生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (9): 1888-1895.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.09.013
李富荣1,2( ), 王旭1,2,*(
), 王旭1,2,*( ), 李庆荣3, 吴志超1,2, 冯起4, 文典1,2, 徐爱平1,2, 赵沛华1,2
), 李庆荣3, 吴志超1,2, 冯起4, 文典1,2, 徐爱平1,2, 赵沛华1,2
收稿日期:2021-07-09
出版日期:2021-09-18
发布日期:2021-12-08
通讯作者:
*王旭(1981年生),女,研究员,主要从事农产品质量安全方面的研究。E-mail: wangxuguangzhou@126.com作者简介:李富荣(1984年生),女,副研究员,博士,主要从事农产品产地环境安全控制方面的研究。E-mail: lifr0314@163.com
基金资助:
LI Furong1,2( ), WANG Xu1,2,*(
), WANG Xu1,2,*( ), LI Qingrong3, WU Zhichao1,2, FENG Qi4, WEN Dian1,2, XU Aiping1,2, ZHAO Peihua1,2
), LI Qingrong3, WU Zhichao1,2, FENG Qi4, WEN Dian1,2, XU Aiping1,2, ZHAO Peihua1,2
Received:2021-07-09
Online:2021-09-18
Published:2021-12-08
摘要:
针对华南地区酸性菜地土壤缺硼特性和重金属污染风险较高的现状,为解决如何保障缺硼土壤上的农产品高品质安全种植和农业废弃物资源的有效利用等问题提供数据支撑。以蚕沙为土壤调理剂,结合外源硼添加进行复合调控,探讨其对铅镉复合污染土壤的土壤理化性质、重金属铅镉有效态含量的影响。结果表明,2%和6%的蚕沙添加量在不同硼处理下都能使土壤pH值显著提高,增加幅度达49.5%;使土壤有机质、碱解氮、有效磷、速效钾和有效态硼含量等土壤理化性质也得到明显改善。而不同蚕沙添加量对土壤重金属有效态含量的影响效果与元素类别有关,其中对有效态镉含量的影响效果并不显著;对有效态铅含量的降低效果则十分显著。在铅镉复合污染土壤上进行蚕沙复合硼的处理表现为,在6%蚕沙添加量下,0.5 mg∙kg-1硼添加处理使土壤有效态镉含量较未添加硼时有所增加,而当硼添加量为2.0 mg∙kg-1时,土壤有效态镉含量又显著下降;而其他蚕沙添加量处理下,土壤有效态镉含量在复合不同硼处理之间无明显差异。就土壤有效态铅含量而言,两种蚕沙添加量均使其较未加蚕沙时明显下降,降低量达98.9%。对不同因素的交互效应分析可见,“硼+蚕沙”二因素对土壤重金属有效态镉和铅含量存在一定的交互效应,且其影响作用大于单一硼处理,但单一蚕沙处理相对上述两种处理对土壤有效态镉和铅含量的影响更大。该研究结果将为解决农业废弃物资源利用、降低土壤重金属的生物有效性和提升耕地生产力提供科学的参考依据。
中图分类号:
李富荣, 王旭, 李庆荣, 吴志超, 冯起, 文典, 徐爱平, 赵沛华. 蚕沙复合硼调理剂对酸性菜地土壤镉铅的钝化效应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(9): 1888-1895.
LI Furong, WANG Xu, LI Qingrong, WU Zhichao, FENG Qi, WEN Dian, XU Aiping, ZHAO Peihua. Passivation Effect of Silkworm Excrement Composited Boron Conditioner on Cd and Pb in Acid Vegetable Soil[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(9): 1888-1895.
| 试验材料 Materials | 土壤 Soil | 蚕沙 Silkworm excrement |
|---|---|---|
| pH值 pH value | 5.62 | 7.67 |
| w(有机质Organic matter)/% | 10.23 | 39.99 |
| w(全氮 Total nitrogen)/% | 0.048 | 1.97 |
| w(碱解氮 Alkali-hydro N)/(mg∙kg-1) | 21.03 | 2.9×103 |
| w(有效磷 Available P)/(mg∙kg-1) | 144.4 | 5.8×103 |
| w(速效钾 Available K)/(mg∙kg-1) | 240.2 | 1.4×104 |
| w(全镉 Total Cd)/(mg∙kg-1) | 0.053 | 1.01 |
| w(全铅 Total Pb)/(mg∙kg-1) | 143.05 | 36.32 |
| w(有效态镉 Available Cd)/(mg∙kg-1) | 0.007 | 0.0012 |
| w(有效态铅 Available Pb)/(mg∙kg-1) | 0.28 | 0.0036 |
表1 试验所用土壤和蚕沙有机肥的基本理化性质
Table 1 Basic physical and chemical properties of soil and silkworm excrement used in the experiment
| 试验材料 Materials | 土壤 Soil | 蚕沙 Silkworm excrement |
|---|---|---|
| pH值 pH value | 5.62 | 7.67 |
| w(有机质Organic matter)/% | 10.23 | 39.99 |
| w(全氮 Total nitrogen)/% | 0.048 | 1.97 |
| w(碱解氮 Alkali-hydro N)/(mg∙kg-1) | 21.03 | 2.9×103 |
| w(有效磷 Available P)/(mg∙kg-1) | 144.4 | 5.8×103 |
| w(速效钾 Available K)/(mg∙kg-1) | 240.2 | 1.4×104 |
| w(全镉 Total Cd)/(mg∙kg-1) | 0.053 | 1.01 |
| w(全铅 Total Pb)/(mg∙kg-1) | 143.05 | 36.32 |
| w(有效态镉 Available Cd)/(mg∙kg-1) | 0.007 | 0.0012 |
| w(有效态铅 Available Pb)/(mg∙kg-1) | 0.28 | 0.0036 |
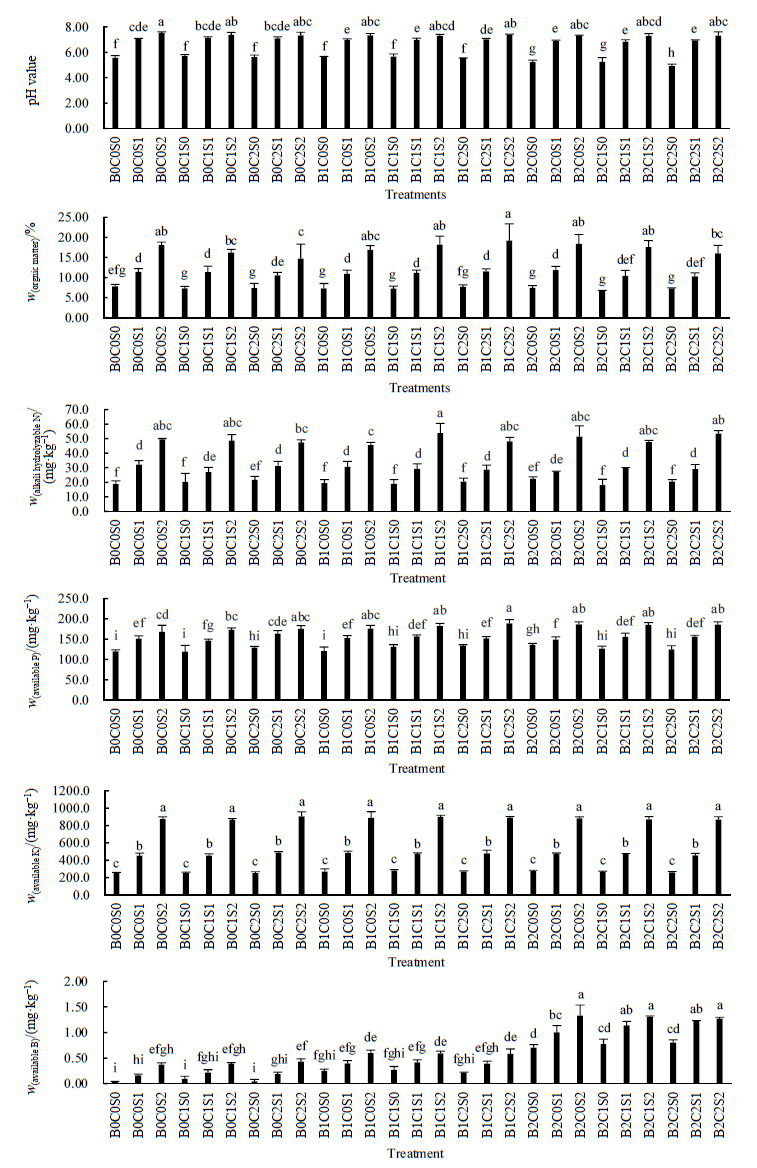
图1 不同处理对土壤基本理化性质的影响 不同处理中大写字母B、C、S分别表示硼、镉和蚕沙添加。如B0C0S0为对照,外源硼、镉、蚕沙添加量均为0;B2C2S2是指外源硼、土壤镉、蚕沙处理分别为B2(2.0 mg∙kg-1)、C2(2.8 mg∙kg-1)、S2(60 g∙kg-1)。不同小写字母表示各处理之间差异显著性(P<0.05),n=3,下同
Fig. 1 Effect of different treatments on the basic physical and chemical properties of soil In the different treatments, the capital letters B, C and S indicated boron, cadmium and silkworm excrement addition respectively. For example, B0C0S0 was the control which meant the addition of boron, cadmium and silkworm sand were 0; B2C2S2 was the treatment of the addition amounts with B2 (2.0 mg∙kg-1), C2 (2.8 mg∙kg-1) and S2 (60 g∙kg-1), respectively. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different soil depth in the same succession stage at the level of 0.05, n=3, the same as below
| 处理 Treatment | pH值 pH value | 有机质 Organic Matter | 碱解氮 Alkali-hydro N | 有效磷 Available P | 速效钾 Available K | 有效态硼 Available B | 有效态镉 Available Cd | 有效态铅 Available Pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | 1.08** | 5.09 | 4.09 | 652.02** | 175.46 | 6.53 | 0.03** | 0.32** |
| S | 54.92** | 1350.55** | 12229.96** | 38301.69** | 5354983.33** | 1.62** | 6.83** | 2.75** |
| Cd | 0.03 | 5.21 | 9.57 | 428.52** | 3474.38 | 0.13 | 4.26** | 0.02 |
| B*S | 0.66** | 9.85 | 30.96 | 468.66 | 494.03 | 0.12 | 0.06** | 0.62** |
| B*Cd | 0.02 | 19.9 | 58.45 | 509.06 | 4401.79 | 0.25 | 0.04** | 0.02 |
| S* Cd | 0.17 | 3.8 | 22.04 | 30.97 | 1060.23 | 0.13 | 7.07** | 0.04 |
| B*S*Cd | 0.17 | 13.08 | 181.3 | 646.82 | 1712.27 | 0.2 | 0.07** | 0.03 |
表2 不同处理下的多因素方差分析
Table 2 Multivariate analysis of variance for different treatments
| 处理 Treatment | pH值 pH value | 有机质 Organic Matter | 碱解氮 Alkali-hydro N | 有效磷 Available P | 速效钾 Available K | 有效态硼 Available B | 有效态镉 Available Cd | 有效态铅 Available Pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | 1.08** | 5.09 | 4.09 | 652.02** | 175.46 | 6.53 | 0.03** | 0.32** |
| S | 54.92** | 1350.55** | 12229.96** | 38301.69** | 5354983.33** | 1.62** | 6.83** | 2.75** |
| Cd | 0.03 | 5.21 | 9.57 | 428.52** | 3474.38 | 0.13 | 4.26** | 0.02 |
| B*S | 0.66** | 9.85 | 30.96 | 468.66 | 494.03 | 0.12 | 0.06** | 0.62** |
| B*Cd | 0.02 | 19.9 | 58.45 | 509.06 | 4401.79 | 0.25 | 0.04** | 0.02 |
| S* Cd | 0.17 | 3.8 | 22.04 | 30.97 | 1060.23 | 0.13 | 7.07** | 0.04 |
| B*S*Cd | 0.17 | 13.08 | 181.3 | 646.82 | 1712.27 | 0.2 | 0.07** | 0.03 |
| [1] |
CAI L M, XU Z C, REN M Z, et al., 2012. Source identification of eight hazardous heavy metals in agricultural soils of Huizhou, Guangdong Province, China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 78: 2-8.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
CHEN D M, CHEN D Q, XUE R R, et al., 2019. Effects of boron, silicon and their interactions on cadmium accumulation and toxicity in rice plants[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 367: 447-455.
DOI URL |
| [3] | ERIKSSON J E, 1989. The influence of pH, soil type and time on adsorption and uptake by plants of Cd added to the soil[J]. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 48: 317-335. |
| [4] |
IVÁN F, CARLOS G, CALA V, et al., 2017. The use of spent mushroom compost to enhance the ability of Atriplex halimus to phytoremediate contaminated mine soils[J]. Environmental Technology, 38(9): 1075-1084.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
LI F R, WEN D, WANG F H, et al., 2019. Derivation of soil Pb/Cd/As thresholds for safety of vegetable planting: A case study for pakchoi in Guangdong Province, China[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 18(1): 179-189.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
LI F R, WANG X, WANG F H, et al., 2021. A risk-based approach for the safety analysis of eight trace elements in Chinese flowering cabbage (Brassica parachinensis L.) in China[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, DOI: 10.1002/jsfa.11209.
DOI |
| [7] |
MPATANI F M, HAN R P, ARYEE A A, et al., 2021. Adsorption performance of modified agricultural waste materials for removal of emerging micro-contaminant bisphenol A: A comprehensive review[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 780: 146629-146629.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
QIAN Z Z, TANG L Z, ZHUANG S Y, et al., 2020. Effects of biochar amendments on soil water retention characteristics of red soil at south China[J]. Biochar, 2(4): 479-488.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
QIN G W, NIU Z D, YU J D, et al., 2021. Soil heavy metal pollution and food safety in China: Effect, sources and removing technology[J]. Chemosphere, DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129205.
DOI |
| [10] |
QIN S Y, LIU H G, E, RENGEL Z, et al., 2020. Boron inhibits cadmium uptake in wheat (Triticum aestivum) by regulating gene expression[J]. Plant Science, DOI: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2020.110522.
DOI |
| [11] |
RIAZ M, YAN L, WU X W, et al., 2018. Boron increases root elongation by reducing aluminum induced disorganized distribution of HG epitopes and alterations in subcellular cell wall structure of trifoliate orange roots[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 165: 202-210.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
SETIA R, DHALIWAL S S, SINGH R, et al., 2020. Phytoavailability and human risk assessment of heavy metals in soils and food crops around Sutlej river, India[J]. Chemosphere, DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020. 128321.
DOI |
| [13] |
WANG R G, GUO J K, XU Y M, et al., 2016. Evaluation of silkworm excrement and mushroom dreg for the remediation of multiple heavy metal/metalloid contaminated soil using pakchoi[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 124: 239-247.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
WANG R G, GUO J K, XU Y M, et al., 2016. Evaluation of silkworm excrement and mushroom dreg for the remediation of multiple heavy metal/metalloid contaminated soil using pakchoi[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 124: 239-247.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
WU J H, SONG Q M, ZHOU J Y, et al., 2021. Cadmium threshold for acidic and multi-metal contaminated soil according to Oryza sativa L. Cadmium accumulation: Influential factors and prediction model[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, DOI: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020. 111420.
DOI |
| [16] |
WU X W, SONG H X, GUAN C Y, et al., 2020a. Boron mitigates cadmium toxicity to rapeseed (Brassica napus) shoots by relieving oxidative stress and enhancing cadmium chelation onto cell walls[J]. Science of the Total Environment, DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114546.
DOI |
| [17] |
WU Z C, WANG F H, LIU S, et al., 2016. Comparative responses to silicon and selenium in relation to cadmium uptake, compartmentation in roots, and xylem transport in flowering Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris L.) under cadmium stress[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 131: 173-180.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
WU X W, SONG H X, GUAN C Y, et al., 2020b. Boron alleviates cadmium toxicity in Brassica napus by promoting the chelation of cadmium onto the root cell wall components[J]. Science of the Total Environment, DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138833.
DOI |
| [19] |
XIAO W D, YE X Z, ZHANG Q, et al., 2018. Evaluation of cadmium transfer from soil to leafy vegetables: Influencing factors, transfer models, and indication of soil threshold contents[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 164: 355-362.
DOI URL |
| [20] | 蔡轩, 龙新宪, 种云霄, 等, 2015. 无机-有机混合改良剂对酸性重金属复合污染土壤的修复效应[J]. 环境科学学报, 35(12): 3991-4002. |
| CAI X, LONG X X, CHONG Y X, et al., 2015. Inorganic-organic amendments for immobilization of metal contaminants in an acidic soil[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 35(12): 3991-4002. | |
| [21] | 杜应琼, 廖新荣, 黄志尧, 等, 2000. pH和质地对土壤供硼影响的研究[J]. 土壤与环境, 9(2): 125-128. |
| DU YQ, LIAO X R, HUANG Z Y, et al., 2000. Effects of soil pH and texture on soil B supply[J]. Soil and Environmental Sciences, 9(2): 125-128. | |
| [22] | 杜应琼, 疏仁宗, 王富华, 等, 2015. 镉污染土壤上偏施氮磷钾肥对蕹菜产量及镉积累的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 24(3): 511-516. |
| DU Y Q, SU R Z, WANG F H, et al., 2015. Effects of partial NPK fertilizer application on the yield and Cd accumulation of water spinach in Cd contaminated soil[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 24(3): 511-516. | |
| [23] | 黄永东, 杜应琼, 陈永坚, 等, 2018. 农业废弃物生物炭理化性质的差异及对菜心产量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 27(2): 356-363. |
| HUANG Y D, DU Y Q, CHEN Y J, et al., 2018. Physicochemical properties of biochars originated from different agricultural wastes and their impact on the yield of Brassica campestris L.[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 27(2): 356-363. | |
| [24] | 黄赛花, 刘通, 黄友良, 等, 2021. 蚯蚓粪复配硼钼调理剂对土壤改良和茄子生长的影响作用[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(3): 523-531. |
| HUANG S H, LIU T, HUANG Y L, et al., 2021. Effects of molybdenumand boron-enriched earthworm cast As a soil conditioner on soil improvement and eggplant growth[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(3): 523-531. | |
| [25] | 黎秋君, 黎大荣, 王英辉, 等, 2013. 3种有机物料对土壤理化性质和重金属有效态的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 27(6): 182-185. |
| LI QJ, LI D R, WANG Y H, et al., 2013. Effects of three kinds of organic materials on physicochemical properties and available heavy metals in soil[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 27(6): 182-185. | |
| [26] | 李苹, 付弘婷, 张发宝, 等, 2015. 蚕沙有机肥对作物产量、品质及土壤性质的影响[J]. 南方农业学报, 46(7): 1195-1199. |
| LI P, FU H T, ZHANG F B, et al., 2015. Effects of silkworm excrement-derived organic fertilizer on yield and quality of crops and soil property[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 46(7): 1195-1199. | |
| [27] | 刘登彪, 蒋成爱, 张嘉慧, 等, 2014. 不同硼浓度对三种超富集植物吸收硼及重金属的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 33(6): 1106-1111. |
| LIU D B, JIANG C A, ZHANG J H, et al., 2014. Effects of Boron concentrations on uptake of boron and heavy metals by three hyperaccumulators[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 33(6): 1106-1111. | |
| [28] | 刘顺翱, 胡钧铭, 吴昊, 等, 2021. 蚕沙与海泡石联合施用对水稻根际土壤Cd生物有效性及籽粒Cd富集的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 40(8): 1686-1695. |
| LIU S X, HU J M, WU H, et al., 2021. Effects of the combined application of silkworm excrement and sepiolite on Cd bioavailability in rhizosphere soil and Cd accumulation in grains of rice[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 40(8): 1686-1695. | |
| [29] | 刘宇庆, 刘燕, 范红梅, 2009. 硼对植物细胞的影响及与其它元素关系的研究进展[J]. 中国土壤与肥料 (5): 1-4, 9. |
| LIU YQ, LIU Y, FAN H M, 2009. Review of boron and plant cells and its relationship with other elements[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China (5): 1-4, 9. | |
| [30] | 罗开萍, 黄艳玲, 秦豪, 等, 2020. 蚕沙钝化材料对矿区周边农田土壤镉锌污染的钝化效果研究[J]. 轻工科技, 36(11): 62-63, 90. |
| LUO K P, HUANG Y L, QIN H, et al., 2020. Study on the passivation effect of silkworm excrement passivation material on cadmium and zinc pollution of farmland soil around mining area[J]. Guangxi Journal of Light Industry, 36(11): 62-63, 90. | |
| [31] | 王运华, 徐芳森, 鲁剑巍, 2015. 中国农业中的硼[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社. |
| WANG Y H, XU F S, LU J W, 2015. Boron in Chinese agriculture[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Publishing House. | |
| [32] | 魏益华, 邱素艳, 张金艳, 等, 2019. 农业废弃物中重金属含量特征及农用风险评估[J]. 农业工程学报, 35(14): 212-220. |
| WEI Y H, QIU S Y, ZHANG J Y, et al., 2019. Characteristic of heavy metal contents in agricultural wastes and agricultural risk assessment[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 35(14): 212-220. | |
| [33] | 肖艳辉, 何金明, 潘春香, 等, 2015. 茴香对镉胁迫下钼硼锌协同处理的响应及精油组分的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 24(9): 1570-1575. |
| XIAO Y H, HE J M, PAN C X, et al., 2015. Effects of Molybdenum, Boron and Zinc Coordination Treatment on Response and Essential Oil Components of Fennel Plant under Cadmium Stress[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 24(9): 1570-1575. | |
| [34] | 肖艳辉, 李应文, 邹碧, 等, 2021. 钝化剂抑制南方污染农田籽粒苋吸收重金属的效应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(4): 825-833. |
| XIAO Y H, LI Y W, ZHOU B, et al., 2021. Reduction of heavy metal uptake by amaranth by 3 soil amendments in contaminated farmland of South China[J]. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 30(4): 825-833. | |
| [35] | 徐蒙蒙, 涂春艳, 黄河, 等, 2018. 淹水条件下蚕沙复配材料对酸性水稻土中镉铅钝化的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 12(4): 1182-1189. |
| XU M M, TU C Y, HUANG H, et al., 2018. Effect of silkworm excrement composites on passivation of cadmium and lead in acid paddy soil under flooded condition[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 12(4): 1182-1189. | |
| [36] | 严静娜, 覃霞, 梁定国, 等, 2015. 同热解温度蚕沙生物质炭对土壤镉、铅钝化效果研究[J]. 西南农业学报, 28(4): 1752-1756. |
| YAN J N, QIN X, LIANG D G, et al., 2015. Immobilization of cadmium and lead in contaminated soils by using biochars prepared with silkworm at different temperatures[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 28(4): 1752-1756. | |
| [37] | 张贺, 杨静, 周吉祥, 等, 2021. 连续施用土壤改良剂对砂质潮土团聚体及作物产量的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 27(5): 791-801. |
| ZHANG H, YANG J, ZHOU J X, et al., 2021. Effects of organic and inorganic amendments on aggregation and crop yields in sandy fluvo-aquic soil[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 27(5): 791-801. |
| [1] | 杜丹丹, 高瑞忠, 房丽晶, 谢龙梅. 旱区盐湖盆地土壤重金属空间变异及对土壤理化因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1123-1132. |
| [2] | 李传福, 朱桃川, 明玉飞, 杨宇轩, 高舒, 董智, 李永强, 焦树英. 有机肥与脱硫石膏对黄河三角洲盐碱地土壤团聚体及其有机碳组分的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 878-888. |
| [3] | 冯树娜, 吕家珑, 何海龙. KI淋洗对黄绵土汞污染的去除效果及土壤理化性状的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 776-783. |
| [4] | 陈敏毅, 朱航海, 佘伟铎, 尹光彩, 黄祖照, 杨巧玲. 珠三角某遗留造船厂场地土壤重金属人体健康风险评估及源解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 794-804. |
| [5] | 肖洁芸, 周伟, 石佩琪. 土壤重金属含量高光谱反演[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 175-182. |
| [6] | 黄宏, 郑欣芸, 李迎东, 赵旭, 俞锦辰, 汪振华. 大陈岛海域不同年龄褐菖鲉对重金属富集作用研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1885-1891. |
| [7] | 马闯, 王雨阳, 周通, 吴龙华. 污染土壤颗粒态有机质镉锌富集特征及其解吸行为研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1892-1900. |
| [8] | 陶玲, 黄磊, 周怡蕾, 李中兴, 任珺. 污泥-凹凸棒石共热解生物炭对矿区土壤重金属生物有效性和环境风险的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1637-1646. |
| [9] | 李莹, 张洲, 杨高明, 祖艳群, 李博, 陈建军. 湿地植物根系泌氧能力和根表铁膜与根系吸收重金属的关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1657-1666. |
| [10] | 罗松英, 李秋霞, 邱锦坤, 邓素炎, 李一锋, 陈碧珊. 南三岛土壤-红树植物系统中重金属形态特征及迁移转化规律[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1409-1416. |
| [11] | 董乐恒, 王旭刚, 陈曼佳, 王子豪, 孙丽蓉, 石兆勇, 吴琪琪. 光照和避光条件下石灰性水稻土Fe氧化还原与Cu活性关系研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1448-1455. |
| [12] | 高鹏, 高品, 孙蔚旻, 孔天乐, 黄端仪, 刘华清, 孙晓旭. 蜈蚣草根际及内生微生物群落对砷污染胁迫的响应机制研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1225-1234. |
| [13] | 彭红丽, 谭海霞, 王颖, 魏建梅, 冯阳. 不同种植模式下土壤重金属形态分布差异与生态风险评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1235-1243. |
| [14] | 黄敏, 赵晓峰, 梁荣祥, 王鹏忠, 戴安然, 何晓曼. 3种螯合剂对Cd、Cu复合污染土壤淋洗修复的对比研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1244-1252. |
| [15] | 朱立安, 张会化, 程炯, 李婷, 林梓, 李俊杰. 珠江三角洲林业用地土壤重金属潜在生态风险格局分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1253-1262. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
