生态环境学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (7): 1007-1019.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2025.07.002
周依湘1,2( ), 唐斌2, 付成忠1,2, 许榕钦2,3, 周东静2,4, 王俊丽1,*(
), 唐斌2, 付成忠1,2, 许榕钦2,3, 周东静2,4, 王俊丽1,*( ), 郑晶2,*(
), 郑晶2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-10-23
出版日期:2025-07-18
发布日期:2025-07-11
通讯作者:
*E-mail: 作者简介:周依湘(1999年生),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为环境与健康。E-mail: 2138505547@qq.com
基金资助:
ZHOU Yixiang1,2( ), TANG Bin2, FU Chengzhong1,2, XU Rongqin2,3, ZHOU Dongjing2,4, WANG Junli1,*(
), TANG Bin2, FU Chengzhong1,2, XU Rongqin2,3, ZHOU Dongjing2,4, WANG Junli1,*( ), ZHENG Jing2,*(
), ZHENG Jing2,*( )
)
Received:2024-10-23
Online:2025-07-18
Published:2025-07-11
摘要:
为探究北江中下游地区典型饮用水源地水体和沉积物中双酚类化合物(BPs)和溴代阻燃剂[BFRs;包括多溴联苯醚(PBDEs)和新型BFRs(NBFRs)]的污染状况和风险水平,测定了14个饮用水源地水体和沉积物中BPs和BFRs的含量,分析其沉积物-水分配系数,并评价其生态风险与健康风险。结果显示:在丰水期,北江中下游水源水中BPs、PBDEs和NBFRs的总质量浓度分别为13.0-360 ng∙L−1、<LOD(检出限)-70.3 ng∙L−1、<LOD-36.6 ng∙L−1;枯水期相应的质量浓度分别为<LOD-275 ng∙L−1、<LOD-17.1 ng∙L−1、<LOD-7.31 ng∙L−1;沉积物中BPs、PBDEs和NBFRs的总质量分数分别为<LOD-34.4 ng∙g−1、0.734-12.5 ng∙g−1和<LOD-1.89 ng∙g−1。其中,水源水中的主要污染物为双酚A(BPA)、2,4,4′−三溴联苯醚(BDE28)和六氯二溴辛烷(HCDBCO),沉积物中为双酚B(BPB)、十溴联苯醚(BDE209)和HCDBCO;PBDEs在丰水期水体中的含量高于枯水期,且在河流型水源地水体中的含量高于湖库型水源地。BPs和PBDEs的沉积物-水分配系数(lgKd)与有机碳归一化分配系数(lgKoc)显著相关,表明总有机碳对其分配行为有显著的影响。水源水中BPs和BFRs的生态风险、非致癌风险及致癌风险值均小于相应的安全阈值,表明北江中下游水源水中BPs和BFRs对生态环境及人体健康造成的风险较低。研究结果可为饮用水源中BPs和BFRs的健康风险管控提供基础数据。
中图分类号:
周依湘, 唐斌, 付成忠, 许榕钦, 周东静, 王俊丽, 郑晶. 北江中下游水源地双酚类化合物和溴代阻燃剂的污染特征及风险评估[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(7): 1007-1019.
ZHOU Yixiang, TANG Bin, FU Chengzhong, XU Rongqin, ZHOU Dongjing, WANG Junli, ZHENG Jing. Occurrence and Associated Risk Assessment of Bisphenols and Brominated Flame Retardants in the Water Sources of the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Beijiang River[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2025, 34(7): 1007-1019.
| 中文全称 | 简称 | CAS号 | 辛醇水分配系数LogKow1) | 母离子质荷比(m/z) | 子离子质荷比(m/z) | 碰撞电压/eV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 双酚类化合物(BPs) | 双酚A | BPA | 80-05-7 | 3.64 | 227 | 133 | −25.0 |
| 双酚B | BPB | 77-40-7 | 4.15 | 241 | 212 | −25.0 | |
| 4,4′−亚乙烯联苯酚 | BPE | 2081-08-5 | 3.19 | 213 | 198 | −25.0 | |
| 双酚F | BPF | 620-92-8 | 2.76 | 199 | 105 | −25.0 | |
| 双酚P | BPP | 2167-51-3 | 6.1 | 345 | 133 | −70.0 | |
| 双酚S | BPS | 80-09-1 | 2.14 | 249 | 92.0 | −55.0 | |
| 双酚Z | BPZ | 843-55-0 | 5.78 | 267 | 145 | −55.0 | |
| 双酚AF | BPAF | 1478-61-1 | 3.96 | 335 | 265 | −40.0 | |
| 双酚AP | BPAP | 1571-75-1 | 4.33 | 289 | 274 | −25.0 | |
| 双酚BP | BPBP | 1844-01-5 | 5.6 | 351 | 274 | −22.0 | |
| 双酚M | BPM | 13595-25-0 | -2) | 345 | 133 | −36.0 | |
| 双酚G | BPG | 127-54-8 | 6.3 | 311 | 296 | −30.0 | |
| 多溴联苯醚(PBDEs) | 2,4,4′−三溴联苯醚 | BDE28 | 41318-75-6 | 5.88 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - |
| 2,2′,4,4′−四溴联苯醚 | BDE47 | 5436-43-1 | 6.77 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - | |
| 2,2′,4,4′,5−五溴联苯醚 | BDE99 | 60348-60-9 | 6.84 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - | |
| 2,2′,4,4′,6−五溴联苯醚 | BDE100 | 189084-64-8 | 6.51 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - | |
| 2,2,4,4,5,5−六溴联苯醚 | BDE153 | 68631-49-2 | 7.13 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - | |
| 2,2′,4,4′,5,6′−六溴联苯醚 | BDE154 | 207122-15-4 | 7.39 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - | |
| 2,2′,3,4,4′,5,6−七溴联苯醚 | BDE183 | 207122-16-5 | 7.14 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - | |
| 十溴联苯醚 | BDE209 | 1163-19-5 | 12.1 | - | 489 (487) | - | |
| 新型溴代阻燃剂(NBFRs) | 2,4,6−三溴苯基烯丙基醚 | ATE | 3278-89-5 | - | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - |
| 1,2−二溴−4−(1,2−二溴乙基)环己烷 | TBECH | 3322-93-8 | 5.24 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - | |
| 1,2,5,6−四溴环辛烷 | TBCO | 3194-57-8 | 5.24 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - | |
| 2,3,4,5,6−五溴乙苯 | PBEB | 85-22-3 | 7.48 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - | |
| 2−溴烯丙基−2,4,6−三溴苯醚 | BATE | 99717-56-3 | - | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - | |
| 六溴苯 | HBB | 87-82-1 | 7.33 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - | |
| (2,3−二溴丙基) (2,4,6−三溴苯基)醚 | DPTE | 35109-60-5 | 6.34 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - | |
| 1,2,3,4,5−五溴苯 | PBBZ | 608-90-2 | 6.44 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - | |
| 2,3,5,6−四溴对二甲苯 | p−TBX | 23488-38-2 | 6.65 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - | |
| 五溴甲苯 | PBT | 87-83-2 | 6.99 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - | |
| 六氯二溴辛烷 | HCDBCO | 51936-55-1 | 7.91 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - | |
| 1,2−双(2,4,6−三溴苯氧基)乙烷 | BTBPE | 37853-59-1 | 9.15 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - | |
| 四溴邻氯甲苯 | TBCT | 39569-21-6 | 7.33 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - |
表1 目标化合物的基本信息
Table 1 Basic information of the target compounds
| 中文全称 | 简称 | CAS号 | 辛醇水分配系数LogKow1) | 母离子质荷比(m/z) | 子离子质荷比(m/z) | 碰撞电压/eV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 双酚类化合物(BPs) | 双酚A | BPA | 80-05-7 | 3.64 | 227 | 133 | −25.0 |
| 双酚B | BPB | 77-40-7 | 4.15 | 241 | 212 | −25.0 | |
| 4,4′−亚乙烯联苯酚 | BPE | 2081-08-5 | 3.19 | 213 | 198 | −25.0 | |
| 双酚F | BPF | 620-92-8 | 2.76 | 199 | 105 | −25.0 | |
| 双酚P | BPP | 2167-51-3 | 6.1 | 345 | 133 | −70.0 | |
| 双酚S | BPS | 80-09-1 | 2.14 | 249 | 92.0 | −55.0 | |
| 双酚Z | BPZ | 843-55-0 | 5.78 | 267 | 145 | −55.0 | |
| 双酚AF | BPAF | 1478-61-1 | 3.96 | 335 | 265 | −40.0 | |
| 双酚AP | BPAP | 1571-75-1 | 4.33 | 289 | 274 | −25.0 | |
| 双酚BP | BPBP | 1844-01-5 | 5.6 | 351 | 274 | −22.0 | |
| 双酚M | BPM | 13595-25-0 | -2) | 345 | 133 | −36.0 | |
| 双酚G | BPG | 127-54-8 | 6.3 | 311 | 296 | −30.0 | |
| 多溴联苯醚(PBDEs) | 2,4,4′−三溴联苯醚 | BDE28 | 41318-75-6 | 5.88 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - |
| 2,2′,4,4′−四溴联苯醚 | BDE47 | 5436-43-1 | 6.77 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - | |
| 2,2′,4,4′,5−五溴联苯醚 | BDE99 | 60348-60-9 | 6.84 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - | |
| 2,2′,4,4′,6−五溴联苯醚 | BDE100 | 189084-64-8 | 6.51 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - | |
| 2,2,4,4,5,5−六溴联苯醚 | BDE153 | 68631-49-2 | 7.13 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - | |
| 2,2′,4,4′,5,6′−六溴联苯醚 | BDE154 | 207122-15-4 | 7.39 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - | |
| 2,2′,3,4,4′,5,6−七溴联苯醚 | BDE183 | 207122-16-5 | 7.14 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - | |
| 十溴联苯醚 | BDE209 | 1163-19-5 | 12.1 | - | 489 (487) | - | |
| 新型溴代阻燃剂(NBFRs) | 2,4,6−三溴苯基烯丙基醚 | ATE | 3278-89-5 | - | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - |
| 1,2−二溴−4−(1,2−二溴乙基)环己烷 | TBECH | 3322-93-8 | 5.24 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - | |
| 1,2,5,6−四溴环辛烷 | TBCO | 3194-57-8 | 5.24 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - | |
| 2,3,4,5,6−五溴乙苯 | PBEB | 85-22-3 | 7.48 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - | |
| 2−溴烯丙基−2,4,6−三溴苯醚 | BATE | 99717-56-3 | - | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - | |
| 六溴苯 | HBB | 87-82-1 | 7.33 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - | |
| (2,3−二溴丙基) (2,4,6−三溴苯基)醚 | DPTE | 35109-60-5 | 6.34 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - | |
| 1,2,3,4,5−五溴苯 | PBBZ | 608-90-2 | 6.44 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - | |
| 2,3,5,6−四溴对二甲苯 | p−TBX | 23488-38-2 | 6.65 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - | |
| 五溴甲苯 | PBT | 87-83-2 | 6.99 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - | |
| 六氯二溴辛烷 | HCDBCO | 51936-55-1 | 7.91 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - | |
| 1,2−双(2,4,6−三溴苯氧基)乙烷 | BTBPE | 37853-59-1 | 9.15 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - | |
| 四溴邻氯甲苯 | TBCT | 39569-21-6 | 7.33 | - | 79.0 (81.0) | - |
| 化合物 | 丰水期水体中质量浓度/(ng∙L−1) | 枯水期水体中质量浓度/(ng∙L−1) | p值 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 检出率/% | 中值 | 范围 | 检出率/% | 中值 | 范围 | |||
| BPA | 100 | 30.1 | 12.6-351 | 92.9 | 30.2 | <LOD-228 | 0.890 | |
| BPB | 78.6 | 0.414 | <LOD-0.935 | 42.9 | <LOD | <LOD-49.8 | - | |
| BPE | 28.6 | <LOD | <LOD-10.6 | 42.9 | <LOD | <LOD-5.75 | - | |
| BPP | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 14.3 | <LOD | <LOD-0.940 | - | |
| BPS | 57.1 | 0.349 | <LOD-8.03 | 92.9 | 0.648 | <LOD-15.0 | 0.087 | |
| BPAF | 92.9 | 0.577 | <LOD-2.354 | 71.4 | 0.308 | <LOD-3.72 | 0.088 | |
| BPG | 21.4 | <LOD | <LOD-2.08 | 35.7 | <LOD | <LOD-1.34 | - | |
| ∑BPs | 100 | 33.1 | 13.0-360 | 92.9 | 41.3 | <LOD-275 | 0.550 | |
| BDE28 | 71.4 | 0.694 | <LOD-69.6 | 57.1 | 0.72 | <LOD-17.1 | 0.541 | |
| BDE99 | 64.3 | 0.534 | <LOD-0.957 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | - | |
| BDE153 | 7.1 | <LOD | <LOD-0.260 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | - | |
| BDE183 | 7.1 | <LOD | <LOD-0.474 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | - | |
| BDE209 | 42.9 | <LOD | <LOD-2.69 | 14.3 | <LOD | <LOD-0.289 | - | |
| ∑PBDEs | 92.9 | 2.59 | <LOD-70.3 | 64.3 | 0.72 | <LOD-17.1 | 0.036 | |
| TBCT | 42.9 | <LOD | <LOD-0.346 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | - | |
| DPTE | 42.9 | <LOD | <LOD-7.33 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | - | |
| HBB | 21.4 | <LOD | <LOD-6.34 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | - | |
| HCDBCO | 28.6 | <LOD | <LOD-35.1 | 14.3 | <LOD | <LOD-7.31 | - | |
| ∑NBFRs | 71.4 | 3.12 | <LOD-36.6 | 14.3 | <LOD | <LOD-7.31 | - | |
表2 水源水中BPs和BFRs的质量浓度
Table 2 Mass concentrations of BPs and BFRs in source water
| 化合物 | 丰水期水体中质量浓度/(ng∙L−1) | 枯水期水体中质量浓度/(ng∙L−1) | p值 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 检出率/% | 中值 | 范围 | 检出率/% | 中值 | 范围 | |||
| BPA | 100 | 30.1 | 12.6-351 | 92.9 | 30.2 | <LOD-228 | 0.890 | |
| BPB | 78.6 | 0.414 | <LOD-0.935 | 42.9 | <LOD | <LOD-49.8 | - | |
| BPE | 28.6 | <LOD | <LOD-10.6 | 42.9 | <LOD | <LOD-5.75 | - | |
| BPP | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 14.3 | <LOD | <LOD-0.940 | - | |
| BPS | 57.1 | 0.349 | <LOD-8.03 | 92.9 | 0.648 | <LOD-15.0 | 0.087 | |
| BPAF | 92.9 | 0.577 | <LOD-2.354 | 71.4 | 0.308 | <LOD-3.72 | 0.088 | |
| BPG | 21.4 | <LOD | <LOD-2.08 | 35.7 | <LOD | <LOD-1.34 | - | |
| ∑BPs | 100 | 33.1 | 13.0-360 | 92.9 | 41.3 | <LOD-275 | 0.550 | |
| BDE28 | 71.4 | 0.694 | <LOD-69.6 | 57.1 | 0.72 | <LOD-17.1 | 0.541 | |
| BDE99 | 64.3 | 0.534 | <LOD-0.957 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | - | |
| BDE153 | 7.1 | <LOD | <LOD-0.260 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | - | |
| BDE183 | 7.1 | <LOD | <LOD-0.474 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | - | |
| BDE209 | 42.9 | <LOD | <LOD-2.69 | 14.3 | <LOD | <LOD-0.289 | - | |
| ∑PBDEs | 92.9 | 2.59 | <LOD-70.3 | 64.3 | 0.72 | <LOD-17.1 | 0.036 | |
| TBCT | 42.9 | <LOD | <LOD-0.346 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | - | |
| DPTE | 42.9 | <LOD | <LOD-7.33 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | - | |
| HBB | 21.4 | <LOD | <LOD-6.34 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | - | |
| HCDBCO | 28.6 | <LOD | <LOD-35.1 | 14.3 | <LOD | <LOD-7.31 | - | |
| ∑NBFRs | 71.4 | 3.12 | <LOD-36.6 | 14.3 | <LOD | <LOD-7.31 | - | |
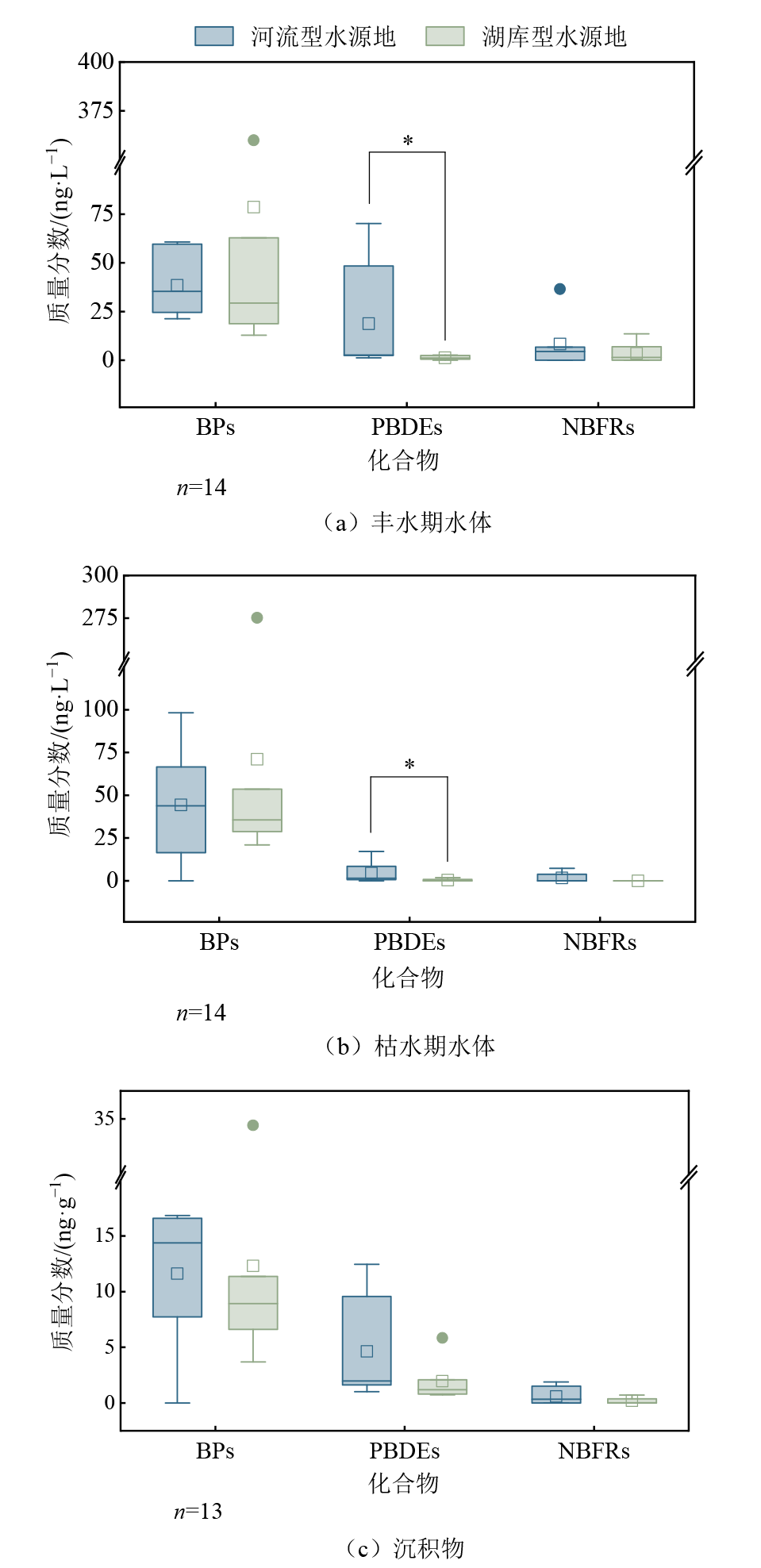
图3 不同类型水源地水体和沉积物中BPs、PBDEs、NBFRs的含量分布 *表示差异显著(p<0.05)
Figure 3 Distribution of contents of BPs, PBDEs and NBFRs in the water of different types of water sources
| 化合物 | 沉积物中质量分数/(ng∙g−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 检出率/% | 中值 | 范围 | |
| BPA | 84.6 | 3.25 | <LOD-4.47 |
| BPB | 61.5 | 4.41 | <LOD-12.8 |
| BPE | 46.2 | <LOD | <LOD-25.7 |
| BPS | 15.4 | <LOD | <LOD-0.130 |
| BPAF | 61.5 | 0.028 | <LOD-0.718 |
| ∑BPs | 92.3 | 9.64 | <LOD-34.4 |
| BDE28 | 15.4 | <LOD | <LOD-0.475 |
| BDE47 | 61.5 | 0.250 | <LOD-2.29 |
| BDE99 | 100 | 0.651 | 0.305-2.78 |
| BDE153 | 100 | 0.099 | 0.028-0.973 |
| BDE183 | 53.8 | 0.244 | <LOD-1.41 |
| BDE209 | 100 | 0.388 | 0.082-10.4 |
| ∑PBDEs | 100 | 1.73 | 0.734-12.5 |
| TBCT | 38.5 | <LOD | <LOD-0.057 |
| PBT | 23.1 | <LOD | <LOD-0.659 |
| DPTE | 30.8 | <LOD | <LOD-0.744 |
| HBB | 38.5 | <LOD | <LOD-0.746 |
| HCDBCO | 7.70 | <LOD | <LOD-1.57 |
| ∑NBFRs | 53.8 | 0.057 | <LOD-1.89 |
表3 沉积物中BPs、BFRs的质量分数
Table 3 Mass concentrations of BPs and BFRs in the sediment
| 化合物 | 沉积物中质量分数/(ng∙g−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 检出率/% | 中值 | 范围 | |
| BPA | 84.6 | 3.25 | <LOD-4.47 |
| BPB | 61.5 | 4.41 | <LOD-12.8 |
| BPE | 46.2 | <LOD | <LOD-25.7 |
| BPS | 15.4 | <LOD | <LOD-0.130 |
| BPAF | 61.5 | 0.028 | <LOD-0.718 |
| ∑BPs | 92.3 | 9.64 | <LOD-34.4 |
| BDE28 | 15.4 | <LOD | <LOD-0.475 |
| BDE47 | 61.5 | 0.250 | <LOD-2.29 |
| BDE99 | 100 | 0.651 | 0.305-2.78 |
| BDE153 | 100 | 0.099 | 0.028-0.973 |
| BDE183 | 53.8 | 0.244 | <LOD-1.41 |
| BDE209 | 100 | 0.388 | 0.082-10.4 |
| ∑PBDEs | 100 | 1.73 | 0.734-12.5 |
| TBCT | 38.5 | <LOD | <LOD-0.057 |
| PBT | 23.1 | <LOD | <LOD-0.659 |
| DPTE | 30.8 | <LOD | <LOD-0.744 |
| HBB | 38.5 | <LOD | <LOD-0.746 |
| HCDBCO | 7.70 | <LOD | <LOD-1.57 |
| ∑NBFRs | 53.8 | 0.057 | <LOD-1.89 |
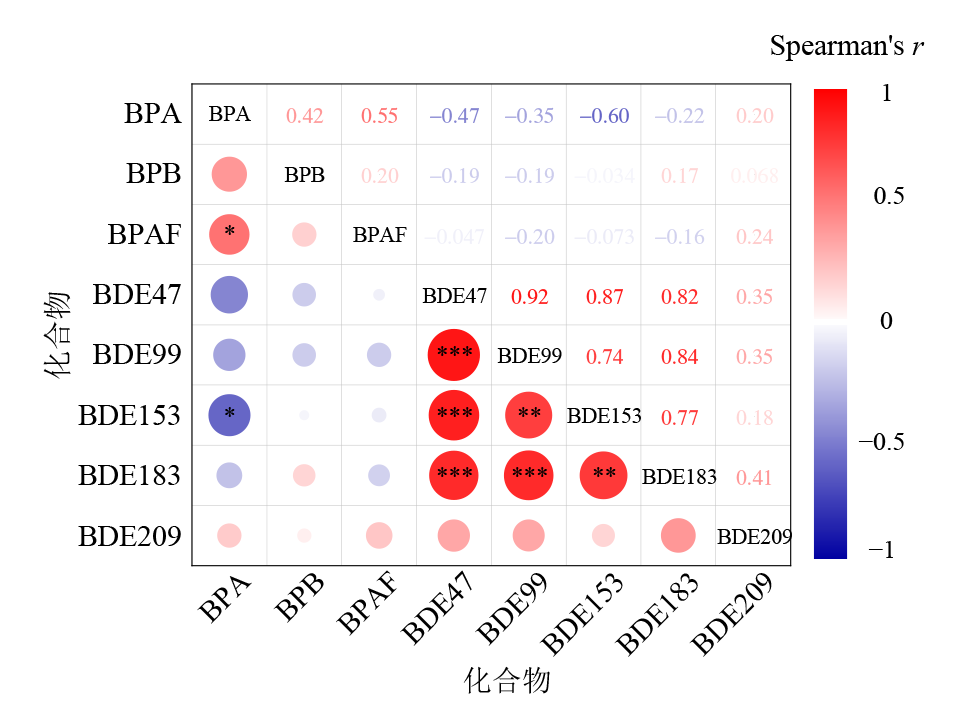
图4 沉积物中不同污染物之间的Spearman秩相关分析结果
Figure 4 Results of Spearman rank correlation analysis between different contaminants in sediments *:p≤0.05;**:p≤0.01;***:p≤0.001
| 化合物 | lgKd值/(L∙kg−1) | p值 | lgKoc值/(L∙kg−1) | p值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 河流型水源地 | 湖库型水源地 | 河流型水源地 | 湖库型水源地 | |||
| BPA | 1.75-2.30(2.09) | 0.520-2.54(1.84) | 0.830 | 2.16-2.66(2.44) | 0.45-2.63(1.84) | 0.133 |
| BPB | 4.16-4.49(4.30) | 3.95-4.38(4.16) | 0.351 | 4.32-4.72(4.56) | 4.03-4.64(4.34) | 0.351 |
| BPAF | 1.07-2.62(1.75) | 1.91-2.21(2.06) | 0.367 | 1.23-2.72(2.12) | 2.10-2.47(2.29) | 0.293 |
| ∑BPs | 2.34-2.82(2.60) | 1.43-3.42(2.36) | 0.391 | 2.50-3.35(2.95) | 1.36-3.51(2.31) | 0.317 |
| BDE99 | 2.86-3.63(3.19) | 2.56-3.59(3.13) | 0.378 | 3.12-4.08(3.43) | 2.65-3.52(2.99) | 0.240 |
| ∑PBDEs | 1.32-4.00(2.76) | 2.62-3.35(3.07) | 1.00 | 1.59-4.32(3.10) | 2.29-3.46(2.97) | 0.317 |
表4 丰水期各类型水源地中BPs和BFRs的沉积物-水分配特征
Table 4 Distributional characterization between sediment and water of BPs and BFRs in different types of water sources
| 化合物 | lgKd值/(L∙kg−1) | p值 | lgKoc值/(L∙kg−1) | p值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 河流型水源地 | 湖库型水源地 | 河流型水源地 | 湖库型水源地 | |||
| BPA | 1.75-2.30(2.09) | 0.520-2.54(1.84) | 0.830 | 2.16-2.66(2.44) | 0.45-2.63(1.84) | 0.133 |
| BPB | 4.16-4.49(4.30) | 3.95-4.38(4.16) | 0.351 | 4.32-4.72(4.56) | 4.03-4.64(4.34) | 0.351 |
| BPAF | 1.07-2.62(1.75) | 1.91-2.21(2.06) | 0.367 | 1.23-2.72(2.12) | 2.10-2.47(2.29) | 0.293 |
| ∑BPs | 2.34-2.82(2.60) | 1.43-3.42(2.36) | 0.391 | 2.50-3.35(2.95) | 1.36-3.51(2.31) | 0.317 |
| BDE99 | 2.86-3.63(3.19) | 2.56-3.59(3.13) | 0.378 | 3.12-4.08(3.43) | 2.65-3.52(2.99) | 0.240 |
| ∑PBDEs | 1.32-4.00(2.76) | 2.62-3.35(3.07) | 1.00 | 1.59-4.32(3.10) | 2.29-3.46(2.97) | 0.317 |
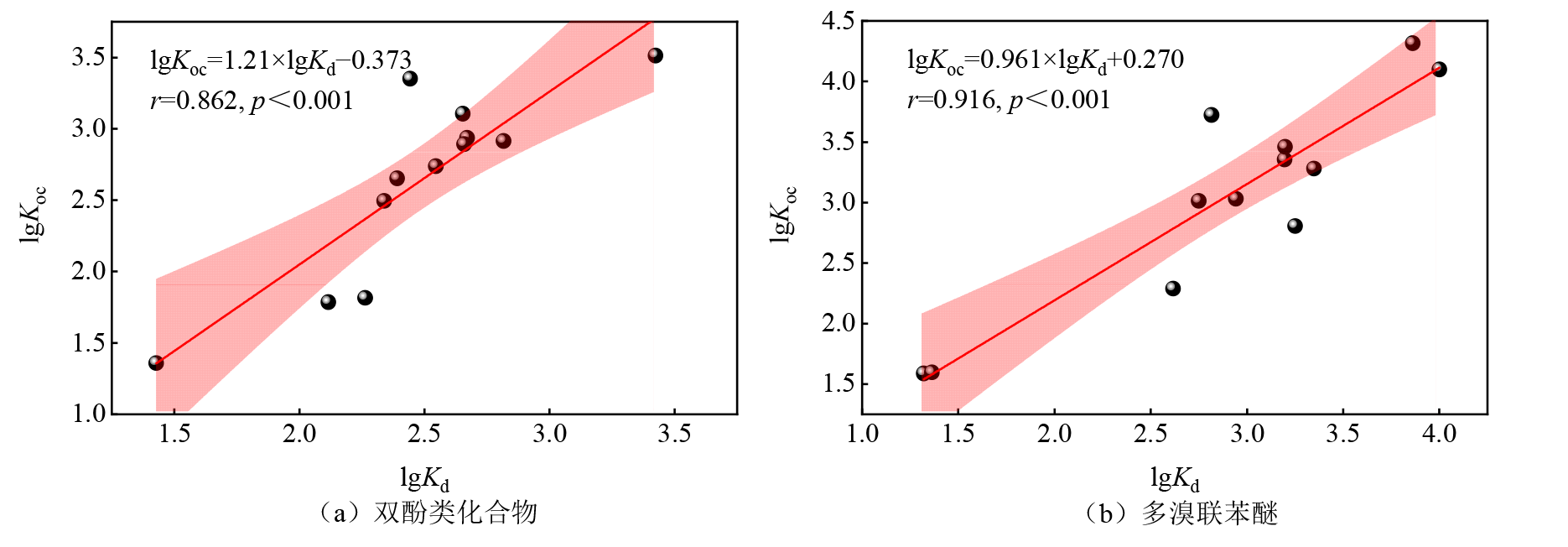
图5 饮用水源地环境中BPs(a)和PBDEs(b)的lgKd、lgKoc值之间的相关性分析结果
Figure 5 Results of correlation analysis between lgKd and lgKoc of BPs (a) and PBDEs (b) in drinking water source environment
| [1] | ADAMOVSKY O, GROH K J, BIALK-BIELINSKA A, et al., 2024. Exploring BPA alternatives: Environmental levels and toxicity review[J]. Environment International, 189: 108728. |
| [2] | BERGER M L, SHAW S D, ROLSKY C B, et al., 2023. Alternative and legacy flame retardants in marine mammals from three northern ocean regions[J]. Environmental Pollution, 335: 122255. |
| [3] | BRIDSON J H, GAUGLER E C, SMITH D A, et al., 2021. Leaching and extraction of additives from plastic pollution to inform environmental risk: A multidisciplinary review of analytical approaches[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 414: 125571. |
| [4] | CATENZA C J, FAROOQ A, SHUBEAR N S, et al., 2021. A targeted review on fate, occurrence, risk and health implications of bisphenol analogues[J]. Chemosphere, 268: 129273. |
| [5] | CHEN D, KANNAN K, TAN H L, et al., 2016. Bisphenol analogues other than BPA: Environmental occurrence, human exposure, and toxicity: A review[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 50(11): 5438-5453. |
| [6] |
CHEN L G, HUANG Y M, PENG X C, et al., 2009. PBDEs in sediments of the Beijiang River, China: Levels, distribution, and influence of total organic carbon[J]. Chemosphere, 76(2): 226-231.
DOI PMID |
| [7] | CHEN M Q, JIANG J Y, GAN Z W, et al., 2019. Grain size distribution and exposure evaluation of organophosphorus and brominated flame retardants in indoor and outdoor dust and PM10 from Chengdu, China[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 365: 280-288. |
| [8] | CHEN Y P, ZHAO Y, ZHAO M M, et al., 2021. Potential health risk assessment of HFRs, PCBs, and OCPs in the Yellow River basin[J]. Environmental Pollution, 275: 116648. |
| [9] | CHENG J O, KO F C, 2018. Occurrence of PBDEs in surface sediments of metropolitan rivers: Sources, distribution pattern, and risk assessment[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 637-638: 1578-1585. |
| [10] | FRIES E, SÜHRING R, 2023. The unusual suspects: Screening for persistent, mobile, and toxic plastic additives in plastic leachates[J]. Environmental Pollution, 335: 122263. |
| [11] | FU J, ZHANG H B, LI R J, et al., 2023. Spatial distribution, source, and ecological risk of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and hexabromocyclododecanes (HBCDs) in Jiaozhou Bay, China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 192: 114978. |
| [12] | GAO Y, XIAO S K, WU Q, et al., 2023. Bisphenol analogues in water and sediment from the Beibu Gulf, South China Sea: Occurrence, partitioning and risk assessment[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 857(Part 2): 159445. |
| [13] | HALEEM N, KUMAR P, ZHANG C, et al., 2024. Microplastics and associated chemicals in drinking water: A review of their occurrence and human health implications[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 912: 169594. |
| [14] | HARRAD S, DRAGE D S, SHARKEY M, et al., 2020. Perfluoroalkyl substances and brominated flame retardants in landfill-related air, soil, and groundwater from Ireland[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 705: 135834. |
| [15] | HE W, LIU W X, QIN N, et al., 2019. Impact of organic matter and meteorological factors on the long-term trend, seasonality, and gas/particle partitioning behavior of atmospheric PBDEs[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 659: 1058-1070. |
| [16] | HE W, QIN N, KONG X Z, et al., 2013. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in the surface sediments and suspended particulate matter (SPM) from Lake Chaohu, a large shallow Chinese lake[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 463-464: 1163-1173. |
| [17] |
HOU L, JIANG J Y, GAN Z W, et al., 2019. Spatial distribution of organophosphorus and brominated flame retardants in surface water, sediment, groundwater, and wild fish in Chengdu, China[J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 77(2): 279-290.
DOI PMID |
| [18] | HOU R, LIN L, LI H X, et al., 2021. Occurrence, bioaccumulation, fate, and risk assessment of novel brominated flame retardants (NBFRs) in aquatic environments: A critical review[J]. Water Research, 198: 117168. |
| [19] |
HUANG Y D, ZHANG D N, YANG Y, et al., 2018. Distribution and partitioning of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in sediments from the Pearl River Delta and Guiyu, South China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 235: 104-112.
DOI PMID |
| [20] | HUANG Z, ZHAO J L, YANG Y Y, et al., 2020. Occurrence, mass loads and risks of bisphenol analogues in the Pearl River Delta region, South China: Urban rainfall runoff as a potential source for receiving rivers[J]. Environmental Pollution, 263(Part B): 114361. |
| [21] |
JIN H B, ZHU L Y, 2016. Occurrence and partitioning of bisphenol analogues in water and sediment from Liaohe River Basin and Taihu Lake, China[J]. Water Research, 103: 343-351.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | LAN Y Y, GAO X, XU H W, et al., 2024. 20 years of polybrominated diphenyl ethers on toxicity assessments[J]. Water Research, 249: 121007. |
| [23] | LAO Z, LI H, LIAO Z, et al., 2023. Spatiotemporal transitions of organophosphate esters (OPEs) and brominated flame retardants (BFRs) in sediments from the Pearl River Delta, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 855: 158807. |
| [24] | LEE S Y, RA K T, MOON H B, 2021. Severe contamination and time trends of legacy and novel halogenated flame retardants in multiple environmental media from Lake Shihwa, Korea: Effectiveness of regulatory action[J]. Chemosphere, 279: 130620. |
| [25] | LI M, GONG X Y, TAN Q W, et al., 2024. A review of occurrence, bioaccumulation, and fate of novel brominated flame retardants in aquatic environments: A comparison with legacy brominated flame retardants[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 939: 173224. |
| [26] | LIANG H Y, ZHANG Y H, DU S L, et al., 2024. Heavy metals in sediments of the river-lake system in the Dianchi basin, China: Their pollution, sources, and risks[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 957: 177652. |
| [27] | LIANG X Y, XIE R M, HE Y Q, et al., 2023. Broadening the lens on bisphenols in coastal waters: Occurrence, partitioning, and input fluxes of multiple novel bisphenol S derivatives along with BPA and BPA analogues in the Pearl River Delta, China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 322: 121194. |
| [28] | LING S Y, ZHOU S Q, TAN J Q, et al., 2022. Brominated flame retardants (BFRs) in sediment from a typical e-waste dismantling region in Southern China: Occurrence, spatial distribution, composition profiles, and ecological risks[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 824: 153813. |
| [29] | LIU L, ZHEN X M, WANG X M, et al., 2020. Legacy and novel halogenated flame retardants in seawater and atmosphere of the Bohai Sea: Spatial trends, seasonal variations, and influencing factors[J]. Water Research, 184: 116117. |
| [30] | LIU L, ZHEN X M, WANG X M, et al., 2021b. Spatio-temporal variations and input patterns on the legacy and novel brominated flame retardants (BFRs) in coastal rivers of north China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 283: 117093. |
| [31] | LIU Y H, CUI S, MA Y, et al., 2021a. Brominated flame retardants (BFRs) in marine food webs from Bohai Sea, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 772: 145036. |
| [32] | LIU Y H, ZHANG S H, SONG N H, et al., 2017. Occurrence, distribution and sources of bisphenol analogues in a shallow Chinese freshwater lake (Taihu Lake): Implications for ecological and human health risk[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 599-600: 1090-1098. |
| [33] | LUO Y M, SHI W Z, YOU M T, et al., 2021. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in the Danjiangkou Reservoir, China: Identification of priority PBDE congeners[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(10): 12587-12596. |
| [34] |
PEI J, YAO H, WANG H, et al., 2018. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in water, surface sediment, and suspended particulate matter from the Yellow River, China: Levels, spatial and seasonal distribution, and source contribution[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 129(1): 106-113.
DOI PMID |
| [35] | QIU W H, LIU S, CHEN H H, et al., 2021. The comparative toxicities of BPA, BPB, BPS, BPF, and BPAF on the reproductive neuroendocrine system of zebrafish embryos and its mechanisms[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 406: 124303. |
| [36] | SANTOS C R D, ARCANJO G S, ARAÚJO A A D, et al., 2024. Occurrence, environmental risks, and removal of bisphenol A and its analogues by membrane bioreactors[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 494: 153278. |
| [37] | TANG Z, LIU Z H, WANG H, et al., 2023. Twelve natural estrogens and ten bisphenol analogues in eight drinking water treatment plants: Analytical method, their occurrence and risk evaluation[J]. Water Research, 243: 120310. |
| [38] | WANG N, LAI C, XU F H, et al., 2023a. A review of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and novel brominated flame retardants in Chinese aquatic environment: Source, occurrence, distribution, and ecological risk assessment[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 904: 166180. |
| [39] | WANG T, HE Z X, YANG J, et al., 2022. Riverine transport dynamics of PBDEs and OPFRs within a typical e-waste recycling zone: Implications for sink-source interconversion[J]. Water Research, 220: 118677. |
| [40] | WANG Y L, FENG Y Y, CHEN Y L, et al., 2023b. Annual flux estimation and source apportionment of PCBs and PBDEs in the middle reach of Yangtze River, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 885(3): 163772. |
| [41] | WANG Z W, JIA H L, JIANG Y, et al., 2023c. Bioaccumulation of novel brominated flame retardants in crucian carp (Carassius auratus): Implications for electronic waste recycling area monitoring[J]. Environmental Research, 239(Part 2): 117412. |
| [42] | XIE Y H, LI M, MA J Y, et al., 2024. Occurrence and distribution of legacy and novel brominated flame retardants in river and sediments in Southwest China: A seasonal investigation[J]. Environmental Research, 262(Part 1): 119842. |
| [43] |
XIONG J K, LI G Y, AN T C, et al., 2016. Emission patterns and risk assessment of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and bromophenols in water and sediments from the Beijiang River, South China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 219: 596-603.
DOI PMID |
| [44] |
YAN Z Y, LIU Y H, YAN K, et al., 2017. Bisphenol analogues in surface water and sediment from the shallow Chinese freshwater lakes: Occurrence, distribution, source apportionment, and ecological and human health risk[J]. Chemosphere, 184: 318-328.
DOI PMID |
| [45] | ZHANG H F, ZHANG Y P, LI J B, et al., 2019. Occurrence and exposure assessment of bisphenol analogues in source water and drinking water in China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 655: 607-613. |
| [46] | ZHANG S, FAN Y F, QIAN X, et al., 2024a. Occurrence, source apportionment and ecological risk of bisphenol analogues in river sediments in areas with different land use patterns[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 359: 121041. |
| [47] | ZHANG S, FAN Y F, QIAN X, et al., 2024b. Spatiotemporal distribution, source apportionment, and ecological risk of bisphenol analogues in a highly urbanized river basin[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 920: 170964. |
| [48] | ZHAO Y, CHEN Y P, 2023. Coming ecological risks of organochlorine pesticides and novel brominated flame retardants in the Yellow River Basin[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 857: 159296. |
| [49] |
ZHOU S N, SIDDIQUE S, LAVOIE L, et al., 2014. Hexachloronorbornene-based flame retardants in humans: Levels in maternal serum and milk[J]. Environment International, 66: 11-17.
DOI PMID |
| [50] | 白云松, 付青, 涂响, 等, 2023. 北江中上游流域阻燃剂污染特征和风险评估[J]. 环境科学研究, 36(4): 704-714. |
| BAI Y S, FU Q, TU X, et al., 2023. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of flame retardants in middle and upper reaches of Beijiang River Basin[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 36(4): 704-714. | |
| [51] | 国家环境保护局科技标准司, 2003. 地表水和污水监测技术规范: HJ/T 91—2002[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社: 8-11. |
| Science and Technology Standards Department of the National Environmental Protection Administration, 2003. Technical Specifications Requirements for Monitoring of Surface Water and Waste Water: HJ/T 91—2002[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press: 8-11. | |
| [52] | 黄晨晨, 曾艳红, 管克兰, 等, 2024. 黑臭水体沉积物中新型溴代阻燃剂的污染特征[J]. 中国环境科学, 44(7): 3945-3954. |
| HUANG C C, ZENG Y H, GUAN K L, et al., 2024. Occurrence, spatial distribution, and risk assessment of novel brominated flame retardants in sediments from black-odorous rivers[J]. China Environmental Science, 44(7): 3945-3954. | |
| [53] | 环境保护部, 2013. 中国人群暴露参数手册[M]. 北京: 中国环境出版社: 89-90. |
| Ministry of Environmental Protection, 2013. Exposure Factors Handbook of Chinese Population[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press: 89-90. | |
| [54] |
李艳, 顾华, 杨胜利, 等, 2018. 北京典型灌区表层土壤与农产品酚类含量及人体健康风险评估[J]. 生态环境学报, 27(12): 2343-2351.
DOI |
| LI Y, GU H, YANG S L, et al., 2018. Study on concentrations of phenols in topsoils and agricultural products and health risk assessment in the typical irrigation district of Beijing city[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 27(12): 2343-2351. | |
| [55] | 邱鹏, 刘芃岩, 王晓冰, 等, 2019. 白洋淀入湖河流水体中多溴联苯醚的浓度分布特征[J]. 环境污染与防治, 41(1): 81-84. |
| QIU P, LIU P Y, WANG X B, et al., 2019. Concentration distribution characteristics of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in the water flows into Baiyangdian Lake[J]. Environmental Pollution and Control, 41(1): 81-84. | |
| [56] | 武宇圣, 黄天寅, 张家根, 等, 2023. 淮河下游湖泊表层水和沉积物中PPCPs分布特征及风险评估[J]. 环境科学, 44(6): 3217-3227. |
| WU Y S, HUANG T Y, ZHANG J G, et al., 2023. Distribution characteristics and risk assessment of PPCPs in surface water and sediments of lakes in the lower reaches of the Huaihe River[J]. Environmental Science, 44(6): 3217-3227. | |
| [57] | 熊仕茂, 王秀珍, 罗伟铿, 等, 2021. 北江中下游内分泌干扰物的空间分布、生态风险及产业相关性[J]. 环境化学, 40(12): 3803-3814. |
| XIONG S M, WANG X Z, LUO W K, et al., 2021. Spatial distribution, ecological risk and industry-dependence of endocrine disrupting chemicals in the Beijiang River, south China[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 40(12): 3803-3814. | |
| [58] | 赵燕燕, 王玲, 楼迎华, 等, 2015. 气质联用测定胶州湾北岸潮间带底泥中的新型溴代阻燃剂[J]. 环境化学, 34(2): 339-346. |
| ZHAO Y Y, WANG L, LOU Y H, et al., 2015. Determination of new brominated flame retardants in the north shore of Jiaozhou Bay intertidal sediments by gas chromatography mass spectrometry[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 34(2): 339-346. |
| [1] | 田蜜, 廖日权, 张健, 董凤凤, 唐建辉. 钦州湾全氟/多氟烷基化合物的污染特征及生态风险评估[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(7): 1020-1028. |
| [2] | 赵曦, 韦斯. 超短链PFASs类新污染物的环境特性、全球水平、来源及风险[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(7): 1064-1078. |
| [3] | 陈思宇, 孙丽娟, 苏枞枞, 于兴娜. 太原市春夏季VOCs组成特征及其对二次有机气溶胶和臭氧的贡献[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(4): 548-555. |
| [4] | 丛鑫, 张怀迪, 张荣, 赵琛, 陈坤, 刘寒冰. 基于Meta分析的近10年中国农田土壤重金属污染特征与风险解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(9): 1451-1459. |
| [5] | 卢聪. 生物炭负载纳米零价铁对沉积物中十溴二苯乙烷去除效果及机制[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(8): 1279-1288. |
| [6] | 张俊美, 王志宇, 杨本勇, 杨书申, 杨凌霄. PM2.5中水溶性有机碳的污染特征、吸光特性和来源研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(7): 1072-1078. |
| [7] | 何艺, 秦欣欣, 张翔, 孙楠, 杨雅淋, 连军锋. 微塑料断面分布的不均一性——以赣江水域赣州段为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(4): 626-632. |
| [8] | 蒋皓, 吴启堂. 石油烃污染敏感场地健康风险筛选误差的概率方法分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(4): 645-654. |
| [9] | 蒋伯琪, 浮天, 程昳璇, 苏枞枞, 沈建东, 于谨铖, 于兴娜. 沈阳市臭氧污染特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(1): 72-79. |
| [10] | 陈鸿展, 区晖, 叶四化, 张倩华, 周树杰, 麦磊. 珠江广州段水体微塑料的时空分布特征及生态风险评估[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(9): 1663-1672. |
| [11] | 陈敏毅, 朱航海, 佘伟铎, 尹光彩, 黄祖照, 杨巧玲. 珠三角某遗留造船厂场地土壤重金属人体健康风险评估及源解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 794-804. |
| [12] | 李文菁, 黄月群, 黄亮亮, 李向通, 苏琼源, 孙扬言. 北部湾海洋鱼类微塑料污染特征及其风险评估[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(11): 1913-1921. |
| [13] | 王默雷, 李智慧, 陈来国, 郭送军, 刘明, 王硕, 陆海涛. 城市垃圾焚烧厂烟气及周边土壤中多溴联苯醚的污染特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1582-1589. |
| [14] | 樊珂宇, 高原, 赖子尼, 曾艳艺, 刘乾甫, 李海燕, 麦永湛, 杨婉玲, 魏敬欣, 孙金辉, 王超. 珠三角河网鱼类微塑料污染特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1590-1598. |
| [15] | 李秀华, 赵玲, 滕应, 骆永明, 黄标, 刘冲, 刘本乐, 赵其国. 贵州汞矿区周边农田土壤汞镉复合污染特征空间分布及风险评估[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1629-1636. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
