生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (4): 652-662.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.04.002
韦家怡1,2( ), 李铖2,*(
), 李铖2,*( ), 吴志峰1,3,4, 张莉5, 吉冬青2, 程炯2
), 吴志峰1,3,4, 张莉5, 吉冬青2, 程炯2
收稿日期:2021-12-10
出版日期:2022-04-18
发布日期:2022-06-22
通讯作者:
*李铖(1984年生),女,副研究员,博士,研究领域为景观生态学和城市生态学。E-mail: licheng@soil.gd.cn作者简介:韦家怡(1997年生),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为土地利用和景观生态。E-mail: 709970914@qq.com
基金资助:
WEI Jiayi1,2( ), LI Cheng2,*(
), LI Cheng2,*( ), WU Zhifeng1,3,4, ZHANG Li5, JI Dongqing2, CHENG Jiong2
), WU Zhifeng1,3,4, ZHANG Li5, JI Dongqing2, CHENG Jiong2
Received:2021-12-10
Online:2022-04-18
Published:2022-06-22
摘要:
城市化引发诸多环境问题,如何协调城市建设空间与生态空间的矛盾,已成为中国国土空间规划领域的重大课题之一。确定区域生态安全格局,优化生态廊道是国土空间规划的重要步骤,也是后续开展生态保护和恢复的关键,如何科学识别显得尤为重要。该文以粤港澳大湾区为例,综合考虑自然资源本底条件和关键生态环境问题,基于生态系统功能重要性和生态系统敏感性评价识别生态源地,利用最小累积阻力模型识别生态廊道,构建区域生态安全格局。基于生态系统重要性和生态敏感性评价结果修正重力模型,并结合廊道连通性指数,进一步识别重要生态廊道。结果显示,生态源地面积为20371 km2,占区域总面积的36.7%,主要位于北部林地广布的山地丘陵区、自然保护区和港澳郊野公园。由于城市化快速发展,污染水平高,生态服务供给低,研究区中部不存在或仅存在较少生态源地。区域内共有潜在生态廊道36条,总长2300 km,呈东西两侧环绕式分布。廊道分级结果显示,高重要-低连通廊道最多(22条),其次是低重要-低连通(6条)和低重要-高连通廊道(5条),高重要-高连通廊道最少(3条)。针对不同类别的廊道,建议因地制宜地采取措施进行保护和管理。
中图分类号:
韦家怡, 李铖, 吴志峰, 张莉, 吉冬青, 程炯. 粤港澳大湾区生态安全格局及重要生态廊道识别[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 652-662.
WEI Jiayi, LI Cheng, WU Zhifeng, ZHANG Li, JI Dongqing, CHENG Jiong. Identifying Ecological Security Patterns and Prioritizing Ecological Corridors in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(4): 652-662.
| 数据 Data | 时间, 分辨率 Time, Resolution | 数据来源及处理 Data sources and processing |
|---|---|---|
| 道路数据 Road data | 2017年, 矢量数据 | 国家地理信息公共服务平台 ( |
| 植被覆盖 Vegetation coverage | 2018年, 250 m | MODIS/Terra Vegetation Indices 16-Day L3 Global |
| 土壤 Soil | 2009年, 1 km | 全球土壤数据库 ( |
| 年均降雨 Annual rainfall | 2008-2018年, 30 m | 国家气象科学数据中心, 经Anusplin处理 ( |
| 自然保护区 Nature reserve | 国家级、省级 | 来源于林业局、自然保护区名录等相关资料, 经整理获得 |
| 风景名胜区和港澳郊野公园兴趣面,港澳工厂兴趣点 Area of Interst (AOI) of scenic area and country parks in Hong Kong and Macao, Point of Interst (POI) of factories in Hong Kong and Macao | 2018年, 矢量数据 | 高德开放平台 ( |
| 水环境、大气环境重点排污企业 Key sewage enterprises of water and atmosphere | 2018年, 矢量数据 | 市级环境局公开资料,经地理编码处理 Environment Bureau’s public information, processed by geocoding |
| 潜在蒸散发 Potential evapotranspiration | 1970-2000年, 1 km | 全球干旱指数和潜在蒸散气候数据集v2 ( |
| 国家标准 National standard | 现行标准 | 全国标准信息公共服务平台 ( |
| 降雨侵蚀力 Rainfall erosivity | 1986-2015年, 250 m | 国家科技基础条件平台—国家地球系统科学数据中心 ( |
| PM2.5年均浓度 Annual average concentration of PM2.5 | 2018年, 0.05°×0.05° | Hammer et al. ( |
| 土地利用 Land use | 2018年, 30 m | 资源环境科学与数据中心 ( |
| 高程 Elevation | 30 m | 地理空间数据云 ( |
| 夜间灯光 Night light | 2018年, 500 m | 全球“类NPP-VIIRS”夜间灯光数据集 (Chen et al., |
表1 数据来源
Table 1 Data source
| 数据 Data | 时间, 分辨率 Time, Resolution | 数据来源及处理 Data sources and processing |
|---|---|---|
| 道路数据 Road data | 2017年, 矢量数据 | 国家地理信息公共服务平台 ( |
| 植被覆盖 Vegetation coverage | 2018年, 250 m | MODIS/Terra Vegetation Indices 16-Day L3 Global |
| 土壤 Soil | 2009年, 1 km | 全球土壤数据库 ( |
| 年均降雨 Annual rainfall | 2008-2018年, 30 m | 国家气象科学数据中心, 经Anusplin处理 ( |
| 自然保护区 Nature reserve | 国家级、省级 | 来源于林业局、自然保护区名录等相关资料, 经整理获得 |
| 风景名胜区和港澳郊野公园兴趣面,港澳工厂兴趣点 Area of Interst (AOI) of scenic area and country parks in Hong Kong and Macao, Point of Interst (POI) of factories in Hong Kong and Macao | 2018年, 矢量数据 | 高德开放平台 ( |
| 水环境、大气环境重点排污企业 Key sewage enterprises of water and atmosphere | 2018年, 矢量数据 | 市级环境局公开资料,经地理编码处理 Environment Bureau’s public information, processed by geocoding |
| 潜在蒸散发 Potential evapotranspiration | 1970-2000年, 1 km | 全球干旱指数和潜在蒸散气候数据集v2 ( |
| 国家标准 National standard | 现行标准 | 全国标准信息公共服务平台 ( |
| 降雨侵蚀力 Rainfall erosivity | 1986-2015年, 250 m | 国家科技基础条件平台—国家地球系统科学数据中心 ( |
| PM2.5年均浓度 Annual average concentration of PM2.5 | 2018年, 0.05°×0.05° | Hammer et al. ( |
| 土地利用 Land use | 2018年, 30 m | 资源环境科学与数据中心 ( |
| 高程 Elevation | 30 m | 地理空间数据云 ( |
| 夜间灯光 Night light | 2018年, 500 m | 全球“类NPP-VIIRS”夜间灯光数据集 (Chen et al., |
| 指标 Indicators | 因子 Factors | 敏感性分级Sensitivity grade | 分级标准 Grading criteria | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1低敏感 Mildly sensitive | 3中度敏感 Moderately sensitive | 5高度敏感 Highly sensitive | 7极敏感 Extremely sensitive | |||
| 生境 Habitat | 土地利用类型 | 建设用地, 未利用地 | 耕地 | 草地 | 水域, 林地, 自然保护区, 森林公园 | 甘琳等, |
| 植被覆盖度/% | 0-0.35 | >0.35-0.5 | >0.5-0.65 | >0.65 | 王媛等, | |
| 水环境 Water environment | 距水体距离/m | >1500 | 1000-1500 | 500-1000 | 0-500 | Xiao et al., |
| 距水环境重点排污企业距离/m | >12000 | >8000-12000 | >4000-8000 | 0-4000 | Xiao et al., | |
| 土壤环境 Soil environment | 土壤侵蚀量/(t∙km-2) | 0-500 | >500-1000 | >1000-5000 | >5000 | 水利部标准 |
| 大气环境 Atmospheric environment | 距大气环境重点排污企业距离/m | >13200 | >8800-13200 | >4400-8800 | 0-4400 | 国家标准 |
| PM2.5年均浓度/(μg∙m-3) | 18-23 | 23-27 | 27-32 | 32-36 | 等间距法 | |
表2 生态系统敏感性评价指标体系
Table 2 Evaluation index system of ecological sensitivity
| 指标 Indicators | 因子 Factors | 敏感性分级Sensitivity grade | 分级标准 Grading criteria | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1低敏感 Mildly sensitive | 3中度敏感 Moderately sensitive | 5高度敏感 Highly sensitive | 7极敏感 Extremely sensitive | |||
| 生境 Habitat | 土地利用类型 | 建设用地, 未利用地 | 耕地 | 草地 | 水域, 林地, 自然保护区, 森林公园 | 甘琳等, |
| 植被覆盖度/% | 0-0.35 | >0.35-0.5 | >0.5-0.65 | >0.65 | 王媛等, | |
| 水环境 Water environment | 距水体距离/m | >1500 | 1000-1500 | 500-1000 | 0-500 | Xiao et al., |
| 距水环境重点排污企业距离/m | >12000 | >8000-12000 | >4000-8000 | 0-4000 | Xiao et al., | |
| 土壤环境 Soil environment | 土壤侵蚀量/(t∙km-2) | 0-500 | >500-1000 | >1000-5000 | >5000 | 水利部标准 |
| 大气环境 Atmospheric environment | 距大气环境重点排污企业距离/m | >13200 | >8800-13200 | >4400-8800 | 0-4400 | 国家标准 |
| PM2.5年均浓度/(μg∙m-3) | 18-23 | 23-27 | 27-32 | 32-36 | 等间距法 | |

图2 生境质量(a)、碳储量(b)、土壤保持(c)、水源涵养(d)和生态重要性分级(e)
Figure 2 Habitat quality (a), carbon storage (b), soil conservation (c), water conservation (d) and ecological importance classification (e)
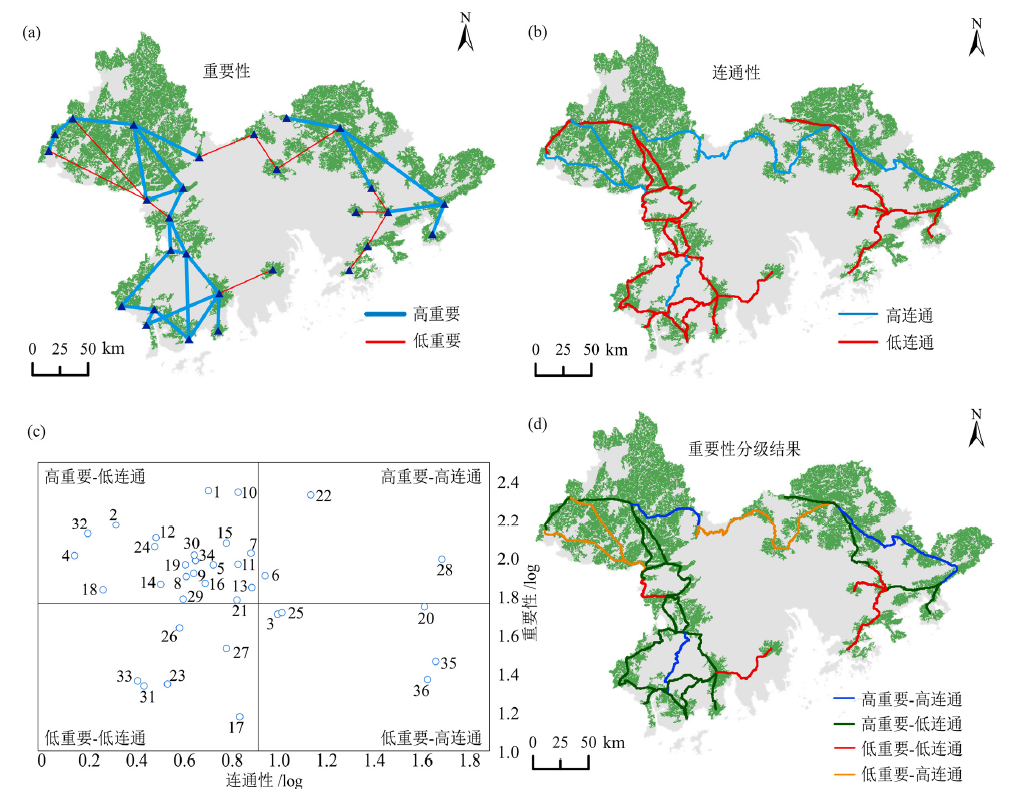
图6 生态廊道重要性(a)、连通性(b)、重要性-连通性四象限图(c)和重要性分级结果(d)
Figure 6 Importance (a), connectivity (b), importance-connectivity four-quadrant diagram (c) and priority classification of ecological corridors classification (d)
| [1] |
BAI Y, OCHUODHO T O, YANG J, 2019. Impact of land use and climate change on water-related ecosystem services in Kentucky, USA[J]. Ecological Indicators, 102(6141): 51-64.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
CAO Y N, KONG L Q, ZHANG L F, et al., 2021. The balance between economic development and ecosystem service value in the process of land urbanization: A case study of China's land urbanization from 2000 to 2015 [J]. Land Use Policy, 108(2): 105536.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
CHEN Z Q, YU B L, YANG C S, et al., 2021. An extended time series (2000-2018) of global NPP-VIIRS-like nighttime light data from a cross-sensor calibration[J]. Earth System Science Data, 13(3): 889-906.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
CHEUNG K C, POON B H T, LAN C Y, et al., 2003. Assessment of metal and nutrient concentrations in river water and sediment collected from the cities in the Pearl River Delta, South China[J]. Chemosphere, 52(9): 1431-1440.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
DONG J Q, PENG J, LIU Y X, et al., 2020. Integrating spatial continuous wavelet transform and kernel density estimation to identify ecological corridors in megacities[J]. Landscape and Urban Planning, 199(7): 103815.
DOI URL |
| [6] | FOLTÊTE J C, 2019. How ecological networks could benefit from landscape graphs: A response to the paper by Spartaco Gippoliti and Corrado Battisti[J]. Land use policy: The International Journal Covering All Aspects of Land Use, 80: 391-394. |
| [7] |
HAMMER M S, DONKELAAR A V, LI C, et al., 2020. Global estimates and long-term trends of fine particulate matter concentrations (1998-2018)[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 54(13): 7879-7890.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
HU M M, LI Z T, WANG Y F, et al., 2019. Spatio-temporal changes in ecosystem service value in response to land-use/cover changes in the Pearl River Delta[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 149: 106-114.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
HU M M, WANG Y F, XIA B C, et al., 2020. How to balance ecosystem services and economic benefits?-A case study in the Pearl River Delta, China[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 271(12): 110917.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
HUANG J M, HU Y C, ZHENG F Y, 2020. Research on recognition and protection of ecological security patterns based on circuit theory: A case study of Jinan City[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(11): 12414-12427.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
JIANG H, PENG J, DONG J Q, et al., 2021. Linking ecological background and demand to identify ecological security patterns across the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area in China[J]. Landscape Ecology, 36(7): 1-16.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
JIANG W Y, CAI Y L, TIAN J J, 2019. The application of minimum cumulative resistance model in the evaluation of urban ecological land use efficiency[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 12(23): 1-7.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
JIAO M Y, WANG Y F, HU M M, et al., 2021. Spatial deconstruction and differentiation analysis of early warning for ecological security in the Pearl River Delta, China[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, DOI: 10.1016/j.scs.2020.102557.
DOI |
| [14] |
KANG J M, ZHANG X, ZHU X W, et al., 2021. Ecological security pattern: A new idea for balancing regional development and ecological protection. A case study of the Jiaodong Peninsula, China[J]. Global Ecology and Conservation, DOI: 10.1016/j.gecco.2021.e01472.
DOI |
| [15] |
LI S C, XIAO W, ZHAO Y L, et al., 2020. Incorporating ecological risk index in the multi-process MCRE model to optimize the ecological security pattern in a semi-arid area with intensive coal mining: A case study in northern China[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119143.
DOI |
| [16] |
PENG J, PAN Y J, LIU Y X, et al., 2018b. Linking ecological degradation risk to identify ecological security patterns in a rapidly urbanizing landscape[J]. Habitat International, 71: 110-124.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
PENG J, YANG Y, LIU Y X, et al., 2018a. Linking ecosystem services and circuit theory to identify ecological security patterns[J]. Science of the total environment, 644: 781-790.
DOI URL |
| [18] | PENG J, ZHAO S Q, DONG J Q, et al., 2019. Applying ant colony algorithm to identify ecological security patterns in megacities[J]. Environmental Modelling & Software, 117(1): 214-222. |
| [19] |
SUN X, LI F, 2017. Spatiotemporal assessment and trade-offs of multiple ecosystem services based on land use changes in Zengcheng, China[J]. Science of the total environment, 609: 1569-1581.
DOI URL |
| [20] | WILLIAMS J C, SNYDER S A, 2005. Restoring habitat corridors in fragmented landscapes using optimization and percolation models[J]. Environmental Modeling & Assessment, 10(3): 239-250. |
| [21] |
XIAO S C, WU W J, GUO J, et al., 2020. An evaluation framework for designing ecological security patterns and prioritizing ecological corridors: application in Jiangsu Province, China[J]. Landscape Ecology, 35(11): 2517-2534.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
ZHANG L Q, PENG J, LIU Y X, et al., 2017. Coupling ecosystem services supply and human ecological demand to identify landscape ecological security pattern: A case study in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China[J]. Urban Ecosystems, 20(3): 701-714.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
ZHAO M Y, PENG J, LIU Y X, et al., 2018. Mapping watershed-level ecosystem service bundles in the Pearl River Delta, China[J]. Ecological Economics, 152: 106-117.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
ZHOU R B, LIN M Z, GONG J Z, et al., 2019. Spatiotemporal heterogeneity and influencing mechanism of ecosystem services in the Pearl River Delta from the perspective of LUCC[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 29(5): 831-845.
DOI URL |
| [25] | 陈德权, 兰泽英, 李玮麒, 2019. 基于最小累积阻力模型的广东省陆域生态安全格局构建[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 35(7): 826-835. |
| CHEN D Q, LAN Z Y, LI W Q, 2019. Construction of land ecological security in Guangdong Province from the perspective of ecological demand[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 35(7): 826-835. | |
| [26] | 丁宇, 张雷, 曾祥坤, 2019. 粤港澳大湾区生态功能网络构建及对策[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 35(5): 573-581. |
| DING Y, ZHANG L, ZENG X K, 2019. The construction of an ecological function network and its application in the Greater Bay Area, China[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 35(5): 573-581. | |
| [27] | 古璠, 黄义雄, 陈传明, 等, 2017. 福建省自然保护区生态网络的构建与优化[J]. 应用生态学报, 28(3): 1013-1020. |
| GU F, HUANG Y X, CHEN C M, et al., 2017. Construction and optimization of ecological network for nature reserves in Fujian Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 28(3): 1013-1020. | |
| [28] | 甘琳, 陈颖彪, 吴志峰, 等, 2018. 近20年粤港澳大湾区生态敏感性变化[J]. 生态学杂志, 37(8): 2453-2462. |
| GAN L, CHEN Y B, WU Z F, et al., 2018. The variation of ecological sensitivity in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area in recent 20 years[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 37(8): 2453-2462. | |
| [29] | 官卫华, 何流, 姚士谋, 等, 2007. 城市生态廊道规划思路与策略研究--以南京为例[J]. 现代城市研究, 22(1): 51-58. |
| GUAN W H, HE L, YAO S M, et al., 2007. Thoughts and strategy research of urban ecological corridor planning: Taking Nanjing as an example[J]. Modern Urban Research, 22(1): 51-58. | |
| [30] | 何建华, 潘越, 刘殿锋, 2020. 生态网络视角下武汉市湿地生态格局分析[J]. 生态学报, 40(11): 3590-3601. |
| HE J H, PAN Y, LIU D F, 2020. Analysis of the wetland ecological pattern in Wuhan City from the perspective of ecological network[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(11): 3590-3601. | |
| [31] | 康秀亮, 刘艳红, 2007. 生态系统敏感性评价方法研究[J]. 安徽农业科学, 35(33): 10569-10571. |
| KANG X L, LIU Y H, 2007. Study on ecological sensitivity evaluation method[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 35(33): 10569-10571. | |
| [32] | 孔繁花, 尹海伟, 2008. 济南城市绿地生态网络构建[J]. 生态学报, 28(4): 1711-1719. |
| KONG F H, YIN H W, 2008. Developing green space ecological networks in Jinan City[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 28(4): 1711-1719. | |
| [33] | 康洁铭, 刘雨, 朱晓伟, 等, 2020. 胶东半岛生态安全格局识别与优化布局[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 36(8): 1015-1025. |
| KANG J M, LIU Y, ZHU X W, et al., 2020. Identification and optimization of ecological security pattern in Jiaodong Peninsula[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 36(8): 1015-1025. | |
| [34] | 李敏, 2016. 基于InVEST模型的生态系统服务功能评价研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学: 8-9. |
| LI M, 2016. Ecosystem services evaluation based on InVEST model[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University: 8-9. | |
| [35] | 李怡, 赵小敏, 郭熙, 等, 2021. 基于InVEST和MCR模型的南方山地丘陵区生态保护红线优化[J]. 自然资源学报, 36(11): 2980-2994. |
|
LI Y, ZHAO X M, GUO X, et al., 2021. Optimization of ecological red line in the hilly region of Southern China based on InVEST and MCR model[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 36(11): 2980-2994.
DOI URL |
|
| [36] |
林媚珍, 刘汉仪, 周汝波, 等, 2021. 多情景模拟下粤港澳大湾区生态系统服务评估与权衡研究[J]. 地理研究, 40(9): 2657-2669.
DOI |
| LIN M Z, LIU H Y, ZHOU R B, et al., 2021. Evaluation and trade-offs of ecosystem services in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area under multi-scenario simulation[J]. Geographical Research, 40(9): 2657-2669. | |
| [37] | 马克明, 傅伯杰, 黎晓亚, 等, 2004. 区域生态安全格局: 概念与理论基础[J]. 生态学报, 24(4): 761-768. |
| MA K M, FU B J, LI X Y, et al., 2004. The regional pattern for ecological security (RPES): The concept and theoretical basis[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 24(4): 761-768. | |
| [38] | 马世发, 劳春华, 江海燕, 2021. 基于生态安全格局理论的国土空间生态修复分区模拟——以粤港澳大湾区为例[J]. 生态学报, 41(9): 3441-3448. |
| MA S F, LAO C H, JIANG H Y, 2021. Ecological restoration zoning of territorial space based on the pattern simulation of eco-security scenario: A case study of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(9): 3441-3448. | |
| [39] | 毛诚瑞, 代力民, 齐麟, 等, 2020. 基于生态系统服务的流域生态安全格局构建——以辽宁省辽河流域为例[J]. 生态学报, 40(18): 6486-6494. |
| MAO C R, DAI L M, QI L, et al., 2020. Constructing ecological security pattern based on ecosystem services: A case study in Liaohe River Basin, Liaoning Province, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(18): 6486-6494. | |
| [40] | 牛沛航, 冯艳芬, 王芳, 2021. 粤港澳大湾区珍稀濒危动物适宜分布区[J]. 生态学杂志, 40(8): 2467-2477. |
| NIU P H, FENG Y F, WANG F, 2021. Suitable distribution area for rare and endangered animals in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 40(8): 2467-2477. | |
| [41] | 欧阳志云, 王效科, 苗鸿, 2000. 中国生态环境敏感性及其区域差异规律研究[J]. 生态学报, 20(1): 10-13. |
| OUYANG Z Y, WANG X K, MIAO H, 2000. China's eco-environmental sensitivity and its spatial heterogeneity[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 20(1): 10-13. | |
| [42] | 潘美慧, 伍永秋, 任斐鹏, 等, 2010. 基于USLE的东江流域土壤侵蚀量估算[J]. 自然资源学报, 25(12): 2154-2164. |
| PAN M H, WU Y Q, REN F P, et al., 2010. Estimating soil erosion in the Dongjiang River Basin based on USLE[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 25(12): 2154-2164 | |
| [43] | 彭建, 郭小楠, 胡熠娜, 等, 2017a. 基于地质灾害敏感性的山地生态安全格局构建——以云南省玉溪市为例[J]. 应用生态学报, 28(2): 627-635. |
| PENG J, GUO X N, HU Y N, et al., 2017. Construvting ecological security patterns in mountain areas based on geological disaster sensitivity: A case study in Yuxi City, Yunnan Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 28(2): 627-635. | |
| [44] | 彭建, 赵会娟, 刘焱序, 等, 2017b. 区域生态安全格局构建研究进展与展望[J]. 地理研究, 36(3): 407-419. |
| PENG J, ZHAO H J, LIU Y X, et al., 2017. Research progress and prospect on regional ecological security pattern construction[J]. Geographical Research, 36(3): 407-419. | |
| [45] |
史娜娜, 韩煜, 王琦, 等, 2021. 新疆南部地区风沙扩散风险评价及景观格局优化[J]. 地理学报, 76(1): 73-86.
DOI |
| SHI N N, HAN Y, WANG Q, et al., 2021. Risk assessment of sandstorm diffusion and landscape pattern optimization in southern Xinjiang[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 76(1): 73-86. | |
| [46] | 王浩, 马星, 杜勇, 2021. 基于生态系统服务重要性和生态敏感性的广东省生态安全格局构建[J]. 生态学报, 41(5): 1705-1715. |
| WANG H, MA X, DU Y, 2021. Constructing ecological security patterns based on ecological service importance and ecological sensitivity in Guangdong Province[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(5): 1705-1715. | |
| [47] | 王金华, 黄华梅, 贾后磊, 等, 2020. 粤港澳大湾区海岸带生态系统保护和修复策略[J]. 生态学报, 40(23): 8430-8439. |
| WANG J H, HUANG H M, JIA H L, et al., 2020. Discussion on the strategies of coastal ecosystem protection and restoration in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(23): 8430-8439. | |
| [48] | 王世豪、 黄麟、 徐新良, 等, 2020. 粤港澳大湾区生态系统服务时空演化及其权衡与协同特征[J]. 生态学报, 40(23): 8403-8416. |
| WANG S H, HUANG L, XU X L, et al., 2020. Spatial and temporal evolution of ecosystem services and its trade-offs and synergies in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(23): 8403-8416. | |
| [49] | 王秀明, 赵鹏, 龙颖贤, 等, 2022. 基于生态安全格局的粤港澳地区陆域空间生态保护修复重点区域识别[J]. 生态学报, 42(2): 1-12. |
| WANG X M, ZHAO P, LONG Y X, et al., 2022. Identification of key areas of land space ecological protection and restoration based on the pattern of ecological security in Guangdong, Hong Kong and Macau[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42(2): 1-12. | |
| [50] | 王媛, 周长威, 2019. 黔中城市群景观生态安全格局构建[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 35(9): 1111-1117. |
| WANG Y, ZHOU C W, 2019. Landscape ecological security pattern in central Guizhou urban agglomeration[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 35(9): 1111-1117. | |
| [51] | 吴隽宇, 张一蕾, 江伟康, 2020. 粤港澳大湾区生态系统碳储量时空演变[J]. 风景园林, 27(10): 57-63. |
| WU J Y, ZHANG Y L, JIANG W K, 2020. Spatio-temporal evolution of ecosystem carbon storage in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area[J]. Landscape Architecture, 27(10): 57-63. | |
| [52] | 吴茂全, 胡蒙蒙, 汪涛, 等, 2019. 基于生态安全格局与多尺度景观连通性的城市生态源地识别[J]. 生态学报, 39(13): 4720-4731. |
| WU M Q, HU M M, WANG T, et al., 2019. Recognition of urban ecological source area based on ecological security pattern and multi-scale landscape connectivity[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(13): 4720-4731. | |
| [53] | 吴健生, 罗可雨, 马洪坤, 等, 2020. 基于生态系统服务与引力模型的珠三角生态安全与修复格局研究[J]. 生态学报, 40(23): 8417-8429. |
| WU J S, LUO K Y, MA H K, et al., 2020. Ecological security and restoration pattern of Pearl River Delta, based on ecosystem service and gravity model[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(23): 8417-8429. | |
| [54] | 王耕, 王佳雯, 2021. 丹东沿海地区土地利用变化对生境质量的影响研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(3): 621-630. |
| WANG G, WANG J W, 2021. Study on the impact of land use change on habitat quality in Dandong Coastal Area[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(3): 621-630. | |
| [55] | 吴献文, 陈颖彪, 2021. 基于自然资源本底数据的珠三角城市群生态敏感性评估分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(05): 976-983. |
| WU X W, CHEN Y B, 2021. Ecological sensitivity assessment based on natural resource data[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(5): 976-983. | |
| [56] | 熊善高, 秦昌波, 于雷, 等, 2018. 基于生态系统服务功能和生态敏感性的生态空间划定研究——以南宁市为例[J]. 生态学报, 38(22): 7899-7911. |
| XIONG S G, QIN C B, YU L, et al., 2018. Methods to identify the boundary of ecological space based on ecosystem service functions and ecological sensitivity: A case study of Nanning City[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(22): 7899-7911. | |
| [57] |
杨志广, 蒋志云, 郭程轩, 等, 2018. 基于形态空间格局分析和最小累积阻力模型的广州市生态网络构建[J]. 应用生态学报, 29(10): 3367-3376.
PMID |
|
YANG Z G, JIANG Z Y, GUO C X, et al., 2018. Construction of ecological network using morphological spatial pattern analysis and minimal cumulative resistance models in Guangzhou City, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 29(10): 3367-3376.
DOI PMID |
|
| [58] | 虞文娟, 任田, 周伟奇, 等, 2020. 区域城市扩张对森林景观破碎化的影响——以粤港澳大湾区为例[J]. 生态学报, 40(23): 8474-8481. |
| YU W J, REN T, ZHOU W Q, et al., 2020. Forest fragmentation and its relationship with urban expansion in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Great Bay Area, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(23): 8474-8481. | |
| [59] | 湛社霞, 2018. 粤港澳大湾区常规大气污染物变化趋势与影响因素研究[D]. 广州: 中国科学院大学 (中国科学院广州地球化学研究所): 107-108. |
| ZHAN S X, 2018. Research on changing trend and influencing factors of conventional air pollutants in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay area[D]. Guangzhou: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences): 107-108. | |
| [60] | 张海波, 2014. 南方丘陵山地带水源涵养与土壤保持功能变化及其区域生态环境响应[D]. 长沙: 湖南师范大学: 31-32. |
| ZHANG H B, 2014. The function of water and soil conservation and its ecological environmental responses, in hilly and mountainous regions of South, China[D]. Changsha: Hunan Normal University: 31-32. | |
| [61] | 张剑波, 2016. 广州陆域生物多样性生态安全格局构建研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学: 14-15. |
| ZHANG J B, 2016. Research on the construction of ecological security pattern of biodiversity in the land area of Guangzhou[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology: 14-15. | |
| [62] | 张玥, 许端阳, 李霞, 等, 2020. 中-老交通走廊核心区生态廊道构建与关键节点识别[J]. 生态学报, 40(6): 1933-1943. |
| ZHANG Y, XU D Y, LI X, et al., 2020. Construction of ecological corridors and identification of key nodes in the core area of China-Laos transportation corridors[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(6): 1933-1943. | |
| [63] | 张宝春, 陈彦军, 李伟铿, 等, 2011. 基于GIS的珠三角区域空气质量时空特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 20(4): 600-605. |
| ZHANG B C, CHEN Y J, LI W K, et al., 2011. The research of spatial and temporal characteristics on air quality level in Pearl River Delta based on GIS[J]. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 20(4): 600-605. | |
| [64] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部, 2016. 环境空气质量标准 (GB 3095—2012)[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, 2016. Ambient air quality standards (GB 3095—2012)[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. | |
| [65] | 中华人民共和国卫生部, 2012. 纺织业卫生防护距离(GB/T 18080.1-2012)[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China, 2012. Health protection zone for textile industry - Part 1:otton, chemical fiber textile and dyeing finishing industry (GB/T 18080.1-2012)[S]. Beijing: China Standards Publishing House. | |
| [66] | 中华人民共和国卫生部, 2013. 煤制气业卫生防护距离(GB/T 17222—2012)[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China, 2013. Health protection zone for coal gas industry (GB/T 17222—2012)[S]. Beijing: China Standards Publishing House. | |
| [67] | 周汝波, 林媚珍, 吴卓, 等, 2020. 基于生态系统服务重要性的粤港澳大湾区生态安全格局构建[J]. 生态经济, 36(7): 189-196. |
|
ZHOU R B, LIN M Z, WU Z, et al., 2020. Construction of ecological security in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area from the perspective of importance of ecosystem services[J]. Ecological Economy, 36(7): 189-196.
DOI URL |
|
| [68] | 朱杰, 龚健, 李靖业, 2020. 青藏高原东部生态敏感区生境质量时空演变特征——以青海省河湟谷地为例[J]. 资源科学, 42(5): 991-1003. |
| ZHU J, GONG J, LI J Y, 2020. Spatiotemporal change of habitat quality in ecologically sensitive sensitive areas of eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: A case study of the Hehuang Valley, Qinghai Province[J]. Resources Science, 42(5): 991-1003. |
| [1] | 许静, 廖星凯, 甘崎旭, 周茅先. 基于MSPA与电路理论的黄河流域甘肃段生态安全格局构建[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 805-813. |
| [2] | 何艳虎, 龚镇杰, 吴海彬, 蔡宴朋, 杨志峰, 陈晓宏. 粤港澳大湾区城市生态效率时空演变及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 469-480. |
| [3] | 张平江, 党国锋. 基于MCR模型与蚁群算法的洮河流域生态安全格局构建[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 481-491. |
| [4] | 冯娴慧, 曾芝琳. 粤港澳大湾区植被覆盖特征与变化趋势的自然驱动力研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1713-1724. |
| [5] | 阮惠华, 许剑辉, 张菲菲. 2001—2020年粤港澳大湾区植被和地表温度时空变化研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1510-1520. |
| [6] | 魏建兵, 郑泓, 程雨露, 王阳. 基于CiteSpace的生态安全格局研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 835-844. |
| [7] | 易浪, 孙颖, 尹少华, 魏晓. 生态安全格局构建:概念、框架与展望[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 845-856. |
| [8] | 李平星, 邹露. 基于土地利用变化的生态廊道识别和建设成本研究——以南京东郊地区为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 277-285. |
| [9] | 廖彤, 熊鑫, 王在华, 杨夏捷, 黄映楠, 冯嘉颖. 世界三大湾区大气污染治理经验及对粤港澳大湾区的启示[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2242-2250. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
