生态环境学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (3): 389-398.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.03.007
收稿日期:2023-12-14
出版日期:2024-03-18
发布日期:2024-05-08
通讯作者:
*卫伟。E-mail: weiwei@rcees.ac.cn作者简介:黄玥(1994年生),女,博士研究生,主要从事景观生态学方向研究。E-mail: yuehuang_st@rcees.ac.cn
基金资助:
HUANG Yue1,2( ), WEI Wei1,3,*(
), WEI Wei1,3,*( ), CHEN Shengnan1
), CHEN Shengnan1
Received:2023-12-14
Online:2024-03-18
Published:2024-05-08
摘要:
黄土高原降雨稀少,水分供应不足,植物生长用水普遍受限。通过热扩散式探针(TDP)于2022年生长季(5-10月)对黄土高原龙滩流域侧柏(Platycladus orientalis)和柠条(Caragana korshinskii)的树干液流密度进行连续观测,同步监测气象因子和土壤含水量。对该地区主要树种的蒸腾耗水特征及其环境响应机制进行分析,旨在解析不同植被的用水规律与干旱适应能力。结果表明,1)生长季内,侧柏液流密度日变化为单峰型,液流峰值分布在0.448-0.537 g∙m−2∙h−1。柠条液流密度日变化为双峰型,2个液流峰值分布在0.0276-0.0393 g∙m−2∙h−1和0.0315-0.0436 g∙m−2∙h−1。2)侧柏液流密度主要受太阳辐射影响(r2=0.773,P=0.036),其次为饱和水汽压差(r2=0.320,P=0.041)。柠条液流密度主要受饱和水汽压差影响(r2=0.678,P=0.011),其次为相对湿度(r2=0.564,P=0.044)。3)在生长季内的不同时期,降雨后侧柏和柠条液流密度均显著高于降雨前。可利用能同时反映太阳辐射和饱和水汽压差的蒸腾变量模拟液流密度变化,降雨前后的侧柏、柠条液流密度均与蒸腾变量呈正向指数关系。通过对比降雨前后植被水力导度(拟合参数b值)发现:与侧柏相比,柠条液流密度受降雨影响更强烈,而侧柏的水分适应能力较强。综合研究结果表明:侧柏、柠条液流密度对环境的响应存在差异,柠条是降雨敏感型植物,侧柏是降雨不敏感型植物。研究结果可为当地造林树种选择及森林水资源管理提供科学依据。
中图分类号:
黄玥, 卫伟, 陈胜楠. 黄土高原侧柏和柠条树干液流日变化及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(3): 389-398.
HUANG Yue, WEI Wei, CHEN Shengnan. Sap Flow Characteristics of Platycladus orientalis and Caragana korshinskii and Its Response to Environmental Factors in the Loess Plateau[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(3): 389-398.
| 月份 | 月降雨量/ mm | 太阳辐射/ (W∙m−2) | 大气温度/ ℃ | 相对湿度/ % | 饱和水汽压差/ kPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5月 | 11.40 | 213.45±40.33 | 15.14±4.98 | 52.58±10.78 | 1.35±0.66 |
| 6月 | 32.00 | 239.29±60.73 | 20.39±6.73 | 48.60±11.58 | 2.02±0.97 |
| 7月 | 47.80 | 226.03±49.50 | 21.46±8.92 | 60.70±19.55 | 1.12±0.67 |
| 8月 | 46.00 | 176.60±30.17 | 21.16±7.60 | 73.93±23.12 | 0.56±0.34 |
| 9月 | 11.20 | 170.66±20.15 | 15.24±4.91 | 65.77±18.47 | 0.36±0.11 |
| 10月 | 7.00 | 123.84±12.66 | 9.24±4.55 | 61.69±10.03 | 0.30±0.08 |
表1 2022年生长季气象因子月变化特征
Table 1 Monthly variations of meteorological factors during the growing season of 2022
| 月份 | 月降雨量/ mm | 太阳辐射/ (W∙m−2) | 大气温度/ ℃ | 相对湿度/ % | 饱和水汽压差/ kPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5月 | 11.40 | 213.45±40.33 | 15.14±4.98 | 52.58±10.78 | 1.35±0.66 |
| 6月 | 32.00 | 239.29±60.73 | 20.39±6.73 | 48.60±11.58 | 2.02±0.97 |
| 7月 | 47.80 | 226.03±49.50 | 21.46±8.92 | 60.70±19.55 | 1.12±0.67 |
| 8月 | 46.00 | 176.60±30.17 | 21.16±7.60 | 73.93±23.12 | 0.56±0.34 |
| 9月 | 11.20 | 170.66±20.15 | 15.24±4.91 | 65.77±18.47 | 0.36±0.11 |
| 10月 | 7.00 | 123.84±12.66 | 9.24±4.55 | 61.69±10.03 | 0.30±0.08 |

图3 侧柏、柠条液流密度对太阳辐射、大气温度、相对湿度、饱和水汽压差的响应
Figure 3 Responses of sap flow density for Platycladus orientalis and Caragana korshinskii to solar radiation, atmospheric temperature, relative humidity, and vapor pressure deficit

图4 生长季内不同时期降雨前后气象因子与土壤含水量变化
Figure 4 Changes in meteorological factors and soil water content before and after rainfall events during different periods of the growing season
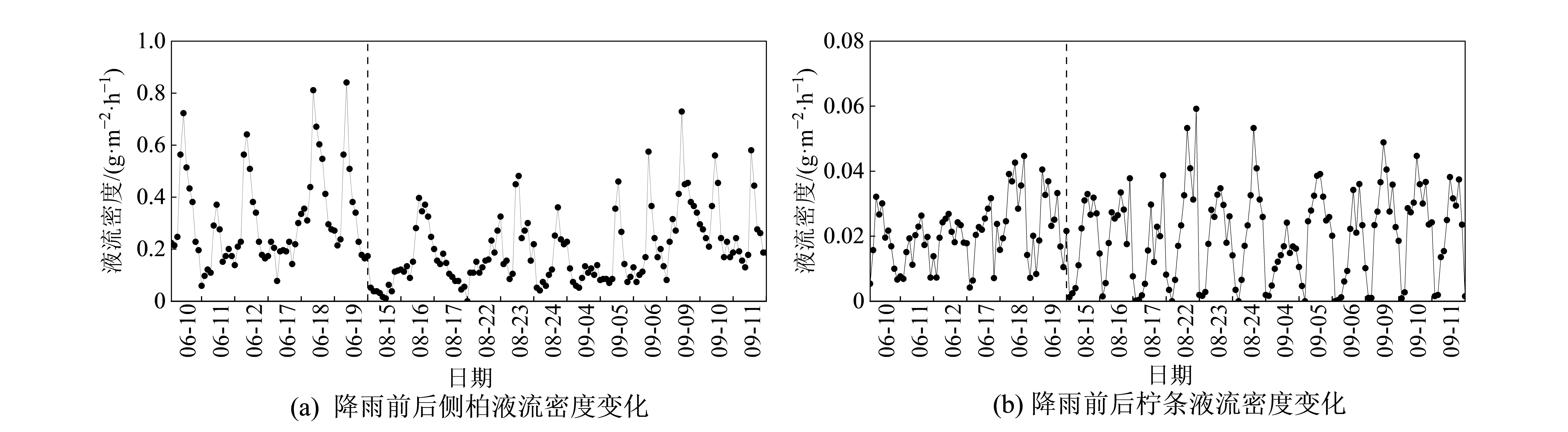
图5 生长季内不同时期降雨前后侧柏、柠条液流变化
Figure 5 Changes in sap flow density in Platycladus orientalis and Caragana korshinskii before and after rainfall events during different periods of the growing season
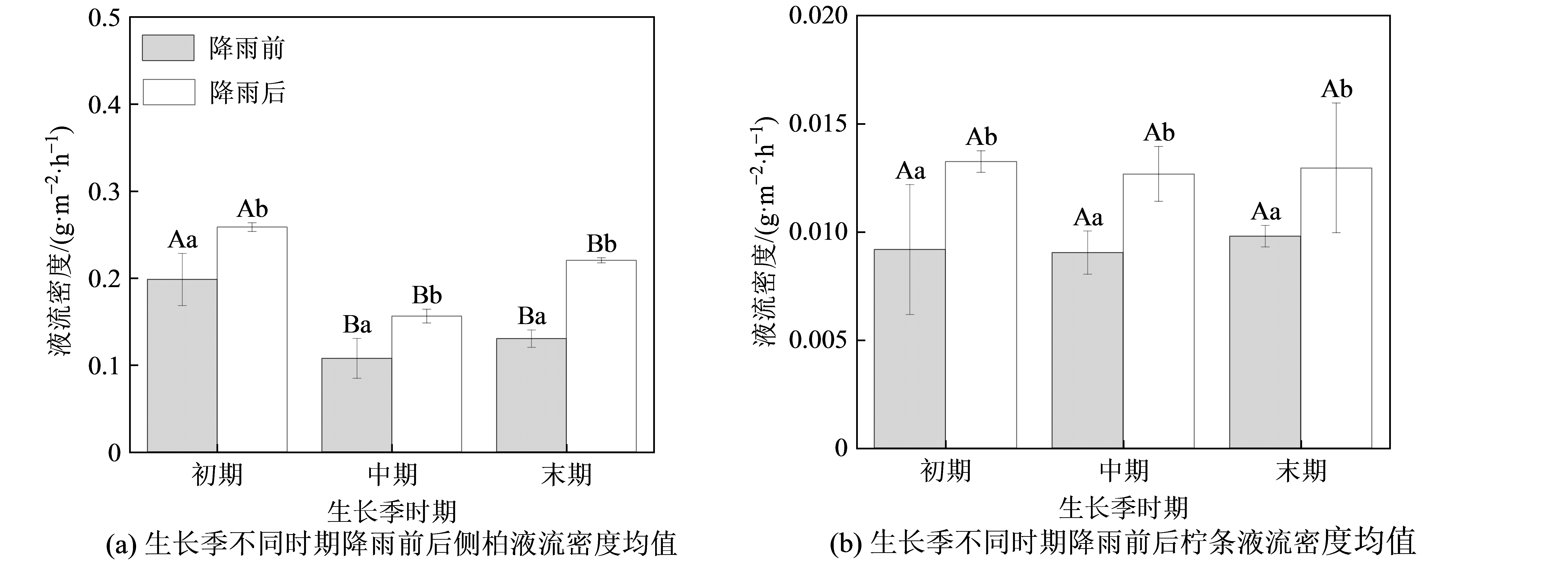
图6 生长季内不同时期降雨前后侧柏、柠条液流密度均值 不同大写字母表示生长季内不同时期差异显著(P<0.05),不同小写字母表示降雨前后差异显著(P<0.05)
Figure 6 Mean sap flow density of Platycladus orientalis and Caragana korshinskii measured before and after rainfall events during different periods of the growing season
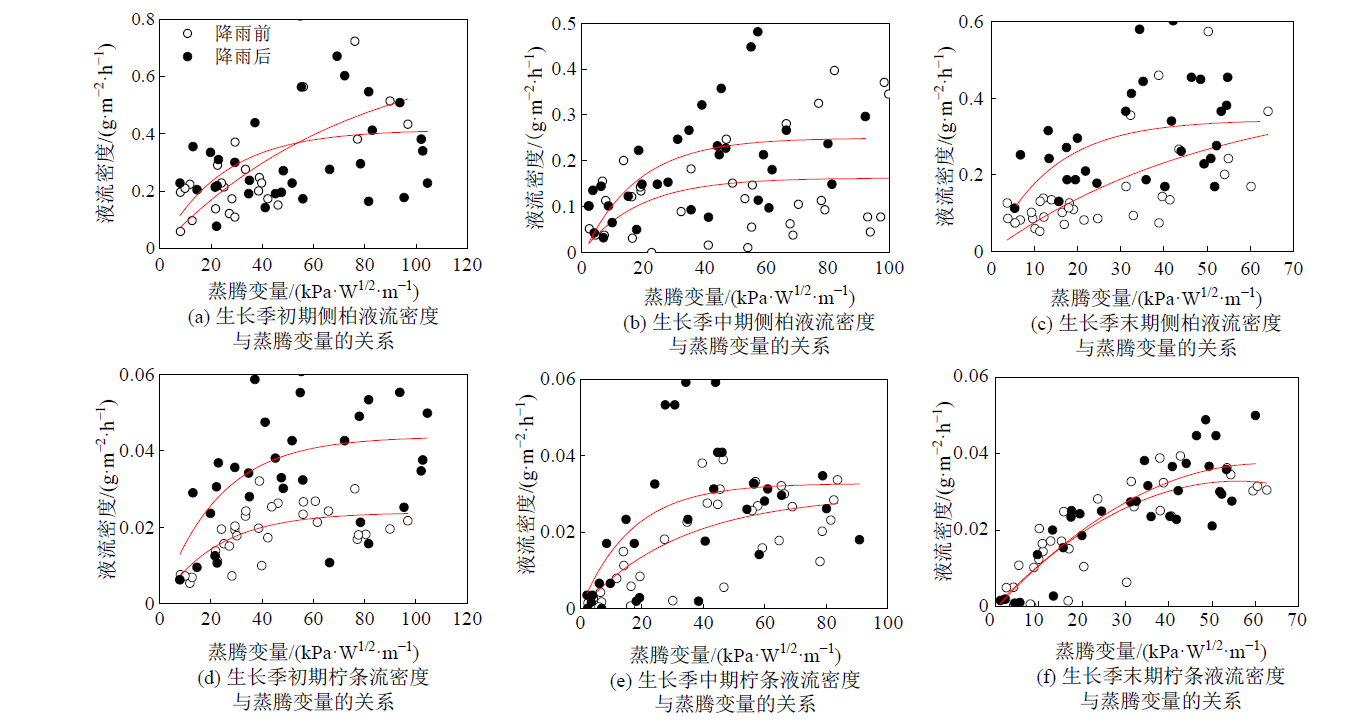
图7 生长季内不同时期降雨前后侧柏、柠条液流密度和蒸腾变量的关系
Figure 7 The relationship between sap flow density and transpiration variable of Platycladus orientalis and Caragana korshinskii before and after rainfall events during different periods of the growing season
| 树种 | 生长季内时期 | 降雨前 | 降雨后 | 拟合参数检验 | 树种 | 生长季内时期 | 降雨前 | 降雨后 | 拟合参数检验 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 侧柏 | 初期 | a=0.717 b=0.013 P=0.013 | a=0.414 b=0.041 P=0.033 | P=0.052 P=0.008 | 柠条 | 初期 | a=0.024 b=0.045 P=0.002 | a=0.029 b=0.044 P=0.004 | P=0.047 P=0.072 |
| 中期 | a=0.163 b=0.054 P=0.011 | a=0.255 b=0.118 P=0.009 | P=0.023 P=0.043 | 中期 | a=0.030 b=0.025 P=0.048 | a=0.033 b=0.121 P=0.010 | P=0.007 P=0.036 | ||
| 末期 | a=0.432 b=0.019 P=0.009 | a=0.322 b=0.546 P=0.002 | P=0.068 P=0.001 | 末期 | a=0.031 b=0.042 P=0.004 | a=0.048 b=0.027 P=0.006 | P=0.028 P=0.031 |
表2 生长季内不同时期降雨前后侧柏、柠条液流密度和蒸腾变量的拟合方程
Table 2 Fitting equations for sap flow density and transpiration variable of Platycladus orientalis and Caragana korshinskii before and after rainfall events in different periods of the growing season
| 树种 | 生长季内时期 | 降雨前 | 降雨后 | 拟合参数检验 | 树种 | 生长季内时期 | 降雨前 | 降雨后 | 拟合参数检验 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 侧柏 | 初期 | a=0.717 b=0.013 P=0.013 | a=0.414 b=0.041 P=0.033 | P=0.052 P=0.008 | 柠条 | 初期 | a=0.024 b=0.045 P=0.002 | a=0.029 b=0.044 P=0.004 | P=0.047 P=0.072 |
| 中期 | a=0.163 b=0.054 P=0.011 | a=0.255 b=0.118 P=0.009 | P=0.023 P=0.043 | 中期 | a=0.030 b=0.025 P=0.048 | a=0.033 b=0.121 P=0.010 | P=0.007 P=0.036 | ||
| 末期 | a=0.432 b=0.019 P=0.009 | a=0.322 b=0.546 P=0.002 | P=0.068 P=0.001 | 末期 | a=0.031 b=0.042 P=0.004 | a=0.048 b=0.027 P=0.006 | P=0.028 P=0.031 |
| [1] |
CHEN D Y, WANG Y K, WANG X, et al., 2016. Effects of branch removal on water use of rain-fed jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.) plantations in Chinese semiarid Loess Plateau region[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 178: 258-270.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
CHEN Z X, WANG G H, PAN Y H, et al., 2021. Water use patterns differed notably with season and slope aspect for Caragana korshinskii on the Loess Plateau of China[J]. Catena, 198: 105028.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
CHEN Z X, WANG G H, YANG X L, et al., 2023. Water competition among the coexisting Platycladus orientalis, Prunus davidiana and Medicago sativa in a semi-arid agroforestry system[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 279: 108206.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
CHEN Z S N, ZHANG Z Q, SUN G, et al., 2020. Biophysical controls on nocturnal sap flow in plantation forests in a semi-arid region of northern China[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 284: 107904.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
DAI J J, ZHAO Y, WANG L, 2023. Characteristics and modelling of sap flow of degraded Populus simonii in areas where the ecology is vulnerable[J]. Land Degradation Development, 34(2): 493-505.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
DONG M Y, WANG B Q, JINAG Y, et al., 2019. Environmental controls of diurnal and seasonal variations in the stem radius of Platycladus orientalis in northern China[J]. Forests, 10(9): 784.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
FANG S M, ZHAO C Y, JIAN S Q, 2016. Canopy transpiration of Pinus tabulaeformis plantation forest in the Loess Plateau region of China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75: 1-9.
DOI URL |
| [8] | FANG W W, LU N, LIU J B, et al., 2023. Responses of sap flow density of two shrub species to rainfall classes on the semiarid Loess Plateau of China[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 14: 123724. |
| [9] |
FANG W W, LU N, ZHANG Y, et al., 2018. Responses of nighttime sap flow to atmospheric and soil dryness and its potential roles for shrubs on the Loess Plateau of China[J]. Journal of plant ecology, 11(5): 717-729.
DOI |
| [10] |
HE Q Y, YAN M J, ZHANG J G, 2018. Sap flow of Robinia pseudoacacia in response to rainfall exclusion treatment and environment factors in a sub-humid area in Loess Plateau[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 42(4): 466-474.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
HUO J Q, SHI Y F, ZHANG H X, et al., 2021. More sensitive to drought of young tissues with weak water potential adjustment capacity in two desert shrubs[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 790: 148103.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
LI Y Q, ZHU L W, OUYANG L, et al., 2023. Environmental controls on transpiration of Schima superba trees with different tree sizes under ten years’ climate fluctuations in south subtropics, China[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 539: 120995.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
LIU G B, ZHAO J Z, LIAO T, et al., 2021. Histological dissection of cutting-inducible adventitious rooting in Platycladus orientalis reveals developmental endogenous hormonal homeostasis[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 170: 113817.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
JIA J B, CHEN Y, LU J, et al., 2022. Water uptake pattern by coniferous forests in two habitats linked to precipitation changes in subtropical monsoon climate region, China[J]. Forests, 13(5): 708.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
JIAN S Q, WU Z N, HU C H, et al., 2016. Sap flow in response to rainfall pulses for two shrub species in the semiarid Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Hydrology and Hydromechanics, 64(2): 121-132.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
JIAN S, ZHAO C Y, FANG S M, et al., 2015. Effects of different vegetation restoration on soil water storage and water balance in the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 206: 85-96.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
JIAO L, LU N, FANG W W, et al., 2019. Determining the independent impact of soil water on forest transpiration: A case study of a black locust plantation in the Loess Plateau, China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 572: 671-681.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
PEI Y W, HUANG L M, SHAO M A, et al., 2023. Water use pattern and transpiration of Mongolian pine plantations in relation to stand age on northern Loess Plateau of China[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 330: 109320.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
QI S J, SHENG T Z, HONG C H, et al., 2022. Integrating potential distribution of dominant vegetation and land use into ecological restoration in the Yellow River Basin, China[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 19(10): 2886-2904.
DOI |
| [20] |
QIAN J, ZHENG H, WANG P F, et al., 2017. Assessing the ecohydrological separation hypothesis and seasonal variations in water use by Ginkgo biloba L. in a subtropical riparian area[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 553: 486-500.
DOI URL |
| [21] | QIU D X, XU R R, WU C X, et al., 2023. Effects of vegetation restoration on soil infiltrability and preferential flow in hilly gully areas of the Loess Plateau, China[J]. Catena, 221(Part A): 106770. |
| [22] |
TANG W Z, YANG H S, WANG W E, et al., 2022. Effects of water allocation process on greenhouse gas emissions in drip-irrigated apple orchards on the Loess Plateau, China[J]. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 338: 108077.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
TARDIEU F, SIMONNEAU T, 1998. Variability of species among stomatal control under fluctuating soil water status and evaporative demand: Modeling isohydric and anisohydric behaviours[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 49: 419-432.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
THIDAR M, GONG D Z, MEI X R, et al., 2020. Mulching improved soil water, root distribution and yield of maize in the Loess Plateau of Northwest China[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 241: 106340.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
TONG Y Q, LIU J, HAN X, et al., 2023. Radial and seasonal variation of sap flow and its response to meteorological factors in sandy Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica plantations in the Three North Shelterbelt of China[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 328: 109239.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
WANG D, GAO G Y, LI J R, et al., 2020. Sap flow dynamics of xerophytic shrubs differ significantly among rainfall categories in the Loess Plateau of China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 585: 124815.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
WANG G H, CHEN Z X, YANG X L, et al., 2022. Effect of simulated precipitation regimes on sap flow and water use efficiency for xerophytic Caragana korshinskii[J]. Ecological Indicators, 143(8): 109309.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
WANG G H, SHEN Y Y, YANG X L, et al., 2019. Scaling up sap flow measurements from the stem scale to the individual scale for multibranched Caragana korshinskii on the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Forests, 10(9): 785.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
WANG S, FU B J, GAO G Y, et al., 2013. Responses of soil moisture in different land cover types to rainfall events in a re-vegetation catchment area of the Loess Plateau, China[J]. Catena, 101: 122-128.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
WU B C, ZHOU L J, QI S, et al., 2021. Effect of habitat factors on the understory plant diversity of Platycladus orientalis plantations in Beijing mountainous areas based on MaxEnt model[J]. Ecological Indicators, 129: 107917.
DOI URL |
| [31] | WU W J, CHEN G J, MENG T F, et al., 2023. Effect of different vegetation restoration on soil properties in the semi-arid Loess Plateau of China[J]. Catena, 220(Part A): 106630. |
| [32] |
YU S P, GUO J B, LIU Z B, et al., 2023. Impacts of environmental and canopy conditions on the nighttime sap flow of larch plantations in the Liupan Mountains, China[J]. Journal of Forestry Research, 34: 1927-1940.
DOI |
| [33] |
ZHANG R F, XU X L, LIU M X, et al., 2019. Hysteresis in sap flow and its controlling mechanisms for a deciduous broad-leaved tree species in a humid karst region[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 62: 1744-1755.
DOI |
| [34] |
ZHANG Y, LI W, YAN H M, et al., 2022. Canopy transpiration and stomatal conductance dynamics of Ulmus pumila L. and Caragana korshinskii Kom. plantations on the Bashang Plateau, China[J]. Forests, 13(7): 1081.
DOI URL |
| [35] | ZHANG H D, WEI W, CHEN L D, et al., 2015. Analysis of sap flow characteristics of the Chinese pine in typical Loess Plateau region of China[J]. Huan Jing Ke Xue=Huanjing Kexue, 36(1): 349-356. |
| [36] |
ZHANG J G, GUAN J H, SHI W Y, et al., 2015. Interannual variation in stand transpiration estimated by sap flow measurement in a semi‐arid black locust plantation, Loess Plateau, China[J]. Ecohydrology, 8(1): 137-147.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
ZHANG Q Y, JIA X X, SHAO M, et al., 2018. Sap flow of black locust in response to short-term drought in southern Loess Plateau of China[J]. Scientific Reports, 8(1): 6222.
DOI PMID |
| [38] |
ZHOU S S, LIU W Z, LIN W, et al., 2017. The ratio of transpiration to evapotranspiration in a rainfed maize field on the Loess Plateau of China[J]. Water Science and Technology: Water Supply, 17(1): 221-228.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
陈丽茹, 李秧秧, 2018. 沙柳和柠条茎水力学特性对模拟降雨改变的响应[J]. 应用生态学报, 29(2): 507-514.
DOI |
| CHEN L R, LI Y Y, 2018. Responses of stem hydraulic traits in Salix psammophila and Caragana korshinskii to manipulated precipitation variation[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 29(2): 507-514. | |
| [40] | 傅伯杰, 刘彦随, 曹智, 等, 2023. 黄土高原生态保护和高质量发展现状、问题与建议[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 38(8): 1110-1117. |
| FU B J, LIU Y S, CAO Z, et al., 2023. Current conditions, issues, and suggestions for ecological protection and high-quality development in Loess Plateau. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences[J]. Policy and Management Research, 38(8): 1110-1117. | |
| [41] |
韩磊, 展秀丽, 王芳, 等, 2018. 河东沙区侧柏树干液流与蒸腾驱动因子的时滞效应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 27(8): 1417-1423.
DOI |
| HAN L, ZHAN X L, WANG F, et al., 2018. Time lag effect between stem sap flow and driving factors of transpiration of Platycladus orientalis in east sandy land of Yellow River[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 27(8): 1417-1423. | |
| [42] |
何秋月, 闫美杰, 张建国, 等, 2018. 黄土高原半湿润区刺槐树干液流对人工截留降雨输入及环境因子的响应[J]. 植物生态学报, 42(4): 466-474.
DOI |
|
HE Q Y, YAN M J, ZHANG J G, 2018. Sap flow of Robinia pseudoacacia in response to rainfall exclusion treatment and environment factors in a sub-humid area in Loess Plateau[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 42(4): 466-474.
DOI URL |
|
| [43] | 洪光宇, 王晓江, 高孝威, 等, 2023. 毛乌素沙地杨柴液流变化对气象因子的响应[J]. 生态学报, 43(4): 1635-1645. |
| HONG G Y, WANG X J, GAO X W, et al., 2023. Responses of sap flow of Hedysarum leave to climatic factors in Mu Us Sandy land[J]. Acta Ecological Sinica, 43(4): 1635-1645. | |
| [44] | 李蓝君, 宋孝玉, 夏露, 等, 2018. 黄土高原沟壑区典型造林树种蒸散发对气候变化的响应[J]. 农业工程学报, 34(20): 148-159. |
| LI L J, SONG X Y, XIA L, et al., 2018. Response of evaporation and transpiration of typical afforestation tree species to climate changes in gully region of Loess Plateau[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 34(20): 148-159. | |
| [45] |
刘文娜, 贾剑波, 余新晓, 等, 2017. 华北山区侧柏冠层气孔导度特征及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 应用生态学报, 28(10): 3217-3226.
DOI |
| LIU W N, JIAO J B, YU X X, et al., 2017. Characteristics of canopy stomatal conductance of Platycladus orientalis and its responses to environmental factors in the mountainous area of North China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 28(10): 3217-3226. | |
| [46] | 刘潇潇, 李国庆, 闫美杰, 等, 2017. 黄土高原主要树种树干液流研究进展[J]. 水土保持研究, 24(3): 369-373. |
| LIU X X, LI G Q, YAN M J, et al., 2017. Research progress on stem sap flow in major tree species on the Loess Plateau[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 24(3): 369-373. | |
| [47] | 孙亚荣, 陈云明, 王亚娟, 等, 2023. 黄土丘陵区柠条人工林土壤水分动态变化特征及降雨特征对其影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 37(1): 272-279. |
| SUN Y R, CHEN Y M, WANG Y J, et al., 2023. Dynamic variation characteristics of soil moisture in Caragana korshinskii plantation in loess hilly area and the influence of rainfall characteristics on it[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 37(1): 272-279. | |
| [48] | 温杰, 陈云明, 唐亚坤, 等, 2017. 黄土丘陵区油松、沙棘生长旺盛期树干液流密度特征及其影响因素[J]. 应用生态学报, 28(3): 763-771. |
| WEN J, CHEN Y M, TANG Y K, et al., 2017. Characteristics and affecting factors of sap flow density of Pinus tabuliformis and Hippophae rhamnoides in growing season in the hilly region of the Loess Plateau, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 28(3): 763-771. | |
| [49] |
吴旭, 陈云明, 唐亚坤, 2015. 黄土丘陵区刺槐和侧柏人工林树干液流特征及其对降水的响应[J]. 植物生态学报, 39(12): 1176-1187.
DOI |
|
WU X, CHEN Y M, TANG Y K, 2015. Sap flow characteristics and its responses to precipitation in Robinia pseudoacacia and Platycladus orientalis planta tions[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 39(12): 1176-1187.
DOI URL |
|
| [50] | 吴旭, 牛耀彬, 荀梦瑶, 等, 2022. 黄土丘陵区优势造林树种水分来源对季节性干旱的响应[J]. 生态学报, 42(10): 4101-4112. |
| WU X, NIU Y B, XUN M Y, et al., 2022. Responses of water source to seasonal drought of dominant afforestation treespecies in the loess hilly region of China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42(10): 4101-4112. | |
| [51] | 夏永秋, 邵明安, 2008. 黄土高原半干旱区柠条 (Caragana korshinskii) 树干液流动态及其影响因子[J]. 生态学报, 28(4): 1376-1382. |
| XIA Y Q, SHAO M A, 2008. The sap flow dynamics of Caragana korshinskii and the influence of environmental factors in semi-arid region of the Loess Plateau[J]. Acta Ecological Sinica, 28(4): 1376-1382. | |
| [52] |
杨洁, 吕金林, 何秋月, 等, 2019. 黄土丘陵区辽东栎和刺槐树干液流时滞效应与蒸腾特征的关联性[J]. 应用生态学报, 30(8): 2607-2613.
DOI |
| YANG J, LÜ J L, HE Q Y, et al., 2019. Time lag of stem sap flow and its relationships with transpiration characteristics in Quercus liaotungensis and Robina pseudoacacia in the loess hilly region, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 30(8): 2607-2613. | |
| [53] |
臧春鑫, 杨劼, 袁劼, 等, 2009. 毛乌素沙地中间锦鸡儿整株丛的蒸腾特征[J]. 植物生态学报, 33(4): 719-727.
DOI |
| ZANG C X, YANG J, YUAN J, et al., 2009. Transpiration characteristics of individual shrubs of Caragana intermedia in MU US sandy land of north-central China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 33(4): 719-727. | |
| [54] | 张荣, 毕华兴, 焦振寰, 等, 2022. 生长季刺槐树干液流昼夜变化特征及其对气象因子的响应[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 39(6): 1238-1246. |
| ZHANG R, BI H X, JIAO Z H, et al., 2022. Diurnal and nocturnal changes in stem sap flow of Robinia pseudoacacia during growing season and its response to meteorological factors[J]. Journal of Zhejiang A & F University, 39(6): 1238-1246. | |
| [55] |
张潇, 武娟娟, 贾国栋, 等, 2023. 降水控制对侧柏液流变化特征及其水分来源的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 47(11): 1585-1599.
DOI |
|
ZHANG J, WU J J, JIA G D, et al., 2023. Effects of precipitation variations on characteristics of sap flow and water source of Platycladus orientalis[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 47(11): 1585-1599.
DOI |
|
| [56] | 赵平, 2011. 整树水力导度协同冠层气孔导度调节森林蒸腾[J]. 生态学报, 31(4): 1164-1173. |
| ZHAO P, 2011. On the coordinated regulation of forest transpiration by hydraulic conductanceand canopy stomatal conductance[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31(4): 1164-1173. |
| [1] | 王琳, 卫伟. 黄土高原典型县域生态系统服务变化特征及驱动因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1140-1148. |
| [2] | 王云, 郑西来, 曹敏, 李磊, 宋晓冉, 林晓宇, 郭凯. 滨海含水层咸-淡水过渡带反硝化性能与控制因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 980-988. |
| [3] | 张林, 周飘, 齐实, 张岱, 伍冰晨, 崔冉冉. 侧柏人工林林分空间结构对林下草本多样性的差异性影响及其关联度[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1794-1801. |
| [4] | 肖国举, 李秀静, 郭占强, 胡延斌, 王静. 贺兰山东麓土壤有机碳对玉米生长发育及水分利用的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1754-1764. |
| [5] | 齐月, 张强, 胡淑娟, 蔡迪花, 赵福年, 陈斐, 张凯, 王鹤龄, 王润元. 黄土高原地区气候变化及其对冬小麦生产潜力的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1521-1529. |
| [6] | 张恒宇, 孙树臣, 吴元芝, 安娟, 宋红丽. 黄土高原不同植被密度条件下土壤水、碳、氮分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 875-884. |
| [7] | 李少宁, 陶雪莹, 李慧敏, 赵娜, 徐晓天, 鲁绍伟. 侧柏和垂柳释放有益BVOCs组分生长季动态变化特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 257-264. |
| [8] | 刘江, 朱丽杰, 张开, 王晓明, 王立为, 高西宁. 不同生育期干旱胁迫/复水对大豆光合特性及产量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 286-296. |
| [9] | 赵安周, 田新乐. 基于GEE平台的1986-2021年黄土高原植被覆盖度时空演变及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2124-2133. |
| [10] | 杨艳, 周德成, 宫兆宁, 刘子源, 张良侠. 基于植被生产力的黄土高原地区生态脆弱性及其控制因子分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 1951-1958. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
