生态环境学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (6): 946-957.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.06.012
刘泽碧1,2( ), 毛旭锋1,2,*(
), 毛旭锋1,2,*( ), 吴艺1,2, 宋秀华3, 于红妍4, 金鑫1,2, 杜凯1,2, 谢顺邦3
), 吴艺1,2, 宋秀华3, 于红妍4, 金鑫1,2, 杜凯1,2, 谢顺邦3
收稿日期:2024-03-18
出版日期:2024-06-18
发布日期:2024-07-30
通讯作者:
* 毛旭锋。E-mail: maoxufeng@yeah.com作者简介:刘泽碧(1999年生),女,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为湿地生态过程。E-mail: liuzebi06@163.com
基金资助:
LIU Zebi1,2( ), MAO Xufeng1,2,*(
), MAO Xufeng1,2,*( ), WU Yi1,2, SONG Xiuhua3, YU Hongyan4, JIN Xin1,2, DU Kai1,2, XIE Shunbang3
), WU Yi1,2, SONG Xiuhua3, YU Hongyan4, JIN Xin1,2, DU Kai1,2, XIE Shunbang3
Received:2024-03-18
Online:2024-06-18
Published:2024-07-30
摘要:
由于水体富营养化引发的水华在高原湿地生态系统的暴发频率日益增加,对当地生态系统健康产生负面的影响。为分析蓝藻水华及其生消全过程中浮游生物群落结构变化特征,以青海省西宁市海湖湿地为研究区,于2022年3月(水华暴发期)、4月(水华衰退期)和5月(水华结束期)对6处监测点的浮游生物群落开展调查,通过R软件的Vegan包和rdacca.hp包对影响浮游生物群落结构的环境因子进行定量分析。结果表明,1)3个时期共鉴定出浮游植物7门94种、浮游动物4门46种;螺形龟甲轮虫(Keratella cochlearis)在3个时期均为优势动物。2)浮游生物密度和生物量呈现由上游向下游增加的趋势;浮游植物和浮游动物呈现相反的变化趋势,浮游植物生物量在衰退期达到最大值(63.84 mg·L−1),而浮游动物生物量在结束期达到最大(6.76 mg·L−1)。3)Pearson相关性和典范对应分析(CCA)结果显示,浮游生物优势种在水华不同时期的主要影响因素存在差异,浮游植物和浮游动物在暴发期分别受TN和水温的影响显著(p<0.05),在衰退期分别受NH4+-N和TP的影响显著(p<0.05),而在结束期分别受pH和水温的影响显著(p<0.05)。4)基于浮游动物多样性指数的水质评价结果显示,海湖湿地水体介于中污与无污之间,水质状态表现为良好。5)变差分解(VPA)和层次分割(HP)分析发现,水温对浮游植物群落结构的影响最大(13.01%)(p<0.01),而TN对浮游动物群落结构的影响最大(6.70%)(p>0.01)。该研究表明,蓝藻水华显著影响海湖湿地浮游生物群落结构的演替。研究结果对利用环境手段进行水华治理具有重要意义。
中图分类号:
刘泽碧, 毛旭锋, 吴艺, 宋秀华, 于红妍, 金鑫, 杜凯, 谢顺邦. 海湖湿地水体蓝藻水华期浮游生物群落特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(6): 946-957.
LIU Zebi, MAO Xufeng, WU Yi, SONG Xiuhua, YU Hongyan, JIN Xin, DU Kai, XIE Shunbang. Characteristics of Plankton Community and Its Influencing Factors during Algal Blooms Period in the Haihu Wetland[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(6): 946-957.
| Shannon多样性指数 | Pielou均匀度指数 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数值范围 | 评价标准 | 数值范围 | 评价标准 | |
| 0‒1 | 重污 | 0‒0.3 | 重污 | |
| 1‒3 | 中污 | 0.3‒0.5 | 中污 | |
| >3 | 轻污或无污 | 0.5‒0.8 | 轻污或无污 | |
表1 生态指数水质评价标准
Table 1 Water quality evaluation criteria of the ecological index
| Shannon多样性指数 | Pielou均匀度指数 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数值范围 | 评价标准 | 数值范围 | 评价标准 | |
| 0‒1 | 重污 | 0‒0.3 | 重污 | |
| 1‒3 | 中污 | 0.3‒0.5 | 中污 | |
| >3 | 轻污或无污 | 0.5‒0.8 | 轻污或无污 | |
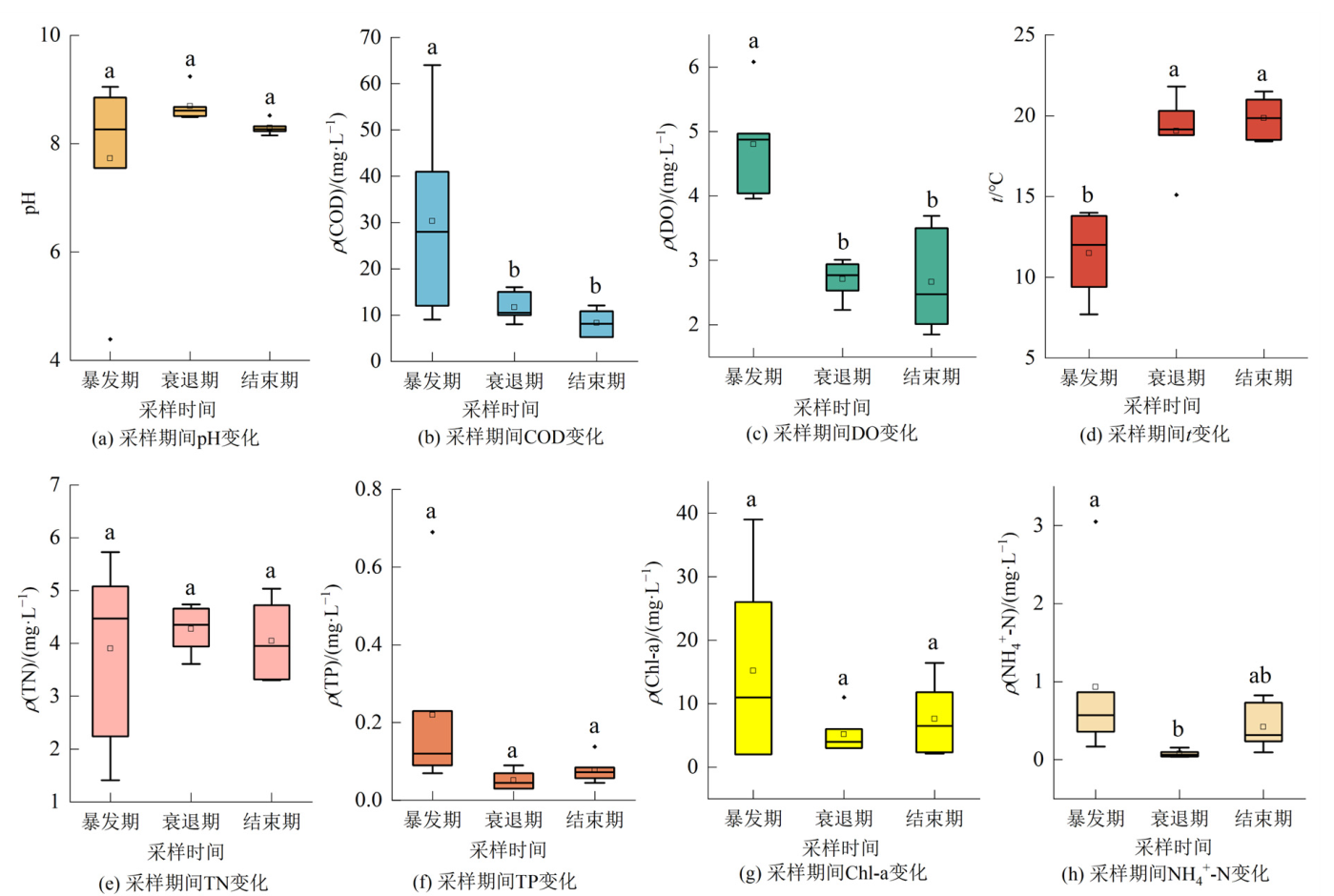
图2 水体理化指标特征 图中pH、COD、DO、t、TN、TP、Chl-a、NH4+-N分别代表酸碱度、化学需氧量、溶解氧、水温、总氮、总磷、叶绿素、氨氮;p<0.05
Figure 2 Characteristics of physicochemical indexes of water bodies
| 编号 | 优势种 | 门 | 时间 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 暴发期 | 衰退期 | 结束期 | |||
| Sp1 | 鱼害微囊藻 Microcystis ichthyoblabe | 蓝藻门 | + | ||
| Sp2 | 颤藻 Oscillatoria sp. | 蓝藻门 | + | ||
| Sp3 | 卷曲长胞藻 Dolichospermum circinale | 蓝藻门 | + | ||
| Sp4 | 浮丝藻 Planktothrix sp. | 蓝藻门 | + | ||
| Sp5 | 假鱼腥藻 Pseudoanabaena sp. | 蓝藻门 | + | ||
| Sp6 | 鼓藻 Cosmarium sp. | 绿藻门 | + | ||
| Sp7 | 颗粒直链藻 Melosira granulata | 硅藻门 | + | ||
| Sp8 | 纤细等片藻 Diatoma tenue | 硅藻门 | + | ||
| Sp9 | 舟形藻 Navicula sp. | 硅藻门 | + | + | |
| Sp10 | 喙头舟形藻 Navicula rhynchocephala | 硅藻门 | + | ||
| Sp11 | 长圆舟形藻 Navicula oblonga | 硅藻门 | + | ||
| Sp12 | 放射舟形藻 Navicula radiosa | 硅藻门 | + | ||
| Sp13 | 菱形藻 Surirella sp. | 硅藻门 | + | ||
| Sp14 | 类S形菱形藻 Nizschia sigmoidea | 硅藻门 | + | ||
| Sp15 | 针杆藻 Synedra sp. | 硅藻门 | + | ||
| Sp16 | 窗纹藻 Epithemia sp. | 硅藻门 | + | ||
| Sp17 | 小环藻 Cyclotella sp. | 硅藻门 | + | ||
| Sp18 | 变异直链藻 Melosira varians | 硅藻门 | + | ||
| Sp19 | 直链藻 Melosira sp. | 硅藻门 | + | ||
| Sp20 | 梅尼小环藻 Cyclotella meneghiniana | 硅藻门 | + | ||
| Sp21 | 表壳虫 Arcella sp. | 原生动物 | + | ||
| Sp22 | 草履虫 Parameciidae sp. | 原生动物 | + | ||
| Sp23 | 侠盗虫属 Strobilidium sp. | 原生动物 | + | ||
| Sp24 | 纤毛虫未定种 | 原生动物 | + | ||
| Sp25 | 萼花臂尾轮虫 Brachionus calyciflorus | 轮虫 | + | ||
| Sp26 | 壶状臂尾轮虫 Brachionus urceus | 轮虫 | + | ||
| Sp27 | 臂尾轮虫 Brachionus sp. | 轮虫 | + | + | |
| Sp28 | 角突臂尾轮虫 Brachionus angularis | 轮虫 | + | ||
| Sp29 | 螺形龟甲轮虫 Keratella cochlearis | 轮虫 | + | + | + |
| Sp30 | 疣毛轮虫 Synchaeta sp. | 轮虫 | + | ||
| Sp31 | 暗小异尾轮虫 Trichocerca pusilla | 轮虫 | + | ||
| Sp32 | 广布中剑水蚤 Mesocyclops leuckarti | 轮虫 | + | ||
| Sp33 | 等刺温剑水蚤 Thermocyclops kawamurai | 桡足类 | + | ||
| Sp34 | 无节幼体 Nauplius | 桡足类 | + | + | |
表2 水华期浮游生物优势种
Table 2 Dominant plankton species during bloom
| 编号 | 优势种 | 门 | 时间 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 暴发期 | 衰退期 | 结束期 | |||
| Sp1 | 鱼害微囊藻 Microcystis ichthyoblabe | 蓝藻门 | + | ||
| Sp2 | 颤藻 Oscillatoria sp. | 蓝藻门 | + | ||
| Sp3 | 卷曲长胞藻 Dolichospermum circinale | 蓝藻门 | + | ||
| Sp4 | 浮丝藻 Planktothrix sp. | 蓝藻门 | + | ||
| Sp5 | 假鱼腥藻 Pseudoanabaena sp. | 蓝藻门 | + | ||
| Sp6 | 鼓藻 Cosmarium sp. | 绿藻门 | + | ||
| Sp7 | 颗粒直链藻 Melosira granulata | 硅藻门 | + | ||
| Sp8 | 纤细等片藻 Diatoma tenue | 硅藻门 | + | ||
| Sp9 | 舟形藻 Navicula sp. | 硅藻门 | + | + | |
| Sp10 | 喙头舟形藻 Navicula rhynchocephala | 硅藻门 | + | ||
| Sp11 | 长圆舟形藻 Navicula oblonga | 硅藻门 | + | ||
| Sp12 | 放射舟形藻 Navicula radiosa | 硅藻门 | + | ||
| Sp13 | 菱形藻 Surirella sp. | 硅藻门 | + | ||
| Sp14 | 类S形菱形藻 Nizschia sigmoidea | 硅藻门 | + | ||
| Sp15 | 针杆藻 Synedra sp. | 硅藻门 | + | ||
| Sp16 | 窗纹藻 Epithemia sp. | 硅藻门 | + | ||
| Sp17 | 小环藻 Cyclotella sp. | 硅藻门 | + | ||
| Sp18 | 变异直链藻 Melosira varians | 硅藻门 | + | ||
| Sp19 | 直链藻 Melosira sp. | 硅藻门 | + | ||
| Sp20 | 梅尼小环藻 Cyclotella meneghiniana | 硅藻门 | + | ||
| Sp21 | 表壳虫 Arcella sp. | 原生动物 | + | ||
| Sp22 | 草履虫 Parameciidae sp. | 原生动物 | + | ||
| Sp23 | 侠盗虫属 Strobilidium sp. | 原生动物 | + | ||
| Sp24 | 纤毛虫未定种 | 原生动物 | + | ||
| Sp25 | 萼花臂尾轮虫 Brachionus calyciflorus | 轮虫 | + | ||
| Sp26 | 壶状臂尾轮虫 Brachionus urceus | 轮虫 | + | ||
| Sp27 | 臂尾轮虫 Brachionus sp. | 轮虫 | + | + | |
| Sp28 | 角突臂尾轮虫 Brachionus angularis | 轮虫 | + | ||
| Sp29 | 螺形龟甲轮虫 Keratella cochlearis | 轮虫 | + | + | + |
| Sp30 | 疣毛轮虫 Synchaeta sp. | 轮虫 | + | ||
| Sp31 | 暗小异尾轮虫 Trichocerca pusilla | 轮虫 | + | ||
| Sp32 | 广布中剑水蚤 Mesocyclops leuckarti | 轮虫 | + | ||
| Sp33 | 等刺温剑水蚤 Thermocyclops kawamurai | 桡足类 | + | ||
| Sp34 | 无节幼体 Nauplius | 桡足类 | + | + | |
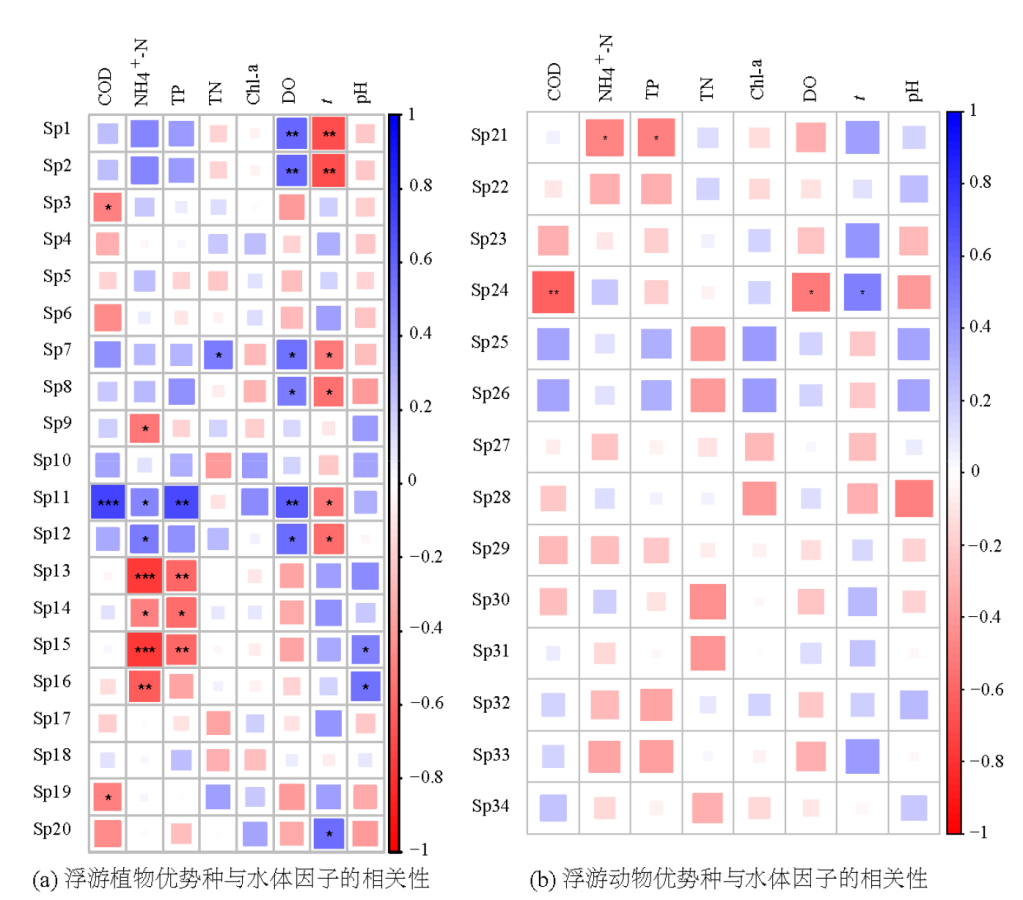
图6 浮游生物优势种与水体因子的相关性 图例颜色表示相关性程度;“***”表示p<0.001,“**”表示0.001≤p<0.01,“*”表示0.01≤p<0.05
Figure 6 Correlation between plankton dominant species and water factors
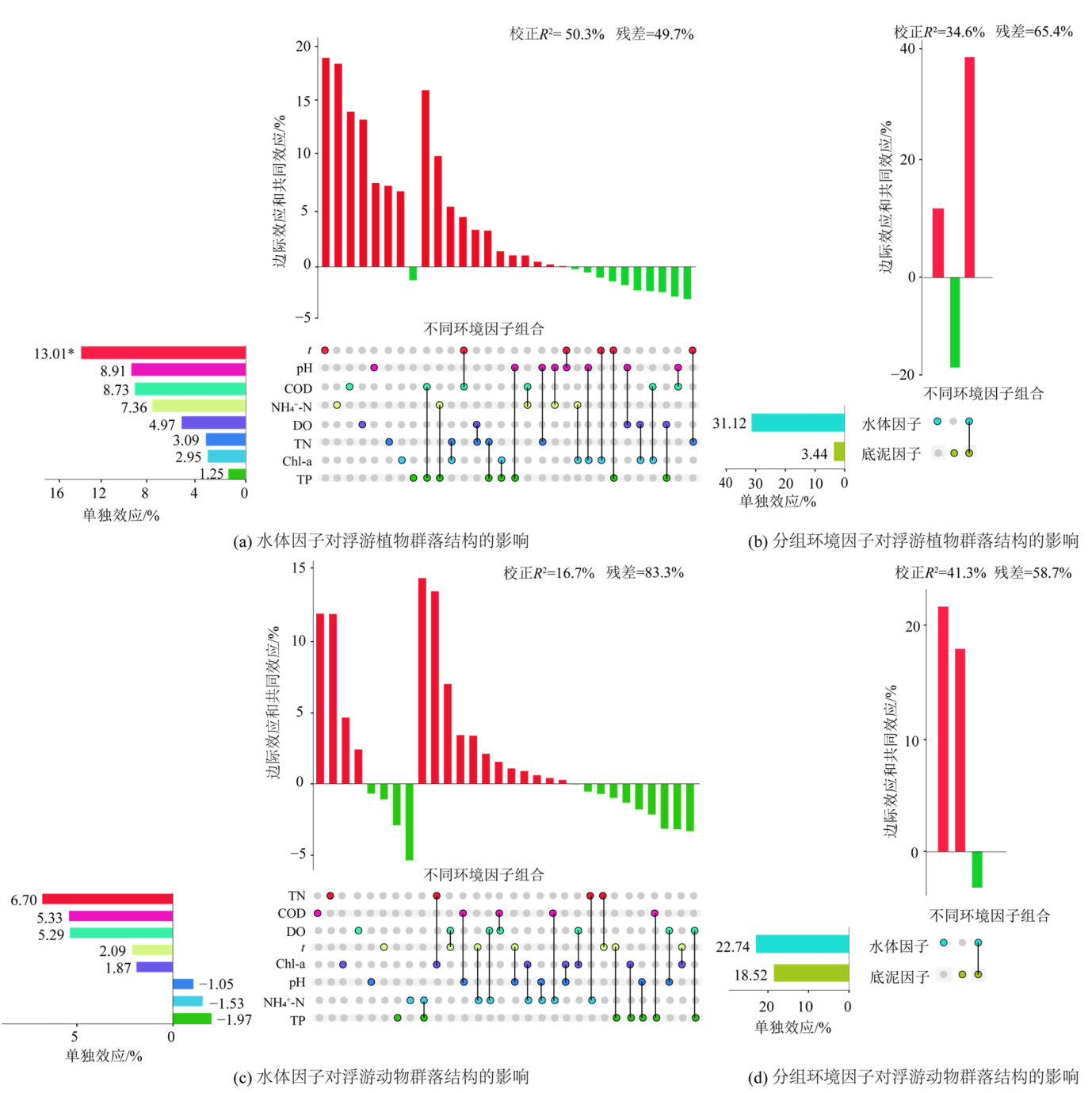
图8 环境因子对浮游生物群落结构影响的相对重要性 在右下方的点阵图中,每行对应一个环境因子或一个环境因子组。每列中的孤立点表示各环境因子的边际效应,多点间连线表示这些环境因子间的共同效应。右上方柱状图中的纵坐标表示各组分解释的变差百分比(来自变差分解),横坐标表示不同环境因子组合。各环境因子的单独效应(来自层次分割)展示在左侧的横向柱状图中,纵轴分别对应右侧点阵图的环境因子,横轴表示单独效应,单独效应的值为该环境因子的边际效应加上与其他环境因子的共同效应的平均分配值。*,p<0.05
Figure 8 The relative importance of environmental factors on plankton community structure
| [1] | CALBET A, LANDRY M R, 2004. Phytoplankton growth, microzooplankton grazing, and carbon cycling in marine systems[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 49(1): 51-57. |
| [2] | CHOU W R, FANG L S, WANG W H, et al., 2011. Environmental influence on coastal phytoplankton and zooplankton diversity: A multivariate statistical model analysis[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184(9): 5679-5688. |
| [3] | DE S C L, DA M M D, 2009. Hydrodynamics-driven plankton community in a shallow lake[J]. Aquatic Ecology, 43(1): 73-84. |
| [4] | DUAN H Y, YAO X J, ZHANG D H, et al., 2022. Long-Term temporal and spatial monitoring of Cladophora blooms in Qinghai Lake based on multi-source remote sensing images[J]. Remote Sensing, 14(4): 853. |
| [5] | GUBELIT Y I, BEREZINA N A, 2010. The causes and consequences of algal blooms: The Cladophora glomerata bloom and the Neva estuary (Eastern Baltic Sea)[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 61(4): 183-188. |
| [6] | HO J C, MICHALAK A M, 2019. Exploring temperature and precipitation impacts on harmful algal blooms across continental U.S. lakes[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 65(5): 992-1009. |
| [7] | HU B J, HU X R, NIE X H, et al., 2019. Seasonal and inter-annual community structure characteristics of zooplankton driven by water environment factors in a sub-lake of Lake Poyang, China[J]. PeerJ, 7: e7590. |
| [8] |
WANG L, WANG X Y, JIN X B, et al., 2017. Analysis of algae growth mechanism and water bloom prediction under the effect of multi-affecting factor[J]. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 24(3): 556-562.
DOI PMID |
| [9] | WANG Y M, ZHOU P P, ZHOU W C, et al., 2023. Network analysis indicates microbial assemblage differences in life stages of Cladophora[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 89(3): e0211222. |
| [10] | WU Z H, YUAN X G, XIONG X, et al., 2024. Cladophora as ecological engineer: a new test from the largest lake of Qinghai-Tibet plateau with filamentous algal blooms[J]. Water Biology and Security, 3(1): 100210. |
| [11] | ZHU H, XIONG X, AO H Y, et al., 2020. Cladophora reblooming after half a century: Effect of climate change-induced increases in the water level of the largest lake in Tibetan Plateau[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(33): 42175-42181. |
| [12] |
白海锋, 王怡睿, 宋进喜, 等, 2022. 渭河浮游生物群落结构特征及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 31(1): 117-130.
DOI |
|
BAI H F, WANG Y R, SONG J X, et al., 2022. Characteristics of plankton community structure and its relation to environmental factors in Weihe River, China[J]. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 31(1): 117-130.
DOI |
|
| [13] | 陈红, 刘清, 潘建雄, 等, 2019. 灞河城市段浮游生物群落结构时空变化及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 生态学报, 39 (1): 173-184. |
| CHEN H, LIU Q, PAN J X, et al., 2019. Spatial and temporal variation of the plankton community and its relationship with environmental factors in the city section of the Ba River[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(1): 173-184. | |
| [14] | 陈佳琪, 赵坤, 曹玥, 等, 2020. 鄱阳湖浮游动物群落结构及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 生态学报, 40(18):6644-6658 |
| CHEN J Q, ZHAO K, CAO Y, et al., 2020. Zooplankton community structure and its relationship with environmental factors in Poyang Lake[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(18): 6644-6658. | |
| [15] | 陈学杨, 丁东生, 崔正国, 等, 2024. 靖海湾富营养化海域浮游动物群落变化及其影响因素[J]. 渔业科学进展, 45(2): 14-27. |
| CHEN X Y, DING D S, CUI Z G, et al., 2024. Changes and influencing factors of the zooplankton community in the eutrophic waters of Jinghai Bay[J]. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 45(2): 14-27. | |
| [16] | 陈振林, 2024. 贵州习水国家级自然保护区浮游生物群落结构及水质评价[J/OL]. 广西科学, 1-17 [2024-06-02]. https://doi.org/10.13656/j.cnki.gxkx.20240304.001. |
| CHEN Z L, 2024. The plankton community structure and water quality evaluation in Xishui National Nature Reserve, Guizhou[J/OL]. Guangxi Sciences, 1-17 [2024-06-02]. https://doi.org/10.13656/j.cnki.gxkx.20240304.001. | |
| [17] | 代涛涛, 钟家有, 杨平, 等, 2023. 东江源区浮游生物群落结构特征和主要环境因子及水质评价[J]. 环境科学与技术, 46(S2): 17-24. |
| DAI T T, ZHONG J Y, YANG P, et al., 2023. Plankton community structure characteristics, main environmental factors and water quality evaluation in Dongjiang River basin[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 46(S2): 17-24. | |
| [18] | 戴承钧, 2023. 黄河源区白河流域浮游动物群落结构特征及水生态健康评价[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学: 25-30. |
| DAI C J, 2023. Zooplankton in the basin of the Yellow River source area: Community structure and characteristics and assessment of water ecological health[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Technology: 25-30. | |
| [19] |
董瑶, 俞胡伟, 刘智硕, 等, 2024. 东莞市河道底泥特征及作为绿化种植土的可行性研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 40(5): 69-73.
DOI |
|
DONG Y, YU H W, LIU Z S, et al., 2024. Research on the characteristics of river substrates in Dongguan and their feasibility as greening planting soil[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 40(5): 69-73.
DOI |
|
| [20] | 高锴, 李泽利, 赵兴华, 等, 2024. 于桥水库浮游植物群落时空动态及影响因素分析[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 41(1): 125-137. |
| GAO K, LI Z L, ZHAO X H, et al., 2024. Spatiotemporal dynamics of and influencing factors on the phytoplankton community in the Yuqiao reservoir[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 41(1): 125-137. | |
| [21] | 国家环境保护总局, 2002. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社: 24-284. |
| State Environmental Protection Administration, 2002. Methods for Water and Wastewater Monitoring and Analysis[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press: 24-284. | |
| [22] | 环境保护部, 2009. 水质采样技术指导: HJ 494—2009 [S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社: 1-15. |
| Ministry of Environmental Protection, 2009. Water Quality—Guidance on Sampling Techniques: HJ 494—2009 [S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press: 1-15. | |
| [23] | 环境保护部, 2013. 水环境监测规范: SL 219—2013 [S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社: 1-13. |
| Ministry of Environmental Protection, 2013. Code for Water Environment Monitoring: SL 219—2013 [S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press: 1-13. | |
| [24] | 何俊超, 王国玉, 白伟岚, 等, 2021. 海绵城市建设助力人居环境品质提升——以西宁为例[J]. 城乡建设 (12): 19-24. |
| HE J C, WANG G Y, BAI W L, et al., 2021. Sponge city construction helps improve the quality of habitat environment: Taking Xining as an example[J]. Urban and Rural Development (12): 19-24. | |
| [25] |
胡芳, 刘聚涛, 温春云, 等, 2023. 抚河流域浮游植物群落结构特征及其水生态状况评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 32(4): 744-755.
DOI |
| HU F, LIU J T, WEN C Y, et al., 2023. Phytoplankton community structure and evaluation of aquatic ecological conditions in Fu River basin[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 32(4): 744-755. | |
| [26] | 李博, 苏巍, 黄涛, 等, 2023. 金沙江下游浮游植物群落生态特征及与环境因子关系[J]. 水生态学杂志, 44(4): 18-28. |
| LI B, SU W, HUANG T, et al., 2023. Phytoplankton community ecology and its relationship with environmental factors in the lower Jinsha River[J]. Journal of Hydroecology, 44(4): 18-28. | |
| [27] | 李宁, 陈阿兰, 杨春江, 等, 2017. 城镇化对湟水河上游水质和底栖动物群落结构的影响[J]. 生态学报, 37(10): 3570-3576. |
| LI N, CHEN A L, YANG C J, et al., 2017. Impacts of urbanization on water quality and macrobenthos community structure upstream in the Huangshui River[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37(10): 3570-3576. | |
| [28] | 李晴, 李曌, 丁森, 等, 2024. 湟水河着生藻类群落结构特征及影响因子分析[J]. 环境科学与技术, 47(1): 1-12. |
| LI Q, LI Z, DING S, et al., 2024. Structure characteristics and driving variables of periphyton algae community in Huangshui River[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 47(1): 1-12. | |
| [29] | 李涛, 刘晔, 陈纪朝, 等, 2024. 不同载体固定活性污泥原位修复轻度淤积底泥的效能[J]. 市政技术, 42(2): 207-213. |
| LIU T, LIU Y, CHEN J C, et al., 2024. Effectiveness of fixed activated sludge with different carriers to in-situ remediate mildly silted sediment[J]. Journal of Municipal Technology, 42(2): 207-213. | |
| [30] | 梁东, 夏军, 宋进喜, 等, 2021. 基于eDNA技术的渭河浮游动物多样性及关键种生态位特征[J]. 环境科学, 42(10): 4708-4716. |
| LIANG D, XIA J, SONG J X, et al., 2021. Based on eDNA diversity of zooplankton and niche characteristics of keystone species in the Weihe River[J]. Environmental Science, 42(10): 4708-4716. | |
| [31] | 刘洋, 安瑞志, 杨号, 等, 2024. 西藏拉鲁湿地浮游植物群落时空分布特征及其驱动因子[J]. 湖泊科学, 36(2): 403-417. |
| LIU Y, AN R Z, YANG H, et al., 2024. Spatial-temporal distribution characteristics and its driving factors of phytoplankton community in Lhalu wetland, Tibet, China[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 36(2): 403-417. | |
| [32] | 吕梦茹, 丁奕帆, 张瑞, 等, 2023. 紧水滩水库后生浮游动物群落结构及水质营养状态评价[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 32(2): 354-364. |
| LÜ M R, DING Y F, ZHANG R, et al., 2023. Evaluation of metazooplankton community structure and water quality in Jinshuitan reservoir[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 32(2): 354-364. | |
| [33] | 吕翔宇, 朱梦圆, 马永山, 等, 2023. 太湖流域典型水源水库藻类水华的促发条件[J]. 湖泊科学, 35(5): 1516-1528. |
| LÜ X Y, ZHU M Y, MA Y S, et al., 2023. Driving factors of algal blooms in drinking-water reservoirs in Lake Taihu basin[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 35(5): 1516-1528. | |
| [34] | 欧阳添, 赵璐, 纪璐璐, 等, 2022. 蓝藻水华过程中优势种群演替模式、效应及驱动因子分析[J]. 环境科学, 43(10): 4480-4488. |
| OU Y T, ZHAO L, JI L L, et al., 2022. Succession pattern and consequences of the dominant species during Cyanobacterial bloom and its influencing factors[J]. Environmental Science, 43(10): 4480-4488. | |
| [35] | 欧奕君, 江志兵, 徐满秋, 等, 2024. 甬江口浮游植物时空分布特征及驱动因子[J/OL]. 应用生态学报, 1-12 [2024-06-02]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1253.Q.20240308.1523.002.html. |
| OU Y J, JIANG Z B, XU M Q, et al., 2024. Temporal and spatial variations and driving factors of phytoplankton in Yongjiang River estuary[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 1-12 [2024-06-02]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1253.Q.20240308.1523.002.html. | |
| [36] | 孙儒泳, 1992. 动物生态学原理[M]. 北京: 北京师范大学出版社: 350-360. |
| SUN R Y, 1992. Principles of animal ecology[M]. Beijing: Beijing Normal University Press: 350-360. | |
| [37] | 孙瑞欣, 徐丽, 梁荣昌, 等, 2024. 鹤地水库不同生境浮游植物群落结构特征及其与环境因子的关系[J/OL]. 环境科学, 1-15[2024-06-02]. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.202311178. |
| SUN R X, XU L, LIANG R C, et al., 2024. Structural characteristics of phytoplankton communities and its relationship with environmental factors in different habitats of Hedi reservoir[J]. Environmental Science, 1-15 [2024-06-02]. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.202311178. | |
| [38] | 谈海燕, 2021. 西宁市湟水河湿地公园景观提升及海绵化改造规划设计[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学: 7-9. |
| TAN H Y, 2021. Landscape enhancement and sponge transformation planning and design of Huangshui River wetland park in Xining city[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University: 7-9. | |
| [39] | 谈金豪, 蔺丹清, 代培, 等, 2021. 镇江长江豚类省级自然保护区浮游动物群落结构特征及影响因素[J]. 生态学报, 41(16): 6494-6505. |
| TAN J H, LIN D Q, DAI P, et al., 2021. Zooplankton community structure and its key factors of Yangtze Dolphin Nature Reserve in Jiangsu Province[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(16): 6494-6505. | |
| [40] | 童雄, 罗沛, 刘锋, 等, 2019. 绿狐尾藻分解及其氮磷释放特征[J]. 环境科学, 40(7): 3118-3125. |
| TONG X, LUO P, LIU F, et al., 2019. Decomposition of Myriophyllum aquaticum and the associated release of nitrogen and phosphorus[J]. Environmental Science, 40(7): 3118-3125. | |
| [41] | 王海邻, 刘玉飞, 任玉芬, 等, 2019. 北京市河流秋季浮游动物群落特征分析[J]. 环境科学, 40(8): 3568-3576. |
| WANG H L, LIU Y F, REN Y F, et al., 2019. Analysis of river zooplankton community characteristics in autumn in Beijing[J]. Environmental Science, 40(8): 3568-3576. | |
| [42] | 魏念, 余丽梅, 杜开开, 等, 2022. 三峡库区干流浮游植物群落结构及环境影响因子相关性分析[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 31(3): 615-623. |
| WEI N, YU L M, DU K K, et al., 2022. Phytoplankton communities and correlations analysis of environmental factors in mainstream of Three Gorges reservoir[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 31(3): 615-623. | |
| [43] | 魏印心, 胡鸿钧, 2006. 中国淡水藻类[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 300-899. |
| WEI Y X, HU H J, 2006. Freshwater algae of China[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 300-899. | |
| [44] | 吴文仙, 2016. 太湖水体和底泥中总微囊藻与产毒微囊藻丰度的分布特征[D]. 上海: 华东理工大学: 41-42. |
| WU W X, 2016. Unique spatiotemporal distribution of total and toxic Microcystis populations in water and sediment in Lake Taihu[D]. Shanghai: East China University of Science and Technology: 41-42. | |
| [45] | 夏星辉, 吴琼, 牟新利, 2012. 全球气候变化对地表水环境质量影响研究进展[J]. 水科学进展, 23(1): 124-133. |
| XIA X H, WU Q, MOU X L, 2012. Advances in impacts of climate change on surface water quality[J]. Advances in Water Science, 23(1): 124-133. | |
| [46] | 向丽, 周伟, 任君, 等, 2022. 基于DPSIRM模型的高原城市湿地生态安全评价——以湟水流域西宁段为例[J]. 生态学杂志, 41(10): 2064-2071. |
|
XIANG L, ZHOU W, REN J, et al., 2022. Ecological security evaluation of plateau urban wetland based on DPSIRM model: With Xining section of Huangshui basin as an example[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 41(10): 2064-2071.
DOI |
|
| [47] | 徐赛赛, 刘飞, 陈诗雨, 等, 2023. 西藏柴曲藏布流域大型底栖动物群落结构与浮游生物、环境因子的相关性分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 43(8): 418-427. |
| XU S S, LIU F, CHEN S Y, et al., 2023. Correlation analysis of macrobenthos community structure with plankton and environmental factors in the Chaiqu zangbo basin in Tibet[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 43(8): 418-427. | |
| [48] | 许秋瑾, 朱延忠, 郑丙辉, 等, 2011. 我国东部与云贵湖区富营养化控制标准对比研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 31(12): 2046-2051. |
| XU Q J, ZHU Y Z, ZHENG B H, et al., 2011. Comparative study on lake eutrophication control standards in eastern and Yunnan-Guizhou lake region of China[J]. China Environmental Science, 31(12): 2046-2051. | |
| [49] | 杨清, 李晓东, 杨胜娴, 等, 2023. 雅鲁藏布江中游丰水期原生动物群落多样性及其影响因子[J]. 生物多样性, 31(4): 100-115. |
| YANG Q, LI X D, YANG S X, et al., 2023. Protozoan community diversity and its impact factor in the middle reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River in the wet season[J]. Biodiversity Science, 31(4): 100-115. | |
| [50] | 杨威, 孙雨琛, 张婷婷, 等, 2020. 富营养化对小型湖泊浮游甲壳动物群落结构及多样性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 40(14): 4874-4882. |
| YANG W, SUN Y C, ZHANG T T, et al., 2020. Impact of eutrophication on the community structure and species diversity of crustacean zooplankton in small lakes[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(14): 4874-4882. | |
| [51] | 张建波, 王丑明, 黄代中, 等, 2023. 洞庭湖后生浮游动物群落结构及水质生物学评价[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 32(2): 394-402. |
| ZHANG J B, WANG C M, HUANG D Z, et al., 2023. Community characteristics and bioassessment of metazooplankton in Dongting Lake[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 32(2): 394-402. | |
| [52] | 赵文, 2005. 水生生物学[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社: 5-8. |
| ZHAO W, 2005. Aquatic biology[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press: 5-8. | |
| [53] | 周凤霞, 陈剑虹, 2005. 淡水微型生物图谱[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社: 53-178. |
| ZHOU F X, CHEN J H, 2005. Atlas of Freshwater Microorganisms[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press: 53-178. |
| [1] | 潘家响, 朱明飞, 秦念慈, 肖晶, 刘晨, 李秋华. 贵州高原车田河浮游植物功能群时空特征及水环境质量评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(6): 935-945. |
| [2] | 夏凡, 韩怡蒙, 周剑兴, 谢丹妮. 氮和硫在人为扰动的青藏高原高寒森林中的分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(5): 689-698. |
| [3] | 闫兴蕊, 龚平, 王小萍, 商立海, 李一农, 毛飞剑, 牛学锐, 张勃. 三江源地区土壤和牧草中的有机氯污染物:分布、来源和生态风险[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(3): 428-438. |
| [4] | 陈懂懂, 霍莉莉, 赵亮, 陈昕, 舒敏, 贺福全, 张煜坤, 张莉, 李奇. 青海高寒草地水热因子对土壤微生物生物量碳、氮空间变异的贡献——基于增强回归树模型[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1207-1217. |
| [5] | 王家一, 孙亭亭, 沙润钰, 谌婷红, 邢冉, 秦伯强, 施文卿. 富营养化湖泊蓝藻打捞减污降碳效果模拟研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1108-1114. |
| [6] | 胡芳, 刘聚涛, 温春云, 韩柳, 文慧. 抚河流域浮游植物群落结构特征及其水生态状况评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 744-755. |
| [7] | 樊艳翔, 雷社平, 解建仓. 广东省河流水体富营养化综合评价及分异特征——基于博弈论组合赋权法与VIKOR模型[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(10): 1811-1821. |
| [8] | 嵇晓燕, 王姗姗, 杨凯, 任蓓. 2016—2020年中国地表水中总氮浓度时空变化特征分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1184-1192. |
| [9] | 杨冲, 王春燕, 王文颖, 毛旭峰, 周华坤, 陈哲, 索南吉, 靳磊, 马华清. 青藏高原黄河源区高寒草地土壤营养特征变化及质量评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 896-908. |
| [10] | 崔键, 杜易, 丁程成, 李金凤, 高方述, 常雅军, 张继彪, 刘晓静, 姚东瑞. 中国湖泊水体磷的赋存形态及污染治理措施进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 621-633. |
| [11] | 何瑞, 蒋然, 杨芳, 张心凤, 林键銮, 朱小平, 彭松耀. 茂名近岸海域中、小型浮游动物群落特征及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 142-150. |
| [12] | 胡琳, 李思悦. 不同空间尺度土地利用结构与景观格局对龙川江流域水质的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(7): 1470-1481. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
