生态环境学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (9): 1463-1472.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2025.09.013
收稿日期:2025-01-23
出版日期:2025-09-18
发布日期:2025-09-05
通讯作者:
*E-mail: lisc@cug.edu.cn
作者简介:梁秋燕(2001年生),女,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为长时段土地利用/覆被变化及其生态环境效应评价。E-mail: liangqiuyan@cug.edu.cn
基金资助:
LIANG Qiuyan1( ), SONG Mingjie2, ZHANG Dou3, LI Shicheng1,4,*(
), SONG Mingjie2, ZHANG Dou3, LI Shicheng1,4,*( )
)
Received:2025-01-23
Online:2025-09-18
Published:2025-09-05
摘要:
土地利用变化模拟对拟定未来区域规划、开展潜在风险评估具有重大的意义。然而,现有的土地利用变化模拟研究,在生态安全方面考量不足,难以给生态文明建设及可持续发展提供充分的科学支撑。以昆明市为对象,在构建生态安全格局的基础上,将Markov与PLUS模型耦合,对生态安全情景下昆明市2030年和2050年的土地利用变化进行模拟,并与惯性发展情景的模拟结果进行对比。研究发现,1)昆明市现存在15块生态源地,总面积约为7400 km2,呈现西部、北部聚集成片,东部零散分布的空间格局;另有43条重要生态廊道,总长度约为1150 km,增强了各生态源地间的连通性。2)2030年和2050年的土地利用模拟结果显示,在生态安全情景下,土地利用扩张主要在生态源地与生态廊道之外,且在此情景下的昆明市林地面积占比较高,土地利用模拟结果更契合区域发展的需求;而在惯性发展情景下,土地利用呈现无序扩张的态势,建设用地侵占生态生产用地的现象突出,并且至2050年呈现出逐渐侵占滇池水体的趋势。该研究对昆明市关键生态区域的识别,以及对不同情景下长时段土地利用的模拟结果,可为昆明市可持续发展目标和土地利用规划提供科学依据。
中图分类号:
梁秋燕, 宋明洁, 张豆, 李士成. 基于生态安全格局的昆明市2030年和2050年土地利用模拟[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(9): 1463-1472.
LIANG Qiuyan, SONG Mingjie, ZHANG Dou, LI Shicheng. Prediction of Land Use in Kunming in 2030 and 2050 Incorporating Ecological Security Pattern[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2025, 34(9): 1463-1472.
| 数据类型 | 数据名称 | 数据来源 |
|---|---|---|
| 土地利用 | 2000、2010、2020年土地利用分类 | 武汉大学( |
| 自然因素 | 海拔高度、地面坡度 | 地理空间数据云( |
| 年降水量、年平均温度、归一化植被指数(NDVI) | 中国科学院资源环境科学与数据中心( | |
| 社会经济因素 | GDP、人口密度 | 中国科学院资源环境科学与数据中心( |
| 交通区位因素 | 水系、主要铁路、主要公路、居民点 | 全国地理信息资源目录服务系统( |
| 政策限制因素 | 自然保护区 | 全国地理信息资源目录服务系统( |
表1 数据来源信息汇总
Table 1 The summary of data source information
| 数据类型 | 数据名称 | 数据来源 |
|---|---|---|
| 土地利用 | 2000、2010、2020年土地利用分类 | 武汉大学( |
| 自然因素 | 海拔高度、地面坡度 | 地理空间数据云( |
| 年降水量、年平均温度、归一化植被指数(NDVI) | 中国科学院资源环境科学与数据中心( | |
| 社会经济因素 | GDP、人口密度 | 中国科学院资源环境科学与数据中心( |
| 交通区位因素 | 水系、主要铁路、主要公路、居民点 | 全国地理信息资源目录服务系统( |
| 政策限制因素 | 自然保护区 | 全国地理信息资源目录服务系统( |
| 威胁因子 | 最大影响距离/km | 影响权重 | 衰变关系 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 耕地 | 6 | 0.7 | 线性 |
| 建设用地 | 8 | 1 | 指数 |
| 道路 | 5 | 0.5 | 线性 |
表2 威胁因子参数
Table 2 Parameters of threat factors
| 威胁因子 | 最大影响距离/km | 影响权重 | 衰变关系 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 耕地 | 6 | 0.7 | 线性 |
| 建设用地 | 8 | 1 | 指数 |
| 道路 | 5 | 0.5 | 线性 |
| 土地利用类型 | 生境适宜度 | 威胁因子 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 耕地 | 建设用地 | 道路 | ||
| 耕地 | 0.4 | 0 | 0.7 | 0.3 |
| 林地 | 1 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.5 |
| 草地 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.4 |
| 建设用地 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 水域 | 0.9 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.4 |
| 未利用地 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
表3 不同土地利用类型的生境适宜度及其对威胁因子的敏感度
Table 3 Habitat suitability of different land use types and their sensitivity to threat factors
| 土地利用类型 | 生境适宜度 | 威胁因子 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 耕地 | 建设用地 | 道路 | ||
| 耕地 | 0.4 | 0 | 0.7 | 0.3 |
| 林地 | 1 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.5 |
| 草地 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.4 |
| 建设用地 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 水域 | 0.9 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.4 |
| 未利用地 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| 阻力因子 | 阻力等级 | 权重 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 土地利用 | 林地 | 水域 | 草地 | 耕地 | 建设用地/未利用地 | 0.42 |
| 坡度/° | 0-8 | 8-16 | 16-24 | 24-34 | 34-80 | 0.15 |
| 高程/m | 687-1673 | 1673-2042 | 2042-2365 | 2365-2887 | 2887-4281 | 0.08 |
| NDVI | 0.82-0.92 | 0.72-0.82 | 0.57-0.72 | 0.36-0.57 | 0.04-0.36 | 0.27 |
| 到道路距离/ m | 4706-10558 | 3151-4706 | 1954-3151 | 874-1954 | 0-874 | 0.08 |
表4 生态阻力因子及阻力值
Table 4 Ecological resistance factor and resistance value
| 阻力因子 | 阻力等级 | 权重 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 土地利用 | 林地 | 水域 | 草地 | 耕地 | 建设用地/未利用地 | 0.42 |
| 坡度/° | 0-8 | 8-16 | 16-24 | 24-34 | 34-80 | 0.15 |
| 高程/m | 687-1673 | 1673-2042 | 2042-2365 | 2365-2887 | 2887-4281 | 0.08 |
| NDVI | 0.82-0.92 | 0.72-0.82 | 0.57-0.72 | 0.36-0.57 | 0.04-0.36 | 0.27 |
| 到道路距离/ m | 4706-10558 | 3151-4706 | 1954-3151 | 874-1954 | 0-874 | 0.08 |
| 土地利用情景 | 耕地 | 林地 | 草地 | 建设 用地 | 水域 | 未利 用地 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2030年惯性发展情景 | 6911.9 | 11448.1 | 1841.7 | 397.3 | 405.8 | 11.1 |
| 2050年惯性发展情景 | 6534.9 | 12064.2 | 1453.2 | 543.9 | 409.3 | 10.3 |
| 2030年生态安全情景 | 6388.9 | 11896.9 | 1950.7 | 364.4 | 409.6 | 5.3 |
| 2050年生态安全情景 | 5348.3 | 13227.6 | 1568.9 | 449.2 | 418.7 | 3.2 |
表5 两种情景下土地利用面积
Table 5 The area of land use under two scenarios km2
| 土地利用情景 | 耕地 | 林地 | 草地 | 建设 用地 | 水域 | 未利 用地 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2030年惯性发展情景 | 6911.9 | 11448.1 | 1841.7 | 397.3 | 405.8 | 11.1 |
| 2050年惯性发展情景 | 6534.9 | 12064.2 | 1453.2 | 543.9 | 409.3 | 10.3 |
| 2030年生态安全情景 | 6388.9 | 11896.9 | 1950.7 | 364.4 | 409.6 | 5.3 |
| 2050年生态安全情景 | 5348.3 | 13227.6 | 1568.9 | 449.2 | 418.7 | 3.2 |
| 土地利用类型 | 耕地 | 林地 | 草地 | 建设用地 | 水域 | 未利用地 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 权重 | 0.475 | 1.00 | 0 | 0.607 | 0.527 | 0.529 |
表6 邻域因子权重
Table 6 The weight of neighborhood
| 土地利用类型 | 耕地 | 林地 | 草地 | 建设用地 | 水域 | 未利用地 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 权重 | 0.475 | 1.00 | 0 | 0.607 | 0.527 | 0.529 |
| 土地利用类型 | 惯性发展情景 | 生态安全情景 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅳ | Ⅴ | Ⅵ | Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅳ | Ⅴ | Ⅵ | ||
| Ⅰ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Ⅱ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Ⅲ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Ⅳ | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| Ⅴ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| Ⅵ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
表7 土地利用转换成本矩阵
Table 7 Land use conversion cost matrix
| 土地利用类型 | 惯性发展情景 | 生态安全情景 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅳ | Ⅴ | Ⅵ | Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅳ | Ⅴ | Ⅵ | ||
| Ⅰ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Ⅱ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Ⅲ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Ⅳ | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| Ⅴ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| Ⅵ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
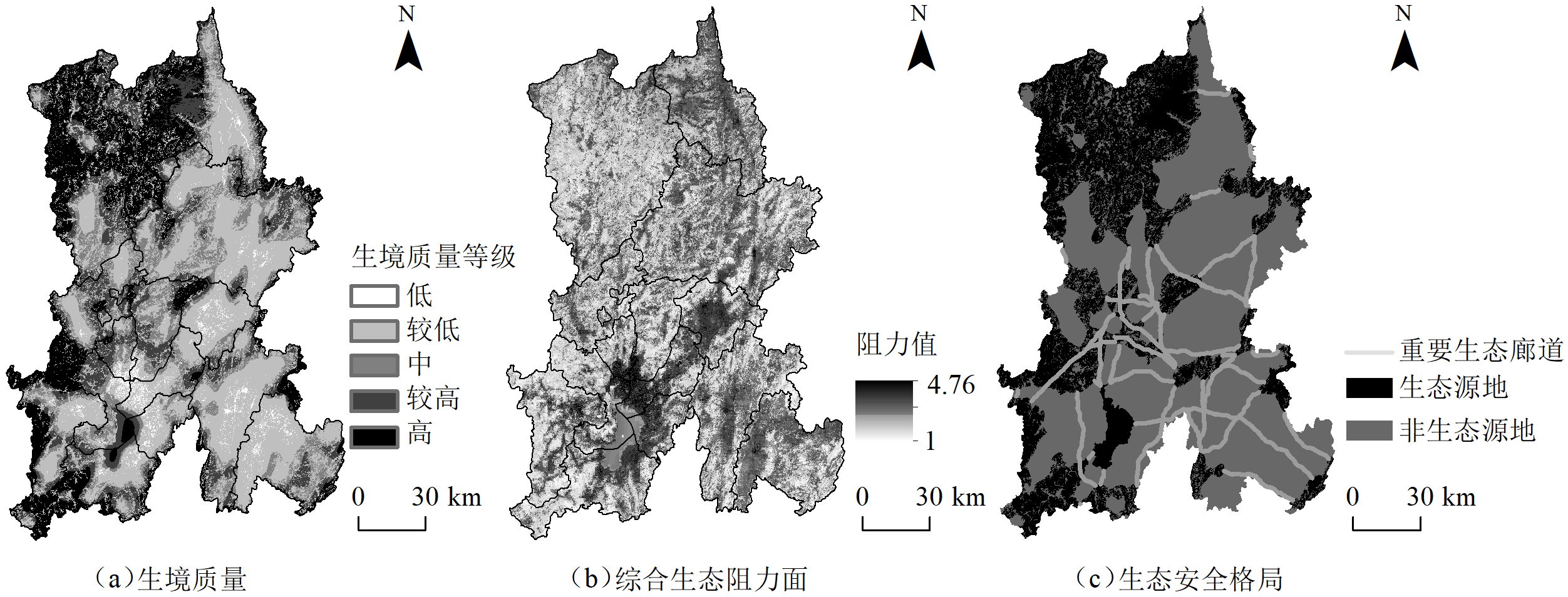
图3 昆明市生境质量、综合生态阻力面和生态安全格局空间分布
Figure 3 Spatial distribution of habitat quality, comprehensive ecological resistance surface and ecological security pattern of Kunming
| 土地利用类型 | 2050年惯性发展情景 | 2050年生态安全情景 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅳ | Ⅴ | Ⅵ | Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅳ | Ⅴ | Ⅵ | |||
| 2020年 | I | 6535 | 490 | 0 | 31 | 2 | 0 | 5110 | 1864 | 0 | 70 | 12 | 2 | |
| II | 0 | 11025 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 11028 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| III | 0 | 540 | 1467 | 187 | 8 | 0 | 238 | 329 | 1569 | 64 | 1 | 2 | ||
| IV | 0 | 0 | 0 | 314 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 314 | 0 | 0 | ||
| V | 0 | 9 | 0 | 11 | 383 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 397 | 0 | ||
| VI | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 8 | ||
| 总计 | 6535 | 12064 | 1467 | 544 | 395 | 10 | 5348 | 13227 | 1569 | 449 | 410 | 12 | ||
表8 2020-2050年昆明市土地利用转移矩阵
Table 8 Land use transfer matrix of Kunming from 2020 to 2050 km2
| 土地利用类型 | 2050年惯性发展情景 | 2050年生态安全情景 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅳ | Ⅴ | Ⅵ | Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅳ | Ⅴ | Ⅵ | |||
| 2020年 | I | 6535 | 490 | 0 | 31 | 2 | 0 | 5110 | 1864 | 0 | 70 | 12 | 2 | |
| II | 0 | 11025 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 11028 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| III | 0 | 540 | 1467 | 187 | 8 | 0 | 238 | 329 | 1569 | 64 | 1 | 2 | ||
| IV | 0 | 0 | 0 | 314 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 314 | 0 | 0 | ||
| V | 0 | 9 | 0 | 11 | 383 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 397 | 0 | ||
| VI | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 8 | ||
| 总计 | 6535 | 12064 | 1467 | 544 | 395 | 10 | 5348 | 13227 | 1569 | 449 | 410 | 12 | ||
| [1] | HE F, YANG J, ZHANG Y Q, et al., 2023. Does partition matter? A new approach to modeling land use change[J]. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, 106: 102041. |
| [2] | LI X, CHEN Y M, LIU X P, et al., 2017. Experiences and issues of using cellular automata for assisting urban and regional planning in China[J]. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 31(8): 1606-1629. |
| [3] | LIANG X, GUAN Q F, CLARKE K C, et al., 2021. Understanding the drivers of sustainable land expansion using a patch-generating land use simulation (PLUS) model: A case study in Wuhan, China[J]. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, 85: 101569. |
| [4] | LI L, HUANG X J, YANG H, 2023. Scenario-based urban growth simulation by incorporating ecological-agricultural-urban suitability into a Future Land Use Simulation model[J]. Cities, 137: 104334. |
| [5] | MACAL C M, NORTH M J, 2010. Tutorial on agent-based modelling and simulation[J]. Journal of Simulation, 4(3): 151-162. |
| [6] | XU Q L, YANG K, WANG G L, et al., 2015. Agent-based modeling and simulations of land-use and land-cover change according to ant colony optimization: A case study of the Erhai Lake Basin, China[J]. Natural Hazards, 75(1): 95-118. |
| [7] | ZHANG P P, SONG M J, LU Q Q, 2024. Mapping ecological security patterns based on ecosystem service valuation in the Qinling-Daba Mountain Area, China: A multi-scenario study for development and conservation tradeoffs[J]. Land, 13(10): 1629. |
| [8] | ZHENG Z H, WANG J, NI J H, et al., 2024. Lacustrine wetlands landscape simulation and multi-scenario prediction based on the Patch-Generating Land-Use Simulation model: A case study on Shengjin Lake Reserve, China[J]. Remote Sensing, 16(22): 4169. |
| [9] | 崔旺来, 蔡莉, 奚恒辉, 等, 2022. 基于土地利用/覆盖变化的浙江大湾区生态安全评价及多情景模拟分析[J]. 生态学报, 42(6): 2136-2148. |
| CUI W L, CAI L, XI H H, et al., 2022. Ecological security assessment and multi-scenario simulation analysis of Zhejiang Greater Bay Area based on LUCC[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42(6): 2136-2148. | |
| [10] |
冯琳, 雷国平, 2024. 基于生态安全格局的东北典型黑土区生态保护红线划定与优化[J]. 自然资源学报, 39(2): 426-445.
DOI |
|
FENG L, LEI G P, 2024. Research on the delineation and optimization of ecological protection redline based on the perspective of ecological security pattern in typical black soil areas of northeast China[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 39(2): 426-445.
DOI |
|
| [11] | 胡露, 冯彬, 白文科, 等, 2023. 四川大熊猫保护地生境质量时空演变特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 42(9): 2204-2211. |
|
HU L, FENG B, BAI W K, et al., 2023. Spatiotemporal variations of habitat quality in protected area of giant panda in Sichuan Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 42(9): 2204-2211.
DOI |
|
| [12] | 黄杰, 李永乐, 2024. 淮河生态经济带城市生态韧性空间差异及动态演进[J]. 信阳师范学院学报(自然科学版), 37(1): 1-10. |
| HUANG J, LI Y L, 2024. Spatial variation and dynamic evolution of urban ecological resilience in the Huaihe River Ecological Economic Belt[J]. Journal of Xinyang Normal University(Natural Science Edition), 37(1): 1-10. | |
| [13] | 李思源, 倪欢, 牛晓楠, 等, 2024. 闽三角城市群土地利用与生态系统服务价值时空演变及未来多情景模拟[J]. 地理与地理信息科学, 40(5): 28-34, 41. |
| LI S Y, NI H, NIU X N, et al., 2024. Spatio-temporal evolution and future multi-scenario simulation of land use and ecosystem service value in Fujian Delta Urban Agglomeration[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 40(5): 28-34, 41. | |
| [14] |
彭建, 赵会娟, 刘焱序, 等, 2017. 区域生态安全格局构建研究进展与展望[J]. 地理研究, 36(3): 407-419.
DOI |
| PENG J, ZHAO H J, LIU Y X, et al., 2017. Research progress and prospect on regional ecological security pattern construction[J]. Geographical Research, 36(3): 407-419. | |
| [15] | 尚俊, 蔡海生, 龙月, 等, 2021. 基于InVEST模型的鄱阳湖区生境质量时空演化及其变迁特征分析[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 30(8): 1901-1915. |
| SHANG J, CAI H S, LONG Y, et al., 2021. Temporal-spatial distribution and transition of habitat quality in Poyang Lake Region based on InVEST model[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 30(8): 1901-1915. | |
| [16] | 徐靖, 王金洲, 2023. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》主要内容及其影响[J]. 生物多样性, 31(4): 7-15. |
| XU J, WANG J Z, et al., 2023. Analysis of the main elements and implications of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework[J]. Biodiversity Science, 31(4): 7-15. | |
| [17] | 王保盛, 廖江福, 祝薇, 等, 2019. 基于历史情景的FLUS模型邻域权重设置——以闽三角城市群2030年土地利用模拟为例[J]. 生态学报, 39(12): 4284-4298. |
| WANG B S, LIAO J F, ZHU W, et al., 2019. The weight of neighborhood setting of the FLUS model based on a historical scenario: A case study of land use simulation of urban agglomeration of the Golden Triangle of Southern Fujian in 2030[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(12): 4284-4298. | |
| [18] |
韦家怡, 李铖, 吴志峰, 等, 2022. 粤港澳大湾区生态安全格局及重要生态廊道识别[J]. 生态环境学报, 31(4): 652-662.
DOI |
| WEI J Y, LI C, WU Z F, et al., 2022. Identifying ecological security patterns and prioritizing ecological corridors in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 31(4): 652-662. | |
| [19] |
王琦, 王辉, 虞虎, 2023. 基于生态安全格局的国家公园边界划定——以雅鲁藏布大峡谷国家公园为例[J]. 自然资源学报, 38(4): 951-965.
DOI |
|
WANG Q, WANG H, YU H, 2023. Demarcation of national park boundary based on ecological security pattern: A case study of Yarlung Zangbo Grand Canyon National Park[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 38(4): 951-965.
DOI |
|
| [20] |
许宝荣, 刘一川, 董莹, 等, 2021. 基于InVEST模型的兰州地区生境质量评价[J]. 中国沙漠, 41(5): 120-129.
DOI |
|
XU B R, LIU Y C, DONG Y, et al., 2021. Evaluation of habitat quality in Lanzhou Region based on InVEST model[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 41(5): 120-129.
DOI |
|
| [21] |
熊锦惠, 岳文泽, 陈阳, 等, 2021. 面向SDGs的城市扩张多情景模拟——以 “一带一路” 中亚区为例[J]. 自然资源学报, 36(4): 841-853.
DOI |
| XIONG J H, YUE W Z, CHEN Y, et al., 2021. Multi-scenario urban expansion simulation for SDGs: Taking the Central Asian region along the Belt and Road as an example[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 36(4): 841-853. | |
| [22] |
肖瑶, 刘渺渺, 梁冠敏, 等, 2023. 基于多尺度情景的闽三角地区林地生态网络构建[J]. 生态环境学报, 32(10): 1750-1759.
DOI |
| XIAO Y, LIU M M, LIANG G M, et al., 2023. Construction of forest ecological network in the Min River Delta based on multi-scale scenarios[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 32(10): 1750-1759. | |
| [23] | 肖建英, 戴津津, 方昕然, 等, 2024. 基于PLUS模型的徐州市生态系统服务价值多情景模拟研究[J]. 中国土地科学, 38(4): 125-134. |
| XAIO J Y, DAI J J, FANG X R, et al., 2024. Multiple scenario simulation of ecosystem service value in Xuzhou City based on PLUS model[J]. China Land Science, 38(4): 125-134. | |
| [24] |
严冬, 李爱农, 南希, 等, 2016. 基于Dyna-CLUE改进模型和SD模型耦合的山区城镇用地情景模拟研究——以岷江上游地区为例[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 18(4): 514-525.
DOI |
| YAN D, LI A N, NAN X, et al., 2016. The study of urban land scenario simulation in mountain area based on modified Dyna-CLUE model and SDM: A case study of the upper reaches of Minjiang River[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 18(4): 514-525. | |
| [25] | 杨姗姗, 邹长新, 沈渭寿, 等, 2016. 基于生态红线划分的生态安全格局构建——以江西省为例[J]. 生态学杂志, 35(1): 250-258. |
| YANG S S, ZOU C X, SHEN W S, et al., 2016. Construction of ecological security patterns based on ecological red line: A case study of Jiangxi Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 35(1): 250-258. | |
| [26] |
杨金礼, 吴洋洋, 李思亮, 等, 2024. 雄安新区 “三生空间” 耦合协调评估及生态安全格局优化[J]. 生态环境学报, 33(11): 1816-1826.
DOI |
| YANG J L, WU Y Y, LI S L, et al., 2024. Assessing the coupling and coordination of ‘production-living-ecological’ spaces in Xiong’an New Area: Towards an optimized ecological security pattern[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 33(11): 1816-1826. | |
| [27] | 张振克, 牛继强, 程启先, 等, 2023. 淮河流域信阳段生态旅游廊道及生态旅游区建设[J]. 信阳师范学院学报(自然科学版), 36(4): 517-522. |
| ZHANG Z K, NIU J Q, CHENG Q X, et al., 2023. Construction of eco-tourism corridor and eco-tourism area in Xinyang Section of Huaihe River Basin[J]. Journal of Xinyang Normal University(Natural Science Edition), 36(4): 517-522. |
| [1] | 吴雨桐, 於冉, 余祺琪, 王成, 张紫涵. 皖江流域生境质量评价及多情景优化研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(6): 961-973. |
| [2] | 张继, 杨世琦, 赵磊, 冯介玲, 陈艳英. 基于InVEST模型的重庆市“一带三屏”生境质量时空演变特征分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(2): 167-180. |
| [3] | 马月伟, 陈玉美, 张盛蓝, 桂雅丽, 陈艳梅. 夹金山脉大熊猫栖息地生境质量与人类活动强度耦合协调研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(2): 197-208. |
| [4] | 李海燕, 杨涛, 廖依琳, 屈亚婕. 渭河流域(陕西段)河流生境质量分布格局及驱动力分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(7): 1153-1162. |
| [5] | 方吉, 吴啸, 宫清华, 韦泽棉, 王颖佳. 南方滨海农业县国土空间生态修复规划策略——以广东省徐闻县为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(7): 1019-1026. |
| [6] | 许静, 廖星凯, 甘崎旭, 周茅先. 基于MSPA与电路理论的黄河流域甘肃段生态安全格局构建[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 805-813. |
| [7] | 张平江, 党国锋. 基于MCR模型与蚁群算法的洮河流域生态安全格局构建[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 481-491. |
| [8] | 陈乐, 卫伟. 西北旱区典型流域土地利用与生境质量的时空演变特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1909-1918. |
| [9] | 韦家怡, 李铖, 吴志峰, 张莉, 吉冬青, 程炯. 粤港澳大湾区生态安全格局及重要生态廊道识别[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 652-662. |
| [10] | 魏建兵, 郑泓, 程雨露, 王阳. 基于CiteSpace的生态安全格局研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 835-844. |
| [11] | 易浪, 孙颖, 尹少华, 魏晓. 生态安全格局构建:概念、框架与展望[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 845-856. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
