生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (6): 1244-1252.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.06.021
黄敏1( ), 赵晓峰1, 梁荣祥2, 王鹏忠1, 戴安然1, 何晓曼1
), 赵晓峰1, 梁荣祥2, 王鹏忠1, 戴安然1, 何晓曼1
收稿日期:2022-02-10
出版日期:2022-06-18
发布日期:2022-07-29
作者简介:黄敏(1973年生),女,副教授,博士,主要从事土壤环境与区域生态方面的研究。E-mail: huangmin@whut.edu.cn
基金资助:
HUANG Min1( ), ZHAO Xiaofeng1, LIANG Rongxiang2, WANG Pengzhong1, DAI Anran1, HE Xiaoman1
), ZHAO Xiaofeng1, LIANG Rongxiang2, WANG Pengzhong1, DAI Anran1, HE Xiaoman1
Received:2022-02-10
Online:2022-06-18
Published:2022-07-29
摘要:
乙二胺四乙酸(EDTA)是目前重金属污染土壤修复中常用的高效淋洗剂,但其难以降解,对环境存在二次污染风险。该研究以EDTA为对照,选取谷氨酸N,N-二乙酸(GLDA)和亚氨基二琥珀酸(IDS)两种易降解材料为螯合淋洗剂,通过振荡模拟淋洗试验研究了4种典型条件下两种材料对土壤Cd、Cu的洗脱率,探讨了Cd、Cu复合污染土壤的淋洗修复技术中两种材料复配替代EDTA的可行性。结果显示,采用单一淋洗剂时,GLDA利于洗脱土壤Cd,而IDS利于洗脱土壤Cu;在试验的各条件下GLDA对土壤中Cd的洗脱率为47.64%—66.32%,IDS对土壤中Cu的洗脱率为25.44%—34.65%,均不及EDTA对土壤中Cd、Cu的洗脱率(分别为71.49%—74.11%和27.07%—39.12%);降低淋洗剂pH有利于提高土壤Cd、Cu的洗脱率;重金属与IDS、GLDA的物质的量比分别为1:5、1:10时土壤Cd、Cu的综合淋洗效果较优。IDS与GLDA混配的物质的量比为4:6时,土壤Cd、Cu的洗脱率分别为71.75%和33.61%,Cd洗脱率比同等用量的EDTA高出3.40个百分点,而Cu洗脱率仅比EDTA低5.89个百分点。综合考虑重金属洗脱率、螯合剂用量及淋洗时间等因素,建议在重金属污染土壤的淋洗修复中,调节重金属与螯合剂总量的物质的量比为1:10,淋洗体系固液比为1:10,淋洗时间为8 h,IDS和GLDA以物质的量比4:6复配,并分2次淋洗,该参数条件下土壤中Cd、Cu的洗脱效果与等量的EDTA相当。以上结果可为可生物降解螯合剂提升重金属污染土壤的淋洗修复效率提供理论参考。
中图分类号:
黄敏, 赵晓峰, 梁荣祥, 王鹏忠, 戴安然, 何晓曼. 3种螯合剂对Cd、Cu复合污染土壤淋洗修复的对比研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1244-1252.
HUANG Min, ZHAO Xiaofeng, LIANG Rongxiang, WANG Pengzhong, DAI Anran, HE Xiaoman. Comparison of Three Chelating Agents to Remove the Cd and Cu in Contaminated Soil[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(6): 1244-1252.
| 类型 Soil type | 质地 Soil texture | pH | 阳离子交换量 Cation exchange capacity/ (cmol∙kg-1) | 有机碳质量分数 w(soil organic carbon)/ (g∙kg-1) | Cd质量分数 w(Cd)/ (mg∙kg-1) | Cu质量分数 w(Cu)/ (mg∙kg-1) | Zn质量分数 w(Zn)/ (mg∙kg-1) | As质量分数 w(As)/ (mg∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黄棕壤 Yellow brown soil | 砂壤土Sandy loam | 5.66 | 10.0 | 12.6 | 14.01 | 1370 | 180 | 145 |
表1 供试土壤的基本性质
Table 1 Basic characteristics of the tested soil
| 类型 Soil type | 质地 Soil texture | pH | 阳离子交换量 Cation exchange capacity/ (cmol∙kg-1) | 有机碳质量分数 w(soil organic carbon)/ (g∙kg-1) | Cd质量分数 w(Cd)/ (mg∙kg-1) | Cu质量分数 w(Cu)/ (mg∙kg-1) | Zn质量分数 w(Zn)/ (mg∙kg-1) | As质量分数 w(As)/ (mg∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黄棕壤 Yellow brown soil | 砂壤土Sandy loam | 5.66 | 10.0 | 12.6 | 14.01 | 1370 | 180 | 145 |
| 淋洗时间 Leaching time/h | 重金属与螯合剂物质的量比a Ratio of amount of substance of heavy metal to chelating agent | 淋洗剂pH pH of leaching agent | 体系固液比 Ratio of solid to liquid | IDS与GLDA复配比例b Mixing ratio of IDS to GLDA | 淋洗次数c Leaching times | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 单一 淋洗 Single leaching | 淋洗时间 Leaching time/h | 1-36 | 1:1 | 7 | 1:10 | — | 1 |
| 重金属与螯合剂物质的量比 Ratio of amount of substance of heavy metal to chelating agent | 8 | 1:10-1:1 | 7 | 1:10 | — | 1 | |
| 淋洗剂pH pH of leaching agent | 8 | 1:1 | 4-10 | 1:10 | — | 1 | |
| 体系固液比 Ratio of solid to liquid | 8 | 1:1 | 7 | 1:25-1:5 | — | 1 | |
| 复配 淋洗 Mixing leaching | 复配比例 Mixing ratio of IDS to GLDA | 8 | 1:10 | 7 | 1:10 | 1:9-5:5 | 1 |
| 淋洗次数 Leaching times | 8 | 1:10 | 7 | 1:10 | 4:6 | 1-4 | |
表2 淋洗试验的处理设置
Table 2 Treatment design for the leaching experiment
| 淋洗时间 Leaching time/h | 重金属与螯合剂物质的量比a Ratio of amount of substance of heavy metal to chelating agent | 淋洗剂pH pH of leaching agent | 体系固液比 Ratio of solid to liquid | IDS与GLDA复配比例b Mixing ratio of IDS to GLDA | 淋洗次数c Leaching times | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 单一 淋洗 Single leaching | 淋洗时间 Leaching time/h | 1-36 | 1:1 | 7 | 1:10 | — | 1 |
| 重金属与螯合剂物质的量比 Ratio of amount of substance of heavy metal to chelating agent | 8 | 1:10-1:1 | 7 | 1:10 | — | 1 | |
| 淋洗剂pH pH of leaching agent | 8 | 1:1 | 4-10 | 1:10 | — | 1 | |
| 体系固液比 Ratio of solid to liquid | 8 | 1:1 | 7 | 1:25-1:5 | — | 1 | |
| 复配 淋洗 Mixing leaching | 复配比例 Mixing ratio of IDS to GLDA | 8 | 1:10 | 7 | 1:10 | 1:9-5:5 | 1 |
| 淋洗次数 Leaching times | 8 | 1:10 | 7 | 1:10 | 4:6 | 1-4 | |
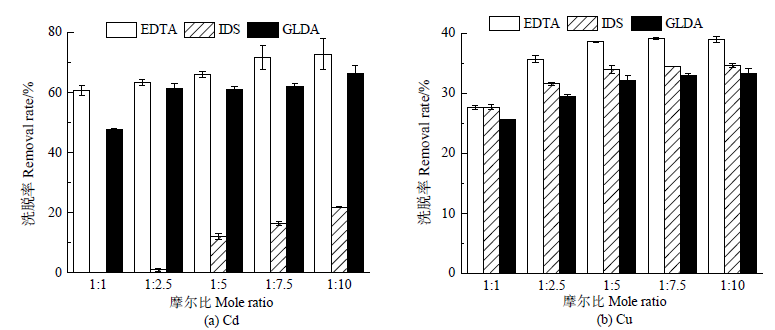
图2 重金属与螯合剂不同物质的量比下土壤中Cd、Cu的洗脱率
Figure 2 Removal rates of Cd and Cu in soil under various ratios of amount of substance of heavy metal to chelating agent
| 淋洗剂 Leaching agent | Cd 洗脱率 Removal rate of Cd/% | Cu 洗脱率 Removal rate of Cu/% | 综合毒性消减指数 Total toxicity reduction index |
|---|---|---|---|
| EDTA | 68.35 | 39.51 | 1757 |
| IDS | 21.75 | 34.65 | 608 |
| GLDA | 66.32 | 33.30 | 1694 |
| IDS:GLDA=5:5 | 61.70 | 33.77 | 1582 |
| IDS:GLDA=4:6 | 71.75 | 33.61 | 1827 |
| IDS:GLDA=3:7 | 65.63 | 35.06 | 1681 |
| IDS:GLDA=2:8 | 68.24 | 34.57 | 1743 |
| IDS:GLDA=1:9 | 65.00 | 33.82 | 1663 |
表3 螯合剂复配不同比例下淋洗土壤的综合毒性消减指数
Table 3 Total toxicity reduction index of the leached soil with mixed agents under different mixture ratio
| 淋洗剂 Leaching agent | Cd 洗脱率 Removal rate of Cd/% | Cu 洗脱率 Removal rate of Cu/% | 综合毒性消减指数 Total toxicity reduction index |
|---|---|---|---|
| EDTA | 68.35 | 39.51 | 1757 |
| IDS | 21.75 | 34.65 | 608 |
| GLDA | 66.32 | 33.30 | 1694 |
| IDS:GLDA=5:5 | 61.70 | 33.77 | 1582 |
| IDS:GLDA=4:6 | 71.75 | 33.61 | 1827 |
| IDS:GLDA=3:7 | 65.63 | 35.06 | 1681 |
| IDS:GLDA=2:8 | 68.24 | 34.57 | 1743 |
| IDS:GLDA=1:9 | 65.00 | 33.82 | 1663 |
| 淋洗剂 Leaching agent | 土壤利用方式及其Cd、Cu洗脱率 Utilization mode of soil and removal rate of Cd and Cu | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|
| IDS与GLDA复配 IDS and GLDA compound | 冶炼厂附近农田土壤,Cd、Cu的洗脱率分别为82.71%和41.36% | 本研究 |
| EDTA | 冶炼厂附近农田土壤,Cd、Cu的洗脱率分别为68.35%和39.51% | 本研究 |
| EDTA | 工业场地土壤,Cd、Cu的洗脱率分别为56.99%和72.98% | Zou et al., |
| 衣康酸-丙烯酸共聚物(IA-AA) Itaconic-acrylic acid copolymer | 矿区土壤,Cd的洗脱率为65.65% | 姚瑶等, |
| 柠檬酸与氯化铁复配 The citric acid and ferric chloride compound | 稻田土壤,Cd的洗脱率达74.50% | 曹坤坤等, |
| 磷酸氨基酸盐 Phosphate amino acid salt | 稻田土壤,Cd的洗脱率为55.40% | 季蒙蒙等, |
| 柠檬酸 The citric acid | 矿场附近旱地土壤,Cu的洗脱率为37.65% | 易龙生等, |
表4 同类研究中最适条件下对重金属污染土壤淋洗效果对比
Table 4 Comparison of leaching effects on heavy metal in contaminated soil under optimal conditions in similar studies
| 淋洗剂 Leaching agent | 土壤利用方式及其Cd、Cu洗脱率 Utilization mode of soil and removal rate of Cd and Cu | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|
| IDS与GLDA复配 IDS and GLDA compound | 冶炼厂附近农田土壤,Cd、Cu的洗脱率分别为82.71%和41.36% | 本研究 |
| EDTA | 冶炼厂附近农田土壤,Cd、Cu的洗脱率分别为68.35%和39.51% | 本研究 |
| EDTA | 工业场地土壤,Cd、Cu的洗脱率分别为56.99%和72.98% | Zou et al., |
| 衣康酸-丙烯酸共聚物(IA-AA) Itaconic-acrylic acid copolymer | 矿区土壤,Cd的洗脱率为65.65% | 姚瑶等, |
| 柠檬酸与氯化铁复配 The citric acid and ferric chloride compound | 稻田土壤,Cd的洗脱率达74.50% | 曹坤坤等, |
| 磷酸氨基酸盐 Phosphate amino acid salt | 稻田土壤,Cd的洗脱率为55.40% | 季蒙蒙等, |
| 柠檬酸 The citric acid | 矿场附近旱地土壤,Cu的洗脱率为37.65% | 易龙生等, |
| [1] | CHULSUNG K, YONGWOO L, SAY K O, 2003. Factors affecting EDTA extraction of lead from lead-contaminated soils[J]. Chemosphere, 51(9): 845-853. |
| [2] | DOROTA K, 2011. Cu(II), Zn(II), Co(II) and Pb(II) removal in the presence of the complexing agent of a new generation[J]. Desalination, 267(2): 175-183. |
| [3] | FERNANDES M C, COX L, HERMOSIN M C, et al., 2003. Adsorption-desorption of metalaxyl as affecting dissipation and leaching in soils: role of mineral and organic components[J]. Pest Management Science, 59(5): 545-552. |
| [4] | GHESTEM J P, BERMOND A, 1998. EDTA extractability of trace metals in polluted soils: A chemical-physical study[J]. Environmental Technology, 19(4): 409-416. |
| [5] | GUO X F, ZHAO G H, ZHANG G X, et al., 2018. Effect of mixed chelators of EDTA, GLDA, and citric acid on bioavailability of residual heavy metals in soils and soil properties[J]. Chemosphere, 209: 776-782. |
| [6] | HAKANSON L, 1980. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: a sedimentological approach[J]. Water Research, 14(8): 975-1001. |
| [7] | HAUTHAL H G, 2009. Sustainable detergents and cleaners, progress on ingredients, nanoparticles, analysis, environment[J]. Tenside Surfactants Detergents, 46(1): 53-62. |
| [8] | HYVONEN H, ORAMA M, SAARINEN H, et al., 2003 Studies on biodegradable chelating ligands: complexation of iminodisuccinic acid (ISA) with Cu(II), Zn(II), Mn(II) and Fe(Ⅲ) ions in aqueous solution[J]. Green Chemistry, 5(4): 410-414. |
| [9] | LUO J, CAI L M, QI S H, et al., 2018. The interactive effects between chelator and electric fields on the leaching risk of metals and the phytoremediation efficiency of Eucalyptus globulus[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 202: 830-837. |
| [10] | MAKINO T, SUGAHARA K, SAKURAI Y, et al., 2006. Remediation of cadmium contamination in paddy soils by washing with chemicals: Selection of washing chemicals[J]. Environmental Pollution, 144(1): 2-10. |
| [11] | POLETTINI A, POMI R, ROLLE E, 2007. The effect of operating variables on chelant-assisted remediation of contaminated dredged sediment[J]. Chemosphere, 66(5): 866-77. |
| [12] | SIMON G, ANELA K, DOMEN L, 2020. Soil washing with biodegradable chelating agents and EDTA: Technological feasibility, remediation efficiency and environmental sustainability[J]. Chemosphere, 257: 1-8. |
| [13] | SUANON F, SUN Q, DIMON B, et al., 2016. Heavy metal removal from sludge with organic chelators: Comparative study of N, N-bis (carboxymethyl) glutamic acid and citric acid[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 166: 341-347. |
| [14] | TANDY S, BOSSART K, MUELLER R, et al., 2004. Extraction of heavy metals from soils using biodegradable chelating agents[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 38(3): 937-944. |
| [15] | WANG K, LIU Y H, SONG Z G, et al., 2019. Effects of biodegradable chelator combination on potentially toxic metals leaching efficiency in agricultural soils[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 182: 1-8. |
| [16] | WASAY S A, BARRINGTON S F, TOKUNAGA S, 1998. Remediation of soils polluted by heavy metals using salts of organic acids and chelating agents[J]. Environmental Technology, 19(4): 369-379. |
| [17] | WU Q, DUAN G Q, CUI Y R, et al., 2015. Removal of heavy metal species from industrial sludge with the aid of biodegradable iminodisuccinic acid as the chelating ligand[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22(2): 1144-1150. |
| [18] | ZINNAT A B, ISMAIL M R, HIKARU S, et al., 2013. Effect of extraction variables on the biodegradable chelant-assisted removal of toxic metals from artificially contaminated European reference soils[J]. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 224(3): 1-21. |
| [19] | ZOU Z L, QIU R L, ZHANG W H, et al., 2009. The study of operating variables in soil washing with EDTA[J]. Environmental Pollution, 157(1): 229-236. |
| [20] | 曹坤坤, 张沙沙, 胡学玉, 等, 2022. 复合淋洗条件下农用地耕作层土壤去镉效率及其功能调节[J]. 环境科学, 43(2): 1023-1030. |
| CAO K K, ZHANG S S, HU X Y, et al., 2022. Effect of composite leaching on cadmium removal efficiency in plow layer soil of agricultural land and its functional regulation[J]. Environmental Science, 43(2): 1023-1030. | |
| [21] | 陈志良, 雷国建, 苏耀明, 等, 2015. 茶皂素与EDTA淋洗对土壤中铅、锌形态的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 24(8): 1394-1398. |
| CHEN Z L, LEI G J, SU Y M, et al., 2015. Effects of EDTA, saponin on the speciation of the metal forms of Pb and Zn in complexly-contaminated soils[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 24(8): 1394-1398. | |
| [22] | 冯俊生, 张俏晨, 2014. 土壤原位修复技术研究与应用进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 23(11): 1861-1867. |
| FENG J S, ZHANG Q C, 2014. A review on the study on practice of soil remediation in situ[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 23(11): 1861-1867. | |
| [23] | 环境保护部, 国土资源部, 2014. 全国土壤污染状况调查公报[EB/OL]. 北京: 生态环境部, [2021-09-18]. http://www.gov.cn/foot/2014-04/17/content_2661768.htm. |
| Environmental Protection Department, The Ministry of Land and Resources, 2014. Report on the national general survey of soil contamination[EB/OL]. Beijing: Ministry of Ecological Environment, [2021-09-18]. http://www.gov.cn/foot/2014-04/17/content_2661768.htm. | |
| [24] | 季蒙蒙, 王星星, 马欢欢, 等, 2021. 磷酸氨基酸盐对Cd污染土壤的淋洗效果[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 40(2): 329-337. |
| JI M M, WANG X X, MA H H, et al., 2021. Removal of Cd from contaminated soil using amino acid salt[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 40(2): 329-337. | |
| [25] | 罗璐瑕, 胡忻, 2008. 利用生物可降解螯合剂[S,S]-乙二胺二琥珀酸浸提沉积物中重金属的影响因素研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 27(3): 932-936. |
| LUO L X, HU X, 2008. Factors affecting the extraction of heavy metals in sediments using biodegradable [S,S]- ethylene diamine disuccinic acid[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 27(3): 932-936. | |
| [26] | 覃建军, 唐盛爽, 蒋凯, 等, 2020. 螯合剂GLDA对象草修复镉污染农田的影响[J]. 环境科学, 41(8): 3862-3869. |
| TAN J J, TANG S S, JIANG K, et al., 2020. Effects of chelate GLDA on the remediation of cadmium contaminated farmland by pennisetum purpureum schum[J]. Environmental Science, 41(8): 3862-3869. | |
| [27] | 吴青, 崔延瑞, 汤晓晓, 等, 2015. 生物可降解螯合剂谷氨酸N,N-二乙酸四钠对污泥中重金属萃取效率的研究[J]. 环境科学, 36(5): 1733-1738. |
| WU Q, CUI Y R, TANG X X, et al., 2015. Extraction of heavy metals from sludge using biodegradable chelating agent N,N-bis (carboxymethyl) glutamic acid tetrasodium[J]. Environmental Science, 36(5): 1733-1738. | |
| [28] | 吴长彧, 王亚权, 李静, 2007. 绿色螯合剂亚氨基二琥珀酸的合成及螯合性能[J]. 化学工业与工程, 24(2): 121-124. |
| WU Z Y, WANG Y Q, LI J, 2007. Synthesis of iminodisuccinic acid and its chelating ability[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering, 24(2): 121-124. | |
| [29] | 徐雷, 代惠萍, 魏树和, 2021. 淋洗剂在重金属污染土壤修复中的研究进展[J]. 中国环境科学, 41(11): 5237-5244. |
| XU L, DAI H P, WEI S H, 2021. Advances of washing agents in remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil[J]. China Environmental Science, 41(11): 5237-5244. | |
| [30] | 姚瑶, 张世熔, 王怡君, 等, 2018. 3种环保型淋洗剂对重金属污染土壤的淋洗效果[J]. 环境工程学报, 12(7): 2039-2046. |
| YAO Y, ZHANG S R, WANG Y J, et al., 2018. Effects of different environmentally friendly washing agents on removal of soilheavy metals[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 12(7): 2039-2046. | |
| [31] | 易龙生, 王文燕, 刘阳, 等, 2014. 柠檬酸、EDTA和茶皂素对重金属污染土壤的淋洗效果[J]. 安全与环境学报, 14(1): 225-228. |
| YI L S, WANG W Y, LIU Y, et al., 2014. Removal effects of the citric acid, EDTA and saponin on heavy metal contaminated soil[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 14(1): 225-228. | |
| [32] | 尹雪, 陈家军, 吕策, 2014. 螯合剂复配对实际重金属污染土壤洗脱效率影响及形态变化特征[J]. 环境科学, 35(2): 733-739. |
| YIN X, CHEN J J, LÜ C, 2014. Impact of compounded chelants on removal of heavy metals and characteristics of morphologic change in soil from heavy metals contaminated sites[J]. Environmental Science, 35(2): 733-739. | |
| [33] | 张金永, 朱玉婷, 王明新, 等, 2020. 还原增溶强化EGTA淋洗修复重金属污染土壤[J]. 环境科学, 41(5): 2390-2397. |
| ZHANG J Y, ZHU Y T, WANG M X, et al., 2020. Remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil by EGTA washing enhanced with reduction solubilization[J]. Environmental Science, 41(5): 2390-2397. | |
| [34] | 赵小健, 2013. 基于Hakanson潜在生态风险指数的某垃圾填埋场土壤重金属污染评价[J]. 环境监控与预警, 5(4): 43-44. |
| ZHAO X J, 2013. Pollution evaluation of heavy metals in soil of landfill site based on the potential ecological risk index proposed by Hakanson[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Forewarning, 5(4): 43-44. | |
| [35] | 中国环境监测总站, 1990. 中国土壤元素背景值[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社: 334-346. |
| China National Environmental Monitoring Centre, 1990. The element background values of Chinese soil[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press: 334-346. | |
| [36] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部, 2018. 土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准 (试行): GB 15618-2018[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| Ministry of Ecological and Environmental, PRC, 2018. Soil environmental quality, agricultural land, soil pollution risk management and control standards (on trial): GB 15618-2018[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press. | |
| [37] | 朱光旭, 郭庆军, 杨俊兴, 等, 2013. 淋洗剂对多金属污染尾矿土壤的修复效应及技术研究[J]. 环境科学, 34(9): 3690-3696. |
| ZHU G X, GUO Q J, YANG J X, et al., 2013. Research on the effect and technique of remediation for multi-metal contaminated tailing soils[J]. Environmental Science, 34(9): 3690-3696. |
| [1] | 杜丹丹, 高瑞忠, 房丽晶, 谢龙梅. 旱区盐湖盆地土壤重金属空间变异及对土壤理化因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1123-1132. |
| [2] | 赵良侠, 高坤, 黄婷婷, 高也, 琚唐丹, 蒋秋阳, 金珩, 熊蕾, 汤在琳, 高灿红. 玉米籽粒高/低镉积累自交系不同生育期的镉累积特性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 766-775. |
| [3] | 冯树娜, 吕家珑, 何海龙. KI淋洗对黄绵土汞污染的去除效果及土壤理化性状的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 776-783. |
| [4] | 陈敏毅, 朱航海, 佘伟铎, 尹光彩, 黄祖照, 杨巧玲. 珠三角某遗留造船厂场地土壤重金属人体健康风险评估及源解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 794-804. |
| [5] | 杨耀东, 陈玉梅, 涂鹏飞, 曾清如. 经济作物轮作模式下镉污染农田修复潜力[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 627-634. |
| [6] | 刘抗旱, 郑刘根, 张理群, 丁丹, 单士锋. 复合型植物源活化剂强化蜈蚣草修复砷污染土壤的效应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 635-642. |
| [7] | 肖洁芸, 周伟, 石佩琪. 土壤重金属含量高光谱反演[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 175-182. |
| [8] | 黄宏, 郑欣芸, 李迎东, 赵旭, 俞锦辰, 汪振华. 大陈岛海域不同年龄褐菖鲉对重金属富集作用研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1885-1891. |
| [9] | 马闯, 王雨阳, 周通, 吴龙华. 污染土壤颗粒态有机质镉锌富集特征及其解吸行为研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1892-1900. |
| [10] | 花莉, 成涛之, 梁智勇. 固定化混合菌对陕北黄土地区石油污染土壤的修复效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1610-1615. |
| [11] | 陶玲, 黄磊, 周怡蕾, 李中兴, 任珺. 污泥-凹凸棒石共热解生物炭对矿区土壤重金属生物有效性和环境风险的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1637-1646. |
| [12] | 房献宝, 张智钧, 赖阳晴, 叶脉, 刁增辉. 新型污泥生物炭对土壤重金属Cr和Cd的修复研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1647-1656. |
| [13] | 李莹, 张洲, 杨高明, 祖艳群, 李博, 陈建军. 湿地植物根系泌氧能力和根表铁膜与根系吸收重金属的关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1657-1666. |
| [14] | 罗松英, 李秋霞, 邱锦坤, 邓素炎, 李一锋, 陈碧珊. 南三岛土壤-红树植物系统中重金属形态特征及迁移转化规律[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1409-1416. |
| [15] | 董乐恒, 王旭刚, 陈曼佳, 王子豪, 孙丽蓉, 石兆勇, 吴琪琪. 光照和避光条件下石灰性水稻土Fe氧化还原与Cu活性关系研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1448-1455. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
