in Duyun abandoned lead-zinc mining area[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou Normal University:8-14. | |
| [13] | 罗松英, 柯思茵, 王嘉琦, 等, 2019. 湛江市郊蔬菜地土壤重金属空间分布特征及来源分析[J]. 南方农业学报, 50(8): 1709-1717. |
| LUO S Y, KE S Y, WANG J Q, et al., 2019. Spatial distribution characteristics and source analysis of heavy metals in vegetable soil of Zhanjiang suburb[J]. Acta Agriculturae Sinica, 50(8): 1709-1717. | |
| [14] | 马建华, 马诗院, 陈云增, 2014. 河南某污灌区土壤-作物-人发系统重金属迁移与积累[J]. 环境科学学报, 34(6): 1517-1526. |
| MA J H, MA S Y, CHEN Y Z, 2014. Migration and accumulation of heavy metals in the soil-crop-human hair system of a sewage irrigation area in Henan[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 34(6): 1517-1526. | |
| [15] | 马萍, 2019. 果蔬产品安全及快速检测方法应用探究[J]. 食品安全导刊 (15): 64. |
| MA P, 2019. Application of safety and rapid detection methods for fruit and vegetable products[J]. Food Safety Guide (15): 64. | |
| [16] | 聂继云, 董雅凤, 2002. 果园重金属污染的危害与防治[J]. 中国果树 (1): 47-50. |
| NIE J Y, DONG Y F, 2002. Hazards and prevention of heavy metal pollution in orchards[J]. China Fruit Trees (1): 47-50. | |
| [17] | 庞荣丽, 吴斯洋, 党琪, 等, 2019. 葡萄对重金属吸收能力的差异性研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 33(12): 96-101. |
| PANG R L, WU S Y, DANG Q, et al., 2019. Study on the difference in the absorption capacity of grapes to heavy metals[J]. Arid Area Resources and Environment, 33(12): 96-101. | |
| [18] | 王露, 2018. 关中地区土壤—樱桃系统中重金属污染研究[D]. 西安: 陕西师范大学:3-14. |
| WANG L, 2018. Study on heavy metal pollution in soil-cherry system in Guanzhong area[D]. Xi’an: Shaanxi Normal University:3-14. | |
| [19] | 王宇, 2014. 2009—2013年宁德市食品污染物中铅、镉的监测与分析[D]. 厦门: 集美大学: 28. |
| WANG Y, 2014. Monitoring and analysis of lead and cadmium in food pollutants in Ningde City from 2009to 2013 [D]. Xiamen: Jimei University: 28. | |
| [20] | 吴洋, 杨军, 周小勇, 等, 2015. 广西都安县耕地土壤重金属污染风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 36(8): 2964-2971. |
| WU Y, YANG J, ZHOU X Y, et al., 2015. Risk assessment of heavy metal contamination in farmland soil in Du’an Autonomous County of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China[J]. Environmental Science, 36(8): 2964-2971. | |
| [21] | 许炼烽, 刘腾辉, 1996. 广东土壤环境背景值和临界含量的地带性分异[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 17(4): 58-62. |
| XU L F, LIU T H, 1996. The zonal differentiation of soil environmental background values and critical contents in Guangdong[J]. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 17(4): 58-62. | |
| [22] | 徐争启, 倪师军, 庹先国, 等, 2008. 潜在生态危害指数法评价中重金属毒性系数计算[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 32(2): 112-115. |
| XU Z Q, NI S J, TUO X G, et al., 2008. Calculation of the toxicity coefficient of heavy metals in the evaluation of potential ecological hazard index method[J]. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 32(2): 112-115. | |
| [23] | 杨彦, 李良忠, 于云江, 等, 2012. 基于统计分析的太湖流域某市农业活动区重金属污染特征及来源[J]. 环境科学研究, 25(12): 1319-1327. |
| YANG Y, LI L Z, YU Y J, et al., 2012. Characteristics and sources of heavy metal pollution in agricultural activity areas in a city of Taihu Basin based on statistical analysis[J]. Environmental Science Research, 25(12): 1319-1327. | |
| [24] | 叶嘉敏, 余厚平, 简敏菲, 等, 2016. 鄱阳湖流域农田重金属污染的生态风险评估[J]. 江西师范大学学报(自然科学版), 40(4): 429-436. |
| YE J M, YU H P, JIAN M F, et al., 2016. The ecological risk assessment of the heavy metals pollution on the typical wetland and farmland of Poyang Lake[J]. Journal of Jiangxi Normal University (Natural Science), 40(4): 429-436. | |
| [25] | 张默, 2010. 胶州湾东北沿岸盐渍土壤与碱蓬中的微量元素[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所):3-12. |
| ZHANG M, 2010. Trace elements in saline soil and Suaeda in the northeast coast of Jiaozhou Bay[D]. Qingdao: Graduate School of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Institute of Oceanology):3-12. | |
| [26] | 郑国璋, 岳乐平, 2008. 洛川苹果园地土壤重金属污染调查与评价[J]. 土壤通报, 39(2): 402-405. |
| ZHENG G Z, YUE L P, 2008. Survey and evaluation of heavy metal pollution in soil of Luochuan apple orchard[J]. Soil Bulletin, 39(2): 402-405. | |
| [27] | 郑堃, 任宗玲, 覃小泉, 等, 2018. 韶关工矿区水稻土和稻米中重金属污染状况及风险评价[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 37(5): 915-925. |
| ZHENG K, REN Z L, QIN X Q, et al., 2018. Pollution status and risk assessment of heavy metals in paddy soil and rice in Shaoguan industrial and mining area[J]. Journal of Agricultural Environmental Sciences, 37(5): 915-925. | |
| [28] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部,2018. 土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准 (试行): GB 15618—2018 [S]. 北京:中国环境出版社. |
| Ministry of Ecology andEnvironment of the People's Republic of China,2018. Soil Environmental Quality Standards for Agricultural Land Soil Pollution Risk Control (Trial): GB 15618—2018 [S]. Beijing:China Environmental Publishing House. | |
| [29] | 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会,国家食品药品监督管理总局,2018. GB 2762—2017《食品安全国家标准食品中污染物限量》[J]. 中国食品卫生杂志, 30(3): 329-340. |
| State Food andDrug Administration, National Health and Family Planning Commission,2018. PRC GB 2762—2017, “national food safety standard limits of pollutants in foods”[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Hygiene, 30(3): 329-340. |
| [1] | 杜丹丹, 高瑞忠, 房丽晶, 谢龙梅. 旱区盐湖盆地土壤重金属空间变异及对土壤理化因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1123-1132. |
| [2] | 李传福, 朱桃川, 明玉飞, 杨宇轩, 高舒, 董智, 李永强, 焦树英. 有机肥与脱硫石膏对黄河三角洲盐碱地土壤团聚体及其有机碳组分的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 878-888. |
| [3] | 陈俊芳, 吴宪, 刘啸林, 刘娟, 杨佳绒, 刘宇. 不同土壤水分下元素化学计量对微生物多样性的塑造特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 898-909. |
| [4] | 董智今, 张呈春, 展秀丽, 张维福. 宁夏河东沙地生物土壤结皮及其下伏土壤养分的空间分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 910-919. |
| [5] | 周沁苑, 董全民, 王芳草, 刘玉祯, 冯斌, 杨晓霞, 俞旸, 张春平, 曹铨, 刘文亭. 放牧方式对高寒草地瑞香狼毒根际土壤团聚体及有机碳特征的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 660-667. |
| [6] | 潘昱伶, 璩向宁, 李琴, 王磊, 王筱平, 谭鹏, 崔庚, 安雨, 佟守正. 黄河宁夏段典型滩涂湿地土壤理化因子空间分布特征及其对微地形的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 668-677. |
| [7] | 赵维彬, 唐丽, 王松, 刘玲玲, 王树凤, 肖江, 陈光才. 两种生物炭对滨海盐碱土的改良效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 678-686. |
| [8] | 冯树娜, 吕家珑, 何海龙. KI淋洗对黄绵土汞污染的去除效果及土壤理化性状的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 776-783. |
| [9] | 陈敏毅, 朱航海, 佘伟铎, 尹光彩, 黄祖照, 杨巧玲. 珠三角某遗留造船厂场地土壤重金属人体健康风险评估及源解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 794-804. |
| [10] | 张林, 齐实, 周飘, 伍冰晨, 张岱, 张岩. 北京山区针阔混交林地土壤有机碳含量的影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 450-458. |
| [11] | 秦浩, 李蒙爱, 高劲, 陈凯龙, 张殷波, 张峰. 芦芽山不同海拔灌丛土壤细菌群落组成和多样性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 459-468. |
| [12] | 唐海明, 石丽红, 文丽, 程凯凯, 李超, 龙泽东, 肖志武, 李微艳, 郭勇. 长期施肥对双季稻田根际土壤氮素的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 492-499. |
| [13] | 刘抗旱, 郑刘根, 张理群, 丁丹, 单士锋. 复合型植物源活化剂强化蜈蚣草修复砷污染土壤的效应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 635-642. |
| [14] | 樊慧琳, 张佳敏, 李欢, 王艳玲. 坡耕地稻田剖面磷的储存格局与流失风险研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 283-291. |
| [15] | 宋孝帅, 丁武泉, 刘新敏, 李廷真. 离子特异性效应对紫色土孔隙状况的影响机制研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 292-298. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
